Validation and Bias Correction of Monthly δ18O Precipitation Time Series from ECHAM5-Wiso Model in Central Europe
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data Sources
3. Methods
3.1. Bias Correction Methodologies
3.1.1. Linear Bias Removal (LIN)
3.1.2. Empirical Quantile Mapping (EQM)
3.1.3. Scaling (SCL)
3.1.4. Generalized Additive Models (GAMs)
3.2. Goodness-of-Fit Statistics
4. Results
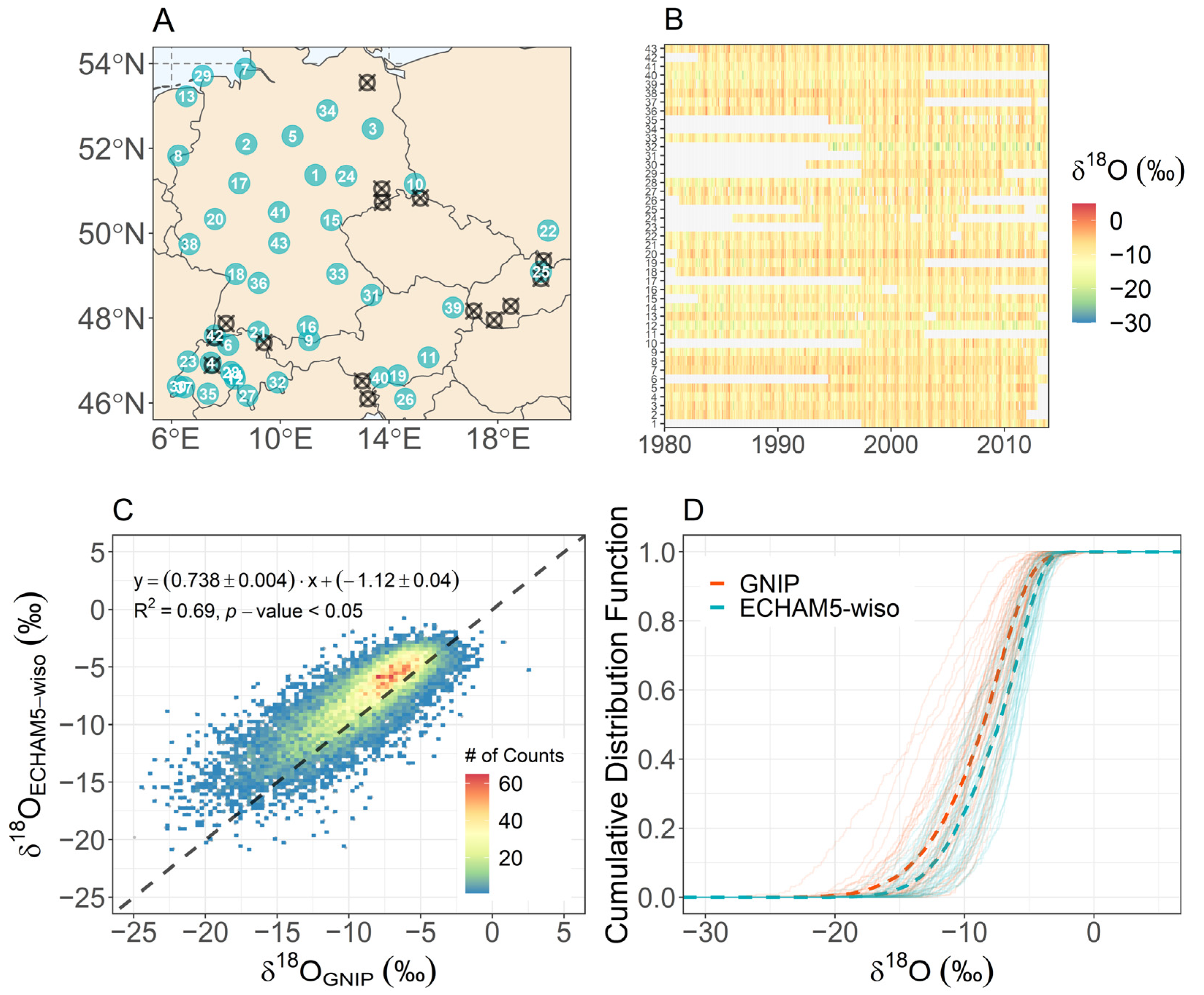
4.1. Validation of δ18OECHAM5-wiso over Central Europe
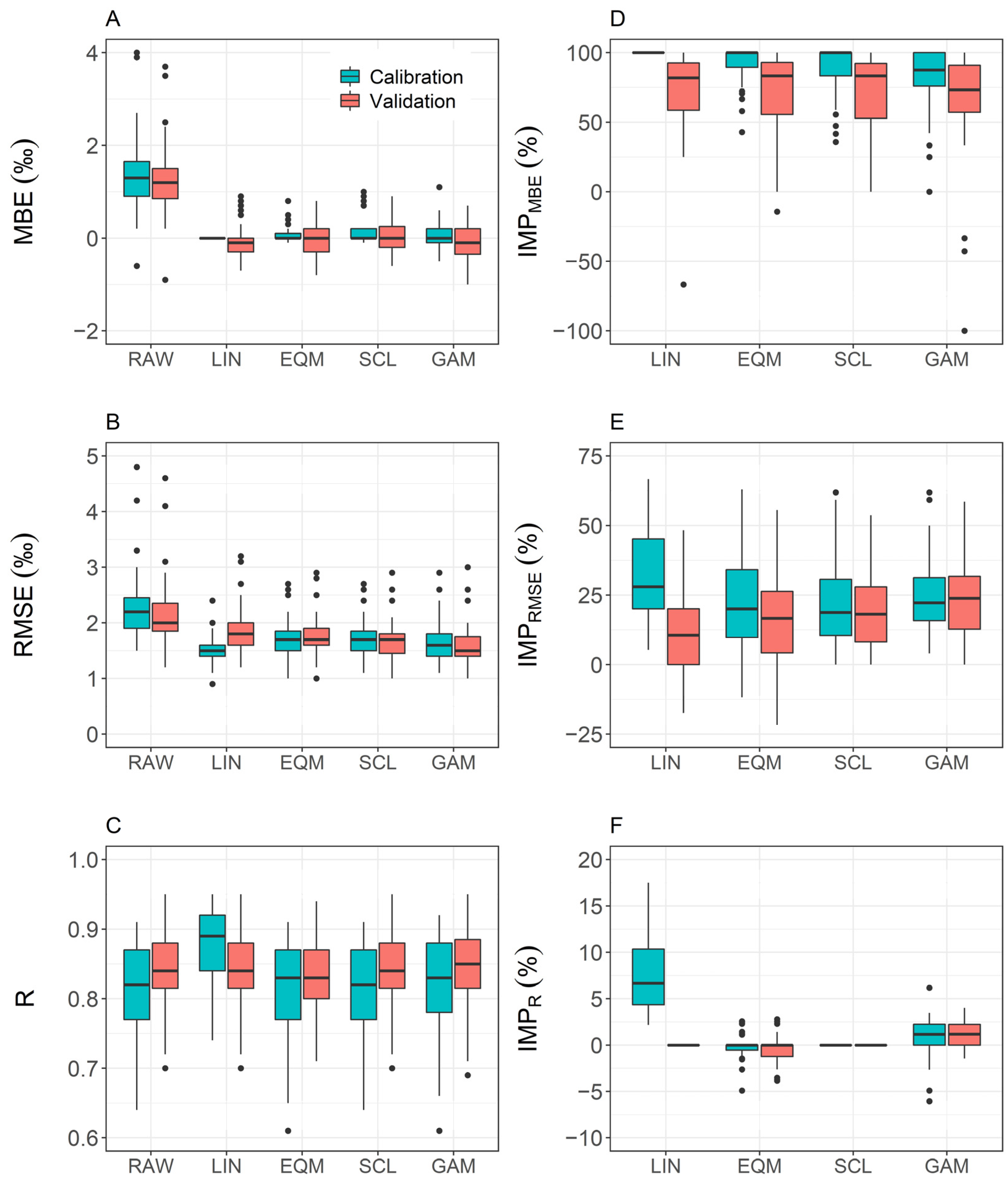
4.2. Bias Correction of δ18OECHAM5-wiso
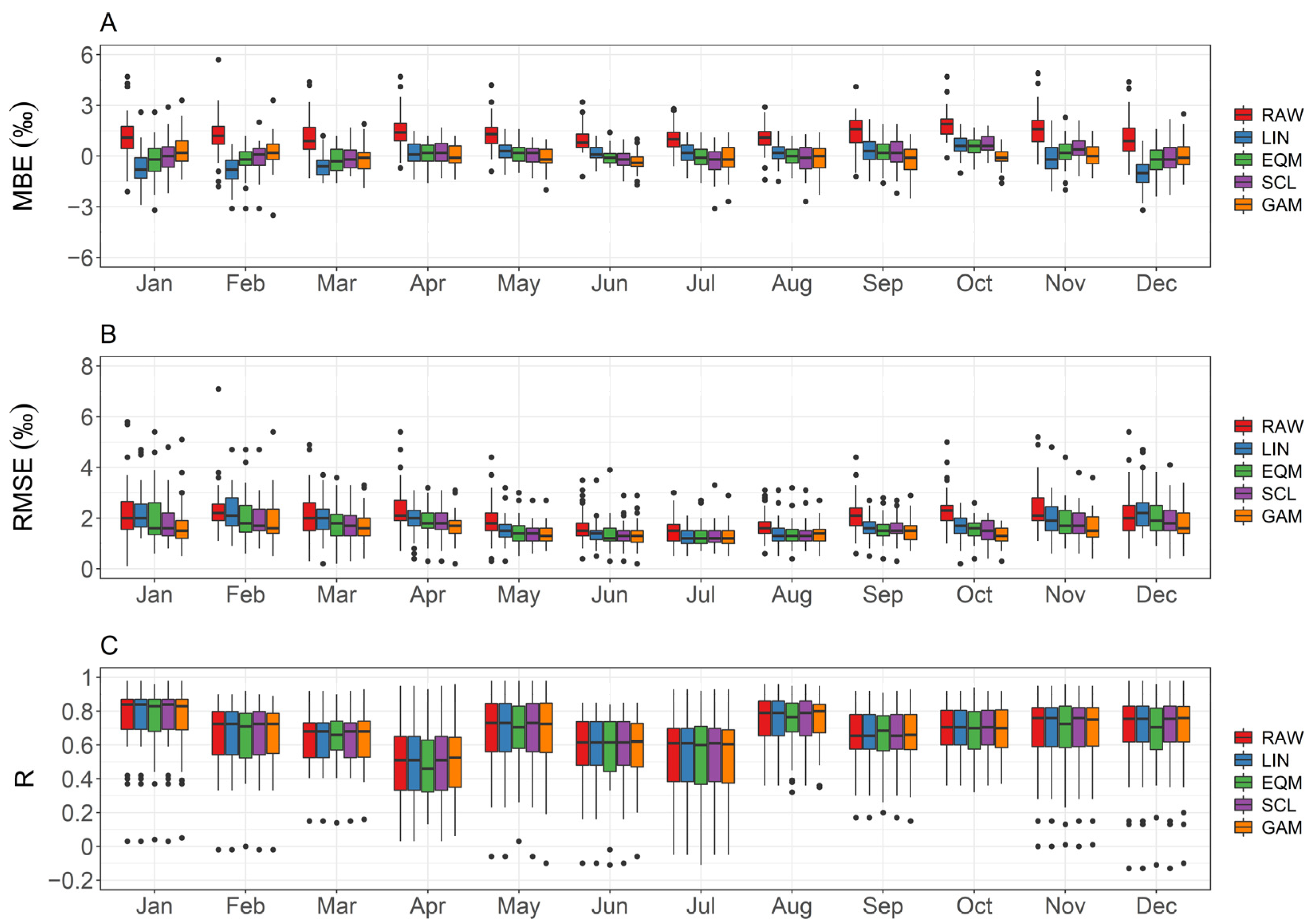
4.3. Long-Term Performance and Seasonal Amplitude of Bias-Corrected δ18OECHAM5-wiso
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bigeleisen, J. Chemistry of isotopes. Science 1965, 147, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dansgaard, W. Stable isotopes in precipitation. Tellus 1964, 16, 436–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gat, J.R. Oxygen and hydrogen isotopes in the hydrologic cycle. Ann. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 1996, 24, 225–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- IAEA/WMO. Global Network of Isotopes in Precipitation. The GNIP Database. Available online: https://nucleus.iaea.org/wiser (accessed on 1 February 2022).
- Hoffmann, G.; Werner, M.; Heimann, M. Water isotope module of the ECHAM atmospheric general circulation model: A study on timescales from days to several years. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 16871–16896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, G.; LeGrande, A.; Hoffmann, G. Water isotope expressions of intrinsic and forced variability in a coupled ocean-atmosphere model. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, D10103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-E.; Fung, I.; DePaolo, D.; Fennig, C.C. Analysis of the global distribution of water isotopes using the NCAR atmospheric general circulation model. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, D16306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, K.; Kanamitsu, M.; Noone, D.; Oki, T. Historical isotope simulation using reanalysis atmospheric data. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D19108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risi, C.; Bony, S.; Vimeux, F.; Jouzel, J. Water stable isotopes in the LMDZ4 general circulation model: Model evaluation for present day and past climates and applications to climatic interpretations of tropical isotopic records. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D12118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tindall, J.C.; Valdes, P.J.; Sime, L.C. Stable water isotopes in HadCM3: Isotopic signature of El Nino Southern Oscillation and the tropical amount effect. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, D04111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Werner, M.; Langebroek, P.M.; Carlsen, T.; Herold, M.; Lohmann, G. Stable water isotopes in the ECHAM5 general circulation model: Toward high-resolution isotope modeling on a global scale. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, 15109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurita, K.; Noone, D.; Risi, C.; Schmidt, G.A.; Yamada, H.; Yoneyama, K. Intraseasonal isotopic variation associated with the Madden-Julian Oscillation. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, D24101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, S.; Noone, D.D.; Buenning, N.; Emile-Geay, J.; Zhou, Y. SPEEDY-IER: A fast atmospheric GCM with water isotope physics. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 73–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturm, K.; Hoffmann, G.; Langmann, B.; Stichler, W. Simulation of delta O-18 in precipitation by the regional circulation model REMOiso. Hydrol. Processes 2005, 19, 3425–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfahl, S.; Wernli, H.; Yoshimura, K. The isotopic composition of precipitation from a winter storm—A case study with the limited-area model COSMOiso. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 1629–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delavau, C.J.; Stadnyk, T.; Holmes, T. Examining the impacts of precipitation isotope input (δ18Oppt) on distributed, tracer-aided hydrological modelling. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 2595–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, P.; Zhang, X.J.; Chen, J. Bias correcting isotope-equipped GCMs outputs to build precipitation oxygen isoscape for Eastern China. J. Hydrol. 2020, 589, 125153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, Y.; He, Z.; Tian, F.; Wei, Z.; Tian, L. Can we use precipitation isotope outputs of isotopic general circulation models to improve hydrological modeling in large mountainous catchments on the Tibetan Plateau? Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 25, 6151–6172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottek, M.; Grieser, J.; Beck, C.; Rudolf, B.; Rubel, F. World Map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification updated. Meteorol. Z. 2006, 15, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, M. ECHAM5-wiso simulation data-present-day, mid-Holocene, and Last Glacial Maximum. PANGAEA. Available online: https://doi.org/10.1594/PANGAEA.902347 (accessed on 1 February 2022). [CrossRef]
- Butzin, M.; Werner, M.; Masson-Delmotte, V.; Risi, C.; Frankenberg, C.; Gribanov, K.; Jouzel, J.; Zakharov, V.I. Variations of oxygen-18 in West Siberian precipitation during the last 50 years. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 5853–5869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Langebroek, P.M.; Werner, M.; Lohmann, G. Climate information imprinted in oxygen-isotopic composition of precipitation in Europe. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2016, 311, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polo, J.; Fernández-Peruchena, C.M.; Salamalikis, V.; Mazorra-Aguiar, L.; Turpin, M.; Martín-Pomares, L.; Kazantzidis, A.; Blanc, P.; Remund, J. Benchmarking on improvement and site-adaptation techniques for modeled solar radiation datasets. Solar Energy 2020, 201, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudmundsson, L.; Bremnes, J.; Haugen, J.; Engen-Skaugen, T. Technical note: Downscaling RCM precipitation to the station scale using statistical transformations—A comparison of methods. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 3383–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Themeßl, M.J.; Gobiet, A.; Heinrich, G. Empirical-statistical downscaling and error correction of regional climate models and its impact on the climate change signal. Clim. Chang. 2012, 112, 449–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piani, C.; Weedon, G.P.; Best, M.; Gomes, S.M.; Viterbo, P.; Hagemann, S.; Haerter, J.O. Statistical bias correction of global simulated daily precipitation and temperature for the application of hydrological models. J. Hydrol. 2010, 395, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teutschbein, C.; Seibert, J. Bias correction of regional climate model simulations for hydrological climate-change impact studies: Review and evaluation of different methods. J. Hydrol. 2012, 456–457, 12–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrac, M.; Marbaix, P.; Paillard, D.; Naveau, P. Non-linear statistical downscaling of present and LGM precipitation and temperatures over Europe. Clim. Past 2007, 3, 669–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Latombe, G.; Burke, A.; Vrac, M.; Levavasseur, G.; Dumas, C.; Kageyama, M.; Ramstein, G. Comparison of spatial downscaling methods of general circulation model results to study climate variability during the Last Glacial Maximum. Geosci. Model Dev. 2018, 11, 2563–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beyer, R.; Krapp, M.; Manica, A. An empirical evaluation of bias correction methods for palaeoclimate simulations. Clim. Past 2020, 16, 1493–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, T.J.; Tibshirani, R.J. Generalized Additive Models; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, S.N. Fast stable restricted maximum likelihood and marginal likelihood estimation of semiparametric generalized linear models. J. R. Stat. Soc. B 2011, 73, 3–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cauquoin, A.; Werner, M. High-resolution nudged isotope modeling with ECHAM6-wiso: Impacts of updated model physics and ERA5 reanalysis data. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2021, 13, e2021MS002532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Faiia, A.M.; Posmentier, E.S. Seasonality of isotopes in precipitation: A global perspective. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, D08116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allen, S.T.; Jasechko, S.; Berghuijs, W.R.; Welker, J.M.; Goldsmith, G.R.; Kirchner, J.W. Global sinusoidal seasonality in precipitation isotopes. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 3423–3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kirchner, J.W. Aggregation in environmental systems–Part 1: Seasonal tracer cycles quantify young water fractions, but not mean transit times, in spatially heterogeneous catchments. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 279–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salamalikis, V.; Argiriou, A.A.; Dotsika, E. Periodicity analysis of δ18O in precipitation over Central Europe: Time–frequency considerations of the isotopic ‘temperature’ effect. J. Hydrol. 2016, 534, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salamalikis, V.; Argiriou, A.A. Validation and Bias Correction of Monthly δ18O Precipitation Time Series from ECHAM5-Wiso Model in Central Europe. Oxygen 2022, 2, 109-124. https://doi.org/10.3390/oxygen2020010
Salamalikis V, Argiriou AA. Validation and Bias Correction of Monthly δ18O Precipitation Time Series from ECHAM5-Wiso Model in Central Europe. Oxygen. 2022; 2(2):109-124. https://doi.org/10.3390/oxygen2020010
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalamalikis, Vasileios, and Athanassios A. Argiriou. 2022. "Validation and Bias Correction of Monthly δ18O Precipitation Time Series from ECHAM5-Wiso Model in Central Europe" Oxygen 2, no. 2: 109-124. https://doi.org/10.3390/oxygen2020010
APA StyleSalamalikis, V., & Argiriou, A. A. (2022). Validation and Bias Correction of Monthly δ18O Precipitation Time Series from ECHAM5-Wiso Model in Central Europe. Oxygen, 2(2), 109-124. https://doi.org/10.3390/oxygen2020010






