Effective Removal of Geosmin from Aqueous Solution Using Bentonite–Alginate–Magnetic Composite
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Magnetite Nanoparticles
2.3. Preparation of Bent-alg-mag Beads
2.4. Characterization of Adsorbent
2.5. Adsorption Experiments
2.6. Kinetic and Isotherm Studies
2.7. Regeneration Experiments
2.8. Geosmin Determination
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of the Magnetic Adsorbent
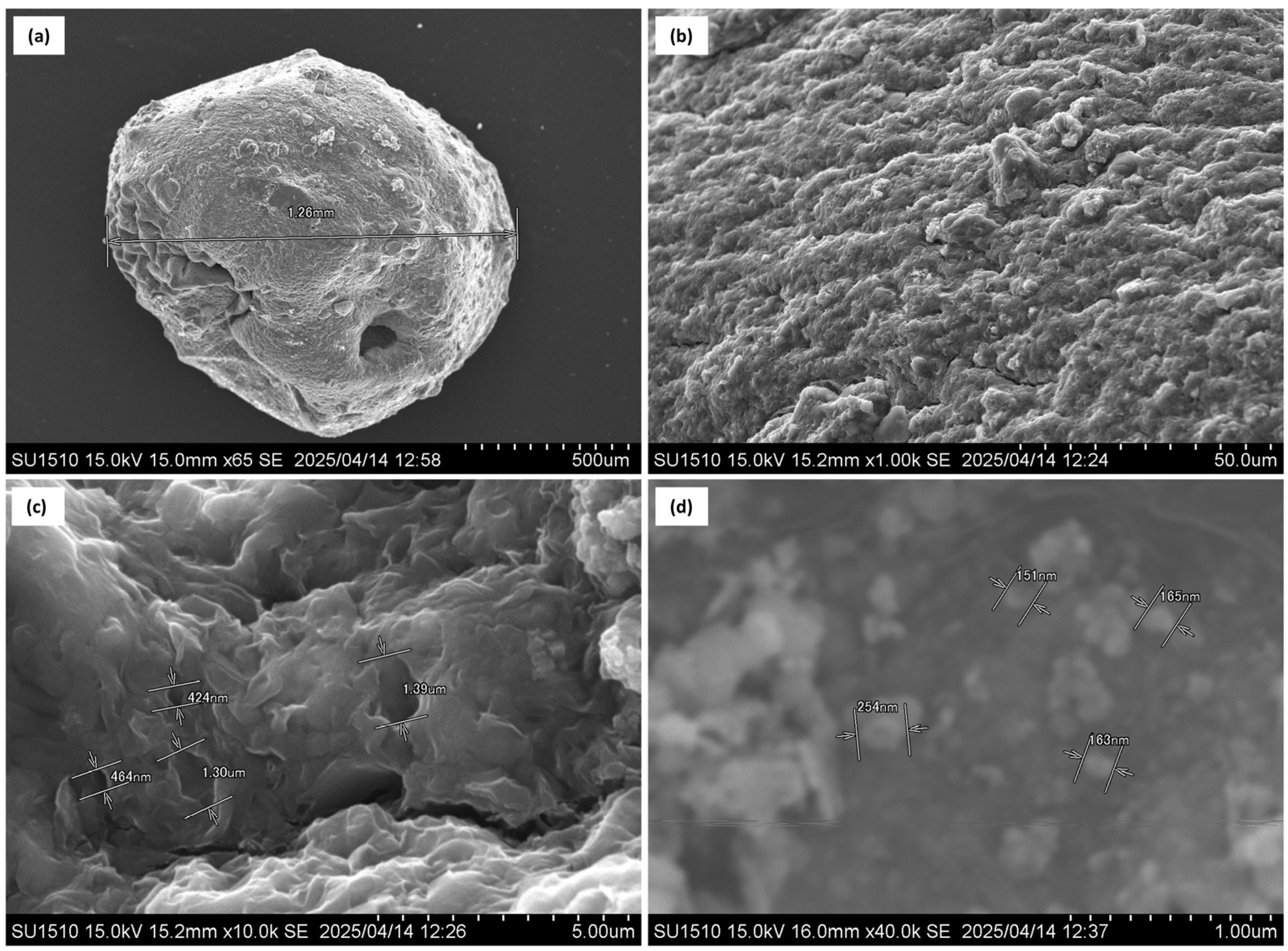
3.1.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy
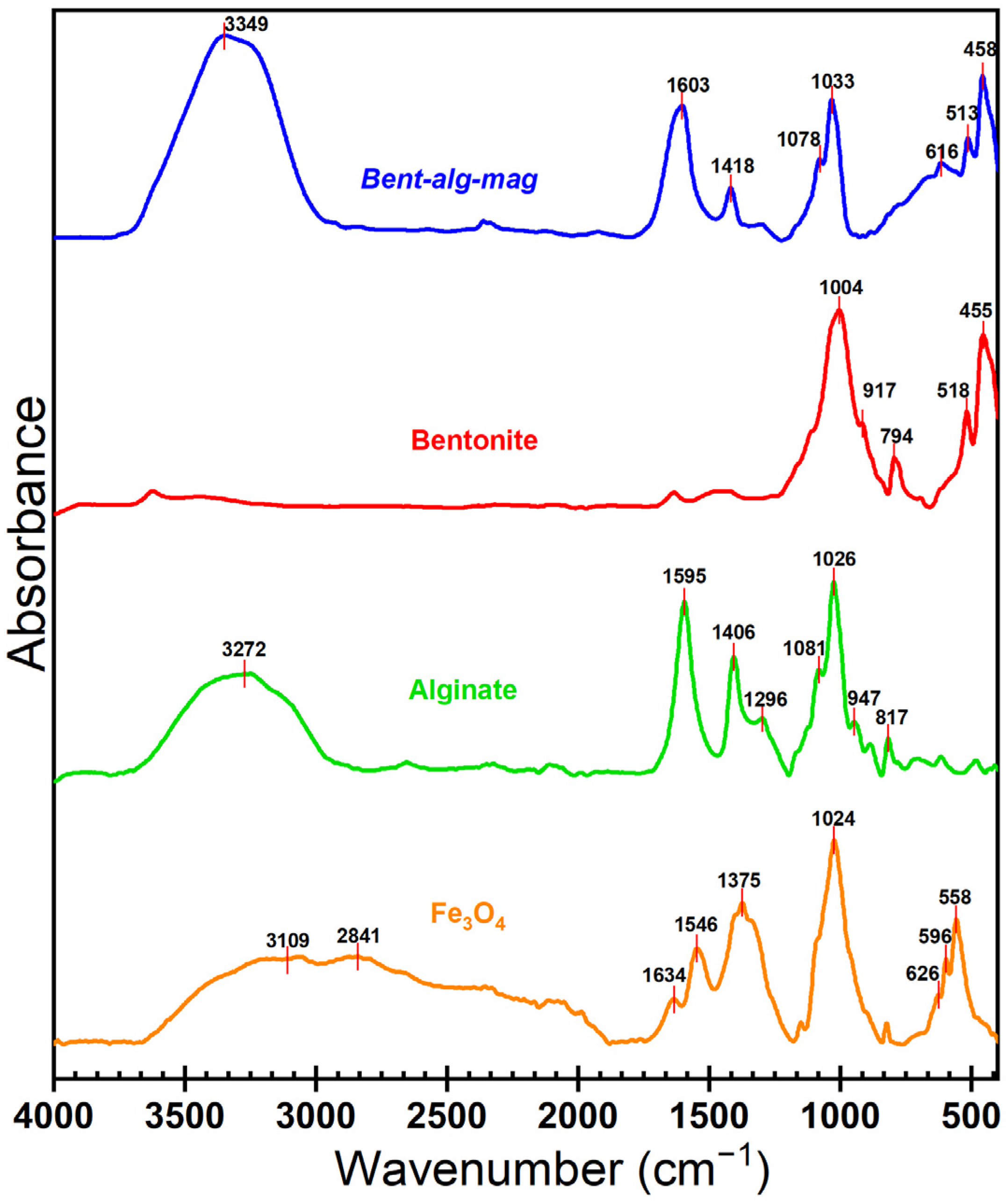
3.1.2. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
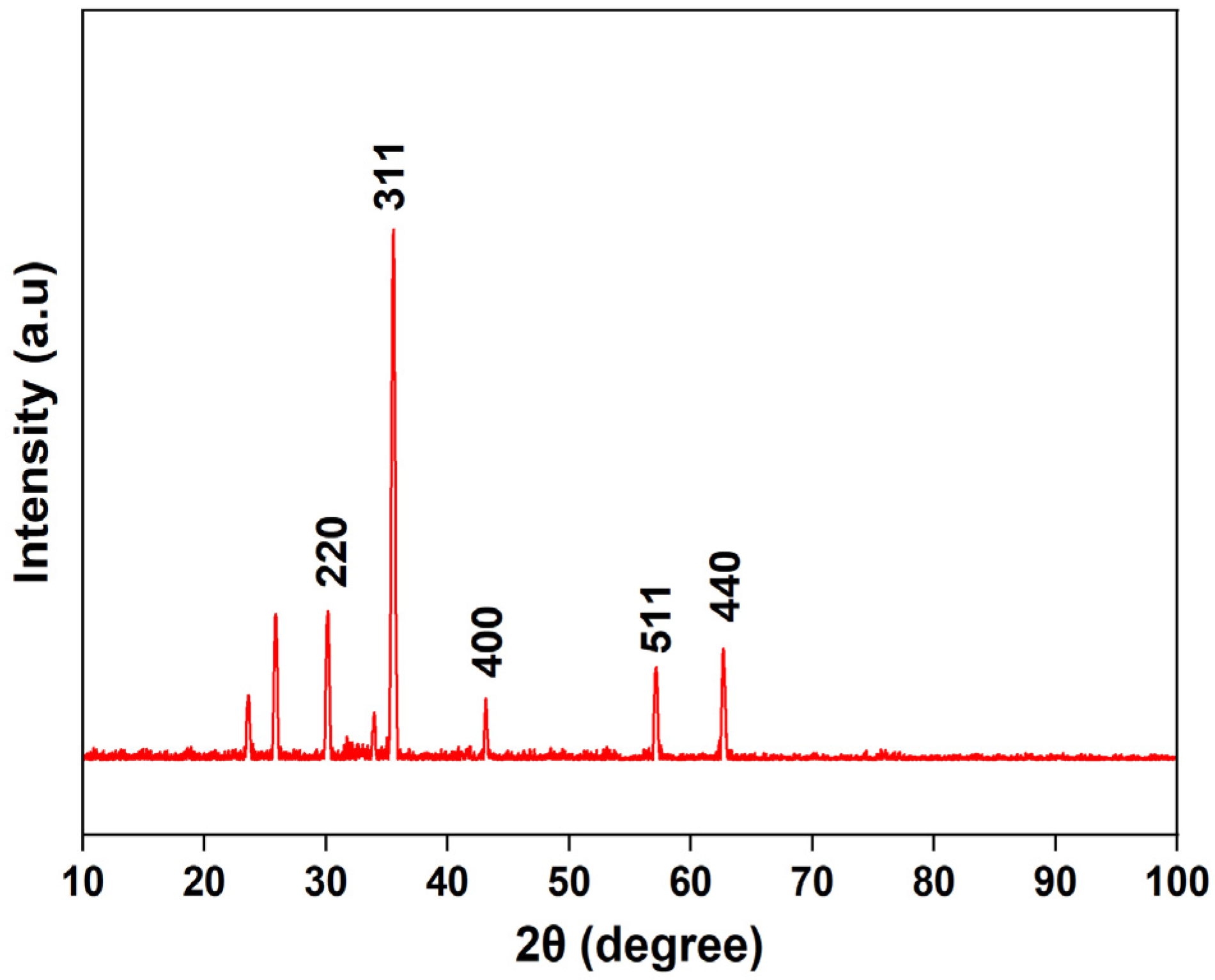
3.1.3. Powder X-Ray Diffraction
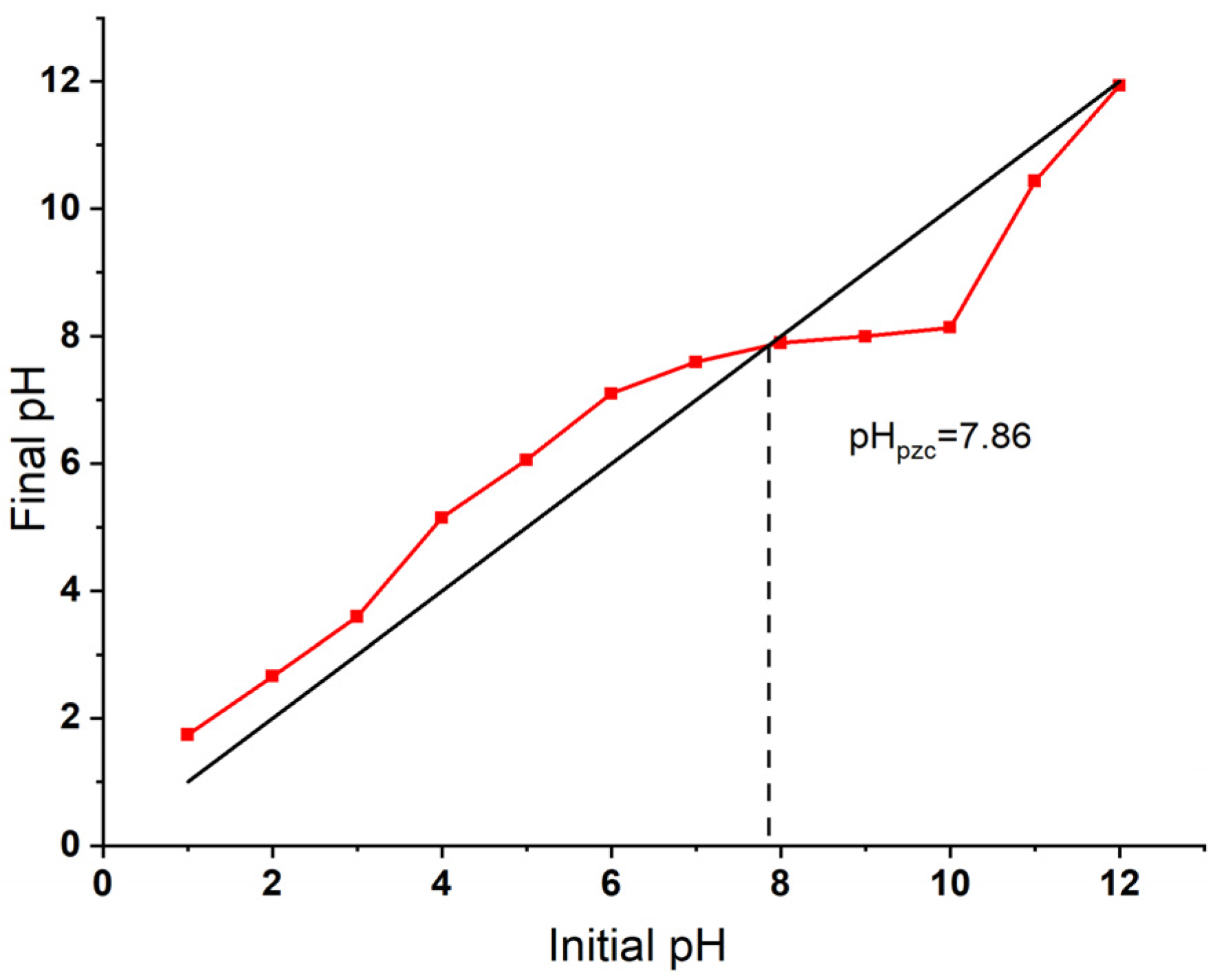
3.1.4. Point of Zero Charge (pHpzc)
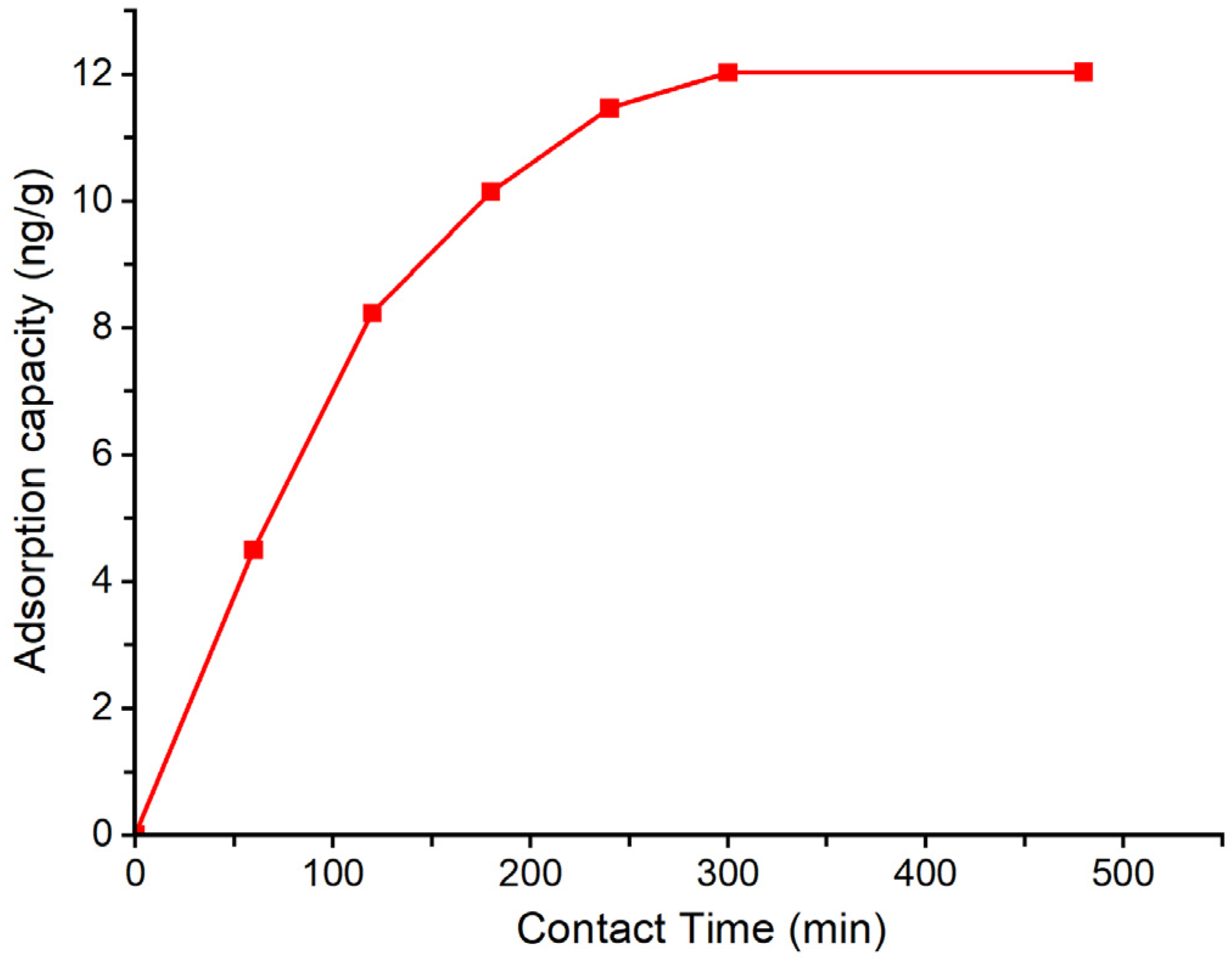
3.2. Effect of Contact Time
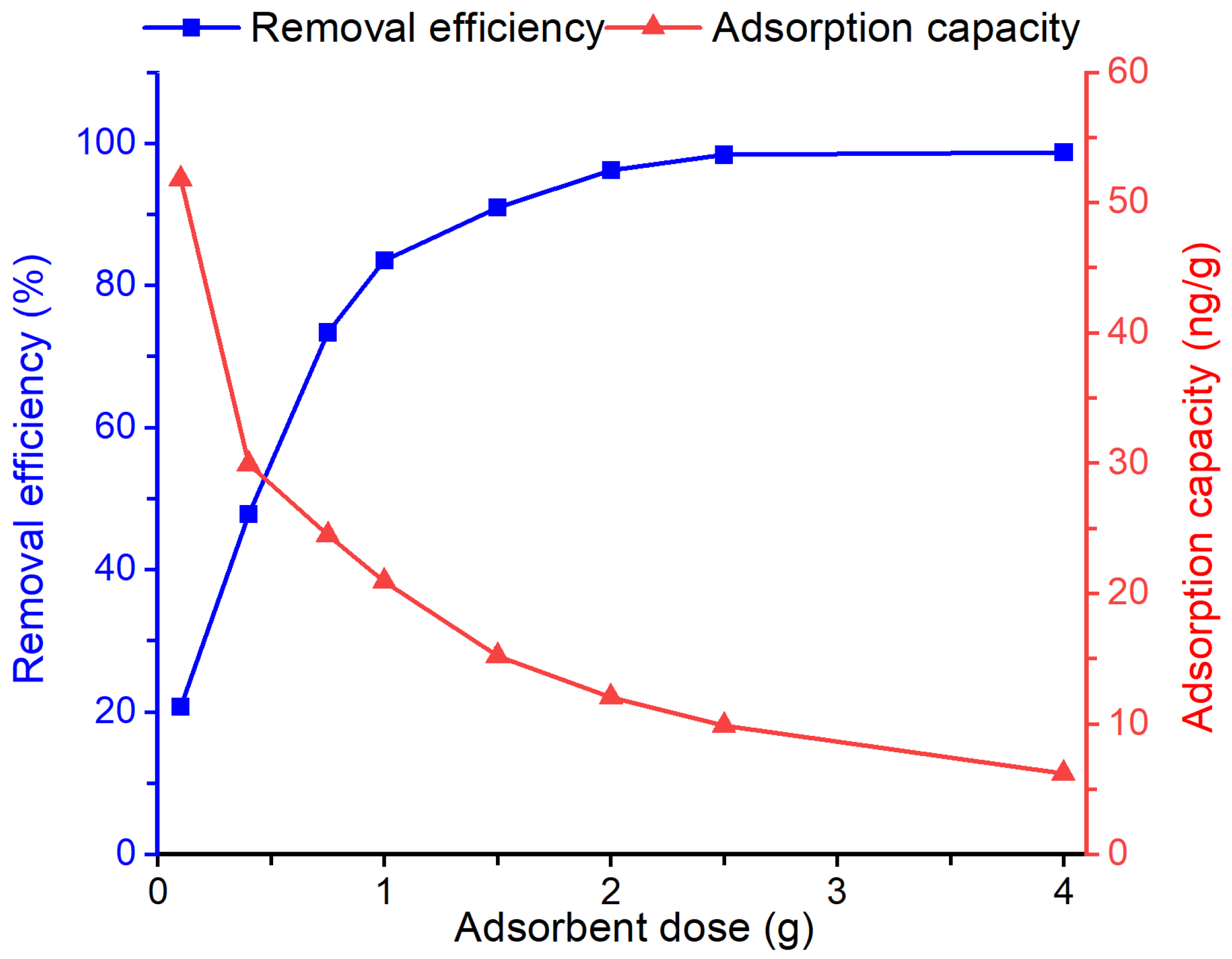
3.3. Effect of Dosage
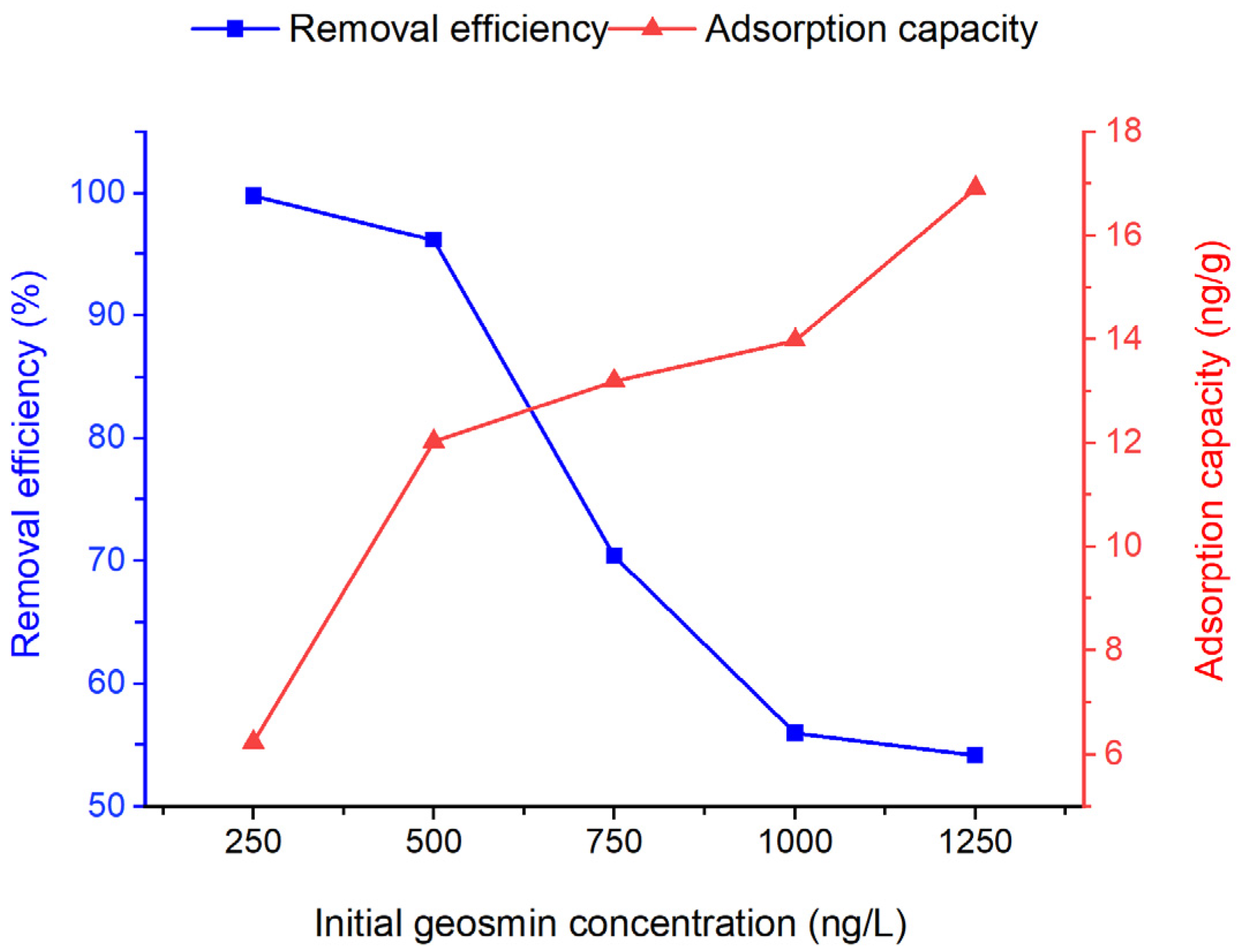
3.4. Effect of Initial Concentration of Geosmin
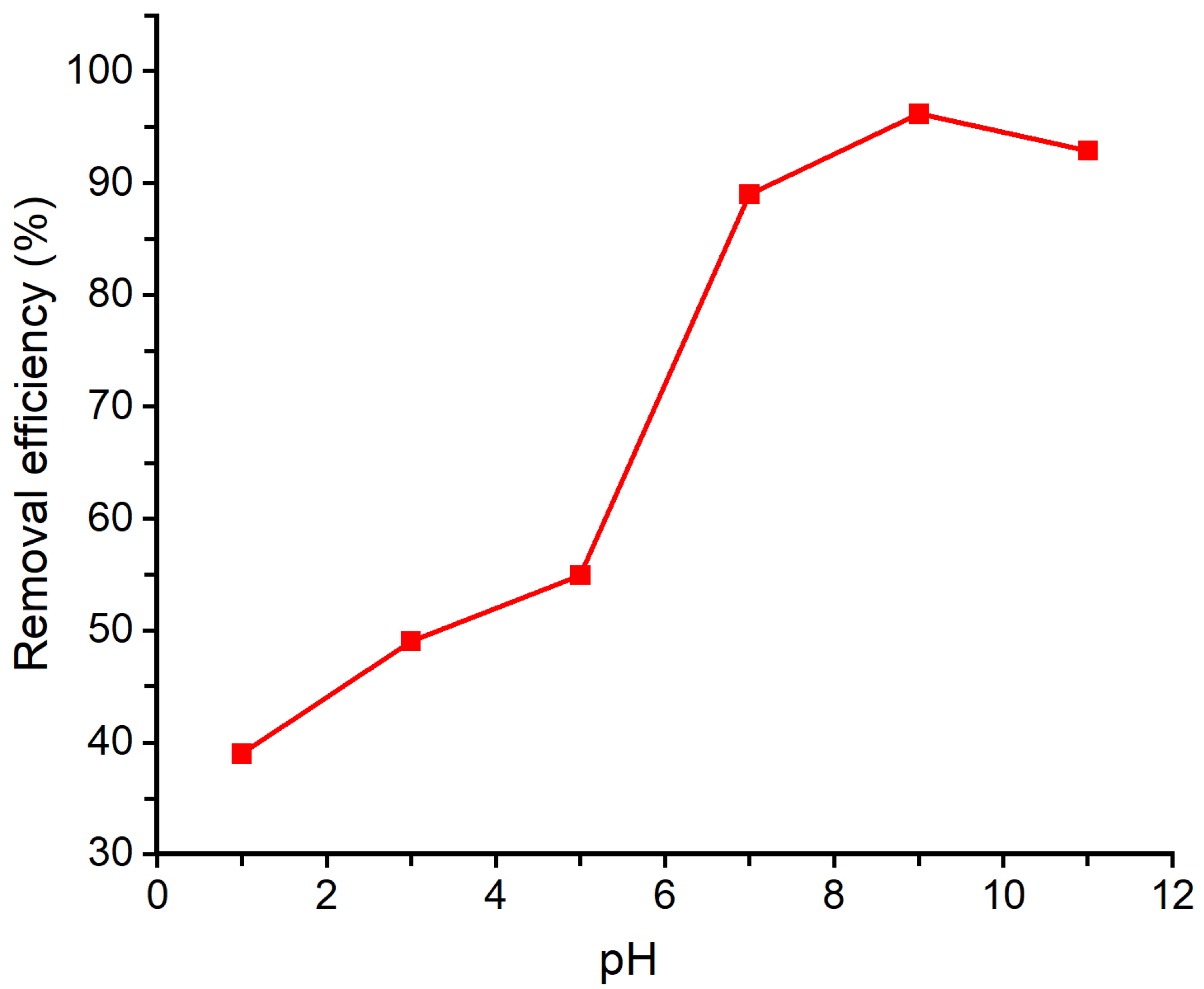
3.5. Effect of Initial pH
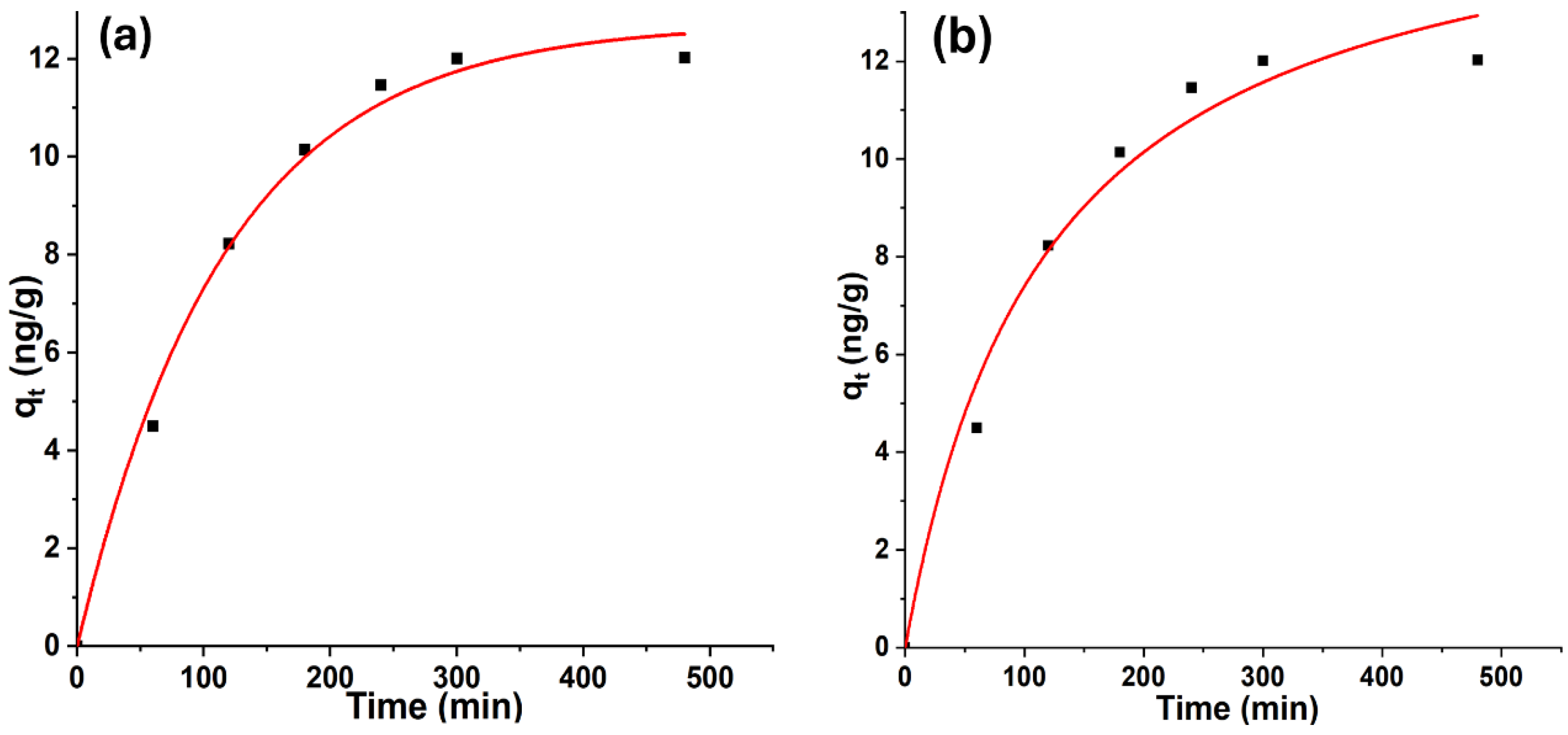
3.6. Adsorption Kinetic Study
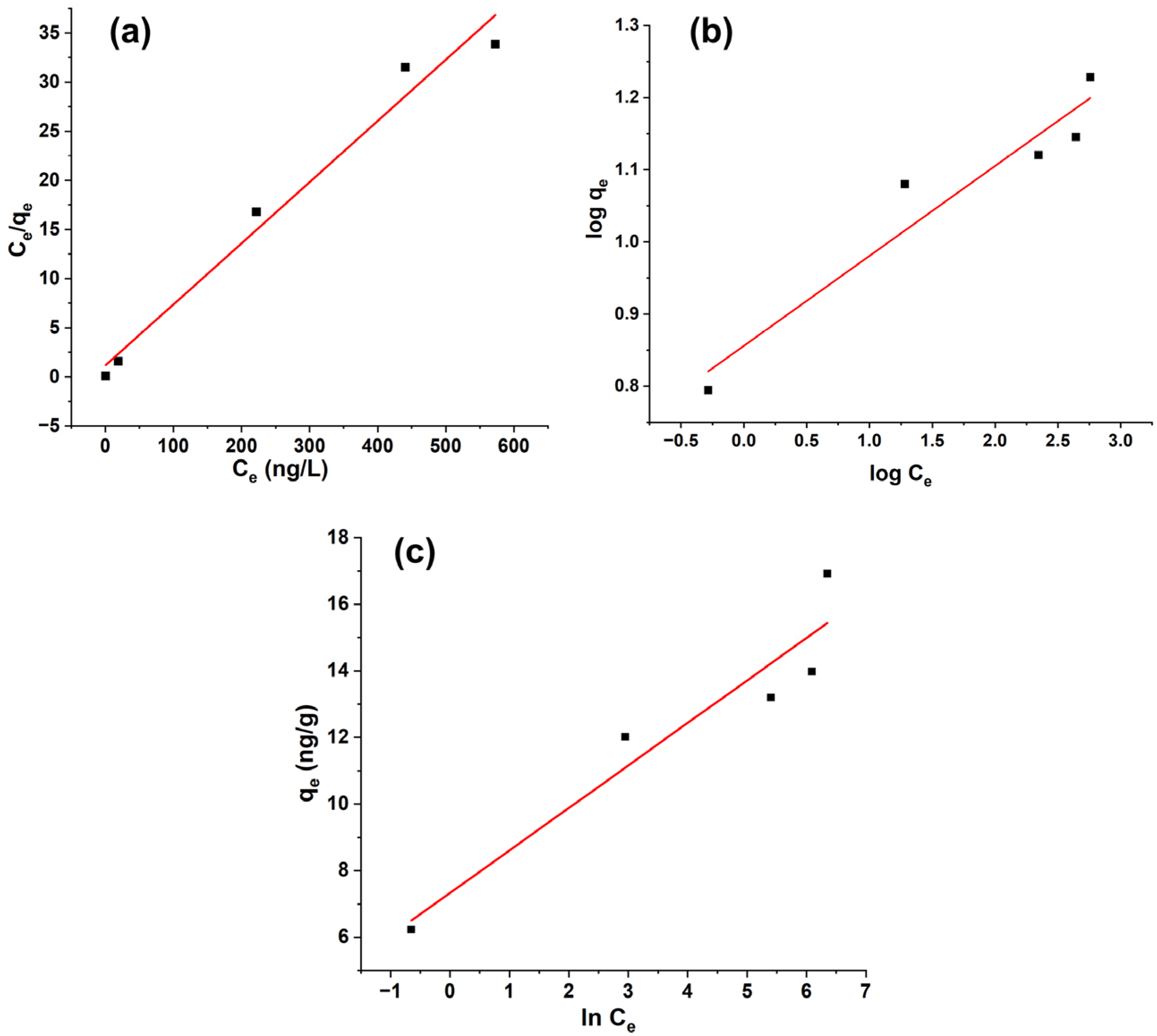
3.7. Adsorption Isotherm Study
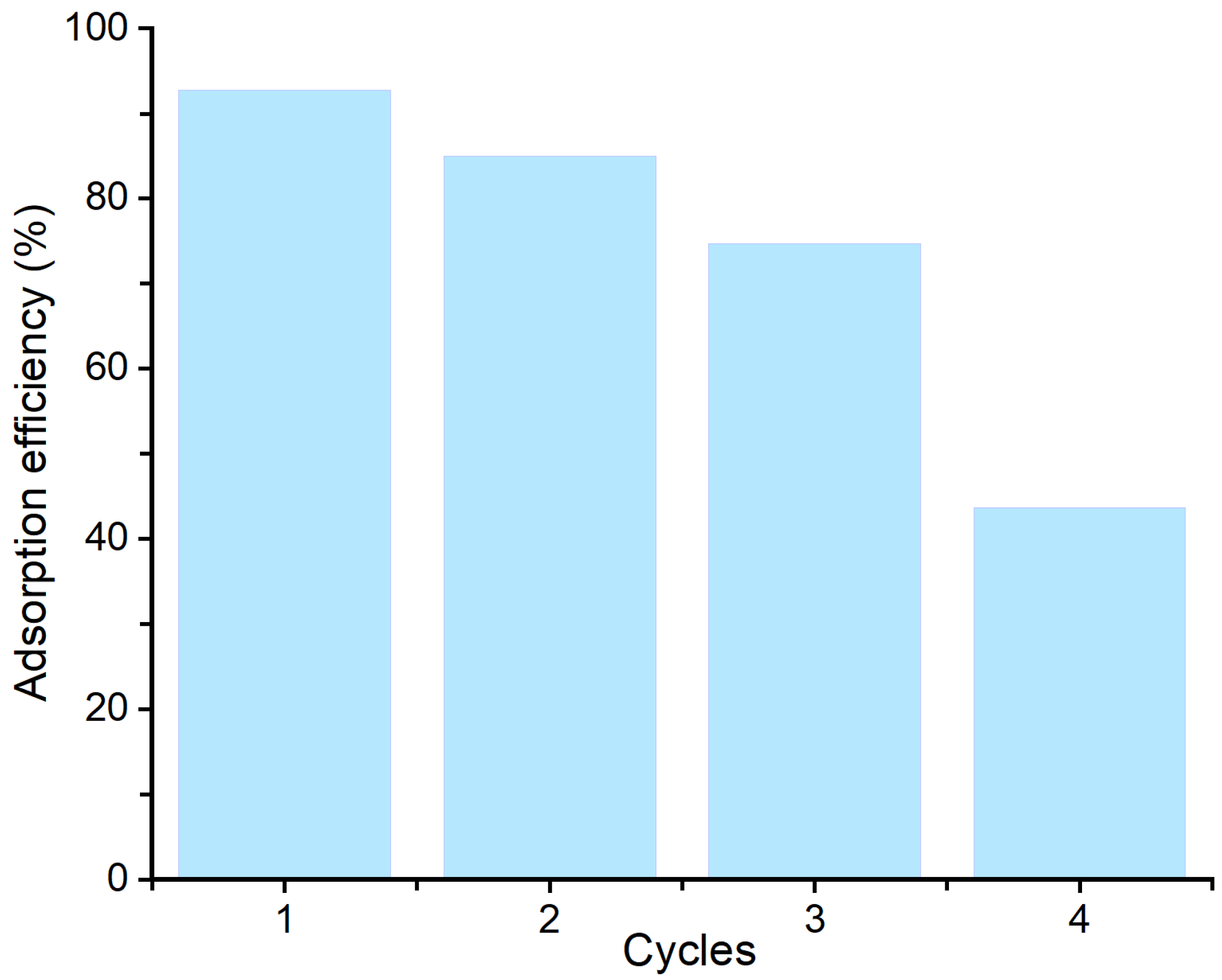
3.8. Reusability Studies
3.9. Comparison of the Adsorption Efficiency of Various Adsorbents for Geosmin
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Bent-alg-mag | Bentonite–alginate–magnetic |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy |
| GCMS | Gas chromatography/mass spectrometry |
| SPME | Solid-phase microextraction |
| PFO | Pseudo-first-order |
| PSO | Pseudo-second-order |
| NOM | Natural organic matter |
References
- Li, L.; Yang, S.; Yu, S.; Zhang, Y. Variation and Removal of 2-MIB in Full-Scale Treatment Plants with Source Water from Lake Tai, China. Water Res. 2019, 162, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suffet, I.M.; Khiari, D.; Bruchet, A. The Drinking Water Taste and Odor Wheel for the Millennium: Beyond Geosmin and 2-Methylisoborneol. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 40, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jüttner, F.; Watson, S.B. Biochemical and Ecological Control of Geosmin and 2-Methylisoborneol in Source Waters. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 4395–4406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.L.; Boyer, G.L.; Zimba, P.V. A Review of Cyanobacterial Odorous and Bioactive Metabolites: Impacts and Management Alternatives in Aquaculture. Aquaculture 2008, 280, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godo, T.; Saki, Y.; Nojiri, Y.; Tsujitani, M.; Sugahara, S.; Hayashi, S.; Kamiya, H.; Ohtani, S.; Seike, Y. Geosmin-Producing Species of Coelosphaerium (Synechococcales, Cyanobacteria) in Lake Shinji, Japan. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ömür-Özbek, P.; Little, J.; Dietrich, A. Ability of Humans to Smell Geosmin, 2-MIB and Nonadienal in Indoor Air When Using Contaminated Drinking Water. Water Sci. Technol. 2007, 55, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, D.; Westerhoff, P.; Brawley-Chesworth, A. Removal of 2-Methylisoborneol and Geosmin in Surface Water Treatment Plants in Arizona. J. Water Supply Res. Technol.—AQUA 2002, 51, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Li, X.; Liu, T.; Li, X.; Cui, Y.; Xu, L.; Huo, S.; Zou, B.; Qian, J.; Ma, A.; et al. Removal of Taste and Odor Compounds from Water: Methods, Mechanism and Prospects. Catalysts 2023, 13, 1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klausen, M.; Grønborg, O. Pilot Scale Testing of Advanced Oxidation Processes for Degradation of Geosmin and MIB in Recirculated Aquaculture. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2010, 10, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonopoulou, M.; Evgenidou, E.; Lambropoulou, D.; Konstantinou, I. A Review on Advanced Oxidation Processes for the Removal of Taste and Odor Compounds from Aqueous Media. Water Res. 2014, 53, 215–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Xu, D.; Li, F.; Fu, M.-L. Removal Efficiency and Possible Pathway of Odor Compounds (2-Methylisoborneol and Geosmin) by Ozonation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 117, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeldt, E.J.; Melcher, B.; Linden, K.G. UV and UV/H2O2 Treatment of Methylisoborneol (MIB) and Geosmin in Water. J. Water Supply Res. Technol.—AQUA 2005, 54, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Bolton, J.R.; Andrews, S.A.; Hofmann, R. UV/Chlorine Control of Drinking Water Taste and Odour at Pilot and Full-Scale. Chemosphere 2015, 136, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustapha, S.; Tijani, J.; Ndamitso, M.; Abdulkareem, A.; Shuaib, D.; Mohammed, A. A Critical Review on Geosmin and 2-Methylisoborneol in Water: Sources, Effects, Detection, and Removal Techniques. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhadi, S.; Huck, P.; Slawson, R. Removal of Geosmin and 2-Methylisoborneol by Biological Filtration. Water Sci. Technol. 2004, 49, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonopoulou, M.; Tzamaria, A.; Pedrosa, M.F.; Ribeiro, A.R.; Silva, A.M.; Kaloudis, T.; Hiskia, A.; Vlastos, D. Spirulina-Based Carbon Materials as Adsorbents for Drinking Water Taste and Odor Control: Removal Efficiency and Assessment of Cyto-Genotoxic Effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 927, 172227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bong, T.; Kang, J.-K.; Yargeau, V.; Nam, H.-L.; Lee, S.-H.; Choi, J.-W.; Kim, S.-B.; Park, J.-A. Geosmin and 2-Methylisoborneol Adsorption Using Different Carbon Materials: Isotherm, Kinetic, Multiple Linear Regression, and Deep Neural Network Modeling Using a Real Drinking Water Source. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 314, 127967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoschke, K.; Engel, C.; Börnick, H.; Worch, E. Adsorption of Geosmin and 2-Methylisoborneol onto Powdered Activated Carbon at Non-Equilibrium Conditions: Influence of NOM and Process Modelling. Water Res. 2011, 45, 4544–4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, D.; Newcombe, G.; Sztajnbok, P. The Application of Powdered Activated Carbon for MIB and Geosmin Removal: Predicting PAC Doses in Four Raw Waters. Water Res. 2001, 35, 1325–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, Y.; Nakao, S.; Sakamoto, A.; Taniguchi, T.; Pan, L.; Matsushita, T.; Shirasaki, N. Adsorption Capacities of Activated Carbons for Geosmin and 2-Methylisoborneol Vary with Activated Carbon Particle Size: Effects of Adsorbent and Adsorbate Characteristics. Water Res. 2015, 85, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Huang, Y.; Nie, Z.; Hofmann, R. The Effect of Water Temperature on the Removal of 2-Methylisoborneol and Geosmin by Preloaded Granular Activated Carbon. Water Res. 2020, 183, 116065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, Y.; Nakano, Y.; Hiroshi, H.; Ando, N.; Matsushita, T.; Ohno, K. Geosmin and 2-Methylisoborneol Adsorption on Super-Powdered Activated Carbon in the Presence of Natural Organic Matter. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 62, 2664–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Chen, X.; Qiu, L.; Xu, H.; Fan, L.; Meng, S.; Jiang, Z.; Song, C. N-Doping/KOH Synergy in Waste Moss Biochar for Geosmin Removal in Aquaculture Water: Elucidating Surface Functionalization and Activation Mechanisms. Biology 2025, 14, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosa, K.; Nakamura, G.; Miyabayashi, K.; Ishisaki, H.; Takahashi, Y. Adsorption of Geosmin and 2-MIB to Porous Coordination Polymer MIL-53 (Al). J. Water Environ. Technol. 2022, 20, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.-H.; Lee, H.-J.; Kim, W.-J.; Park, H.-G.; Cho, J.-S.; Heo, J.-S. Adsorptive Removal of 2-Methylisoborneol and Geosmin in Raw Water Using Activated Carbon and Zeolite. Korean J. Environ. Agric. 2001, 20, 244–251. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.; Xue, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Sugiura, N.; Yang, Y.; Li, M.; Chen, N.; Ying, Z.; Lei, Z. Development of Long-Life-Cycle Tablet Ceramic Adsorbent for Geosmin Removal from Water Solution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 2091–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, L.; Zuo, Y.; Huang, Y.; Song, L. Adsorption of 2-Methylisoborneol and Geosmin by a Low-Cost Hybrid Adsorbent Synthesized from Fly Ash and Bentonite. J. Water Supply Res. Technol.—AQUA 2011, 60, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, J.A.; Ahmad Zaini, M.A.; Surajudeen, A.; Aliyu, E.-N.U.; Omeiza, A.U. Surface Modification of Low-Cost Bentonite Adsorbents—A Review. Part. Sci. Technol. 2019, 37, 538–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S. A Comprehensive Review on Recent Developments in Bentonite-Based Materials Used as Adsorbents for Wastewater Treatment. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 241, 1091–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Xie, C.; Agar, O.T.; Barrow, C.J.; Dunshea, F.R.; Suleria, H.A. Alginates from Brown Seaweeds as a Promising Natural Source: A Review of Its Properties and Health Benefits. Food Rev. Int. 2024, 40, 2682–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abka-Khajouei, R.; Tounsi, L.; Shahabi, N.; Patel, A.K.; Abdelkafi, S.; Michaud, P. Structures, Properties and Applications of Alginates. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braccini, I.; Pérez, S. Molecular Basis of Ca2+-Induced Gelation in Alginates and Pectins: The Egg-Box Model Revisited. Biomacromolecules 2001, 2, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-M.; Xu, G.; Liu, Y.; He, T. Magnetic Fe3O4 Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Application in Water Treatment. Nanosci. Nanotechnol.-Asia 2011, 1, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akchiche, Z.; Abba, A.; Saggai, S. Magnetic Nanoparticles for the Removal of Heavy Metals from Industrial Wastewater. Alger. J. Chem. Eng. AJCE 2021, 1, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhlaghi, N.; Najafpour-Darzi, G. Manganese Ferrite (MnFe2O4) Nanoparticles: From Synthesis to Application—A Review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 103, 292–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, F.; Huang, K.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S. Preparation of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles with Adjustable Morphology. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 475, 898–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasooriya, I.L.; Senavirathna, M.D.H.J.; Wang, W. Application of Activated Carbon/Alginate Composite Beads for the Removal of 2-Methylisoborneol from Aqueous Solution. AppliedChem 2025, 5, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davranche, M.; Lacour, S.; Bordas, F.; Bollinger, J.-C. An Easy Determination of the Surface Chemical Properties of Simple and Natural Solids. J. Chem. Educ. 2003, 80, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senavirathna, M.D.H.J.; Jayasekara, M.A.D.D. Temporal Variation of 2-MIB and Geosmin Production by Pseudanabaena Galeata and Phormidium Ambiguum Exposed to High-intensity Light. Water Environ. Res. 2023, 95, e10834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayati-Ashtiani, M. Characterization of Nano-Porous Bentonite (Montmorillonite) Particles Using FTIR and BET-BJH Analyses. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2011, 28, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, R.R.; Lalhmunsiama; Bajaj, H.C.; Lee, S.-M. Activated Bentonite as a Low-Cost Adsorbent for the Removal of Cu(II) and Pb(II) from Aqueous Solutions: Batch and Column Studies. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 34, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Loh, M.; Aziz, J. Preparation and Characterization of Activated Carbon from Oil Palm Wood and Its Evaluation on Methylene Blue Adsorption. Dye. Pigment. 2007, 75, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saarai, A.; Kasparkova, V.; Sedlacek, T.; Sáha, P. On the Development and Characterisation of Crosslinked Sodium Alginate/Gelatine Hydrogels. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2013, 18, 152–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mollah, M.Z.; Faruque, M.R.; Bradley, D.; Khandaker, M.U.; Al Assaf, S. FTIR and Rheology Study of Alginate Samples: Effect of Radiation. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2023, 202, 110500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobato, N.C.C.; Mansur, M.B.; de Mello Ferreira, A. Characterization and Chemical Stability of Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Magnetic Nanoparticles. Mater. Res. 2017, 20, 736–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldron, R. Infrared Spectra of Ferrites. Phys. Rev. 1955, 99, 1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shipunova, V.O.; Nikitin, M.P.; Lizunova, A.A.; Ermakova, M.A.; Deyev, S.M.; Petrov, R.V. Polyethyleneimine-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles for Cell Labeling and Modification. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. 2013, 452, 245–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Xu, L.; Jiang, W.; Xuan, Y.; Lu, W.; Li, Z.; Yang, S.; Gu, Z. Adsorption Mechanism of Rhein-Coated Fe3O4 as Magnetic Adsorbent Based on Low-Field NMR. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 1052–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aichour, A.; Zaghouane-Boudiaf, H. Synthesis and Characterization of Hybrid Activated Bentonite/Alginate Composite to Improve Its Effective Elimination of Dyes Stuff from Wastewater. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azaria, S.; Nussinovitch, A.; Nir, S.; Mordechai, S.; van Rijn, J. Removal of Geosmin and 2-Methylisoborneol from Aquaculture Water by Novel, Alginate-Based Carriers: Performance and Metagenomic Analysis. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 42, 102125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafuka, A.; Nagasato, T.; Yamamura, H. Application of Graphene Oxide for Adsorption Removal of Geosmin and 2-Methylisoborneol in the Presence of Natural Organic Matter. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.; An, B.M.; So, S.; Chae, A.; Song, K.G. Simultaneous Control of Algal Micropollutants Based on Ball-Milled Powdered Activated Carbon in Combination with Permanganate Oxidation and Coagulation. Water Res. 2020, 185, 116263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alver, A.; Baştürk, E.; Altaş, L.; Işık, M. A Solution of Taste and Odor Problem with Activated Carbon Adsorption in Drinking Water: Detailed Kinetics and Isotherms. Desalin. Water Treat. 2022, 252, 300–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, A.; Khan, Z.; Maqbool, N.; Qazi, I.A.; Awan, M.A. Comparison of Adsorption Capability of Activated Carbon and Metal Doped TiO2 for Geosmin and 2-MIB Removal from Water. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 479103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.; Losso, J.N.; Marshall, W.E.; Rao, R.M. Physical and Chemical Properties of Selected Agricultural Byproduct-Based Activated Carbons and Their Ability to Adsorb Geosmin. Bioresour. Technol. 2002, 84, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Peng, F.; Li, H.; Wang, C.; Yang, Z. Adsorption of Geosmin and 2-Methylisoborneol onto Granular Activated Carbon in Water: Isotherms, Thermodynamics, Kinetics, and Influencing Factors. Water Sci. Technol. 2019, 80, 644–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Kinetic Models | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | ||||
| R2 | qe (ng/g) | K1 | R2 | qe (ng/g) | K2 |
| 0.9918 | 12.72 | 8.56 × 10−3 | 0.9757 | 16.10 | 5.27 × 10−4 |
| Isotherm Models | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Langmuir | Freundlich | Temkin | |||
| Parameters | Parameters | Parameters | |||
| qmax (ng/g) | 16.064 | KF (L/mg) | 7.177 | BT | 1.275 |
| KL (L/ng) | 0.054 | N | 8.029 | KT | 313.812 |
| R2 | 0.9705 | R2 | 0.902 | R2 | 0.8824 |
| RL | <1 | ||||
| Adsorbent | Dose (g/L) | Initial Concentration (ng/L) | Removal Efficiency (%) | Contact Time (min) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tablet ceramic adsorbent (akadama mud, wheat starch and Fe2O3) | 20 | 200 | 82% | 600 | [26] |
| Fly ash and bentonite hybrid adsorbent | 0.015 | 42–234 | 63.7% | 60 | [27] |
| Non-activated biochar KOH-activated N-doped biochar | 0.25 0.25 | 1000 | 91.3% 94.4% | 120 | [23] |
| Powdered Activated carbon | 0.1 | 100,000 | 94% | 90 | [53] |
| Fe-TiO2 Pt-TiO2 Granular Activated Carbon | 0.125 | 700 | 96% 99% 82% | 60 | [54] |
| <80 Mesh powdered activated carbon Calgon Filtrasorb 400 Steam-activated pecan shell Scientific carbons Acid-activated pecan shell CO2-activated pecan shell Steam-activated bagasse | 0.15 | 10,000 | >98% | 120 | [55] |
| Granular activated carbon | 0.16 | 700 | 98% | 120 | [56] |
| Bent-alg-mag beads | 40 | 500 | 96.18% | 480 | Present study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Balasooriya, I.L.; Senavirathna, M.D.H.J. Effective Removal of Geosmin from Aqueous Solution Using Bentonite–Alginate–Magnetic Composite. AppliedChem 2026, 6, 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem6010008
Balasooriya IL, Senavirathna MDHJ. Effective Removal of Geosmin from Aqueous Solution Using Bentonite–Alginate–Magnetic Composite. AppliedChem. 2026; 6(1):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem6010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleBalasooriya, Iresha Lakmali, and Mudalige Don Hiranya Jayasanka Senavirathna. 2026. "Effective Removal of Geosmin from Aqueous Solution Using Bentonite–Alginate–Magnetic Composite" AppliedChem 6, no. 1: 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem6010008
APA StyleBalasooriya, I. L., & Senavirathna, M. D. H. J. (2026). Effective Removal of Geosmin from Aqueous Solution Using Bentonite–Alginate–Magnetic Composite. AppliedChem, 6(1), 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem6010008






