Molecular Docking Assessment of Limonoids from Cameroonian Entandrophragma Species as Potential Inhibitors of Anopheles gambiae Acetylcholinesterase (AChE)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. The Limonoids Involved in This Study
2.2. Geometry Optimization
2.3. Molecular Docking
2.4. Molecular Dynamics Simulation
2.5. Trajectory Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Geometry Optimization
3.2. Molecular Docking Simulation
3.3. Molecular Dynamics Simulation
3.3.1. Root Mean Square Deviation (RMSD)
3.3.2. Root Mean Square Fluctuations
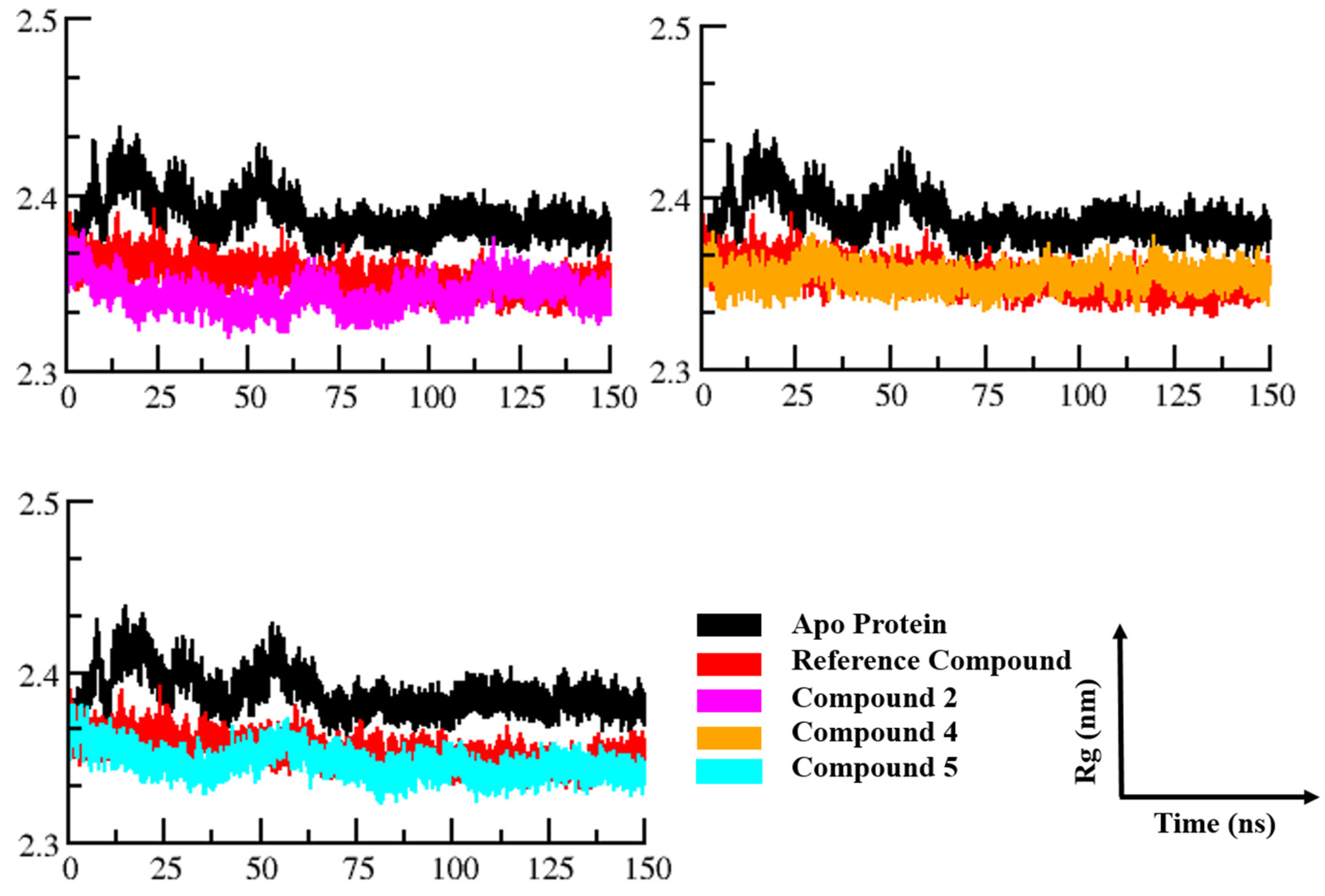
3.3.3. Radius of Gyration
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Happi, G.M.; Nangmo, P.K.; Dzouemo, L.C.; Kache, S.F.; Kouam, A.D.K.; Wansi, J.D. Contribution of Meliaceous plants in furnishing lead compounds for antiplasmodial and insecticidal drugs development. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 285, 114906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Happi, G.M.; Meikeu, L.Z.; Sikam, K.G.; Dzouemo, L.C.; Wansi, J.D. Mushrooms (Basidiomycetes) as a significant source of biologically active compounds for malaria control. Nat. Res. Hum. Health 2022, 2, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Happi, G.M.; Ahmed, S.A.; Kemayou, G.P.M.; Salau, S.; Dzouemo, L.C.; Sikam, K.G.; Yimtchui, M.T.; Wansi, J.D. Bioassay-guided isolation of antiplasmodial compounds from Hypericum lanceolatum Lam. (Hypericaceae), their cytotoxicity and molecular docking. BioMed Res. Int. 2023, 2023, 4693765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Happi, G.M.; Ntabo, V.K.; Soh, D.; Wansi, J.D. Potential of Streptomyces in producing antiplasmodial lead compounds. Nat. Res. Hum. Health 2023, 3, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Happi, G.M.; Kouam, S.F.; Talontsi, F.M.; Lamshöft, M.; Zühlke, S.; Bauer, J.O.; Strohmann, C.; Spiteller, M. Antiplasmodial and cytotoxic triterpenoids from the bark of the Cameroonian medicinal plant Entandrophragma congoënse. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 604–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alout, H.; Labbe, P.; Berthomieu, A.; Djogbenou, L.; Leonetti, J.P.; Fort, P.; Weill, M. Novel AChE inhibitors for sustainable insecticide resistance management. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trang, A.; Khandhar, P.B. Physiology, Acetylcholinesterase; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021; Available online: https://europepmc.org/article/nbk/nbk539735 (accessed on 9 March 2023).
- Hematpoor, A.; Liew, S.Y.; Azirun, M.S.; Awang, K. Insecticidal activity and the mechanism of action of three phenylpropanoids isolated from the roots of Piper sarmentosum Roxb. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Happi, G.M.; Ngadjui, B.T.; Green, I.R.; Kouam, S.F. Phytochemistry and pharmacology of the genus Entandrophragma over the 50 years from 1967 to 2018: A ‘golden’ overview. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2018, 70, 1431–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Happi, H.M.; Kemayou, G.P.M.; Stammler, H.G.; Neumann, B.; Ismail, M.; Kouam, S.F.; Wansi, J.D.; Tchouankeu, J.C.; Frese, M.; Lenta, B.N.; et al. Three phragmalin-type limonoids orthoesters and the structure of odoratone isolated from the bark of Entandrophragma candollei (Meliaceae). Phytochemistry 2021, 181, 112537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Saraf, S. Limonoids: Overview of significant bioactive triterpenes distributed in plants kingdom. Biol. Pharmaceut. Bull. 2006, 29, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Happi, G.M.; Kouam, S.F.; Talontsi, F.M.; Zühlke, S.; Lamshöft, M.; Spiteller, M. Minor secondary metabolites from the bark of Entandrophragma congoënse (Meliaceae). Fitoterapia 2015, 102, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Happi, G.M.; Talontsi, F.M.; Laatsch, H.; Zühlke, S.; Ngadjui, B.T.; Spiteller, M.; Kouam, S.F. seco-Tiaminic acids B and C: Identification of two 3,4-seco-tirucallane triterpenoids isolated from the root of Entandrophragma congoënse (Meliaceae). Fitoterapia 2018, 124, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Happi, G.M.; Wouamba, S.C.N.; Ismail, M.; Kouam, S.F.; Frese, M.; Lenta, B.N.; Sewald, N. Ergostane-type steroids from the Cameroonian ‘white tiama’ Entandrophragma angolense. Steroids 2020, 156, 108584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, T.O.; Abolaji, A.O.; Omale, S.; Longdet, Y.I.; Kutshik, J.R.; Oyetayo, O.B.; Adegboyega, A.E.; Sagay, A. Benzo[a]pyrene and Benzo[a]pyrene-7,8-dihydrodiol-9,10-epoxide induced locomotor and reproductive senescence and altered biochemical parameters of oxidative damage in Canton-S Drosophila melanogaster. Toxicol. Rep. 2021, 8, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menozzi, P.; Shi, M.A.; Lougarre, A.; Tang, Z.H.; Fournier, D. Mutations of acetylcholinesterase which confer insecticide resistance in Drosophila melanogaster populations. BMC Evol. Biol. 2004, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seniya, C.; Khan, G.J.; Uchadia, K. Identification of a potential herbal inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase associated Alzheimer’s disorders using molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation. Biochem. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 705451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Akisanya, A.; Bevan, C.W.L.; Hirst, J.; Halsall, T.G.; Taylor, D.A.H. West African timbers. Part III. Petroleum extracts from the genus Entandrophragma. J. Chem. Soc. 1960, 3827–3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchouankeu, J.C.; Tsamo, E.; Sondengam, B.L.; Conolly, J.D.; Rycroft, D.S. Entilins A and B, two novel heptanortriterpenoid derivatives from Entandrophragma utile (Meliaceae): Structural elucidation using 2D NMR long-range δC/δH correlation experiments. Tetrahedron Lett. 1990, 31, 4505–4508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniewski, W.M.; Gumulka, M.; Pankowska, E.; Bloszyk, E. Entilin C, a novel heptanortriterpenoid from Entandrophragma utile (Meliaceae). Pol. J. Chem. 1994, 68, 499–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaaf, O.; Jarvis, A.P.; van der Esch, S.A.; Giagnacovo, G.; Oldham, N.J. Rapid and sensitive analysis of azadirachtin and related triterpenoids from neem (Azadirachta indica) by high-performance liquid chromatography–atmospheric pressure chemical ionization mass spectrometry. J. Chrom. A 2000, 886, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, K.; Chattopadhyay, I.; Banerjee, R.K.; Bandopadhyay, U. Biological Activities and Medicinal Properties of Neem (Azadirachta indica). Curr. Sci. 2002, 82, 1336–1345. [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis, P.A.; Morgan, E.D. Analysis of small samples of limonoids of neem (Azadirachta indica) using solid phase extraction from tissue culture. Phytochem. Anal. 2000, 11, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndung’u, M.; Hassanali, A.; Hooper, A.M.; Chhabra, S.; Miller, T.A.; Paul, R.L.; Torto, B. Ring A-seco mosquito larvicidal limonoids from Turraea wakefieldii. Phytochemistry 2003, 64, 817–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndung’u, M.; Torto, B.; Knols, B.G.J.; Hassanali, A. Laboratory evaluation of some eastern African Meliaceae as sources of larvicidal botanicals for Anopheles gambiae. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2004, 24, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndung’u, M.W.; Kaoneka, B.; Hassanali, A.; Lwande, W.; Hooper, A.M.; Tayman, F.; Zerbe, O.; Torto, B. New mosquito larvicidal tetranortriterpenoids from Turraea wakefieldii and Turraea floribunda. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 5027–5031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 09, Revision 09W (No. 09); Gaussian Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2016; Available online: https://gaussian.com/ (accessed on 9 March 2023).
- Ul-Haq, Z.; Khan, A.; Ashraf, S.; Morales-Bayuelo, A. Quantum mechanics and 3D-QSAR studies on thienopyridine analogues: Inhibitors of IKKβ. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halgren, T.A. Merck molecular force field. I. Basis, form, scope, parameterization, and performance of MMFF94. J. Comp. Chem. 1996, 17, 490–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemical Computing Group Inc. Molecular Operating Environment (MOE), 2013.08; Chemical Computing Group Inc.: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2016; Volume 354. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Q.; Wong, D.M.; Robinson, H.; Ding, H.; Lam, P.C.H.; Totrov, M.M.; Carlier, P.R.; Li, J. Crystal structure of acetylcholinesterase catalytic subunits of the malaria vector Anopheles gambiae. Insect Sci. 2018, 25, 721–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera—A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comp. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, P.; Vanamamalai, V.K.; Jali, I.; Sharma, S. In silico prediction of the animal susceptibility and virtual screening of natural compounds against SARS-CoV-2: Molecular dynamics simulation based analysis. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 906955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Chandrasekhar, J.; Madura, J.D.; Impey, R.W.; Klein, M.L. Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 79, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornak, V.; Abel, R.; Okur, A.; Strockbine, B.; Roitberg, A.; Simmerling, C. Comparison of multiple Amber force fields and development of improved protein backbone parameters. Proteins 2006, 65, 712–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martyna, G.J.; Klein, M.L.; Tuckerman, M. Nosé–Hoover chains: The canonical ensemble via continuous dynamics. J. Chem. Phys. 1992, 97, 2635–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martoňák, R.; Laio, A.; Parrinello, M. Predicting crystal structures: The Parrinello-Rahman method revisited. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 90, 075503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adelusi, T.; Oyedele, A.Q.K.; Boyenle, I.D.; Ogunlana, A.T.; Adeyemi, R.O.; Ukachi, C.D.; Idris, M.O.; Olaoba, O.T.; Adedotun, I.O.; Kolawole, O.E.; et al. Molecular modeling in drug discovery. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2022, 29, 100880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyedele, A.Q.K.; Adelusi, T.I.; Ogunlana, A.T.; Adeyemi, R.O.; Atanda, O.E.; Babalola, M.O.; Ashiru, M.A.; Ayoola, I.J.; Boyenle, I.D. Integrated virtual screening and molecular dynamics simulation revealed promising drug candidates of p53-MDM2 interaction. J. Mol. Model. 2022, 28, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyedele, A.Q.K.; Ogunlana, A.T.; Boyenle, I.D.; Adeyemi, A.O.; Rita, T.O.; Adelusi, T.I.; Abdul-Hammed, M.; Elegbeleye, O.E.; Odunitan, T.T. Docking covalent targets for drug discovery: Stimulating the computer-aided drug design community of possible pitfalls and erroneous practices. Mol. Divers. 2023, 27, 1879–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashiru, M.A.; Ogunyemi, S.O.; Temionu, O.R.; Ajibare, A.C.; Cicero-Mfon, N.C.; Ihekuna, O.A.; Jagun, M.O.; Abdulmumin, L.; Adisa, Q.K.; Asibor, Y.E.; et al. Identification of EGFR inhibitors as potential agents for cancer therapy: Pharmacophore-based modeling, molecular docking, and molecular dynamics investigations. J. Mol. Model. 2023, 29, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
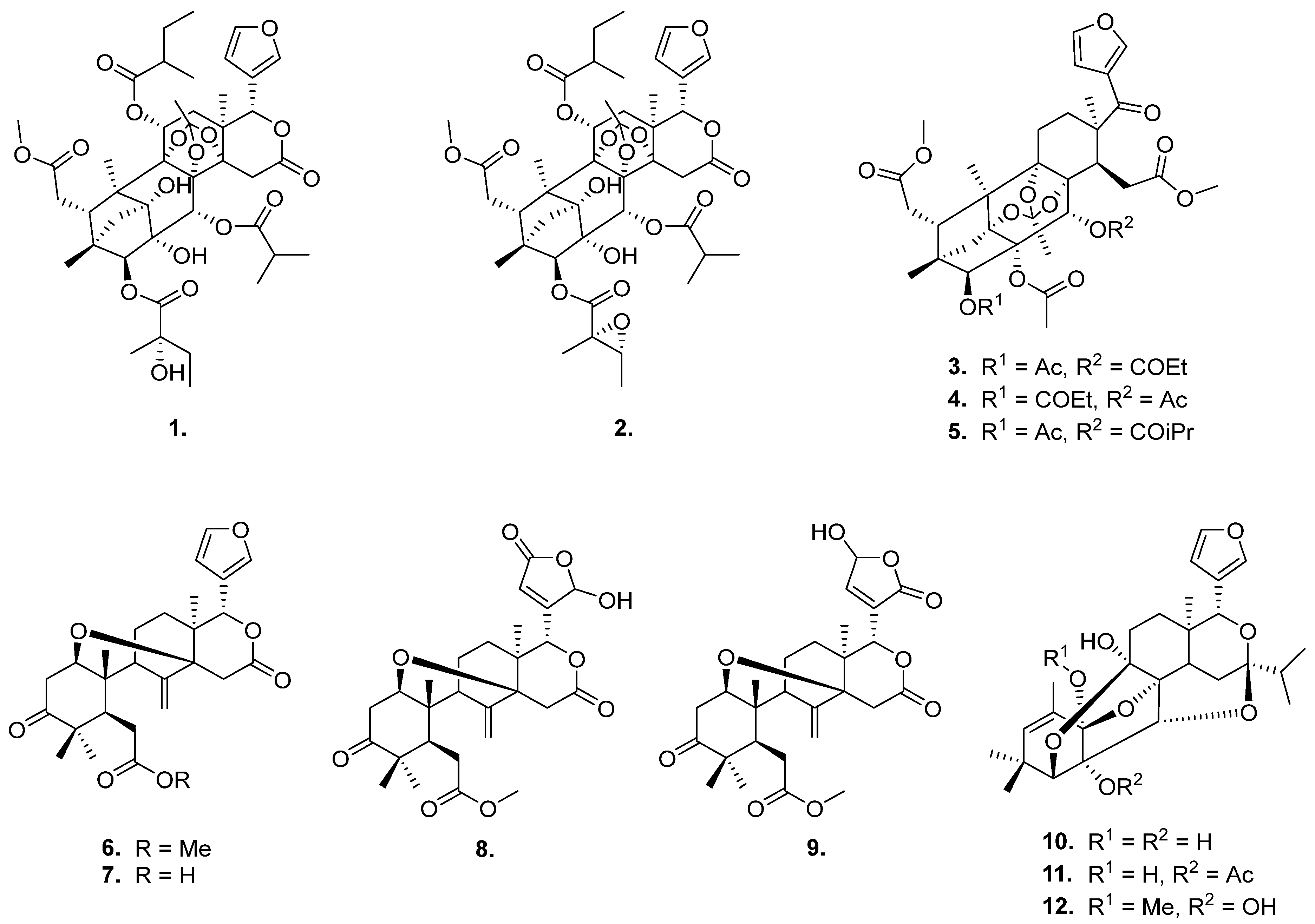
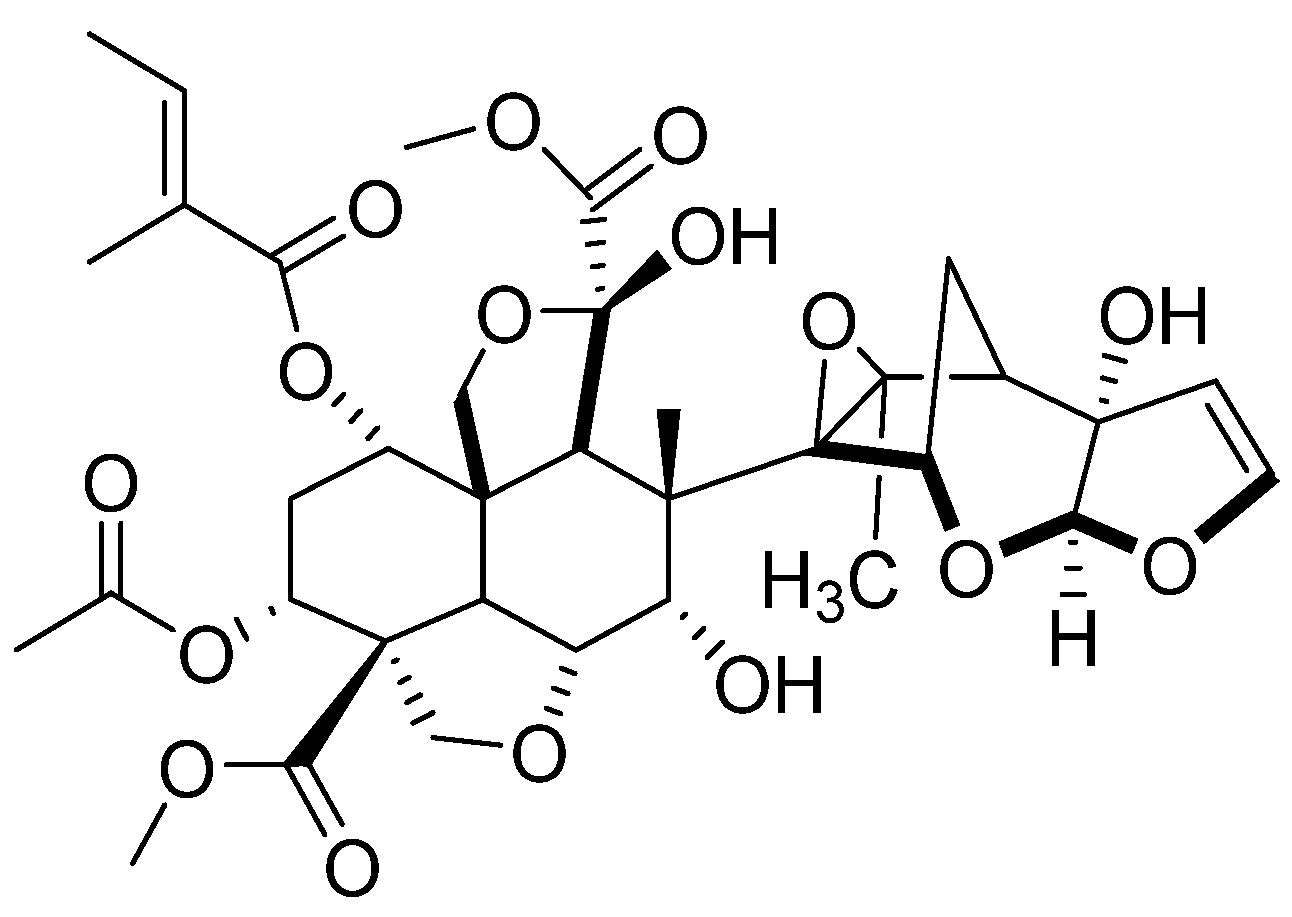
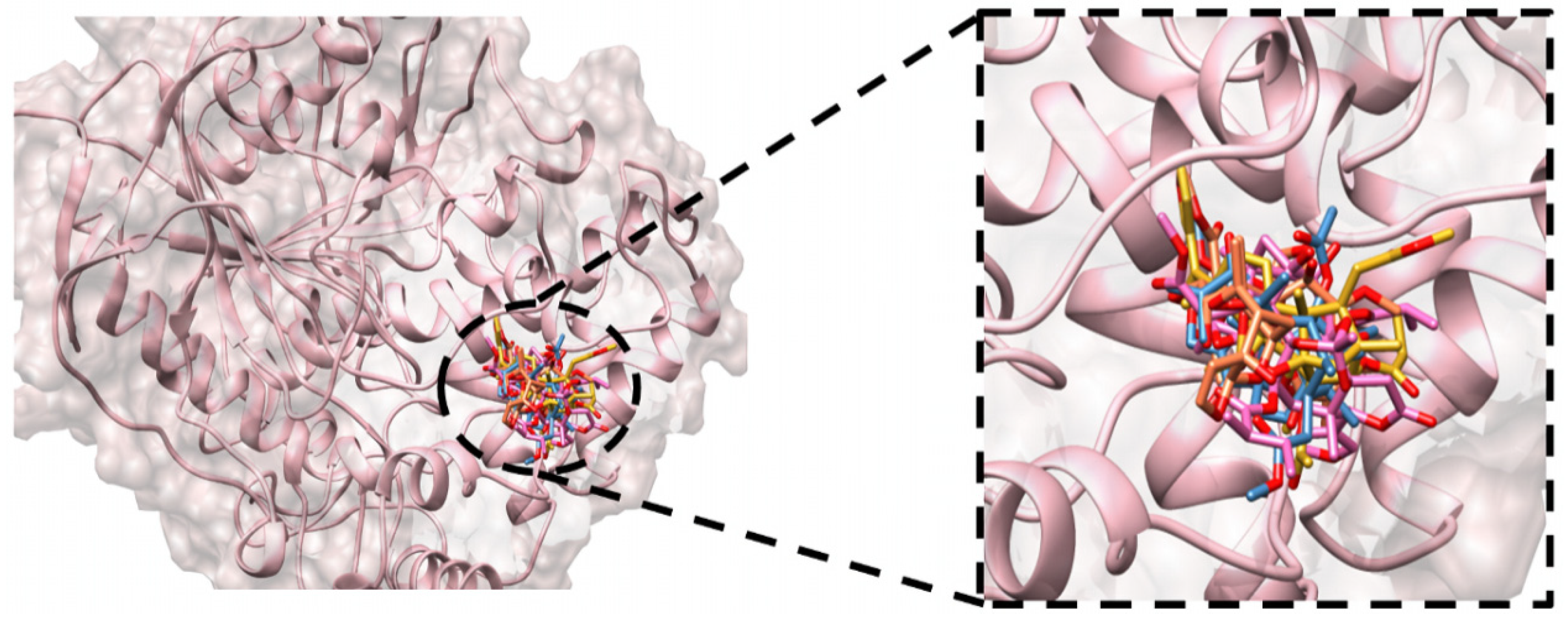
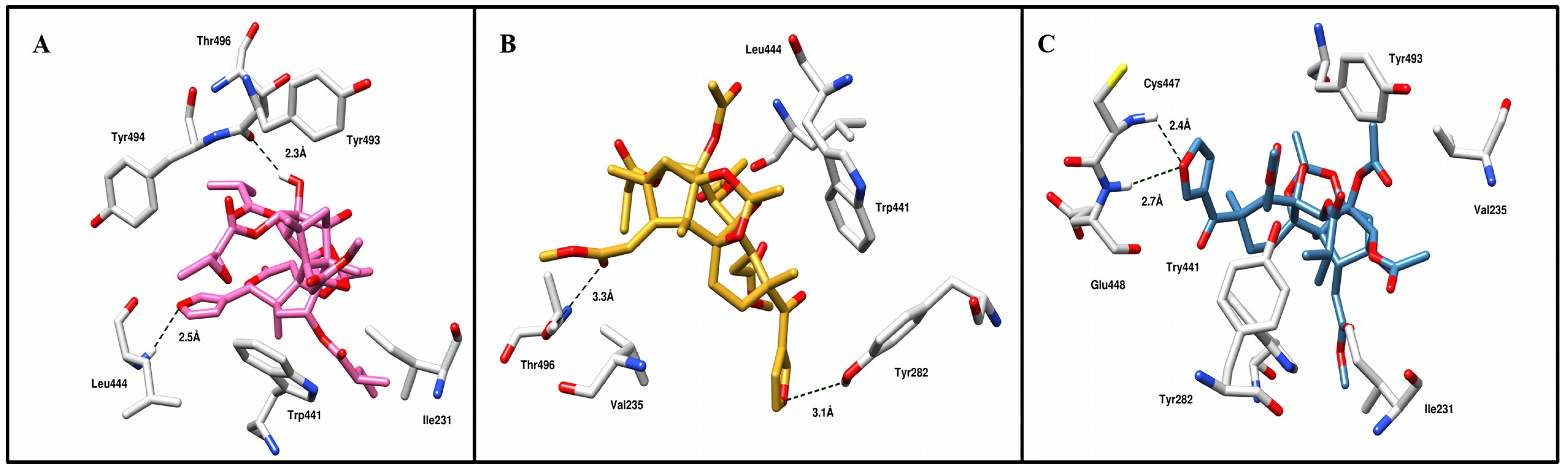


| Compounds | Optimized 3D Structure | Energy (Hartree) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 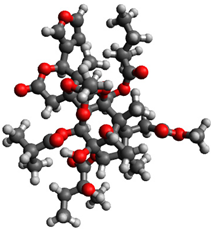 | −1.186023 |
| 2 | 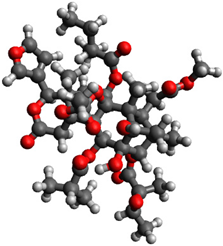 | −1.116389 |
| 3 | 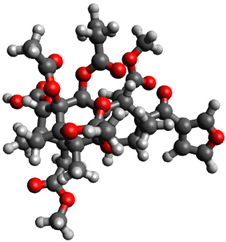 | −1.038584 |
| 4 | 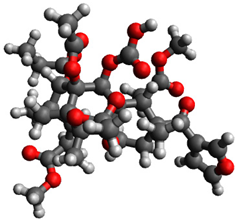 | −1.035614 |
| 5 |  | −1.046825 |
| 6 |  | −0.442500 |
| 7 | 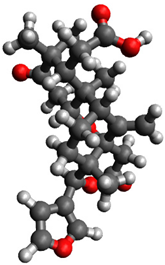 | −0.448302 |
| 8 |  | −0.584515 |
| 9 |  | −0.582419 |
| 10 |  | −0.551982 |
| 11 | 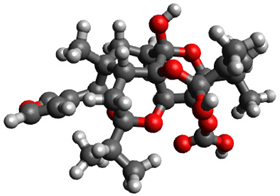 | −0.671810 |
| 12 | 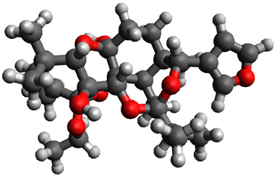 | −0.549421 |
| Azadirachtin |  | −0.845361 |
| Compound | Docking Score (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|
| 1 | −6.18 |
| 2 | −6.45 |
| 3 | −5.76 |
| 4 | −7.00 |
| 5 | −7.28 |
| 6 | −5.24 |
| 7 | −5.41 |
| 8 | −6.10 |
| 9 | −5.40 |
| 10 | −5.68 |
| 11 | −6.00 |
| 12 | −5.16 |
| Azadirachtin | −6.22 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Happi, G.M.; Haider, S.; Ahmed, S.A.; Ul-Haq, Z. Molecular Docking Assessment of Limonoids from Cameroonian Entandrophragma Species as Potential Inhibitors of Anopheles gambiae Acetylcholinesterase (AChE). AppliedChem 2024, 4, 320-332. https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem4040020
Happi GM, Haider S, Ahmed SA, Ul-Haq Z. Molecular Docking Assessment of Limonoids from Cameroonian Entandrophragma Species as Potential Inhibitors of Anopheles gambiae Acetylcholinesterase (AChE). AppliedChem. 2024; 4(4):320-332. https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem4040020
Chicago/Turabian StyleHappi, Gervais Mouthé, Sajjad Haider, Sikiru Akinyeye Ahmed, and Zaheer Ul-Haq. 2024. "Molecular Docking Assessment of Limonoids from Cameroonian Entandrophragma Species as Potential Inhibitors of Anopheles gambiae Acetylcholinesterase (AChE)" AppliedChem 4, no. 4: 320-332. https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem4040020
APA StyleHappi, G. M., Haider, S., Ahmed, S. A., & Ul-Haq, Z. (2024). Molecular Docking Assessment of Limonoids from Cameroonian Entandrophragma Species as Potential Inhibitors of Anopheles gambiae Acetylcholinesterase (AChE). AppliedChem, 4(4), 320-332. https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem4040020








