Abstract
The multifaceted health benefits of curcumin (Curcuma longa), attributed to its antioxidant, antitumor, and anti-inflammatory activities, have drawn significant scientific attention. Curcumin shows promise as a potential modulator of macrophage polarization, offering a natural strategy for managing inflammation and promoting tissue repair. However, a limiting factor for this beneficial molecule is its limited bioavailability due to its low solubility in water. This study aimed to quantify the effect of curcumin gold nanoparticle (CurAuNP)-mediated ultrasound irradiation on THP-1-derived macrophages as potential therapeutic targets. The photoreduction method was applied to synthesize the gold nanoparticles with curcumin as a ligand (CurAu). The effect of adding polyethylene glycol in the synthesis process was studied (CurAuPEG). CurAuNP characterization included UV/Vis, Zeta potential, transmission electron microscopy, and FTIR. The amount of singlet oxygen released by curcumin and CurAuNPs was quantified by observing 1.3-diphenylisobenzofuran quenching upon ultrasound irradiation (1 MHz and 1 W/cm2). The results indicated that ultrasound therapy for 4 min with CurAuNPs significantly enhanced singlet oxygen generation and reduced macrophage viability compared to curcumin alone. The increased sonoluminescence and curcumin delivery facilitated by CurAuNPs led to greater curcumin activation. Consequently, CurAuNPs could offer promising therapeutic options for modulating macrophage polarization in pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory stages.
1. Introduction
Curcumin, extracted from the natural spice turmeric (Curcuma longa L.), is one of the most investigated naturally occurring compounds with a wide range of potential therapeutic properties [1]. Commonly used in Indian and Southeast Asian cuisine, curcumin has been linked to various potential health benefits and medical properties, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anticancer effects, pain relief, and improved brain function and heart health [1,2,3]. In vitro studies using cancer cell lines show that curcumin is preferentially taken up compared to healthy cell lines [4]. Curcumin exhibits antitumor activity in breast, lung, head and neck, prostate, and brain cancers [5].
Curcumin can modulate macrophage polarization, which helps to resolve inflammation, promote tissue repair, and regulate immune responses [6]. Macrophages are essential innate immune system components, subdivided into the M1 and M2 phenotypes [7,8]. M1 macrophages mediate pro-inflammatory processes and participate in removing foreign bodies [9]. In contrast, M2 macrophages exhibit anti-inflammatory activity that is particularly relevant in inflammatory diseases [10]. According to the environmental signals, macrophages possess remarkable plasticity, allowing them to switch between their activated M1 state and the M2 phenotype and vice versa. Downregulating M1 or repolarizing M1 macrophages to M2 macrophages in inflammatory disorders are two practical approaches to suppressing inflammation. Yaoyao Zhou et al. observed that curcumin modulates macrophage polarization by inhibiting the toll-like receptor 4 expression and signaling pathways [11]. Sahaoxi Yan et al. studied the anti-inflammatory effects of curcumin on a mouse myocardial infarction model by regulating macrophage polarization [12]. They concluded that curcumin suppressed the M1-induced inflammation by modulating macrophage polarization partly via the AMPK pathway. There is a close relationship between macrophages and tumors. Recently, Ge SK et al. investigated the underlying mechanism of the antitumor effect of curcumin in colorectal cancer cells, focusing on the M2 polarization of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) [13]. They concluded that MACC1 and inhibition of M2 polarization of TAMs may mediate the antiproliferative and anti-migratory effects of curcumin in colorectal cancer cells. Elham Abdollahi et al. observed that curcumin enhances antitumor immunity via macrophage polarization and ameliorates inflammatory diseases, including autoimmune issues, nephropathy, chronic serum sickness, stroke, and atherosclerosis [14].
Curcumin can generate reactive oxygen species (ROS) under light or ultrasound (US) excitations, indicating potential applications in photodynamic (PDT) and sonodynamic (SDT) therapies [4,15,16,17]. SDT is a noninvasive therapeutic approach with promising applications in various fields, including cancer, inflammatory disease management, antimicrobial therapy, and environmental remediation. Its effectiveness relies on the synergistic effect of low-intensity ultrasound and sonosensitization [18,19,20,21].
SDT requires low-intensity ultrasound, a sonosensitizer, and molecular oxygen [22]. Ultrasound waves can penetrate much deeper into tissues compared to the light used in PDT. This makes SDT beneficial for treating deeper tumors or lesions that are inaccessible with light. The excitation of sonosensitizers is followed by the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and cell apoptosis [23]. Ultrasound waves trigger mechanical effects like temperature rise, membrane disruption, and physicochemical and biological consequences, primarily through cavitation. Cavity bubbles pulsate in two ways: stable cavitation and inertial cavitation. During inertial cavitation implosion, a cascade of events unfolds: sound waves, high-pressure jets, water breakdown, light emission, or sonoluminescence that mediates ROS production [24]. The predominant ROS generated is singlet oxygen, a highly reactive molecule that oxidizes cellular components like mitochondria and DNA, leading to irreversible damage. Additionally, free radicals like hydroxyl radicals can trigger chain reactions that further damage cells [25]. Ultimately, these combined effects culminate in cellular events, including membrane disruption, DNA fragmentation, and cell death.
Curcumin possesses a sonodynamic effect on THP-1-derived macrophages, inducing apoptosis or necrosis [17,26]. However, nanotechnology offers several promising approaches for delivering curcumin specifically to cancer cells or inflamed tissues, overcoming limitations like low solubility and bioavailability [27]. Nanoparticle (NP)-based sonosensitizers or sononanosensitizers can overcome these limitations [28,29,30,31,32]. Several promising approaches for delivering curcumin, specifically to cancer cells, have been proposed with some nanoparticle carriers, for example, liposomes, polymeric nanoparticles, and gold nanoparticles [33]. With their remarkable optical properties, gold nanoparticles emerge as powerful tools for precise drug delivery [34].
Several studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of curcumin as a reducing and stabilizing agent in gold nanoparticle (AuNP) synthesis [35]. Sreelakshmi et al. [36] successfully synthesized AuNPs using curcumin at a high pH (11) in the primary media. Singh et al. [37] highlighted the efficiency of curcumin as a reducing agent at elevated temperatures (90 °C) for AuNP synthesis. Kurdi et al. prepared AuNPs with different shapes and sizes using curcumin and several surfactants [38]. Courrol et al. proposed photoreduction as a simple and rapid approach to generating curcumin gold nanoparticles [39].
Sonosensitizer nanoparticles, as curcumin, represent a groundbreaking class of nanosensitizers for SDT. Coating AuNPs with curcumin can significantly enhance their targeting and uptake by macrophages [6,33]. Acting as therapeutic agents and ultrasound-activated sensitizers, they deliver and activate potent payloads like singlet oxygen directly within targeted tissues [31]. The nanoscale size of sonosensitizers facilitates their efficient cellular uptake and penetrates deep into tissues. AuNPs act as nucleation sites for ultrasonic cavitation, effectively decreasing the cavitation threshold and boosting the cavitation rate. The combined effect of these factors can facilitate curcumin delivery, significantly enhancing its effectiveness while minimizing side effects [40,41]. Several reports indicate the dual role of curcumin-based nanoparticles in photothermal (PTT) and SDT therapies [24,42].
This study compared the effectiveness of curcumin and photoreduced curcumin–gold nanoparticles in reducing THP-1-derived macrophages under ultrasound irradiation, exploring their potential for treating inflammatory diseases.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles Associated with Curcumin [CurAuNPs]
Tetrachloroauric acid trihydrate (HAuCl4·3H2O), polyethylene glycol 4000 (PEG 4000), and curcumin (Curcuma Longa) powder were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich Corp. (St. Louis, MO, USA).
The nanoparticles (CurNPs) were prepared by mixing 9.4 mmol of HAuCl4 with a curcumin solution (2, 4, or 8 mmol of curcumin in 2 mL of ethanol) in 98 mL of distilled water. Ten milliliter fractions of the mixtures were exposed to a 300 watt Cermax Xenon lamp (3.6 W/cm2) for 15 min. After the photoreduction process, the solution’s pHs (approximately 3.9–4.3) were adjusted to ~7.0 using NaOH. The effect of adding PEG 4000 during the synthesis was evaluated.
The calculated AuNPs concentrations in CurAu (Cur-2 mmol), CurAuPEG (Cur-2 mmol), Cur(2×)Au (Cur-4 mmol), and Cur(4×)Au (Cur-8 mmol) were ~40.8 μg/L, 4.5 μg/L, 20.9 μg/L, and 8.8 μg/L, respectively.
2.2. Nanoparticles Characterization
The ultraviolet–visible (UV-Vis) absorption spectra were measured using 10 mm quartz cells on a Multispec-1501 spectrophotometer (Shimadzu Corp., Kyoto, Japan). A Jeol (Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany) transmission electron microscope (TEM) was used to characterize the shape and size of CurAuNPs. The effective surface charges of the CurAuNPs were determined using a Zetasizer (Malvern Instruments, Worcestershire, UK) for Zeta potential analysis. Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) spectra were obtained on a Shimadzu Prestige-21 spectrometer (Shimadzu Corp., Kyoto, Japan) from 4000 cm−1 to 400 cm−1. After dropping onto glass slides and drying in a desiccator for 24 h, the CurAuNPs were prepared as KBr pellets for analysis. A Fluorolog 3 fluorimeter (Horiba, Kyoto, Japan) with excitation at 450 nm was used to measure the fluorescence spectra of the CurAuNPs.
2.3. Study of Singlet Oxygen Released by Ultrasound Irradiation
The generation of singlet oxygen (1O2) during ultrasound (US) irradiation was studied by monitoring the quenching of the DPBF [1.3-diphenylisobenzofuran] absorption band at 422 nm [43]. DPBF reacts with 1O2 to form an endoperoxide, which decomposes to 1,2-dibenzoylbenzene [44]. In this experiment, 1.0 mL of either curcumin solution (2 mmol) or CurAuNP solution (prepared with and without PEG) and 1.0 mL of DPBF (4 μM) were irradiated with therapeutic ultrasound Sonic Compact (HTM Eletrônica, São Paulo, Brazil) at 1 W/cm2 intensity and 1 MHz frequency for 0 to 5 min. The irradiation was performed in a quartz cuvette with the ultrasound transducer positioned laterally. After each irradiation, the sample was immediately analyzed in a UV-Vis spectrometer.
While DPBF can react with various radical species in complex biological systems [36], we assumed 1O2 to be the primary reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated here. Therefore, the amount of 1O2 generated during irradiation time ([1O2]t) was calculated based on the decrease in DPBF concentration [[DPBF]0 − [DPBF]t] using the Beer Law [45].
where A0 and At are the absorbance values of the solutions at λ = 422 nm before and after irradiation time t and εDPBF is the molar absorption coefficient of the DPBF at λ = 417 nm, measured in DMSO as εDPBF = 23,000 L/(mol cm) [46].
[1O2]t = [DPBF]0 − [DPBF]t = [A0/εDPBF] − [At/εDPBF]
2.4. Cell Culture
Human monocytic leukemia THP-1 cells were obtained from the Banco de Células do Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brazil. The cells were cultured in Roswell Park Memorial Institute 1640 (RPMI 1640) medium (Sigma-Aldrich Corp., St. Louis, MO, USA) containing 10% bovine fetal serum. The Ethics Committee of UNIFESP approved the protocol of this study (CEUA no. 1147091113).
THP-1 cells (5000 cells/well) were plated in 96-well plates and incubated at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2 in 95% air. They were differentiated into macrophages by adding 75 nM of Phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate (PMA, Sigma-Aldrich Corp., St, Louis, MO, USA) for 48 h. After differentiation and aspiration of non-attached cells, the adherent macrophages were washed with RPMI 1640 medium three times and then incubated in cell culture medium at 37 °C.
2.5. Cytotoxicity of Nanoparticles
Differentiation and treatment groups:
Control (CC): THP-1 cells were cultured in 500 μL of culture medium without any treatment.
Experimental curcumin (Cur): Cells in 100, 80, 40, 20, 10, 5, and 0 µL of curcumin solution (2 mmol) and culture medium (400, 420, 460, 480, 490, 495, and 500 µL). This resulted in final curcumin concentrations ranging from 200 µM to 0 µM;
Experimental curcumin-gold nanoparticles (CurAuNPs): CurAuNPs with different concentrations (100, 80, 40, 20, 10, 5, 2, and 0 µL) and culture medium (400, 420, 460, 480, 490, 495, 498, and 500 µL).
Positive control: Cells were treated with a known toxic agent (latex solution) to validate the assay.
Negative control: Cells were treated with a complete culture medium and NaCl solution to establish baseline viability.
Cell viability MTS assay (Sigma-Aldrich Corp., St, Louis, MO, USA):
After 24 h incubation with the respective treatments, all solutions were removed. Each well then received 100 μL of fresh RPMI culture medium and 20 μL of MTS dye solution. After a 2 h incubation, allowing viable cells to convert the MTS dye to a colored product, the absorbance at 490 nm was measured using a plate reader (Molecular Devices LLC, Sunnyvale, CA, USA). This absorbance directly correlates with the number of viable cells and serves as a quantitative measure of cytotoxicity.
For a 1 h incubation, macrophages were exposed to 200 μL of CurAuNPs and then imaged using a Nikon TS100 (Nikon Instruments Inc., Tokyo, Japan).
2.6. Ultrasound Irradiation
Macrophages were incubated for 24 h with 500 mL of culture medium alone, or 40 mL of curcumin solution or gold nanoparticles (CurAu, CurAu PEG, and Cur(4×)Au) in 460 mL of culture medium. A therapeutic ultrasound Sonic Compact (HTM Eletrônica, São Paulo, Brazil) transducer with a diameter of 3.5 cm, continuous wave mode, 1 MHz resonance frequency, and 1 W/cm2 intensity was positioned below the cell plate. A thin layer of sterile ultrasound gel (RMC Gel Clínico, Amparo, SP, Brazil) was used between the transducer and the plate. Each cell group was then irradiated separately for 2 min or 4 min. Notably, the temperature increase during the 2 min irradiation was less than 0.5 °C. Following ultrasound treatment, the cells were washed with PBS (phosphate buffered saline, Sigma-Aldrich Corp., St. Louis, MO, USA) and incubated with a fresh medium containing MTS reagent for 4 h before absorbance measurements at 490 nm.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD) unless otherwise specified. Differences less than 0.05 (p < 0.05) were considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of CurAuNPs
Figure 1A shows the UV-Vis spectra obtained for curcumin and CurAu solutions. The curcumin solution exhibits an absorption band of around 427 nm. In CurAu, a Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) band appears at around 535 nm after photoreduction. The inset Figure of Figure 1A shows the emission peak of curcumin in water at ~550 nm before and after the photoreduction process when excited at ~450 nm. The spectrum obtained for the CurcAu PEG after the photoreduction process is observed in Figure 1B, showing an SPR band larger than CurAuNPs.
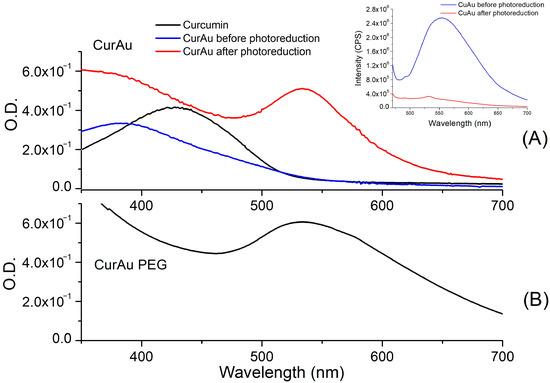
Figure 1.
UV-Vis spectra obtained for (A) Curcumin and CurAu before and after the photoreduction process; inside Figure: fluorescence spectra obtained with excitation at 450 nm, and (B) CurAuPEG.
Figure 2 illustrates the effect of varying the curcumin concentration at a fixed gold concentration. Increasing curcumin concentration led to a stronger SPR band and enhanced light scattering. Notably, Cur(2×)AuNPs exhibited the highest SPR intensity.
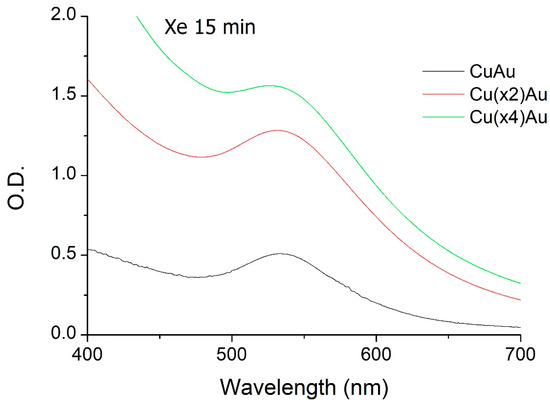
Figure 2.
UV-Vis spectra of CurAu nanoparticles prepared with 9.4 mmol HAuCl4 and different curcumin concentrations (2, 4, and 8 mmol).
Figure 3A–C shows electron microscopy images of CurAu, Cur(2×)Au, and Cur(4×)Au nanoparticles. These images reveal that increasing curcumin concentration promotes nanoparticle agglomeration. Average diameters were measured as ~9.6 nm for CurAu (Figure 3D), 12.0 nm for Cur(2×)Au, 16.0 nm for Cur(4×)Au, and 20.0 nm for CurAuPEG.
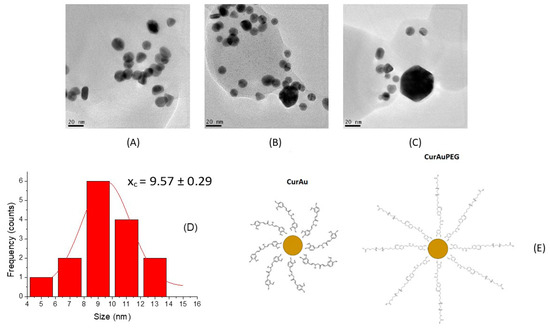
Figure 3.
TEM images for (A) CurAu, (B) Cur(2×)Au, and (C) Cur(4×)Au. (D) Size distribution obtained for CurAu. (E) CurAu and CurAuPEG.
According to Table 1, both CurAu and CurAuPEG exhibit moderate stability, as evidenced by their Zeta potential. However, CurAuPEG displays greater stability despite having a larger size compared to CurAuNPs.

Table 1.
Sizes and zeta potential of gold nanoparticles with and without PEG.
Vibrational spectroscopy (FTIR) was used to identify the functional groups present in the nanoparticle solutions. For comparison, spectra were acquired for curcumin, CurAu with and without PEG, and Cu(2×)Au and Cu(4×)Au. The results are presented in Figure 4.
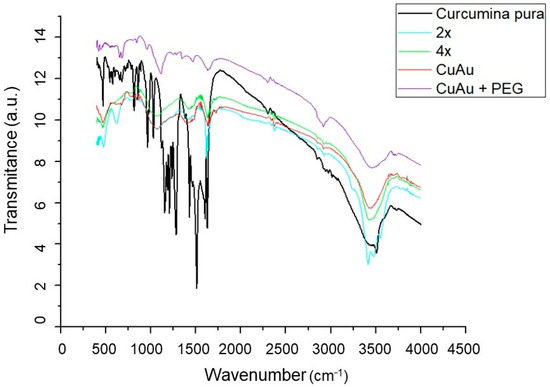
Figure 4.
FTIR spectra obtained for curcumin, Cur(2×)Au and Cur(4×)Au, and CurAu with and without PEG.
Curcumin presents signature peaks of phenolic O-H stretching vibration around 3510 cm−1. The peaks around 1628 cm−1 correspond to (C=O) stretching and, at 1597 cm−1, are attributed to the symmetric aromatic ring stretching vibrations (C=Cring) [47]. The peak at 1428 cm−1 corresponds to C-C vibration. The enol C-O peak appears at 1278 cm−1 and C–O–C stretching vibrations at 1024 cm−1. It is possible to notice that the C=O band in curcumin decreases in the spectra of the nanoparticles, appearing in CurAuNPs around 1740 cm−1, suggesting the conversion of keto to enol form due to the irradiation process in the synthesis of nanoparticles.
3.2. Singlet Oxygen [1O2] Release from CurAuNPs under Ultrasound Irradiation
Singlet oxygen production during US irradiation (1 MHz and 1 W/cm2) was measured indirectly using the DPBF probe in the presence of Curcumin, CurAuNPs, and CurAuPEG. Singlet oxygen reacts with DPBF, forming an unstable endoperoxide intermediate with a different absorption spectrum. Figure 5 shows a decrease in the DPBF band at 422 nm as irradiation time increases from 0 to 5 min. Although the DPBF band in Figure 5A (curcumin) persists even after 5 min, a complete absorption decrease occurs within 3 min for both CurAu and CurAuPEG (Figure 5B,C). This suggests higher 1O2 release in these cases. Figure 5D shows that CurAuPEG generates ten times more 1O2 than curcumin after 4 min of US irradiation, reaching a concentration of ~5.5 μmol/L.

Figure 5.
DPBF in the presence of (A) curcumin, (B) CurAu, and (C) CurAuPEG absorption decrease under US irradiation (1 MHz and 1 W/cm2) from 0 to 5 min. (D) 1O2 generation by the time.
3.3. Cell Viability Study
Cell viability assay was used to determine the toxicity of curcumin and CurAuNPs. Figure 6 shows the number of viable THP-1 cells as a function of different dilutions of curcumin (2 mmol), CurAu, CuAuPEG, Cur(2×)Au, and Cur(4×)Au solutions. The percentage of cell viability was calculated as follows:
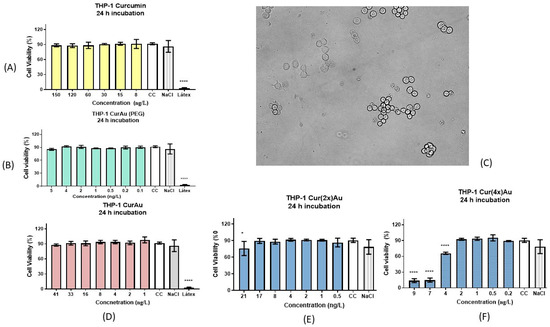
Figure 6.
Cell viability test for THP-1: cells incubated for 24 h with (A) curcumin, (B) CurAu + PEG nanoparticles, (C) THP1 macrophages incubated with CurAuNPs for 1 h, (D) CurAu nanoparticles without PEG, (E) Cur(2×)Au, and (F) Cur(4×)Au. Data were compared using the ANOVA test followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons tests, [*]: p < 0.1 and [****]: p < 0.0001. Error bars: SEM (standard error of means).
Figure 6C shows the aspect of THP-1 cells treated with CurAuNPs (~80 ng/L) for 1 h. Figure 6A,B,D,E shows that the solutions of curcumin, CurAuPEG, CurAu, and Cur(2×)AuNPs did not induce significant cell death in any studied concentration. Cur(4×)AuNPs showed a moderate cytotoxic effect against THP-1-derived macrophages with a half-maximal inhibitory concentration of 3.65 ng/L (Figure 6F).
3.4. Ultrasound Irradiation
THP-1 macrophages were incubated with CurAuPEG, CurAu, Cur(4×)Au, or curcumin for 24 h, followed by ultrasound (US) irradiation at 1 W/cm2 and 1 MHz for 2 or 4 min. After a 4-h incubation post-irradiation, cell viability was assessed using the MTS assay. The results are presented in Figure 7.
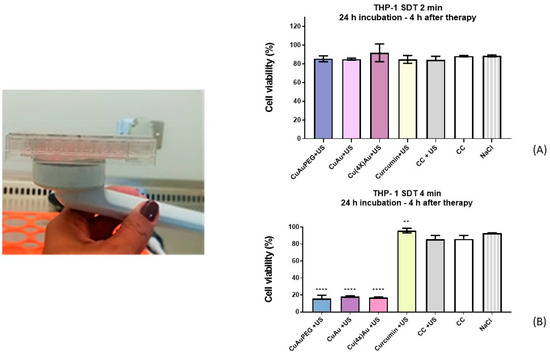
Figure 7.
Ultrasound irradiation of THP-1 incubated with CurAu PEG, CurAu, Cur(4×)Au, and Curcumin for (A) 2 min and (B) 4 min. Data were compared using the ANOVA test followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons tests, [**]: p < 0.01 [****]: p < 0.0001. Error bars: SEM (standard error of means).
From the obtained results, it is possible to observe significant cell death associated with irradiation for 4 min (Figure 7B) for cells incubated with CurAuPEG, CurAu, and Cur(4×)Au. Control cells remained viable after exposure to US irradiation. The cell survival rates in the CurAu groups were much lower than for the curcumin group.
The ultrasound irradiation performed for 2 min (Figure 7A) does not induce cell death.
4. Discussion
Emerging evidence from both in vitro and in vivo studies suggests that curcumin exerts potent modulatory effects on macrophage polarization in inflammatory diseases, from cancer and autoimmune disorders to renal inflammation, stroke, and atherosclerosis [13]. While curcumin exhibits promising therapeutic potential, its poor solubility and bioavailability limit its clinical applications [48]. Research efforts have explored curcumin conjugation with gold nanoparticles (CurAuNPs) to overcome these limitations and improve therapeutical potential.
In this study, gold nanoparticles capped with curcumin were produced by photoreduction. The β-diketone group in the curcumin molecule is responsible for the intramolecular hydrogen atom transfer, which leads to the formation of two different forms of the molecule, known as “keto” and “enol” tautomers, as illustrated in Figure 8, the photoreduction process converts curcumin’s keto form into the enol form. This mechanism involves the reduction of Au3+ to Au+ via the removal of the ketone, followed by the conversion of Au+ to Au0 and stabilization of the gold nanoparticles. While curcumin solution before photoreduction is highly fluorescent, when excited at 450 nm, CurAuNPs become non-fluorescent, as observed in Figure 1A (inset Figure).
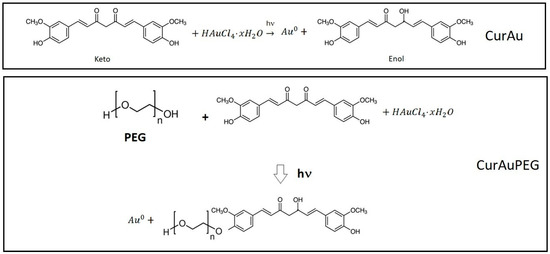
Figure 8.
Conversion of the keto form of curcumin into enol form by the photoreduction process and PEG-Cur conjugation.
According to the results shown in Figure 3, the increase in curcumin concentration during the synthesis process caused noticeable nanoparticle aggregation. In the case of CurAuPEG (PEG-Cur conjugation, Figure 8), PEG is linked to curcumin through ester bonds [49]. The presence of curcumin and PEG on the surface of nanoparticles was confirmed in FTIR spectra shown in Figure 4.
The effects of ultrasound irradiation (1 MHz and 1 W/cm2) on Curcumin, CurAu, and CurAuPEG solutions were studied and the results are shown in Figure 5. The DPBF probe was used with the prepared solutions to observe the release of singlet oxygen. The increase in irradiation time was observed to lead to a higher 1O2 concentration in all samples.
The mechanism of 1O2 generation differs between curcumin solution and CurAuNPs. During ultrasound irradiation of curcumin solution, violent bubble expansion and collapse generate intense heat, pressure, and sonoluminescence. The sonoluminescence can excite oxygen molecules into reactive oxygen species (ROS), including singlet oxygen (1O2). CurAuNP solutions act as nucleation sites for acoustic cavitation, significantly lowering the cavitation threshold, promoting bubble formation, and amplifying the sonoluminescence [41]. Consequently, after 4 min of US irradiation, CurAuPEG and CurAu generated higher 1O2 concentrations than curcumin: ~5.5 µmol/L, 4.0 µmol/L, and 1.5 µmol/L, respectively. Sazgarnia et al. observed, through chemical dosimetry, that the sonoluminescence signal detected in a gel phantom containing gold nanoparticles-conjugated PpIX was higher than that observed with PpIX alone [50]. In addition, literature suggests that the number of nucleation sites on the nanoparticle surface increases with particle size [51]. Figure 5D corroborates this, showcasing that more nucleation sites and cavitation bubbles must occur around CurAuPEG (20 nm) compared to CurAuNPs (9.6 nm).
Macrophages incubated with curcumin and exposed to ultrasound irradiation experience an interaction between activated curcumin and molecular oxygen, producing cytotoxic ROS, especially singlet oxygen, which ultimately leads to cell death [42,52,53,54,55]. Wang F. et al. investigated the sonodynamic effect of curcumin on THP-1-derived macrophages using slightly different parameters than our study [17]. Their experiment employed a curcumin concentration (40.7 µmol/L), higher ultrasound intensity (2 W/cm2), and lower frequency (0.86 MHz) compared to ours (~53 µmol/L, 1 W/cm2, 1 MHz). They also utilized a pulsed irradiation approach with shorter durations (5–15 min) than our continuous wave irradiation. The authors observed no sonodynamic effect at 5 min of irradiation but witnessed a significant decrease in cell viability (52%) after 15 min.
Results presented in Figure 6 depict the cell viability of THP-1-derived macrophages after treatment with CurAuNPs and free curcumin. As illustrated, curcumin, CurAu, CurAuPEG, and Cur(2×)Au displayed minimal toxicity towards the macrophages. Interestingly, a significant shift occurs with Cur(4×)AuNPs, exhibiting an IC50 (half-maximal inhibitory concentration) of approximately 3.65 ng/L. This observation implies increased curcumin molecules on the nanoparticle surface trigger a dose-dependent cytotoxic effect [56]. Conjugation of curcumin at the surface of nanoparticles may facilitate the uptake of curcumin at the cellular level [57]. CurNPs can be internalized by macrophages through phagocytosis, micropinocytosis, and endocytosis mediated by clathrin or caveolin [58]. CurNPs must actively target endocytic receptors on macrophage surfaces using C-type lectin receptors or the mannose receptor, inducing changes at the cell surface [58]. These findings hold significant implications for designing safe and effective therapeutic agents based on CurAuNPs. While high curcumin conjugation enhances potential targeting and cell uptake, it can also induce unwanted toxicity. Therefore, carefully optimizing the curcumin-to-gold ratio is crucial for harnessing the therapeutic benefits while minimizing detrimental side effects.
The synergistic combination of CurAuNPs and ultrasound in sonodynamic therapy (SDT) relies on two crucial aspects: efficient cellular uptake of curcumin and ultrasound-induced release of its active molecules. As shown in Figure 7A, exposing macrophages to ultrasound for 2 min did not trigger any noticeable changes in cell viability, regardless of their pre-treatment with curcumin or any of the CurAuNP variants (CurAuPEG, CurAu, and Cur(4×)Au). However, the scenario changed when the irradiation time was extended to 4 min. Figure 7B reveals a pronounced decrease in cell viability for the CurAuPEG, CurAu, and Cur(4×)Au groups compared to the control and curcumin-only groups. Interestingly, these reductions were comparable across the three CurAuNP types, exhibiting 16–18% cell viability values. These findings suggest that ultrasound exposure in combination with CurAuNPs triggers time-dependent cell death in macrophages. While the exact mechanism remains to be fully elucidated, several possibilities could be considered. (1) Sonodynamic effect: CurAuNP solutions act as nucleation sites for acoustic cavitation, significantly lowering the cavitation threshold, promoting bubble formation, and amplifying the sonoluminescence. The increased availability of curcumin leads to further activation, mediating macrophage polarization. Consequently, CurAuNPs could enhance macrophage polarization, potentially offering therapeutic options for both pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory stages as illustrated in Figure 9. (2) Direct effects of nanoparticles: The presence of gold nanoparticles might potentiate the mechanical force of ultrasound, causing membrane disruption or other cellular damage. (3) Combined effects: A synergistic interplay between curcumin’s sonodynamic effect and the US physical impact on the nanoparticles and surrounding cells could contribute to the observed cytotoxicity.
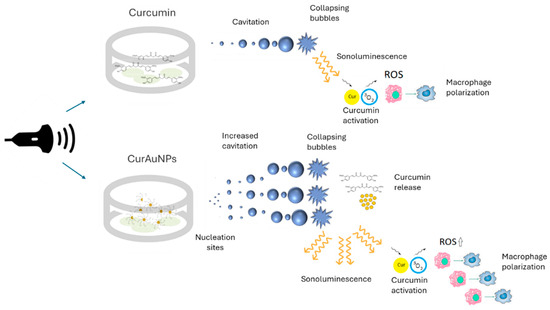
Figure 9.
Sonodinamic effect: Comparison between curcumin and CurAuNPs.
Although CurAuPEG appears to induce a higher level of cell death, the observed differences in cell viability between CurAuPEG, CurAu, and Cur(4×)Au groups were not statistically significant. This intriguing finding prompts us to hypothesize that a threshold exists for triggering significant cell death, potentially linked to the mechanisms underlying macrophage resistance to reactive oxygen species (ROS) [59,60]. Macrophages can exhibit intrinsic resistance to ROS-mediated cell death through various mechanisms, including inhibiting cell death signaling pathways, upregulation of antioxidant defense mechanisms, and metabolic reprogramming. We propose that the observed lack of statistically significant differences in cell viability might indicate that the ROS generated by these formulations fall below the threshold required to overcome macrophage resistance mechanisms. CurAuPEG may be approaching this threshold but has not crossed it yet, potentially explaining its slightly higher, albeit statistically insignificant, cell death effect.
Interestingly, elevated ROS levels in inflamed tissues can promote M2 polarization. CurAuNPs could potentially disrupt the delicate inflammatory equilibrium promoting the release of ROS, which could influence the M1/M2 balance with the interaction of ultrasound. Furthermore, the released curcumin directly mediated macrophage polarization [14,61]. Therefore, CurAuNPs could influence macrophage polarization, potentially offering therapeutic options for pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory stages. However, further research is needed to clearly understand and harness the ability of CurAuNPs to modulate macrophage phenotype for tailored therapeutic applications.
For clinical settings, repeated short bursts of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound, known as dose fractionation, are considered more favorable [52]. This approach reduces potential tissue damage while still achieving therapeutic efficacy. Further research is warranted to unravel the precise mechanisms behind this observed time-dependent cell death and its potential implications for therapeutic applications of CurAuNPs in sonodynamic therapy.
Although additional research is warranted, a range of conditions encompassing both inflammatory and non-inflammatory pathologies, including but not limited to rheumatoid arthritis, atherosclerosis, osteoarthritis, lupus erythematosus, tumor metastasis, and glioblastoma, have the potential to derive therapeutic benefits from ultrasound irradiation facilitated by CurAuNPs [6,16,62]. Ultrasound therapy utilizing CurAuNPs offers several advantages compared to alternative treatments, including straightforward administration, reduced toxicity, and outstanding selectivity.
5. Conclusions
Our study successfully synthesized CurAuNPs through a photoreduction method, employing curcumin as a dual functional agent for reduction and stabilization. While curcumin solution generated 1.5 µmol/L of singlet oxygen after 4 min of ultrasound irradiation, CurAuPEG and CurAu exhibited significantly higher concentrations, reaching ~5.5 µmol/L and 4.0 µmol/L, respectively. Toxicity tests on THP-1-derived macrophages revealed a significant impact on cell viability only for CurAuNPs with high curcumin concentrations (Cur(4×)AuNPs), as evidenced by an IC50 of approximately 3.65 ng/L. Furthermore, under ultrasound irradiation conditions (1 MHz, 1 W/cm2 for 4 min), THP-1-derived macrophage viability was remarkably reduced cell viability to ~18% in the presence of CurAuNPs, regardless of PEGylation or variations in nanoparticle curcumin concentration. Considering the potential of curcumin released with the ultrasound interaction to modulate macrophage polarization, CurAuNPs could influence macrophage polarization, potentially offering therapeutic options for both pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory stages. However, in vivo models are required to elucidate the underlying mechanisms and optimize therapeutic efficacy for future clinical translation.
Author Contributions
B.H.T. and K.d.O.G.: methodology, investigation. D.P.V.: methodology, investigation, formal analysis, conceptualization. L.C.C.: writing—review and editing, writing—original draft preparation, supervision, project administration, funding acquisition, formal analysis, conceptualization. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by The National Institute of Science and Technology Complex Fluids (INCT-FCX) grant 2014/50983-3 and The São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP) grant 2022/14030-8.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The Ethics Committee of UNIFESP approved the protocol of this study (CEUA no. 1147091113).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data supporting the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author due to privacy.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Multi-user Centers of ABC Federal University (UFABC), Energy and Nuclear Research Institute (IPEN/CNEN-SP).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Sundaram, C.; Malani, N.; Ichikawa, H. Curcumin: The Indian solid gold. In The Molecular Targets and Therapeutic Uses of Curcumin in Health and Disease; Aggarwal, B.B., Surh, Y.J., Shishodia, S., Eds.; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2007; Volume 595, pp. 1–75. [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Harikumar, K.B. Potential therapeutic effects of curcumin, the anti-inflammatory agent, against neurodegenerative, cardiovascular, pulmonary, metabolic, autoimmune and neoplastic diseases. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2009, 41, 40–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, P.; Sundaram, C.; Jhurani, S.; Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Aggarwal, B.B. Curcumin and cancer: An “old-age” disease with an “age-old” solution. Cancer Lett. 2008, 267, 133–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazantzis, K.T.; Koutsonikoli, K.; Mavroidi, B.; Zachariadis, M.; Alexiou, P.; Pelecanou, M.; Politopoulos, K.; Alexandratou, E.; Sagnou, M. Curcumin derivatives as photosensitizers in photodynamic therapy: Photophysical properties and in vitro studies with prostate cancer cells. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2020, 19, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomeh, M.A.; Hadianamrei, R.; Zhao, X.B. A Review of Curcumin and Its Derivatives as Anticancer Agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momtazi-Borojeni, A.A.; Abdollahi, E.; Nikfar, B.; Chaichian, S.; Ekhlasi-Hundrieser, M. Curcumin as a potential modulator of M1 and M2 macrophages: New insights in atherosclerosis therapy. Heart Fail. Rev. 2019, 24, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.Y.; Geng, X.F.; Hou, J.X.; Wu, G.S. New insights into M1/M2 macrophages: Key modulators in cancer progression. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paoli, F.; Staels, B.; Chinetti-Gbaguidi, G. Macrophage Phenotypes and Their Modulation in Atherosclerosis. Circ. J. 2014, 78, 1775–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, P.J.; Wynn, T.A. Protective and pathogenic functions of macrophage subsets. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 723–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Italiani, P.; Boraschi, D. From monocytes to M1/M2 macrophages: Phenotypical vs. functional differentiation. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.Y.; Zhang, T.T.; Wang, X.F.; Wei, X.W.; Chen, Y.Z.; Guo, L.Y.; Zhang, J.F.; Wang, C.Q. Curcumin Modulates Macrophage Polarization through the Inhibition of the Toll-like Receptor 4 Expression and Its Signaling Pathways. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 36, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.X.; Zhou, M.; Zheng, X.Y.; Xing, Y.Y.; Dong, J.; Yan, M.W.; Li, R. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Curcumin on the Mouse Model of Myocardial Infarction through Regulating Macrophage Polarization. Mediat. Inflamm. 2021, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, S.K.; Sun, X.; Sang, L.M.; Zhang, M.; Yan, X.B.; Ju, Q.; Ma, X.F.; Xu, M. Curcumin inhibits malignant behavior of colorectal cancer cells by regulating M2 polarization of tumor-associated macrophages and metastasis associated in colon cancer 1 (MACC1) expression. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2023, 102, 1202–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdollahi, E.; Johnston, T.P.; Ghaneifar, Z.; Vahedi, P.; Goleij, P.; Azhdari, S.; Moghaddam, A.S. Immunomodulatory Therapeutic Effects of Curcumin on M1/M2 Macrophage Polarization in Inflammatory Diseases. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2023, 16, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noorafshan, A.; Ashkani-Esfahani, S. A Review of Therapeutic Effects of Curcumin. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 2032–2046. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Wang, J.H.; Jiang, J.Q.; Zhang, C.M.; Zhao, M.; Chen, Z.; Wang, N.; Hu, D.D.; Liu, X.Y.; Peng, H.S.; et al. Sonodynamic therapy in atherosclerosis by curcumin nanosuspensions: Preparation design, efficacy evaluation, and mechanisms analysis. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2020, 146, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.P.; Gao, Q.P.; Guo, S.Y.; Cheng, J.L.; Sun, X.; Li, Q.N.; Wang, T.Y.; Zhang, Z.G.; Cao, W.W.; Tian, Y. The Sonodynamic Effect of Curcumin on THP-1 Cell-Derived Macrophages. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 737264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenthal, I.; Sostaric, J.Z.; Riesz, P. Sonodynamic therapy—A review of the synergistic effects of drugs and ultrasound. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2004, 11, 349–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canaparo, R.; Foglietta, F.; Barbero, N.; Serpe, L. The promising interplay between sonodynamic therapy and nanomedicine. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2022, 189, 114495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costley, D.; Mc Ewan, C.; Fowley, C.; McHale, A.P.; Atchison, J.; Nomikou, N.; Callan, J.F. Treating cancer with sonodynamic therapy: A review. Int. J. Hyperth. 2015, 31, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, C.; Zhang, Y.L.; Hidru, T.H.; Zhi, L.Y.; Tao, M.X.; Zou, L.X.; Chen, C.; Li, H.H.; Liu, Y. Sonodynamic therapy: A potential treatment for atherosclerosis. Life Sci. 2018, 207, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, W.K.; Shen, E.; Hu, B. Induction of the apoptosis of cancer cell by sonodynamic therapy: A review. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 2012, 24, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.R.; Dai, Z.F. Design and Challenges of Sonodynamic Therapy System for Cancer Theranostics: From Equipment to Sensitizers. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2002178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayani, Z.; Vais, R.D.; Soratijahromi, E.; Mohammadi, S.; Sattarahmady, N. Curcumin-gold-polyethylene glycol nanoparticles as a nanosensitizer for photothermal and sonodynamic therapies: In vitro and animal model studies. Photodiagn Photodyn. Ther. 2021, 33, 102139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, X.J.; Zhao, S.J.; Xu, T.; Huang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Lan, M.H.; Lin, C.W.; Zheng, X.L.; Wang, P.F. Advances and perspectives in organic sonosensitizers for sonodynamic therapy. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 445, 214087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.B.; Sun, X.Y.; Zhu, X.; Lv, F.X.; Zhong, Z.Y.; Zhang, F.; Guo, W.H.; Cao, W.W.; Yang, L.M.; Tian, Y. Apoptosis of THP-1 Derived Macrophages Induced by Sonodynamic Therapy Using a New Sonosensitizer Hydroxyl Acetylated Curcumin. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeid, M.A.; Alsaadi, M.; Aljabali, A.A. Recent updates in curcumin delivery. J. Liposome Res. 2023, 33, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, K.D.; Vieira, D.P.; Courrol, L.C. Synthesis and characterization of aminolevulinic acid gold nanoparticles: Photo and sonosensitizer agent for atherosclerosis. J. Lumin. 2018, 197, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalvez, K.D.; Vieira, D.P.; Courrol, L.C. Study of THP-1 Macrophage Viability after Sonodynamic Therapy Using Methyl Ester of 5-Aminolevulinic Acid Gold Nanoparticles. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2018, 44, 2009–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, X.Q.; Zheng, Y.Y.; Chen, Y. Micro/Nanoparticle-Augmented Sonodynamic Therapy (SDT): Breaking the Depth Shallow of Photoactivation. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 8097–8129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.Y.; Zhang, X.; Han, R.B.; Yang, P.M.; Ma, H.F.; Song, Y.; Lu, Z.C.; Yin, W.D.; Wu, X.X.; Wang, H. Nanoparticles in sonodynamic therapy: State of the art review. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 50697–50705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurindo, L.F.; de Carvalho, G.M.; Zanuso, B.D.; Figueira, M.E.; Direito, R.; Goulart, R.D.; Buglio, D.S.; Barbalho, S.M. Curcumin-Based Nanomedicines in the Treatment of Inflammatory and Immunomodulated Diseases: An Evidence-Based Comprehensive Review. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantino, M.; Corno, C.; Colombo, D.; Perego, P. Curcumin and Related Compounds in Cancer Cells: New Avenues for Old Molecules. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 889816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurapov, P.B.; Bakhtenko, E.Y. Gold Nanoparticles in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Cancer. Bull. Russ. State Med. Univ. 2018, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, D.; El Kurdi, R. Curcumin as a novel reducing and stabilizing agent for the green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles. Green. Chem. Lett. Rev. 2021, 14, 474–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreelakshmi, C.; Goel, N.; Datta, K.K.R.; Addlagatta, A.; Ummanni, R.; Reddy, B.V.S. Green Synthesis of Curcumin Capped Gold Nanoparticles and Evaluation of Their Cytotoxicity. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. Lett. 2013, 5, 1258–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.K.; Jagannathan, R.; Khandelwal, P.; Abraham, P.M.; Poddar, P. In situ synthesis and surface functionalization of gold nanoparticles with curcumin and their antioxidant properties: An experimental and density functional theory investigation. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 1882–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Kurdi, R.; Patra, D. Capping of supramolecular curcubit 7 uril facilitates formation of Au nanorods during pre-reduction by curcumin. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 553, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos Courrol, D.; Teixeira, B.H.; Pereira, C.B.; Franzolin, M.R.; Courrol, L.C. Pegylated Curcumin with Gold Nanoparticles: Antimicrobial Agent Evaluation. J. Biomed. Eng. Biosci. 2016, 3, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaney, L.J.; Isguven, S.; Eisenbrey, J.R.; Hickok, N.J.; Forsberg, F. Making waves: How ultrasound-targeted drug delivery is changing pharmaceutical approaches. Mater. Adv. 2022, 3, 3023–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornsby, T.K.; Kashkooli, F.M.; Jakhmola, A.; Kolios, M.C.; Tavakkoli, J. Multiphysics Modeling of Low-Intensity Pulsed Ultrasound Induced Chemotherapeutic Drug Release from the Surface of Gold Nanoparticles. Cancers 2023, 15, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilbeigi, S.; Ranjbar, A.; Zahraie, N.; Vais, R.D.; Monjezi, M.R.; Sattarahmady, N. Sonodynamic therapy of pancreatic cancer cells based on synergistic chemotherapeutic effects of selenium-PEG-curcumin nanoparticles and gemcitabine. Appl. Phys. A 2023, 129, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belfield, K.D.; Bondar, M.V.; Przhonska, O.V. Singlet oxygen quantum yield determination for a fluorene-based two-photon photosensitizer. J. Fluoresc. 2006, 16, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carloni, P.; Damiani, E.; Greci, L.; Stipa, P.; Tanfani, F.; Tartaglini, E.; Wozniak, M. On the use of 1,3-diphenylisobenzofuran (dpbf)—Reactions with carbon and oxygen-centered radicals in model and natural systems. Res. Chem. Intermed. 1993, 19, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fudimura, K.A.; Seabra, A.B.; Santos, M.C.; Haddad, P.S. Synthesis and Characterization of Methylene Blue-Containing Silica-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles for Photodynamic Therapy. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2017, 17, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogunsipe, A.; Maree, D.; Nyokong, T. Solvent effects on the photochemical and fluorescence properties of zinc phthalocyanine derivatives. J. Mol. Struct. 2003, 650, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, P.R.K.; Sreelakshmi, G.; Muraleedharan, C.V.; Joseph, R. Water soluble complexes of curcumin with cyclodextrins: Characterization by FT-Raman spectroscopy. Vibrat. Spectrosc. 2012, 62, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helson, L. Curcumin (diferuloylmethane) delivery methods: A review. Biofactors 2013, 39, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yakub, G.; Manolova, N.E.; Rashkov, I.B.; Markova, N.; Toshkova, R.; Georgieva, A.; Mincheva, R.; Toncheva, A.; Raquez, J.M.; Dubois, P. Pegylated Curcumin Derivative: Water-Soluble Conjugates with Antitumor and Antibacterial Activity. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 36403–36414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sazgarnia, A.; Shanei, A.; Eshghi, H.; Hassanzadeh-Khayyat, M.; Esmaily, H.; Shanei, M.M. Detection of sonoluminescence signals in a gel phantom in the presence of Protoporphyrin IX conjugated to gold nanoparticles. Ultrasonics 2013, 53, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanei, A.; Shanei, M.M. Effect of gold nanoparticle size on acoustic cavitation using chemical dosimetry method. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 34, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daneshvar, F.; Salehi, F.; Kayani, Z.; Sattarahmady, N.; Vais, R.D.; Azarpira, N. Fractionated Sonodynamic Therapy Using Gold@Poly(ortho-aminophenol) Nanoparticles and Multistep Low-Intensity Ultrasound Irradiation to Treat Melanoma Cancer: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2023, 49, 1299–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozlem Caliskan, S.; Ozen, H.; Kaya, I.; Ilikci Sagkan, R.; Ertabaklar, H. An In Vitro Study on Sonodynamic Therapy of Leishmania tropica Using curcumin. Mikrobiyol. Bul. 2022, 56, 706–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahamse, H.; Hamblin, M.R. New photosensitizers for photodynamic therapy. Biochem. J. 2016, 473, 347–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.C.; Patchva, S.; Aggarwal, B.B. Therapeutic Roles of Curcumin: Lessons Learned from Clinical Trials. AAPS J. 2013, 15, 195–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNally, S.J.; Harrison, E.M.; Ross, J.A.; Garden, O.J.; Wigmore, S.J. Curcumin induces heme oxygenase 1 through generation of reactive oxygen species, p38 activation and phosphatase inhibition. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2007, 19, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunwar, A.; Barik, A.; Mishra, B.; Rathinasamy, K.; Pandey, R.; Priyadarsini, K.I. Quantitative cellular uptake, localization and cytotoxicity of curcumin in normal and tumor cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2008, 1780, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, R.G.D.; Reis, B.; Costas, B.; Lima, S.A.C.; Reis, S. Modulation of Macrophages M1/M2 Polarization Using Carbohydrate-Functionalized Polymeric Nanoparticles. Polymers 2021, 13, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomovskaya, Y.V.; Kobyakova, M.I.; Senotov, A.S.; Lomovsky, A.I.; Minaychev, V.V.; Fadeeva, I.S.; Shtatnova, D.Y.; Krasnov, K.S.; Zvyagina, A.I.; Akatov, V.S.; et al. Macrophage-like THP-1 Cells Derived from High-Density Cell Culture Are Resistant to TRAIL-Induced Cell Death via Down-Regulation of Death-Receptors DR4 and DR5. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virag, L.; Jaen, R.I.; Regdon, Z.; Bosca, L.; Prieto, P. Self-defense of macrophages against oxidative injury: Fighting for their own survival. Redox Biol. 2019, 26, 101261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, S.; Rius-Perez, S. Macrophage Polarization and Reprogramming in Acute Inflammation: A Redox Perspective. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.J.; Huang, W.; Zhang, W.W.; Mei, J.W.; Zhu, C. A Tale of Two Immune Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Crosstalk Between Macrophages and T Cells in the Synovium. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 655477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).