Advances in Modeling and Interpretability of Deep Neural Sleep Staging: A Systematic Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
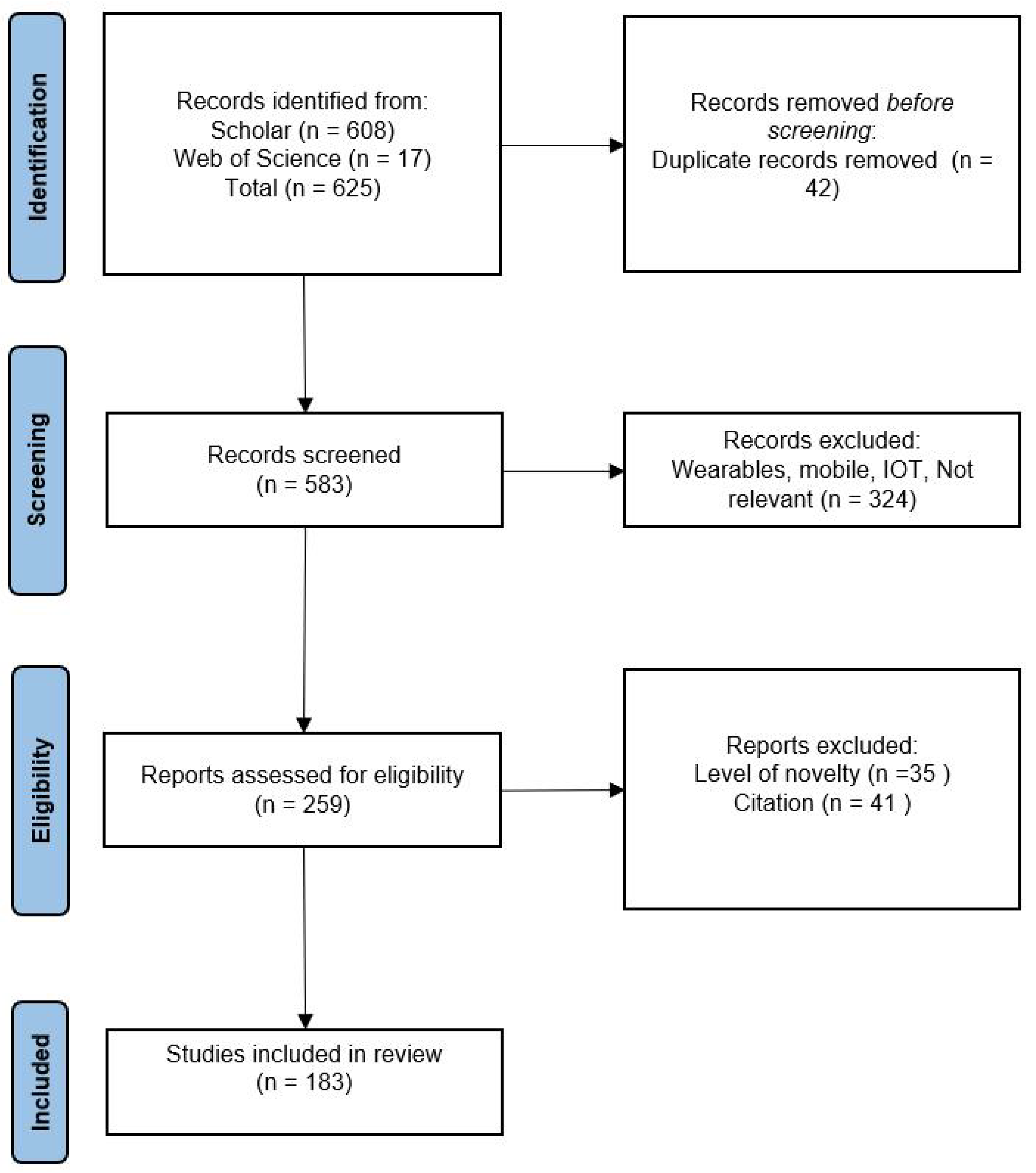
2. Method
2.1. Design
2.2. Metrics
3. Datasets
3.1. Data Description
- SleepEDF (all versions): SleepEDF [12] is a publicly available dataset of physiological signals with corresponding sleep annotations. The initial version of this dataset was small and was originally published in 2002. In 2013, version 1 was published, which was greatly expanded to contain 61 PSGs with accompanying hypnograms. In March 2018, the database was further expanded to version 2 containing 197 PSGs with accompanying hypnograms. Each subject wore a modified Walkman-like cassette-tape recorder to record their normal activities. For each subject, two PSGs of about 20 h each were recorded during two subsequent day–night periods at the subjects’ homes. PSG recordings include EEG from Fpz-Cz and Pz-Oz electrode locations, EOG, and submental chin EMG signals. Corresponding hypnograms (sleep patterns) for these recordings were manually annotated by well-trained technicians according to the Rechtschaffen and Kales manual, and are also available. Annotation consists of sleep stages W, R, 1, 2, 3, 4, M (Movement time), and “not scored”. The Sleep EDF dataset has been used in numerous studies to develop and evaluate algorithms for automatic sleep staging recognition problems, as well as to investigate various aspects of sleep and its disorders. Papers using this dataset include [13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22].
- MASS: This is an open-access and collaborative database of laboratory-based PSG recordings [23]. The aim of the dataset is to offer a consistent and readily available data source for evaluating different systems developed to automate sleep analysis. The MASS dataset is unique in its size and scope, with the cohort consisting of 200 complete nights of polysomnograms, recorded from a diverse group of individuals (97 males and 103 females) with an average age of 40.6 years (ranging from 18 to 76 years). The dataset provides a valuable resource for researchers and practitioners working in the field of sleep analysis, with a focus on benchmarking and improving automated sleep analysis systems. This dataset includes polysomnographic recordings of sleep patterns, as well as related data such as participants’ medical histories and sleep questionnaires. All recordings feature a sampling frequency of 256 Hz and an EEG montage of 4–20 channels plus standard EOG, EMG, ECG, and respiratory signals. Papers using this dataset include [14,15,24,25].
- SHHS: The Sleep Heart Health Study (SHHS) dataset [26] was collected as part of a study aimed at investigating the relationship between sleep-disordered breathing and cardiovascular disease. This dataset collected data from over 6441 healthy participants without treatment of sleep apnea, with an age over 40 years for the first round (SHHS-1). A second polysomnogram (SHHS-2) was obtained from 3295 of the participants. The dataset includes PSG recordings, as well as data on demographics, medical history, and sleep habits. The PSG recordings were scored by certified technicians using standard criteria for sleep staging, respiratory events, and other sleep-related events. The dataset also includes information on the presence and severity of sleep-disordered breathing, such as apnea and hypopnea. The SHHS dataset has been used in numerous studies investigating various aspects of sleep and sleep-disordered breathing. The dataset is publicly available through the National Sleep Research Resource. Papers using this dataset include [9,18,27,28,29,30,31].
- CAP: The Cyclic Alternating Pattern (CAP) is a periodic EEG activity observed during non-REM (NREM) sleep. The CAP Sleep dataset [32] is comprised of 108 polysomnographic recordings collected at the Sleep Disorders Center of the Ospedale Maggiore in Parma, Italy. These recordings encompass a minimum of three EEG channels, EOG, EMG of the submentalis muscle, bilateral anterior tibial EMG, respiratory signals, and EKG. The CAP Sleep dataset includes 108 polysomnographic recordings from the Sleep Disorders Center of Ospedale Maggiore in Parma, Italy. The data include recordings from 16 healthy subjects and 92 pathological recordings with various sleep disorders, such as Nocturnal Frontal Lobe Epilepsy (NFLE), REM Sleep Behavior Disorder (RBD), Periodic Limb Movement (PLM), insomnia, narcolepsy, Sleep-Disordered Breathing (SDB), and bruxism. The recordings contain data from multiple sources including EEG, EOG, and ECG, along with muscle and respiration signals.
- ISRUC: The ISRUC-Sleep dataset [33] is a comprehensive polysomnographic (PSG) resource aimed at aiding sleep research. This dataset features data from adults, including healthy individuals and those suffering from sleep disorders, with some on sleep medication. The dataset is organized to accommodate different research goals, with information from 100 subjects each with one recording session, eight subjects with two sessions each for tracking changes over time, and 10 healthy subjects in a single session for comparison studies. Each PSG recording contains electrophysiological and pneumological signals, among other contextual details, all of which have been visually scored by two human experts. Papers using this dataset include [16,24].
- MESA: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA) [34,35] is a long-term study sponsored by the National Heart Lung and Blood Institute (NHLBI), focusing on the development and progression of subclinical cardiovascular disease in over 6800 ethnically diverse individuals. Between 2010 and 2012, a subset of participants undertook a Sleep Exam (MESA Sleep), which studied how sleep variations and disorders correlate with subclinical atherosclerosis. The raw sleep data, including polysomnography and actigraphy, are publicly accessible for further research. Papers using this dataset include [27].
- Bonn database: The Bonn-Barcelona micro- and macro- EEG database [36] comprises 960 multichannel EEG signals, each with a duration of 32 s, extracted from long-term EEG data. The selection process did not involve any clinical criteria, such as the presence or absence of epileptiform activity, and all data are de-identified. Papers using this dataset include [37].
- UCD: The St. Vincent’s University Hospital/University College Dublin Sleep Apnea Database [38] consists of 25 full overnight polysomnograms, accompanied by a simultaneous three-channel Holter ECG, collected from adult subjects suspected of having sleep-disordered breathing. The subjects, aged between 28 and 68 years with no known cardiac disease or autonomic dysfunction, were randomly selected over six months from patients referred to St Vincent’s University Hospital’s Sleep Disorders Clinic. Polysomnograms were obtained using the Jaeger–Toennies system, capturing a variety of signals including EEG, EOG, EMG, ECG, and body position, among others. Additionally, three-channel Holter ECGs were recorded using a Reynolds Lifecard CF system. All data are available in EDF format. Papers using this dataset include [39,40].
- MIT-BIH Polysomnographic: The MIT-BIH Polysomnographic Database [41] contains over 80 h of four-, six-, and seven-channel polysomnographic recordings. Each recording includes a beat-by-beat annotated ECG signal, as well as EEG and respiration signals annotated in relation to sleep stages and apnea. These data are collected in Boston’s Beth Israel Hospital Sleep Laboratory. Papers using this dataset include [29].
- DREAMS: The DREAMS Databases [43] consist of recordings annotated in microevents or in sleep stages by several experts. They were acquired in a sleep laboratory of a Belgium hospital using a digital 32-channel polygraph (BrainnetTM System of MEDATEC, Brussels, Belgium). This database is split into 8 databases according to the annotation carried out. Papers using this dataset include [20,21].
- You Snooze You Win: The PhysioNet/Computing in Cardiology Challenge 2018: This dataset was contributed by the Massachusetts General Hospital’s (MGH) Computational Clinical Neurophysiology Laboratory (CCNL) and the Clinical Data Animation Laboratory (CDAC) [44]. The dataset consists of 1985 subjects and the sleep stages were annotated by clinical staff based on the American Academy of Sleep Medicine manual with six sleep stages noted in 30 s intervals: wakefulness, stage 1, stage 2, stage 3, rapid eye movement (REM), and undefined. Certified technologists also annotated waveforms for the presence of arousals interrupting sleep, classifying them into various categories such as spontaneous arousals, respiratory effort related arousals (RERA), bruxisms, and others. The physiological signals recorded during the subjects’ sleep include EEG, EOG, EMG, ECG, and oxygen saturation (SaO). All signals, excluding SaO, were sampled at 200 Hz and measured in microvolts. SaO was resampled to 200 Hz and measured as a percentage. Papers using this dataset include [31].
3.2. Data Preprocessing
3.3. Addressing Dataset Deficiencies
4. Modeling
4.1. Transfer Learning and Domain Adaptation
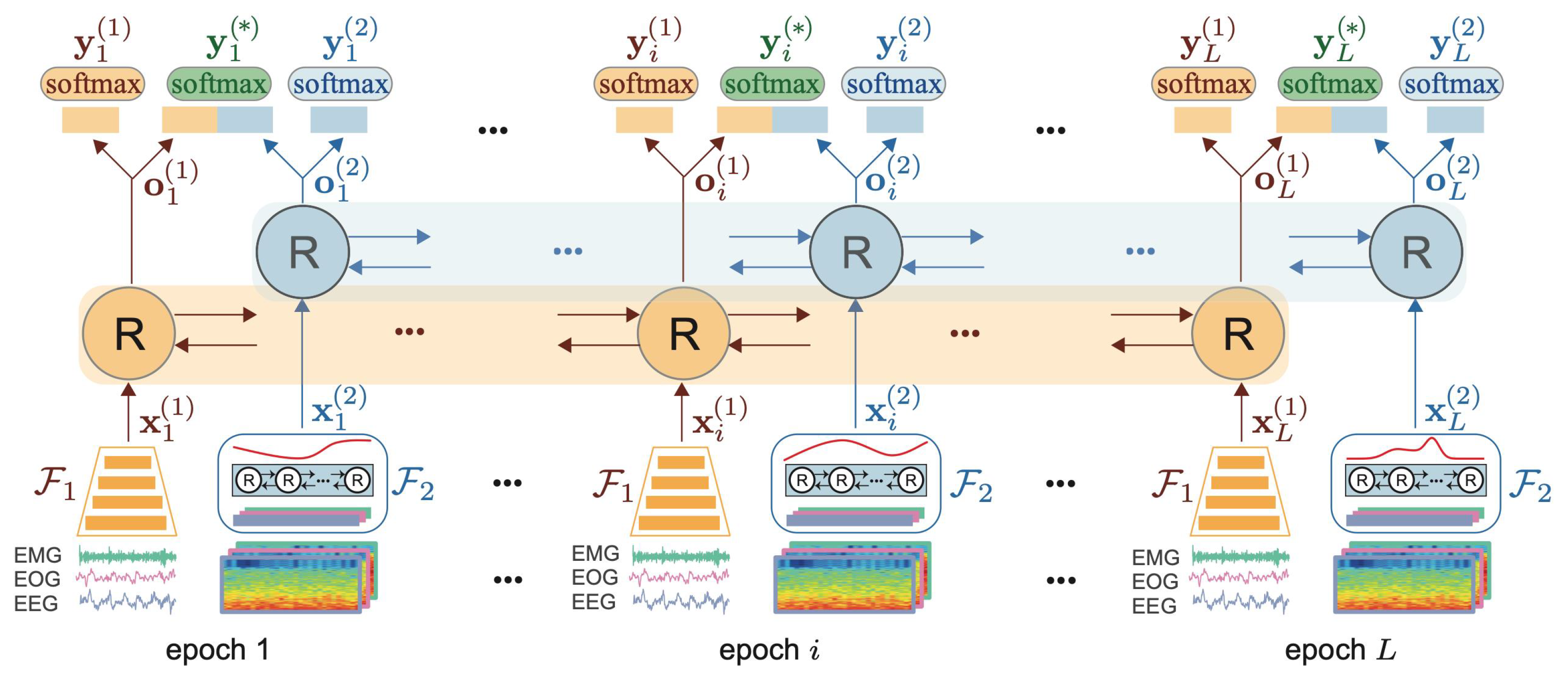
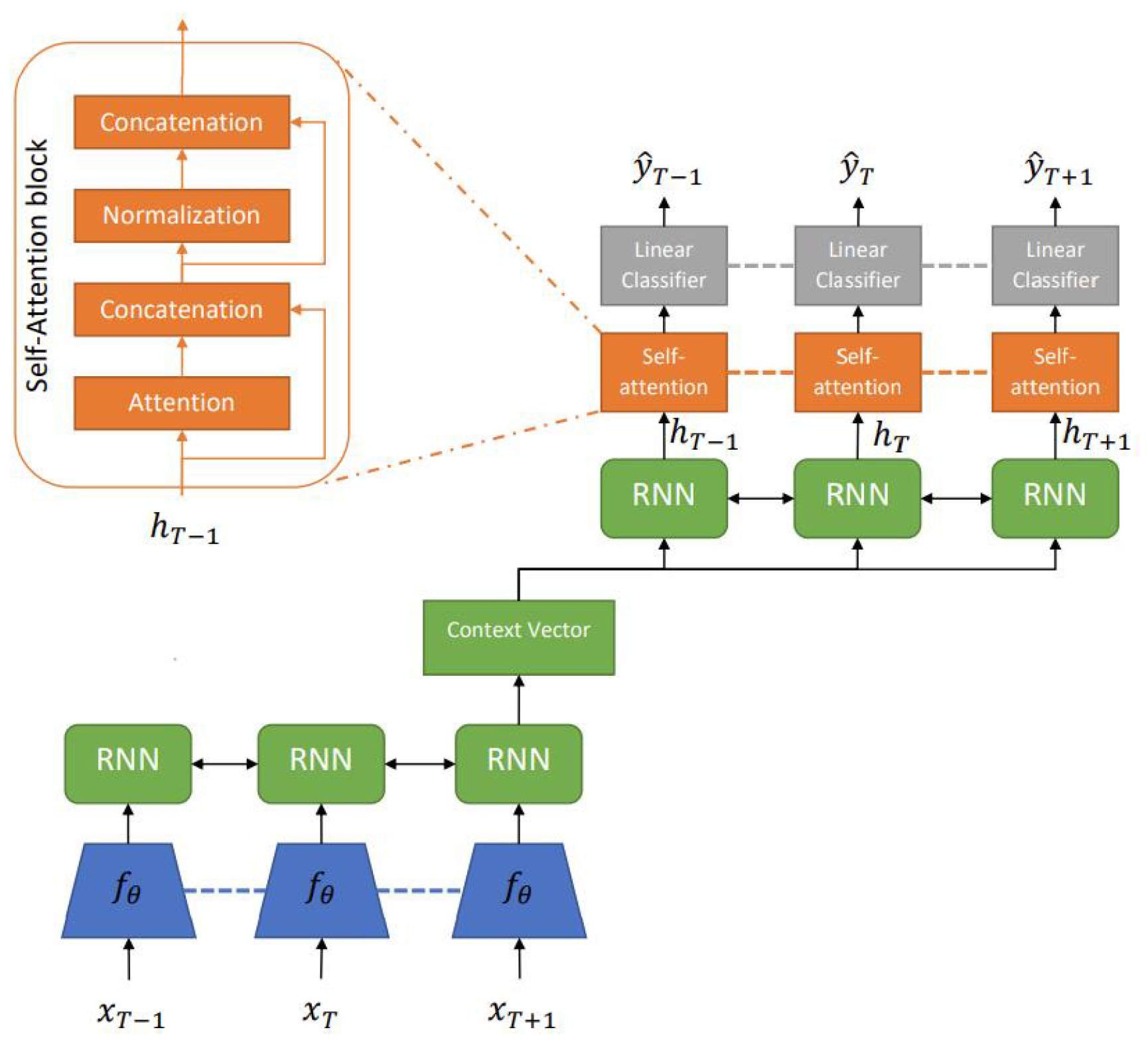
4.2. Convolutional and Recurrent Models
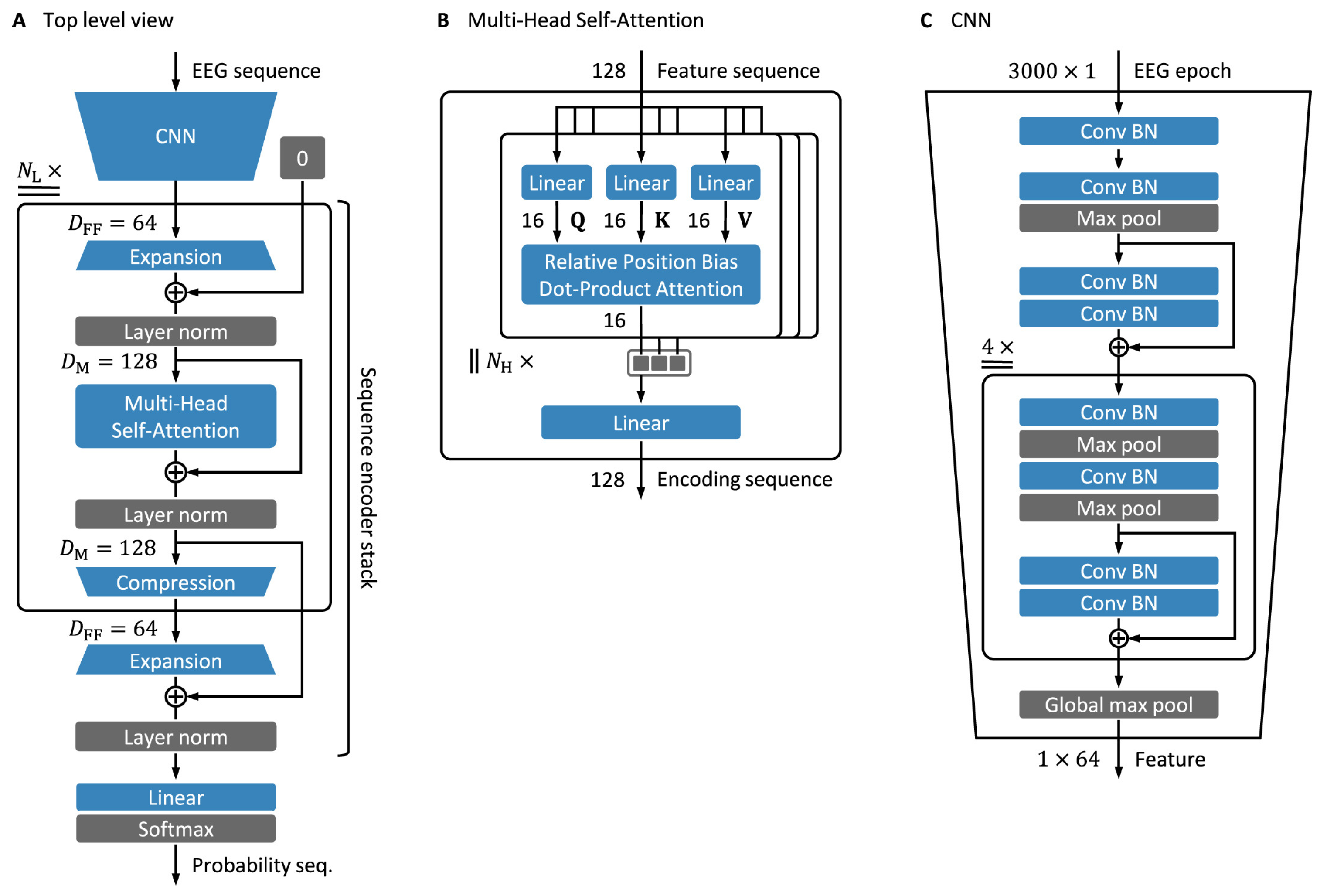
4.3. Transformer-Based Models
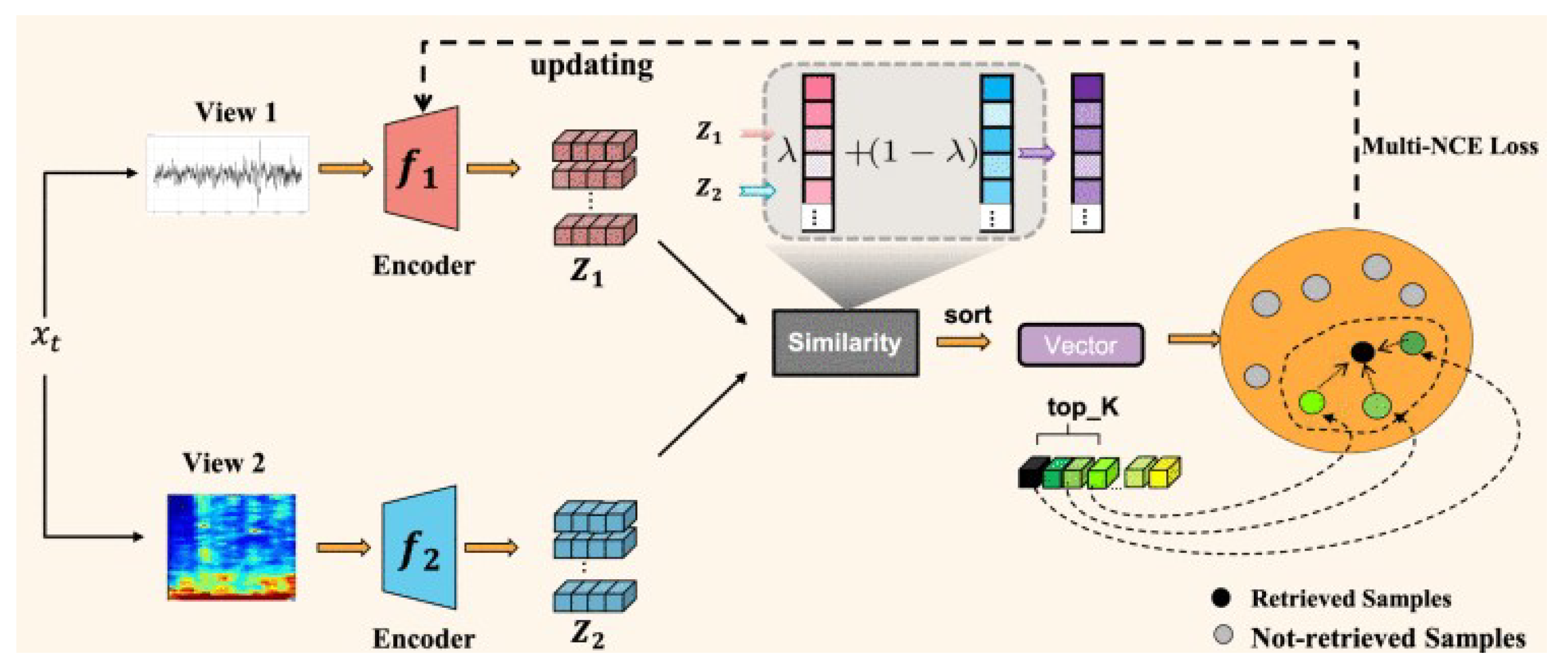
4.4. Contrastive Learning
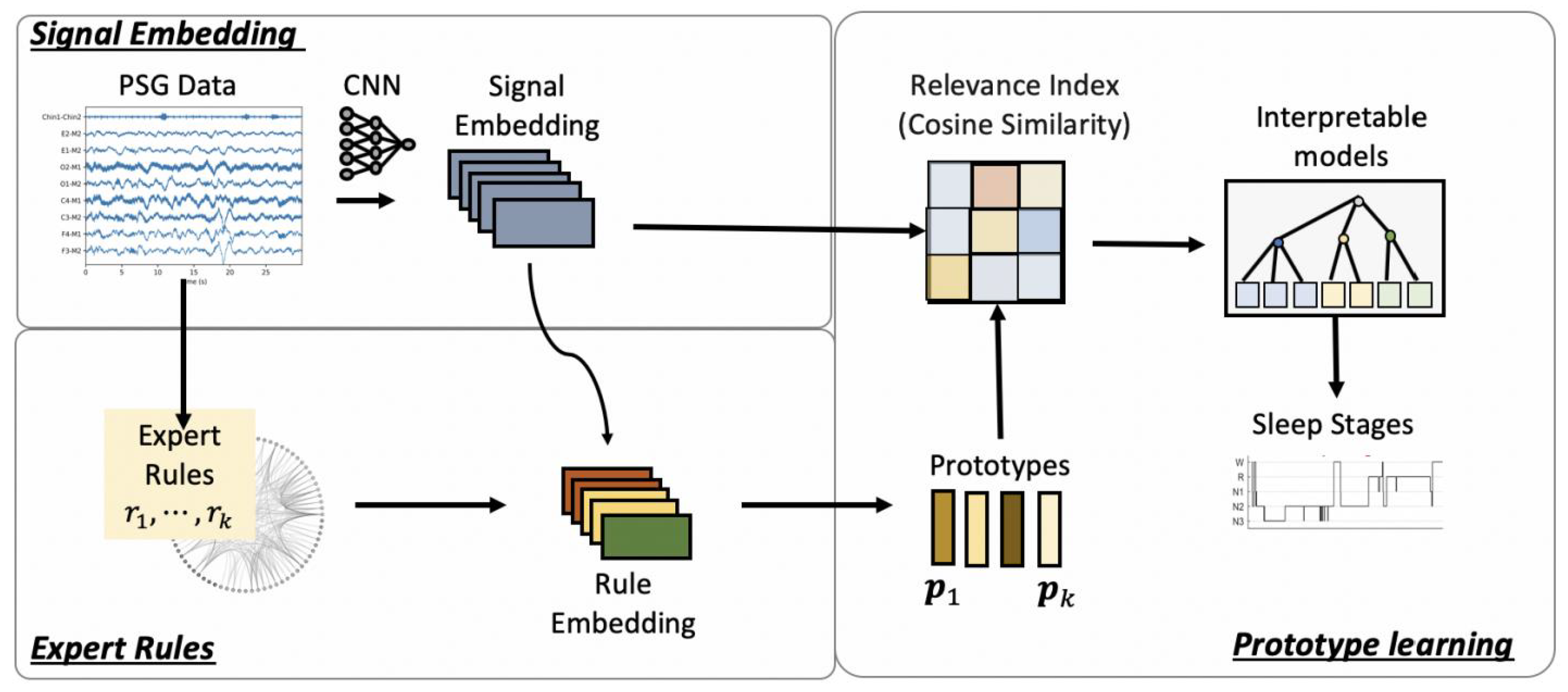
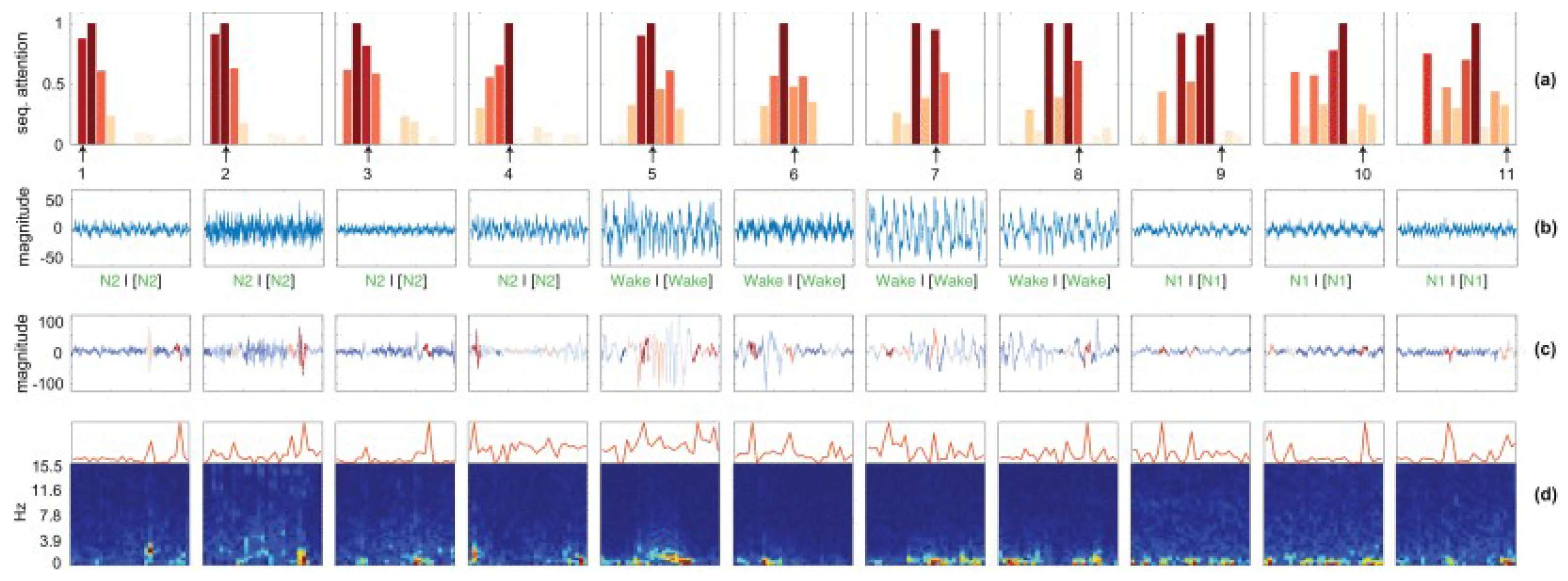
5. Interpretability
6. Discussion
6.1. General Observations
6.2. Quantitative Observations
| Model | Year | EDF-20 | EDF-78 | MASS | SHHS | CAP | DRM-SUB | ISRUC | SVUH-UCD | WSC | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SeqSleepNet [25] | 2018 | 0.809 | 0.776 | 0.815 | 0.838 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| U-Time [82] | 2019 | 0.79 | 0.76 | 0.80 | 0.80 | 0.68 | – | 0.77 | 0.73 | – | 0.85 |
| IITNet [79] | 2019 | 0.78 | 0.79 | – | 0.81 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| GraphSleepNet [171] | 2020 | – | – | 0.834 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Xsleepnet [78] | 2020 | 0.813 | 0.778 | 0.823 | 0.847 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| RobustSleepNet [77] | 2021 | 0.817 | 0.779 | 0.825 | 0.80 | 0.738 | – | – | – | – | – |
| CCRRSleepNet [132] | 2021 | 0.78 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| SalientSleepNet [147] | 2021 | 0.83 | 0.795 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| SleepTransformer [166] | 2021 | – | 0.789 | – | 0.828 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Cross-Modal [167] | 2022 | – | 0.785 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| MtCLSS [175] | 2022 | 0.80 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 0.74 |
| MAtt [146] | 2022 | - | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 0.7471 |
| PearNet [85] | 2022 | 0.793 | 0.753 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| CMS2-Net [176] | 2022 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 0.71 |
| SleepContextNet [59] | 2022 | 0.79 | 0.76 | – | 0.81 | 0.71 | – | – | – | – | – |
| mulEEG [56] | 2022 | – | 0.6850 | – | 0.7366 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Liu et al. [18] | 2022 | 0.862 | 0.852 | – | 0.835 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| MVF-SleepNet [88] | 2022 | – | – | – | – | – | – | 0.795 | – | – | – |
| TrustSleepNet [30] | 2022 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 0.82 |
| SoftVotingSleepNet [152] | 2022 | 0.81 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Kim et al. [128] | 2022 | 0.838 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| CRFs [149] | 2022 | 0.79 | – | – | – | – | 0.76 | – | 0.66 | – | – |
| IDNN [159] | 2022 | 0.81 | 0.76 | – | – | – | – | – | – | 0.75 | – |
| CAttSleepNet [138] | 2022 | 0.78 | 0.74 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| ISENet [140] | 2022 | – | 0.79 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Bi-RNN [102] | 2022 | 0.8404 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| S2MAML [186] | 2022 | – | – | – | – | – | 0.821 | 0.888 | 0.904 | 0.863 | – |
| Pei et al. [103] | 2022 | – | – | – | 0.76 | – | – | – | 0.58 | – | – |
| SleepExpertNet [87] | 2022 | – | 0.87 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| CDNN [96] | 2022 | – | – | – | – | – | – | 0.854 | – | – | 0.734 |
| Van Der Donckt et al. [122] | 2022 | 0.812 | 0.766 | 0.803 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| SleepyCo [174] | 2022 | – | 0.787 | 0.811 | 0.83 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| ENGELBERT [170] | 2022 | 0.823 | 0.794 | 0.799 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| CoSleepNet [51] | 2023 | 0.8181 | – | – | – | – | 0.7693 | 0.715 | – | – | 0.674 |
| MaskSleepNet [163] | 2023 | – | 0.847 | 0.847 | – | – | – | – | – | – | 0.812 |
| SHNN [127] | 2023 | – | 0.7051 | – | – | – | 0.6955 | – | – | – | – |
| Siamese AE [187] | 2023 | 0.79 | – | 0.81 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| BSTT [184] | 2023 | – | – | 0.8437 | – | – | – | 0.7678 | – | – | – |
| NAMRTNet [185] | 2023 | – | 0.808 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Model | Year | CNN | RNN | GNN | Transf. | Contr. Lear. | Interp. | #No. Par. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SeqSleepNet [25] | 2018 | – | ✓ | – | – | – | – | ∼0.2 M |
| U-Time [82] | 2019 | ✓ | – | – | – | – | – | ∼1.2 M |
| IITNet [79] | 2019 | ✓ | ✓ | – | – | – | – | – |
| GraphSleepNet [171] | 2020 | – | – | ✓ | – | – | – | – |
| Xsleepnet [78] | 2020 | ✓ | ✓ | – | – | – | – | ∼5.8 M |
| RobustSleepNet[77] | 2021 | – | ✓ | – | – | – | – | ∼0.18 M |
| CCRRSleepNet [132] | 2021 | ✓ | ✓ | – | – | – | – | – |
| SalientSleepNet [147] | 2021 | ✓ | – | – | – | – | – | ∼0.9 M |
| SleepTransformer [166] | 2021 | – | – | – | ✓ | – | ✓ | ∼3.7 M |
| Cross-Modal [167] | 2022 | ✓ | – | – | ✓ | – | ∼4.05 M | |
| MtCLSS [175] | 2022 | ✓ | – | – | – | ✓ | – | – |
| MAtt [146] | 2022 | ✓ | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| PearNet [85] | 2022 | ✓ | – | ✓ | – | – | – | – |
| CMS2-Net [176] | 2022 | ✓ | – | – | – | ✓ | – | – |
| SleepContextNet [59] | 2022 | ✓ | ✓ | – | – | – | – | – |
| mulEEG [56] | 2022 | ✓ | – | – | – | ✓ | – | ∼0.6 M |
| Liu et al. [18] | 2022 | ✓ | – | – | – | – | – | |
| MVF-SleepNet [88] | 2022 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| TrustSleepNet [30] | 2022 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| SoftVotingSleepNet [152] | 2022 | ✓ | – | – | – | – | – | ∼0.79 M |
| Kim et al. [128] | 2022 | ✓ | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| CRFs [149] | 2022 | ✓ | ✓ | – | – | – | – | ∼0.76 M |
| IDNN [159] | 2022 | ✓ | ✓ | – | – | – | ✓ | – |
| CAttSleepNet [138] | 2022 | ✓ | ✓ | – | – | – | – | – |
| ISENet [140] | 2022 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Bi-RNN [102] | 2022 | ✓ | ✓ | – | – | – | – | – |
| S2MAML [186] | 2022 | ✓ | – | – | – | – | – | ∼0.6 M |
| Pei et al. [103] | 2022 | ✓ | ✓ | – | – | – | – | – |
| SleepExpertNet [87] | 2022 | ✓ | ✓ | – | – | – | – | – |
| CDNN [96] | 2022 | ✓ | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Van Der Donckt et al. [122] | 2022 | – | – | – | – | – | ✓ | – |
| SleepyCo [174] | 2022 | ✓ | – | – | – | ✓ | – | – |
| ENGELBERT [170] | 2022 | ✓ | – | – | ✓ | – | – | ∼0.49 M |
| CoSleepNet [51] | 2023 | ✓ | ✓ | – | – | – | – | – |
| LPT-Based [81] | 2023 | ✓ | – | – | – | – | – | ∼0.16 M |
| MaskSleepNet [163] | 2023 | ✓ | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| SHNN [127] | 2023 | ✓ | ✓ | – | – | – | – | – |
| Siamese AE [187] | 2023 | ✓ | ✓ | – | – | – | – | – |
| BSTT [184] | 2023 | – | – | ✓ | ✓ | – | – | – |
| NAMRTNet [185] | 2023 | ✓ | – | – | – | – | – | – |
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Selected Models with Details
Appendix A.1. XsleepNet [78]
Appendix A.2. EpochNet [81]
Appendix A.3. CrossModal Transformer [167]
Appendix A.4. GraphSleepNet [171]
Appendix A.5. mulEEG [56]
Appendix A.6. CoSleep [173]
Appendix B. Data Modalities
| Dataset | EEG | EOG | EMG |
|---|---|---|---|
| SleepEDF | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| MASS | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| SHHS | ✓ | × | × |
| CAP | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| ISRUC | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| DRM-SUB | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| SVUH-UCD | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
References
- Alhola, P.; Polo-Kantola, P. Sleep deprivation: Impact on cognitive performance. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2007, 3, 553–567. [Google Scholar]
- Tramonti Fantozzi, M.P.; Banfi, T.; Di Galante, M.; Ciuti, G.; Faraguna, U. Sleep deprivation-induced changes in baseline brain activity and vigilant attention performance. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1690. [Google Scholar]
- Stowe, R.C.; Afolabi-Brown, O. Pediatric polysomnography—A review of indications, technical aspects, and interpretation. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2020, 34, 9–17. [Google Scholar]
- Berry, R.B.; Brooks, R.; Gamaldo, C.E.; Harding, S.M.; Marcus, C.; Vaughn, B.V. The AASM manual for the scoring of sleep and associated events. In Rules, Terminology and Technical Specifications; American Academy of Sleep Medicine: Darien, IL, USA, 2012; Volume 176, p. 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Phan, H.; Mikkelsen, K. Automatic sleep staging of EEG signals: Recent development, challenges, and future directions. Physiol. Meas. 2022, 43, 04TR01. [Google Scholar]
- Craik, A.; He, Y.; Contreras-Vidal, J.L. Deep learning for electroencephalogram (EEG) classification tasks: A review. J. Neural Eng. 2019, 16, 031001. [Google Scholar]
- Sri, T.R.; Madala, J.; Duddukuru, S.L.; Reddipalli, R.; Polasi, P.K. A Systematic Review on Deep Learning Models for Sleep Stage Classification. In Proceedings of the 2022 6th International Conference on Trends in Electronics and Informatics (ICOEI), Tirunelveli, India, 28–30 April 2022; pp. 1505–1511. [Google Scholar]
- Moher, D.; Shamseer, L.; Clarke, M.; Ghersi, D.; Liberati, A.; Petticrew, M.; Shekelle, P.; Stewart, L.A. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst. Rev. 2015, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Fabbri, D.; Upender, R.; Kent, D. Automated sleep stage scoring of the Sleep Heart Health Study using deep neural networks. Sleep 2019, 42, zsz159. [Google Scholar]
- Danker-hopfe, H.; Anderer, P.; Zeitlhofer, J.; Boeck, M.; Dorn, H.; Gruber, G.; Heller, E.; Loretz, E.; Moser, D.; Parapatics, S.; et al. Interrater reliability for sleep scoring according to the Rechtschaffen & Kales and the new AASM standard. J. Sleep Res. 2009, 18, 74–84. [Google Scholar]
- Delgado, R.; Tibau, X.A. Why Cohen’s Kappa should be avoided as performance measure in classification. PloS ONE 2019, 14, e0222916. [Google Scholar]
- Kemp, B.; Zwinderman, A.H.; Tuk, B.; Kamphuisen, H.A.; Oberye, J.J. Analysis of a sleep-dependent neuronal feedback loop: The slow-wave microcontinuity of the EEG. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2000, 47, 1185–1194. [Google Scholar]
- Yildirim, O.; Baloglu, U.B.; Acharya, U.R. A deep learning model for automated sleep stages classification using PSG signals. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 599. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, W.; Wang, Z.; Hong, H.; Chi, Z.; Feng, D.D.; Grunstein, R.; Gordon, C. A residual based attention model for eeg based sleep staging. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2020, 24, 2833–2843. [Google Scholar]
- Supratak, A.; Guo, Y. TinySleepNet: An efficient deep learning model for sleep stage scoring based on raw single-channel EEG. In Proceedings of the 2020 42nd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Virtual, 20–24 July 2020; pp. 641–644. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.; Seong, E.; Chae, D.K. Self-supervised learning with attention-based latent signal augmentation for sleep staging with limited labeled data. In Proceedings of the 31st International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI-22), Vienna, Austria, 23–29 July 2022; pp. 3868–3876. [Google Scholar]
- Mai, X.; Yu, T. BootstrapNet: An Contrastive Learning Model for Sleep Stage Scoring based on Raw Single-Channel Electroencephalogram. In Proceedings of the 2021 2nd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computer Engineering (ICAICE), Hangzhou, China, 5–7 November 2021; pp. 303–308. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Luo, S.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Xiao, H. Extracting multi-scale and salient features by MSE based U-structure and CBAM for sleep staging. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2022, 31, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yang, P.; Nan, F.; Zhang, Y.; Rao, Y.; Du, F. A novel feature relearning method for automatic sleep staging based on single-channel EEG. Complex Intell. Syst. 2022, 9, 41–50. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Zhu, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H. A single-channel EEG based automatic sleep stage classification method leveraging deep one-dimensional convolutional neural network and hidden Markov model. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 68, 102581. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, R.; Ganesan, R.A. Reliable sleep staging of unseen subjects with fusion of multiple EEG features and RUSBoost. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 70, 103061. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.; Liu, G.; Tang, X.; Bai, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, X. Improved Model Accuracy Based on a Simple Frame of Temporal-Correlation Representation Method in Sleep Staging. In Proceedings of the 2022 3rd International Conference on Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning (PRML), Chengdu, China, 22–24 July 2022; pp. 216–222. [Google Scholar]
- O’reilly, C.; Gosselin, N.; Carrier, J.; Nielsen, T. Montreal Archive of Sleep Studies: An open-access resource for instrument benchmarking and exploratory research. J. Sleep Res. 2014, 23, 628–635. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Z.; Lin, Y.; Wang, J.; Ning, X.; He, Y.; Zhou, R.; Zhou, Y.; Li-wei, H.L. Multi-view spatial-temporal graph convolutional networks with domain generalization for sleep stage classification. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2021, 29, 1977–1986. [Google Scholar]
- Phan, H.; Andreotti, F.; Cooray, N.; Chén, O.Y.; De Vos, M. SeqSleepNet: End-to-end hierarchical recurrent neural network for sequence-to-sequence automatic sleep staging. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2019, 27, 400–410. [Google Scholar]
- Sleep Heart Health Study (SHHS). Available online: https://biolincc.nhlbi.nih.gov/studies/shhs/ (accessed on 3 January 2018).
- Sridhar, N.; Shoeb, A.; Stephens, P.; Kharbouch, A.; Shimol, D.B.; Burkart, J.; Ghoreyshi, A.; Myers, L. Deep learning for automated sleep staging using instantaneous heart rate. NPJ Digit. Med. 2020, 3, 106. [Google Scholar]
- Van Steenkiste, T.; Groenendaal, W.; Deschrijver, D.; Dhaene, T. Automated sleep apnea detection in raw respiratory signals using long short-term memory neural networks. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2018, 23, 2354–2364. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Li, Q.; Liu, C.; Shashikumar, S.P.; Nemati, S.; Clifford, G.D. Deep learning in the cross-time frequency domain for sleep staging from a single-lead electrocardiogram. Physiol. Meas. 2018, 39, 124005. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Ma, F. TrustSleepNet: A Trustable Deep Multimodal Network for Sleep Stage Classification. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE-EMBS International Conference on Biomedical and Health Informatics (BHI), Ioannina, Greece, 27–30 September 2022; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Biswal, S.; Sun, H.; Goparaju, B.; Westover, M.B.; Sun, J.; Bianchi, M.T. Expert-level sleep scoring with deep neural networks. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2018, 25, 1643–1650. [Google Scholar]
- Terzano, M.G.; Parrino, L.; Sherieri, A.; Chervin, R.; Chokroverty, S.; Guilleminault, C.; Hirshkowitz, M.; Mahowald, M.; Moldofsky, H.; Rosa, A.; et al. Atlas, rules, and recording techniques for the scoring of cyclic alternating pattern (CAP) in human sleep. Sleep Med. 2001, 2, 537–554. [Google Scholar]
- Khalighi, S.; Sousa, T.; Santos, J.M.; Nunes, U. ISRUC-Sleep: A comprehensive public dataset for sleep researchers. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2016, 124, 180–192. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.Q.; Cui, L.; Mueller, R.; Tao, S.; Kim, M.; Rueschman, M.; Mariani, S.; Mobley, D.; Redline, S. The National Sleep Research Resource: Towards a sleep data commons. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2018, 25, 1351–1358. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Wang, R.; Zee, P.; Lutsey, P.L.; Javaheri, S.; Alcántara, C.; Jackson, C.L.; Williams, M.A.; Redline, S. Racial/ethnic differences in sleep disturbances: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA). Sleep 2015, 38, 877–888. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez, C.G.; Niediek, J.; Mormann, F.; Andrzejak, R.G. Seizure onset zone lateralization using a non-linear analysis of micro vs. macro electroencephalographic recordings during seizure-free stages of the sleep-wake cycle from epilepsy patients. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 553885. [Google Scholar]
- Nagabushanam, P.; Thomas George, S.; Radha, S. EEG signal classification using LSTM and improved neural network algorithms. Soft Comput. 2020, 24, 9981–10003. [Google Scholar]
- Goldberger, A.L.; Amaral, L.A.; Glass, L.; Hausdorff, J.M.; Ivanov, P.C.; Mark, R.G.; Mietus, J.E.; Moody, G.B.; Peng, C.K.; Stanley, H.E. PhysioBank, PhysioToolkit, and PhysioNet: Components of a new research resource for complex physiologic signals. Circulation 2000, 101, e215–e220. [Google Scholar]
- Loh, H.W.; Ooi, C.P.; Vicnesh, J.; Oh, S.L.; Faust, O.; Gertych, A.; Acharya, U.R. Automated detection of sleep stages using deep learning techniques: A systematic review of the last decade (2010–2020). Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8963. [Google Scholar]
- Mashrur, F.R.; Islam, M.S.; Saha, D.K.; Islam, S.R.; Moni, M.A. SCNN: Scalogram-based convolutional neural network to detect obstructive sleep apnea using single-lead electrocardiogram signals. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 134, 104532. [Google Scholar]
- Ichimaru, Y.; Moody, G. Development of the polysomnographic database on CD-ROM. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 1999, 53, 175–177. [Google Scholar]
- Penzel, T.; Moody, G.B.; Mark, R.G.; Goldberger, A.L.; Peter, J.H. The apnea-ECG database. In Proceedings of the Computers in Cardiology (CinC), Cambridge, MA, USA, 24–27 September 2000; pp. 255–258. [Google Scholar]
- Devuyst, S.; Dutoit, T.; Kerkhofs, M. The DREAMS Databases and Assessment Algorithm; Zenodo: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ghassemi, M.M.; Moody, B.E.; Lehman, L.W.H.; Song, C.; Li, Q.; Sun, H.; Mark, R.G.; Westover, M.B.; Clifford, G.D. You snooze, you win: The physionet/computing in cardiology challenge 2018. In Proceedings of the Computers in Cardiology (CinC), Maastricht, The Netherlands, 23–26 September 2018; Volume 45, pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, Z.; Chen, H. Automatic sleep stage classification based on a two-channel electrooculogram and one-channel electromyogram. Physiol. Meas. 2022, 43, 07NT02. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, L.; Chen, W.; Tamura, T.; Ono, N.; Altaf-Ul-Amin, M.; Kanaya, S.; Huang, M. Automated sleep staging via parallel frequency-cut attention. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2023, 31, 1974–1985. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Q.; Lei, H.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, G. A Multi-scale Residual Convolutional Neural Network for Sleep Staging Based on Single Channel Electroencephalography Signal. 2021. preprint (Version 1). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, P.; Yuan, Z.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, X.; Wang, Z.; Du, B. Multi-subband and Multi-subepoch Time Series Feature Learning for EEG-based Sleep Stage Classification. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Joint Conference on Biometrics (IJCB), Shenzhen, China (virtual), 4–7 August 2021; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Ling, B.W.K. Sleeping stage classification based on joint quaternion valued singular spectrum analysis and ensemble empirical mode decomposition. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2022, 71, 103086. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, C.E.; Chen, G.T.; Liao, P.Y. An EEG spectrogram-based automatic sleep stage scoring method via data augmentation, ensemble convolution neural network, and expert knowledge. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 70, 102981. [Google Scholar]
- Efe, E.; Ozsen, S. CoSleepNet: Automated sleep staging using a hybrid CNN-LSTM network on imbalanced EEG-EOG datasets. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2023, 80, 104299. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Sun, C.; Chen, C.; Jiang, X.; Liu, X.; Zhao, X.; Meng, L.; Dai, C.; Chen, W. EEG data augmentation: Towards class imbalance problem in sleep staging tasks. J. Neural Eng. 2020, 17, 056017. [Google Scholar]
- Grill, J.B.; Strub, F.; Altché, F.; Tallec, C.; Richemond, P.; Buchatskaya, E.; Doersch, C.; Avila Pires, B.; Guo, Z.; Gheshlaghi Azar, M.; et al. Bootstrap your own latent—A new approach to self-supervised learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 21271–21284. [Google Scholar]
- Eldele, E.; Ragab, M.; Chen, Z.; Wu, M.; Kwoh, C.K.; Li, X.; Guan, C. Time-series representation learning via temporal and contextual contrasting. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.14112. [Google Scholar]
- Mohsenvand, M.N.; Izadi, M.R.; Maes, P. Contrastive representation learning for electroencephalogram classification. In Proceedings of the Machine Learning for Health (PMLR), Virtual, 11 December 2020; pp. 238–253. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, V.; Reddy, L.; Kumar Sharma, S.; Dadi, K.; Yarra, C.; Bapi, R.S.; Rajendran, S. mulEEG: A multi-view representation learning on EEG signals. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), Singapore, 18–22 September 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 398–407. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q.; Zhou, D.; Wang, J.; Shen, J.; Kettunen, L.; Cong, F. Convolutional Neural Network Based Sleep Stage Classification with Class Imbalance. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Padua, Italy, 18–23 July 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Efe, E.; Özsen, S. A New Approach for Automatic Sleep Staging: Siamese Neural Networks. Trait. Signal 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Li, J.; Guo, Y. SleepContextNet: A temporal context network for automatic sleep staging based single-channel EEG. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2022, 220, 106806. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.; Du, L.; Wang, P.; Xia, P.; Liu, Z.; Song, Y.; Chen, X.; Fang, Z. Single-channel EEG sleep staging based on data augmentation and cross-subject discrepancy alleviation. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 149, 106044. [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, B.C.; Small, K.; Brodley, C.E.; Trikalinos, T.A. Class imbalance, redux. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE 11th International Conference on Data Mining (KDD) Workshops, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 11 December 2011; pp. 754–763. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, D.; Xu, Q.; Wang, J.; Xu, H.; Kettunen, L.; Chang, Z.; Cong, F. Alleviating class imbalance problem in automatic sleep stage classification. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Kenton, J.D.M.W.C.; Toutanova, L.K. BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies (NAACL-HLT), Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–7 June 2019; pp. 4171–4186. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, T.; Mann, B.; Ryder, N.; Subbiah, M.; Kaplan, J.D.; Dhariwal, P.; Neelakantan, A.; Shyam, P.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; et al. Language models are few-shot learners. Adv. Neural Inf. Process 2020, 33, 1877–1901. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Andreotti, F.; Phan, H.; Cooray, N.; Lo, C.; Hu, M.T.; De Vos, M. Multichannel sleep stage classification and transfer learning using convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 17–21 July 2018; pp. 171–174. [Google Scholar]
- ElMoaqet, H.; Eid, M.; Ryalat, M.; Penzel, T. A deep transfer learning framework for sleep stage classification with single-channel EEG signals. Sensors 2022, 22, 8826. [Google Scholar]
- Supratak, A.; Dong, H.; Wu, C.; Guo, Y. DeepSleepNet: A model for automatic sleep stage scoring based on raw single-channel EEG. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2017, 25, 1998–2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Liao, Y.; Han, S.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Z.; Xie, X. Multichannel Multidomain-Based Knowledge Distillation Algorithm for Sleep Staging With Single-Channel EEG. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Br. 2022, 69, 4608–4612. [Google Scholar]
- Supratak, A.; Haddawy, P. Quantifying the impact of data characteristics on the transferability of sleep stage scoring models. Artif. Intell. Med. 2023, 139, 102540. [Google Scholar]
- Eldele, E.; Ragab, M.; Chen, Z.; Wu, M.; Kwoh, C.K.; Li, X.; Guan, C. ADAST: Attentive cross-domain EEG-based sleep staging framework with iterative self-training. IEEE Trans. Emerg. 2022, 7, 210–221. [Google Scholar]
- Nasiri, S.; Clifford, G.D. Attentive adversarial network for large-scale sleep staging. In Proceedings of the Machine Learning for Healthcare (MLHC) (PMLR), Durham, NC, USA, 7–8 August 2020; pp. 457–478. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, R.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, Y. Unsupervised sleep staging system based on domain adaptation. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 69, 102937. [Google Scholar]
- Heremans, E.R.; Phan, H.; Borzée, P.; Buyse, B.; Testelmans, D.; De Vos, M. From unsupervised to semi-supervised adversarial domain adaptation in electroencephalography-based sleep staging. J. Neural Eng. 2022, 19, 036044. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Zhu, H.; Jiang, X.; Meng, L.; Chen, C.; Fu, C.; Yu, H.; Dai, C.; Chen, W. Unsupervised domain adaptation by statistics alignment for deep sleep staging networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2022, 30, 205–216. [Google Scholar]
- Phan, H.; Chén, O.Y.; Koch, P.; Mertins, A.; De Vos, M. Deep transfer learning for single-channel automatic sleep staging with channel mismatch. In Proceedings of the 2019 27th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), A CorUña, Spain, 2–6 September 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Guillot, A.; Thorey, V. RobustSleepNet: Transfer learning for automated sleep staging at scale. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2021, 29, 1441–1451. [Google Scholar]
- Phan, H.; Chén, O.Y.; Tran, M.C.; Koch, P.; Mertins, A.; De Vos, M. XSleepNet: Multi-view sequential model for automatic sleep staging. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 44, 5903–5915. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, H.; Back, S.; Lee, S.; Park, D.; Kim, T.; Lee, K. Intra-and inter-epoch temporal context network (IITNet) using sub-epoch features for automatic sleep scoring on raw single-channel EEG. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2020, 61, 102037. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, T.; Luo, W.; Yu, F. Convolution-and attention-based neural network for automated sleep stage classification. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4152. [Google Scholar]
- Zan, H.; Yildiz, A. Local Pattern Transformation-Based convolutional neural network for sleep stage scoring. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2023, 80, 104275. [Google Scholar]
- Perslev, M.; Jensen, M.H.; Darkner, S.; Jennum, P.J.; Igel, C. U-Time: A fully convolutional network for time series segmentation applied to sleep staging. In Proceedings of the NeurIPS, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019; pp. 4415–4426. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015, Proceedings, Part III 18; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Mousavi, S.; Afghah, F.; Acharya, U.R. SleepEEGNet: Automated sleep stage scoring with sequence to sequence deep learning approach. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216456. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Tian, Y.; Wang, S.; Sheng, M.; Zheng, X. PearNet: A Pearson Correlation-based Graph Attention Network for Sleep Stage Recognition. In Proceedings of the 9th of the IEEE International Conference on Data Science and Advanced Analytics (DSAA), Virtual, 13–16 October 2022; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Stine, R.A. Graphical interpretation of variance inflation factors. Am. Stat. 1995, 49, 53–56. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, Y.T.; Kim, H.; Kim, J.B.; Kim, D.J. SleepExpertNet: High-performance and class-balanced deep learning approach inspired from the expert neurologists for sleep stage classification. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2023, 14, 8067–8083. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Ma, W.; Zhao, G.; Fan, X. MVF-sleepnet: Multi-view fusion network for sleep stage classification. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2022. ahead of print. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Yao, R.; Ge, W.; Gao, J. Orthogonal convolutional neural networks for automatic sleep stage classification based on single-channel EEG. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2020, 183, 105089. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, H.; Tu, S.; Xu, L. Recsleepnet: An automatic sleep staging model based on feature reconstruction. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), Virtual, 9–12 December 2021; pp. 1458–1461. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Z.; Cai, X.; Zheng, G.; Wang, J.; Lin, Y. SleepPrintNet: A multivariate multimodal neural network based on physiological time-series for automatic sleep staging. IEEE Trans. Artif. Intell. 2020, 1, 248–257. [Google Scholar]
- Jadhav, P.; Rajguru, G.; Datta, D.; Mukhopadhyay, S. Automatic sleep stage classification using time–frequency images of CWT and transfer learning using convolution neural network. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 40, 494–504. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, F.; Liang, Q. OCRNN: An orthogonal constrained recurrent neural network for sleep analysis based on EEG data. Ad. Hoc. Netw. 2020, 104, 102178. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Qi, Y.; Ding, X.; Zhao, J.; Sang, T.; Lee, M. A deep learning method approach for sleep stage classification with eeg spectrogram. Int. J. Environ. Res. Pub. Health 2022, 19, 6322. [Google Scholar]
- Urtnasan, E.; Park, J.U.; Joo, E.Y.; Lee, K.J. Deep convolutional recurrent model for automatic scoring sleep stages based on single-lead ECG signal. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1235. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, K.; Kwon, S.; Yeo, W.H. Automatic and accurate sleep stage classification via a convolutional deep neural network and nanomembrane electrodes. Biosensors 2022, 12, 155. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Guan, Y. DeepSleep convolutional neural network allows accurate and fast detection of sleep arousal. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 18. [Google Scholar]
- Olesen, A.N.; Jørgen Jennum, P.; Mignot, E.; Sorensen, H.B.D. Automatic sleep stage classification with deep residual networks in a mixed-cohort setting. Sleep 2021, 44, zsaa161. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, R.; Li, F.; Zhou, D.; Ristaniemi, T.; Cong, F. A deep learning model for automatic sleep scoring using multimodality time series. In Proceedings of the 2020 28th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), Dublin, Ireland, 23–27 August 2021; pp. 1090–1094. [Google Scholar]
- Van Der Donckt, J.; Van Der Donckt, J.; Deprost, E.; Vandenbussche, N.; Rademaker, M.; Vandewiele, G.; Van Hoecke, S. Do not sleep on traditional machine learning: Simple and interpretable techniques are competitive to deep learning for sleep scoring. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2023, 81, 104429. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, R.; Li, F.; Zhou, D.D.; Ristaniemi, T.; Cong, F. Automatic sleep scoring: A deep learning architecture for multi-modality time series. J. Neurosci. Methods 2021, 348, 108971. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Z.; Huang, C.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y. Deep Learning Model of Sleep EEG Signal by Using Bidirectional Recurrent Neural Network Encoding and Decoding. Electronics 2022, 11, 2644. [Google Scholar]
- Pei, W.; Li, Y.; Siuly, S.; Wen, P. A hybrid deep learning scheme for multi-channel sleep stage classification. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2022, 71, 889–905. [Google Scholar]
- Michielli, N.; Acharya, U.R.; Molinari, F. Cascaded LSTM recurrent neural network for automated sleep stage classification using single-channel EEG signals. Comput. Biol. Med. 2019, 106, 71–81. [Google Scholar]
- Fiorillo, L.; Favaro, P.; Faraci, F.D. Deepsleepnet-lite: A simplified automatic sleep stage scoring model with uncertainty estimates. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2021, 29, 2076–2085. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, M.; Li, Y.; Su, M.; Xu, Z.; Wang, C.; Kang, D.; Li, H.; Mu, X.; Ding, X.; et al. Automated multi-model deep neural network for sleep stage scoring with unfiltered clinical data. Sleep Breath. 2020, 24, 581–590. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Blanco, E.; Rivero, D.; Pazos, A. Convolutional neural networks for sleep stage scoring on a two-channel EEG signal. Soft Comput. 2020, 24, 4067–4079. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, T.; Hwang, J.; Lee, H. Trier: Template-guided neural networks for robust and interpretable sleep stage identification from eeg recordings. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2009.05407. [Google Scholar]
- Barnes, L.D.; Lee, K.; Kempa-Liehr, A.W.; Hallum, L.E. Detection of sleep apnea from single-channel electroencephalogram (EEG) using an explainable convolutional neural network (CNN). PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0272167. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, I.N.; Lee, C.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, H.; Kim, D.J. An ensemble deep learning approach for sleep stage classification via single-channel EEG and EOG. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Information and Communication Technology Convergence (ICTC), Jeju, Republic of Korea, 21–23 October 2020; pp. 394–398. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Gu, Z.; Lin, Z.; Yu, Z.; Li, Y. An automatic sleep staging model combining feature learning and sequence learning. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Advanced Computational Intelligence (ICACI), Dali, China, 14–16 August 2020; pp. 419–425. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Li, H.; Mehendale, S.; Guan, Y. Auto-annotating sleep stages based on polysomnographic data. Patterns 2022, 3, 100371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sors, A.; Bonnet, S.; Mirek, S.; Vercueil, L.; Payen, J.F. A convolutional neural network for sleep stage scoring from raw single-channel EEG. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2018, 42, 107–114. [Google Scholar]
- Abou Jaoude, M.; Sun, H.; Pellerin, K.R.; Pavlova, M.; Sarkis, R.A.; Cash, S.S.; Westover, M.B.; Lam, A.D. Expert-level automated sleep staging of long-term scalp electroencephalography recordings using deep learning. Sleep 2020, 43, zsaa112. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Sun, C.; Long, M.; Chen, C.; Chen, W. Eognet: A novel deep learning model for sleep stage classification based on single-channel eog signal. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 573194. [Google Scholar]
- Anandakumar, M.; Pradeepkumar, J.; Kappel, S.L.; Edussooriya, C.U.; De Silva, A.C. A Knowledge Distillation Framework for Enhancing Ear-EEG Based Sleep Staging with Scalp-EEG Data. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2211.02638. [Google Scholar]
- Mikkelsen, K.; De Vos, M. Personalizing deep learning models for automatic sleep staging. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1801.02645. [Google Scholar]
- Brandmayr, G.; Hartmann, M.; Furbass, F.; Dorffner, G. Self-attention long-term dependency modelling in electroencephalography sleep stage prediction. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Information Processing, Sanur, Bali, Indonesia, 8–12 December 2021; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; pp. 379–390.
- Satapathy, S.K.; Loganathan, D. Automated classification of multi-class sleep stages classification using polysomnography signals: A nine-layer 1D-convolution neural network approach. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 82, 8049–8091. [Google Scholar]
- Phan, H.; Andreotti, F.; Cooray, N.; Chén, O.Y.; De Vos, M. Joint classification and prediction CNN framework for automatic sleep stage classification. IEEE. Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 66, 1285–1296. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Yan, R.; Mahini, R.; Wei, L.; Wang, Z.; Mathiak, K.; Liu, R.; Cong, F. End-to-end sleep staging using convolutional neural network in raw single-channel EEG. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 63, 102203. [Google Scholar]
- Van Der Donckt, J.; Van Der Donckt, J.; Deprost, E.; Rademaker, M.; Vandewiele, G.; Van Hoecke, S. Do not sleep on linear models: Simple and interpretable techniques outperform deep learning for sleep scoring. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2207.07753. [Google Scholar]
- Parekh, N.; Dave, B.; Shah, R.; Srivastava, K. Automatic sleep stage scoring on raw single-channel EEG: A comparative analysis of CNN architectures. In Proceedings of the 2021 Fourth International Conference on Electrical, Computer and Communication Technologies (ICECCT), Erode, India, 15–17 September 2021; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, R.; Xia, Y.; Wang, Q. Dual-modal and multi-scale deep neural networks for sleep staging using EEG and ECG signals. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 66, 102455. [Google Scholar]
- Khalili, E.; Asl, B.M. Automatic sleep stage classification using temporal convolutional neural network and new data augmentation technique from raw single-channel EEG. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2021, 204, 106063. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Lu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, Z.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, P.; Liu, W. A novel sleep staging network based on multi-scale dual attention. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2022, 74, 103486. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Cao, W.; Feng, L.; Wang, M.; Geng, T.; Zhou, J.; Gao, D. Shnn: A single-channel eeg sleep staging model based on semi-supervised learning. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 213, 119288. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.; Lee, S.M.; Choi, S. Automatic sleep stages classification using multi-level fusion. Biomed. Eng. Lett. 2022, 12, 413–420. [Google Scholar]
- Jadhav, P.; Mukhopadhyay, S. Automated sleep stage scoring using time-frequency spectra convolution neural network. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, D.; Wang, J.; Hu, G.; Zhang, J.; Li, F.; Yan, R.; Kettunen, L.; Chang, Z.; Xu, Q.; Cong, F. SingleChannelNet: A model for automatic sleep stage classification with raw single-channel EEG. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2022, 75, 103592. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Chen, P.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y. A dual-stream deep neural network integrated with adaptive boosting for sleep staging. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2023, 79, 104150. [Google Scholar]
- Neng, W.; Lu, J.; Xu, L. CCRRSleepNet: A hybrid relational inductive biases network for automatic sleep stage classification on raw single-channel eeg. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 456. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; Zhao, J.; Bo, D.; Panfeng, A.; Guo, H.; Yuan, Z. MRNet: A Multi-scale Residual Network for EEG-based Sleep Staging. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Shenzhen, China, 18-22 July 2021; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Goshtasbi, N.; Boostani, R.; Sanei, S. SleepFCN: A fully convolutional deep learning framework for sleep stage classification using single-channel electroencephalograms. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2022, 30, 2088–2096. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.; Chen, C.; Li, W.; Fan, J.; Chen, W. A hierarchical neural network for sleep stage classification based on comprehensive feature learning and multi-flow sequence learning. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2019, 24, 1351–1366. [Google Scholar]
- Phyo, J.; Ko, W.; Jeon, E.; Suk, H.I. TransSleep: Transitioning-Aware attention-based deep neural network for sleep staging. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2022, 53, 4500–4510. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, S.; Han, F.; Nie, Z.; Lo, B.; Zhang, Y. Hybrid manifold-deep convolutional neural network for sleep staging. Methods 2022, 202, 164–172. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Zhang, B.; Lv, H.; Hu, S.; Xu, Z.; Tuergong, Y. CAttSleepNet: Automatic end-to-end sleep staging using attention-based deep neural networks on single-channel EEG. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5199. [Google Scholar]
- Banville, H.; Wood, S.U.; Aimone, C.; Engemann, D.A.; Gramfort, A. Robust learning from corrupted EEG with dynamic spatial filtering. NeuroImage 2022, 251, 118994. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Ren, L.; Zhou, X.; Yan, K. An improved neural network based on SENet for sleep stage classification. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2022, 26, 4948–4956. [Google Scholar]
- Phan, H.; Andreotti, F.; Cooray, N.; Chén, O.Y.; De Vos, M. Automatic sleep stage classification using single-channel eeg: Learning sequential features with attention-based recurrent neural networks. In Proceedings of the 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 17–21 July 2018; pp. 1452–1455. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, C.E.; Liao, P.Y.; Lin, Y.S. A self-attention-based ensemble convolution neural network approach for sleep stage classification with merged spectrogram. In Proceedings of the 2021 Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference (APSIPA ASC), Tokyo, Japan, 14–17 December 2021; pp. 1262–1268. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Jia, K.; Ma, F.; Xun, G.; Wang, Y.; Su, L.; Zhang, A. A hybrid self-attention deep learning framework for multivariate sleep stage classification. BMC Bioinform. 2019, 20, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Xun, G.; Ma, F.; Suo, Q.; Xue, H.; Jia, K.; Zhang, A. A novel channel-aware attention framework for multi-channel eeg seizure detection via multi-view deep learning. In Proceedings of the Biomedical and Health Informatics (BHI), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 4–7 March 2018; pp. 206–209. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, F.; Chitta, R.; Zhou, J.; You, Q.; Sun, T.; Gao, J. Dipole: Diagnosis prediction in healthcare via attention-based bidirectional recurrent neural networks. In Proceedings of the Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (KDD), Halifax, NS, Canada, 13–17 August 2017; pp. 1903–1911. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Y.T.; Chou, J.L.; Wei, C.S. MAtt: A Manifold Attention Network for EEG Decoding. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 31116–31129. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Z.; Lin, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Xie, P.; Zhang, Y. SalientSleepNet: Multimodal salient wave detection network for sleep staging. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2105.13864. [Google Scholar]
- Eldele, E.; Chen, Z.; Liu, C.; Wu, M.; Kwoh, C.K.; Li, X.; Guan, C. An attention-based deep learning approach for sleep stage classification with single-channel EEG. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2021, 29, 809–818. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Wu, W.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H. A novel sleep stage contextual refinement algorithm leveraging conditional random fields. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Fang, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y. A deep learning approach with conditional random field for automatic sleep stage scoring. In Proceedings of the Conference on Electronic Information Technology and Computer Engineering (EITCE), Xiamen, China, 22–24 October 2021; pp. 901–906. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, J.K.; Lee, T.; Delos Reyes, R.D.; Hong, J.; Tran, H.H.; Lee, D.; Jung, J.; Yoon, I.Y. Confidence-Based Framework Using Deep Learning for Automated Sleep Stage Scoring. Nat. Sci. Sleep 2021, 13, 2239–2250. [Google Scholar]
- Neshov, N.; Tonchev, K.; Velchev, Y.; Manolova, A.; Poulkov, V. SoftVotingSleepNet: Majority Vote of Deep Learning Models for Sleep Stage Classification from Raw Single EEG Channel. In Proceedings of the International Black Sea Conference on Communications and Networking (BlackSeaCom), Sofia, Bulgaria, 6–9 June 2022; pp. 298–302. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, D.; Chen, P.; Li, W.; Li, X. Dual-CNN based multi-modal sleep scoring with temporal correlation driven fine-tuning. Neurocomputing 2021, 420, 317–328. [Google Scholar]
- Khare, S.K.; Bajaj, V.; Taran, S.; Sinha, G. Multiclass sleep stage classification using artificial intelligence based time-frequency distribution and CNN. In Artificial Intelligence-Based Brain-Computer Interface; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Erdenebayar, U.; Kim, Y.J.; Park, J.U.; Joo, E.Y.; Lee, K.J. Deep learning approaches for automatic detection of sleep apnea events from an electrocardiogram. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2019, 180, 105001. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, D.; Xu, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Hu, G.; Kettunen, L.; Chang, Z.; Cong, F. LightSleepNet: A lightweight deep model for rapid sleep stage classification with spectrograms. In Proceedings of the 2021 43rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Virtual, 1–5 November 2021; pp. 43–46. [Google Scholar]
- Sanghavi, S.; Vaid, P.; Rathod, P.; Srivastava, K. SpectroTemporalNet: Automated Sleep Stage Scoring with Stacked Generalization. In Proceedings of the 2021 Second International Conference on Electronics and Sustainable Communication Systems (ICESC), Coimbatore, India, 4–6 August 2021; pp. 1256–1263. [Google Scholar]
- Begawan, I.A.; Djamal, E.C.; Djajasasmita, D.; Kasyidi, F.; Nugraha, F. Sleep Stage Identification Based on EEG Signals Using Parallel Convolutional Neural Network and Recurrent Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Advanced Computer Science and Information Systems (ICACSIS), Depok, Indonesia, 1–3 October 2022; pp. 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Baek, J.; Lee, C.; Yu, H.; Baek, S.; Lee, S.; Lee, S.; Park, C. Automatic Sleep Scoring Using Intrinsic Mode Based on Interpretable Deep Neural Networks. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 36895–36906. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.; Ryu, J.; Kim, K.K.; Took, C.C.; Mandic, D.P.; Park, C. Motor imagery classification using mu and beta rhythms of EEG with strong uncorrelating transform based complex common spatial patterns. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2016, 2016, 1489692. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Z.; Cai, X.; Jiao, Z. Multi-modal physiological signals based squeeze-and-excitation network with domain adversarial learning for sleep staging. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 3464–3471. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Liu, W.; Wu, J.; Cao, L.; Meng, Q.; Kennedy, P.J. Training deep neural networks on imbalanced data sets. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–29 July 2016; pp. 4368–4374. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Zhou, W.; Fu, C.; Wu, Y.; Shen, N.; Shu, F.; Yu, H.; Chen, C.; Chen, W. MaskSleepNet: A Cross-modality Adaptation Neural Network for Heterogeneous Signals Processing in Sleep Staging. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2023, 27, 2353–2364. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, S.; Ko, W.; Mulyadi, A.W.; Suk, H.I. Efficient continuous manifold learning for time series modeling. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.03379. [Google Scholar]
- Chien, H.Y.S.; Goh, H.; Sandino, C.M.; Cheng, J.Y. MAEEG: Masked Auto-encoder for EEG Representation Learning. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2211.02625. [Google Scholar]
- Phan, H.; Mikkelsen, K.; Chén, O.Y.; Koch, P.; Mertins, A.; De Vos, M. Sleeptransformer: Automatic sleep staging with interpretability and uncertainty quantification. IEEE. Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 69, 2456–2467. [Google Scholar]
- Pradeepkumar, J.; Anandakumar, M.; Kugathasan, V.; Suntharalingham, D.; Kappel, S.L.; De Silva, A.C.; Edussooriya, C.U. Towards interpretable sleep stage classification using cross-modal transformers. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2208.06991. [Google Scholar]
- Yubo, Z.; Yingying, L.; Bing, Z.; Lin, Z.; Lei, L. MMASleepNet: A multimodal attention network based on electrophysiological signals for automatic sleep staging. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 973761. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Brandmayr, G.; Hartmann, M.; Furbass, F.; Matz, G.; Samwald, M.; Kluge, T.; Dorffner, G. Relational local electroencephalography representations for sleep scoring. Neural Netw. 2022, 154, 310–322. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Z.; Lin, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, R.; Ning, X.; He, Y.; Zhao, Y. GraphSleepNet: Adaptive Spatial-Temporal Graph Convolutional Networks for Sleep Stage Classification. In Proceedings of the 29th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI), Yokohama, Japan, 7–15 January 2021; Volume 2021, pp. 1324–1330. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Xiao, Q.; Deng, J.; Lin, Y. Sleeppriorcl: Contrastive representation learning with prior knowledge-based positive mining and adaptive temperature for sleep staging. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.09966. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, J.; Xiao, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Deng, J.; Lin, Y. Cosleep: A multi-view representation learning framework for self-supervised learning of sleep stage classification. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2021, 29, 189–193. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Yu, Y.; Back, S.; Seo, H.; Lee, K. SleePyCo: Automatic Sleep Scoring with Feature Pyramid and Contrastive Learning. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2209.09452. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Luo, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lo, B. MtCLSS: Multi-Task Contrastive Learning for Semi-Supervised Pediatric Sleep Staging. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2023, 27, 2647–2655. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Yu, W.; Li, Y.; Sun, H.; Zhang, Y.; De Vos, M. CMS2-net: Semi-supervised sleep staging for diverse obstructive sleep apnea severity. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2022, 26, 3447–3457. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Ma, F. Concad: Contrastive learning-based cross attention for sleep apnea detection. In Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases. Applied Data Science Track: European Conference, ECML PKDD 2021, Bilbao, Spain, 13–17 September 2021, Proceedings, Part V 21; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 68–84. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, C.B.; Mondal, A.K.; Bhatia, M.; Panigrahi, B.K.; Gandhi, T.K. SCL-SSC: Supervised Contrastive Learning for Sleep Stage Classification. arXiv 2022. arXiv:2109.07839. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Hussaini, I.; Xiao, C.; Westover, M.B.; Sun, J. SLEEPER: Interpretable Sleep staging via Prototypes from Expert Rules. In Proceedings of the 4th Machine Learning for Healthcare Conference (PMLR), Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 8–10 August 2019; pp. 721–739. [Google Scholar]
- Ellis, C.A.; Zhang, R.; Carbajal, D.A.; Miller, R.L.; Calhoun, V.D.; Wang, M.D. Explainable Sleep Stage Classification with Multimodal Electrophysiology Time-series. In Proceedings of the 2021 43rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Virtual, 1–5 November 2021; pp. 2363–2366. [Google Scholar]
- Troncoso-García, A.; Martínez-Ballesteros, M.; Martínez-Álvarez, F.; Troncoso, A. Explainable machine learning for sleep apnea prediction. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2022, 207, 2930–2939. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, M.T.; Singh, S.; Guestrin, C. “Why should i trust you?” Explaining the predictions of any classifier. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (KDD), San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 1135–1144. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Hussaini, I.; Mitchell, C.S. Serf: Interpretable sleep staging using embeddings, rules, and features. In Proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Information & Knowledge Management (CIKM), Atlanta, GA, USA, 17–21 October 2022; pp. 3791–3795. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Jia, Z. Bstt: A bayesian spatial-temporal transformer for sleep staging. In Proceedings of the 11st International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), Kigali, Rwanda, 1–5 May 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Chen, C.; Meng, K.; Lu, L.; Cheng, X.; Fan, H. NAMRTNet: Automatic Classification of Sleep Stages Based on Improved ResNet-TCN Network and Attention Mechanism. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6788. [Google Scholar]
- Lemkhenter, A.; Favaro, P. Towards sleep scoring generalization through self-supervised meta-learning. In Proceedings of the 2022 44th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Glasgow, UK, 11–15 July 2022; pp. 2961–2966. [Google Scholar]
- You, Y.; Guo, X.; Yang, Z.; Shan, W. A Siamese Network-Based Method for Improving the Performance of Sleep Staging with Single-Channel EEG. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 327. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Tran, D.; Feiszli, M. What makes training multi-modal classification networks hard? In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Virtual, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 12695–12705. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Xiao, D.; Westover, M.B.; Sun, J. Self-supervised eeg representation learning for automatic sleep staging. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.15278. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, N.E.; Shen, Z.; Long, S.R.; Wu, M.C.; Shih, H.H.; Zheng, Q.; Yen, N.C.; Tung, C.C.; Liu, H.H. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proc. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1998, 454, 903–995. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, P.; Etemad, A. Self-supervised learning for ecg-based emotion recognition. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, & Signal Processing (ICASSP), Virtual, 4–8 May 2020; pp. 3217–3221. [Google Scholar]















| Rhythm | Frequency Band (Hz) | Target Stages |
|---|---|---|
| Delta | 1–4 | N3 |
| Theta | 4–8 | N1, REM |
| Alpha | 8–12 | N1, Wake |
| Sigma | 12–16 | N2 |
| Beta | 16–32 | Wake, REM |
| Dataset | Wake% | N1% | N2% | N3% | REM% | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sleep EDF | 19.50 | 6.60 | 42.07 | 13.48 | 18.24 | 42,308 |
| MASS | 9.88 | 7.88 | 50.90 | 13.18 | 18.15 | 57,395 |
| SHHS | 23.08 | 4.01 | 44.20 | 14.64 | 15.07 | 5,421,338 |
| ISRUC (Subgroup 1) | 23.62 | 11.54 | 32.74 | 18.69 | 13.41 | 90,123 |
| ISRUC (Subgroup 2) | 17.18 | 14.88 | 33.98 | 18.80 | 15.16 | 14,207 |
| ISRUC (Subgroup 3) | 19.53 | 13.44 | 30.96 | 22.79 | 13.28 | 8883 |
| UCD | 22.60 | 16.30 | 33.60 | 12.80 | 14.50 | 20,774 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soleimani, R.; Barahona, J.; Chen, Y.; Bozkurt, A.; Daniele, M.; Pozdin, V.; Lobaton, E. Advances in Modeling and Interpretability of Deep Neural Sleep Staging: A Systematic Review. Physiologia 2024, 4, 1-42. https://doi.org/10.3390/physiologia4010001
Soleimani R, Barahona J, Chen Y, Bozkurt A, Daniele M, Pozdin V, Lobaton E. Advances in Modeling and Interpretability of Deep Neural Sleep Staging: A Systematic Review. Physiologia. 2024; 4(1):1-42. https://doi.org/10.3390/physiologia4010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoleimani, Reza, Jeffrey Barahona, Yuhan Chen, Alper Bozkurt, Michael Daniele, Vladimir Pozdin, and Edgar Lobaton. 2024. "Advances in Modeling and Interpretability of Deep Neural Sleep Staging: A Systematic Review" Physiologia 4, no. 1: 1-42. https://doi.org/10.3390/physiologia4010001
APA StyleSoleimani, R., Barahona, J., Chen, Y., Bozkurt, A., Daniele, M., Pozdin, V., & Lobaton, E. (2024). Advances in Modeling and Interpretability of Deep Neural Sleep Staging: A Systematic Review. Physiologia, 4(1), 1-42. https://doi.org/10.3390/physiologia4010001













