Exploring the Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Nannochloropsis sp. Extract
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cultivation of the Microroalgal Species
2.2. Preparation of the NG15 Extract
2.3. Analysis of Carotenoids and Fatty Acid Methyl Esters
2.4. Determination of Total Phenolic and Total Flavonoid Content
2.5. Cell Culture and Viability Assay
2.6. NO Production Assay
2.7. Inhibition of iNOS, COX-2, TNF-α, and IL-6 Expression
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Biochemical Composition of the Methanol Extract of NG15
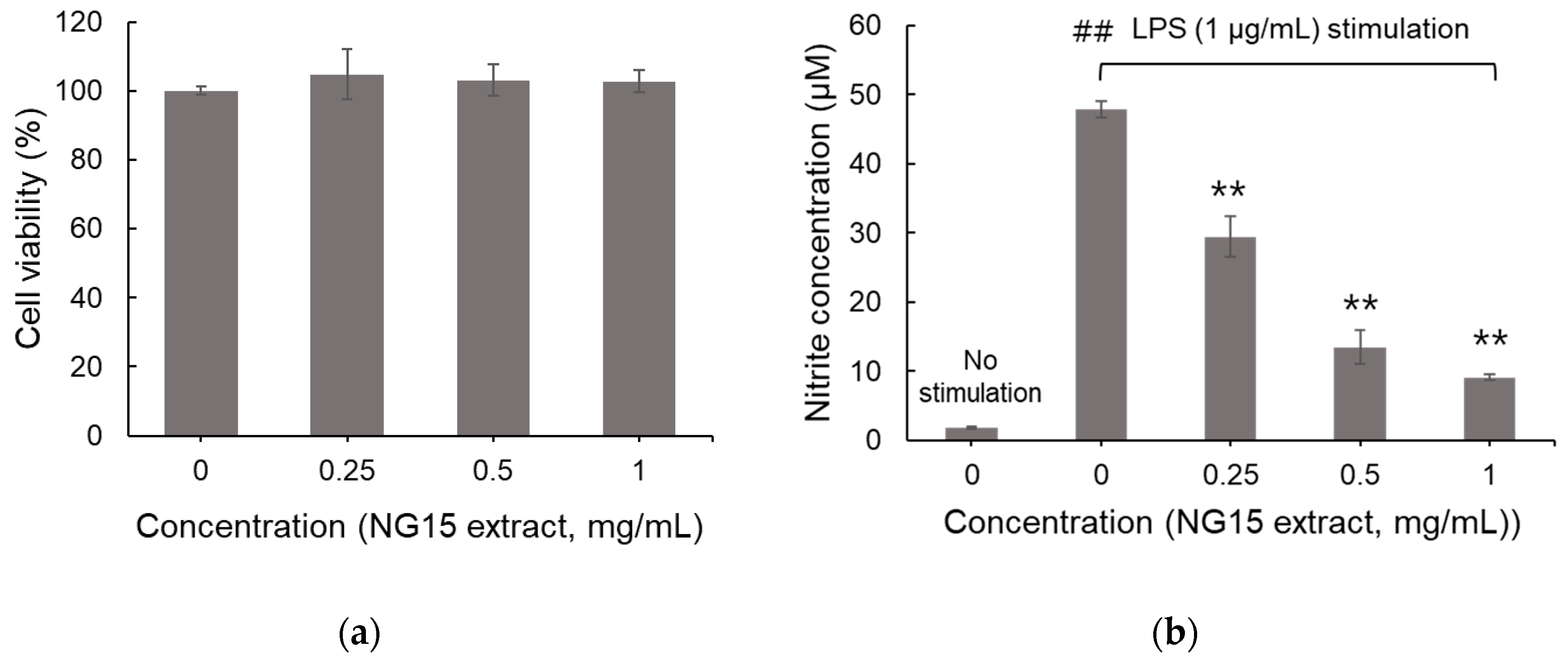
3.2. Effects of NG15 Extract on Cell Viability and LPS-Induced NO Production in RAW 264.7 Cells
3.3. Effects of NG15 Extract on mRNA Expression of iNOS, COX-2, TNF-α, and IL-6
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leiba, J.; Özbilgiç, R.; Hernández, L.; Demou, M.; Lutfalla, G.; Yatime, L.; Nguyen-Chi, M. Molecular Actors of Inflammation and Their Signaling Pathways: Mechanistic Insights from Zebrafish. Biology 2023, 12, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megha, K.B.; Joseph, X.; Akhil, V.; Mohanan, P.V. Cascade of Immune Mechanism and Consequences of Inflammatory Disorders. Phytomedicine 2021, 91, 153712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderton, H.; Wicks, I.P.; Silke, J. Cell death in chronic inflammation: Breaking the cycle to treat rheumatic disease. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2020, 16, 496–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Saeed, A.F.U.H.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, Q.; Xu, H.; Xiao, G.G.; Rao, L.; Duo, Y. Macrophages in immunoregulation and therapeutics. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.E.; Lee, J.S. Advances in the Regulation of Inflammatory Mediators in Nitric Oxide Synthase: Implications for Disease Modulation and Therapeutic Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Hernández, T.; Rustioni, A. Expression of three forms of nitric oxide synthase in peripheral nerve regeneration. J. Neurosci. Res. 1999, 55, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radi, R. Peroxynitrite, a stealthy biological oxidant. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 26464–26472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, A.; Naka, T.; Nakahama, T.; Chinen, I.; Masuda, K.; Nohara, K.; Fujii-Kuriyama, Y.; Kishimoto, T. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor in combination with Stat1 regulates LPS-induced inflammatory responses. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 2027–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulesza, A.; Paczek, L.; Burdzinska, A. The Role of COX-2 and PGE2 in the Regulation of Immunomodulation and Other Functions of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganster, R.T.; Bradley, S.; Shao, L.; Geller, D. Complex regulation of human inducible nitric oxide synthase gene transcription by Stat 1 and NF-κB. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 8638–8643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-W.; Shin, J.-S.; Chung, K.-S.; Lee, Y.-G.; Baek, N.-I.; Lee, K.-T. Anti-Inflammatory Mechanisms of Koreanaside A, a Lignan Isolated from the Flower of Forsythia koreana, against LPS-Induced Macrophage Activation and DSS-Induced Colitis Mice: The Crucial Role of AP-1, NF-κB, and JAK/STAT Signaling. Cells 2019, 8, 1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacchi, S.; Palumbo, P.; Sponta, A.; Coppolino, M.F. Clinical pharmacology of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: A review. Antiinflamm Antiallergy Agents Med. Chem. 2012, 11, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harirforoosh, S.; Asghar, W.; Jamali, F. Adverse effects of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs: An update of gastrointestinal, cardiovascular and renal complications. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 16, 821–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihaylova, R.; Elincheva, V.; Gevrenova, R.; Zheleva-Dimitrova, D.; Momekov, G.; Simeonova, R. Targeting Inflammation with Natural Products: A Mechanistic Review of Iridoids from Bulgarian Medicinal Plants. Molecules 2025, 30, 3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.L.; Kim, C.K.; Kim, T.J.; Sun, J.; Rim, D.; Kim, Y.J.; Ko, S.B.; Jang, H.; Yoon, B.W. Anti-inflammatory effects of fimasartan via akt, erk, and nfkappab pathways on astrocytes stimulated by hemolysate. Inflamm. Res. 2016, 65, 115–123. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos-Romero, S.; Torrella, J.R.; Pagès, T.; Viscor, G.; Torres, J.L. Edible microalgae and their bioactive compounds in the prevention and treatment of metabolic alterations. Nutrients 2021, 13, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Kwon, Y.M.; Kim, K.W.; Kim, J.Y.H. Exploring the Potential of Nannochloropsis sp. Extract for Cosmeceutical Applications. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forján, E.; Garbayo, I.; Henriques, M.; Rocha, J.; Vega, J.; Vílchez, C. UV-A mediated modulation of photosynthetic efficiency, xanthophyll cycle and fatty acid production of Nannochloropsis. Mar. Biotechnol. 2011, 13, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.-N.; Chen, T.-P.; Yang, B.; Liu, J.; Chen, F. Lipid Production from Nannochloropsis. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.L.; Huang, Z.; Mashimo, H.; Bloch, K.D.; Moskowitz, M.A.; Bevan, J.A.; Fishman, M.C. Hypertension in mice lacking the gene for endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Nature 1995, 377, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, N.; García-Blanco, A.; Gavalás-Olea, A.; Loures, P.; Garrido, J.L. Phytoplankton pigment biomarkers: HPLC separation using a pentafluorophenyloctadecyl silica column. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2015, 6, 1199–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egeland, E.S.; Garrido, J.L.; Clementson, L.; Andersen, K.; Thomas, C.T.; Zapata, M.; Airs, R.; Llewellyn, C.; Newman, G.L.; Rodríguez, F.; et al. Data sheets aiding identification of phytoplankton carotenoids and chlorophylls. In Phytoplankton Pigments: Characterization, Chemotaxonomy and Applications in Oceanography; Roy, S., Llewellyn, C., Egeland, E.S., Johnsen, G., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011; pp. 665–822. [Google Scholar]
- Faé Neto, W.A.; Borges Mendes, C.R.; Abreu, P.C. Carotenoid production by the marine microalgae Nannochloropsis oculata in different low-cost culture media. Aquac. Res. 2018, 49, 2527–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Fan, J.; Zhang, X. Phenolic compounds and bioactivity evaluation of aqueous and methanol extracts of Allium mongolicum Regel. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forján Lozano, E.; Garbayo Nores, I.; Casal Bejarano, C.; Vílchez Lobato, C. Enhancement of carotenoid production in Nannochloropsis by phosphate and sulphur limitation. In Communicating Current Research and Educational Topics and Trends in Applied Microbiology; Formatex: Badajoz, Spain, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zanella, L.; Vianello, F. Microalgae of the genus Nannochloropsis: Chemical composition and functional implications for human nutrition. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 68, 103919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubián, L.M.; Montero, O.; Moreno-Garrido, I.; Huertas, I.E.; Sobrino, C.; Valle, M.G.-D.; Parés, G. Nannochloropsis (Eustigmatophyceae) as source of commercially valuable pigments. J. Appl. Phycol. 2000, 12, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Moon, H.; Kwon, Y.M.; Kim, K.W.; Kim, J.Y.H. Comparative Analysis of the Biochemical and Molecular Responses of Nannochloropsis gaditana to Nitrogen and Phosphorus Limitation: Phosphorus Limitation Enhances Carotenogenesis. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Chen, R.; Chen, J.; Yang, N.; Li, K.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, R. Study of the Anti-Inflammatory Mechanism of β-Carotene Based on Network Pharmacology. Molecules 2023, 28, 7540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haoujar, I.; Cacciola, F.; Abrini, J.; Mangraviti, D.; Giuffrida, D.; Oulad El Majdoub, Y.; Kounnoun, A.; Miceli, N.; Fernanda Taviano, M.; Mondello, L.; et al. The Contribution of Carotenoids, Phenolic Compounds, and Flavonoids to the Antioxidative Properties of Marine Microalgae Isolated from Mediterranean Morocco. Molecules 2019, 24, 4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, M.C.; Pinto, D.C.G.A.; Silva, A.M.S. Plant Flavonoids: Chemical Characteristics and Biological Activity. Molecules 2021, 26, 5377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.-M.; Zhang, J.-P.; Skibsted, L.H. Reaction Dynamics of Flavonoids and Carotenoids as Antioxidants. Molecules 2012, 17, 2140–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aktan, F. iNOS-mediated nitric oxide production and its regulation. Life Sci. 2004, 75, 639–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Vliet, A.; Eiserich, J.P.; Cross, C.E. Nitric oxide: A pro-inflammatory mediator in lung disease? Respir. Res. 2000, 1, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calniquer, G.; Khanin, M.; Ovadia, H.; Linnewiel-Hermoni, K.; Stepensky, D.; Trachtenberg, A.; Sedlov, T.; Braverman, O.; Levy, J.; Sharoni, Y. Combined Effects of Carotenoids and Polyphenols in Balancing the Response of Skin Cells to UV Irradiation. Molecules 2021, 26, 1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadad, N.; Levy, R. The synergistic anti-inflammatory effects of lycopene, lutein, β-carotene, and carnosic acid combinations via redox-based inhibition of NF-κB signaling. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 53, 1381–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwivedi, A.K.; Gurjar, V.; Kumar, S.; Singh, N. Molecular basis for nonspecificity of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Drug Discov. Today 2015, 20, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Gene | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
| iNOS | 5′-CCCTTCCGAAGTTTCTGGCAGCAGC-3′ | 5′-GGCTGTCAGAGCCTCGTGGCTTTGG-3′ |
| COX-2 | 5′-ACTCACTCAGTTTGTTGAGTCATTC-3′ | 5′-TTTGATTAGTACTGTAGGGTTAATG-3′ |
| IL-6 | 5′-CAAGAAAGACAAAGCCAGAGTCCTT-3′ | 5′-TGGATGGTCTTGGTCCTTAGCC-3′ |
| TNF-α | 5′-ACAAGCCTGTAGCCCACG-3′ | 5′-TCCAAAGTAGACCTGCCC-3′ |
| β-actin | 5′-AGTGTGACGTTGACATCCGTAAAGA-3′ | 5′-GGACAGTGAGGCCAGGATGG-3′ |
| FAME Component | Content (mg/g Extract) |
|---|---|
| Myristic acid (C14:0) | 7.53 ± 0.37 |
| Myristoleic acid(C14:1) | 0.48 ± 0.01 |
| Palmitic acid (C16:0) | 72.36 ± 4.73 |
| Palmitoleic acid (C16:1 ω7) | 56.42 ± 2.06 |
| Stearic acid (C18:0) | 2.62 ± 0.16 |
| Oleic acid (C18:1 ω9) | 24.54 ± 1.04 |
| Linoleic acid (C18:2 ω6) | 1.48 ± 0.07 |
| γ-Linolenic acid (C18:3 ω6) | 0.67 ± 0.00 |
| Arachidonic acid (C20:4 ω6) | 5.03 ± 0.38 |
| Eicosapentaenoic acid (C20:5 ω3) | 8.52 ± 0.82 |
| Sum | 179.65 ± 9.64 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Moon, H.; Kim, J.Y.H. Exploring the Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Nannochloropsis sp. Extract. Phycology 2026, 6, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology6010003
Moon H, Kim JYH. Exploring the Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Nannochloropsis sp. Extract. Phycology. 2026; 6(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology6010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoon, Hanbi, and Jaoon Young Hwan Kim. 2026. "Exploring the Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Nannochloropsis sp. Extract" Phycology 6, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology6010003
APA StyleMoon, H., & Kim, J. Y. H. (2026). Exploring the Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Nannochloropsis sp. Extract. Phycology, 6(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology6010003






