Diatom-Based Photobiological Treatment of Reverse Osmosis Concentrate: Optimization of Light and Temperature and Biomass Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. ROC Samples
2.2. Diatom
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.4. Photobiological Treatment
2.5. Biomass Characterization and Quantification
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
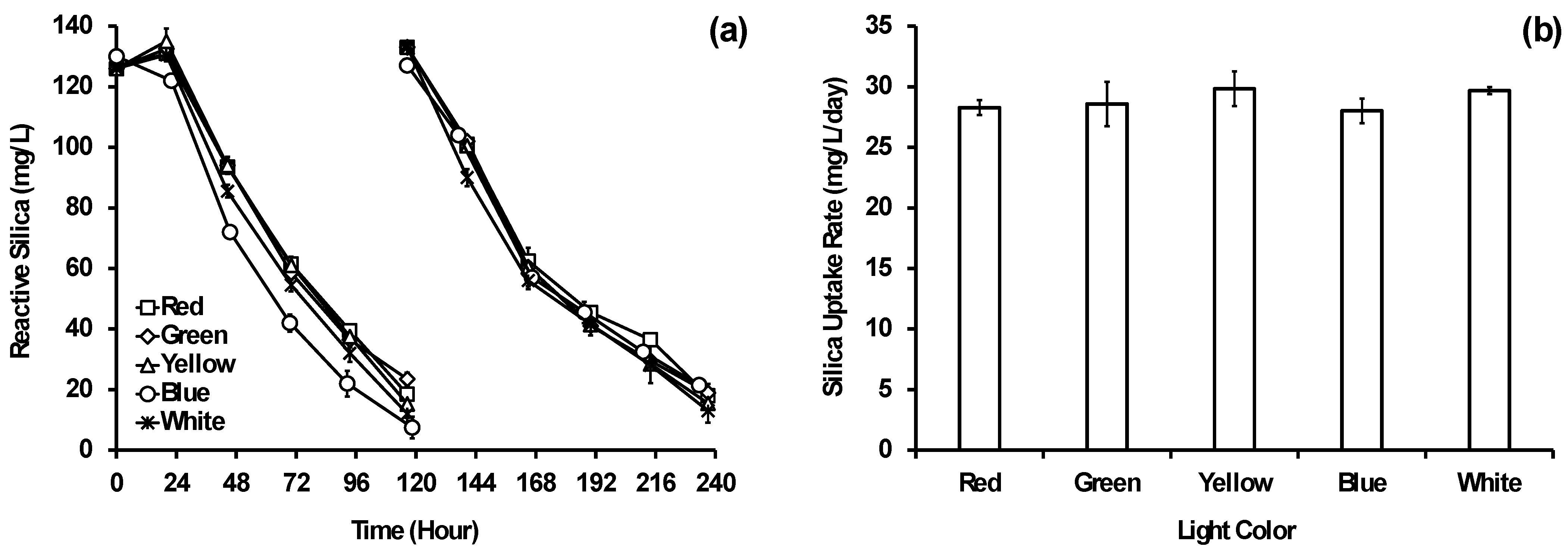
3.1. Impact of Light Temperature on Reactive Silica Removal
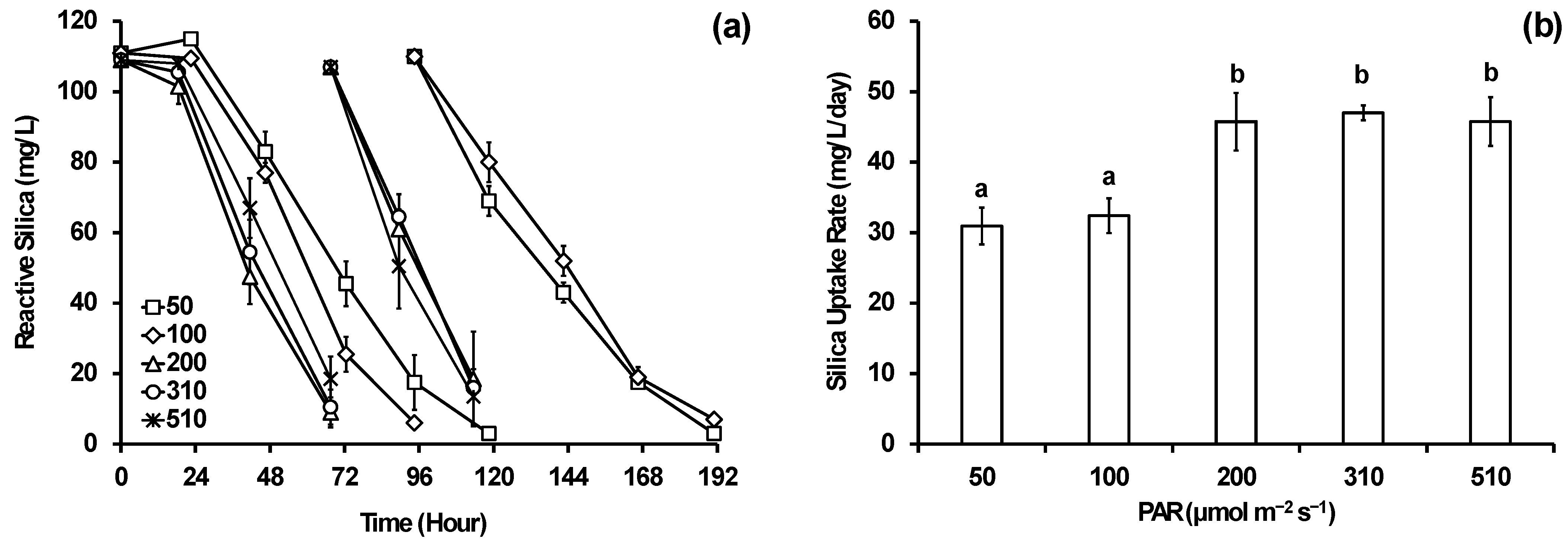
3.2. Impact of Light Color and Intensity on Reactive Silica Removal
3.3. Impact of Temperature on Reactive Silica Removal
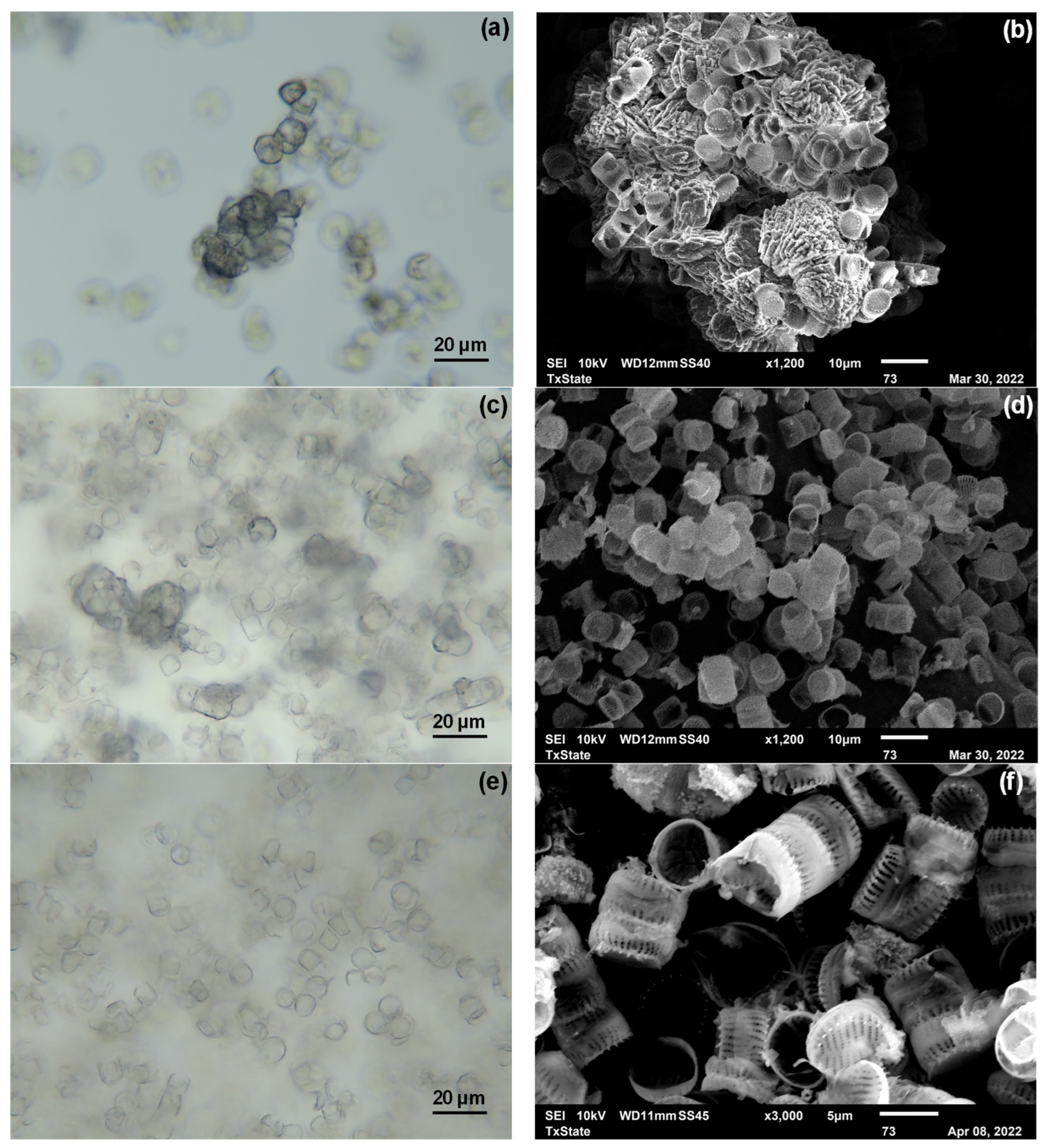
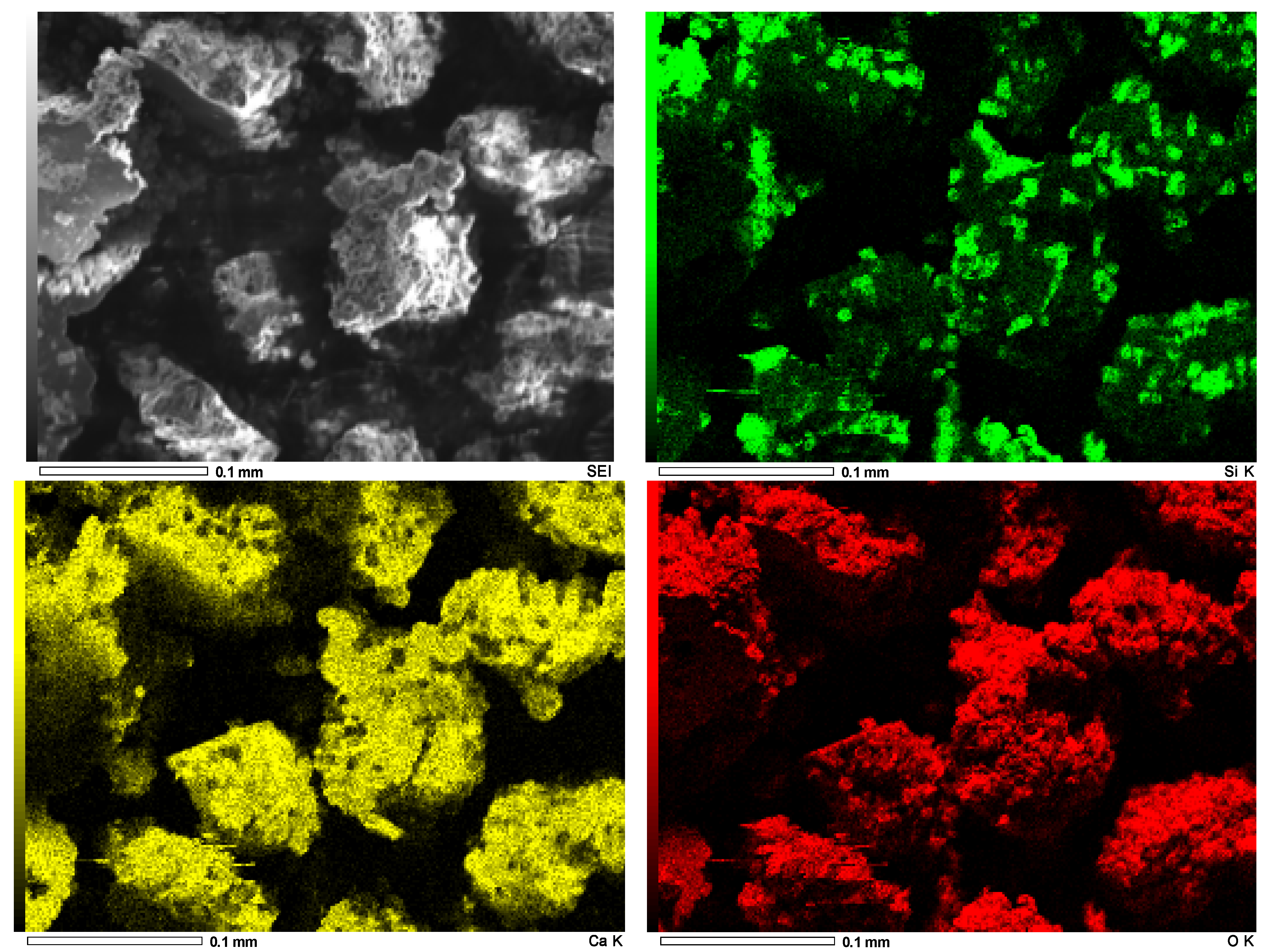
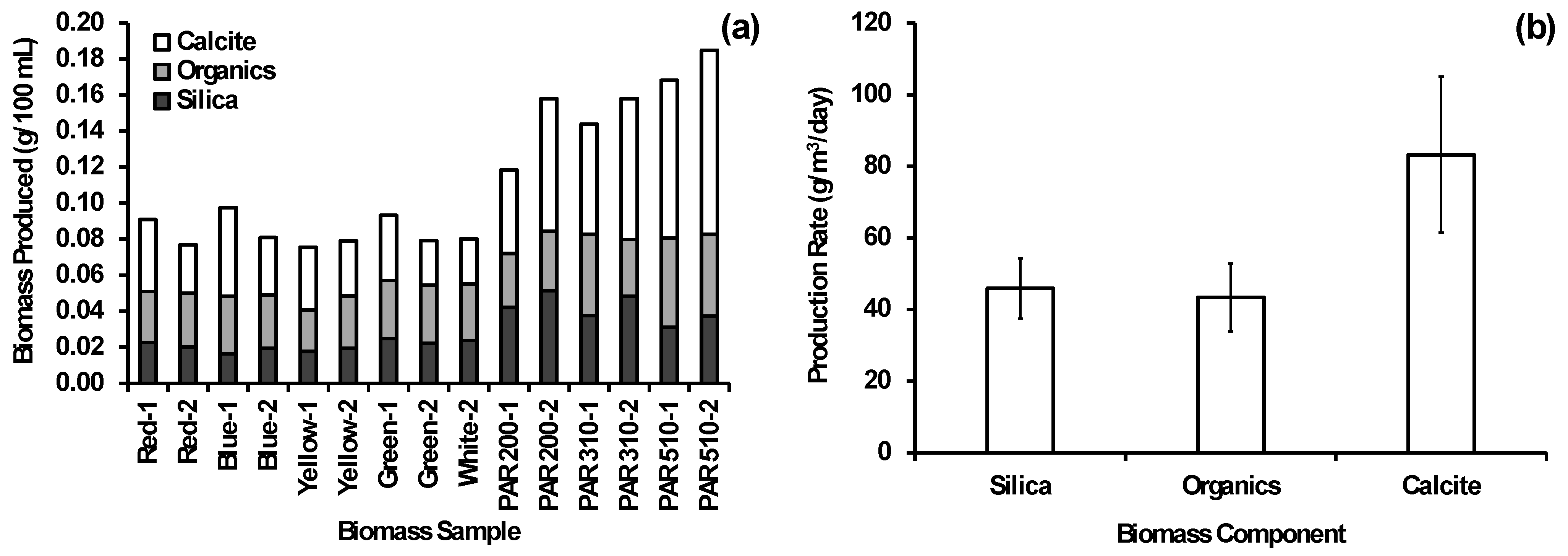
3.4. Biomass Characterization and Quantification
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shemer, H.; Wald, S.; Semiat, R. Challenges and Solutions for Global Water Scarcity. Membranes 2023, 13, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerrity, D.; Pecson, B.; Trussell, R.S.; Trussell, R.R. Potable reuse treatment trains throughout the world. J. Water Supply Res. Technol. Aqua 2013, 62, 321–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremere, I.; Kennedy, M.; Stikker, A.; Schippers, J.C. How water scarcity will effect the growth in the desalination market in the coming 25 years. Desalination 2001, 138, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzanakakis, V.A.; Paranychianakis, N.V.; Angelakis, A.N. Water Supply and Water Scarcity. Water 2020, 12, 2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USGS. Brackish Groundwater in the United States, Professional Paper 1833; U.S. Geological Survey, U.S. Department of Interior: Reston, VA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Texas Water Development Board. The Future of Desalination in Texas—2022 Biennial Report on Seawater and Brackish Groundwater Desalination in Texas. In Proceedings of the 88th Texas Legislative Session, Austin, TX, USA, 1 December 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Shirazi, S.H.; Hernandez, A.J.; Morrison, K. Commissioning a high-recovery brackish groundwater desalination plant in San Antonio. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 2019, 111, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Cath, T.Y.; Robertson, A.P.; Reinhard, M.; Leckie, J.O.; Drewes, J.E. Critical Review of Desalination Concentrate Management, Treatment and Beneficial Use. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2013, 30, 502–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsen, M.S.; Al-Jayyousi, O.R. Brackish water desalination: An alternative for water supply enhancement in Jordan. Desalination 1999, 124, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matin, A.; Rahman, F.; Shafi, H.Z.; Zubair, S.M. Scaling of reverse osmosis membranes used in water desalination: Phenomena, impact, and control; future directions. Desalination 2019, 455, 135–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Garcia, A.; Melian-Martel, N.; Mena, V. Fouling characterization of RO membranes after 11 years of operation in a brackish water desalination plant. Desalination 2018, 430, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramani, A.; DeCarolis, J.; Pearce, W.; Jacangelo, J.G. Vibratory shear enhanced process (VSEP) for treating brackish water reverse osmosis concentrate with high silica content. Desalination 2012, 291, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisitsin, D.; Hasson, D.; Semiat, R. Critical flux detection in a silica scaling RO system. Desalination 2005, 186, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semiat, R.; Sutzkover, I.; Hasson, D. Technique for evaluating silica scaling and its inhibition in RO desalting. Desalination 2001, 140, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, T.Z.; Wallace, A.F.; Zhao, S.; Wang, Z. Mineral scaling in membrane desalination: Mechanisms, mitigation strategies, and feasibility of scaling-resistant membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 579, 52–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-González, A.; Urtiaga, A.M.; Ibáñez, R.; Ortiz, I. State of the art and review on the treatment technologies of water reverse osmosis concentrates. Water Res. 2012, 46, 267–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pramanik, B.K.; Shu, L.; Jegatheesan, V. A review of the management and treatment of brine solutions. Environ. Sci.-Wat. Res. Technol. 2017, 3, 625–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikehata, K.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, J.; Komor, A.T.; Maleky, N.; Anderson, M.A. A novel photobiological process for reverse osmosis concentrate treatment using brackish water diatoms. Water Sci. Technol. Water Suppl. 2018, 18, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, H.V.; Zhao, Y.; Ikehata, K. Factors influencing photobiological treatment process to remove reactive silica from brackish groundwater reverse osmosis concentrate. Desalination 2019, 452, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikehata, K.; Zhao, Y.; Kulkarni, H.V.; Li, Y.; Snyder, S.A.; Ishida, K.P.; Anderson, M.A. Water recovery from advanced water purification facility reverse osmosis concentrate by photobiological treatment followed by secondary reverse osmosis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 8588–8595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Sato, S.; Kodamatani, H.; Fujioka, T.; Ishida, K.P.; Ikehata, K. Optimization of Dissolved Silica Removal from Reverse Osmosis Concentrate by Gedaniella flavovirens for Enhanced Water Recovery. Sustainability 2024, 16, 4052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikehata, K.; Nakamura, N.; Kulkarni, H.V.; Zhao, Y.; Maleky, N.; Sato, S.; Gao, H. Isolation and evaluation of brackish diatoms for the photobiological treatment of reverse osmosis concentrate. J. Water Supply Res. Technol. Aqua 2022, 71, 1083–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, S.; Beakes, G.; Idei, M.; Nagumo, T.; Mann, D.G. Novel sex cells and evidence for sex peromones in diatoms. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.P.; Singh, P. Effect of temperature and light on the growth of algae species: A review. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2015, 50, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwoba, E.G.; Parleyhet, D.A.; Laird, D.W.; Alameh, K.; Moheimani, N.R. Light management technologies for increasing algal photobioreactor efficiency. Algal Res. 2019, 39, 101433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvenda, V.; Hamzah, Y.; Arfianti; Linda, T.M.; Umar, L. Influence of Artificial Light Color on Cellular Respiration of Green Algae Photosynthesis Activity. In Proceedings of the 8th National Physics Seminar, Jakarta, Indonesia, 29–30 June 2019; Volume 2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y. Effects of Temperature, Light Intensity and Quality, Carbon Dioxide, and Culture Medium Nutrients on Growth and Lipid Production of Ettlia oleoabundans; Worcester Polytechnic Institute: Worcester, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ras, M.; Steyer, J.P.; Bernard, O. Temperature effect on microalgae: A crucial factor for outdoor production. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio. 2013, 12, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathinathan, P.; Parab, H.M.; Yusoff, R.; Ibrahim, S.; Vello, V.; Ngoh, G.C. Photobioreactor design and parameters essential for algal cultivation using industrial wastewater: A review. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2023, 173, 113096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.K.W.; Dickie, P.M. Temperature Characteristics of Photosynthetic and Heterotrophic Activities—Seasonal-Variations in Temperate Microbial Plankton. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1987, 53, 2282–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrovic, S.M.; Hitchcock, J.N.; Davie, A.W.; Ryan, D.A. Growth responses of Cyclotella meneghiniana (Bacillariophyceae) to various temperatures. J. Prankton Res. 2010, 32, 1217–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Round, F.E.; Crawford, R.M.; Mann, D.G. The Diatoms—Biology & Morphology of the Genera; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1990; p. 747. [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Jézéquel, V.; Hildebrand, M.; Brzezinski, M.A. Silicon metabolism in diatoms: Implications for growth. J. Phycol. 2000, 36, 821–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marella, T.K.; Lopez-Pacheco, I.Y.; Parra-Saldivar, R.; Dixit, S.; Tiwari, A. Wealth from waste: Diatoms as tools for phycoremediation of wastewater and for obtaining value from the biomass. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 724, 137960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.K.; Seibert, M. Prospects for commercial production of diatoms. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2017, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammes, F.; Verstraete, W. Key roles of pH and calcium metabolism in microbial carbonate precipitation. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2002, 1, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhami, N.K.; Reddy, M.S.; Mukherjee, A. Application of calcifying bacteria for remediation of stones and cultural heritages. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borowitzka, M.A.; Larkum, A.W.D. Calcification in algae: Mechanisms and the role of metabolism. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2008, 6, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, D.M.; Wong, L.S.; Kong, S.Y. Bio-Cementation in Construction Materials: A Review. Materials 2021, 14, 2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riding, R. Microbial carbonates: The geological record of calcified bacterial–algal mats and biofilms. Sedimentology 2002, 47, 179–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukaya, N.; Choi, S.J.; Horikoshi, T.; Kataoka, S.; Endo, A.; Kumai, H.; Hasegawa, M.; Sato, K.; Choi, J.-C. Direct synthesis of tetraalkoxysilanes from silica and alcohols. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 2224–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimouni, V.; Ulmann, L.; Pasquet, V.; Mathieu, M.; Picot, L.; Bougaran, G.; Cadoret, J.P.; Morant-Manceau, A.; Schoefs, B. The potential of microalgae for the production of bioactive molecules of pharmaceutical interest. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2012, 13, 2733–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Water Quality Parameter | Value | Unit | Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calcium | 260 | mg/L | Titration with EDTA (Hach 8204) |
| Magnesium | 400 | mg/L | Titration with EDTA (Hach 8213) |
| Iron | 0.33 | mg/L | USEPA FerroVer® (Hach 8008) |
| Ammonia-N | 5 | mg/L | Salicylate Method (Hach 10031) |
| Chloride | 2370 | mg/L | Silver Nitrate Method (Hach 8207) |
| Sulfate | 4500 | mg/L | USEPA SulfaVer®4 (Hach 8051) |
| Bicarbonate | 605 | mg/L | Phenolphthalein and Total Alkalinity (Hach 8203) |
| Nitrate-N | <0.23 | mg/L | Dimethylphenol Method (Hach 10206) |
| Reactive silica | 133 | mg/L | Silicomolybdate Method (Hach 8185) |
| Orthophosphate | 1.3 | mg/L | USEPA PhosVer®3 (Hach 8048) |
| Total dissolved solids | 10,070 | mg/L | PocketPro Conductivity Tester |
| Conductivity | 15.03 | mS/cm | PocketPro Conductivity Tester |
| Alkalinity | 993 | mg/L as CaCO3 | Phenolphthalein and Total Alkalinity (Hach 8203) |
| Chemical oxygen demand | 39 | mg/L | USEPA Reactor Digestion (Hach 8000) |
| pH | 7.7 | - | PocketPro pH Tester |
| Apparent color at 455 nm | 7 | PtCo Unit | Platinum-Cobalt Standard (Hach 8025) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, H.; Roy, E.; Underwood, M.S.; Adams, H.; Kulkarni, H.V.; Datta, S.; Sato, S.; Ikehata, K. Diatom-Based Photobiological Treatment of Reverse Osmosis Concentrate: Optimization of Light and Temperature and Biomass Analysis. Phycology 2025, 5, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology5010003
Gao H, Roy E, Underwood MS, Adams H, Kulkarni HV, Datta S, Sato S, Ikehata K. Diatom-Based Photobiological Treatment of Reverse Osmosis Concentrate: Optimization of Light and Temperature and Biomass Analysis. Phycology. 2025; 5(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology5010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Han, Emon Roy, Mason S. Underwood, Hunter Adams, Harshad V. Kulkarni, Saugata Datta, Shinya Sato, and Keisuke Ikehata. 2025. "Diatom-Based Photobiological Treatment of Reverse Osmosis Concentrate: Optimization of Light and Temperature and Biomass Analysis" Phycology 5, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology5010003
APA StyleGao, H., Roy, E., Underwood, M. S., Adams, H., Kulkarni, H. V., Datta, S., Sato, S., & Ikehata, K. (2025). Diatom-Based Photobiological Treatment of Reverse Osmosis Concentrate: Optimization of Light and Temperature and Biomass Analysis. Phycology, 5(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology5010003








