Morphological and Molecular Characters Differentiate Common Morphotypes of Atlantic Holopelagic Sargassum
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
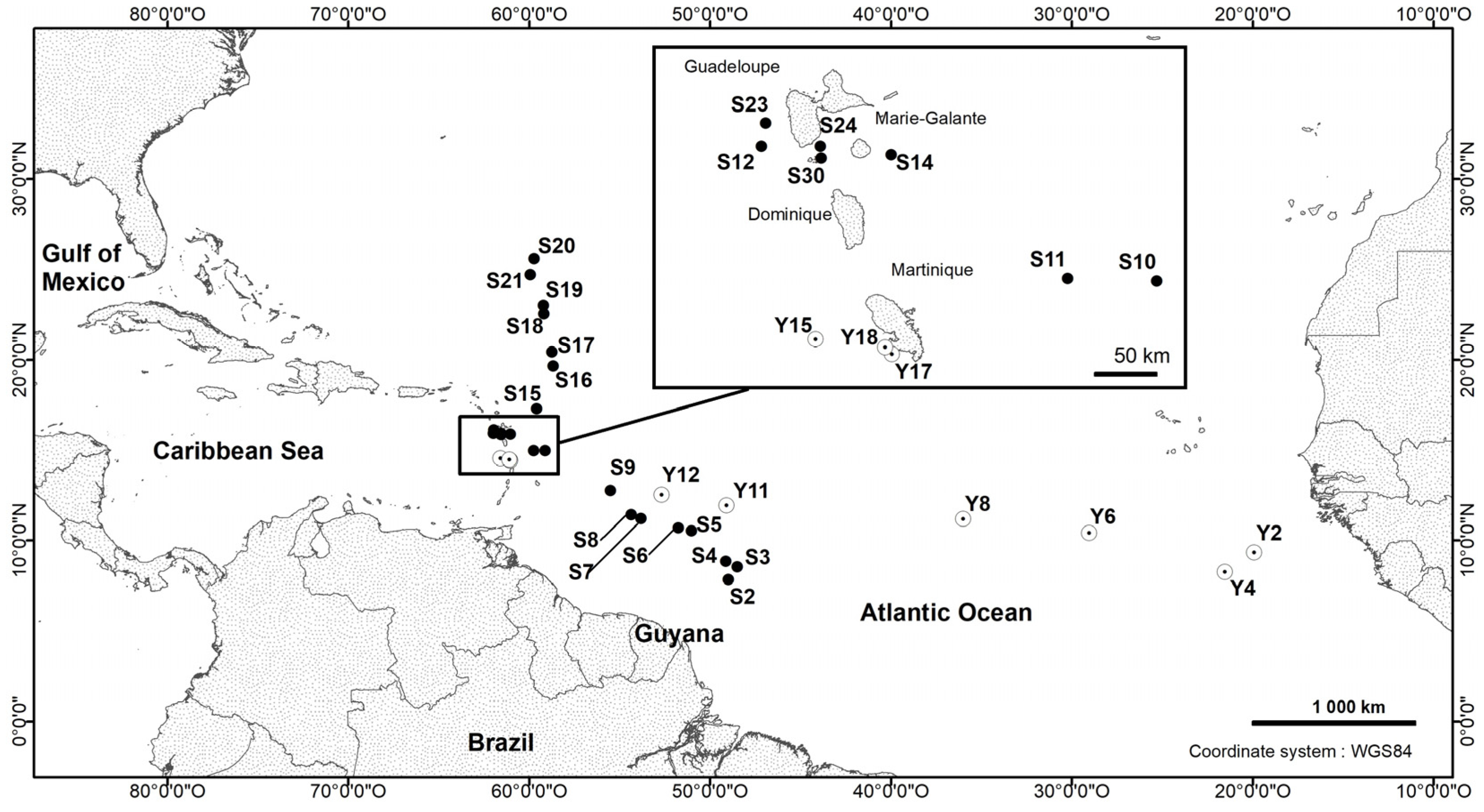
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Morphological Analyses
2.3. DNA Processing and Phylogenetic Analyses
2.3.1. Amplification and Sequencing of Mitochondrial and Plastid Loci
2.3.2. Analysis of Sequence Data
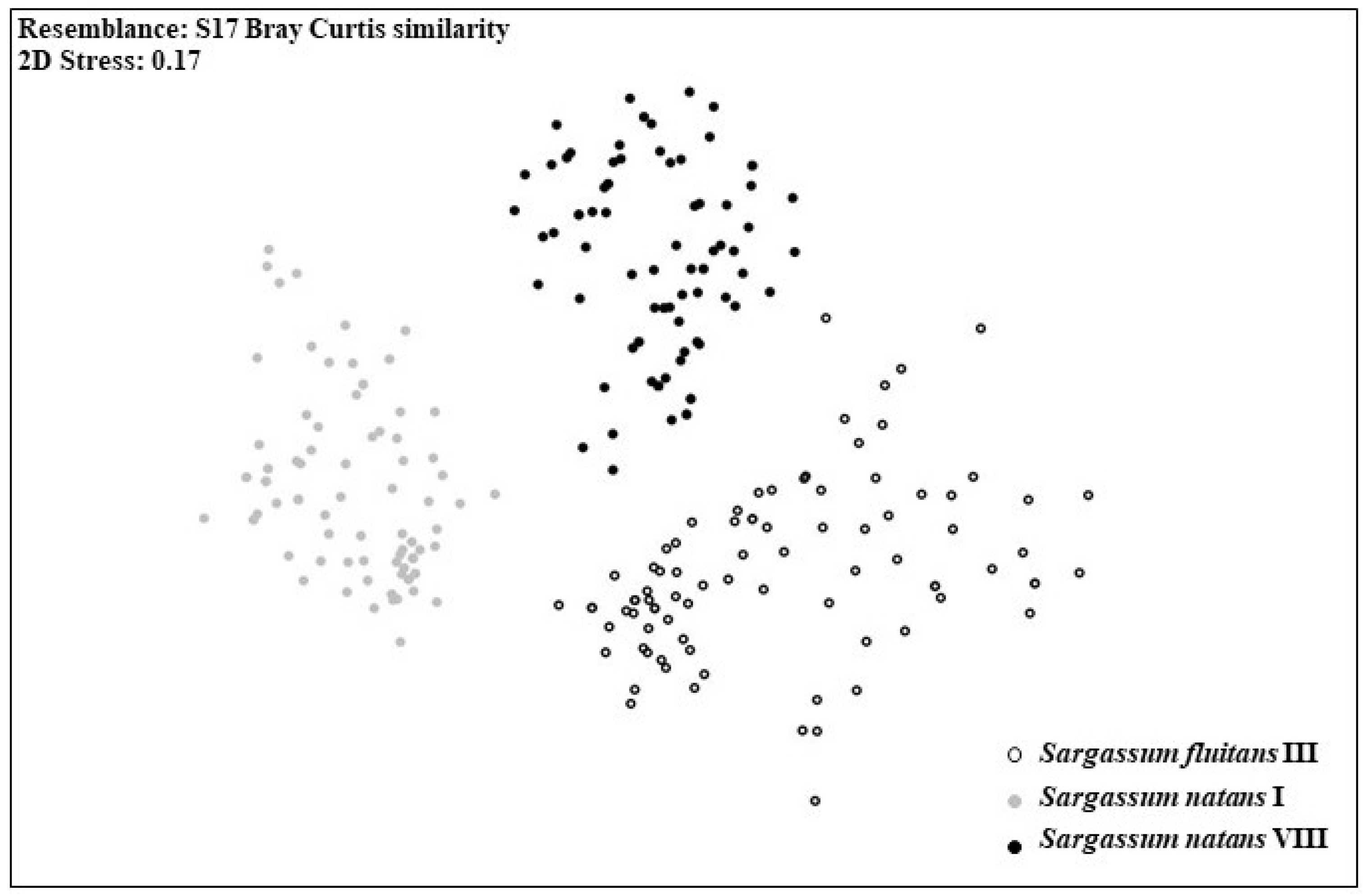
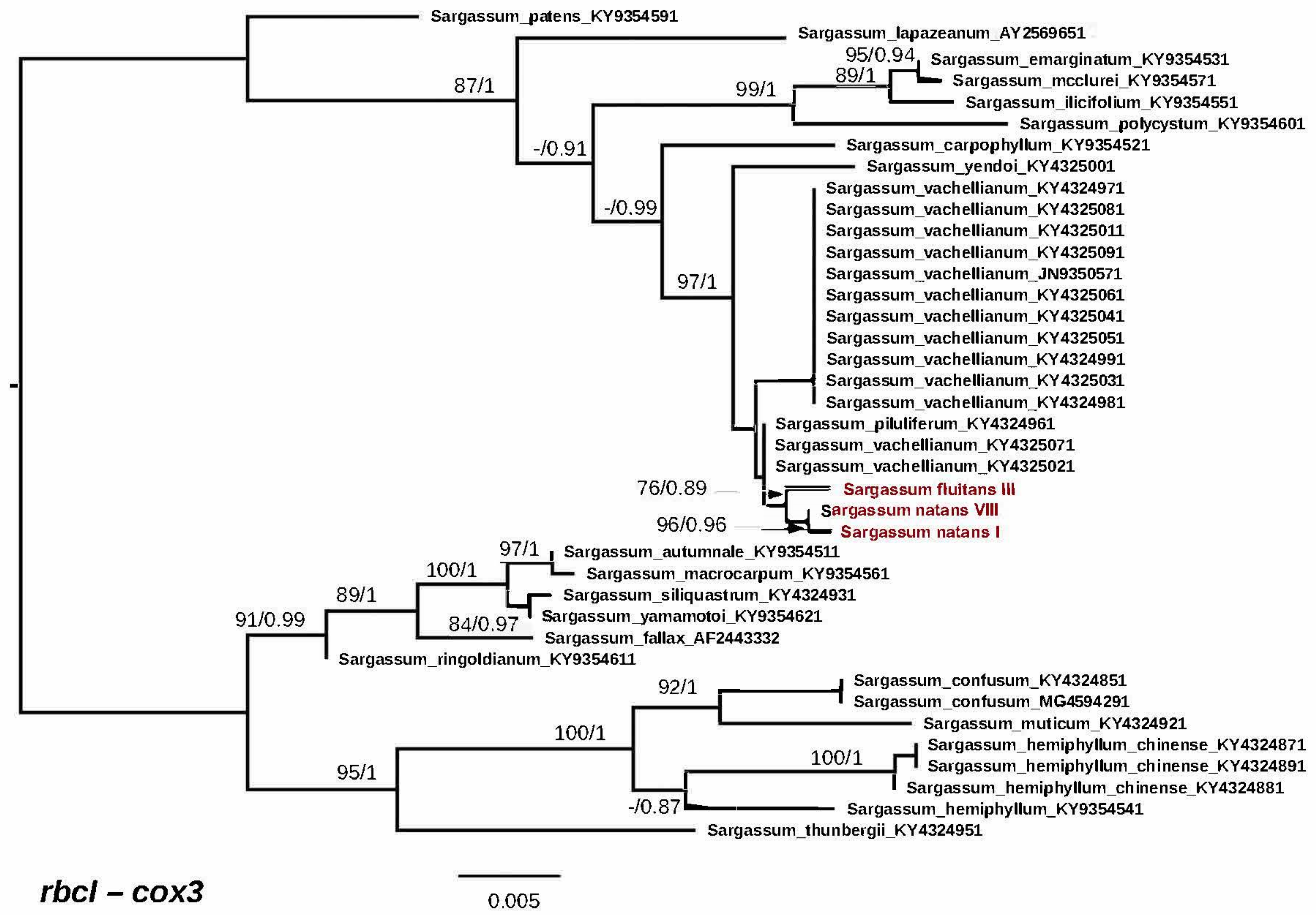
3. Results
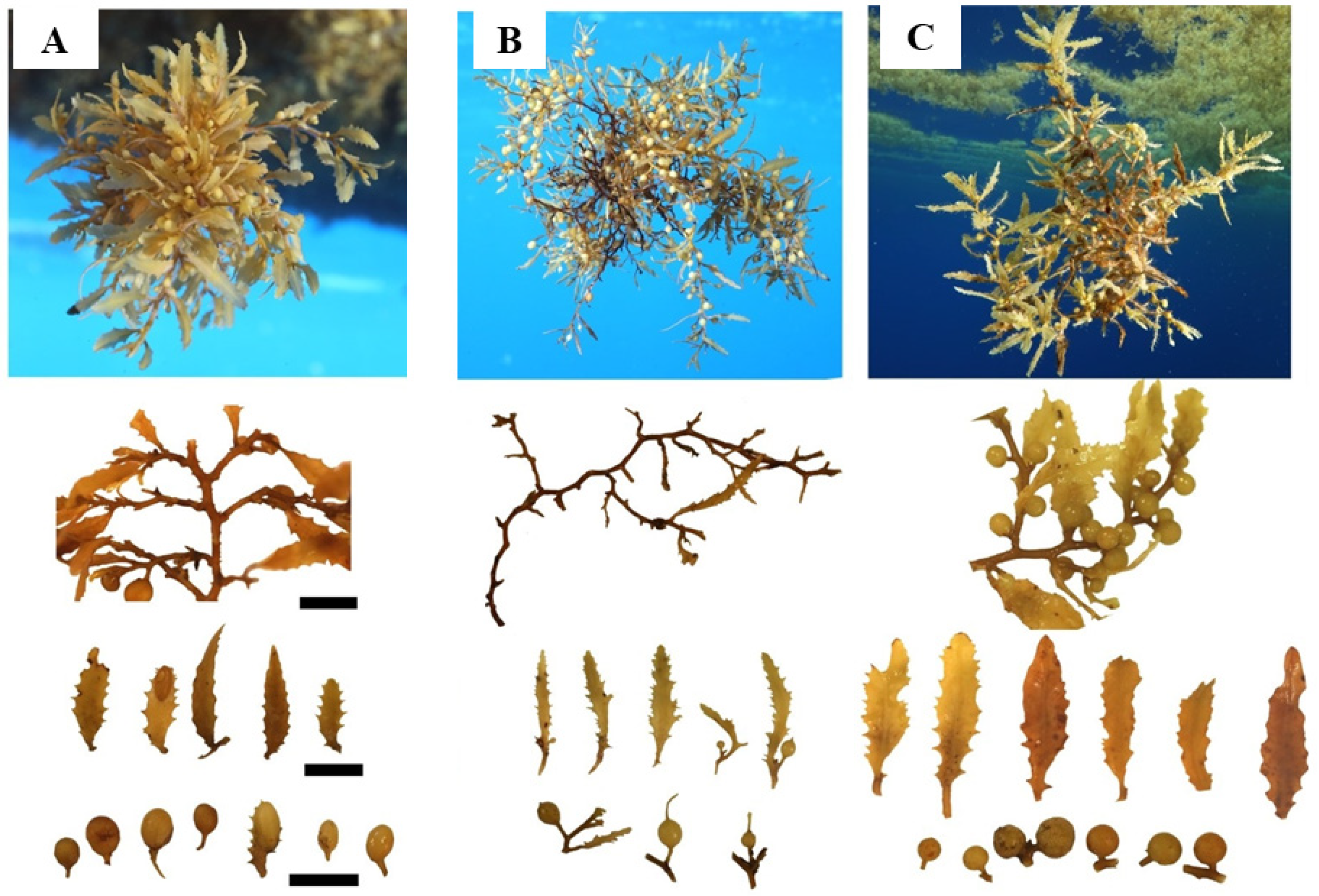
3.1. Morphological Analyses
3.2. Genetic Analyses
4. Discussion
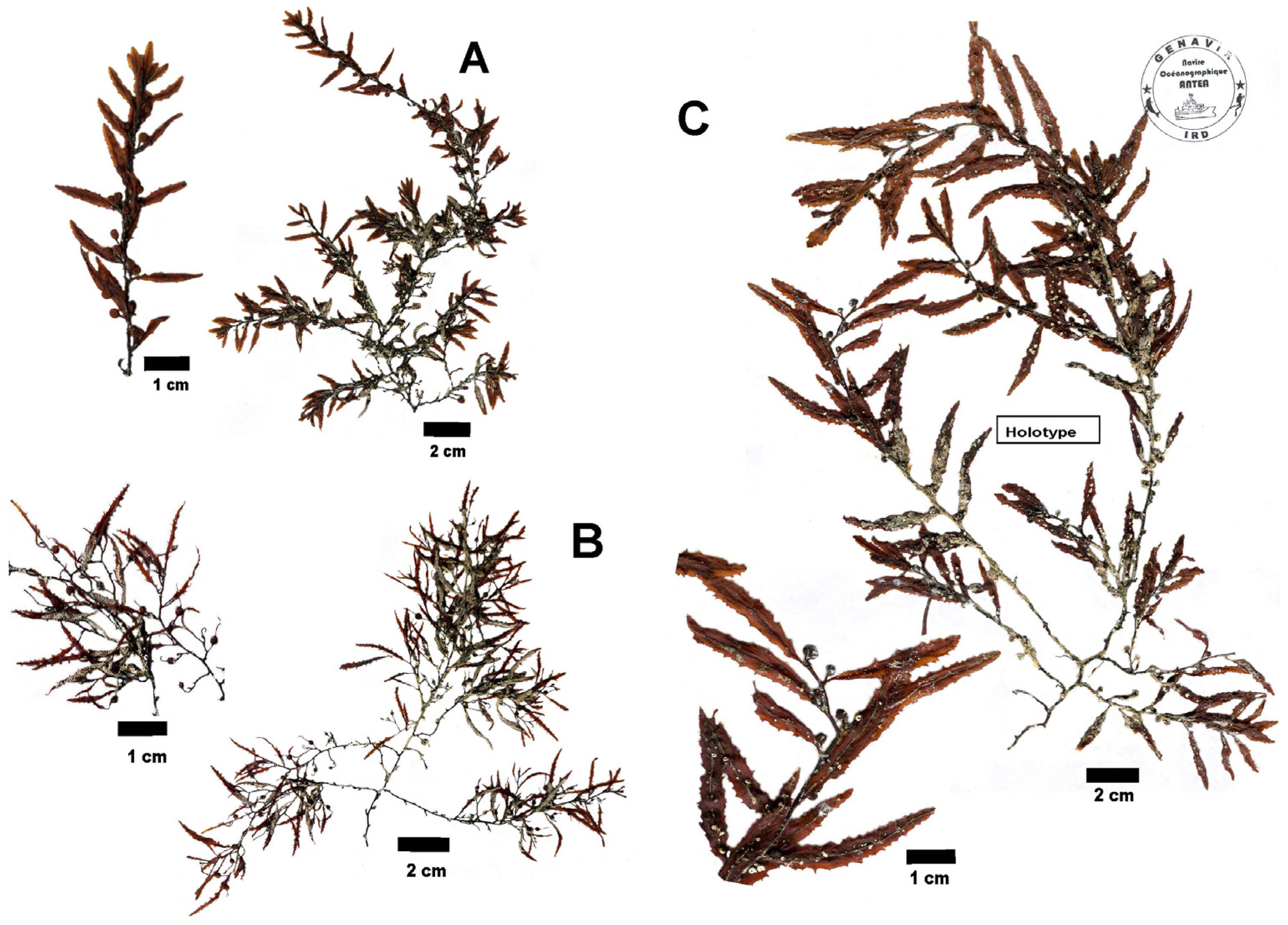
- Species description
- We propose the following new name for the morphotype Sargassum natans VIII.
- Sargassum natans var. wingei Thibaut, Blanfuné, Boudouresque, Siuda & Verlaque var. nov.
- Holotype: Specimen HCOM S10-S1-3 (Holotype deposited in HCOM Herbarium)
- Isotypes: Specimens S10-S1-1 and S10-S1-2, deposited in HCOM Herbarium.
- Type locality: Station 10, tropical Atlantic Ocean, geographic co-ordinates: 14°58.440′ N 59°07.230′ W.
- Etymology: Named for Professor Öjvind Winge, who was the first scientist to distinguish this taxon (as Sargassum sp. VIII) among the pelagic Sargassum specimens.
- Representative material: All samples of Sargassum natans var. wingei collected during the two expeditions (Caribbean and transatlantic expeditions). All samples are deposited in HCOM Herbarium (Table S2).
- Specimens sequenced and Genbank references: New haplotypes produced here are available in GenBank under accession numbers MT422788 to MT422805, and final sequence alignments have been submitted in Zenodo.
- Other descriptions and illustrations: Winge [20] (1923, Figure 13, as Sargassum sp. VIII); Parr [21] (1939, figs 9-10, 12-17, as S. natans (VIII) Winge); Schell et al. [33] (2015, Figure 1 in ref [33], as S. natans VIII Parr); Amaral-Zettler et al. [57] (2017, figs 2c and 2d, as S. natans form VIII); Martin (2016); Govindarajan et al. [109] (2019, Figure 1c, as S. natans VIII) (Table S1).
- Websites: as S. natans VIII: Sea Education Association, Woods Hole (https://www.sea.edu/sea_research/sargassum_ecosystem, accessed on 28 March 2024). Sailors for the Sea (https://sailorsforthesea.org/blog/conservation-heading-towards-bermuda/, accessed on 28 March 2024). Center for Resource Management and Environmental Studies (CERMES), University of West Indies Cave Hill, Barbados.
- (https://www.cavehill.uwi.edu/cermes/research-projects/sargassum/tools-and-guidance.aspx, accessed on 28 March 2024)
- Diagnosis: Plant holopelagic, brown to yellow-brown, without a holdfast or a distinct main axis; branches smooth without cryptostomata, 1–1.5 mm diam., ramified several times; blades simple, shortly pedicellate, flat, lanceolate to broadly lanceolate, without cryptostomata (13) 30–55 (–65) mm long and 3–10 mm wide (L/W ratio: 3–10, typically: 7–8), with coarsely irregularly serrated margins, symmetrical base, and midrib; vesicles (air bladders), more, less, or as much as the blades, smooth, without cryptostomata, spherical, rarely oblong, 2–5 (–7) mm diam., usually without foliaceous margin or apical spine-like appendage; pedicels short, 0.5–2.5 mm long, cylindrical, sometimes foliaceous with toothed margins; receptacles never observed.
- Distribution: Tropical Atlantic Ocean, between 7° and 26° N.
- Habitat: It is one of the three holopelagic taxa of the tropical Atlantic Ocean, with S. fluitans (Børgesen) Børgesen and S. natans (Linnaeus) Gaillon.
- Key for the identification of Atlantic Sargassum species
- 1a. Plants fixed to the substrate; main axis distinct; cryptostomata and receptacles present……………………………………………………….… Benthic species (not treated here)
- 1b. Plants floating, without holdfast and distinct main axis; receptacles absent and cryptostomata absent………………………………………………………..…... Pelagic species (2)
- 2a. Branches thorny; blades lanceolate, 3–8 mm wide and 11–60 mm long (L/W: 4–13), with asymmetrical base; vesicles oblong without apical spine-like or foliaceous appendage but frequently with foliaceous margin, usually more numerous than blades, 1–6 mm diam., with a short pedicel, 0.5–2.5 mm long, cylindrical to winged, sometimes with toothed margins ……………………S. fluitans (Børgesen) Børgesen
- 2b. Branches smooth; blades with symmetrical base; vesicles more spherical, fewer or as numerous as blades ……………………………..……………..………………… (3)
- 3a. Blades linear, narrow, 1–4 mm wide and 13–70 mm long (L/W: 5–22); vesicles, 2–5 mm diam., frequently with a foliaceous margin and an apical spine-like or reduced foliaceous appendage, and with a long pedicel, 1–5 mm long ……………………………………......…S. natans var. natans (Linnaeus) Gaillon
- 3b. Blades lanceolate, broad, 3–10 mm wide and 13–65 mm long (L/W: 3–10); vesicles, 2–7 mm diam., usually without foliaceous margin and apical spine-like appendages, and with a short pedicel, 0.5–2.5 mm long …………S. natans var. wingei nov. var.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, F.; Pang, S.; Chopin, T.; Gao, S.; Shan, T.; Zhao, X.; Li, J. Understanding the Recurrent Large-Scale Green Tide in the Yellow Sea: Temporal and Spatial Correlations between Multiple Geographical, Aquacultural and Biological Factors. Mar. Environ. Res. 2013, 83, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smetacek, V.; Zingone, A. Green and Golden Seaweed Tides on the Rise. Nature 2013, 504, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mineur, F.; Arenas, F.; Assis, J.; Davies, A.J.; Engelen, A.H.; Fernandes, F.; Malta, E.; Thibaut, T.; Van Nguyen, T.; Vaz-Pinto, F.; et al. European Seaweeds under Pressure: Consequences for Communities and Ecosystem Functioning. J. Sea Res. 2015, 98, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapointe, B.E.; Burkholder, J.M.; Van Alstyne, K.L. Harmful Macroalgal Blooms in a Changing World: Causes, Impacts, and Management. In Harmful Algal Blooms; Shumway, S.E., Burkholder, J.M., Morton, S.L., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 515–560. ISBN 978-1-118-99467-2. [Google Scholar]
- Dominguez Almela, V.; Addo, K.A.; Corbett, J.; Cumberbatch, J.; Dash, J.; Marsh, R.; Oxenford, H.; Tonon, T.; Van Der Plank, S.; Webber, M.; et al. Science and Policy Lessons Learned from a Decade of Adaptation to the Emergent Risk of Sargassum Proliferation across the Tropical Atlantic. Environ. Res. Commun. 2023, 5, 061002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Lann, K.; Connan, S.; Stiger-Pouvreau, V. Phenology, TPC and Size-Fractioning Phenolics Variability in Temperate Sargassaceae (Phaeophyceae, Fucales) from Western Brittany: Native versus Introduced Species. Mar. Environ. Res. 2012, 80, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelen, A.H.; Serebryakova, A.; Ang, P.; Britton-Simmons, K.; Mineur, F.; Pedersen, M.F.; Arenas, F.; Fernandez, C.; Steen, H.; Svenson, R.; et al. Circumglobal Invasion by the Brown Seaweed Sargassum Muticum. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Annu. Rev. 2015, 53, 81–126. [Google Scholar]
- Marks, L.; Salinas-Ruiz, P.; Reed, D.; Holbrook, S.; Culver, C.; Engle, J.; Kushner, D.; Caselle, J.; Freiwald, J.; Williams, J.; et al. Range Expansion of a Non-Native, Invasive Macroalga Sargassum horneri (Turner) C. Agardh, 1820 in the Eastern Pacific. BioInvasions Rec. 2015, 4, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchon, C.; Bouchon-Navaro, Y.; Louis, M. A First Record of a Sargassum (Phaeophyta, Algae) Outbreak in a Caribbean Coral Reef Ecosystem. Proc. Gulf Caribb. Fish. Inst. 1992, 41, 171–188. [Google Scholar]
- Done, T.J. Phase Shifts in Coral Reef Communities and Their Ecological Significance. Hydrobiologia 1992, 247, 131–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiger, V.; Payri, C.E. Spatial and Seasonal Variations in the Biological Characteristics of Two Invasive Brown Algae, Turbinaria ornata (Turner) J. Agardh and Sargassum mangarevense (Grunow) Setchell (Sargassaceae, Fucales) Spreading on the Reefs of Tahiti (French Polynesia). Bot. Mar. 1999, 42, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ramon N’Yeurt, A.; Iese, V. The Proliferating Brown Alga Sargassum polycystum in Tuvalu, South Pacific: Assessment of the Bloom and Applications to Local Agriculture and Sustainable Energy. J. Appl. Phycol. 2015, 27, 2037–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Tussenbroek, B.I.; Hernández Arana, H.A.; Rodríguez-Martínez, R.E.; Espinoza-Avalos, J.; Canizales-Flores, H.M.; González-Godoy, C.E.; Barba-Santos, M.G.; Vega-Zepeda, A.; Collado-Vides, L. Severe Impacts of Brown Tides Caused by Sargassum spp. on near-Shore Caribbean Seagrass Communities. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 122, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velázquez-Ochoa, R.; Enríquez, S. Environmental Degradation of the Mexican Caribbean Reef Lagoons. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 191, 114947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stiger-Pouvreau, V.; Mattio, L.; De Ramon N’Yeurt, A.; Uwai, S.; Dominguez, H.; Flórez-Fernández, N.; Connan, S.; Critchley, A.T. A Concise Review of the Highly Diverse Genus Sargassum C. Agardh with Wide Industrial Potential. J. Appl. Phycol. 2023, 35, 1453–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibaut, T.; Blanfuné, A.; Verlaque, M.; Boudouresque, C.-F.; Ruitton, S. The Sargassum Conundrum: Very Rare, Threatened or Locally Extinct in the NW Mediterranean and Still Lacking Protection. Hydrobiologia 2016, 781, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aouissi, M.; Sellam, L.N.; Boudouresque, C.F.; Blanfuné, A.; Derbal, F.; Frihi, H.; Perret-Boudouresque, M.; Rebzani-Zahaf, C.; Verlaque, M.; Thibaut, T. Insights into the Species Diversity of the Genus Sargassum (Phaeophyceae) in the Mediterranean Sea, with a Focus on a Pre-Viously Unnoticed Taxon from Algeria. Medit. Mar. Sci. 2018, 19, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Børgesen, F. The Species of Sargassum Found Along the Coasts of the Danish West Indies With Remarks Upon the Floating Forms of the Sargasso Sea. In Mindeskrift I Anledning af Hundredaaret for Japetus Steenstrups Fødsel; Jungersen, F.E., Warming, E., Eds.; Bianco Luno Bogtrykkeri: Kobenhavn, Denmark, 1914; Volume 32, pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Børgesen, F. Marine Algae of the Danish West Indies. Part II. Phaeophyceae.; Dansk Bot. Arkiv, Bianco Luno Copenhagen, Denmark, 1914; Volume 2.
- Winge, Ø. The Sargasso Sea, Its Boundaries and Vegetation. Report on the Danish Oceanographical Expeditions 1908–1910 to the Mediterranean and Adjacent Seas.; A.F. Høst&søn.: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1923. [Google Scholar]
- Parr, A.E. Quantitative Observations on the Pelagic Sargassum Vegetation of the Western North Atlantic. Bull. Bingham Oceanogr. Collect. 1939, 6, 1–94. [Google Scholar]
- Butler, J.N.; Morris, B.F.; Cadwallader, J.; Stoner, A.W. Studies of Sargassum and the Sargassum Community; Bermuda Biological Station for Research, Special Publication: Bermuda, UK, 1983; pp. 1–307. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, P.; Minzlaff, U.; Schoenle, A.; Schwabe, E.; Hohlfeld, M.; Jeuck, A.; Brenke, N.; Prausse, D.; Rothenbeck, M.; Brix, S.; et al. Potential Contribution of Surface-Dwelling Sargassum Algae to Deep-Sea Ecosystems in the Southern North Atlantic. Deep. Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2018, 148, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ody, A.; Thibaut, T.; Berline, L.; Changeux, T.; André, J.-M.; Chevalier, C.; Blanfuné, A.; Blanchot, J.; Ruitton, S.; Stiger-Pouvreau, V.; et al. From In Situ to Satellite Observations of Pelagic Sargassum Distribution and Aggregation in the Tropical North Atlantic Ocean. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coston-Clements, L.; Settle, L.R.; Hoss, D.E.; Cross, F.A. Utilization of the Sargassum Habitat by Marine Invertebrates and Vertebrates, a Review; US Department of Commerce, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, National Marine Fisheries Service, Southeast Fisheries Science Center, Beaufort Laboratory: St. Petersburg, FL, USA, 1991; Volume 296. [Google Scholar]
- Huffard, C.L.; Von Thun, S.; Sherman, A.D.; Sealey, K.; Smith, K.L. Pelagic Sargassum Community Change over a 40-Year Period: Temporal and Spatial Variability. Mar. Biol. 2014, 161, 2735–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alleyne, K.S.T.; Johnson, D.; Neat, F.; Oxenford, H.A.; Vallѐs, H. Seasonal Variation in Morphotype Composition of Pelagic Sargassum Influx Events Is Linked to Oceanic Origin. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theirlynck, T.; Mendonça, I.R.W.; Engelen, A.H.; Bolhuis, H.; Collado-Vides, L.; Van Tussenbroek, B.I.; García-Sánchez, M.; Zettler, E.; Muyzer, G.; Amaral-Zettler, L. Diversity of the Holopelagic Sargassum Microbiome from the Great Atlantic Sargassum Belt to Coastal Stranding Locations. Harmful Algae 2023, 122, 102369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marmorino, G.O.; Miller, W.D.; Smith, G.B.; Bowles, J.H. Airborne Imagery of a Disintegrating Sargassum Drift Line. Deep. Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2011, 58, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidai, Y.A.; Dash, J.; Tompkins, E.L.; Tonon, T. A Systematic Review of Floating and Beach Landing Records of Sargassum beyond the Sargasso Sea. Environ. Res. Commun. 2020, 2, 122001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Hu, C.; Barnes, B.B.; Mitchum, G.; Lapointe, B.; Montoya, J.P. The Great Atlantic Sargassum Belt. Science 2019, 365, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franks, J.S.; Johnson, D.R.; Ko, D.S. Pelagic Sargassum in the Tropical North Atlantic. GCR 2016, 27, SC6–SC11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schell, J.M.; Goodwin, D.S.; Siuda, A.N.S. Recent Sargassum Inundation Events in the Caribbean: Shipboard Observations Reveal Dominance of a Previously Rare Form. Oceanography 2015, 28, 8–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Hu, C. Predicting Sargassum Blooms in the Caribbean Sea from MODIS Observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 3265–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, R.; Addo, K.A.; Jayson-Quashigah, P.-N.; Oxenford, H.A.; Maxam, A.; Anderson, R.; Skliris, N.; Dash, J.; Tompkins, E.L. Seasonal Predictions of Holopelagic Sargassum Across the Tropical Atlantic Accounting for Uncertainty in Drivers and Processes: The SARTRAC Ensemble Forecast System. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 722524. [Google Scholar]
- Jouanno, J.; Moquet, J.-S.; Berline, L.; Radenac, M.-H.; Santini, W.; Changeux, T.; Thibaut, T.; Podlejski, W.; Ménard, F.; Martinez, J.-M.; et al. Evolution of the Riverine Nutrient Export to the Tropical Atlantic over the Last 15 Years: Is There a Link with Sargassum Proliferation? Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 034042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinanes, J.; Putman, N.F.; Goni, G.; Hu, C.; Wang, M. Monitoring Pelagic Sargassum Inundation Potential for Coastal Communities. J. Oper. Oceanogr. 2023, 16, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanisak, M.D.; Samuel, M.A. Growth Rates in Culture of Several Species of Sargassum from Florida, USA; Springer Netherlands: Sao Paulo, Brazil, 1987; pp. 399–404. [Google Scholar]
- Changeux, T.; Berline, L.; Podlejski, W.; Guillot, T.; Stiger-Pouvreau, V.; Connan, S.; Thibaut, T. Variability in Growth and Tissue Composition (CNP, Natural Isotopes) of the Three Morphotypes of Holopelagic Sargassum. Aquat. Bot. 2023, 187, 103644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbin, M.; Oxenford, H.A. Assessing Growth of Pelagic Sargassum in the Tropical Atlantic. Aquat. Bot. 2023, 187, 103654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magaña-Gallegos, E.; García-Sánchez, M.; Graham, C.; Olivos-Ortiz, A.; Siuda, A.N.S.; Van Tussenbroek, B.I. Growth Rates of Pelagic Sargassum Species in the Mexican Caribbean. Aquat. Bot. 2023, 185, 103614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magaña-Gallegos, E.; Villegas-Muñoz, E.; Salas-Acosta, E.R.; Barba-Santos, M.G.; Silva, R.; Van Tussenbroek, B.I. The Effect of Temperature on the Growth of Holopelagic Sargassum Species. Phycology 2023, 3, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schell, J.M.; Goodwin, D.S.; Volk, R.H.; Siuda, A.N.S. Preliminary Explorations of Environmental Tolerances and Growth Rates of Holopelagic Sargassum Morphotypes. Aquat. Bot. 2024, 190, 103723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miron, P.; Olascoaga, M.J.; Beron-Vera, F.J.; Putman, N.F.; Triñanes, J.; Lumpkin, R.; Goni, G.J. Clustering of Marine-Debris- and Sargassum -Like Drifters Explained by Inertial Particle Dynamics. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL089874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olascoaga, M.J.; Beron-Vera, F.J.; Beyea, R.T.; Bonner, G.; Castellucci, M.; Goni, G.J.; Guigand, C.; Putman, N.F. Physics-Informed Laboratory Estimation of Sargassum Windage. Phys. Fluids 2023, 35, 111702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Sánchez, M.; Graham, C.; Vera, E.; Escalante-Mancera, E.; Álvarez-Filip, L.; Van Tussenbroek, B.I. Temporal Changes in the Composition and Biomass of Beached Pelagic Sargassum Species in the Mexican Caribbean. Aquat. Bot. 2020, 167, 103275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pante, E.; Puillandre, N.; Viricel, A.; Arnaud-Haond, S.; Aurelle, D.; Castelin, M.; Chenuil, A.; Destombe, C.; Forcioli, D.; Valero, M.; et al. Species Are Hypotheses: Avoid Connectivity Assessments Based on Pillars of Sand. Mol. Ecol. 2015, 24, 525–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNeill, J.; Barrie, F.R.; Buck, W.R.; Demoulin, V.; Greuter, W.; Hawksworth, D.L.; Herendeen, P.S.; Knapp, S.; Marhold, K.; Prado, J.; et al. (Eds.) International Code of Nomenclature for Algae, Fungi, and Plants; Regnum Vegetabile; Koeltz Botanical Books: Glashütten, Germany, 2018; Volume 159, ISBN 978-3-946583-16-5. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, W.R. Marine Algae of the Eastern Tropical and Subtropical Coasts of the Americas; The University of Michigan Press: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Uwai, S.; Kogame, K.; Yoshida, G.; Kawai, H.; Ajisaka, T. Geographical Genetic Structure and Phylogeography of the Sargassum horneri/filicinum Complex in Japan, Based on the Mitochondrial Cox3 Haplotype. Mar. Biol. 2009, 156, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattio, L.; Payri, C.E. 190 Years of Sargassum Taxonomy, Facing the Advent of DNA Phylogenies. Bot. Rev. 2011, 77, 31–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draisma, S.G.A.; Ballesteros, E.; Rousseau, F.; Thibaut, T. Dna Sequence Data Demonstrate The Polyphyly of The Genus Cystoseira and Other Sargassaceae Genera (Phaeophyceae) 1. J. Phycol. 2010, 46, 1329–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, N.; Fredericq, S. Biogeographic and Phylogenetic Investigations of the Pantropical Genus Sargassum (Fucales, Phaetophyceae) with Respect to Gulf of Mexico Species. Gulf Mex. Sci. 2000, 18, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, O.; Mattio, L.; Draisma, S.; Fredericq, S.; Diaz-Pulido, G. Morphological and Molecular Assessment of Sargassum (Fucales, Phaeophyceae) from Caribbean Colombia, Including the Proposal of Sargassum Giganteum Sp. Nov., Sargassum Schnetteri Comb. Nov. and Sargassum Section Cladophyllum Sect. Nov. Syst. Biodivers. 2015, 13, 105–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sissini, M.N.; De Barros Barreto, M.B.B.; Széchy, M.T.M.; De Lucena, M.B.; Oliveira, M.C.; Gower, J.; Liu, G.; De Oliveira Bastos, E.; Milstein, D.; Gusmão, F.; et al. The Floating Sargassum (Phaeophyceae) of the South Atlantic Ocean—Likely Scenarios. Phycologia 2017, 56, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Nieto, D.; Oliveira, M.C.; Núñez Resendiz, M.L.; Dreckmann, K.M.; Mateo-Cid, L.E.; Sentíes, A. Molecular Assessment of the Genus Sargassum (Fucales, Phaeophyceae) from the Mexican Coasts of the Gulf of Mexico and Caribbean, with the Description of S. xochitlae Sp. Nov. Phytotaxa 2020, 461, 254–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral-Zettler, L.A.; Dragone, N.B.; Schell, J.; Slikas, B.; Murphy, L.G.; Morrall, C.E.; Zettler, E.R. Comparative Mitochondrial and Chloroplast Genomics of a Genetically Distinct Form of Sargassum Contributing to Recent “Golden Tides” in the Western Atlantic. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dibner, S.; Martin, L.; Thibaut, T.; Aurelle, D.; Blanfuné, A.; Whittaker, K.; Cooney, L.; Schell, J.M.; Goodwin, D.S.; Siuda, A.N.S. Consistent Genetic Divergence Observed among Pelagic Sargassum Morphotypes in the Western North Atlantic. Mar. Ecol. 2022, 43, e12691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiers, B. Index Herbariorum: A Global Directory of Public Herbaria and Associated Staff. New York Botanical Garden’s Virtual Herbarium. Available online: https://sweetgum.nybg.org/science/ih/ (accessed on 24 April 2024).
- Taylor, W.R. The Marine Algae of Florida with Special Reference to the Dry Tortugas Carnegie; Institution of Washington: Washington, DC, USA, 1928; Volume 379. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, W.R. Caribbean Marine Algae of the Allan Hancock Expedition, 1939; The University of Southern California Press: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1942. [Google Scholar]
- Dawes, C.J. Marine Algae of the West Coast of Florida.; University of Miami Press: Oxford, OH, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Littler, D.S.; Littler, M.M. Caribbean Reefs Plants.; OffShore Graphics, Inc.: Deerfield Beach, FL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- John, D.M.; Lawson, G.W.; Ameka, G. The Marine Macroalgae of the Tropical Africa Sub-Region. Nova Hedwig. 2003, iv, 1–217. [Google Scholar]
- Dawes, C.J.; Mathieson, A.C. The Seaweeds of Florida.; University Press of Florida: Gainesville, FL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, K.R.; Warwick, R.M. Changes in Marine Communities: An Approach to Statistical Analysis and Interpretation.; Plymouth Marine Laboratory: Plymouth, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, M.J. Permutation Tests for Univariate or Multivariate Analysis of Variance and Regression. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2001, 58, 626–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R.; Gorley, R.N. Primer v6: User Manual/Tutorial.; Primer-E Ltd.: Plymouth, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, H.S.; Hackett, J.D.; Bhattacharya, D. A Single Origin of the Peridinin- and Fucoxanthin-Containing Plastids in Dinoflagellates through Tertiary Endosymbiosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 11724–11729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Uwai, S.; Yu, S.; Komatsu, T.; Ajisaka, T.; Duan, D. Phylogeographic Heterogeneity of the Brown Macroalga Sargassum horneri (Fucaceae) in the Northwestern Pacific in Relation to Late Pleistocene Glaciation and Tectonic Configurations. Mol. Ecol. 2011, 20, 3894–3909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okonechnikov, K.; Golosova, O.; Fursov, M.; the UGENE team. Unipro UGENE: A Unified Bioinformatics Toolkit. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1166–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple Sequence Alignment with High Accuracy and High Throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.-T.; Schmidt, H.A.; Von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A Fast and Effective Stochastic Algorithm for Estimating Maximum-Likelihood Phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huelsenbeck, J.P.; Ronquist, F. MRBAYES: Bayesian Inference of Phylogenetic Trees. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 754–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronquist, F.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3: Bayesian Phylogenetic Inference under Mixed Models. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1572–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang, D.T.; Chernomor, O.; Von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q.; Vinh, L.S. UFBoot2: Improving the Ultrafast Bootstrap Approximation. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanfear, R.; Calcott, B.; Ho, S.Y.W.; Guindon, S. PartitionFinder: Combined Selection of Partitioning Schemes and Substitution Models for Phylogenetic Analyses. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 29, 1695–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A. FigTree v1. 4. 2012.
- Silberfeld, T.; Leigh, J.W.; Verbruggen, H.; Cruaud, C.; De Reviers, B.; Rousseau, F. A Multi-Locus Time-Calibrated Phylogeny of the Brown Algae (Heterokonta, Ochrophyta, Phaeophyceae): Investigating the Evolutionary Nature of the “Brown Algal Crown Radiation”. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2010, 56, 659–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clement, M.; Posada, D.C.K.A.; Crandall, K.A. TCS: A Computer Program to Estimate Gene Genealogies. Mol. Ecol. 2000, 9, 1657–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Queiroz, K. Species Concepts and Species Delimitation. Syst. Biol. 2007, 56, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, K.; Homma, Y.; Karakisawa, H.; Ishikawa, R.; Uwai, S. Haplotypic Differentiation between Seasonal Populations of Sargassum horneri (Fucales, Phaeophyceae) in Japan. Phycol. Res. 2019, 67, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonsthagen, S.A.; Wilson, R.E.; Chesser, R.T.; Pons, J.-M.; Crochet, P.-A.; Driskell, A.; Dove, C. Recurrent Hybridization and Recent Origin Obscure Phylogenetic Relationships within the ‘White-Headed’ Gull (Larus Sp.) Complex. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2016, 103, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuffisantos, L.; Meira, R.; Ferreira, F.; Santannasantos, B.; Ferreira, L. Morphological Responses of Different Eucalypt Clones Submitted to Glyphosate Drift. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2007, 59, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiger, V.; Horiguchi, T.; Yoshida, T.; Coleman, A.W.; Masuda, M. Phylogenetic Relationships of Sargassum (Sargassaceae, Phaeophyceae) with Reference to a Taxonomic Revision of the Section Phyllocystae Based on ITS-2 nrDNA Sequences. Phycol. Res. 2000, 48, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Stiger, V.; Horiguchi, T. Sargassum boreale sp. Nov. (Fucales, Phaeophyceae) from Hokkaido, Japan. Phycol. Res. 2000, 48, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattio, L.; Payri, C.E.; Stiger-Pouvreau, V. Taxonomic Revision of Sargassum (Fucales, Phaeophyceae) from French Polynesia Based on Morphological And Molecular Analyses 1. J. Phycol. 2008, 44, 1541–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohfritsch, A.; Payri, C.; Stiger, V.; Bonhomme, F. Molecular and Morphological Relationships between Two Closely Related Species, Turbinaria ornata and T. conoides (Sargassaceae, Phaeophyceae). Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2007, 35, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deacon, G.E.R. The Sargasso Sea. Geogr. J. 1942, 99, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryther, J.H. The Sargasso Sea. Sci. Am. 1956, 194, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woelkerling, W.J. On the Epibiotic and Pelagic Chlorophyceae, Phaeophyceae and Rhodophyceae of the Western Sargasso Sea. Rhodora 1975, 77, 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Butler, J.N.; Stoner, A.W. Pelagic Sargassum: Has its Biomass Changed in the Last 50 Years? Deep. Sea Res. 1984, 31, 1259–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niermann, U.; Anders, H.-G.; John, H.-C. Distribution and Abundance of Pelagic Sargassum in Spring 1979. Senckenberg. Marit 1986, 17, 293–302. [Google Scholar]
- Conover, J.T.; Sieburth, M.J. Effect of Sargassum Distribution on its Epibiota and Antibacterial Activity. Bot. Mar. 1964, 6, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryland, J.S. Observations on Some Epibionts of Gulf-Weed, Sargassum natans (l.) Meyen. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1974, 14, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niermann, U. Distribution of Sargassum natans and Some of its Epibionts in the Sargasso Sea. Helgol. Meeresunters. 1986, 40, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calder, D.R. Hydroid Assemblages on Holopelagic Sargassum From the Sargasso Sea at Bermuda. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1995, 56, 537–546. [Google Scholar]
- Weis, J.S. Fauna Associated with Pelagic Sargassum in the Gulf Stream. Am. Midl. Nat. 1968, 80, 554–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fine, M.L. Faunal Variation on Pelagic Sargassum. Mar. Biol. 1970, 7, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoner, A.W.; Greening, H.S. Geographic Variation in the Macrofauna Associates of Pelagic Sargassum and Some Biogeographic Implications. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1984, 20, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, K.L.; Menzies, R.J. Distribution and Production of Sargassum in the Waters off the Carolina Coast. Bot. Mar. 1967, 12, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapointe, B.E. Phosphorous-Limited Photosynthesis and Growth of Sargassum natans and Sargassum fluitans (Phaeophyceae) in the Western North Atlantic. Deep. Sea Res. 1986, 33, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynne, M.J. A Checklist of Benthic Marine Algae of the Tropical and Subtropical Western Atlantic. Can. J. Bot. 1986, 64, 2239–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.W.; Searles, R.B. Seaweeds of the Southeastern United States: Cape Hatteras to Cape Canaveral. Duke University Press: Durham, NC, USA, 1991; 584p.
- de Szechy, M.T.M.; Guedes, P.M.; Baeta-Neves, M.H.; Oliveira, E.N. Verification of Sargassum natans (Linnaeus) Gaillon (Heterokontophyta: Phaeophyceae) from the Sargasso Sea Off the Coast of Brazil, Western Atlantic Ocean. Checklist 2012, 8, 638–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapointe, B.E.; West, L.E.; Sutton, T.T.; Hu, C. Ryther Revisited: Nutrient Excretions by Fishes Enhance Productivity of Pelagic Sargassum in the Western North Atlantic Ocean. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2014, 458, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, E.; Franks, J. Sargassum Factsheet. Gulf and Caribbean Fisheries Institute: Guadeloupe, French, 2015; p. 4. Available online: https://www.gcfi.org/sargassum-influx/ (accessed on 27 February 2024).
- Wynne, M.J. A Checklist of Benthic Marine Algae of the Tropical and Subtropical Western Atlantic: Fifth Revision Nova Hedwigia Beiheft, 153, Bomtraeger Science Publishers, Stuttgart, Germany; 2022. 180 pp.
- Govindarajan, A.F.; Cooney, L.; Whittaker, K.; Bloch, D.; Burdorf, R.M.; Canning, S.; Carter, C.; Cellan, S.M.; Eriksson, F.A.A.; Freyer, H.; et al. The Distribution and Mitochondrial Genotype of the Hydroid Aglaophenia Latecarinata Is Correlated with Its Pelagic Sargassum Substrate Type in the Tropical and Subtropical Wester Atlantic Ocean. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, L.M.; Taylor, M.; Huston, G.; Goodwin, D.S.; Schell, J.M.; Siuda, A.N.S. Pelagic Sargassum Morphotypes Support Different Rafting Motile Epifauna Communities. Mar. Biol. 2021, 168, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGillicuddy, D.J.; Morton, P.L.; Brewton, R.A.; Hu, C.; Kelly, T.B.; Solow, A.R.; Lapointe, B.E. Nutrient and Arsenic Biogeochemistry of Sargassum in the Western Atlantic. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samadi, S.; Barberousse, A. Species. In Handbook of Evolution Thinking in the Sciences; Heams, T., Huneman, P., Lecointre, G., Silberstein, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau, F.; De Reviers, B. Phylogenetic Relationships within the Fucales (Phaeophyceae) Based on Combined Partial SSU+ LSU rDNA Sequence Data. Eur. J. Phycol. 1999, 34, 53–64. [Google Scholar]
- Motomura, T.; Nagasato, C.; Kimura, K. Cytoplasmic Inheritance of Organelles in Brown Algae. J. Plant Res. 2010, 123, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Locus | Primer | Sequence | Annealing | Elongation | Size (bp) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mt spacer IGS | tRNALys-F | CGTTTGGTGAGAACCTTACC | 48 °C, 1 min | 1 min | 250 | [52] |
| tRNALys-R | TACCACTGAGTTATTGCTCCC | |||||
| cox2 | cox2-370F | CAAAGATGGATTCGACGGTTGG | 57 °C, 1 min | 1 min | 406 | [57] |
| cox2-776R | CCGGTATCAAACTCGCCCTT | |||||
| cox3 | cox3-467F | GGTTCAACGACACCCATTT | 50 °C, 1 min | 1 min | 434 | [57] |
| cox3-901R | TAGCGTGATGAGCCCATG | |||||
| 16S rRNA | Sarg-mt16S-F | GTAGTCGGTTGGGTTAGGCC | 60 °C, 1 min | 1 min | 616 | [58] |
| Sarg-mt16S-R | GTTTGAACCCCCGCCAATTC | |||||
| nad6 | Sarg-nad6-F (External) | TATGATTCTTGGGGCTGGT | 56 °C, 1 min | 1 min | 431 | [58] |
| Sarg-nad6-R (External) | GGGATCATTCAAAGCAGAAGA | |||||
| psbA | psbA-F | ATGACTGCTACTTTAGAAAGACG | 49 °C, 1 min | 1 min 30 s | 970 | [69] |
| psbA-R1 | GCTAAATCTARWGGGAAGTTGTG | |||||
| rbcL | rbcL-F | TATGATTGATTT AGTGGTTGG | 51 °C, 1 min 30 s | 2 min | 820 | [70] |
| rbcL-R | GTTCGTCAC TTAAATCTGGTA |
| Source | df | SS | MS | Pseudo-F | P(perm) | Unique perms |
| Morphotype | 2 | 77,756 | 38,878 | 175.73 | 0.001 | 998 |
| Residual | 252 | 55,752 | 221.24 | |||
| Total | 254 | 1.3351 × 105 | ||||
| Groups | t | P(perm) | Unique perms | P(MC) | ||
| S. natans VIII, S. natans I | 14.31 | 0.001 | 999 | 0.001 | ||
| S. natans VIII, S. fluitans III | 10.59 | 0.001 | 999 | 0.001 | ||
| S. natans I, S. fluitans III | 14.93 | 0.001 | 999 | 0.001 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Siuda, A.N.S.; Blanfuné, A.; Dibner, S.; Verlaque, M.; Boudouresque, C.-F.; Connan, S.; Goodwin, D.S.; Stiger-Pouvreau, V.; Viard, F.; Rousseau, F.; et al. Morphological and Molecular Characters Differentiate Common Morphotypes of Atlantic Holopelagic Sargassum. Phycology 2024, 4, 256-275. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology4020014
Siuda ANS, Blanfuné A, Dibner S, Verlaque M, Boudouresque C-F, Connan S, Goodwin DS, Stiger-Pouvreau V, Viard F, Rousseau F, et al. Morphological and Molecular Characters Differentiate Common Morphotypes of Atlantic Holopelagic Sargassum. Phycology. 2024; 4(2):256-275. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology4020014
Chicago/Turabian StyleSiuda, Amy N. S., Aurélie Blanfuné, Skye Dibner, Marc Verlaque, Charles-François Boudouresque, Solène Connan, Deborah S. Goodwin, Valérie Stiger-Pouvreau, Frédérique Viard, Florence Rousseau, and et al. 2024. "Morphological and Molecular Characters Differentiate Common Morphotypes of Atlantic Holopelagic Sargassum" Phycology 4, no. 2: 256-275. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology4020014
APA StyleSiuda, A. N. S., Blanfuné, A., Dibner, S., Verlaque, M., Boudouresque, C.-F., Connan, S., Goodwin, D. S., Stiger-Pouvreau, V., Viard, F., Rousseau, F., Michotey, V., Schell, J. M., Changeaux, T., Aurelle, D., & Thibaut, T. (2024). Morphological and Molecular Characters Differentiate Common Morphotypes of Atlantic Holopelagic Sargassum. Phycology, 4(2), 256-275. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology4020014








