A Double Legendre Polynomial Order N Benchmark Solution for the 1D Monoenergetic Neutron Transport Equation in Plane Geometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Proposed DPN Algorithm
- Express the neutron angular flux of the transport equation as a series of orthogonal half-range Legendre polynomials and spatial moments for neutrons moving in positive and negative direction cosines (±μ) [Equation (2a,b)].
- Since the scattering integral on the RHS of Equation (1a) is expressed as a full-range moment, it is re-expressed as a sum of equivalent half-range moments [Equation (5)].
- The transport equation is then projected over half-range Legendre polynomials in the forward and backward directions to define two coupled first-order ODEs for the spatial moments in each direction [Equation (7e)±].
- After the application of the closure condition to the last moment (with the derivative set to zero), the ODEs are put in vector form, added, and subtracted to form the parity equations [Equation (12a,b)].
- By differentiation, the even parity equation becomes a single inhomogeneous second-order ODE, and the odd parity equation remains first-order [Equation (18)].
- The even parity equation solution is expressed as the sum of the solution to the homogenous and particular parts. Note that the solution to the homogeneous part is constructed from matrix functions with assumed (known) boundary conditions [Equation (24c)].
- With the homogeneous solution known, the particular solution comes from the variation of parameters [Equation (25a)].
- The exiting spatial flux moments are recovered by deriving the response matrix connecting the input moments to the output moments across the slab [Equation (34)].
- The slab’s interior spatial moments then come from adding the parity components (36a)±.
- With known spatial moments, the last step is numerical evaluation of the half-range Legendre series using the Clenshaw algorithm and Wynn-epsilon convergence acceleration.
2.1. DPN Moments and Parity Equations
2.2. The Even/Odd DPN Parity Equations
3. Solution to the Parity Equations
4. The Response Matrix
5. The Final Moment Solution
6. The DPN Approximation
7. Numerical Implementation and Demonstration
7.1. Numerical Implementation for an Isotropic Source
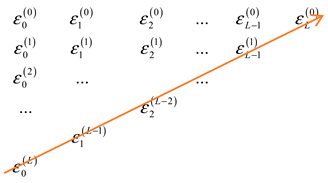
7.2. Numerical Implementation for a Beam Source
8. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Previously Published High-Precision Benchmarks
- The Response Matrix/Discrete Ordinate Method (RM/DOM) [4]
- 2.
- Method of Doubling (MoD) [25]
- 3.
- The Matrix Riccati Equation Method (MREM) [27]
References
- Williams, M.M.R. Mathematical Method in Particle Transport Theory; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Duderstadt, J.J.; Martin, W.R. Transport Theory; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Case, K.M.; Zweifel, P.F. Linear Transport Theory; Addison-Wesley: New York, NY, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Ganapol, B.D. The response matrix discrete ordinates solution to the 1D radiative transfer equation. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2015, 154, 72–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, G.I.; Glasstone, S. Nuclear Reactor Theory; Van Norstrand Reinhold: New York, NY, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Davison, B. Neutron Transport Theory; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1957. [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg, A.M.; Wigner, E.P. The Physicsl Theory of Neutron Chain Reactors; University Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1958. [Google Scholar]
- Wick, G.C. Uber ebene Diffusionsprobleme. Z. Phys. 1943, 121, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshak, R.E. Note on the spherical harmonic method as applied to the Milne problem for a sphere. Phys. Rev. 1947, 71, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mark, J.C. The spherical harmonic method I, National Research Council of Canada, Atomic Energy Project. Rep. MT 1944, 92, 19. [Google Scholar]
- Pomraning, G.C. NSE 1956, 55, 328.
- Federighi, F.D. Nukleonik 1965, 6, 277.
- Lewis, E.E.; Miller, W.F., Jr. Computational Methods of Neutron Transport; American Nuclear Society, Inc.: Westmont, IL, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Lebedev, N.N. Special Functions and Their Applications; Prentice-Hall: New York, NY, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Siewert, C.E. A Concise and Accurate Solution to Chandrasekhar’s Basic Problem in Radiative Transfer. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2000, 64, 109–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benassi, M.; Cotta, R.M.; Siewert, C.E. The PN Method for Radiative Transfer Problems with Reflective Boundary Conditions. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 1983, 30, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.E.; Dias, M.P. Analytical Solutions to the Moment Transport Equations-I. Ann. Nucl. Energy 1984, 10, 515–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, M.D. Advanced Engineering Mathematics, 2nd ed.; Prentice Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: http://icl.cs.utk.edu/lapack-for-windows/lapack (accessed on 30 July 2024).
- Wynn, P. On a device for computing the em(Sn) transformation. Math. Tables Aids Comput. 1956, 10, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisstein, E.W. Clenshaw Recurrence Formula. From MathWorld—A Wolfram Web Resource. Available online: https://mathworld.wolfram.com/ClenshawRecurrenceFormula.html (accessed on 30 July 2024).
- Barichello, L.B.; Siewert, C.E. A New Version of the Discrete-Ordinates Method. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational Heat and Mass Transfer, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 22–26 October 2002; pp. 340–347. [Google Scholar]
- Grant, I.P.; Hunt, G.E. Discrete space theory of radiative transfer I. Fundamentals. Proc. Roy. Soc. A 1969, 313, 183–197. [Google Scholar]
- Lenoble, J. Standard procedures to compute atmospheric radiative transfer in a scattering atmosphere, Radiation Commission. Intl. Assoc. Meteor Atmos. Phys. 1977, 68, 520–522. [Google Scholar]
- Ganapol, B.D. An Extreme Benchmark for Monoenergetic Scattering in Hydrogen; ANS Winter Meeting: Orlando, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- van de Hulst, H.C. A New Look at Multiple Scattering; NASA Institute for Space Studies: New York, NY, USA, 1965.
- Ganapol, B.D. Matrix Riccati Equation Solution of the 1D Radiative Transfer Equation. J. Comput. Theor. Transp. 2021, 50, 297–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| μ\x | 0.0 | 0.05 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.75 | 1.0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1.000E+00 | 3.41328760E-01 | 3.20920611E-01 | 3.01041128E-01 | 2.62366118E-01 | 1.53240509E-01 | 7.07430107E-02 | 0.00000000E+00 |
| −8.000E-01 | 3.92084430E-01 | 3.69683964E-01 | 3.47820410E-01 | 3.05071361E-01 | 1.82180798E-01 | 8.60214436E-02 | 0.00000000E+00 |
| −6.000E-01 | 4.58134371E-01 | 4.33685363E-01 | 4.09782681E-01 | 3.62759573E-01 | 2.24012630E-01 | 1.09614879E-01 | 0.00000000E+00 |
| −4.000E-01 | 5.43854301E-01 | 5.17792855E-01 | 4.92356464E-01 | 4.42065792E-01 | 2.88493773E-01 | 1.50567243E-01 | 0.00000000E+00 |
| −2.000E-01 | 6.45967494E-01 | 6.19276078E-01 | 5.93756446E-01 | 5.43978308E-01 | 3.90966211E-01 | 2.35919292E-01 | 0.00000000E+00 |
| 0.000E+00 | 7.58146459E-01 | 7.22978545E-01 | 6.94563136E-01 | 6.42872374E-01 | 5.00000000E-01 | 3.81715377E-01 | 2.41853541E-01 |
| 2.000E-01 | 1.00000000E+00 | 9.42160751E-01 | 8.90352375E-01 | 8.02157479E-01 | 6.09033789E-01 | 4.80750231E-01 | 3.54032506E-01 |
| 4.000E-01 | 1.00000000E+00 | 9.69316928E-01 | 9.38639544E-01 | 8.78613253E-01 | 7.11506227E-01 | 5.83062169E-01 | 4.56145699E-01 |
| 6.000E-01 | 1.00000000E+00 | 9.79131021E-01 | 9.57479617E-01 | 9.12982318E-01 | 7.75987370E-01 | 6.60525697E-01 | 5.41865629E-01 |
| 8.000E-01 | 1.00000000E+00 | 9.84189969E-01 | 9.67479934E-01 | 9.32267600E-01 | 8.17819202E-01 | 7.15927250E-01 | 6.07915570E-01 |
| 1.000E+00 | 1.00000000E+00 | 9.87275159E-01 | 9.73675082E-01 | 9.44578242E-01 | 8.46759491E-01 | 7.56515359E-01 | 6.58671240E-01 |
| μ\x | 0 | 0.05 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.75 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1.000E+00 | 5.3877491E-01 | 5.1979897E-01 | 4.9826415E-01 | 4.5015758E-01 | 2.8363970E-01 | 1.3670184E-01 | 0.0000000E+00 |
| −8.000E-01 | 6.1358488E-01 | 5.9454278E-01 | 5.7227580E-01 | 5.2122894E-01 | 3.3675659E-01 | 1.6617467E-01 | 0.0000000E+00 |
| −6.000E-01 | 7.0705901E-01 | 6.8953074E-01 | 6.6778458E-01 | 6.1558120E-01 | 4.1317580E-01 | 2.1164480E-01 | 0.0000000E+00 |
| −4.000E-01 | 8.1805757E-01 | 8.0600276E-01 | 7.8820201E-01 | 7.4066647E-01 | 5.2986404E-01 | 2.9042486E-01 | 0.0000000E+00 |
| −2.000E-01 | 9.1606674E-01 | 9.1832709E-01 | 9.1231716E-01 | 8.8438367E-01 | 7.1013555E-01 | 4.5375071E-01 | 0.0000000E+00 |
| 0.000E+00 | 8.7868708E-01 | 9.2867409E-01 | 9.4863473E-01 | 9.5773321E-01 | 8.6865051E-01 | 7.1731075E-01 | 4.8302802E-01 |
| 2.000E-01 | 0.0000000E+00 | 2.0129990E-01 | 3.6476856E-01 | 5.9744092E-01 | 8.4223675E-01 | 7.9950036E-01 | 6.5012804E-01 |
| 4.000E-01 | 0.0000000E+00 | 1.0687614E-01 | 2.0478323E-01 | 3.7093644E-01 | 6.5966190E-01 | 7.2022080E-01 | 6.6508565E-01 |
| 6.000E-01 | 0.0000000E+00 | 7.2711601E-02 | 1.4205915E-01 | 2.6699419E-01 | 5.2395290E-01 | 6.1548983E-01 | 6.1208033E-01 |
| 8.000E-01 | 0.0000000E+00 | 5.5092891E-02 | 1.0870690E-01 | 2.0824783E-01 | 4.3113588E-01 | 5.2849359E-01 | 5.4968216E-01 |
| 1.000E+00 | 0.0000000E+00 | 4.4345690E-02 | 8.8026420E-02 | 1.7060822E-01 | 3.6524695E-01 | 4.6023695E-01 | 4.9305877E-01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ganapol, B.D. A Double Legendre Polynomial Order N Benchmark Solution for the 1D Monoenergetic Neutron Transport Equation in Plane Geometry. Foundations 2024, 4, 422-441. https://doi.org/10.3390/foundations4030027
Ganapol BD. A Double Legendre Polynomial Order N Benchmark Solution for the 1D Monoenergetic Neutron Transport Equation in Plane Geometry. Foundations. 2024; 4(3):422-441. https://doi.org/10.3390/foundations4030027
Chicago/Turabian StyleGanapol, Barry D. 2024. "A Double Legendre Polynomial Order N Benchmark Solution for the 1D Monoenergetic Neutron Transport Equation in Plane Geometry" Foundations 4, no. 3: 422-441. https://doi.org/10.3390/foundations4030027
APA StyleGanapol, B. D. (2024). A Double Legendre Polynomial Order N Benchmark Solution for the 1D Monoenergetic Neutron Transport Equation in Plane Geometry. Foundations, 4(3), 422-441. https://doi.org/10.3390/foundations4030027






