Serum-Derived Macrophage-Activating Factor Exhibits Anti-Tumor Activity via M2-to-M1 Macrophage Reprogramming
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Cells
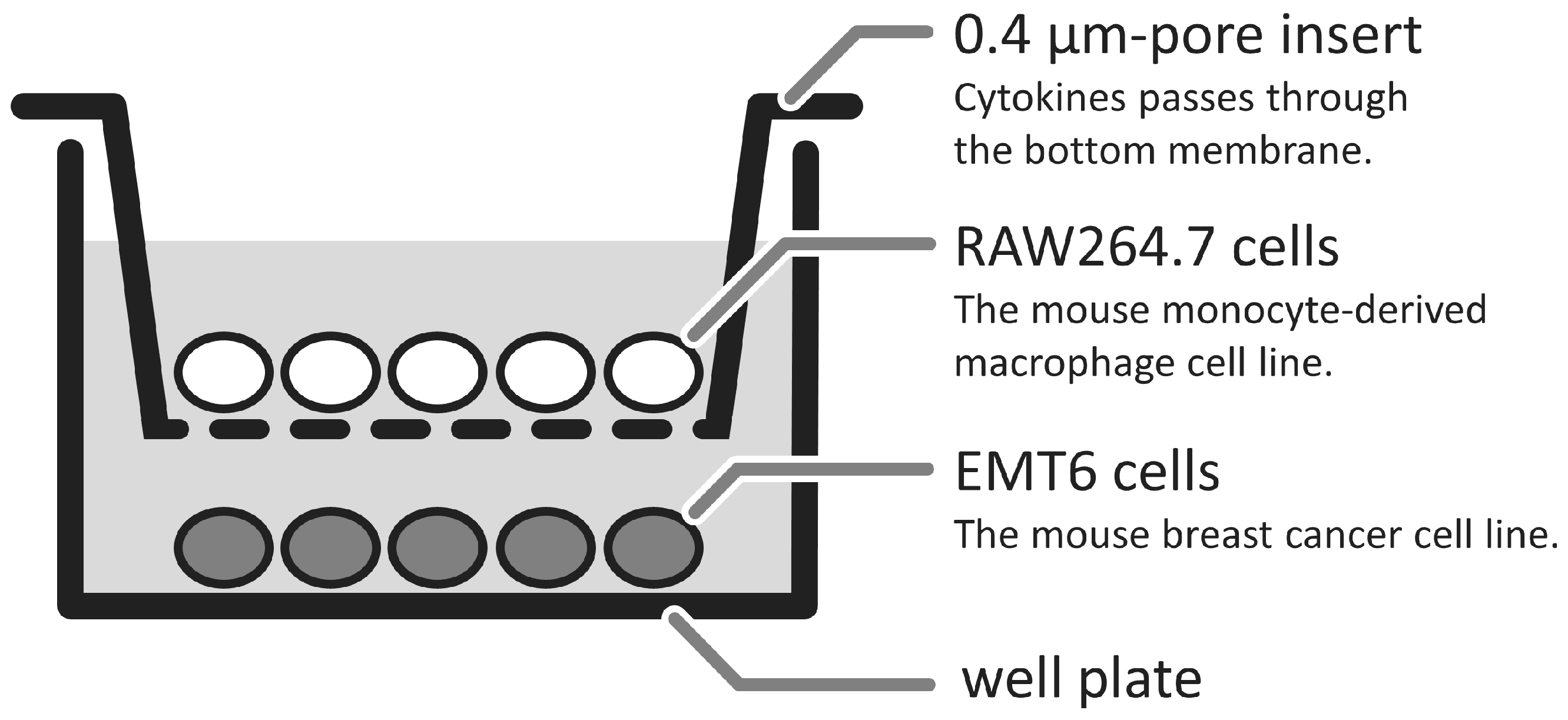
2.3. Co-Culture of RAW264.7 Cells and EMT6 Cells
2.4. Quantitative Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR)
2.5. Nitric Oxide (NO) Assay
2.6. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.7. Evaluation of EMT6 Cell Number for Crystal Violet Staining Assay
2.8. DNA Microarray Analysis
2.9. M2 Polarization of RAW264.7 Cells
2.10. Evaluation of EMT6 Cell Number for Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) Assay
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
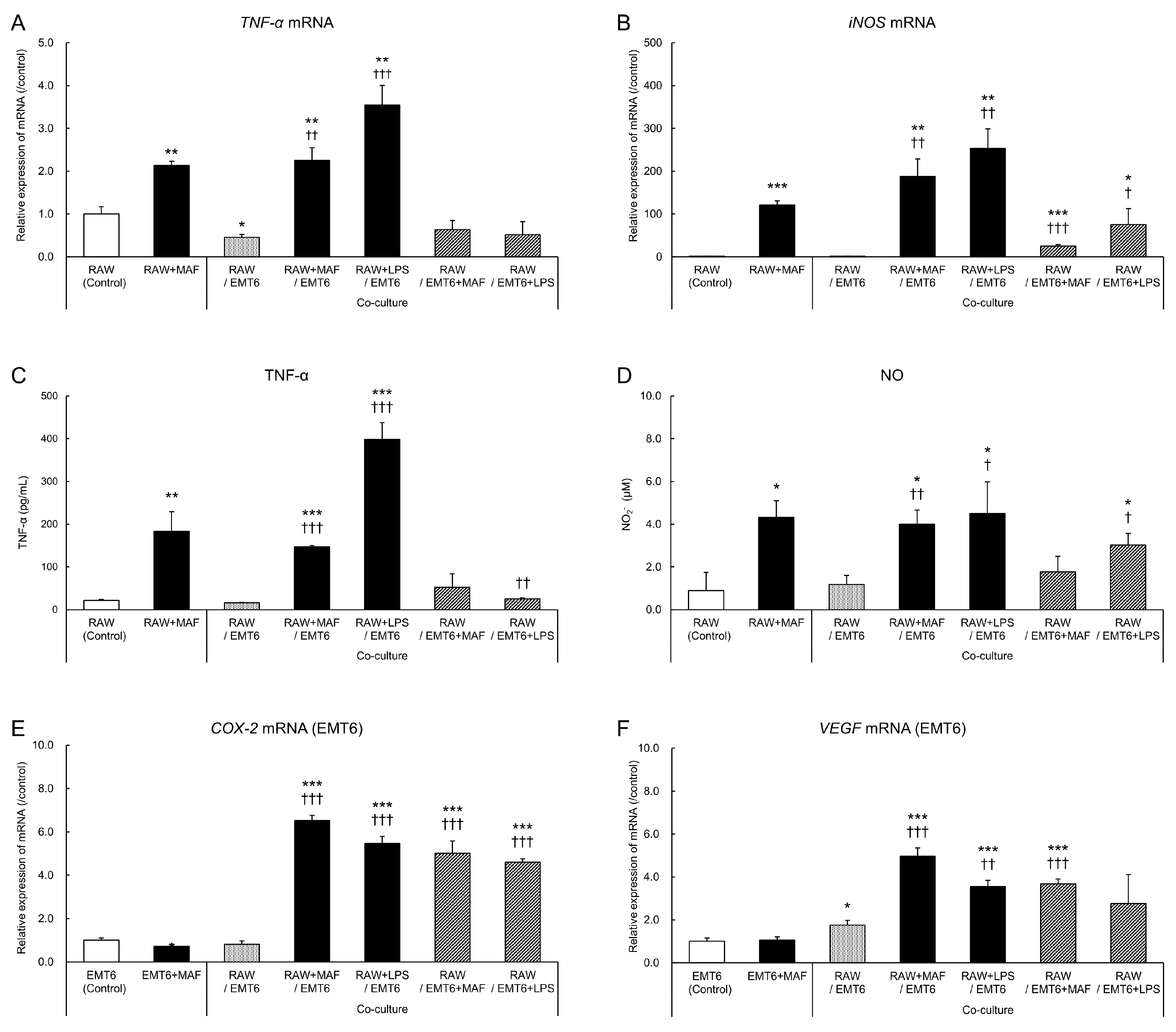
3.1. Changes in GcMAF-Stimulated Cells in a Non-Contact Co-Culture System
3.2. Changes in EMT6 Cells Induced by GcMAF-Stimulated RAW264.7 Cells
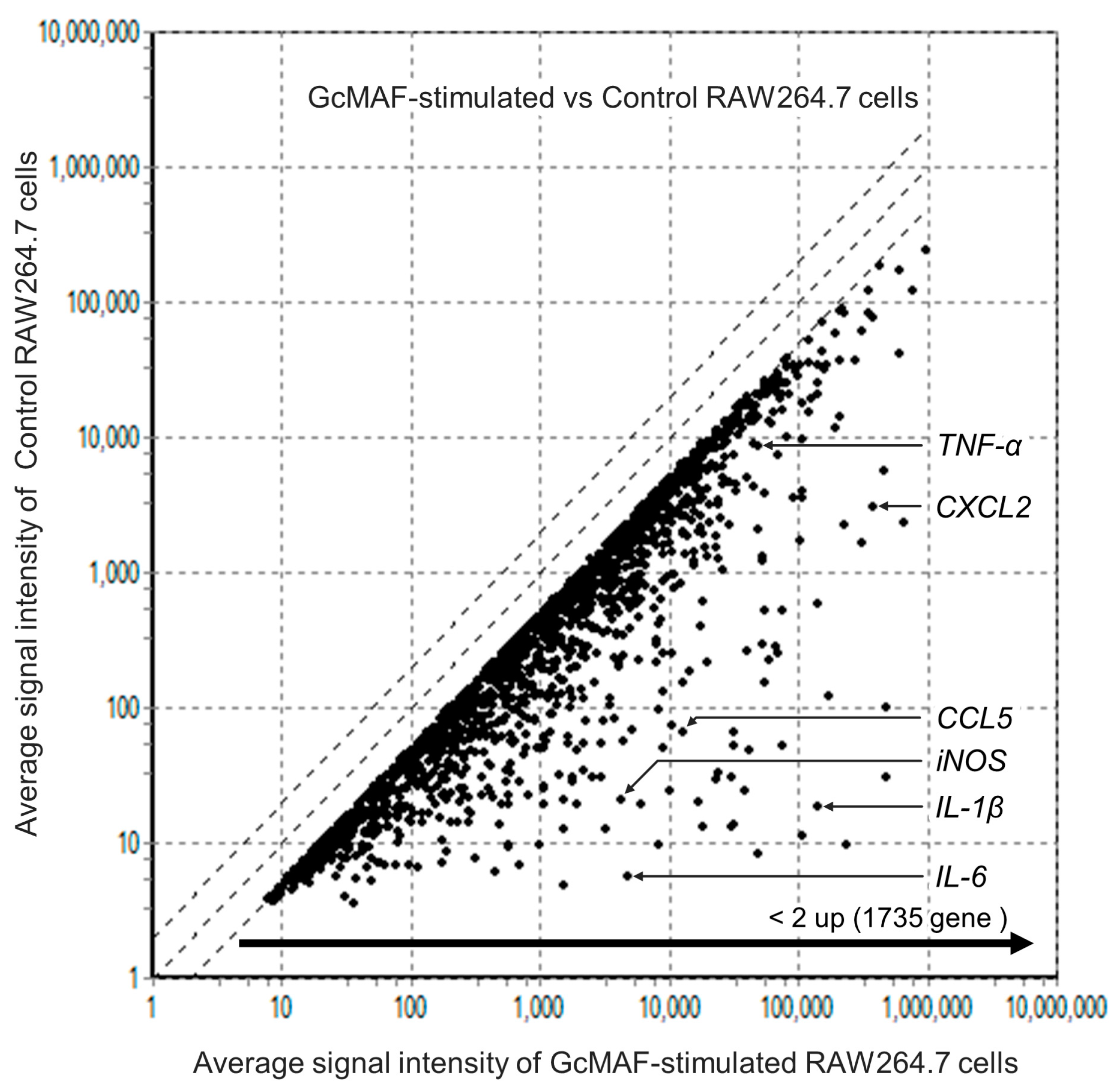
3.3. Comprehensive Analysis of Gene Levels in GcMAF-Stimulated Macrophages Using DNA Arrays
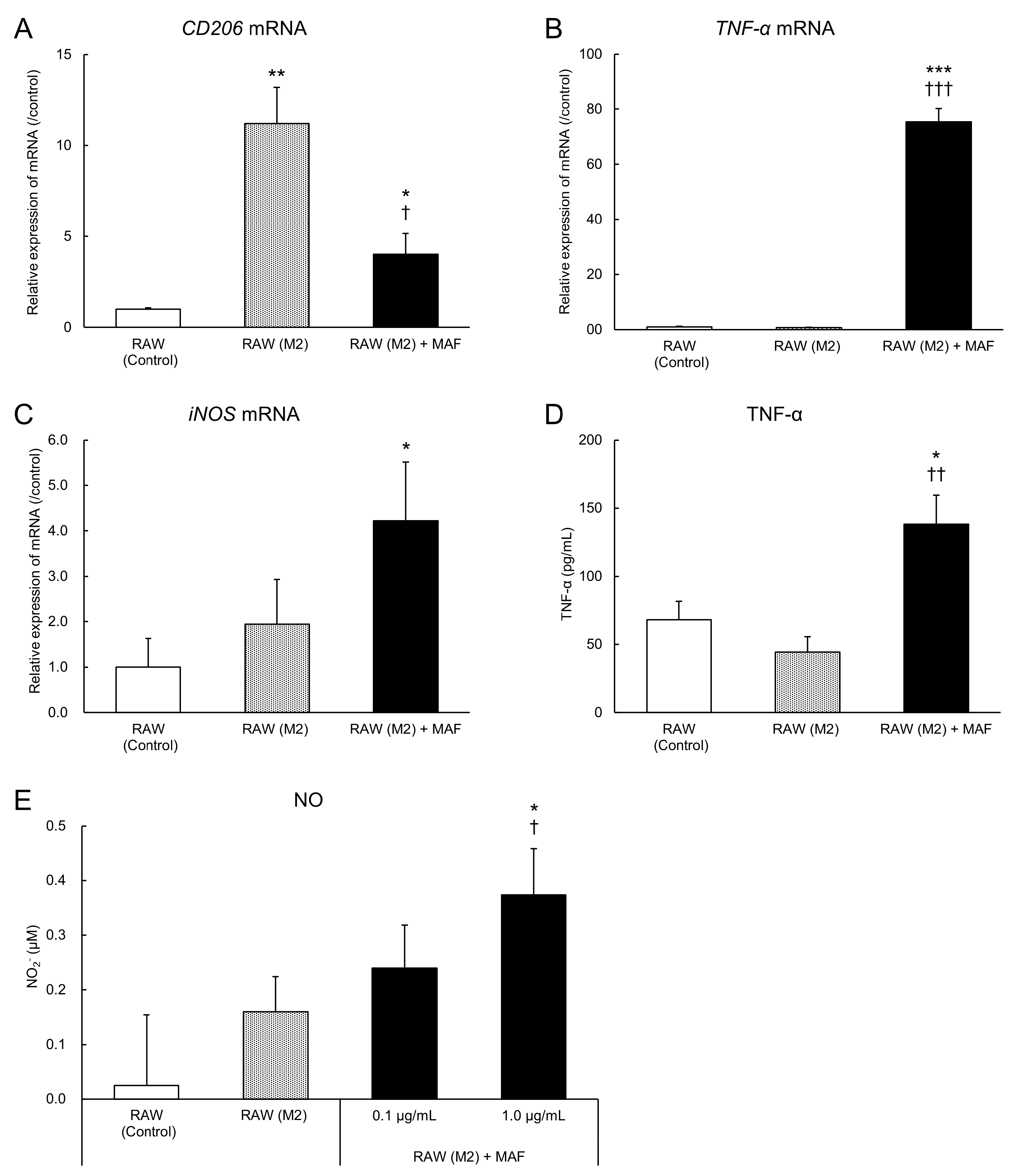
3.4. Evaluation of M2-to-M1 Macrophage Reprogramming by GcMAF
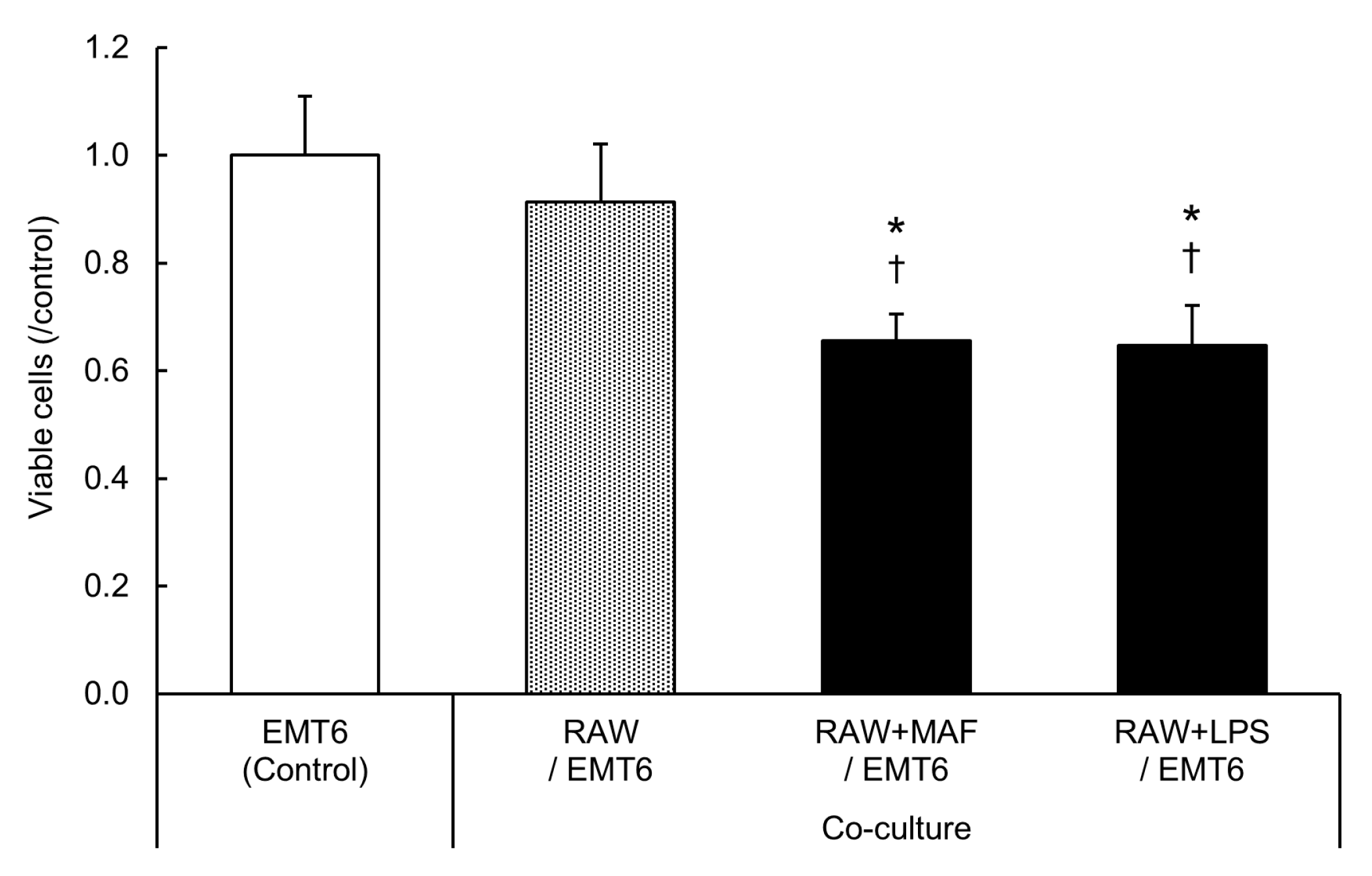
3.5. Suppression of EMT6 Cell Proliferation by GcMAF-Stimulated M2 RAW264.7 Cells
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Daiger, S.P.; Schanfield, M.S.; Cavalli-Sforza, L.L. Group-Specific Component (Gc) Proteins Bind Vitamin D and 25-Hydroxyvitamin D. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1975, 72, 2076–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, P.; Cooke, N. The Multifunctional Properties and Characteristics of Vitamin D-Binding Protein. Trends Endocrinol. Metabol. 2000, 11, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, N.; Homma, S. Vitamin D3 Binding Protein (Group-Specific Component) Is a Precursor for the Macrophage-Activating Signal Factor from Lysophosphatidylcholine-Treated Lymphocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 8539–8543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, N.; Kumashiro, R. Conversion of Vitamin D3 Binding Protein (Group-Specific Component) to a Macrophage Activating Factor by the Stepwise Action of Beta-Galactosidase of B Cells and Sialidase of T Cells. J. Immunol. 1993, 151, 2794–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kisker, O.; Onizuka, S.; Becker, C.M.; Fannon, M.; Flynn, E.; D’Amato, R.; Zetter, B.; Folkman, J.; Ray, R.; Swamy, N.; et al. Vitamin D Binding Protein-Macrophage Activating Factor (DBP-Maf) Inhibits Angiogenesis and Tumor Growth in Mice. Neoplasia 2003, 5, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uto, Y.; Yamamoto, S.; Takeuchi, R.; Nakagawa, Y.; Hirota, K.; Terada, H.; Onizuka, S.; Nakata, E.; Hori, H. Effect of the Gc-Derived Macrophage-Activating Factor Precursor (PreGcMAF) on Phagocytic Activation of Mouse Peritoneal Macrophages. Anticancer Res. 2011, 31, 2489–2492. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nonaka, K.; Onizuka, S.; Ishibashi, H.; Uto, Y.; Hori, H.; Nakayama, T.; Matsuura, N.; Kanematsu, T.; Fujioka, H. Vitamin D Binding Protein-Macrophage Activating Factor Inhibits HCC in SCID Mice. J. Surg. Res. 2012, 172, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inui, T.; Kuchiike, D.; Kubo, K.; Mette, M.; Uto, Y.; Hori, H.; Sakamoto, N. Clinical Experience of Integrative Cancer Immunotherapy with GcMAF. Anticancer Res. 2013, 33, 2917–2919. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- DeNardo, D.G.; Ruffell, B. Macrophages as Regulators of Tumour Immunity and Immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orecchioni, M.; Ghosheh, Y.; Pramod, A.B.; Ley, K. Macrophage Polarization: Different Gene Signatures in M1(LPS+) vs. Classically and M2(LPS–) vs. Alternatively Activated Macrophages. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Guo, N.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, J.; Wei, Q.; Han, M. The Role of Tumor-Associated Macrophages (TAMs) in Tumor Progression and Relevant Advance in Targeted Therapy. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2020, 10, 2156–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rőszer, T. Understanding the Mysterious M2 Macrophage through Activation Markers and Effector Mechanisms. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 816460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitale, I.; Manic, G.; Coussens, L.M.; Kroemer, G.; Galluzzi, L. Macrophages and Metabolism in the Tumor Microenvironment. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, S.; Kohanbash, G.; Liu, S.J.; Alvarado, B.; Carrera, D.; Bhaduri, A.; Watchmaker, P.B.; Yagnik, G.; Di Lullo, E.; Malatesta, M.; et al. Single-Cell Profiling of Human Gliomas Reveals Macrophage Ontogeny as a Basis for Regional Differences in Macrophage Activation in the Tumor Microenvironment. Genome Biol. 2017, 18, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Liang, R.; Lan, T.; Ding, D.; Huang, S.; Shao, J.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, T.; Huang, Y.; Liu, J.; et al. Tumor-Associated Macrophage-Specific CD155 Contributes to M2-Phenotype Transition, Immunosuppression, and Tumor Progression in Colorectal Cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e004219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Shi, P.; Jiang, T.; Yin, H.; Chu, S.; Shi, M.; Bai, J.; Song, J. DKC1 Enhances Angiogenesis by Promoting HIF-1α Transcription and Facilitates Metastasis in Colorectal Cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 668–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delprat, V.; Tellier, C.; Demazy, C.; Raes, M.; Feron, O.; Michiels, C. Cycling Hypoxia Promotes a Pro-Inflammatory Phenotype in Macrophages via JNK/P65 Signaling Pathway. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, G.; Zhu, Y.; Dong, Z.; Shi, L.; Deng, Y.; Li, H. Calmodulin 2 Facilitates Angiogenesis and Metastasis of Gastric Cancer via STAT3/HIF-1A/VEGF-A Mediated Macrophage Polarization. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 727306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacini, S.; Punzi, T.; Morucci, G.; Gulisano, M.; Ruggiero, M. Effects of Vitamin D-Binding Protein-Derived Macrophage-Activating Factor on Human Breast Cancer Cells. Anticancer Res. 2012, 32, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Gregory, K.J.; Zhao, B.; Bielenberg, D.R.; Dridi, S.; Wu, J.; Jiang, W.; Huang, B.; Pirie-Shepherd, S.; Fannon, M. Vitamin D Binding Protein-Macrophage Activating Factor Directly Inhibits Proliferation, Migration, and UPAR Expression of Prostate Cancer Cells. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thyer, L.; Ward, E.; Smith, R.; Fiore, M.; Magherini, S.; Branca, J.; Morucci, G.; Gulisano, M.; Ruggiero, M.; Pacini, S. A Novel Role for a Major Component of the Vitamin D Axis: Vitamin D Binding Protein-Derived Macrophage Activating Factor Induces Human Breast Cancer Cell Apoptosis through Stimulation of Macrophages. Nutrients 2013, 5, 2577–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, G.; Rath, B.; Klameth, L.; Hochmair, M.J. Small Cell Lung Cancer: Recruitment of Macrophages by Circulating Tumor Cells. Oncoimmunology 2016, 5, e1093277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaiyasit, K.; Inui, T.; Wiwanitkit, V. The Use of Gc Protein-Derived Macrophage Activating Factor for Management of Thyroid Cancer. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2015, 11, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Sha, M.-L.; Li, D.; Zhu, Y.-P.; Wang, X.-J.; Jiang, C.-Y.; Xia, S.-J.; Shao, Y. Relaxin Abrogates Renal Interstitial Fibrosis by Regulating Macrophage Polarization via Inhibition of Toll-like Receptor 4 Signaling. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 21044–21053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Font-Nieves, M.; Sans-Fons, M.G.; Gorina, R.; Bonfill-Teixidor, E.; Salas-Pérdomo, A.; Márquez-Kisinousky, L.; Santalucia, T.; Planas, A.M. Induction of COX-2 Enzyme and Down-Regulation of COX-1 Expression by Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) Control Prostaglandin E2 Production in Astrocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 6454–6468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Perez, R.R.; Xu, Y.; Guo, S.; Watters, A.; Zhou, W.; Leibovich, S.J. Leptin Upregulates VEGF in Breast Cancer via Canonic and Non-Canonical Signalling Pathways and NFκB/HIF-1α Activation. Cell Signal 2010, 22, 1350–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.; Young, H.; Hurlstone, A.; Wellbrock, C. Differentiation of THP1 Cells into Macrophages for Transwell Co-Culture Assay with Melanoma Cells. Bio-Protocol 2015, 5, e1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Zhou, J.; Chen, F.; Yu, J.; Li, H.; Li, Q.; Li, W. 13-Methyl-Palmatrubine Shows an Anti-Tumor Role in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer via Shifting M2 to M1 Polarization of Tumor Macrophages. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 104, 108468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uto, Y.; Kawai, T.; Sasaki, T.; Hamada, K.; Yamada, H.; Kuchiike, D.; Kubo, K.; Inui, T.; Mette, M.; Tokunaga, K.; et al. Degalactosylated/Desialylated Bovine Colostrum Induces Macrophage Phagocytic Activity Independently of Inflammatory Cytokine Production. Anticancer Res. 2015, 35, 4487–4492. [Google Scholar]
- Hangai, S.; Kawamura, T.; Kimura, Y.; Chang, C.-Y.; Hibino, S.; Yamamoto, D.; Nakai, Y.; Tateishi, R.; Oshima, M.; Oshima, H.; et al. Orchestration of Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells in the Tumor Microenvironment by Ubiquitous Cellular Protein TCTP Released by Tumor Cells. Nat. Immunol. 2021, 22, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyckoff, J.; Wang, W.; Lin, E.Y.; Wang, Y.; Pixley, F.; Stanley, E.R.; Graf, T.; Pollard, J.W.; Segall, J.; Condeelis, J. A Paracrine Loop between Tumor Cells and Macrophages Is Required for Tumor Cell Migration in Mammary Tumors. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 7022–7029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, J.S.; Landers, R.J.; Underwood, J.C.; Harris, A.L.; Lewis, C.E. Expression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor by Macrophages Is Up-Regulated in Poorly Vascularized Areas of Breast Carcinomas. J. Pathol. 2000, 192, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruns, H.; Büttner, M.; Fabri, M.; Mougiakakos, D.; Bittenbring, J.T.; Hoffmann, M.H.; Beier, F.; Pasemann, S.; Jitschin, R.; Hofmann, A.D.; et al. Vitamin D–Dependent Induction of Cathelicidin in Human Macrophages Results in Cytotoxicity against High-Grade B Cell Lymphoma. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 282ra47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolgova, E.V.; Kirikovich, S.S.; Levites, E.V.; Ruzanova, V.S.; Proskurina, A.S.; Ritter, G.S.; Taranov, O.S.; Varaksin, N.A.; Ryabicheva, T.G.; Leplina, O.Y.; et al. Analysis of the Biological Properties of Blood Plasma Protein with GcMAF Functional Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Takara, T.; Takara, R.; Kobayashi, A.; Shirakata, H.; Ambai, S.; Shinohara, Y.; Uto, Y. Serum-Derived Macrophage-Activating Factor Exhibits Anti-Tumor Activity via M2-to-M1 Macrophage Reprogramming. Int. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 4, 439-449. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtm4030029
Takara T, Takara R, Kobayashi A, Shirakata H, Ambai S, Shinohara Y, Uto Y. Serum-Derived Macrophage-Activating Factor Exhibits Anti-Tumor Activity via M2-to-M1 Macrophage Reprogramming. International Journal of Translational Medicine. 2024; 4(3):439-449. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtm4030029
Chicago/Turabian StyleTakara, Tsuyoshi, Rei Takara, Aya Kobayashi, Hina Shirakata, Shinobu Ambai, Yusei Shinohara, and Yoshihiro Uto. 2024. "Serum-Derived Macrophage-Activating Factor Exhibits Anti-Tumor Activity via M2-to-M1 Macrophage Reprogramming" International Journal of Translational Medicine 4, no. 3: 439-449. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtm4030029
APA StyleTakara, T., Takara, R., Kobayashi, A., Shirakata, H., Ambai, S., Shinohara, Y., & Uto, Y. (2024). Serum-Derived Macrophage-Activating Factor Exhibits Anti-Tumor Activity via M2-to-M1 Macrophage Reprogramming. International Journal of Translational Medicine, 4(3), 439-449. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtm4030029




