Abstract
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) affects 10% of the world’s population. Uremic toxins, such as indoxyl sulfate (IS), p-Cresylsulfate (PCS) and indole acetic acid (IAA), are not sufficiently removed by conventional hemodialysis (HD) and have been associated with inflammation, poor quality of life, bone mineral disease (BMD) and endothelial injury. Online hemodiafiltration (OL-HDF) may promote greater clearance of uremic toxins than HD. However, there are few studies evaluating the effect of OL-HDF on serum levels of IS, PCS, IAA, and biomarkers associated with inflammatory, endothelial, and bone and mineral disorder in the elderly population. We evaluated the effect of 6 months of OL-HDF on the serum concentration of uremic toxins, biomarkers of inflammation, endothelial and bone mineral disorder in older patients on OL-HDF. IS, PCS, and IAA were measured by high-performance liquid chromatography. We included 31 patients (77.4 ± 7.1 years, 64.5% male, 35.5% diabetic, on maintenance dialysis for 45 ± 20 days). From baseline to 6 months there was a decrease in serum concentration of IS but not PCS and IAA. We found no change in serum concentration of inflammatory, endothelial, or mineral and bone biomarkers. In summary, OL-HDF was capable to reduce IS in older patients. Whether this reduction may have an impact on clinical outcomes deserves further evaluation.
1. Introduction
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a public health problem with a worldwide prevalence of 10% and associated with a high morbimortality rate [1]. The progressive loss of filtration capacity results in the accumulation of toxic substances called uremic toxins (UTs) [2,3]. Patients with a glomerular filtration rate < 15 mL/min experience high serum concentrations of UTs and electrolyte imbalance and metabolic acidosis. Renal replacement therapy is often indicated to maintain homeostasis and survival [4]; and hemodialysis (HD) is the modality most widely used. However, HD is not very effective in removing uremic toxins with medium molecular weight or those binding to proteins, such as indoxyl sulfate (IS), p-Cresylsulfate (PCS), and indole acetic acid (IAA) [5,6].
The accumulation of these UTs in patients on HD has been associated with increased inflammation [7], poor quality of life, bone and mineral disease disorders (BMD) [8], endothelial injury, and cardiovascular disease [9]. Moreover, the inflammatory response to UTs has been associated with pathophysiological mechanisms of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and BMD in patients with CKD, mainly in those on HD [10].
IS, PCS, and IAA are associated to signaling of the inflammatory response, endothelial injury, inhibition of endothelial repair and regeneration oxidative stress, CVD, and mortality in patients with CKD [11,12]. IS promotes pro-inflammatory macrophage activation mediated by its uptake through transporters, including OATP2B1, an independent cardiovascular risk factor in CKD [13].
The association between UTs and BMD is based on recent studies that have suggested that IS and PCS might inhibit osteoclast differentiation [14] and impair PTH signaling, which is an essential signal for the regulation of bone metabolism [15]. Additionally, UTs are associated with an impairment of bone quality and bone fragility [15].
Not only the loss of renal filtration function affects calcium, phosphate, 25(OH)D, parathyroid hormone (PTH), and fibroblast grown factor 23 (FGF-23) in patients dialysis patients, but also the inflammation. Recently, it has been observed that in the bone marrow, several immune cells can modulate bone [16]. Hence, the cytokines produced by immune cells and UTs act on osteoblasts and osteoclasts, contributing to injury bone remodeling in patients with CKD [17,18].
Online hemodiafiltration (OL-HDF), a modality that combines diffusion and convection, removes greater amount of medium molecular weight or protein-bound uremic toxins than HD [19]. OL-HDF may potentially reduce the adverse effects of inflammation and BMD. Lin CL et al. have found after 6-months, a reduction in advanced glycation products (AGEs) in patients treated with OL-HDF compared to those on HD [20]. Similarly, Kuo et al. have reported that OL-HDF was able to decrease TNF-α and IL-18 [21]. Den Hoedt et al. have also observed lower levels of CRP and albumin in patients who underwent OL-HDF [22]. Den Hoedt et al. have demonstrated that CRP levels and mortality rate were lower in the OL-HDF group when compared to HD [23]. Panichi V at al. reported that OL-HDF decreases serum levels of CRP and IL-6 in patients switched from low-flux HD to OL-HDF [24].
To date, there is no study on the effects of OL-HDF on serum concentration of IS, PCS, IAA, biomarkers of inflammation, endothelial, and bone in older individuals. Thus, the present study aimed to evaluate the serum concentration of protein-bound uremic toxins, biomarkers of inflammation, and endothelial and bone mineral disease in older patients who switched from high-flux HD to OL-HDF.
2. Results
Out of 40 patients initially included, 9 dropped-out due to COVID-19 (N = 2), kidney transplantation (N = 1) and changed to another dialysis center (N = 6). The final analysis was performed with 31 patients. As detailed in Table 1 most patients were male and the mean age was 77.4 ± 7.1 years. Hypertensive nephrosclerosis (45.2%) and diabetes (35.5%) accounted for most of the underlying kidney disease.

Table 1.
Characteristics of patients.
Table 2 and Figure 1 show a significant decrease in IS concentration after 6 months and a reduction in PCS and IAA that did not reach statistical significance. Creatinine and urea increased after 6 months in OL-HDF treatment (Table 2). IS correlated with PTH (r = 0.41; p < 0.001), phosphate (r = 0.27; p = 0.03), and 25(OH)D (r = −0.35 p < 0.01) (Figure 2).

Table 2.
Uremic toxins, biochemical data, bone mineral disease, endothelial and inflammatory biomarkers at baseline (Pre-OL-HDF) and after 6 months on online hemodiafiltration (Post-OL-HDF).
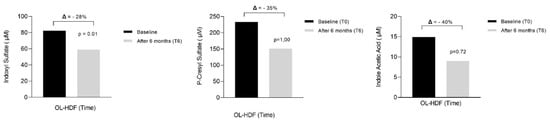
Figure 1.
Percentual change in serum concentration of uremic toxins after 6 months of online hemodiafiltration (OL-HDF).
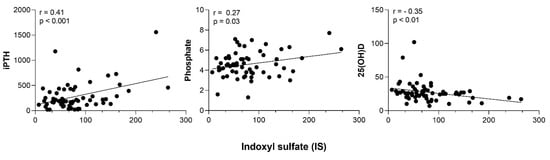
Figure 2.
Correlation between Indoxyl sulfate (IS) and intact parathyroid hormone (iPTH), phosphate and 25 vitamin D.
A sub analysis revealed a reduction in alkaline phosphatase (from 103 ± 39 to 86 ± 25, p = 0.04) and CRP [from 5.30 (1.23–26.0) to 2.44 (1.59–11.1), p = 0.04] in patients who exhibited a reduction in IS and IAA, respectively (Figure 3 and Figure 4).
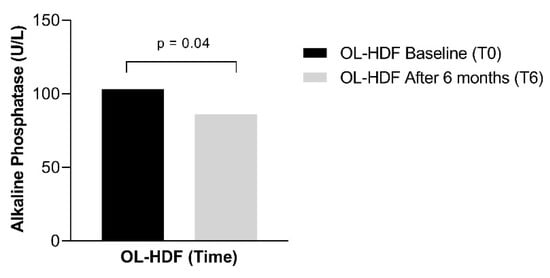
Figure 3.
Alkaline phosphatase serum concentration in patients who showed a reduction in the serum concentration of Indoxyl Sulfate over 6 months of online hemodiafiltration (OL-HDF).
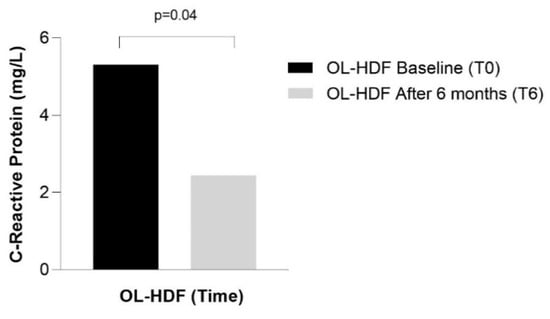
Figure 4.
CRP serum concentration in patients who showed a reduction in the serum concentration of IAA over 6 months of online hemodiafiltration (OL-HDF).
3. Discussion
The proposal of the current research was to evaluate toxin removal by OL-HDF in older patients. The population is ageing and so is the population on dialysis. Age is a risk factor for mortality in dialysis and older patients have a higher risk than younger [25]. OL-HDF is known to be a more appropriate method to avoid hemodynamic instability and therefore with benefits for older individuals. However, there is no study that has focused on toxin removal in elderly patients on OL-HDF.
This study showed that older patients who switched from HD to OL-HDF presented a reduction in the serum concentration of IS after 6 months. Levels of PCS, IAA, inflammatory, endothelial and BMD markers did not change. In addition, we observed an increase in serum concentration of creatinine and urea over 6 months of OL-HDF. This finding could be explained by the appetite improvement after dialysis initiation and the cessation of protein restriction diet. URR and Kt/V are greater in OL-HDF than in conventional hemodialysis. Therefore, the increase in urea and creatinine levels after 6 months on OL-HDF is more likely to be a result of a better protein intake than a reduced dialysis urea and creatinine clearance.
Urea is the most measured toxin in patients on dialysis, and it is used as a surrogate marker of dialysis efficiency. However, urea is a small solute easily removed by dialysis, which is not true for middle molecules. Middle molecules, on the other hand, are not commonly measured in clinical practice and are associated with several adverse outcomes in patients on dialysis. IS, for instance, reacts directly with macrophages and accelerates atherosclerosis [26]. OL-HDF is thought to remove such molecules in a more effective way, and potentially improve dialysis-related clinical symptoms. Greater removal of toxins may lead to improved survival and quality of life for dialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease patients. If this applies also for older patients is still unknown.
In agreement with our data, a previous study enrolling 36 younger patients for six months in OL-HDF, have observed a reduction in IS serum concentrations [27]. Krieter et al., in a study comparing HD and OL-HDF, observed a significant reduction in plasma concentrations of free and total IS and total PCS [28]. These results were not confirmed by Thammathiwat et al. [29]. Krieter et al. have reported that even though serum IS and PCS levels have reduced in OL-HDF, this effect was not sustained in long term [30]. In our study, IS was the only UT that had a significant reduction in 6 months. However, we observed that 35% and 40% of patients had a decrease in PCS and in IAA, respectively, although the results did not reach statistical significance. Patients who experienced such reduction had few/no changes in inflammatory, BMD, and endothelin biomarkers (data not shown).
IS acts as a bone toxin by inhibiting osteoblast differentiation and inducing apoptosis via the caspase pathway [31]. Hence, IS causes bone metabolism disorders by disturbing the osteoblast and/or osteoclast activities [14]. The accumulated IS plays an important role in deteriorating bone mechanical properties in rats by altering the chemical composition of bone, indicating that uremia impairs bone elasticity [32], decreases the osteoblast Wnt/b-catenin signaling and increases the expression of Wnt signaling inhibitors, such as sclerostin and Dickkopf-1 (DKK1) [33]. IS induces skeletal resistance to PTH in cultured osteoblastic cells [34]. We found a reduction in IS, but not in serum levels of sclerostin and FGF-23. Corroborating our findings, Uhlin et al., have observed that FGF-23 remained unchanged after OL-HDF beginning [35]. In contrast, Patrier et al., have evaluated HD versus OL-HDF and observed a significant reduction in FGF-23 in the OL-HDF group [36]. It is worth mentioning that the treatment period was longer, and the population studied consisted of younger patients than those included in our study. Lips et al., have observed a reduction in sclerostin levels after one year and suggested that a high convection volume is needed to achieve such result [37].
We have observed a positive correlation between IS and PTH. Liu WC et al. have reported that IS accumulation leads to bone loss, by causing inhibition of bone turnover, a mechanism not fully understood [33]. In addition, it has been reported that IS can enhance the activity of 24-hydroxylase (CYP24A1) and cause degradation of 25-hydroxyvitamin D and active vitamin D, thereby reducing the concentration of calcitriol [38]. In our study we did not measure 24-hydroxylase to support this hypothesis.
IS stimulates endothelial [39] and vascular injury [40], and the expression of inflammatory proteins [41]. The increase in circulating endothelial extracellular vesicles and high serum levels of OPN is associated with vascular disorders and cardiovascular risk in patients with CKD [42]. In our study, we found no difference in OPN after 6-months of OL-HDF. Likewise, Uhlin et al., have evaluated 35 patients for 6, 12, and 24 months after switching from HD to OL-HDF and did not find a significant difference in OPN levels [43].
We investigated for the first time the impact of OL-HDF on endothelin-1, an endothelial injury biomarker. Endothelin-1 did not correlate with UTs and remained unchanged after 6 months of OL-HDF. In contrast, Jia et al. have evaluated 20 patients comparing HD and OL-HDF and observed an improvement in endothelial function [19]. Rebic et al., in a 1-year prospective longitudinal study, have observed a significant reduction in Endothelin-1 in incident patients on peritoneal dialysis (PD) [44]. Therefore, the removal of endothelin-1 by dialysis treatments and its effects are not fully clarified.
We found no reduction in serum concentrations of inflammatory biomarkers after 6-months from OL-HDF. Some authors have reported that IAA correlated with CRP [45,46]. Agbas et al., have observed a significant reduction in CRP, but no difference for IL-6 and IL-10 [47]. Jia et al. have demonstrated that IL-6 was significantly reduced in OL-HDF versus HD, but no difference was found in CRP levels [19]. Kuo et al. have observed a significant reduction in plasma levels of IL-18 and TNF-a, with no change in CRP and IL-6 levels in patients < 65 years old treated by OL-HDF [21]. Morad et al., in a pediatric population, observed a significant reduction in CRP, IL-6, and TNF-α compared to HD [48]. None of these studies were designed to older patients. Although OL-HDF dialysis treatments are considered better than HD to remove middle molecule size, conflicting results have been reported [48,49,50,51,52]. These results may suggest that inflammatory markers tend to behave differently in the elderly, regardless of the treatment applied [53,54].
Our results should be interpreted with caution due to the small sample size and must be confirmed in a larger study. However, it should be emphasized that OL-HDF in Brazil is still a modest dialysis modality since only private health insurance covered it and most patients do not have it. The dialysis unit from the Hospital Sancta Maggiore offers OL-HDF for all patients allowing this current research to be done. Nonetheless, data generated in Brazil might help grow the literature giving a scientific background to improve the access to this modality to other patients. In addition, there is still a paucity of data on older patients, a population that has increased in prevalence worldwide among those on renal replacement therapy. The current study is, to our knowledge, the first to include specifically older patients on hemodiafiltration. The follow-up of 6 months for older patients on dialysis is adequate to test the impact of toxin removal but short for other endpoints such as cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. In summary, this prospective observational study demonstrated that OL-HDF was capable to reduce IS in older patients. Whether this reduction may have an impact on clinical outcomes deserve further evaluation.
4. Patients and Methods
4.1. Study Design
This is a prospective observational study that evaluated older patients on OL-HDF at baseline and after 6 months. The STROBE checklist [55] was used for this prospective observational study. This study was approved by the Ethical Advisory Committee of the Universidade Nove de Julho/UNINOVE: C.A.A.E# 97475918.5.0000.5511. All patients provided written informed consent.
4.2. Patients
Thirty-one clinically stable patients (n = 31) aged >65 years were continually included. They were recruited at the Hospital Sancta Maggiore, in the period between June 2020 and November 2021. Inclusion criteria were patients with CKD aged >65 years, on OL-HDF, within the first 90 days on renal replacement therapy. No inclusion criteria were: chronic liver disease, auto-immune disease (i.e., systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis), congestive heart failure (Stages III/IV), chronic degenerative neurological disease, chronic use of corticosteroids, use of topical or systemic hormonal therapy, morbid obesity, severe peripheral vascular insufficiency, history of infection and/or inflammation within the latest 1 month, hepatitis B, HIV and/or C virus infection, current COVID-19, current malignancy, and use of antibiotics or anti-inflammatory drugs for less than 1 month before study entry.
Before starting the first OL-HDF session (Pre-OL-HDF) and after 6-months on OL-HDF (Pos-OL-HDF), 20 mL of blood was collected for evaluation of bound protein uremic toxins (IS, PCS, IAA); inflammation markers (PCR, IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-10); endothelial lesion marker (endothelin), endothelial calcification (osteopontin) and bone mineral disease markers (phosphate (Pi), calcium (Ca), PTH, 25(OH)D vitamin (Vit D), sclerostin (SOST), and FGF-23.
4.3. OL-HDF Treatment
OL-HDF was post-dilution, aiming whenever possible convection volume ≥ 22 L/treatment, using high-flux and high efficiency dialyzer (polysulfone model FX100, Fresenius Medical Care®, Bad Homburg, Germany). The blood flow was set at 350 mL/min and dialysate flow at 500 mL/min, adjusted according to the adapt flow sensor of the dialysis machines (Model 5008 Fresenius Medical Care®). Dialysis duration and frequency were adjusted according to the presence of residual renal function. All patients received continuous heparin as an anticoagulant during the procedure.
The composition of the dialysis solution used was CPHD with Glucose 23G/44—(Fresenius Medical Care®) with the following composition: pH: 5.2; Glucose: 1.5%, 2.5% and 4.5%; Calcium: 3.5 mEq/L or 2.5 mEq/L; Potassium: ZERO mEq/L; Sodium: 132 mEq/L or 134 mEq/L; Magnesium: 0.5 mEq/L; Chloride: 96 mEq/L or 101 mEq/L; Lactate: 40 mEq/L.
4.4. Laboratory Methods
Biochemical Parameters
Routine laboratory analyses including serum creatinine measured by a kinetic colorimetric assay based on the Jaffe method (reference/sensitivity 04810716190/0.17 mg/dL), urea by urease (reference/sensitivity 04460715190/3.0 mg/dL), sodium (reference/sensitivity 10825468001/80 mEq/L), and potassium (reference/sensitivity 10825441001/1.5 mEq/L) by Ion Selective Electrode—ISE, calcium by o-cresolftalein (reference/sensitivity 05061482190/0.8 mg/dL), phosphate by UV molybdate (reference/sensitivity 03183793122/0.31 mg/dL), albumin by bromocresol green (reference/sensitivity 03183688122/0.2 g/dL), glucose by hexokinase (reference/sensitivity 04404483190/2.0 mg/dL alkaline phosphatase (alk-p) by International Federation of Clinical Chemistry—IFCC (reference/sensitivity 03333752190/5.0 U/L), intact parathyroid hormone (iPTH) (reference/sensitivity 11972103122/6.0 pg/mL) and vitamin D (reference/sensitivity 07464215190/3.0 ng/mL) by electrochemiluminescence, and high-sensitive C reactive protein (hsCRP) by immunoturbidimetry (reference/sensitivity 04628918190/0.30 mg/L), on the Cobas® 6000 modular platform (Roche Diagnóstica), were performed at pre-OL-HDF and pos-OL-HDF.
4.5. Inflammatory, Endothelial, and Bone Disease Biomarkers
After blood collection according to the study design, a 10 mL aliquot was centrifuged, and the serum was separated and stored in a −80 °C freezer for biomarkers measurement.
IL-6 was measured by ELISA (Quantikine Human hsIL-6, catalog HS600C, R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA), and the intra- and inter-assay CVs were <5% and <7%, respectively. The TNF-α was determined by ELISA (Quantikine Human hsTNF-α, catalog HSTA00E, R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA), and the intra- and inter-assay CVs were <5% and <7%, respectively. The IL-10 was measured by ELISA (Quantikine Human hs IL-10, catalog HS100C, R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA), and the intra- and inter-assay CVs were <5% and <7%, respectively. The endothelin was measured by ELISA (Quantikine Human hs endothelin, catalog DET100, R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA), and the intra- and inter-assay CVs were <6% and <8%, respectively. The osteopontin was measured by ELISA (Quantikine Human osteopontin, catalog DOST00, R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA), and the intra- and inter-assay CVs were <6% and <8%, respectively. The sclerostin was measured by ELISA (Quidel Corp., catalog TE1023HS, San Diego, CA, USA), and the intra- and inter-assay CVs were <6% and <8%, respectively. The FGF-23 was determined by ELISA (Immunotopics Inc. catalog 60–6600, San Diego, CA, USA), and the intra and inter-assay CVs were <6% and <8%, respectively. All serum levels of biomarkers were measured according to the manufactory’s instructions.
Uremic Toxins
Blood samples were centrifuged at 2500 rpm for 15 min and stored at −80 °C. Serum (total and free fractions) IS, PCS, and IAA were quantified by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescent detection, as described by Borges et al. [46].
4.6. Statistical Methods
Data normality was verified by the Shapiro-Wilk test. Continuous numeric variables were expressed according to their parametric or nonparametric distribution, as mean and standard deviation or median and percentiles (25–75%), respectively. Categorical data is described as absolute values and percentages of the total sample. Analyses between baseline and 6 months were performed using the paired T-test or Wilcoxon test, as appropriated. The correlation between independent variables was analyzed using the Pearson or Spearman test, when appropriate.
A significance level of 5% (p < 0.05) was established for the statistical tests. Analyzes were performed using IBM SPSS STATISTICS software for Windows (IBM Corp., Armank, NY, USA) version 25.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.M.E. and M.A.D.; Data curation, A.M.-J.; Formal analysis, P.N.B.C.; Funding acquisition, M.A.D.; Investigation, A.M.-J.; Methodology, L.S.N.; Project administration, M.A.D.; Resources, V.C.F.; Software, A.M.-J.; Supervision, M.A.D.; Validation, W.P.P. and L.C.d.A.S.; Visualization, T.J.M.G. and F.K.; Writing—original draft, A.M.-J.; Writing—review & editing, M.A.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior—Brasil (CAPES)—Finance Code [001] and Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP)—Project [2019/07105-9].
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethical Advisory Committee of the Universidade Nove de Julho/UNINOVE: C.A.A.E# 97475918.5.0000.5511.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bikbov, B.; Purcell, C.A.; Levey, A.S.; Smith, M.; Abdoli, A.; Abebe, M.; Adebayo, O.M.; Afarideh, M.; Agarwal, S.K.; Agudelo-Botero, M.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of chronic kidney disease, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2020, 395, 709–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanholder, R.; Van Laecke, S.; Glorieux, G. What is new in uremic toxicity? Pediatr. Nephrol. 2008, 23, 1211–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikuchi, K.; Itoh, Y.; Tateoka, R.; Ezawa, A.; Murakami, K.; Niwa, T. Metabolomic analysis of uremic toxins by liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2010, 878, 1662–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bindroo, S.; Quintanilla Rodriguez, B.S.; Challa, H.J. Renal Failure. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Maheshwari, V.; Tao, X.; Thijssen, S.; Kotanko, P. Removal of Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins Using Binding Competitors in Hemodialysis: A Narrative Review. Toxins 2021, 13, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madero, M.; Cano, K.B.; Campos, I.; Tao, X.; Maheshwari, V.; Brown, J.; Cornejo, B.; Handelman, G.; Thijssen, S.; Kotanko, P. Removal of Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins during Hemodialysis Using a Binding Competitor. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 14, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocchetti, M.T.; Cosola, C.; Ranieri, E.; Gesualdo, L. Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins and Immunity. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2325, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, H.; Goto, S.; Fukagawa, M. Role of Uremic Toxins for Kidney, Cardiovascular, and Bone Dysfunction. Toxins 2018, 10, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harlacher, E.; Wollenhaupt, J.; Baaten, C.; Noels, H. Impact of Uremic Toxins on Endothelial Dysfunction in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreto, F.C.; Stinghen, A.E.; de Oliveira, R.B.; Franco, A.T.; Moreno, A.N.; Barreto, D.V.; Pecoits-Filho, R.; Drüeke, T.B.; Massy, Z.A. The quest for a better understanding of chronic kidney disease complications: An update on uremic toxins. J. Bras. Nefrol. 2014, 36, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meert, N.; Schepers, E.; Glorieux, G.; Van Landschoot, M.; Goeman, J.L.; Waterloos, M.A.; Dhondt, A.; Van der Eycken, J.; Vanholder, R. Novel method for simultaneous determination of p-cresylsulphate and p-cresylglucuronide: Clinical data and pathophysiological implications. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27, 2388–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanholder, R.; Schepers, E.; Pletinck, A.; Nagler, E.V.; Glorieux, G. The uremic toxicity of indoxyl sulfate and p-cresyl sulfate: A systematic review. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 25, 1897–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, T.; Katsuki, S.; Chen, M.; Decano, J.L.; Halu, A.; Lee, L.H.; Pestana, D.V.S.; Kum, A.S.T.; Kuromoto, R.K.; Golden, W.S.; et al. Uremic Toxin Indoxyl Sulfate Promotes Proinflammatory Macrophage Activation Via the Interplay of OATP2B1 and Dll4-Notch Signaling. Circulation 2019, 139, 78–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mozar, A.; Louvet, L.; Godin, C.; Mentaverri, R.; Brazier, M.; Kamel, S.; Massy, Z.A. Indoxyl sulphate inhibits osteoclast differentiation and function. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27, 2176–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, S.; Fukagawa, M. Uremic Toxicity and Bone in CKD. J. Nephrol. 2017, 30, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzaferro, S.; Bagordo, D.; De Martini, N.; Pasquali, M.; Rotondi, S.; Tartaglione, L.; Stenvinkel, P. Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Bone in Chronic Kidney Disease in the Osteoimmunology Era. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2021, 108, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamprom, W.; Tawonsawatruk, T.; Mas-Oodi, S.; Anansilp, K.; Rattanasompattikul, M.; Supokawej, A. P-cresol and Indoxyl Sulfate Impair Osteogenic Differentiation by Triggering Mesenchymal Stem Cell Senescence. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 18, 744–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desjardins, L.; Liabeuf, S.; Oliveira, R.B.; Louvet, L.; Kamel, S.; Lemke, H.D.; Vanholder, R.; Choukroun, G.; Massy, Z.A. Uremic toxicity and sclerostin in chronic kidney disease patients. Nephrol. Ther. 2014, 10, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, P.; Jin, W.; Teng, J.; Zhang, H.; Zou, J.; Liu, Z.; Shen, B.; Cao, X.; Ding, X. Acute Effects of Hemodiafiltration Versus Conventional Hemodialysis on Endothelial Function and Inflammation: A Randomized Crossover Study. Medicine 2016, 95, e3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locatelli, F.; Manzoni, C.; Viganò, S.; Cavalli, A.; Di Filippo, S. Hemodiafiltration-state of the art. Contrib. Nephrol. 2011, 168, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, H.L.; Chou, C.Y.; Liu, Y.L.; Yang, Y.F.; Huang, C.C.; Lin, H.H. Reduction of pro-inflammatory cytokines through hemodiafiltration. Ren. Fail. 2008, 30, 796–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Hoedt, C.H.; Bots, M.L.; Grooteman, M.P.; van der Weerd, N.C.; Mazairac, A.H.; Penne, E.L.; Levesque, R.; ter Wee, P.M.; Nubé, M.J.; Blankestijn, P.J.; et al. Online hemodiafiltration reduces systemic inflammation compared to low-flux hemodialysis. Kidney Int. 2014, 86, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- den Hoedt, C.H.; Mazairac, A.H.A.; van den Dorpel, M.A.; Grooteman, M.P.C.; Blankestijn, P.J. Effect of hemodiafiltration on mortality, inflammation and quality of life. Contrib. Nephrol. 2011, 168, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panichi, V.; Rizza, G.M.; Paoletti, S.; Bigazzi, R.; Aloisi, M.; Barsotti, G.; Rindi, P.; Donati, G.; Antonelli, A.; Panicucci, E.; et al. Chronic inflammation and mortality in haemodialysis: Effect of different renal replacement therapies. Results from the RISCAVID study. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2008, 23, 2337–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bateman, R.M.; South Yorkshire Hospitals Research Collaboration; Sharpe, M.D.; Jagger, J.E.; Ellis, C.G.; Solé-Violán, J.; López-Rodríguez, M.; Herrera-Ramos, E.; Ruíz-Hernández, J.; Borderías, L.; et al. 36th International Symposium on Intensive Care and Emergency Medicine. Crit. Care 2016, 20, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnani, S.; Atti, M. Uremic Toxins and Blood Purification: A Review of Current Evidence and Future Perspectives. Toxins 2021, 13, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panichi, V.; Rocchetti, M.T.; Scatena, A.; Rosati, A.; Migliori, M.; Pizzarelli, F.; Gesualdo, L. Long term variation of serum levels of uremic toxins in patients treated by post-dilution high volume on-line hemodiafiltration in comparison to standard low-flux bicarbonate dialysis: Results from the REDERT study. J. Nephrol. 2017, 30, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieter, D.H.; Hackl, A.; Rodriguez, A.; Chenine, L.; Moragues, H.L.; Lemke, H.D.; Wanner, C.; Canaud, B. Protein-bound uraemic toxin removal in haemodialysis and post-dilution haemodiafiltration. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2010, 25, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thammathiwat, T.; Tiranathanagul, K.; Limjariyakul, M.; Chariyavilaskul, P.; Takkavatakarn, K.; Susantitaphong, P.; Meesangnin, S.; Wittayalertpanya, S.; Praditpornsilpa, K.; Eiam-Ong, S. Super high-flux hemodialysis provides comparable effectiveness with high-volume postdilution online hemodiafiltration in removing protein-bound and middle-molecule uremic toxins: A prospective cross-over randomized controlled trial. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2021, 25, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieter, D.H.; Kerwagen, S.; Rüth, M.; Lemke, H.D.; Wanner, C. Differences in Dialysis Efficacy Have Limited Effects on Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins Plasma Levels over Time. Toxins 2019, 11, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Kwak, K.A.; Gil, H.W.; Song, H.Y.; Hong, S.Y. Indoxyl sulfate promotes apoptosis in cultured osteoblast cells. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2013, 14, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, Y.; Kazama, J.J.; Yamato, H.; Shimoda, H.; Fukagawa, M. Accumulated uremic toxins attenuate bone mechanical properties in rats with chronic kidney disease. Bone 2013, 57, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.C.; Wu, C.C.; Lim, P.S.; Chien, S.W.; Hou, Y.C.; Zheng, C.M.; Shyu, J.F.; Lin, Y.F.; Lu, K.C. Effect of uremic toxin-indoxyl sulfate on the skeletal system. Clin. Chim. Acta 2018, 484, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nii-Kono, T.; Iwasaki, Y.; Uchida, M.; Fujieda, A.; Hosokawa, A.; Motojima, M.; Yamato, H.; Kurokawa, K.; Fukagawa, M. Indoxyl sulfate induces skeletal resistance to parathyroid hormone in cultured osteoblastic cells. Kidney Int. 2007, 71, 738–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhlin, F.; Magnusson, P.; Larsson, T.E.; Fernström, A. In the backwater of convective dialysis: Decreased 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels following the switch to online hemodiafiltration. Clin. Nephrol. 2015, 83, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patrier, L.; Dupuy, A.M.; Granger Vallée, A.; Chalabi, L.; Morena, M.; Canaud, B.; Cristol, J.P. FGF-23 removal is improved by on-line high-efficiency hemodiafiltration compared to conventional high flux hemodialysis. J. Nephrol. 2013, 26, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lips, L.; de Roij van Zuijdewijn, C.L.M.; Ter Wee, P.M.; Bots, M.L.; Blankestijn, P.J.; van den Dorpel, M.A.; Fouque, D.; de Jongh, R.; Pelletier, S.; Vervloet, M.G.; et al. Serum sclerostin: Relation with mortality and impact of hemodiafiltration. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2017, 32, 1217–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Gao, Z.; Gao, Y. Upregulation of nuclear factor-κB activity mediates CYP24 expression and reactive oxygen species production in indoxyl sulfate-induced chronic kidney disease. Nephrology 2016, 21, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, R.S.D.; Santos, A.F.; Barreto, F.C.; Stinghen, A.E.M. How do Uremic Toxins Affect the Endothelium? Toxins 2020, 12, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adijiang, A.; Goto, S.; Uramoto, S.; Nishijima, F.; Niwa, T. Indoxyl sulphate promotes aortic calcification with expression of osteoblast-specific proteins in hypertensive rats. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2008, 23, 1892–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buendía, P.; Montes de Oca, A.; Madueño, J.A.; Merino, A.; Martín-Malo, A.; Aljama, P.; Ramírez, R.; Rodríguez, M.; Carracedo, J. Endothelial microparticles mediate inflammation-induced vascular calcification. Faseb J. 2015, 29, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzen, J.; Kramer, R.; Kliem, V.; Bode-Boeger, S.M.; Veldink, H.; Haller, H.; Fliser, D.; Kielstein, J.T. Circulating levels of osteopontin are closely related to glomerular filtration rate and cardiovascular risk markers in patients with chronic kidney disease. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 40, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhlin, F.; Fernström, A.; Knapen, M.H.J.; Vermeer, C.; Magnusson, P. Long-term follow-up of biomarkers of vascular calcification after switch from traditional hemodialysis to online hemodiafiltration. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2019, 79, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebic, D.; Rasic, S.; Rebic, V. Influence of endothelin-1 and nitric oxide on left ventricular remodelling in patients on peritoneal dialysis. Ren. Fail. 2014, 36, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, L.; Sallée, M.; Cerini, C.; Poitevin, S.; Gondouin, B.; Jourde-Chiche, N.; Fallague, K.; Brunet, P.; Calaf, R.; Dussol, B.; et al. The cardiovascular effect of the uremic solute indole-3 acetic acid. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 876–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, N.A.; Barros, A.F.; Nakao, L.S.; Dolenga, C.J.; Fouque, D.; Mafra, D. Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins from Gut Microbiota and Inflammatory Markers in Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Ren. Nutr. 2016, 26, 396–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ağbaş, A.; Canpolat, N.; Çalışkan, S.; Yılmaz, A.; Ekmekçi, H.; Mayes, M.; Aitkenhead, H.; Schaefer, F.; Sever, L.; Shroff, R. Hemodiafiltration is associated with reduced inflammation, oxidative stress and improved endothelial risk profile compared to high-flux hemodialysis in children. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morad, A.A.; Bazaraa, H.M.; Abdel Aziz, R.E.; Abdel Halim, D.A.; Shoman, M.G.; Saleh, M.E. Role of online hemodiafiltration in improvement of inflammatory status in pediatric patients with end-stage renal disease. Iran. J. Kidney Dis. 2014, 8, 481–485. [Google Scholar]
- Panichi, V.; Manca-Rizza, G.; Paoletti, S.; Taccola, D.; Consani, C.; Filippi, C.; Mantuano, E.; Sidoti, A.; Grazi, G.; Antonelli, A.; et al. Effects on inflammatory and nutritional markers of haemodiafiltration with online regeneration of ultrafiltrate (HFR) vs online haemodiafiltration: A cross-over randomized multicentre trial. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2006, 21, 756–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filiopoulos, V.; Hadjiyannakos, D.; Metaxaki, P.; Sideris, V.; Takouli, L.; Anogiati, A.; Vlassopoulos, D. Inflammation and oxidative stress in patients on hemodiafiltration. Am. J. Nephrol. 2008, 28, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaslaki, L.R.; Berta, K.; Major, L.; Weber, V.; Weber, C.; Wojke, R.; Passlick-Deetjen, J.; Falkenhagen, D. On-line hemodiafiltration does not induce inflammatory response in end-stage renal disease patients: Results from a multicenter cross-over study. Artif. Organs 2005, 29, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carracedo, J.; Merino, A.; Nogueras, S.; Carretero, D.; Berdud, I.; Ramírez, R.; Tetta, C.; Rodríguez, M.; Martín-Malo, A.; Aljama, P. On-line hemodiafiltration reduces the proinflammatory CD14+CD16+ monocyte-derived dendritic cells: A prospective, crossover study. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 2315–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krabbe, K.S.; Pedersen, M.; Bruunsgaard, H. Inflammatory mediators in the elderly. Exp. Gerontol. 2004, 39, 687–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brüünsgaard, H.; Pedersen, B.K. Age-related inflammatory cytokines and disease. Immunol. Allergy Clin. N. Am. 2003, 23, 15–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuschieri, S. The STROBE guidelines. Saud. J. Anaesth. 2019, 13, S31–S34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).