Enterococcus and COVID-19: The Emergence of a Perfect Storm?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
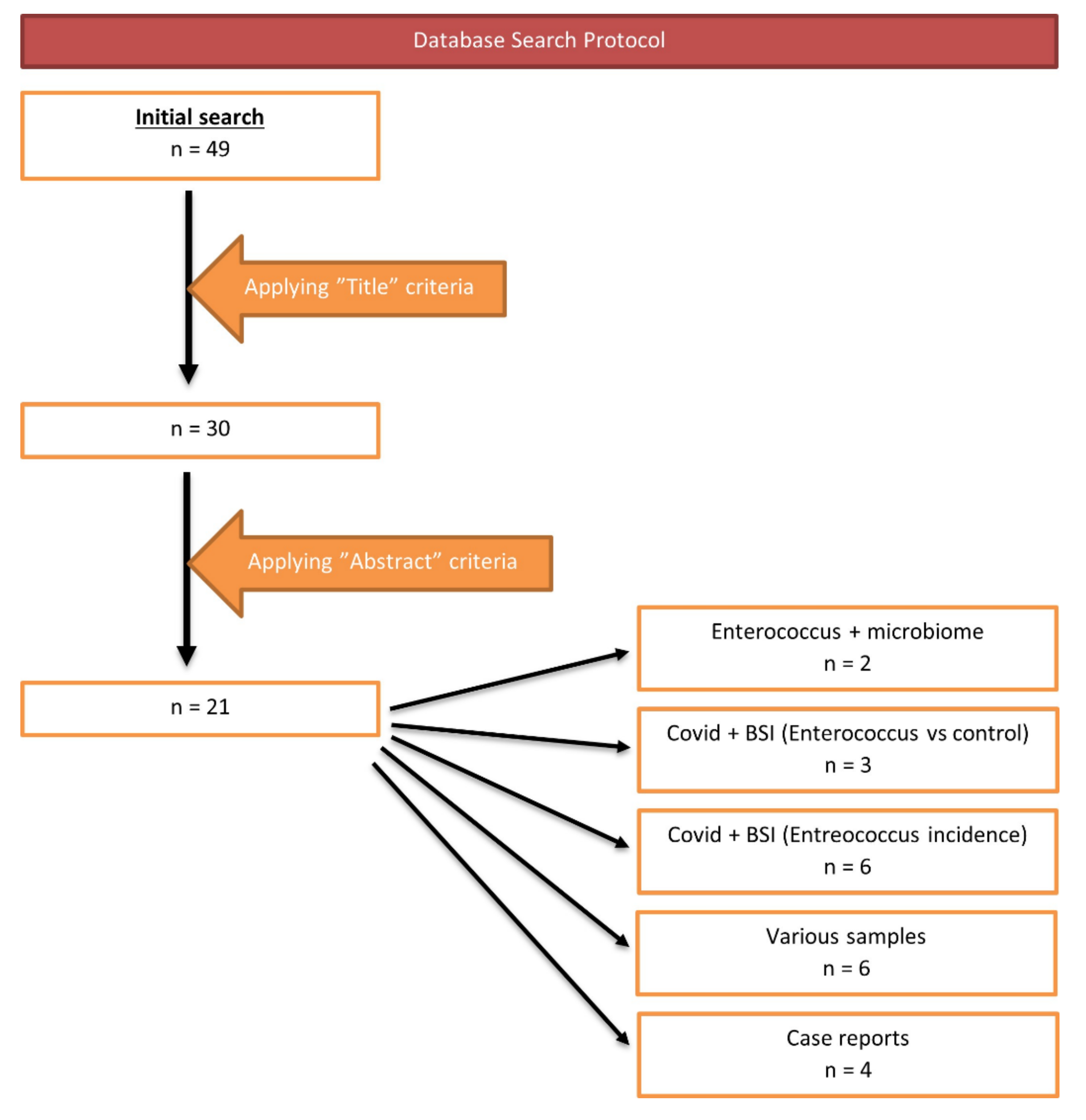
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Enterococcus and Bloodstream Infections
4.2. Enterococcus from Various Samples from COVID-19 Patients
4.3. Enterococcus and Gut Microbiota of COVID-19 Patients
4.4. Enterococcus and COVID-19—Case Reports
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Joshi, A.; Kaur, M.; Kaur, R.; Grover, A.; Nash, D.; El-Mohandes, A. Predictors of COVID-19 Vaccine Acceptance, Intention, and Hesitancy: A Scoping Review. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 698111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberg, O.; Martiny, D.; Rochas, O.; van Belkum, A.; Kozlakidis, Z. Considerations for diagnostic COVID-19 tests. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Oosterhout, C.; Hall, N.; Ly, H.; Tyler, K.M. COVID-19 Evolution during the Pandemic–Implications of New SARS-CoV-2 Variants on Disease Control and Public Health Policies; Bellwether Publishing, Ltd.: Columbia, MD, USA, 2021; Volume 12, pp. 507–508. [Google Scholar]
- Bender, J.K.; Cattoir, V.; Hegstad, K.; Sadowy, E.; Coque, T.M.; Westh, H.; Hammerum, A.M.; Schaffer, L.; Burns, K.; Murchan, S.; et al. Update on prevalence and mechanisms of resistance to linezolid, tigecycline and daptomycin in Enterococci in Europe: Towards a common nomenclature. Drug Resist. Updates 2018, 40, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egan, S.A.; Shore, A.C.; O’Connell, B.; Brennan, G.I.; Coleman, D.C. Linezolid resistance in Enterococcus faecium and Enterococcus faecalis from hospitalized patients in Ireland: High prevalence of the MDR genes optrA and poxtA in isolates with diverse genetic backgrounds. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 1704–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hal, S.J.; Willems, R.J.L.; Gouliouris, T.; Ballard, S.A.; Coque, T.M.; Hammerum, A.M.; Hegstad, K.; Westh, H.T.; Howden, B.P.; Malhotra-Kumar, S.; et al. The global dissemination of hospital clones of Enterococcus faecium. Genome Med. 2021, 13, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.G.; Becattini, S.; Moody, T.U.; Shliaha, P.V.; Littmann, E.R.; Seok, R.; Gjonbalaj, M.; Eaton, V.; Fontana, E.; Amoretti, L.; et al. Microbiota-derived lantibiotic restores resistance against vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus. Nature 2019, 572, 665–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toc, D.A.; Pandrea, S.L.; Botan, A.; Mihaila, R.M.; Costache, C.A.; Colosi, I.A.; Junie, L.M. Enterococcus raffinosus, Enterococcus durans and Enterococcus avium Isolated from a Tertiary Care Hospital in Romania—Retrospective Study and Brief Review. Biology 2022, 11, 598. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2079-7737/11/4/598 (accessed on 21 April 2022). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrisette, T.; Lev, K.L.; Kebriaei, R.; Abdul-Mutakabbir, J.C.; Stamper, K.C.; Morales, S.; Lehman, S.M.; Canfield, G.S.; Duerkop, B.A.; Arias, C.A.; et al. Bacteriophage-Antibiotic Combinations for Enterococcus faecium with Varying Bacteriophage and Daptomycin Susceptibilities. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, e00993-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monticelli, J.; Knezevich, A.; Luzzati, R.; di Bella, S. Clinical management of non-faecium non-faecalis vancomycin-resistant Enterococci infection. Focus on Enterococcus gallinarum and Enterococcus casseliflavus/flavescens. J. Infect. Chemother. 2018, 24, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campanini-Salinas, J.; Andrades-Lagos, J.; Rocha, G.G.; Choquesillo-Lazarte, D.; Dragnic, S.B.; Faúndez, M.; Alarcon, P.; Silva, F.; Vidal, R.; Salas-Huenuleo, E.; et al. A new kind of quinonic-antibiotic useful against multidrug-resistant S. aureus and E. faecium Infections. Molecules 2018, 23, 1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aktas, B.; Aslim, B. Gut-lung axis and dysbiosis in COVID-19. Turk. J. Biol. 2020, 44, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva, A.; Miele, M.C.; di Timoteo, F.; de Angelis, M.; Mauro, V.; Aronica, R.; Al Ismail, D.; Ceccarelli, G.; Pinacchio, C.; d’Ettorre, G.; et al. Persistent Systemic Microbial Translocation and Intestinal Damage During Coronavirus Disease-19. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaibani, P.; D’Amico, F.; Bartoletti, M.; Lombardo, D.; Rampelli, S.; Fornaro, G.; Coladonato, S.; Siniscalchi, A.; Re, M.C.; Viale, P.; et al. The Gut Microbiota of Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 670424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Shi, X.; Fu, W.; Xiang, F.; He, X.; Yang, B.; Wang, X.; Ma, W.-L. Gut microbiota dysbiosis correlates with abnormal immune response in moderate COVID-19 patients with fever. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 2619–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, S.; Troise, O.; Donaldson, H.; Mughal, N.; Moore, L.S.P. Bacterial and fungal coinfection among hospitalized patients with COVID-19: A retrospective cohort study in a UK secondary-care setting. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 1395–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeVoe, C.; Segal, M.R.; Wang, L.; Stanley, K.; Madera, S.; Fan, J.; Schouest, J.; Graham-Ojo, R.; Nichols, A.; Prasad, P.A.; et al. Increased rates of secondary bacterial infections, including Enterococcus bacteremia, in patients hospitalized with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2021, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuntrò, M.; Manisco, A.; Guarneri, D.; Zuglian, G.; Vailati, F.; Passera, M.; Cavallini, M.; Raglio, A.; Farina, C. Blood stream infections during the first wave of COVID-19. A short microbiological retrospective picture at Papa Giovanni XXIII Hospital, Bergamo, Italy. New Microbiol. 2021, 44, 51–58. [Google Scholar]
- Giacobbe, D.R.; Battaglini, D.; Ball, L.; Brunetti, I.; Bruzzone, B.; Codda, G.; Crea, F.; de Maria, A.; Dentone, C.; di Biagio, A.; et al. Bloodstream infections in critically ill patients with COVID-19. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 50, e13319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanisamy, N.; Vihari, N.; Meena, D.S.; Kumar, D.; Midha, N.; Tak, V.; Sharma, A.; Bohra, G.K.; Kothari, N.; Dutt, N.; et al. Clinical profile of bloodstream infections in COVID-19 patients: A retrospective cohort study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abelenda-Alonso, G.; Rombauts, A.; Gudiol, C.; Oriol, I.; Simonetti, A.; Coloma, A.; Rodríguez-Molinero, A.; Izquierdo, E.; Díaz-Brito, V.; Sanmartí, M.; et al. Immunomodulatory therapy, risk factors and outcomes of hospital-acquired bloodstream infection in patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia: A Spanish case–control matched multicentre study (BACTCOVID). Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 1685–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posteraro, B.; de Angelis, G.; Menchinelli, G.; D’inzeo, T.; Fiori, B.; de Maio, F.; Cortazzo, V.; Sanguinetti, M.; Spanu, T. Risk factors for mortality in adult COVID-19 patients who develop bloodstream infections mostly caused by antimicrobial-resistant organisms: Analysis at a large teaching hospital in italy. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonazzetti, C.; Morena, V.; Giacomelli, A.; Oreni, L.; Casalini, G.; Galimberti, L.R.; Bolis, M.; Rimoldi, M.; Ballone, E.; Colombo, R.; et al. Unexpectedly High Frequency of Enterococcal Bloodstream Infections in Coronavirus Disease 2019 Patients Admitted to an Italian ICU: An Observational Study. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 49, E31–E40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Signorini, L.; Moioli, G.; Calza, S.; van Hauwermeiren, E.; Lorenzotti, S.; del Fabro, G.; Renisi, G.; Lanza, P.; Saccani, B.; Zambolin, G.; et al. Epidemiological and Clinical Characterization of Superinfections in Critically Ill Coronavirus Disease 2019 Patients. Crit. Care Explor. 2021, 3, e0430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampmeier, S.; Tönnies, H.; Correa-Martinez, C.L.; Mellmann, A.; Schwierzeck, V.A. Nosocomial cluster of vancomycin resistant Enterococci among COVID-19 patients in an intensive care unit. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2020, 9, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Toole, R.F. The interface between COVID-19 and bacterial healthcare-associated infections. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 1772–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senok, A.; Alfaresi, M.; Khansaheb, H.; Nassar, R.; Hachim, M.; al Suwaidi, H.; Almansoori, M.; Alqaydi, F.; Afaneh, Z.; Mohamed, A.; et al. Coinfections in patients hospitalized with COVID-19: A descriptive study from the United Arab Emirates. Infect. Drug Resist. 2021, 14, 2289–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cultrera, R.; Barozzi, A.; Libanore, M.; Marangoni, E.; Pora, R.; Quarta, B.; Spadaro, S.; Ragazzi, R.; Marra, A.; Sagala, D.; et al. Co-infections in critically ill patients with or without COVID-19: A comparison of clinical microbial culture findings. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeed, N.K.; Al-Khawaja, S.; Alsalman, J.; Almusawi, S.; Albalooshi, N.A.; Al-Biltagi, M. Bacterial co-infection in patients with SARS-CoV-2 in the Kingdom of Bahrain. World J. Virol. 2021, 10, 168–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderaro, A.; Buttrini, M.; Montecchini, S.; Piccolo, G.; Martinelli, M.; Dell’Anna, M.L.; Maio, A.D.; Arcangeletti, M.C.; Maccari, C.; de Conto, F.; et al. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 and other infectious agents in lower respiratory tract samples belonging to patients admitted to intensive care units of a tertiary-care hospital, located in an epidemic area, during the italian lockdown. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, L.T.W.; Beraldo, G.L.; Brito, V.M.; Rosa, M.E.E.; Matos, M.J.R.; de Fonseca, E.K.U.N.; Yokoo, P.; Silva, M.M.A.; Teles, G.B.D.S.; Shoji, H.; et al. Lung cavitation in COVID-19: Co-infection complication or rare evolution? Einstein (Sao Paulo) 2020, 18, eAI5822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Martínez, A.; Fernández-Cruz, A.; Domínguez, F.; Forteza, A.; Cobo, M.; Sánchez-Romero, I.; Asensio, A. Hospital-acquired infective endocarditis during COVID-19 pandemic. Infect. Prev. Pract. 2020, 2, 100080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano, O.K.; Kutzler, H.L.; Rochon, C.; Radojevic, J.A.; Lawlor, M.T.; Hammond, J.A.; Gluck, J.; Feingold, A.D.; Jaiswal, A. Incidental COVID-19 in a heart-kidney transplant recipient with malnutrition and recurrent infections: Implications for the SARS-CoV-2 immune response. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2020, 22, e13367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, D.J.; Sutter, J.S.; Tatooles, A.; Suboc, T.M.; Rao, A.K. Endocarditis Complicated by Severe Aortic Insufficiency in a Patient with COVID-19: Diagnostic and Management Implications. Case Rep. Cardiol. 2020, 2020, 8844255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toc, D.A.; Costache, C.; Botan, A.; Mihaila, R.M.; Colosi, I.A.; Buksa, S.B.; Chiorescu, R.M. Mixed etiology COVID-19 associated pulmonary aspergillosis (Capa)—a case report and brief review of the literature. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toc, D.A.; Butiuc-Keul, A.L.; Iordache, D.; Botan, A.; Mihaila, R.M.; Costache, C.A.; Colosi, I.A.; Chiorean, C.; Neagoe, D.S.; Gheorghiu, L.; et al. Descriptive Analysis of Circulating Antimicrobial Resistance Genes in Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococcus (VRE) during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| No. | Author | Year | Country | Sample | Diagnostic Technique | COVID-19 Patients | Additional Information |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Gaibani, P. et al. [14] | 2021 | Italy | Stool sample | Illumina MiSeq | 69 | The GM of COVID-19 patients showed the enrichment of known or potential opportunistic pathogens, such as Enterococcus, Staphylococcus, Serratia and Collinsella (p value ≤ 0.02) |
| 2 | Zhou, Y. et al. [15] | 2021 | Republic of China | Stool sample | MagPure Stool DNA KF kit B | 127 | Saccharomyces and Enterococcus were significantly enriched in patients with fever |
| No. | Author | Year | Country | Diagnostic Technique | COVID-19 Patients | Non-COVID-19 Patients | Enterococcus Spp. of COVID-19 + | Enterococcus Spp. of COVID-19 − | E. Faecium | E. Faecalis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hughes, S. et al. [16] | 2020 | UK | MALDI-TOF | 836 | 216 | 1 (0.47%) | - | - | - |
| 2 | DeVoe, C. et al. [17] | 2021 | USA | MiSeq | 314 | 14,332 | 8 (2.6%) | 48 (0.3%) | 2 (0.6%) | 6 (1.9%) |
| 3 | Cuntrò, M. et al. [18] | 2021 | Italy | VITEK2 | 1911 | - | 106 (5.54%) | 56 (2.93%) | 32 (1.67%) | 74 (3.78%) |
| No. | Author | Year | Country | Diagnostic Technique | COVID-19 Patients | Enterococcus Spp. of COVID-19 + | E. Faecium | E. Faecalis | VRE | Other Resistances |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Giacobbe, D.R. et al. [19] | 2020 | Italy | VITEK-2 | 78 | 12/45 BSI (26.6%) | 4 (8.8%) | 8 (17.7%) | 1 VRE (E. faecium) | 4/4 E. faecium were ampicillin-resistant (100%) |
| 2 | Palanisamy, N. et al. [20] | 2021 | India | VITEK-2 | 750 | 11/64 BSI (17.2%) | - | - | 2 VRE | 81.8% of Enterococci were MDRO. Ampicillin (81.8%), Ciprofloxacin (81.8%), Tetracycline (54.5%), Erythromycin (90.9%), Teicoplanin (18.1%) |
| 3 | Abelenda-Alonso, G. et al. [21] | 2021 | Spain | - | 100 | 42/169 isolates (24.85%) | 10 (5.91%) | 32 (18.93%) | 1 VRE | - |
| 4 | Posteraro, B. et al. [22] | 2021 | Italy | MALDI-TOF | 293 | 15/58 BSI (20.7%) | 2 (3.44%) | 10 (17.24%) | - | - |
| 5 | Bonazzetti, C. et al. [23] | 2020 | Italy | VITEK MS MALDI-TOF | 89 | 53/93 BSI (55.8%) | 26 (27.95%) | 26 (27.95%) | 5 VRE (E. faecium) | - |
| 6 | Signorini, L. et al. [24] | 2021 | Italy | - | 92 | 6/57 BSI (10.5%) | - | - | 3 VRE | - |
| No. | Author | Year | Country | Sample | Diagnostic Technique | COVID-19 Patients | E. Faecium | E. Faecalis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Kampmeier, S. et al. [25] | 2020 | Germany | Blood culture samples and pleural drainage | MALDI-TOF-MS | 3 | 3 | - |
| 2 | O’Toole, R.F. et al. [26] | 2021 | Spain | Urine | - | 72 | 4 | - |
| Italy | Blood culture | - | 78 | - | 14 | |||
| 3 | Senok, A. et al. [27] | 2021 | United Arab Emirates | Blood and central-line cultures, endotracheal aspirates and urine | BioFire FilmArray | 29,802 | 10 | 18 |
| 4 | Cultrera, R. et al. [28] | 2021 | Italy | Blood, urine, or respiratory specimens obtained with bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) or bronchial aspirate (BASP)/BSI | MALDI-TOF by VITEK MS, VITEK 2 | 28 | 10 | 14 |
| 5 | Saeed, N.K. et al. [29] | 2021 | Kingdom of Bahrain | Blood culture, sputum culture, stool culture, endotracheal aspirate or bronchoalveolar lavage culture | MALDI-TOF MS; BD Phoenix | 261 | 24 | 20 |
| 6 | Calderaro, A. et al. [30] | 2021 | Italy | Lower respiratory tract | MALDI-TOF using a VITEK MS instrument | 90 | 3 | 11 |
| No. | Author | Year | Country | Sample | Diagnostic Technizque | COVID-19 Patients | E. Faecium | E. Faecalis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Amaral, L. et al. [31] | 2020 | Brazil | Nosocomial pneumonia | - | 1 | - | 1 |
| 2 | Ramos-Martínez, A. et al. [32] | 2020 | Spain | Blood or valve culture | - | 2 | - | 2 |
| 3 | Serrano, O.K. et al. [33] | 2020 | USA | Perinephric collection | - | 1 | 1 vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus | |
| 4 | Sanders, D.J. et al. [34] | 2020 | USA | Aortic valve culture | - | 1 | - | 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Toc, D.A.; Mihaila, R.M.; Botan, A.; Bobohalma, C.N.; Risteiu, G.A.; Simut-Cacuci, B.N.; Steorobelea, B.; Troanca, S.; Junie, L.M. Enterococcus and COVID-19: The Emergence of a Perfect Storm? Int. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 2, 220-229. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtm2020020
Toc DA, Mihaila RM, Botan A, Bobohalma CN, Risteiu GA, Simut-Cacuci BN, Steorobelea B, Troanca S, Junie LM. Enterococcus and COVID-19: The Emergence of a Perfect Storm? International Journal of Translational Medicine. 2022; 2(2):220-229. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtm2020020
Chicago/Turabian StyleToc, Dan Alexandru, Razvan Marian Mihaila, Alexandru Botan, Carina Nicoleta Bobohalma, Giulia Andreea Risteiu, Bogdan Nicolae Simut-Cacuci, Bianca Steorobelea, Stefan Troanca, and Lia Monica Junie. 2022. "Enterococcus and COVID-19: The Emergence of a Perfect Storm?" International Journal of Translational Medicine 2, no. 2: 220-229. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtm2020020
APA StyleToc, D. A., Mihaila, R. M., Botan, A., Bobohalma, C. N., Risteiu, G. A., Simut-Cacuci, B. N., Steorobelea, B., Troanca, S., & Junie, L. M. (2022). Enterococcus and COVID-19: The Emergence of a Perfect Storm? International Journal of Translational Medicine, 2(2), 220-229. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtm2020020