Floating Microplastics with Biofilm Changes Feeding Behavior of Climbing Perch Anabas testudineus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
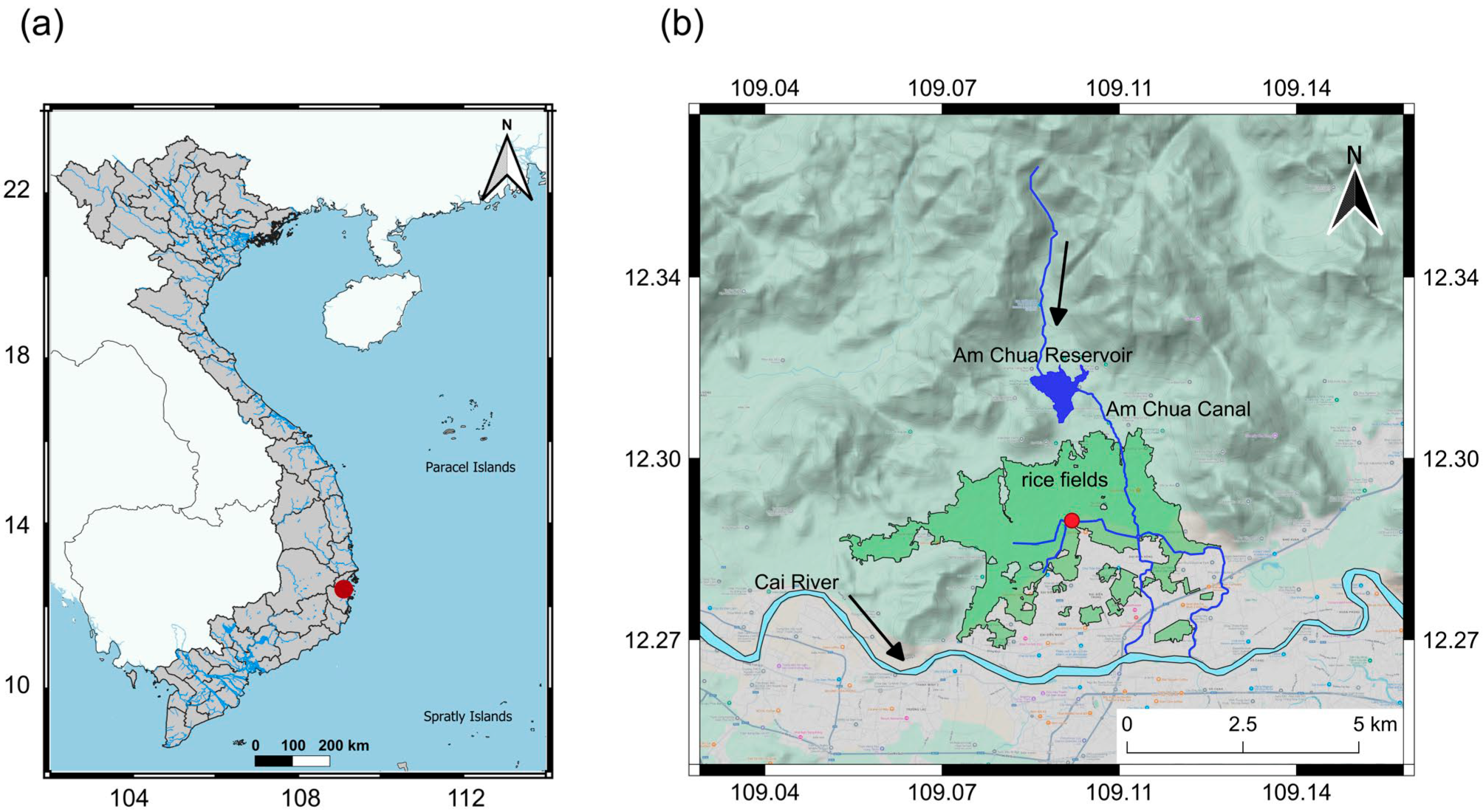
2.1. Sampling Location
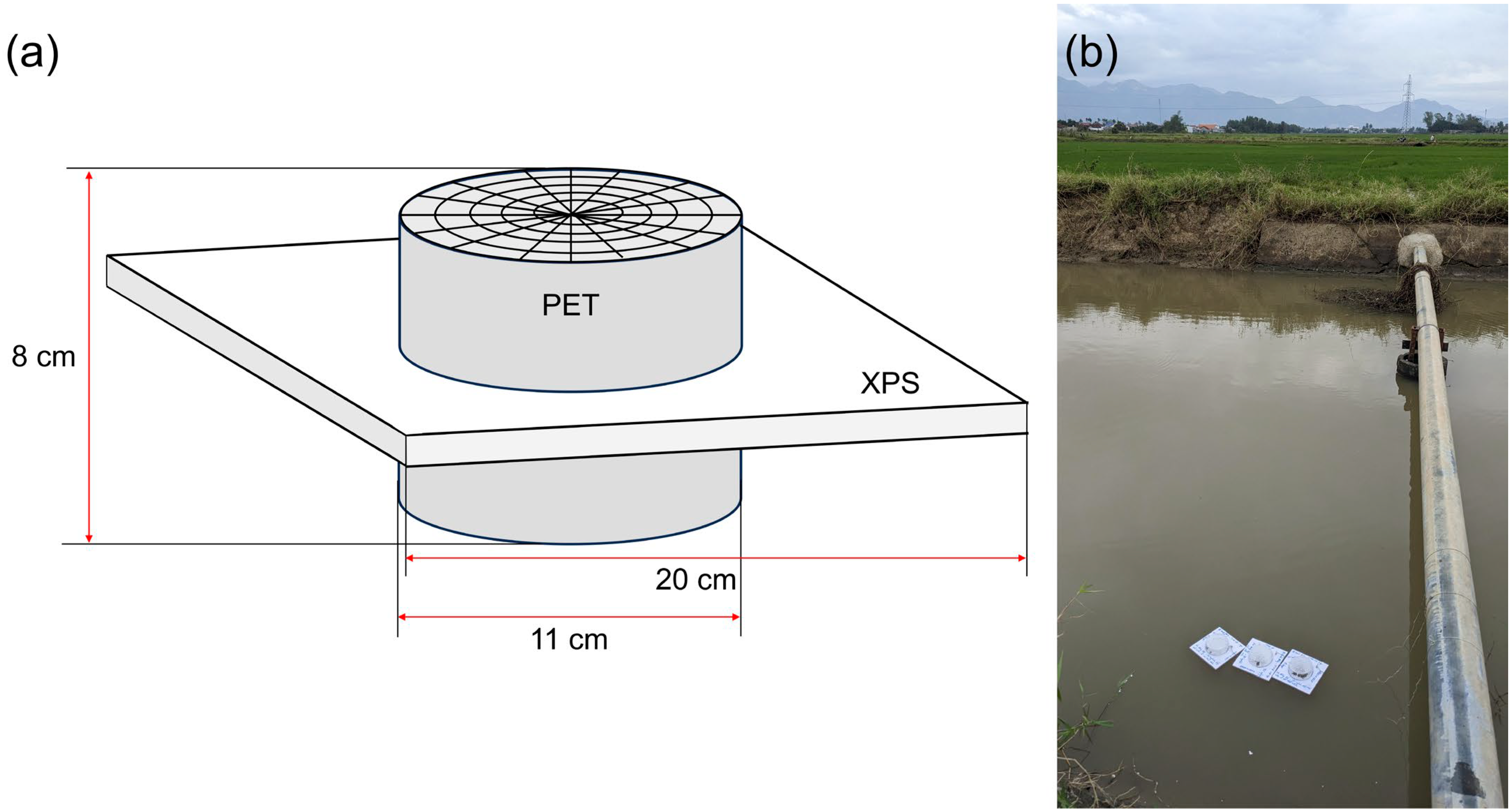
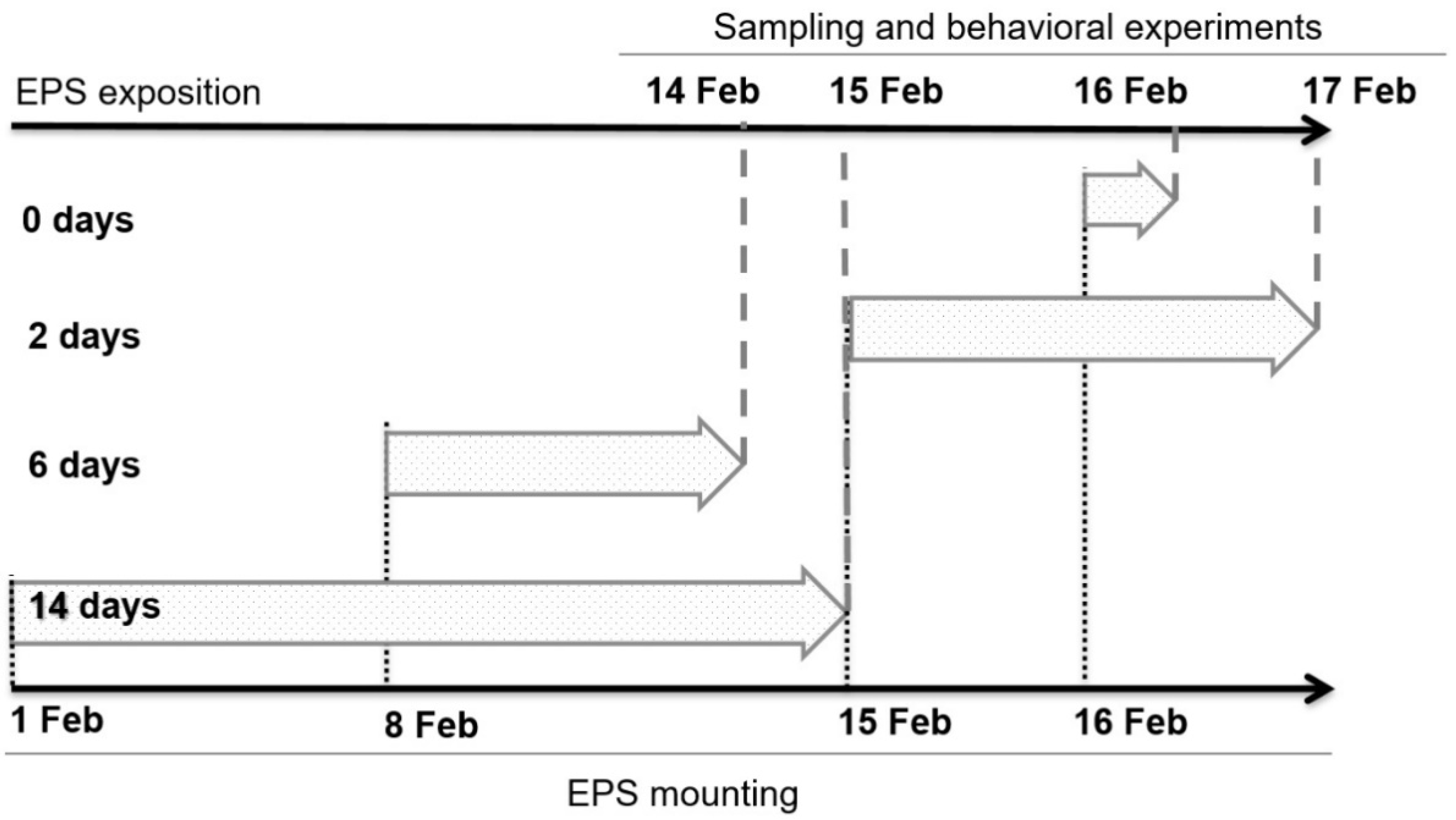
2.2. Formation of Biofilm on Expanded Polystyrene
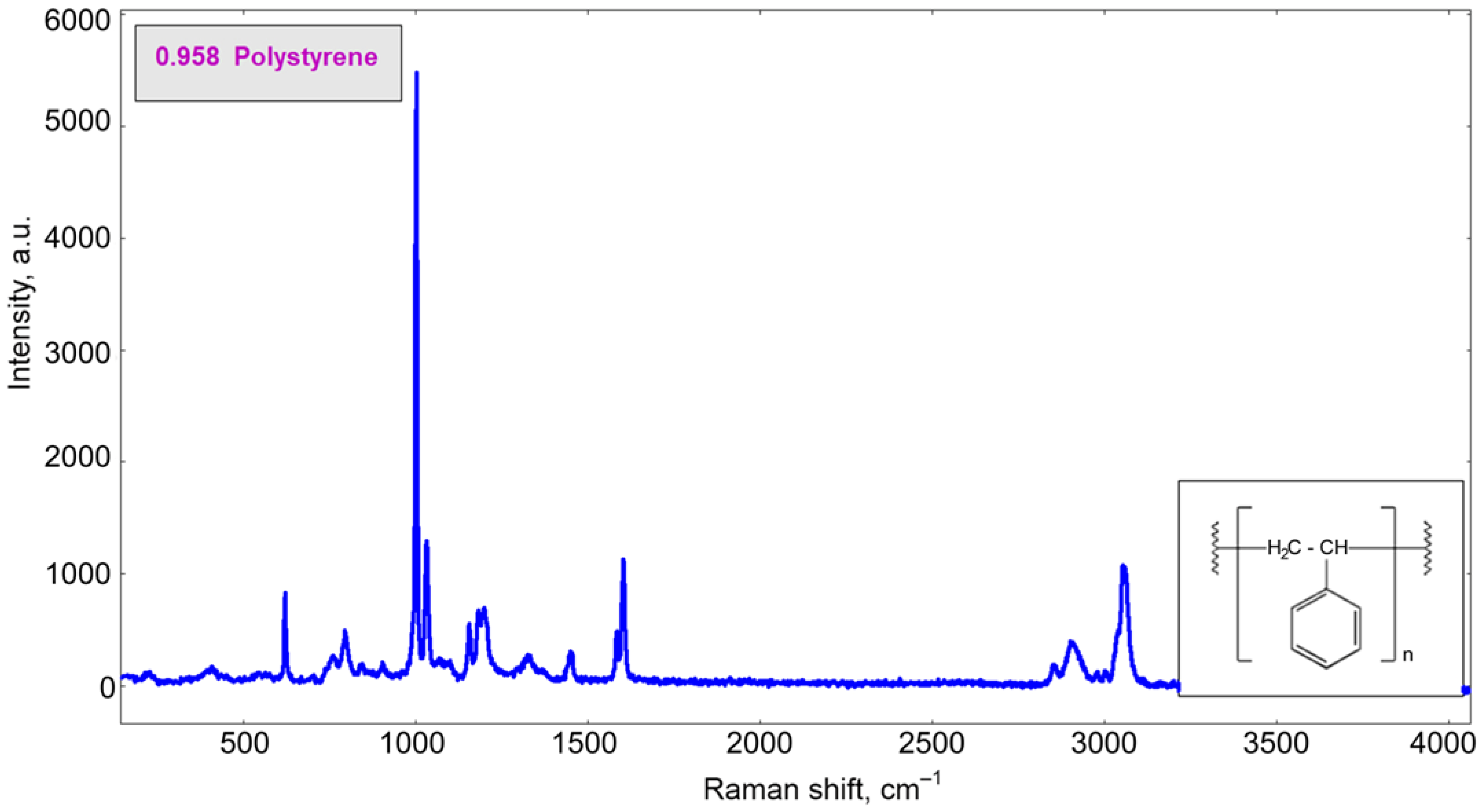
2.3. Biofilm Assessment
2.4. Fish Capturing and Maintenance
2.5. Behavioral Experiment
2.6. Statistical Data Analyses
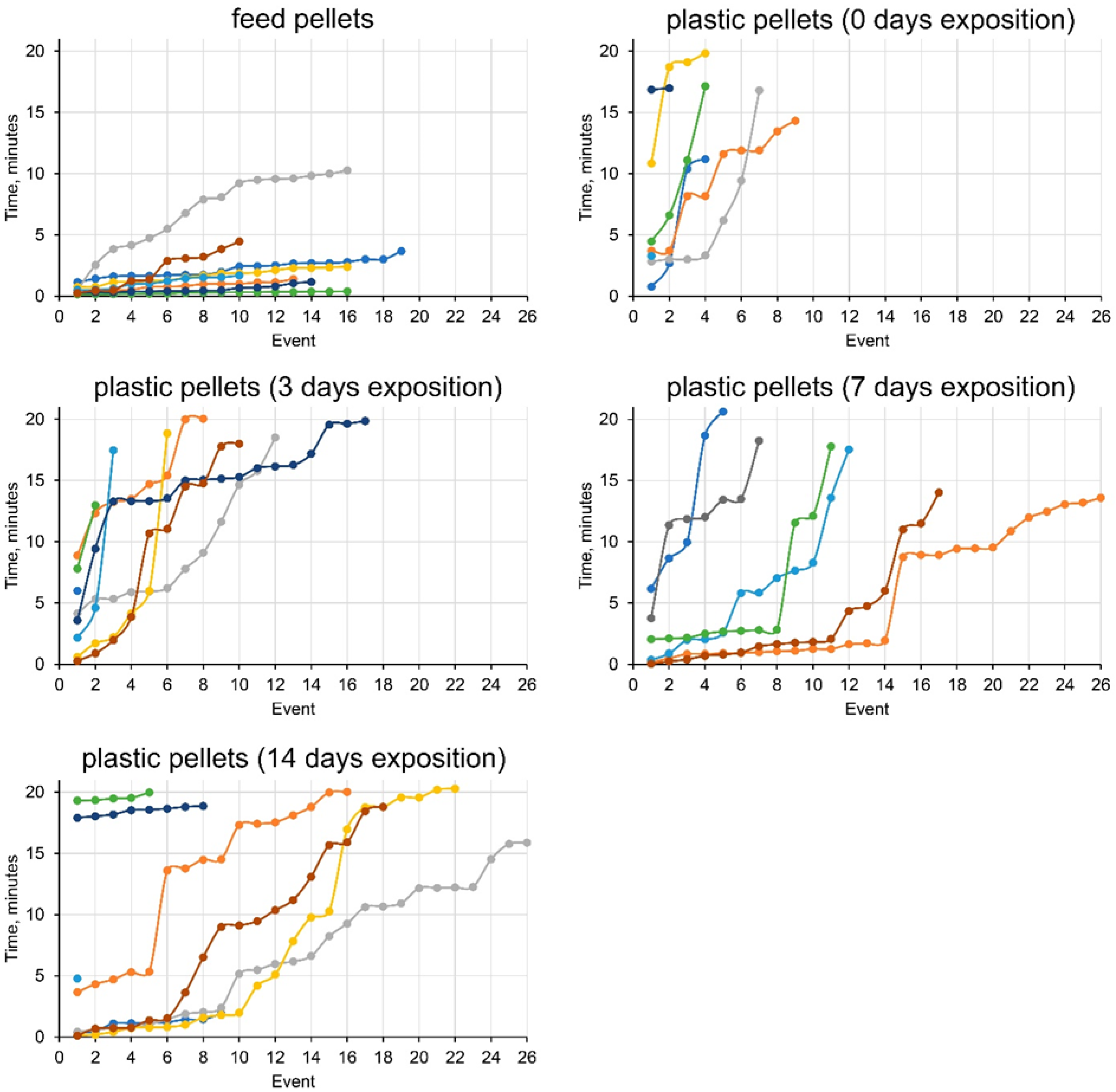
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Sampling Location
3.2. Climbing Perch Feeding Behavior
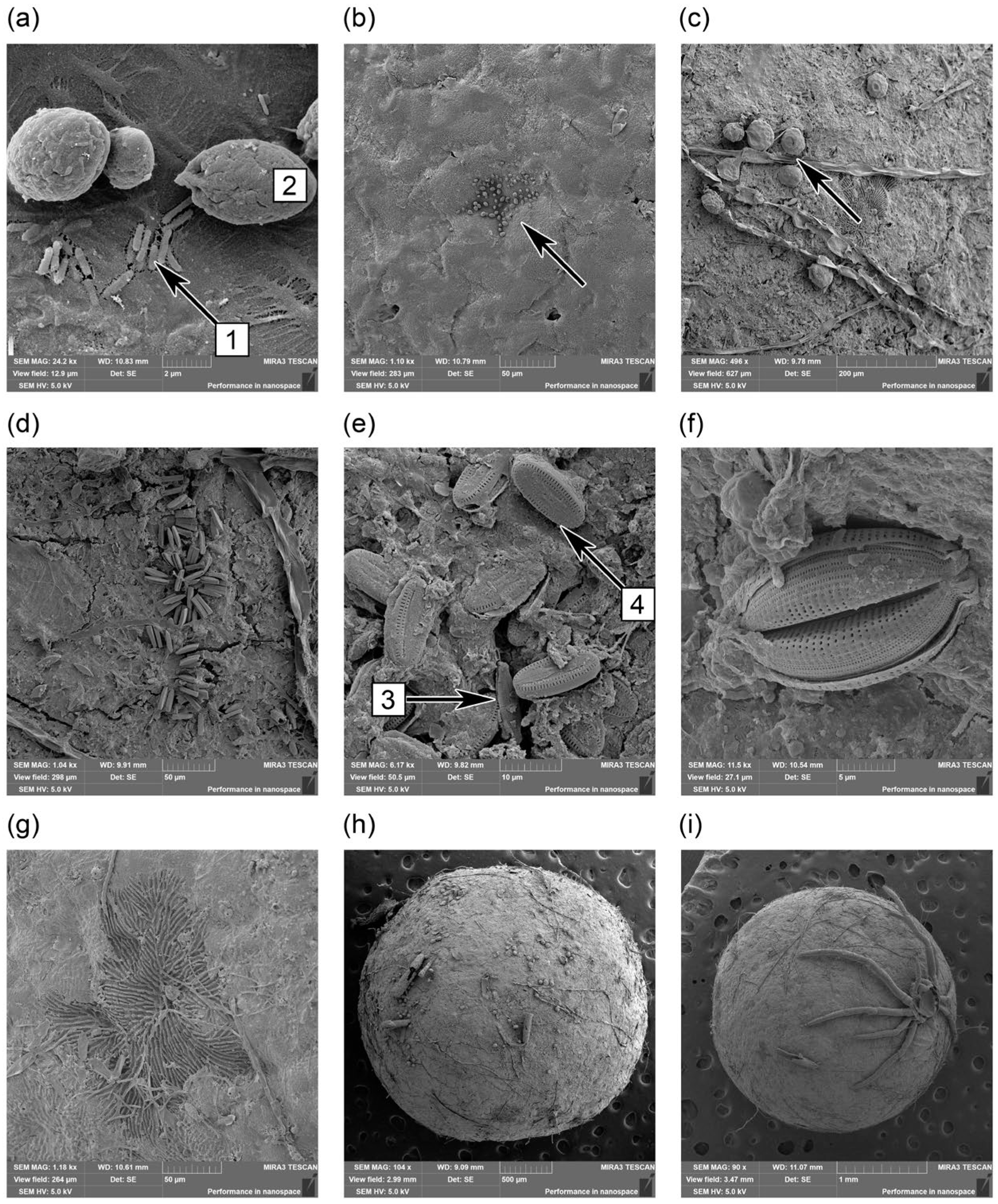
3.3. Biofilm Formation on EPS Surface
4. Discussion
4.1. Feeding Behavior of Climbing Perch
4.2. Some Ecological Features of Biofilm Formation on Plastic Surfaces in Natural Environments
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EPS | Expanded polystyrene |
| PET | polyethylene terephthalate |
| XPS | extruded polystyrene |
Appendix A
| Parameters | First Day | Last Day |
|---|---|---|
| pH | 6.5 | 6.7 |
| Nitrites (NO2) mg/L | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Nitrates (NO3) mg/L | 10.0 | 10.0 |
| Ammonia/Ammonium (NH3/NH4) | 1.0 | 0.5 |
| Phosphates (PO4), mg/L | 1.1 | 0.25 |
| Iron (Fe), mg/L | 6.0 | 1.0 |
| Chlorides, Cl, mg/L | 0 | 0 |
References
- Oliveira, M.; Almeida, M.; Miguel, I. A micro(nano)plastic boomerang tale: A never ending story. Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 112, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kang, S.; Allen, S.; Allen, D.; Gao, T.; Sillanpää, M. Atmospheric microplastics: A review on current status and perspectives. Earth Sci. Rev. 2020, 203, 103118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menéndez-Pedriza, A.; Jaumot, J. Interaction of environmental pollutants with microplastics: A critical review of sorption factors, bioaccumulation, and ecotoxicological effects. Toxics 2020, 8, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Avignon, G.; Gregory-Eaves, I.; Ricciardi, A. Microplastics in lakes and rivers: An issue of emerging significance to limnology. Environ. Rev. 2022, 30, 228–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zettler, E.R.; Mincer, T.J.; Amaral-Zettler, L.A. Life in the “Plastisphere”: Microbial communities on plastic marine debris. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 7137–7146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral-Zettler, L.A.; Zettler, E.R.; Mincer, T.J. Ecology of the plastisphere. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowley, J.; Baker-Austin, C.; Porter, A.; Hartnell, R.; Lewis, C. Oceanic hitchhikers—Assessing pathogen risks from marine microplastic. Trends Microbiol. 2021, 29, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nava, V.; Leoni, B. A critical review of interactions between microplastics, microalgae, and aquatic ecosystem function. Water Res. 2021, 188, 116476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, D.K.A.; Galgani, F.; Thompson, R.C.; Barlaz, M. Accumulation and fragmentation of plastic debris in global environments. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savoca, M.S.; Tyson, C.W.; McGill, M.; Slager, C.J. Odours from marine plastic debris induce food search behaviours in a forage fish. Proc. R. Soc. B 2017, 284, 20171000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ory, N.C.; Gallardo, C.; Lenz, M.; Thiel, M. Capture, swallowing, and ingestion of microplastics by a planktivorous juvenile fish. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 240, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagi, M.; Ono, Y.; Kawaguchi, T. Microplastic pollution in aquatic environments may facilitate misfeeding by fish. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 315, 120457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, E.; Nilsson, N.H.; Lithner, D.; Lassen, C. Hazardous Substances in Plastics: Survey of Chemical Substances in Consumer Products; The Danish Environmental Protection Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2014; No. 132; Available online: https://www2.mst.dk/Udgiv/publications/2014/12/978-87-93283-31-2.pdf (accessed on 25 August 2025).
- Turner, A. Foamed polystyrene in the marine environment: Sources, additives, transport, behavior, and impacts. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 10411–10420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laist, D.W. Overview of the biological effects of lost and discarded plastic debris in the marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1987, 18, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobson, E.S.; Chess, J.R. Trophic relationships among fishes and plankton in the lagoon at Enewetak Atoll, Marshall Islands. Fish Bull. 1977, 76, 133–153. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.; Guo, H.; Zhang, D.; Hu, C.; Jiang, S. Food ingestion, consumption, and selectivity of pompano Trachinotus ovatus (Linnaeus 1758) under different rotifer densities. Aquac. Res. 2015, 46, 2593–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganzha, E.V.; Pavlov, E.D.; Dien, T.D. Risk of expanded polystyrene ingestion by climbing perch Anabas testudineus. Water 2023, 15, 1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank. Vietnam: Plastic Pollution Diagnostics. East Asia and Pacific Region, Marine Plastics Series. 2021. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10986/37693 (accessed on 15 August 2025).
- Veettil, K.B.; Puri, V.; Acharki, S.; Ward, R.D.; Khoa, N.D. Microplastic pollution in Vietnam’s estuarine, coastal and riverine environments: Research advances and future prospects. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2024, 301, 108749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberbeckmann, S.; Osborn, A.M.; Duhaime, M.B. Microbes on a bottle: Substrate, season and geography influence community composition of microbes colonizing marine plastic debris. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, Y.; Ohtsuka, T. Diatoms from paddy fields in northern Laos. Diatom 2005, 21, 71–89. [Google Scholar]
- Dao, T.-S.; Bui, T.N.P. Phytoplankton from Vam Co River in Southern Vietnam. Environ. Manag. Sustain. Dev. 2022, 5, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Lobban, C.S.; Lee, K.-W.; Jung, S.W. Additional floristic study of planktonic and seaweed-associated diatoms in Chuuk, Micronesia. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 2022, 10, 27–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.L.; Tran, T.H.Y.; Tran, T.T. Factors affecting the seasonal succession of phytoplankton functional groups in a tropical floodplain reservoir in Vietnam. Aqua Water. Ecosyst. Soc. 2022, 71, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Huynh, T.G.; Phan, T.C.T.; Tran, T.V.; Nguyen, T.H.; Nguyen, T.K.L. Zooplankton species diversity in Dau Tieng Lake, Vietnam. AACL Bioflux 2025, 18, 712–724. [Google Scholar]
- CCAC Guidelines Committee. CCAC Guidelines on: The Care and Use of Fish in Research, Teaching and Testing; Canadian Council on Animal Care: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Pavlov, E.D.; Dien, T.D.; Ganzha, E.V. Spatial distribution and circadian locomotor activity of invasive armored catfish (Loricariidae) in the freshwater and brackish water. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0296222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OECD. OECD Guideline for Testing of Chemicals, 12th ed.; OECD: Paris, France, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahens, L.; Strady, E.; Kieu-Le, T.-C.; Dris, R.; Boukerma, K.; Rinnert, E.; Gaspery, G.; Tassin, B. Macroplastic and microplastic contamination assessment of a tropical river (Saigon River, Vietnam) transversed by a developing megacity. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 236, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, T.H.; Vu, H.N. The crisis of plastic waste in Vietnam is real. Eur. J. Eng. Technol. Res. 2019, 4, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strady, E.; Kieu Le, T.C.; Truong, T.N.S.; Le, T.M.T.; Nguyen, P.D.; Pham, N.B.; Inamura, Y. Riverine microplastic pollution in Vietnam: A review of current scientific knowledge and legal policies. Appl. Environ. Res. 2023, 45, 251188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, A.-F.M.; El-Ghobashy, A.E.; El-Mezayen, M.M. Effect of feed colour on growth and feed utilization of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus L.) larvae and fingerlings. Aquac. Nutr. 2013, 19, 870–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasumyan, A.O.; Pashchenko, N.I.; Oanh, L.T. Morphology of the olfactory organ in the climbing perch (Anabas testudineus, Anabantidae, Perciformes). Biol. Bull. Russ. Acad. Sci. 2021, 48, 1298–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitcher, T.J.; Magurran, A.E.; Winfield, I.J. Fish in larger shoals find food faster. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 1982, 10, 149–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binoy, V.V.; Thomas, K.J. The climbing perch (Anabas testudineus Bloch), a freshwater fish, prefers larger unfamiliar shoals to smaller familiar shoals. Curr. Sci. 2004, 86, 207–211. Available online: http://cat.inist.fr/?aModele=afficheN&cpsidt=15782241 (accessed on 20 August 2025).
- Zworykin, D.D. The behavior of climbing perch, Anabas testudineus, with novel food in individual and social conditions. J. Ichthyol. 2018, 58, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasumyan, A.O. The taste system in fishes and the effects of environmental variables. J. Fish Biol. 2019, 95, 155–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jørgensen, E.H.; Martinsen, M.; Strøm, V.; Hansen, K.E.; Ravuri, C.S.; Gong, N.; Jobling, M. Long-term fasting in the anadromous Arctic charr is associated with downregulation of metabolic enzyme activity and upregulation of leptin A1 and SOCS expression in the liver. J. Exp. Biol. 2013, 216, 3222–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, F.; Zhang, Z.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, X.; Dong, J.; Ding, X.; Chen, M.; Zhang, X. Effects of food deprivation duration on the behavior and metabolism of black rockfish (Sebastes schlegelii). Fishes 2021, 6, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liem, K.F. Functional Design of the Air Ventilation Apparatus and Overland Excursions by Teleosts; Fieldiana Zoology series, No. 37; Field Museum of Natural History: Chicago, IL, USA, 1987; pp. 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Pavlov, E.D.; Dien, T.D.; Ganzha, E.V. Stress and energy mobilization responses of climbing perch Anabas testudineus during terrestrial locomotion. Stresses 2025, 5, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haave, M.; Gomiero, A.; Schönheit, J.; Nilsen, H.; Olsen, A.B. Documentation of microplastics in tissues of wild coastal animals. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 575058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Takada, H. Microplastic fragments and microbeads in digestive tracts of planktivorous fish from urban coastal waters. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.; Thompson, R.; Galloway, T. The physical impacts of microplastics on marine organisms: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 178, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marui, T.; Caprio, J. Fish chemoreception. In Fish Chemoreception; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberbeckmann, M.; Labrenz, M. First published as a review in advance on June 21, 2019. The annual review of marine science. Mar. Sci. 2020, 12, 209–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coons, A.K.; Busch, K.; Lenz, M.; Hentschel, U.; Borchert, E. Biogeography rather than substrate type determines bacterial colonization dynamics of marine plastics. PeerJ 2021, 9, e12135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bocci, V.; Galafassi, S.; Levantesi, C.; Crognale, S.; Amalfitano, S.; Congestri, R.; Matturro, B.; Rossetti, S.; Di Pippo, F. Freshwater plastisphere: A review on biodiversity, risks, and biodegradation potential with implications for aquatic ecosystem health. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1395401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallbank, J.A.; Lear, G.; Kingsbury, J.M.; Weaver, L.; Doake, F.; Smith, D.A.; Audrézet, F.; Maday, S.D.M.; Gambarini, V.; Donaldson, L.; et al. Into the Plastisphere, where only the generalists thrive: Early insights in Plastisphere microbial community succession. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 841142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.; Li, W.; Adyel, T.M.; Yao, Y.; Deng, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, Y.; Hou, J. Spatio-temporal succession of microbial communities in plastisphere and their potentials for plastic degradation in freshwater ecosystems. Water Res. 2023, 229, 119406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoellein, T.; Rojas, M.; Pink, J.; Gasior, J.; Kelly, J. Anthropogenic litter in urban freshwater ecosystems: Distribution and microbial interactions. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pippo, F.; Crognale, S.; Levantesi, C.; Vitanza, L.; Sighicelli, M.; Pietrelli, L.; Di Vito, S.; Amalfitano, S.; Rossetti, S. Plastisphere in lake waters: Microbial diversity, biofilm structure, and potential implications for freshwater ecosystems. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 310, 119876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, H.S.; Nerheim, M.S.; Carroll, K.A.; Eriksen, M. The plastic-associated microorganisms of the North Pacific Gyre. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 75, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decree 32/2006/ND-CP. Decree 159/2007/ND-CP, on Management of Endangered, Precious and Rare Forest Plants and Animals. Socialist Republic of Vietnam. Available online: https://moj.gov.vn/vbpq/en/lists/vn%20bn%20php%20lut/view_detail.aspx?itemid=3219 (accessed on 15 August 2025).
- National Research Counsil of the National Academics. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, 8th ed.; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- ASAB Ethical Committee; ABS Animal Care Committee. Guidelines for the treatment of animals in behavioural research and teaching. Anim. Behav. 2022, 183, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
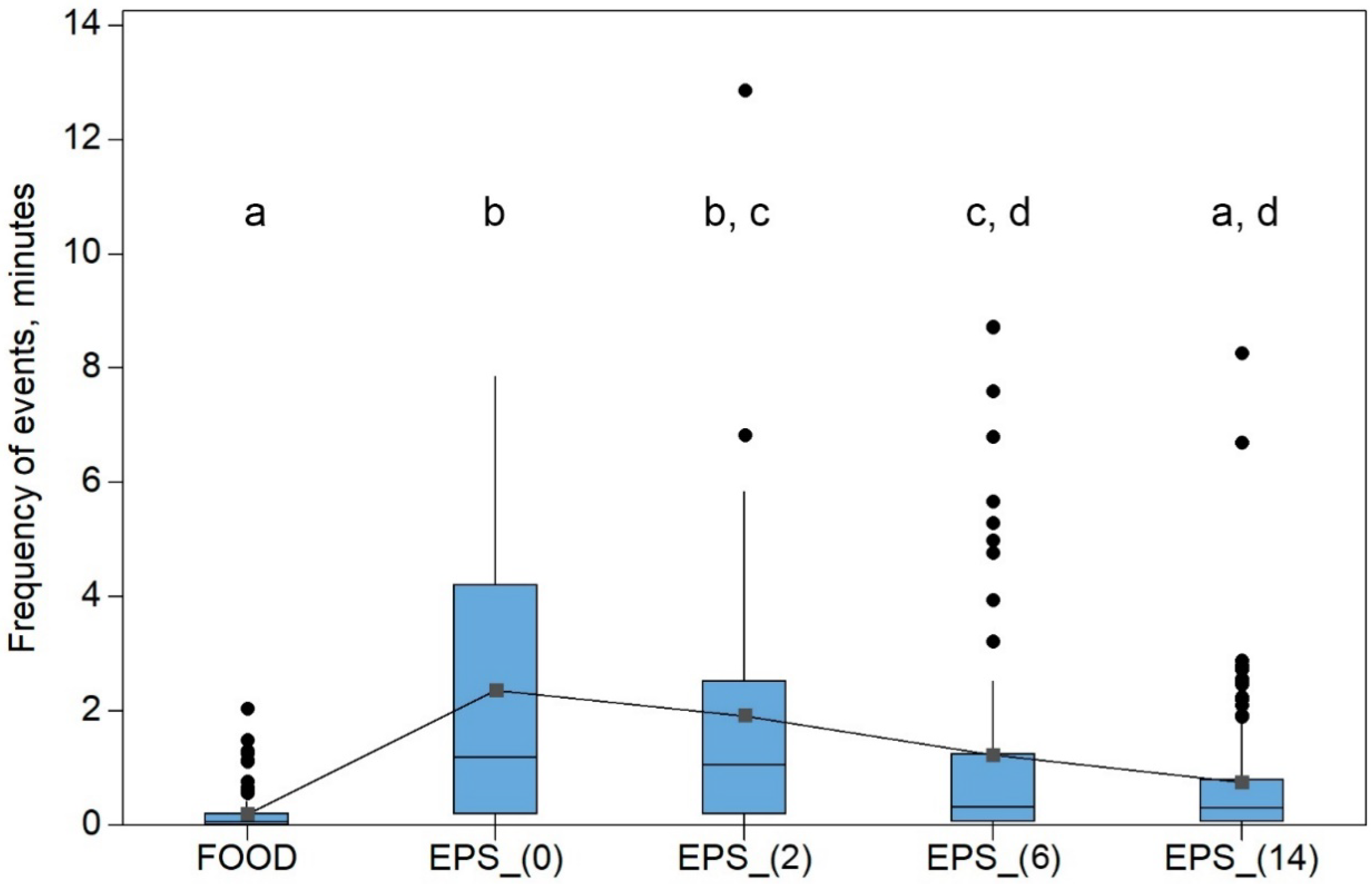

| Parameter | Feed Pellets | Plastic Pellets, 0 Days | Plastic Pellets, 2 Days | Plastic Pellets, 6 Days | Plastic Pellets, 14 days |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pellet grasping, event per fish | 2.4 | 0.6 | 1.2 | 1.6 | 1.9 |
| Maximum number of events (grasping) per trial | 19 | 9 | 17 | 26 | 26 |
| Percentage of events during first five minutes, % | 90.4 | 32.3 | 20.3 | 52.6 | 38.1 |
| Time of the first grasp, minutes M ± SD (min, max) | 0.5 ± 0.32 a (0.2–1.1) | 6.1 ± 5.69 b (0.8–16.9) | 4.2 ± 3.19 b (0.3–8.9) | 2.1 ± 2.45 a,b (0.1–6.2) | 5.8 ± 8.09 a,b (0.1–19.3) |
| Retention time of the pellet, seconds M ± SD (min, max) | N/A | 4.7 ± 6.52 (0–36) | 2.2 ± 2.61 (0–10) | 1.5 ± 2.12 * (0–15) | 1.9 ± 2.22 (0–17) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ganzha, E.V.; Dien, T.D.; Pavlov, E.D. Floating Microplastics with Biofilm Changes Feeding Behavior of Climbing Perch Anabas testudineus. Microplastics 2025, 4, 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics4030062
Ganzha EV, Dien TD, Pavlov ED. Floating Microplastics with Biofilm Changes Feeding Behavior of Climbing Perch Anabas testudineus. Microplastics. 2025; 4(3):62. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics4030062
Chicago/Turabian StyleGanzha, Ekaterina V., Tran Duc Dien, and Efim D. Pavlov. 2025. "Floating Microplastics with Biofilm Changes Feeding Behavior of Climbing Perch Anabas testudineus" Microplastics 4, no. 3: 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics4030062
APA StyleGanzha, E. V., Dien, T. D., & Pavlov, E. D. (2025). Floating Microplastics with Biofilm Changes Feeding Behavior of Climbing Perch Anabas testudineus. Microplastics, 4(3), 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics4030062






