Microplastics Contamination on the Surfaces of Fruits and Vegetables: Abundance, Characteristics, and Exposure Assessment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Extraction and Pretreatment of the Samples
2.3. Quantification of MPs
- No visible cellular or organic matter.
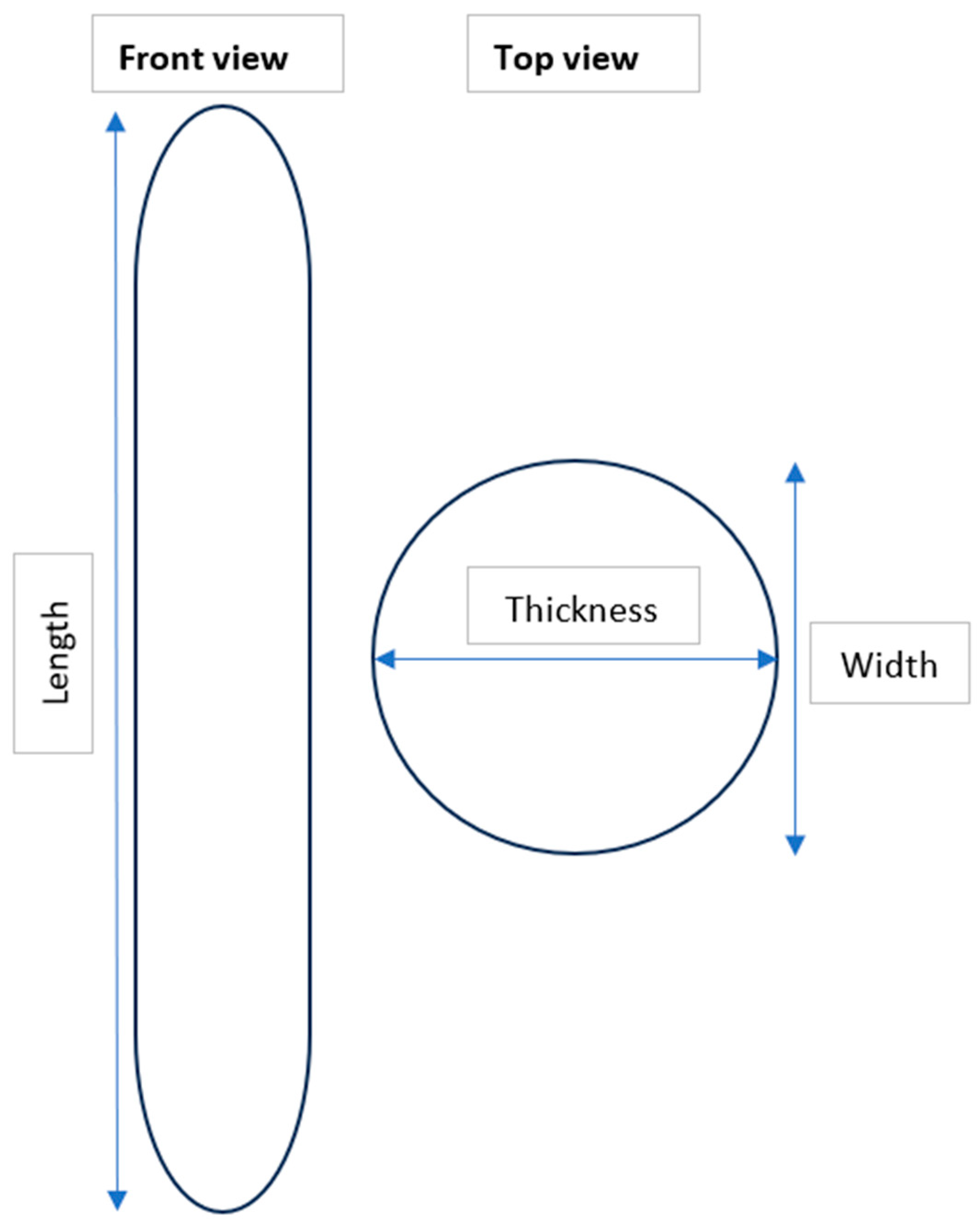
- Clear and well-defined edges.
- Uniform width (W) and thickness (T) along the entire length (L) of fibers.
- Consistent and homogeneous color throughout.
- Presence of slight curvature (not entirely straight) to rule out biological origins.
2.4. Characterization of MPs
2.5. Quality Control
2.6. Exposure Assessment
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Enumeration of MPs
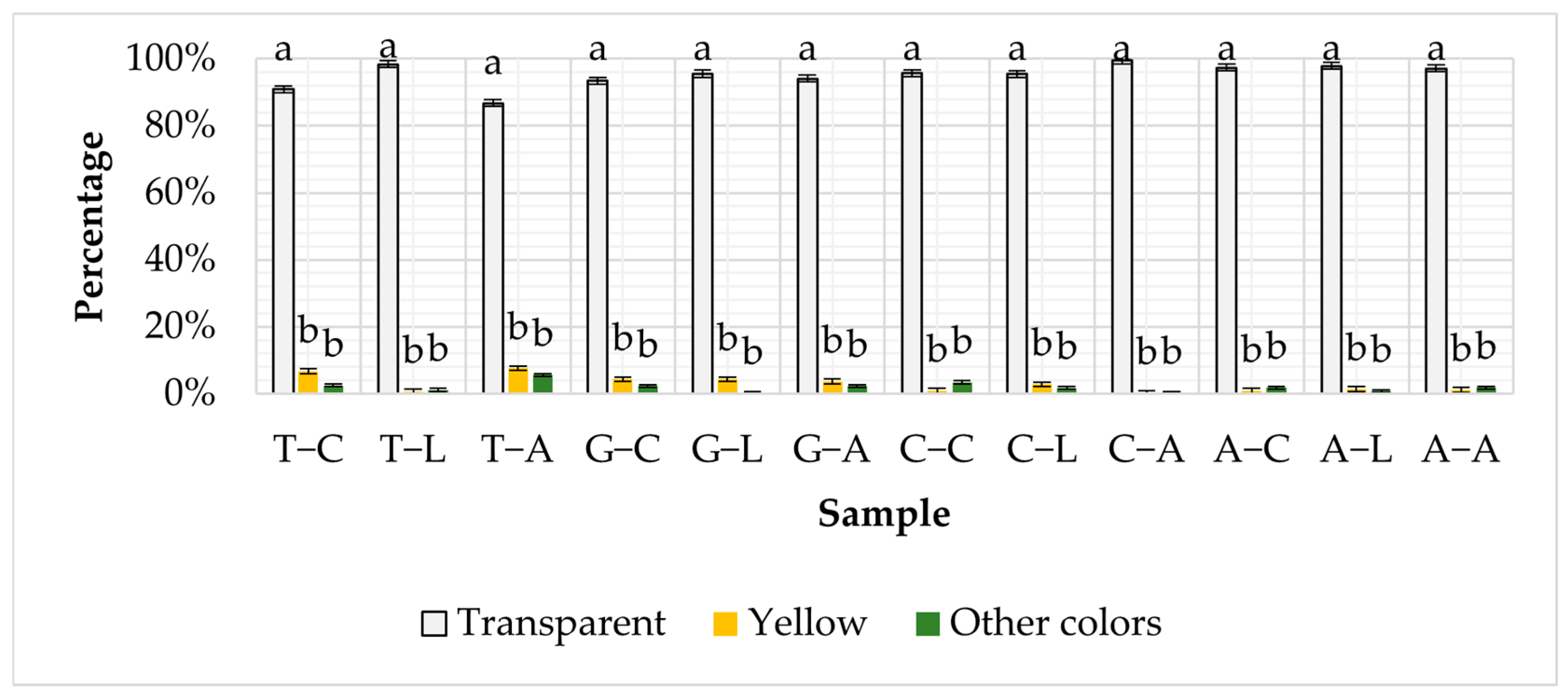
3.2. Color of MPs
3.3. Shape of MPs
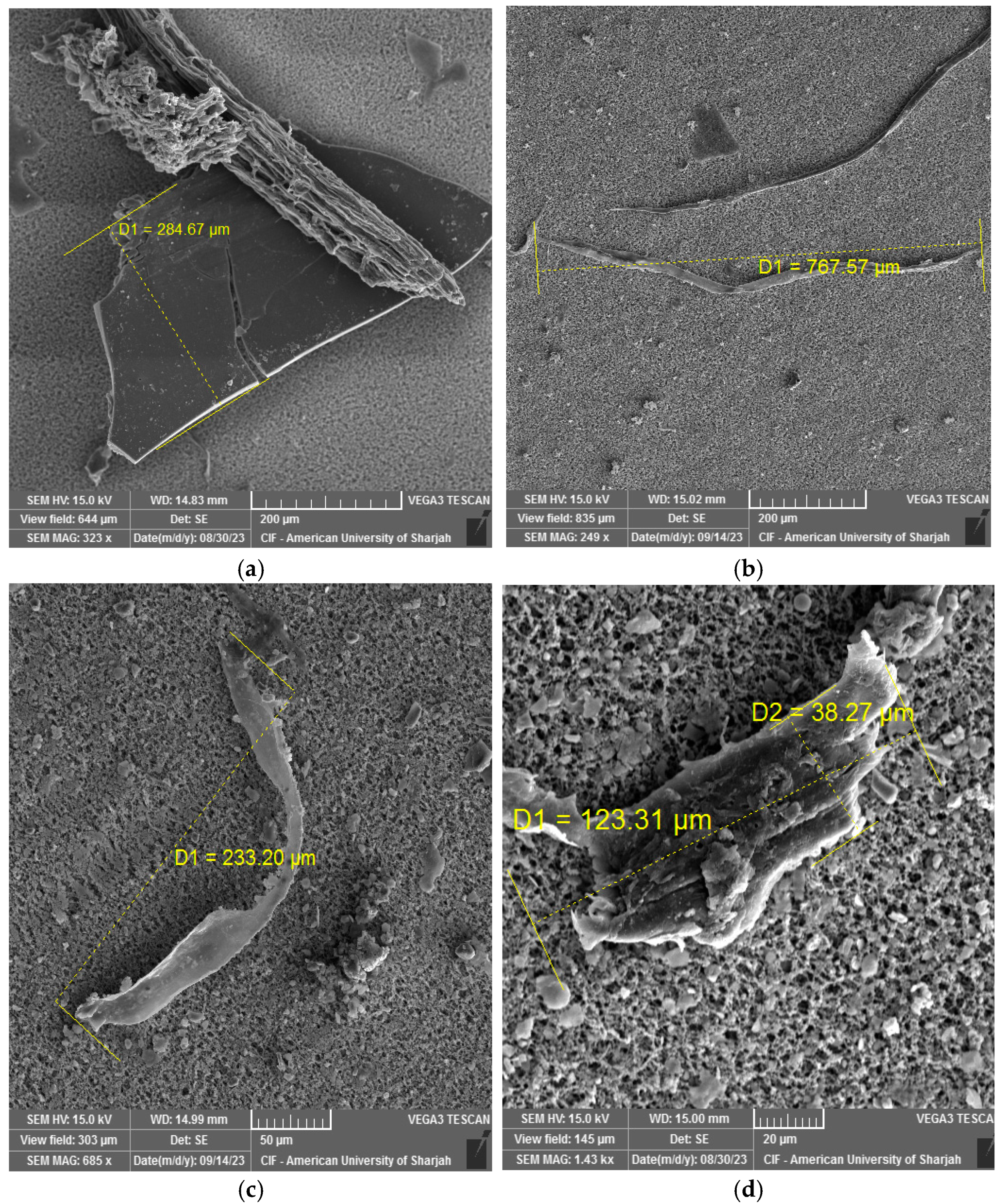
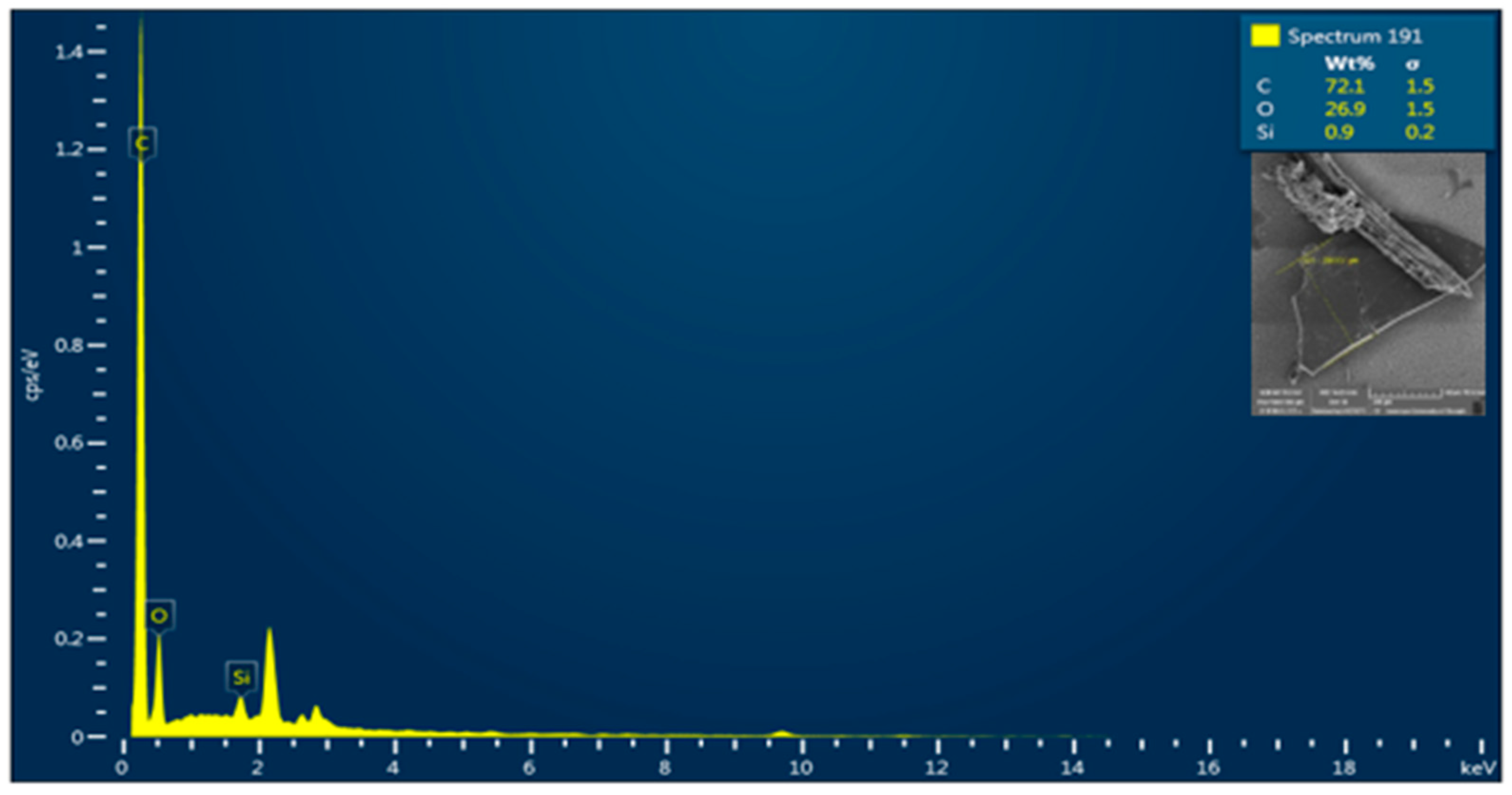
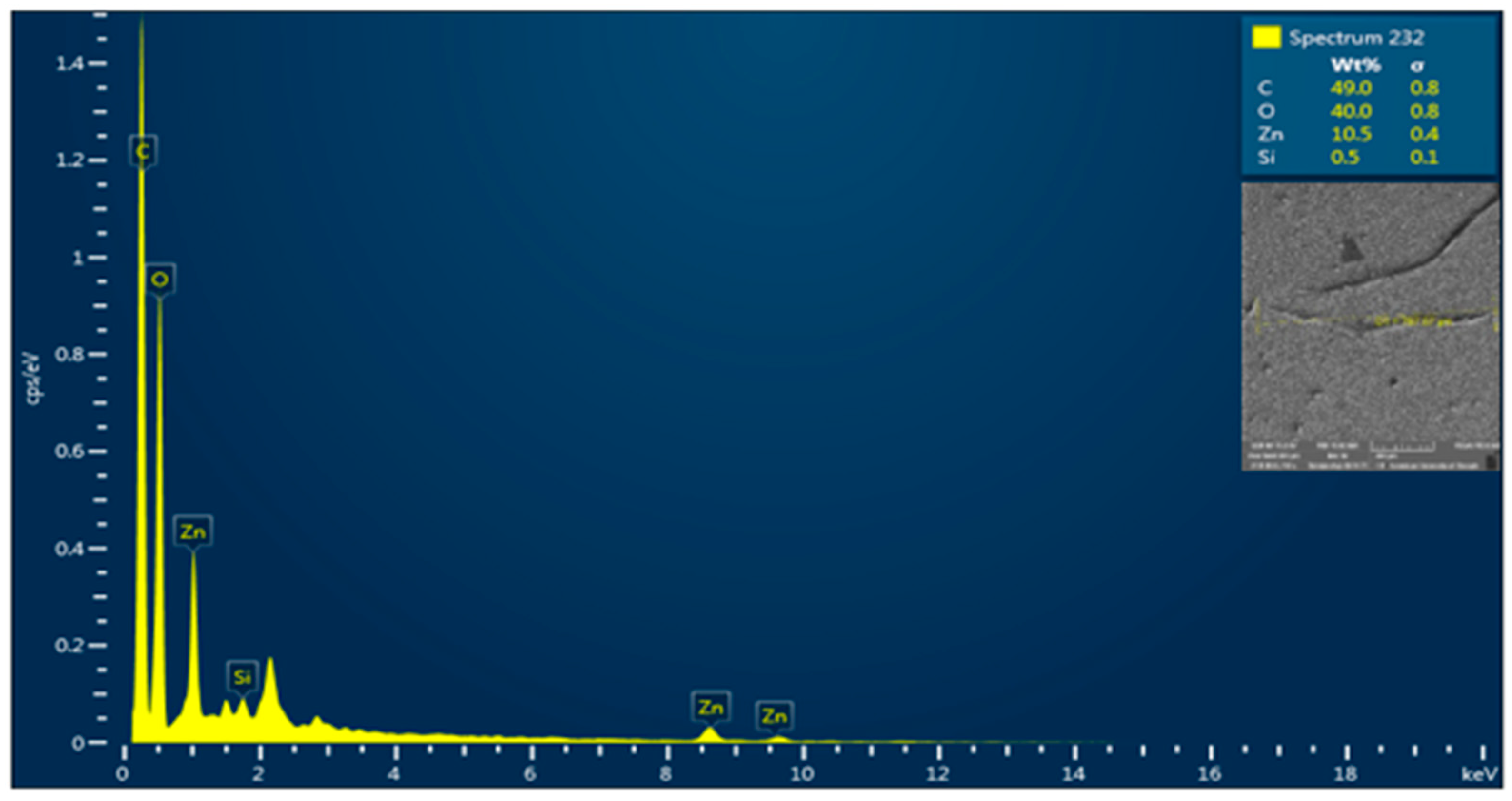
3.4. SEM-EDX Analysis
3.5. Recovery Tests
3.6. Exposure Assessment Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MPs | Microplastics |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| UN | United Nations |
| L | Length |
| T | Thickness |
| W | Width |
| S | Surface area |
| Dg | Geometric mean diameter |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscopy |
| EDX | Energy Dispersion Detector |
| EDI | Estimated daily intake |
| EAI | Estimated annual intake |
| PE | Polyethylene |
| Si | Silicon |
| Zn | Zinc |
| Mg | Magnesium |
| Fe | Iron |
| Al | Aluminum |
| Na | Sodium |
Appendix A
| Blank MPs (n/200 mL) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Tomatoes | Cucumbers | Grapes | Apples |
| 93 | 40 | 130 | 33 |
| MPs Homogeneous Subsets | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Color 1 | Color 2 | Significance | 1 | 2 |
| Other color | Transparent | < 0.001 | 12.4444 | - |
| Yellow | 0.982 | |||
| Transparent | Other color | < 0.001 | - | 395.8889 |
| Yellow | < 0.001 | |||
| Yellow | Other color | 0.982 | 22.2222 | - |
| Transparent | < 0.001 | |||
| MPs Homogeneous Subsets | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Color 1 | Color 2 | Significance | 1 | 2 |
| Other color | Transparent | <0.001 | 11.0000 | - |
| Yellow | 0.923 | |||
| Transparent | Other color | <0.001 | - | 669.6667 |
| Yellow | <0.001 | |||
| Yellow | Other color | 0.923 | 28.4444 | - |
| Transparent | <0.001 | |||
| MPs Homogeneous Subsets | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Color 1 | Color 2 | Significance | 1 | 2 |
| Other color | Transparent | <0.001 | 19.1111 | - |
| Yellow | 0.999 | |||
| Transparent | Other color | <0.001 | - | 1302.4444 |
| Yellow | <0.001 | |||
| Yellow | Other color | 0.999 | 14.2222 | - |
| Transparent | <0.001 | |||
| MPs Homogeneous Subsets | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Color 1 | Color 2 | Significance | 1 | 2 |
| Other color | Transparent | <0.001 | 7.5556 | - |
| Yellow | 0.998 | |||
| Transparent | Other color | <0.001 | - | 406.6667 |
| Yellow | <0.001 | |||
| Yellow | Other color | 0.998 | 4.4444 | - |
| Transparent | <0.001 | |||
References
- Rouch, D. Plastic Future: How to Reduce the Increasing Environmental Footprint of Plastic Packaging; Clarendon Policy & Strategy Group: Melbourne, Australia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee, S.; Sharma, S. Microplastics in our oceans and marine health. Field Actions Sci. Rep. 2019, 19, 54–61. [Google Scholar]
- Shrivastava, A. Plastic Properties and Testing. In Introduction to Plastics Engineering; William Andrew: Norwich, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 49–110. [Google Scholar]
- Webb, H.K.; Arnott, J.; Crawford, R.J.; Ivanova, E.P. Plastic degradation and its environmental implications with special reference to poly (ethylene terephthalate). Polymers 2013, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshamsi, A.M.O.; Tatan, B.M.; Ashoobi, N.M.S.; Mortula, M.M. Emerging pollutants of water supplies and the effect of climate change. Environ. Rev. 2023, 31, 256–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khant, N.A.; Kim, H. Review of Current Issues and Management Strategies of Microplastics in Groundwater Environments. Water 2022, 14, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, H.; Ali, A.; Mortula, M.M.; Attaelmanan, A.G. Evaluation of microplastics in beach sediments along the coast of Dubai, UAE. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 150, 110739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammodat, A.R.; Nassar, S.; Mortula, M.M.; Shamsuzzaman, M. Factors affecting the leaching of micro and nanoplastics in the water distribution system. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 345, 118779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Luo, Y.; Lu, S.; Liu, M.; Song, Y.; Lei, L. Microplastics in soils: Analytical methods, pollution characteristics and ecological risks. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 109, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, K.D.; Covernton, G.A.; Davies, H.L.; Dower, J.F.; Juanes, F.; Dudas, S.E. Human consumption of microplastics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 7068–7074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, H.A.; Velzen, M.J.; Brandsma, S.H.; Vethaak, A.D.; Garcia-Vallejo, J.J.; Lamoree, M.H. Discovery anquantification of plastic particle pollution in human blood. Environ. Int. 2022, 163, 107199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragusa, A.; Svelato, A.; Santacroce, C.; Catalano, P.; Notarstefano, V.; Carnevali, O.; Papa, F.; Rongioletti, M.C.A.; Baiocco, F.; Draghi, S.; et al. Plasticenta: First evidence of microplastics in human placenta. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraluck, A.; Techarang, T.; Bunyapipat, P.; Boonchuwong, K.; Pullaput, Y.; Mordmuang, A. Detection of Microplastics in Human Breast Milk and Its Association with Changes in Human Milk Bacterial Microbiota. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prata, J.C.; da Costa, J.P.; Lopes, I.; Andrady, A.L.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T.A. One health perspective of the impacts of microplastics on animal, human and environmental health. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 777, 146094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Sarkar, A.; Yadav, O.P.; Achari, G.; Slobodnik, J. Potential human health risks due to environmental exposure to nano- and microplastics and knowledge gaps: A scoping review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 757, 143872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirstein, I.V.; Hensel, F.; Gomiero, A.; Iordachescu, L.; Vianello, A.; Wittgren, H.B.; Vollertsen, J. Drinking plastics?—Quantification and qualification of microplastics in drinking water distribution systems by µFTIR and Py-GCMS. Water Res. 2021, 188, 116519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koelmans, A.A.; Nor, N.H.M.; Hermsen, E.; Kooi, M.; Mintenig, S.M.; De France, J. Microplastics in freshwaters and drinking water: Critical review and assessment of data quality. Water Res. 2019, 155, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, S.A.; Welch, V.G.; Neratko, J. Synthetic polymer contamination in bottled water. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oßmann, B.E.; Sarau, G.; Holtmannspötter, H.; Pischetsrieder, M.; Christiansen, S.H.; Dicke, W. Small-sized microplastics and pigmented particles in bottled mineral water. Water Res. 2018, 141, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udovicki, B.; Andjelkovic, M.; Cirkovic-Velickovic, T.; Rajkovic, A. Microplastics in food: Scoping review on health effects, occurrence, and human exposure. Int. J. Food Contam. 2022, 9, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapukotuwa, R.W.M.G.K.; Jayasena, N.; Weerakoon, K.C.; Abayasekara, C.L.; Rajakaruna, R.S. High levels of micro-plastics in commercial salt and industrial salterns in Sri Lanka. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 174, 113239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosuth, M.; Mason, S.A.; Wattenberg, E.V. Anthropogenic contamination of tap water, beer, and sea salt. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebezeit, G.; Liebezeit, E. Non-pollen particulates in honey and sugar. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2013, 30, 2136–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Dai, H.; Gukowsky, J.; Tan, X.; He, L. Detection and quantification of microplastics in commercially bottled edible oil. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2023, 38, 101122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhbarizadeh, R.; Dobaradaran, S.; Nabipour, I.; Tajbakhsh, S.; Darabi, A.H.; Spitz, J. Abundance, composition, and potential intake of microplastics in canned fish. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 160, 111633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dessì, C.; Okoffo, E.D.; O’Brien, J.W.; Gallen, M.; Samanipour, S.; Kaserzon, S.; Rauert, C.; Wang, X.; Thomas, K.V. Plastics contamination of store-bought rice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piyawardhana, N.; Weerathunga, V.; Chen, H.S.; Guo, L.; Huang, P.J.; Ranatunga, R.R.M.K.P.; Hung, C.C. Occurrence of microplastics in commercial marine dried fish in Asian countries. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, A.; Golieskardi, A.; Keong Choo, C.; Larat, V.; Galloway, T.S.; Salamatinia, B. The presence of microplastics in commercial salts from different countries. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plastics—The Facts. 2022. Available online: https://plasticseurope.org/knowledge-hub/plastics-the-facts-2022/ (accessed on 25 August 2025).
- Du, F.; Cai, H.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Q.; Shi, H. Microplastics in take-out food containers. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 399, 122969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hee, Y.Y.; Weston, K.; Suratman, S. The effect of storage conditions and washing on microplastic release from food and drink containers. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2022, 32, 100826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedzierski, M.; Lechat, B.; Sire, O.; Le Maguer, G.; Le Tilly, V.; Bruzaud, S. Microplastic contamination of packaged meat: Occurrence and associated risks. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2020, 24, 100489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, V.P.; Joseph, A.; Goel, S. Microplastics and other harmful substances released from disposable paper cups into hot water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 404, 124118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Shi, Y.; Yang, L.; Xiao, L.; Kehoe, D.K.; Gun’ko, Y.K.; Boland, J.J.; Wang, J.J. Microplastic release from the degradation of polypropylene feeding bottles during infant formula preparation. Nat. Food 2020, 1, 746–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, H.; Khan, M.R.H.; Quadir, M.; Rusch, K.A.; Mondal, P.P.; Orr, M.; Xu, E.G.; Iskander, S.M. Cutting Boards: An Over-looked Source of Microplastics in Human Food? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 8225–8235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, N.; Aqeel, M.; Noman, A.; Rizvi, Z.F. Impact of plastic mulching as a major source of microplastics in agroecosystems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 445, 130455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatan, B.; Mortula, M.M.; Ali, T. Evaluation of microplastics in groundwater within surrounding areas of Sajaa landfill site, Sharjah, United Arab Emirates. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2025, 30, 102114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, Z.; Hashemi, S.H.; Flury, M. Micro- and Mesoplastics in Farmlands with Different Irrigation Water Sources. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2023, 234, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, N.S.; Taylor, M.P.; Wilson, S.P. Quantification and exposure assessment of microplastics in Australian indoor house dust. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 283, 117064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydın, R.B.; Yozukmaz, A.; Şener, İ.; Temiz, F.; Giannetto, D. Occurrence of Microplastics in Most Consumed Fruits and Vegetables from Turkey and public risk assessment for consumers. Life 2023, 13, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveri Conti, G.; Ferrante, M.; Banni, M.; Favara, C.; Nicolosi, I.; Cristaldi, A.; Fiore, M.; Zuccarello, P. Micro- and nano-plastics in edible fruit and vegetables. The first diet risks assessment for the general population. Environ. Res. 2020, 187, 109677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Healthy Diet. 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/healthy-diet (accessed on 25 August 2025).
- Halkos, G.; Gkampoura, E.C. Where do we stand on the 17 Sustainable Development Goals? An overview on progress. Econ. Anal. Policy 2021, 70, 94–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Top 20 Fruits and Vegetables Sold in the U.S. 2021. Available online: https://www.freshproduce.com/resources/consumer-trends/top-20/ (accessed on 25 August 2025).
- Jadhav, E.B.; Sankhla, M.S.; Bhat, R.A.; Bhagat, D.S. Microplastics from food packaging: An overview of human con-sumption, health threats, and alternative solutions. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2021, 16, 100608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.L.; Liu, L.Y.; Hu, Y.B.; Zeng, E.Y.; Guo, Y. Microplastics: A review of analytical methods, occurrence and charac-teristics in food, and potential toxicities to biota. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munno, K.; Helm, P.A.; Jackson, D.A.; Rochman, C.; Sims, A. Impacts of temperature and selected chemical digestion methods on microplastic particles. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2018, 37, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avio, C.G.; Gorbi, S.; Regoli, F. Experimental development of a new protocol for extraction and characterization of mi-croplastics in fish tissues: First observations in commercial species from Adriatic Sea. Mar. Environ. Res. 2015, 111, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, M.; Webb, H.; Lindeque, P.K.; Fileman, E.S.; Halsband, C.; Galloway, T.S. Isolation of microplastics in biota-rich seawater samples and marine organisms. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiffer, F.; Fischer, E.K. Various digestion protocols within microplastic sample processing—Evaluating the resistance of different synthetic polymers and the efficiency of biogenic organic matter destruction. Front. Environ. Sci. 2020, 8, 572424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo-Ruz, V.; Gutow, L.; Thompson, R.C.; Thiel, M. Microplastics in the marine environment: A Review of the methods used for identification and quantification. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 3060–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, M.; Shahnawaz, M.; Shahkeela, S.; Hussain, M.; Ahmad, M.; Khan, S.S. Significance of physical properties of apple fruit influenced by preharvest orchard management factors. Eur. J. Exp. Biol. 2014, 4, 82–89. [Google Scholar]
- Werby, R.A.; Mousa, A. Some physical and mechanical properties of jatropha fruits. J. Agric. Eng. 2016, 33, 475–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvam, S.; Jesuraja, K.; Venkatramanan, S.; Roy, P.D.; Jeyanthi Kumari, V. Hazardous microplastic characteristics and its role as a vector of heavy metal in groundwater and surface water of coastal south India. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 402, 123786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dronjak, L.; Exposito, N.; Rovira, J.; Florencio, K.; Emiliano, P.; Corzo, B.; Schuhmacher, M.; Valero, F.; Sierra, J. Screening of microplastics in water and sludge lines of a drinking water treatment plant in Catalonia, Spain. Water Res. 2022, 225, 119185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Arab Emirates. 2015. Available online: https://app.indexbox.io/table/080810/784/ (accessed on 25 August 2025).
- Copat, C.; Vinceti, M.; D’Agati, M.G.; Arena, G.; Mauceri, V.; Grasso, A.; Fallico, R.; Sciacca, S.; Ferrante, M. Mercury and selenium intake by seafood from the Ionian Sea: A risk evaluation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 100, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fact Sheet. 2020. Available online: https://u.ae/en/about-the-uae/fact-sheet (accessed on 25 August 2025).
- Bohinc, K.; Štukelj, R.; Abram, A.; Jerman, I.; Van de Velde, N.; Vidrih, R. Biophysical Characterization of Autochthonous and New Apple Cultivar Surfaces. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhide, S.; Salvi, D.; Schaffner, D.W.; Karwe, M.V. Effect of Surface Roughness in Model and Fresh Fruit Systems on Microbial Inactivation Efficacy of Cold Atmospheric Pressure Plasma. J. Food Prot. 2017, 80, 1337–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, P.É.; São José, J.F.B.; Zerdas, E.R.M.A.; Andrade, N.J.; Fernandes, C.M.; Silva, L.D. Influence of the hydro-phobicity and surface roughness of mangoes and tomatoes on the adhesion of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium and evaluation of cleaning procedures using surfactin. Food Control 2014, 41, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quevedo, R.; Aguilera, J.M. Characterization of food surface roughness using the glistening points method. J. Food Eng. 2004, 65, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Meng, Y.; Wang, M.; Memon, M.S.; Yang, X. Surface roughness estimation by optimal tactile features for fruits and vegetables. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2017, 14, 1729881417721866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retama, I.; Jonathan, M.P.; Shruti, V.C.; Velumani, S.; Sarkar, S.K.; Roy, P.D.; Rodríguez-Espinosa, P.F. Microplastics in tourist beaches of Huatulco Bay, Pacific coast of southern Mexico. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 113, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, P.L. Degradation of Microplastics in the Environment. In Handbook of Microplastics in the Environment; Rocha-Santos, T., Costa, M., Mouneyrac, C., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Bayram, B.; Ozkan, G.; Kostka, T.; Capanoglu, E.; Esatbeyoglu, T. Valorization and Application of Fruit and Vegetable Wastes and By-Products for Food Packaging Materials. Molecules 2021, 26, 4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perea-Domínguez, X.P.; Hernández-Gastelum, L.Z.; Olivas-Olguin, H.R.; Espinosa-Alonso, L.G.; Valdez-Morales, M.; Medina-Godoy, S. Phenolic composition of tomato varieties and an industrial tomato by-product: Free, conjugated and bound phenolics and antioxidant activity. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 3453–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, B.; Li, F.; Wang, K.; Huang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xie, D. Impact of plastic film mulching on microplastic in farmland soils in Guangdong province, China. Heliyon 2023, 9, e16587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.J.; Hanun, J.N.; Chen, K.Y.; Hassan, F.; Liu, K.T.; Hung, Y.H.; Chang, T.W. Current levels and composition profiles of microplastics in irrigation water. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 318, 120858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shruti, V.C.; Pérez-Guevara, F.; Elizalde-Martínez, I.; Kutralam-Muniasamy, G. First study of its kind on the microplastic contamination of soft drinks, cold tea and energy drinks—Future research and environmental considerations. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 726, 138580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shruti, V.C.; Kutralam-Muniasamy, G.; Pérez-Guevara, F.; Roy, P.D.; Elizalde-Martínez, I. Free, but not microplastic-free, drinking water from outdoor refill kiosks: A challenge and a wake-up call for urban management. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 309, 119800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makhdoumi, P.; Amin, A.A.; Karimi, H.; Pirsaheb, M.; Kim, H.; Hossini, H. Occurrence of microplastic particles in the most popular Iranian bottled mineral water brands and an assessment of human exposure. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 39, 101708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Basantes, M.F.; Nacimba-Aguirre, D.; Conesa, J.A.; Fullana, A. Presence of microplastics in commercial canned tuna. Food Chem. 2022, 385, 132721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haque, M.R.; Ali, M.M.; Ahmed, W.; Siddique, M.A.B.; Akbor, M.A.; Islam, M.S.; Rahman, M.M. Assessment of micro-plastics pollution in aquatic species (fish, crab, and snail), water, and sediment from the Buriganga River, Bangladesh: An ecological risk appraisals. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Guevara, F.; Roy, P.D.; Elizalde-Martínez, I.; Kutralam-Muniasamy, G.; Shruti, V.C. Human exposure to microplastics from urban decentralized pay-to-fetch drinking-water refill kiosks. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 848, 157722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Microplastics in Drinking-Water; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]





| Market | MPs in Produce (n/mm2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tomatoes | Cucumbers | Grapes | Apples | |
| C | 0.055 ± 0.006 | 0.078 ± 0.011 | 0.439 ± 0.081 | 0.119 ± 0.015 |
| L | 0.038 ± 0.024 | 0.049 ± 0.023 | 0.642 ± 0.146 | 0.120 ± 0.039 |
| A | 0.030 ± 0.016 | 0.063 ± 0.030 | 0.891 ± 0.168 | 0.089 ± 0.020 |
| One-Way ANOVA | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Produce | Markets | p-Value | Significance (p < 0.05) |
| Tomatoes | C, L, and A | 0.30 | Not statistically significant |
| Grapes | C, L, and A | 0.31 | Not statistically significant |
| Cucumbers | C, L, and A | 0.47 | Not statistically significant |
| Apples | C, L, and A | 0.18 | Not statistically significant |
| Produce | Color p-Value | Market p-Value | Interaction p-Value | Color Effect | Market Effect | Interaction Effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tomatoes | 9.16 × 10−7 | 0.23 | 0.34 | Significant | Not significant | Not significant |
| Grapes | 1.44 × 10−11 | 0.08 | 0.07 | Significant | Not significant | Not significant |
| Cucumbers | 6.85 × 10−8 | 0.45 | 0.48 | Significant | Not significant | Not significant |
| Apples | 4.68 × 10−11 | 0.13 | 0.11 | Significant | Not significant | Not significant |
| Produce | Shape p-Value | Market p-Value | Interaction p-Value | Shape Effect | Market Effect | Interaction Effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tomatoes | 0.12 | 0.17 | 0.68 | Not significant | Not significant | Not significant |
| Grapes | 0.48 | 0.06 | 0.86 | Not significant | Not significant | Not significant |
| Cucumbers | 0.04 | 0.24 | 0.57 | Marginally significant | Not significant | Not significant |
| Apples | 0.01 | 0.19 | 0.41 | Significant | Not significant | Not significant |
| Particle Size [μm] | Microsphere Type | Weight (g) | Initial Number | Final Number | Recovery [%] | Average ± SD % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 45–53 | Fluorescent rhodamine B PE | 0.0023 | 37,337 | 26,948 | 72 | 73 ± 1.25 |
| 45–53 | 0.0016 | 25,974 | 19,352 | 75 | ||
| 45–53 | 0.0011 | 17,857 | 12,953 | 73 | ||
| 250–300 | Fluorescent orange PE | 0.0053 | 487 | 418 | 86 | 89 ± 2.82 |
| 250–300 | 0.0059 | 542 | 491 | 91 | ||
| 250–300 | 0.0052 | 478 | 434 | 91 | ||
| 425–500 | Fluorescent green PE | 0.0066 | 127 | 120 | 94 | 98 ± 3.38 |
| 425–500 | 0.0059 | 114 | 114 | 100 | ||
| 425–500 | 0.0063 | 122 | 122 | 100 |
| Market | EDI of MPs per kg for Children | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tomatoes | Cucumbers | Grapes | Apples | |
| C | 2.02 × 10−5 | 8.49 × 10−6 | 1.92 × 10−4 | 3.59 × 10−5 |
| L | 1.63 × 10−5 | 5.83 × 10−6 | 2.91 × 10−4 | 3.39 × 10−5 |
| A | 1.13 × 10−5 | 7.01 × 10−6 | 4.04 × 10−4 | 2.40 × 10−5 |
| Market | EDI of MPs per kg for Adults | |||
| Tomatoes | Cucumbers | Grapes | Apples | |
| C | 4.61 × 10−6 | 1.94 × 10−6 | 4.38 × 10−5 | 8.20 × 10−6 |
| L | 3.73 × 10−6 | 1.33 × 10−6 | 6.65 × 10−5 | 7.75 × 10−6 |
| A | 2.58 × 10−6 | 1.60 × 10−6 | 9.24 × 10−5 | 5.48 × 10−6 |
| Market | EAI of MPs | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tomatoes | Cucumbers | Grapes | Apples | |
| C | 0.013 | 0.005 | 0.073 | 0.023 |
| L | 0.010 | 0.004 | 0.111 | 0.022 |
| A | 0.007 | 0.004 | 0.154 | 0.015 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nassar, S.; Tatan, B.; Mortula, M.M.; Fattah, K.P.; Atabay, S. Microplastics Contamination on the Surfaces of Fruits and Vegetables: Abundance, Characteristics, and Exposure Assessment. Microplastics 2025, 4, 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics4030061
Nassar S, Tatan B, Mortula MM, Fattah KP, Atabay S. Microplastics Contamination on the Surfaces of Fruits and Vegetables: Abundance, Characteristics, and Exposure Assessment. Microplastics. 2025; 4(3):61. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics4030061
Chicago/Turabian StyleNassar, Shumayal, Bushra Tatan, Md Maruf Mortula, Kazi Parvez Fattah, and Serter Atabay. 2025. "Microplastics Contamination on the Surfaces of Fruits and Vegetables: Abundance, Characteristics, and Exposure Assessment" Microplastics 4, no. 3: 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics4030061
APA StyleNassar, S., Tatan, B., Mortula, M. M., Fattah, K. P., & Atabay, S. (2025). Microplastics Contamination on the Surfaces of Fruits and Vegetables: Abundance, Characteristics, and Exposure Assessment. Microplastics, 4(3), 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics4030061








