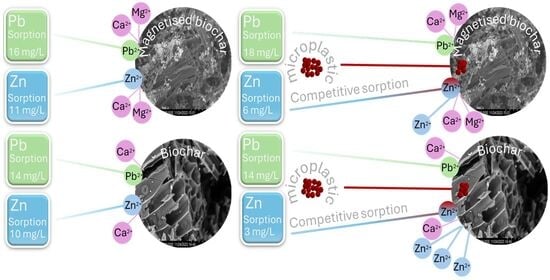
Removal of Co-Occurring Microplastics and Metals in an Aqueous System by Pristine and Magnetised Larch Biochar
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Biochar Characterisation
2.2. Sorption Experiments
2.2.1. Batch Sorption: Study Metal
2.2.2. Batch Sorption Study: Microplastic and Metal
2.3. Water Chemistry and Metal Speciation
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
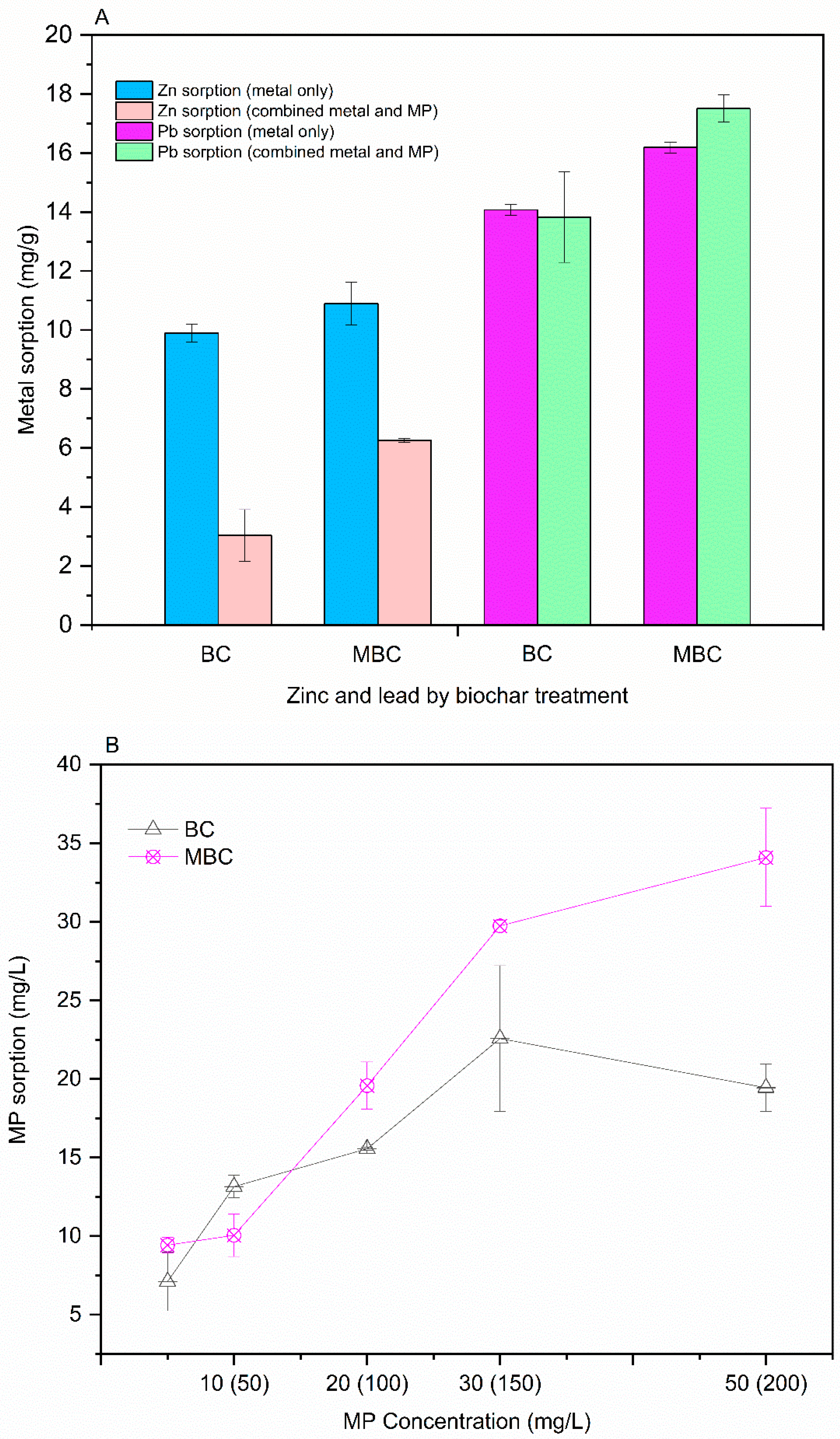
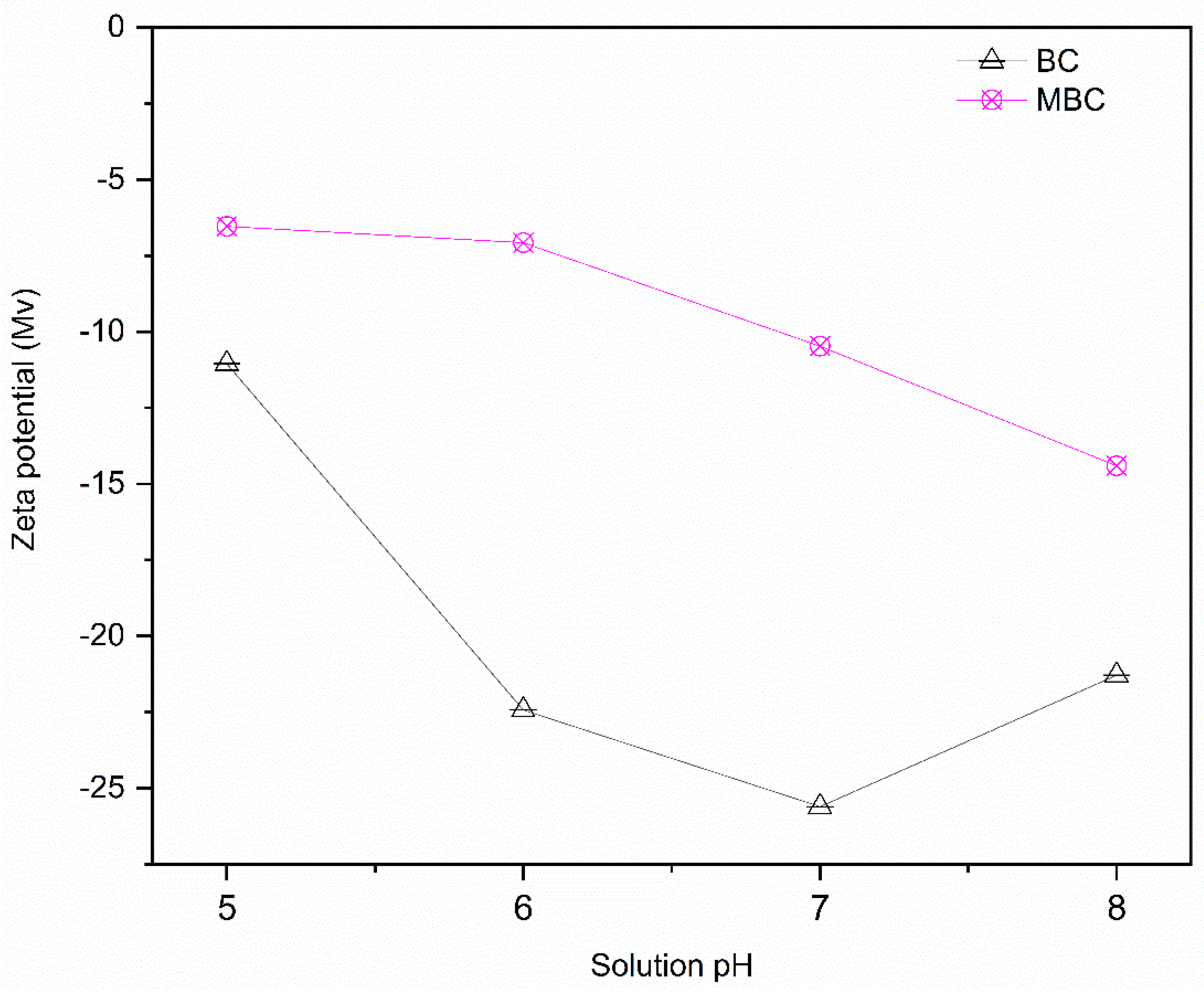
3.1. Contaminant Removal by Pristine Larch Biochar and Magnetised Larch Biochar
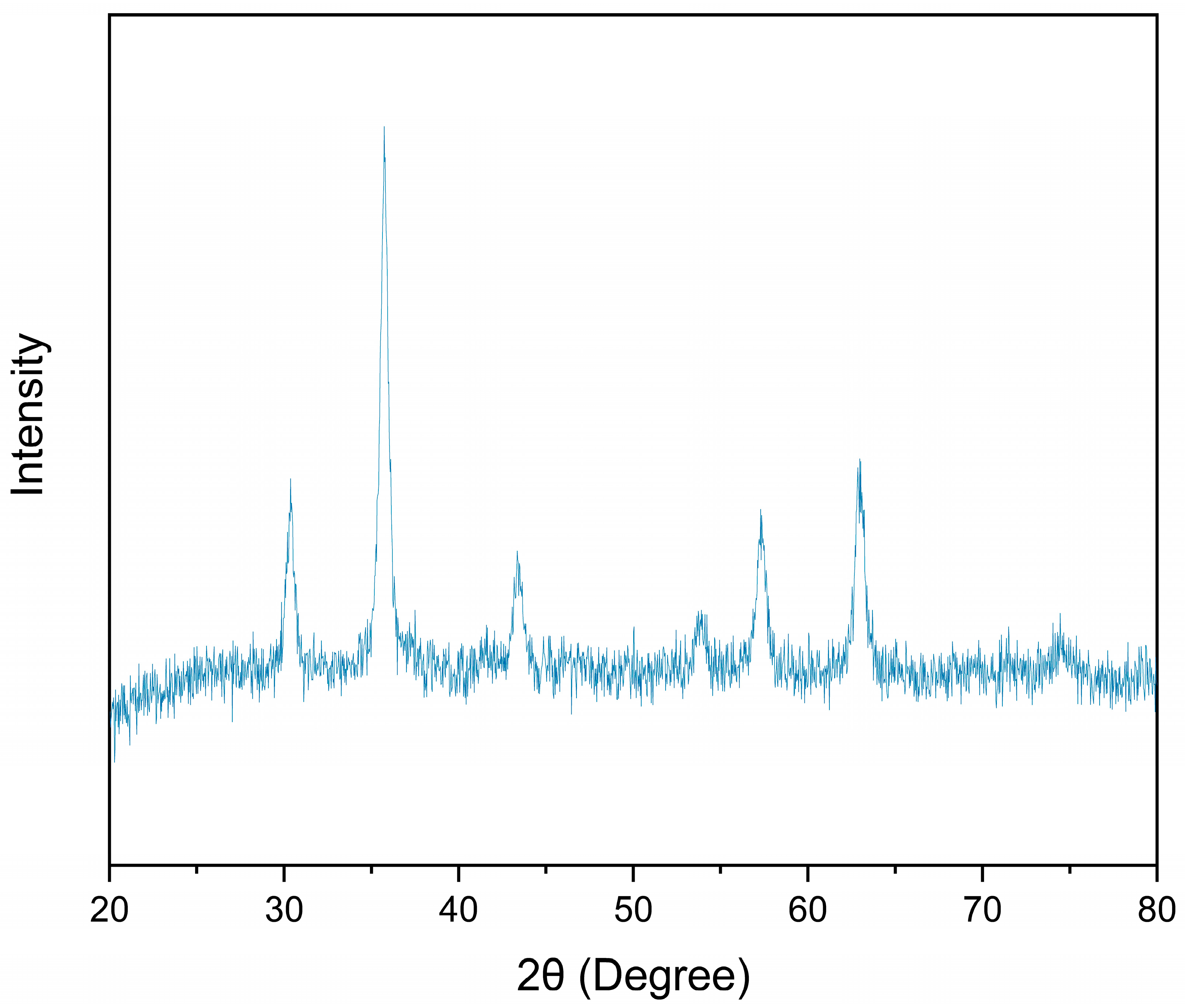
3.2. Biochar Characterisation
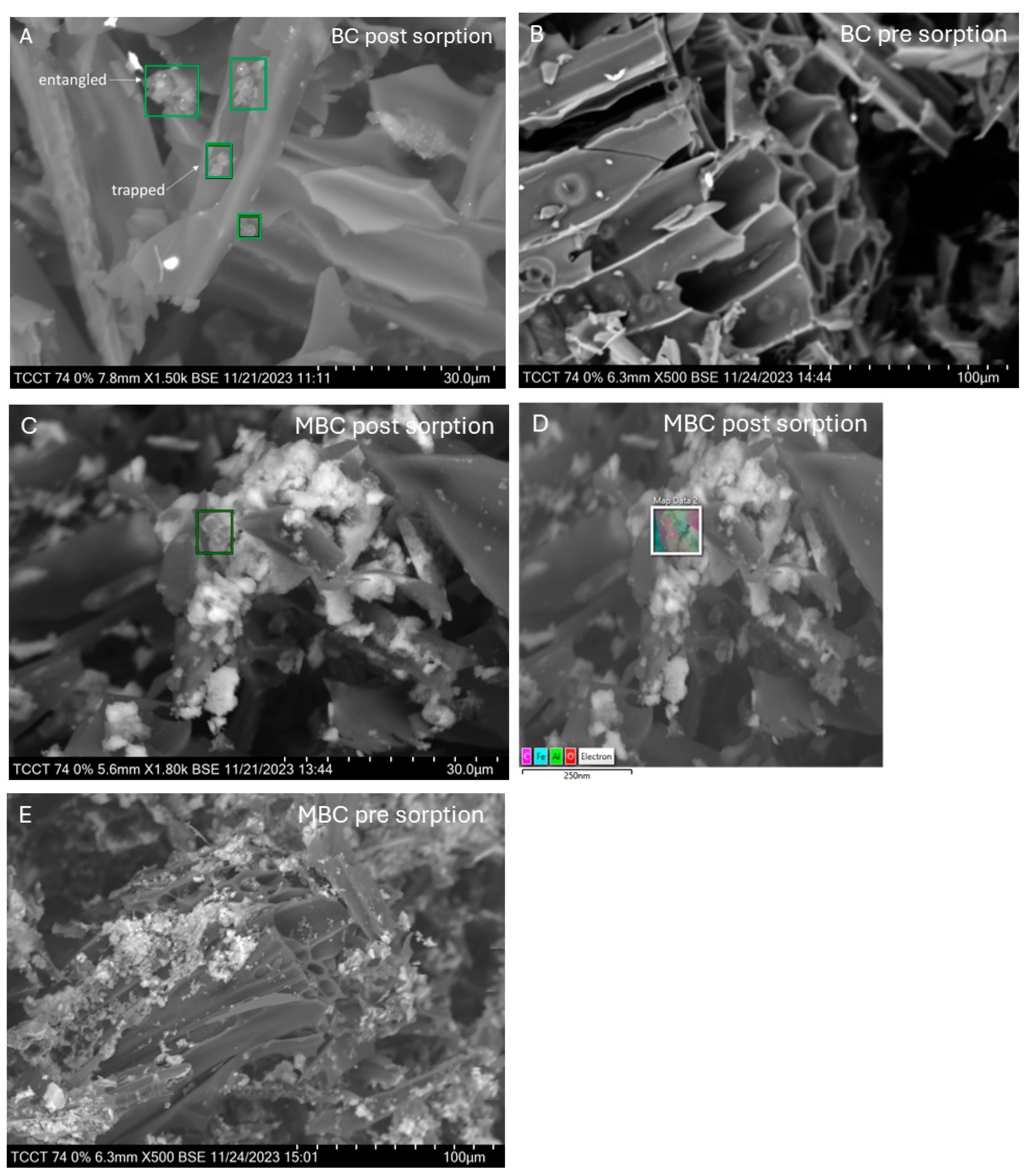
3.3. Materials Analysis
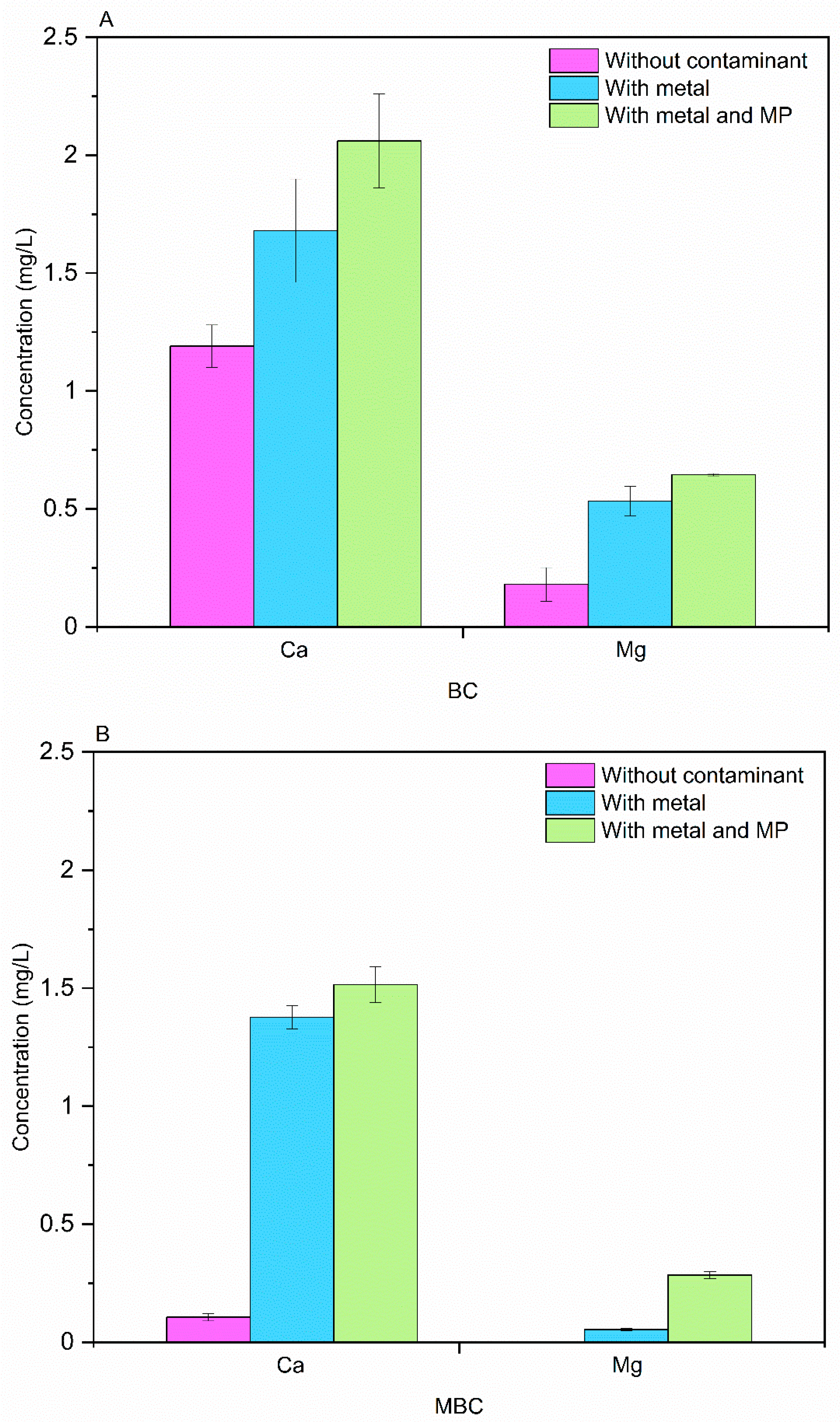
3.4. Aqueous Phase Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MP | Microplastics |
| BC | Pristine larch biochar |
| MBC | Magnetised larch biochar |
References
- Hale, R.C.; Seeley, M.E.; La Guardia, M.J.; Mai, L.; Zeng, E.Y. A Global Perspective on Microplastics; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khant, N.A.; Chia, R.W.; Moon, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, H. Review on the relationship between microplastics and heavy metals in freshwater near mining areas. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 66009–66028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.; Perez-Garcia, P.; Dierkes, R.; Streit, W.R. Microbial enzymes will offer limited solutions to the global plastic pollution crisis. Microb. Biotechnol. 2023, 16, 195–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, M.; Scherer, C.; Alvarez-Muñoz, D.; Brennholt, N.; Bourrain, X.; Buchinger, S.; Fries, E.; Grosbois, C.; Klasmeier, J.; Marti, T.; et al. Microplastics in freshwater ecosystems: What we know and what we need to know. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2014, 26, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelle, S.B.; Ringma, J.; Law, K.L.; Monnahan, C.C.; Lebreton, L.; McGivern, A.; Murphy, E.; Jambeck, J.; Leonard, G.H.; Hilleary, M.A.; et al. Predicted growth in plastic waste exceeds efforts to mitigate plastic pollution. Science 2020, 369, 1515–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cairns, S.; Meza-Rojas, D.; Holliman, P.J.; Robertson, I. Interactions Between Biochar and Nano(Micro)Plastics in the Remediation of Aqueous Media. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2024, 18, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toussaint, B.; Raffael, B.; Angers-Loustau, A.; Gilliland, D.; Kestens, V.; Petrillo, M.; Rio-Echevarria, I.M.; Van den Eede, G. Review of micro- and nanoplastic contamination in the food chain. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2019, 36, 639–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, K.D.; Covernton, G.A.; Davies, H.L.; Dower, J.F.; Juanes, F.; Dudas, S.E. Human Consumption of Microplastics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 7068–7074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cverenkárová, K.; Valachovičová, M.; Mackul’ak, T.; Žemlička, L.; Bírošová, L. Microplastics in the food chain. Life 2021, 11, 1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beane, S.J.; Comber, S.D.W.; Rieuwerts, J.; Long, P. Abandoned metal mines and their impact on receiving waters: A case study from Southwest England. Chemosphere 2016, 153, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Kumar, S. Bioremediation of heavy metals from industrial effluents by endophytes and their metabolic activity: Recent advances. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 339, 125589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, M.; Yoneda, K.; Mohd-Zaki, Z.; Amir, A.; Othman, N. Heavy metals in leachate, impacted soils and natural soils of different landfills in Malaysia: An alarming threat. Chemosphere 2021, 267, 128874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cairns, S.; Todd, A.; Robertson, I.; Byrne, P.; Dunlop, T. Treatment of mine water for the fast removal of zinc and lead by wood ash amended biochar. Environ. Sci. Adv. 2022, 1, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierzba, S. Biosorption of lead(II), zinc(II) and nickel(II) from industrial wastewater by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia and Bacillus subtilis. Pol. J. Chem. Technol. 2015, 17, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budai, P.; Clement, A. Refinement of national-scale heavy metal load estimations in road runoff based on field measurements. Transp. Res. D Transp. Environ. 2011, 16, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairns, S.; Robertson, I.; Sigmund, G.; Street-Perrott, A. The removal of lead, copper, zinc and cadmium from aqueous solution by biochar and amended biochars. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 21702–21715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herath, A.; Datta, D.K.; Bonyadinejad, G.; Salehi, M. Partitioning of heavy metals in sediments and microplastics from stormwater runoff. Chemosphere 2023, 332, 138844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Lo, H.-S.; Wong, H.-M.; Zhou, M.; Wong, C.-Y.; Tam, N.F.-Y.; Cheung, S.-G. Heavy metals contamination of sedimentary microplastics in Hong Kong. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 153, 110977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhof, H.K.; Laforsch, C.; Wiesheu, A.C.; Schmid, J.; Anger, P.M.; Niessner, R.; Ivleva, N.P. Pigments and plastic in limnetic ecosystems: A qualitative and quantitative study on microparticles of different size classes. Water Res. 2016, 98, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ta, A.T.; Babel, S. Microplastic contamination on the lower Chao Phraya: Abundance, characteristic and interaction with heavy metals. Chemosphere 2020, 257, 127234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Xia, S.; Ning, Y.; Pan, X.; Qu, J.; Xu, Y. Effects of microplastics and attached heavy metals on growth, immunity, and heavy metal accumulation in the yellow seahorse, Hippocampus kuda Bleeker. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 149, 110510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, N.; Aqeel, M.; Noman, A.; Khan, S.M.; Akhter, N. Interactions and effects of microplastics with heavy metals in aquatic and terrestrial environments. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 290, 118104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, R.; Tong, L.; Zhang, W. Microplastics in Freshwater Environments: Sources, Fates and Toxicity. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, K.; Lu, N.; Zhang, S.; Wang, W.; Wang, Z.; Guan, J. Uptake of Pb(II) onto microplastic-associated biofilms in freshwater: Adsorption and combined toxicity in comparison to natural solid substrates. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 411, 125115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Mo, Y.; Luo, W.; Xiao, Z.; Jin, C.; Qiu, R. Aqueous aggregation and deposition kinetics of fresh and carboxyl-modified nanoplastics in the presence of divalent heavy metals. Water Res. 2022, 222, 118877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Q.; Tan, X.; Ye, S.; Ma, L.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Chen, Q.; Yang, Y.; Tang, Y. Mechanism analysis of heavy metal lead captured by natural-aged microplastics. Chemosphere 2021, 270, 128624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Biochar Foundation. Guidelines for a Sustainable Production of Biochar; European Biochar Foundation: Arbaz, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Cairns, S.; Robertson, I.; Holliman, P.; Street-Perrott, A. Treatments of wood ash amended biochar to reduce nutrient leaching and immobilise lead, copper, zinc and cadmium in aqueous solution: Column experiments. Environ. Sci. 2022, 8, 1277–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairns, S.; Sigmund, G.; Robertson, I.; Haine, R. Engineered biochar as adsorbent for the removal of contaminants from aqueous medium. In Engineered Biochar: Fundamentals, Preparation, Characterization and Applications; Ramola, S., Masek, O., Mendez, A., Tsubota, T., Eds.; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Q.; Guo, S.; Tang, J.; Lyu, H.; Ri, C.; Sun, H. Enhanced removal of aged and differently functionalized polystyrene nanoplastics using ball-milled magnetic pinewood biochars. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 316, 120696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magid, A.S.I.; Islam, S.; Chen, Y.; Weng, L.; Li, J.; Ma, J.; Li, Y. Enhanced adsorption of polystyrene nanoplastics (PSNPs) onto oxidized corncob biochar with high pyrolysis temperature. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 784, 147115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Wu, J.; Huang, S.; Xin, L.; Zhao, Q. Competitive adsorption behaviors and mechanisms of Cd, Ni, and Cu by biochar when coexisting with microplastics under single, binary, and ternary systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 913, 169524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Meng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Haider, G.; Ge, T.; Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Yu, Y.; Shan, S. Co-pyrolysis of sewage sludge and metal-free/metal-loaded polyvinyl chloride (PVC) microplastics improved biochar properties and reduced environmental risk of heavy metals. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 302, 119092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairns, S.; Chaudhuri, S.; Sigmund, G.; Robertson, I.; Hawkins, N.; Dunlop, T.; Hofmann, T. Wood ash amended biochar for the removal of lead, copper, zinc and cadmium from aqueous solution. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 24, 101961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, L.; He, L.; Zhang, M.; Lv, W.; Yang, K.; Tong, M. Addition of biochar as thin preamble layer into sand filtration columns could improve the microplastics removal from water. Water Res. 2022, 221, 118783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siipola, V.; Pflugmacher, S.; Romar, H.; Wendling, L.; Koukkari, P. Low-cost biochar adsorbents for water purification including microplastics removal. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Sedighi, M.; Lea-Langton, A. Filtration of microplastic spheres by biochar: Removal efficiency and immobilisation mechanisms. Water Res. 2020, 184, 116165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sun, C.; Huang, Q.X.; Chi, Y.; Yan, J.H. Adsorption and thermal degradation of microplastics from aqueous solutions by Mg/Zn modified magnetic biochars. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 419, 126486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, M.; He, L.; Rong, H.; Li, M.; Kim, H. Transport behaviors of plastic particles in saturated quartz sand without and with biochar/Fe3O4-biochar amendment. Water Res. 2020, 169, 115284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, D.; Kumar, H.; Sarswat, A.; Alexandre-Franco, M.; Pittman, C.U. Cadmium and lead remediation using magnetic oak wood and oak bark fast pyrolysis bio-chars. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 236, 513–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; Pi, J.; Zong, M.; Wang, Y.; Li, W.; Liao, Q. Chromium removal using magnetic biochar derived from herb-residue. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 68, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairns, S.; Todd, A.M.L.; Robertson, I.; Byrne, P. Metals Removal from Acid Mine Water by Wood-Ash Amended Biochar. In Proceedings of the IMWA, The IMWA 2022, Christchurch, New Zealand, 6–10 November 2022. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/366325622 (accessed on 22 January 2025).
- Pagnanelli, F.; Moscardini, E.; Giuliano, V.; Toro, L. Sequential extraction of heavy metals in river sediments of an abandoned pyrite mining area: Pollution detection and affinity series. Environ. Pollut. 2004, 132, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, G.; Miah, M.A.; Anawar, H.M.; Chowdhury, D.A.; Ahmad, J.U. Influence of multi-industrial activities on trace metal contamination: An approach towards surface water body in the vicinity of Dhaka Export Processing Zone (DEPZ). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 4181–4190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokhande, R.S.; Singare, P.U.; Pimple, D.S. Toxicity Study of Heavy Metals Pollutants in Waste Water Effluent Samples Collected from Taloja Industrial Estate of Mumbai, India. 2011. Available online: http://journal.sapub.org/re (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- Martínez, J.; Hidalgo, M.; Rey, J.; Garrido, J.; Kohfahl, C.; Benavente, J.; Rojas, D. A multidisciplinary characterization of a tailings pond in the Linares-La Carolina mining district, Spain. J. Geochem. Explor. 2016, 162, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, B.; Lee, X.; Lehmann, J.; Gao, B. Sorption and desorption of Pb(II) to biochar as affected by oxidation and pH. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 634, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Test No. 106: Adsorption—Desorption Using a Batch Equilibrium Method; OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals; OECD: Paris, France, 2000; Section 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavlová, A.; Jachimowicz, P.; Praus, P.; Bednár, P. Environment changes everything. How relevant are laboratory studies of sorption of pollutants on microplastics? A critical review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 115655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhoff, P.T.; Akbar Nakhli, S.A. Reducing Stormwater Runoff and Pollutant Loading with Biochar Addition to Highway Greenways. October 2017, pp. 1–47. Available online: https://trid.trb.org/view/1491582 (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- Kabir, A.H.M.E.; Sekine, M.; Imai, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Kanno, A.; Higuchi, T. Assessing small-scale freshwater microplastics pollution, land-use, source-to-sink conduits, and pollution risks: Perspectives from Japanese rivers polluted with microplastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 768, 144655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasee, S.; Mauricio, J.; Thompson, W.A.; Karnjanapiboonwong, A.; Kasumba, J.; Subbiah, S.; Morse, A.N.; Anderson, T.A. Microplastics in a freshwater environment receiving treated wastewater effluent. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2017, 13, 528–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.; Maung, G.Y.T.; Otiti, J.; Tabucanon, A.S. Land use-based characterization and source apportionment of microplastics in urban storm runoffs in a tropical region. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 329, 121698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker-Jurd, F.N.F.; Abbott, G.D.; Guthery, B.; Parker-Jurd, G.M.C.; Thompson, R.C. Features of the highway road network that generate or retain tyre wear particles. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 26675–26685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkhurst, D.L.; Appelo, C.A.J. User’s Guide to PHREEQC (Version 2): A Computer Program for Speciation, Batch-Reaction, One-Dimensional Transport, and Inverse Geochemical Calculations; U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1999; Volume 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarroll, D. Simple Statistical Tests for Geography; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, C.; Zhu, L.; Lei, S.; Liu, M.; Hong, C.; Che, L.; Wang, J.; Qiu, Y. Lead competition alters the zinc adsorption mechanism on animal-derived biochar. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirenje, T.; Ma, L.Q.; Lu, L. Retention of Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn by wood ash, lime and fume dust. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2006, 171, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Ok, Y.S.; Kim, S.-H.; Cho, J.-S.; Heo, J.-S.; Delaune, R.D.; Seo, D.-C. Competitive adsorption of heavy metals onto sesame straw biochar in aqueous solutions. Chemosphere 2016, 142, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, M.B. Environmental Chemistry of Soils; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, N.; Khandelwal, N.; Ganie, Z.A.; Tiwari, E.; Darbha, G.K. Eco-friendly magnetic biochar: An effective trap for nanoplastics of varying surface functionality and size in the aqueous environment. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 418, 129405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trakal, L.; Veselská, V.; Šafařík, I.; Vítková, M.; Číhalová, S.; Komárek, M. Lead and cadmium sorption mechanisms on magnetically modified biochars. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 203, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Liu, B.; Chen, G. Preparation and application of magnetic biochar in water treatment: A critical review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 711, 134847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Yan, Q.; He, Y.; Wang, X.; Wei, Z.; Liang, D.; Yue, H.; Yun, Y.; Li, G.; Sang, N. Insights into the removal of polystyrene nanoplastics using the contaminated corncob-derived mesoporous biochar from mining area. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 433, 128756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Dan, Y.; Diao, Y.; Liu, F.; Wang, H.; Sang, W.; Zhang, Y. Transport characteristics of polystyrene microplastics in saturated porous media with biochar/Fe3O4-biochar under various chemical conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 847, 157576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, D.; Pittman, C.U.; Bricka, M.; Smith, F.; Yancey, B. Sorption of arsenic, cadmium, and lead by chars produced from fast pyrolysis of wood and bark during bio-oil production. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 310, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, W. Qualitative Organic Analysis Spectrochemical Techniques, 2nd ed.; McGraw-Hill Book Company: London, UK, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, I.M.; Ro, K.S.; Reddy, G.B.; Boykin, D.L.; Klasson, K.T. Efficacy of Chicken Litter and Wood Biochars and Their Activated Counterparts in Heavy Metal Clean up from Wastewater. Agriculture 2015, 5, 806–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Tan, X.; Li, J.; Peng, C.; Wan, P.; Naz, I.; Duan, Z.; Ruan, Y. Innovations in the Development of Promising Adsorbents for the Remediation of Microplastics and Nanoplastics—A Critical Review. Water Res. 2023, 230, 119526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhu, X.; Shi, L.; Li, J.; Li, S.; Lü, J.; Li, Y. Efficient removal of lead from solution by celery-derived biochars rich in alkaline minerals. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 235, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Du, J.; Zhao, T.; Feng, B.; Bian, H.; Shan, S.; Meng, J.; Christie, P.; Wong, M.H.; Zhang, J. Removal of nanoplastics from aqueous solution by aggregation using reusable magnetic biochar modified with cetyltrimethylammonium bromide. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 318, 120897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yang, C.; Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Liu, Z.; Li, C.; Song, F. Efficient removal of microplastics from aqueous solution by a novel magnetic biochar: Performance, mechanism, and reusability. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 26914–26928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchimiya, M.; Lima, I.M.; Klasson, T.; Chang, S.; Wrtelle, L.H.; Rodgers, J.E. Immobilization of Heavy Metal Ions (Cu II, Cd II, Ni II, and Pb II) by Broiler Litter-Derived Biochars in Water and Soil. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 5538–5544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, J.; Joseph, S. Biochar for Environmental Management Science, Technology and Implementation, 2nd ed.; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ganie, Z.A.; Khandelwal, N.; Tiwari, E.; Singh, N.; Darbha, G.K. Biochar-facilitated remediation of nanoplastic contaminated water: Effect of pyrolysis temperature induced surface modifications. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 417, 126096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Biochar Type | O/C | (O + N)/C | H/C | BET Surface Area (m2/g) | Zn (mg/g) | Ca (mg/g) | Mg (mg/g) | P (mg/g) | Fe (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BC | 0.142 | 0.143 | 0.027 | 361.7 | 0.12 | 2.15 | 0.28 | 0.19 | 23.55 |
| MBC | 0.352 | 0.354 | 0.029 | 272.6 | 0.08 | 0.97 | 0.14 | 0.12 | 207.10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cairns, S.; Holliman, P.J.; Robertson, I.; Harrison, B. Removal of Co-Occurring Microplastics and Metals in an Aqueous System by Pristine and Magnetised Larch Biochar. Microplastics 2025, 4, 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics4030054
Cairns S, Holliman PJ, Robertson I, Harrison B. Removal of Co-Occurring Microplastics and Metals in an Aqueous System by Pristine and Magnetised Larch Biochar. Microplastics. 2025; 4(3):54. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics4030054
Chicago/Turabian StyleCairns, Stuart, Peter J. Holliman, Iain Robertson, and Benjamin Harrison. 2025. "Removal of Co-Occurring Microplastics and Metals in an Aqueous System by Pristine and Magnetised Larch Biochar" Microplastics 4, no. 3: 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics4030054
APA StyleCairns, S., Holliman, P. J., Robertson, I., & Harrison, B. (2025). Removal of Co-Occurring Microplastics and Metals in an Aqueous System by Pristine and Magnetised Larch Biochar. Microplastics, 4(3), 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics4030054