Abstract
Harmonization in the analytical framework is needed to detect, define and further categorize plastics released into the environment. In the range of particles smaller than 200 μm, hydrocyclones (HCs) have proven their capacity in removing microplastics efficiently by offering technical advantages at low operational costs. This publication aims to expand scientific knowledge by introducing four commercially available, low-priced microplastics to a pilot-scale HC setting. The physicochemical characteristics of particles as well as the separation efficiency of the test rig were investigated in depth. Particles with a density of >1000 kg/m3 passed the primary vortex and were discharged into the underflow, allowing us to employ standard mode operation. Particles with a density of <1000 kg/m3 entered the secondary vortex and were removed through the overflow. As expected, separation efficiencies were found to be higher for particles revealing a greater density difference when compared with the mobile phase water. Furthermore, an increase in the inlet volume flow revealed significant positive impacts on the separation efficiency for three plastics to a certain threshold. Data on standard and reverse mode operations presented in this publication can lay out an important source for the harmonization and standardization of future HC research, with the goal of overcoming plastic pollution by developing economically competitive separation processes.
1. Introduction
Plastic products have become indispensable in our daily life [1], but their extensive production in combination with an underdeveloped waste management have caused a significant disposal of plastic debris in different sizes virtually present in all environmental compartments [2]. Macroplastics enter the environment directly or indirectly, depending on the state of waste management in its various sectors of use. Due to the influence of UV radiation from the sun and mechanical impacts, macroplastic particles later break down into secondary microplastics and nanoplastics [3,4]. Primary microplastics are incorporated directly into products (e.g., cosmetics and paints) as a functional ingredient and find their way into the environment through their application. The ubiquitous presence of microplastics (MPs) in all aquatic and terrestrial environments [5] up to the highest mountain ranges [6,7] together with their uncertain mechanical and toxicological effects pose a significant threat for all species including human beings [8,9,10,11]. Hence, more and more international and national bills and directives address these polluters and call for a harmonization in the analytical frameworks in order to define and further categorize plastic debris as well as for standardized, accurate, traceable and robust methodologies, from sample preparation to detection, to obtain comparable data on the status of plastic pollution [12,13,14].
As reported before, the availability and validity of the respective data decrease with the size of investigated particles [15]. Manta trawls and other net systems (80–300 μm) are tremendously discriminating particles smaller than their nominal mesh size; in situ pump systems and fractionated filtration devices allow a lower threshold. However, for the quantitative sampling of particles that are >10 μm, filtration is impeded by fast clogging [15,16]. Consequently, centrifugal separators, such as hydrocyclones (HCs), that are widely applied in several industries (e.g., [17,18,19,20] and others) have found their niche in applications dealing with plastic pollution. Separation is based on density differences in the two phases, e.g., solid MP particles and a liquid medium, and the principle of two forces. A centrifugal force pushes the phase with the higher density to the wall, creating a primary vortex that passes through the underflow and a drag force pulling the phase with the lower density into the center, thereby creating the secondary vortex leaving through the overflow (vortex finder) [21]. HCs bear the advantage of good scalability, high throughput, continuous operation, structural simplicity at low operation costs, low energy requirements and no secondary pollution [17,22].
Studies have revealed promising results for separating plastic particles in liquid matrices; however, they prominently rely on shredded plastic particles [1,23,24], which consequently bear difficulties when it comes to the comparison of design variables in the HC setup, e.g., the cone angle, the length of the cylindrical section and many more, thereby effecting the separation efficiency of MPs [23].
This study aims to investigate the separation characteristics of four important, commercially available and low-cost MP bulk solids in a bench-scale hydrocodone setting in depth. Authors propose that data on standard and reverse mode operations presented in this publication can lay out an important source for the harmonization and standardization of future HC-based research, with the goal being to overcome plastic pollution by developing economically competitive separation processes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material Selection and Characterization
The following plastics or elastomers, listed with their respective trade names, were investigated in this study: one high-density polyethylene (HDPE) powder (ET306010), one polypropylene (PP) powder (Eltex P KS001PF), one polystyrol (PS) powder (PrimeCast 101) and one polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) powder (DEGACRYL LP 55/03) were obtained from four different companies (Table 1).

Table 1.
Results of the separation experiments according to variation of particle type, hydrocyclone operation mode and underflow rate. The Δmax (+) and Δmin (−) show the difference between the average value and the minimum and maximum measured value.
Three of these plastics—HDPE, PP and PS—were properly described in the preliminary publication of these authors [14]. Particle density, size distribution and the PMMA shape were determined following the same instructions presented in that previous study. Other basic information was taken from technical information reports and data sheets provided by the manufacturers. All the characteristics for PMMA are presented in Table 1. The particle size distribution of all four investigated plastics is stated in Figure 1.
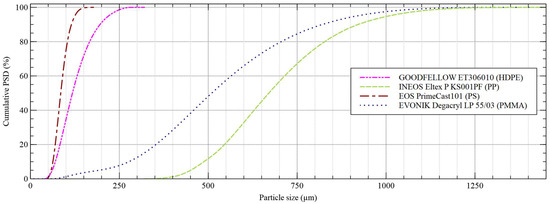
Figure 1.
Particle size distribution (PSD, cumulative) of the microplastic particles used in the experiments. Laser diffraction measurements were conducted using a Malvern Mastersizer 2000E (Malvern Panalytical Ltd., Malvern, UK) with diffraction indexes of 1.54 (ET306010), 1.49 (Eltex P KS001PF), 1.59 (PrimeCast 101) and 1.49 (Degacryl LP 55/03). Parts of the particle details were already published in a previous study [14].
2.2. Separation Experiments
For particle separation, a test rig (see Figure 2, adapted from [25]) was used throughout the experiments. Water (20 °C) was pumped with the circulation pump P1 (KWPK065-040-0250, KSB Austria GmbH, Wiener Neustadt, AUT) from the clean water vessel through the flowmeter F001 (type S030, Bürkert Austria GmbH, Mödling, AUT) to the HC unit Z1. Test particles, introduced with a final feed concentration of 0.5 kg/m3, were injected using a metering device (piston injection with the stepper motor M4). The HC underflow was pumped (P2) through the flowmeter F002 (type 2551, Georg Fischer Piping Systems Ltd, Schaffhausen, CH) to the absolute filter F1 (0.75 μm; LLT-BFBE-2-304-1B and LT-AR-232-WS-1-P-R; HENNLICH GmbH, Suben, AUT) for the gravimetrical determination of the separated particles. The overflow was transferred to the absolute filter F2 (0.75 µm; LLT-BFBE-2-304-2B and LT-AR-232-WS-2-P-R; HENNLICH GmbH, Suben, AUT). Dry mass of particles was determined after drying at 70 °C for 72 h (completely dry).
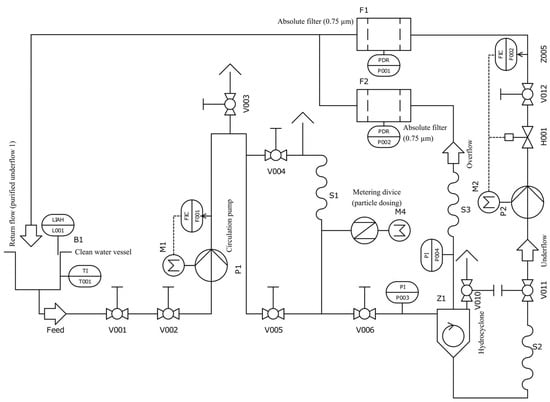
Figure 2.
Experimental setup of the test rig. FIC: flow indication control; LI: level indication; M: motor; P: pump; PD: pressure difference; PI: pressure indicator; S: hose; TI: temperature indication and V: Valve. Adapted and re-designed from a previous study of the authors [25].
Separation efficiency of dried particles was determined according to Equation (1) where is the separation efficiency, the mass of the dried empty filter before the experiment and the mass of the dried loaded filter.
To evaluate energy consumption, the pressure drop between the inlet and the overflow of the HC was measured under variation of the feed flow rate (F001) without underflow. The geometrical dimensions of the used HC, based on an empirical geometrical optimization study [26], are shown in Figure 3.
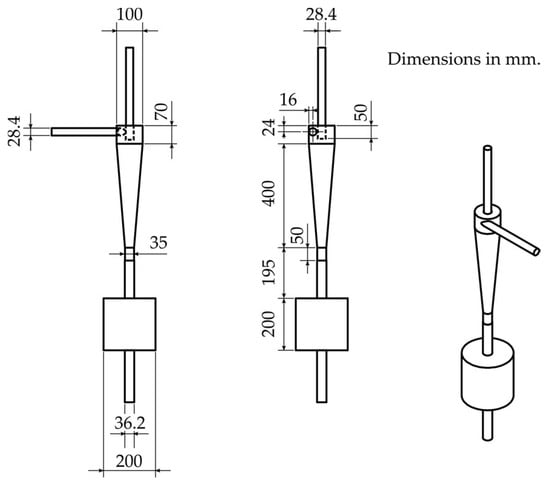
Figure 3.
Hydrocyclone dimensions on the basis of a previous empirical study [26] with variation of the inlet diameter, vortex-finder diameter, vortex-finder length, cone angle and underflow configurations.
3. Results and Discussion
Overall, a total number of 96 separation experiments (32 treatments, n = 3) were carried out on the test rig (Figure 2). PMMA and PS particles, both at ρ > 1000 kg/m3, left with the underflow due to centrifugal force (=standard mode). HDPE and PP particles (ρ < 1000 kg/m3) did so with the overflow (=reverse mode operation). Table 1 and Figure 4 reveal the average separation efficiencies (n = 3) for all four investigated polymers, including minimum and maximum measured values.
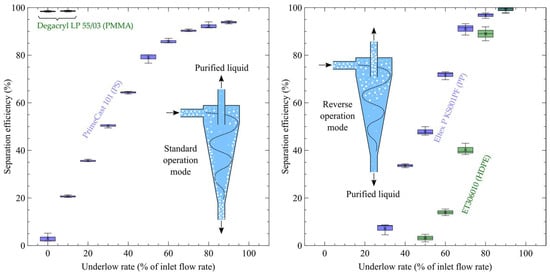
Figure 4.
Standard (left) and reverse mode (right) operations of the hydrocyclone (5 m3/h inlet flow rate) with selected polymers and variation of the underflow rate.
PMMA separation was found to be straightforward, revealing percentages of 98.42% and 98.54% at underflow rates of 10% and 20%, respectively. Particle properties of a relatively large density difference (ρ: 1200.6 kg/m3) to water (ρ: 1000 kg/m3) coupled with relatively large particle size (520 µm) allowed for optimal separation at a low underflow rate. Consequently, there is no need to increase the underflow rate, so maximum (100%) generation of purified liquid is possible. For PS, separation was found to be more challenging, due to minor density differences in relation to water and smaller particle size (Table 1 and Figure 4, left). With 0% underflow, only 3% separation efficiency can be reached. Separation efficiency continuously increased between 10% and 70% underflow rates and thereafter slightly increased at underflow rates of 70% to 90%, thereby revealing efficiencies of 90.36%, 92.34% and 93.85%, respectively.
HDPE particle separation (Figure 4, right) started at a 50% underflow rate (separation efficiency of 3.15%) and thereafter rapidly increased, reaching quantities of 99.12% separation efficiency at a 90% underflow rate. Consequently, at an underflow rate of 50%, almost 50% (2.5 m3/h) of purified liquid can be generated, while all particles are concentrated in the 2.5 m3/h unpurified liquid (overflow of the hydrocyclone). Even greater efficiencies could be detected for PP particles due to greater differences in density (881.9 kg/m3 compared with 949.6 kg/m3 for HDPE). The hydrocyclone was found to be capable of retaining 99.35% of suspended particles at a 90% underflow rate. Furthermore, separation was induced at a 30% underflow rate, revealing a respective average efficiency of 7.16%.
Generally spoken, particles with a density of >1000 kg/m3 are more likely to pass the primary vortex and be discharged into the underflow and particles with a density < 1000 kg/m3 are more likely to enter the secondary vortex and be removed through the overflow [27]. Moreover, the greater the density difference between the particles and water, and the stronger the underflow rate are the higher the centrifugal force acting on the particles is, hence increasing overall separation efficiency.
Three other studies revealed promising results using shredded polymers. In a study by Yuan et al. [1], a composition of PET (ρ: 1300–1380 kg/m3) and PVC (ρ: 1380–1500 kg/m3) fragments that was mingled (mass ratio of 1:3.28) and grinded to a mean particle size of 0.75 mm was introduced into a CaCl2 solution (ρ: 1280 kg/m3) and fed into the test rig in 2% concentrations (v/v). Test results revealed an efficiency above 80%, with purities of PVC and PET reaching 93.2% and 94.5%, respectively. The same polymers were also applied by Fu et al. [23]. The authors grinded PET (ρ: 1.220 kg/m3) and PVC bottles (ρ: 1310 kg/m3) to reach a mass ratio of 3.28:1 suspended in a CaCl2 solution (ρ: 1280 kg/m3) and a 3% feeding regime. At a cone angel of 12°, the authors revealed efficiencies of up to 96.6% for PET in the overflow and 83.4% for PVC in the underflow. Carlson [24] presented a publication on the composition of HDPE (ρ: 970 kg/m3) and PP (ρ: 900 kg/m3) that was uniformly mixed according to a ratio of 1:1 and a particle size ranging from 239 to 1096 μm. The authors used a light medium to reach efficiency of 78.8%. PP was found to have reduced from 1.0% in feed to 0.2% in the underflow. Separation in these publications was conducted using CaCl2 as the liquid medium. The results presented here reveal high capacities for all four investigated plastics, hence allowing more functional applications in existing infrastructure (e.g., wastewater streams and others).
Energy consumption was evaluated using the characteristic pressure drop–volume flow rate diagram of the HC, which is displayed in Figure 5 according to an underflow rate of 0.
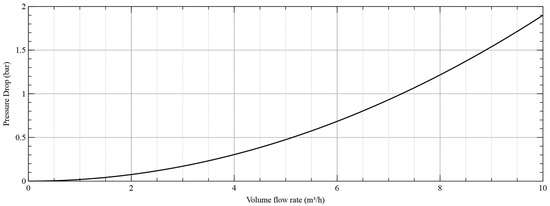
Figure 5.
Pressure drop as a function of the feed volume flow rate (underflow rate = 0). Through multiplication of the pressure drop and the volume underflow rate of each set point, the energy consumption of the hydrocyclone can be estimated. For a typical setpoint (5 m3/h), the power consumption of the hydrocyclone is 66 W (simplified consideration neglecting individual coefficients of performance).
4. Conclusions
HCs treating MPs face unfavorable conditions such as small particle sizes and low density differences. However, due to their beneficial characteristics, HCs bear the potential to fill the analytical gap for microplastic particles smaller than 200 µm in large scale applications.
This study provides a database of the physicochemical properties and separation efficiencies of four commercially available, low-priced MPs. Particles were separated either through standard or reverse mode operations, thereby proofing the flexibility of a HC system in separating fractions with different density characteristics. As expected, higher density differences between target microplastic particles and water had to be compensated with underflow rates raised to a certain threshold. Removal of MPs for all four investigated plastics was shown to be efficient by using water as a liquid medium rather than CaCl2 solution, thereby allowing for a level of functionality that is more applicable in practice. Another characteristic feature of this study is the usage of commercially available microplastic particles in contrast to the particles that were self-made by other authors. This leads to high potential for the harmonization of separation experiments in the microplastic sector.
In future studies, more plastic types and size-distributions must be investigated in depth to allow us to understand released primary and secondary microplastic debris more deeply as well as its removal from ecosystems through HC applications.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.S., M.P., L.D. and F.A.; methodology, T.S., L.D. and F.A.; validation, T.S., M.P., L.D., F.A. and A.W.; formal analysis, M.K.; investigation, T.S. and A.W.; resources, M.K., M.P. and L.D.; data curation, T.S., M.B. and A.W.; writing—original draft preparation, T.S., F.A. and A.W.; writing—review and editing, L.D., M.B., M.K. and M.P.; visualization, T.S., A.W. and M.B.; supervision, M.P.; project administration, T.S., L.D. and F.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Benedikt Stern for laboratory assistance. Moreover, our thanks go to Christian Mayerl, who supported measurements and data analysis in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors Lukas Dür and Florian Alber were employed by the company ecolymer GmbH. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Yuan, H.; Fu, S.; Tan, W.; He, J.; Wu, K. Study on the hydrocyclonic separation of waste plastics with different density. Waste Manag. 2014, 45, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prata, J.C.; da Costa, J.P.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T. Methods for sampling and detection of microplastics in water and sediment: A critical review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 110, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delre, A.; Goudriaan, M.; Morales, V.H.; Vaksmaa, A.; Ndhlovu, R.T.; Baas, M.; Keijzer, E.; de Groot, T.; Zeghal, E.; Egger, M.; et al. Plastic photodegradation under simulated marine conditions. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 187, 114544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavian Petroody, S.S.; Hashemi, S.H.; Škrlep, L.; Mušič, B.; van Gestel, C.A.M.; Sever Škapin, A. UV Light Causes Structural Changes in Microplastics Exposed in Bio-Solids. Polymers 2023, 15, 4322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, T.; Hauk, A.; Walter, U.; Burkhardt-Holm, P. Microplastics profile along the Rhine River. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napper, I.E.; Davies, B.F.R.; Clifford, H.; Elvin, S.; Koldewey, H.J.; Mayewski, P.A.; Miner, K.R.; Potocki, M.; Elmore, A.C.; Gajurel, A.P.; et al. Reaching New Heights in Plastic Pollution—Preliminary Findings of Microplastics on Mount Everest. One Earth 2020, 3, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, M.; Mützel, S.; Primpke, S.; Tekman, M.B.; Trachsel, J.; Gerdts, G. White and wonderful? Microplastics prevail in snow from the Alps to the Arctic. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaax1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Zhang, T.; Song, K.; Sun, Y.; Chen, Y.; Huang, W.; Feng, Z. Microplastics in commercial clams from the intertidal zone of the South Yellow Sea, China. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 905923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Nag, R.; Cummins, E. Human health concerns regarding microplastics in the aquatic environment—From marine to food systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 823, 153730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issac, M.N.; Kandasubramanian, B. Effect of microplastics in water and aquatic systems. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 19544–19562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, K.D.; Covernton, G.A.; Davies, H.L.; Dower, J.F.; Juanes, F.; Dudas, S.E. Human Consumption of Microplastics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 7068–7074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, Y.K.; Wernicke, T.; Pittroff, M.; Witzig, C.S.; Storck, F.R.; Klinger, J.; Zumbülte, N. Microplastic analysis—Are we measuring the same? Results on the first global comparative study for microplastic analysis in a water sample. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, N.B.; Hüffer, T.; Thompson, R.C.; Hassellöv, M.; Verschoor, A.; Daugaard, A.E.; Rist, S.; Karlsson, T.; Brennholt, N.; Cole, M.; et al. Are We Speaking the Same Language? Recommendations for a Definition and Categorization Framework for Plastic Debris. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senfter, T.; Walter, A.; Dür, L.; Alber, F.; Pillei, M. Do We Speak the Same Language for Reference Particles in Microplastic Research? Microplastics 2022, 1, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrandt, L.; Zimmermann, T.; Primpke, S.; Fischer, D.; Gerdts, G.; Pröfrock, D. Comparison and uncertainty evaluation of two centrifugal separators for microplastic sampling. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 414, 125482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios Mendoza, L.M.; Balcer, M. Microplastics in freshwater environments: A review of quantification assessment. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 113, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Paul, P.; Shanbhag, B.K.; Dixon, I.; Kuang, S.; He, L. Emerging application of hydrocyclone in biotechnology and food processing. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 309, 122992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibian, M.; Pazouki, M.; Ghanaie, H.; Abbaspour-Sani, K. Application of hydrocyclone for removal of yeasts from alcohol fermentations broth. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 138, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gama, A.J.A.; Neves, G.A.; Barros, P.L.; Neto, A.T.P.; Alves, J.J.N. Hydrocyclone performance for bentonite clay purification. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2020, 161, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Carmo Precci Lopes, A.; Senfter, T.; Ebner, C.; Senn, M.; Pillei, M.; Kraxner, M.; Robra, S.; Bockreis, A. Separation of biodegradable material from the low calorific fraction of municipal solid waste. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 280, 124681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vimal, A.; Thalaieswaran, S.; Kannan, N.H.; Ganeshan, P.; Venkatesh, S. A review on the Investigation of Hydrocyclone Performance by shape optimization. E3S Web Conf. 2023, 405, 04047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; Zhang, L.; Cui, B.; Zhao, Q.; Jiang, L.; Liu, P.; Wei, D. Research on the particle circulation flow and classification performance of multi-stage cylindrical hydrocyclones. Powder Technol. 2023, 429, 118908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Qian, Y.; Yuan, H.; Fang, Y. Effect of cone angles of a hydrocyclone for the separation of waste plastics with low value of density difference. Waste Manag. 2022, 140, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, D.C. Light Medium Separation of High Density Polyethylene and Polypropylene in a Hydrocyclone. Master’s Thesis, Michigan State University, East Lansing, MI, USA, 1995. Available online: https://www.proquest.com/openview/a19599d209af90b6e330b801bb17ba27/1?pq-origsite=gscholar&cbl=18750&diss=y (accessed on 6 October 2023).
- Senfter, T.; Fritsch, L.; Berger, M.; Kofler, T.; Mayerl, C.; Pillei, M.; Kraxner, M. Sludge thickening in a wastewater treatment plant using a modified hydrocyclone. Carbon Resour. Convers. 2021, 4, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senfter, T. Kontinuierliche Störstoffabtrennung in der Klärschlamm-Co-Fermentation Mittels Zentrifugalabscheider (Continuous Removal of Impurities in Co-Fermentation Plants by Using Centrifugal Separators). Ph.D. Thesis, University of Innsbruck, Innsbruck, Austria, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, M.; Jiang, L.; Wang, H.; Xu, J.; Yang, J. High concentration fine particle separation performance in hydrocyclones. Minerals 2021, 11, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).