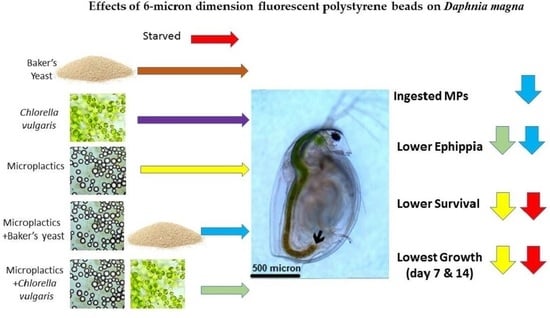
Effect of Polystyrene Microplastics in Different Diet Combinations on Survival, Growth and Reproduction Rates of the Water Flea (Daphnia magna)
Abstract
Highlights
- Microplastics MPs were ingested alone or along with either microalgae Chlorella vulgaris (Cv) or baker’s yeast (By)
- Microplastics decreased survival, growth and reproduction of Daphnia
- High concentrations of microplastics adversely affect Daphnia magna populations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Daphnia Magna Culture
2.2. Microalgae Culture and Stock Concentrations of Microplastics
2.3. Experimental Diets
2.4. Observation of Microplastic Ingestion
2.5. Survival, Growth and Reproductive Performance of Daphnia magna
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
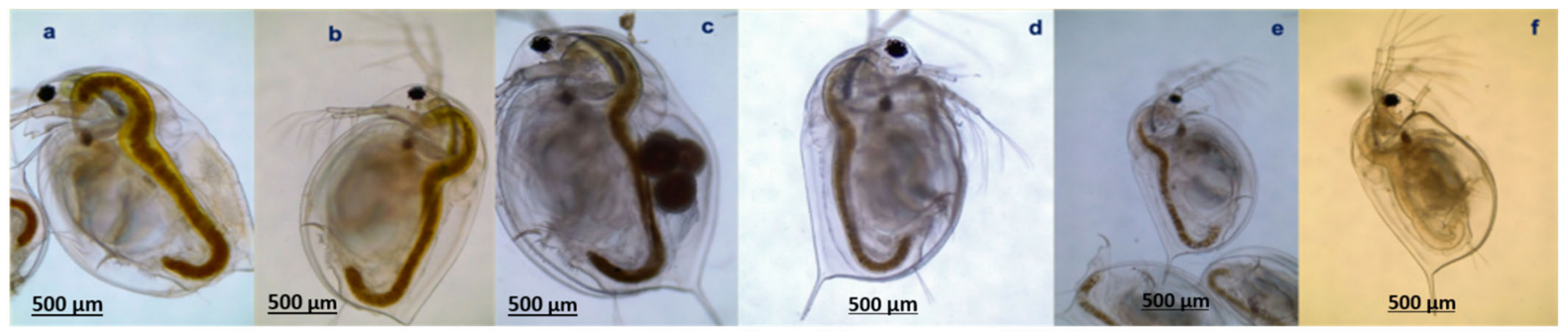
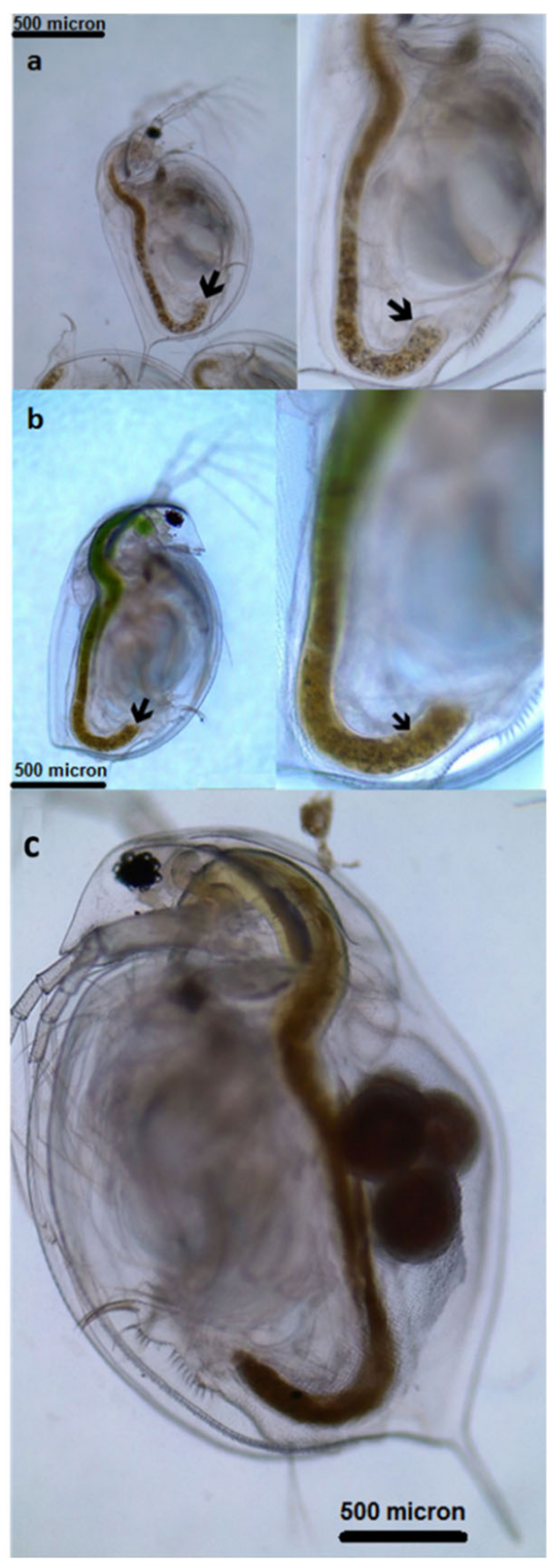
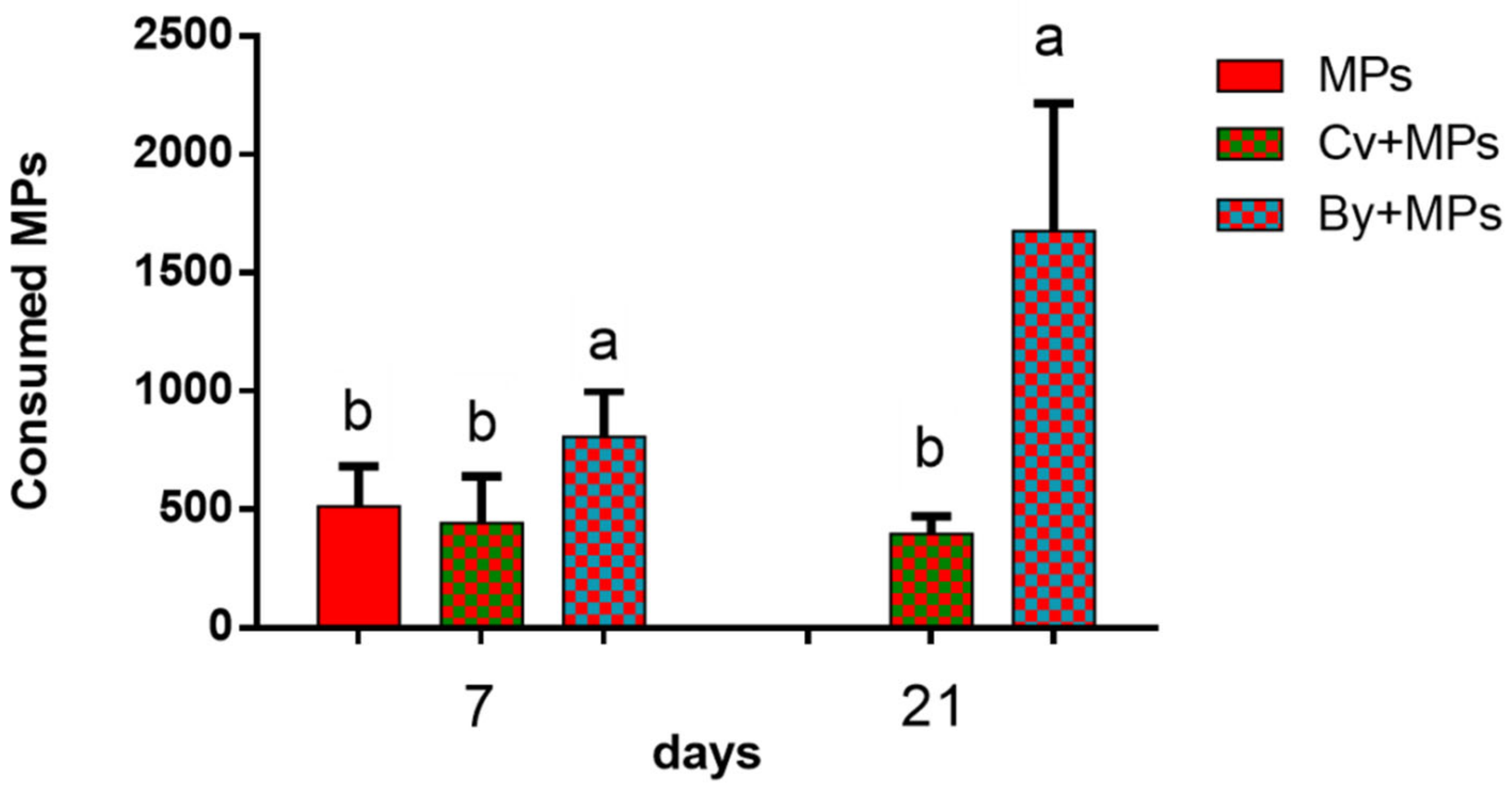
3.1. Ingestion of Microplastics and Microalgae
3.2. Survival of Daphnia magna
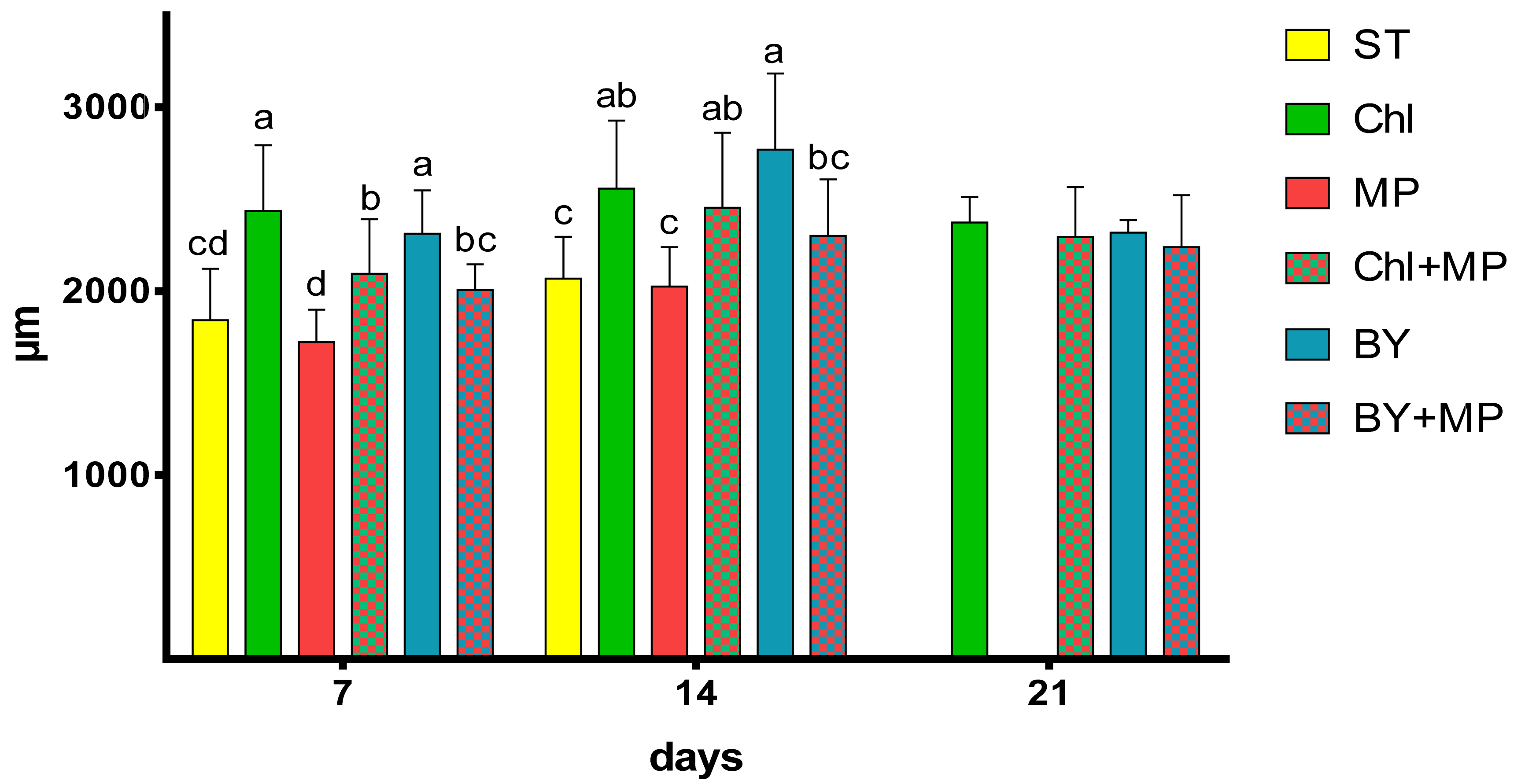
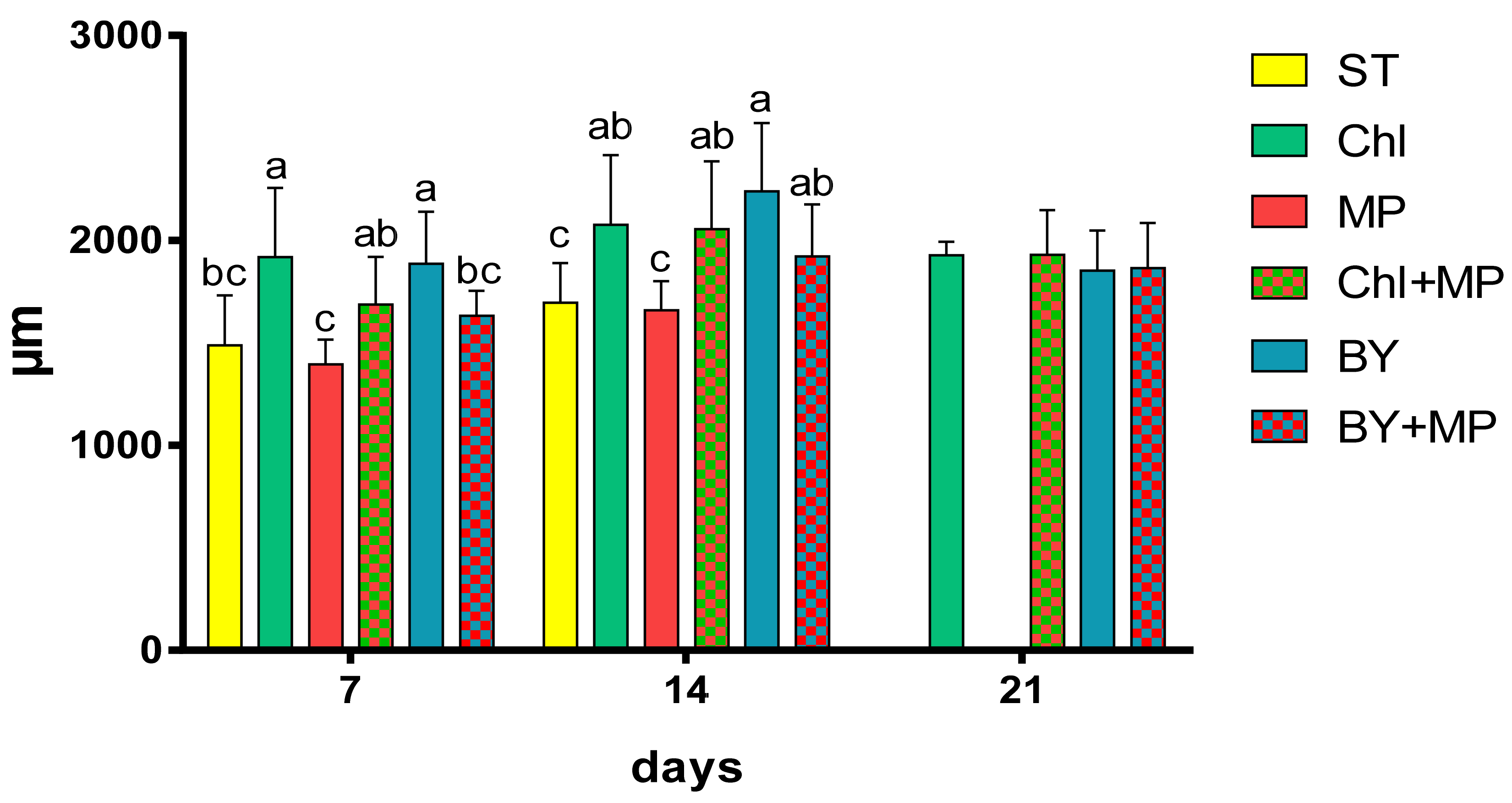
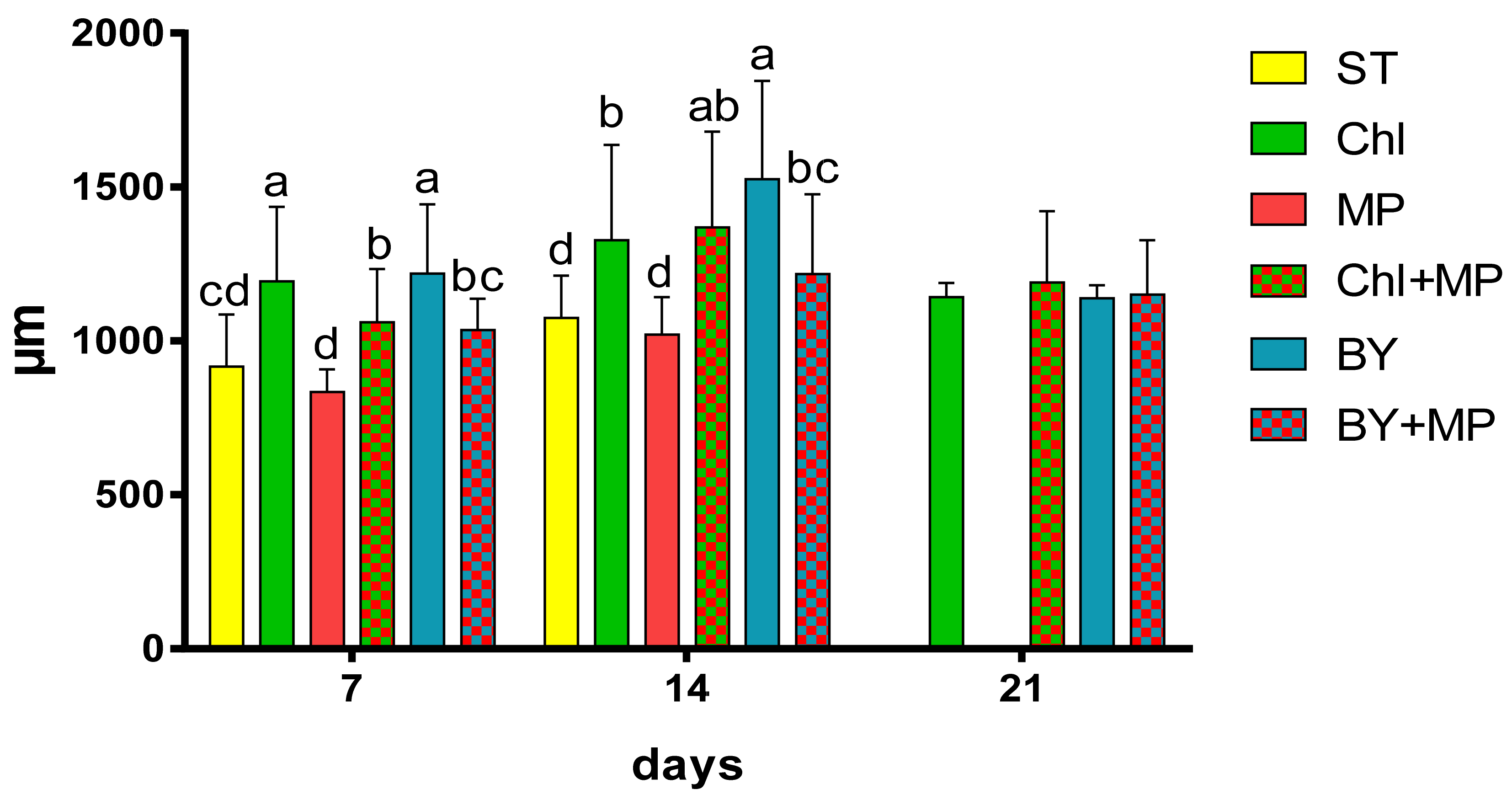
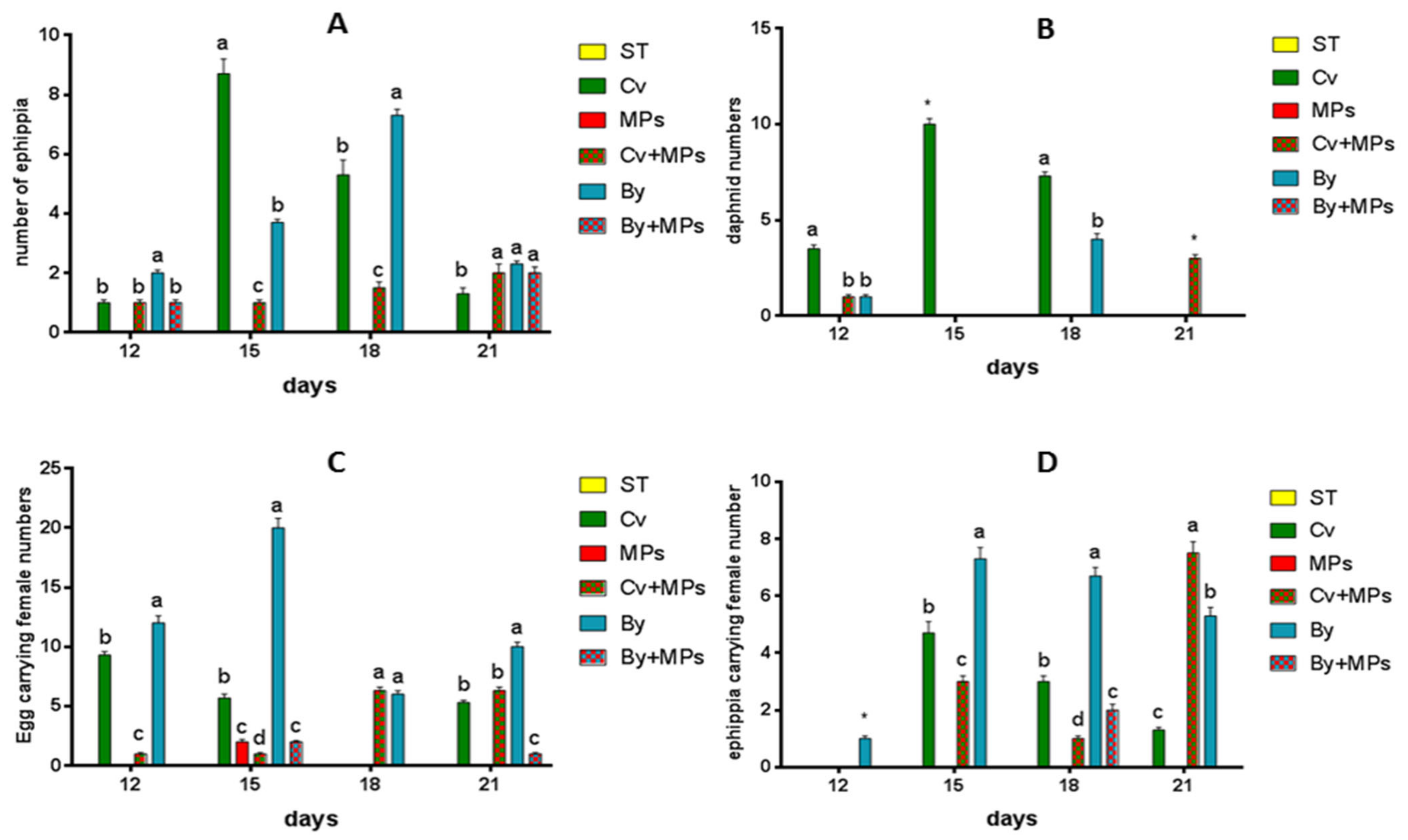
3.3. Effects of Microplastics on the Growth and Reproduction (Total Length and Width, Female Numbers, Egg and Ephippia Numbers, and Dry Weight)
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Europe, P. Plastics–the facts. PlasticEurope 2020, 1, 1–64. [Google Scholar]
- Andrady, A.L. Microplastics in the marine environment. Marine Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1596–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemec, A.; Horvat, P.; Kunej, U.; Bele, M.; Kržan, A. Uptake and effects of microplastic textile fibers on freshwater crustacean Daphnia magna. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, M.; Lindeque, P.; Fileman, E.; Halsband, C.; Goodhead, R.; Moger, J.; Galloway, T.S. Microplastic ingestion by zooplankton. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 6646–6655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aljaibachi, R.; Laird, W.B.; Stevens, F.; Callaghan, A. Impacts of polystyrene microplastics on Daphnia magna: A laboratory and a mesocosm study. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 705, 135800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güven, O.; Gökdağ, K.; Jovanović, B.; Kıdeyş, A.E. Microplastic litter composition of the Turkish territorial waters of the Mediterranean Sea, and its occurrence in the gastrointestinal tract of fish. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, M.A.; Galloway, T.S.; Thompson, R.C. Spatial patterns of plastic debris along estuarine shorelines. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 3404–3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özgüler, Ü.; Demir, A.; Kayadelen, G.C.; Kıdeyş, A.E. Riverine Microplastic Loading to Mersin Bay, Turkey on the North-eastern Mediterranean. Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2021, 22, TRJFAS20253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dris, R.; Imhof, H.K.; Löder, M.G.; Gasperi, J.; Laforsch, C.; Tassin, B. Microplastic contamination in freshwater systems: Methodological challenges, occurrence and sources. In Microplastic Contamination in Aquatic Environments; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 51–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, W.J.; Hong, S.H.; Eo, S. Marine microplastics: Abundance, distribution, and composition. In Microplastic Contamination in Aquatic Environments; Zeng, E.Y., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, F.; Quinn, B. The effects of microplastic on freshwater Hydra attenuata feeding, morphology & reproduction. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windsor, F.M.; Tilley, R.; Tyler, C.R.; Ormerod, S.J. Microplastic ingestion by riverine macroinvertebrates. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 646, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, R.R.; Woodward, J.C.; Rothwell, J.J. Ingestion of microplastics by freshwater tubifex worms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 12844–12851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, M.B.; Bonner, T.H. Occurrence and amount of microplastic ingested by fishes in watersheds of the Gulf of Mexico. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 100, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, S.; Wagner, M. Microplastics are contaminants of emerging concern in freshwater environments: An overview. Freshw. Microplastics 2018, 58, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isinibilir, M.; Svetlichny, L.; Mykitchak, T.; Türkeri, E.E.; Eryalçın, K.M.; Doğan, O.; Can, G.; Yüksel, E.; Kideys, A.E. Microplastic consumption and its effect on respiration rate and motility of Calanus helgolandicus from the Marmara Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 603321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svetlichny, L.; Isinibilir, M.; Mykitchak, T.; Eryalçın, K.M.; Türkeri, E.E.; Yuksel, E.; Kideys, A.E. Microplastic consumption and physiological response in Acartia clausi and Centropages typicus: Possible roles of feeding mechanisms. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 43, 101650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusher, A. Marine anthropogenic litter. In Microplastics in the Marine Environment: Distribution, Interactions and Effects; Bergmann, M., Gutow, L., Klages, M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 245–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, C.; Brennholt, N.; Reifferscheid, G.; Wagner, M. Feeding type and development drive the ingestion of microplastics by freshwater invertebrates. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canniff, P.M.; Hoang, T.C. Microplastic ingestion by Daphnia magna and its enhancement on algal growth. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, C.B.; Won, E.J.; Kang, H.M.; Lee, M.C.; Hwang, D.S.; Hwang, U.K.; Zhou, B.; Soussi, S.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, J.S. Microplastic size-dependent toxicity, oxidative stress induction, and p-JNK and p-p38 activation in the monogonont rotifer (Brachionus koreanus). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 8849–8857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhof, H.K.; Laforsch, C. Hazardous or not–Are adult and juvenile individuals of Potamopyrgus antipodarum affected by non-buoyant microplastic particles? Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorokhova, E. Screening for microplastic particles in plankton samples: How to integrate marine litter assessment into existing monitoring programs? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 99, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilhermino, L.; Martins, A.; Cunha, S.; Fernandes, J.O. Long-term adverse effects of microplastics on Daphnia magna reproduction and population growth rate at increased water temperature and light intensity: Combined effects of stressors and interactions. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 784, 147082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelpsiene, E.; Torstensson, O.; Ekvall, M.T.; Hansson, L.A.; Cedervall, T. Long-term exposure to nanoplastics reduces life-time in Daphnia magna. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bownik, A. Daphnia swimming behaviour as a biomarker in toxicity assessment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faithfull, C.; Huss, M.; Vrede, T.; Karlsson, J.; Bergström, A.K. Transfer of bacterial production based on labile carbon to higher trophic levels in an oligotrophic pelagic system. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2012, 69, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, B.G. The toxicity thresholds of various substances found in industrial wastes as determined by the use of Daphnia magna. Sew. Work. J. 1944, 16, 1156–1165. [Google Scholar]
- Frydkjær, C.K.; Iversen, N.; Roslev, P. Ingestion and egestion of microplastics by the cladoceran Daphnia magna: Effects of regular and irregular shaped plastic and sorbed phenanthrene. Bull. Environ. Contaminat. Toxicol. 2017, 99, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehse, S.; Kloas, W.; Zarfl, C. Short-term exposure with high concentrations of pristine microplastic particles leads to immobilisation of Daphnia magna. Chemosphere 2016, 153, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Test No. 211: Daphnia magna Reproduction Test. In OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 2; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2012; Volume 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oßmann, B.E.; Sarau, G.; Holtmannspötter, H.; Pischetsrieder, M.; Christiansen, S.H.; Dicke, W. Small-sized microplastics and pigmented particles in bottled mineral water. Water Res. 2018, 141, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pivokonsky, M.; Cermakova, L.; Novotna, K.; Peer, P.; Cajthaml, T.; Janda, V. Occurrence of microplastics in raw and treated drinking water. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 1644–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Li, Y.; Li, B. Is color a matter of concern during microplastic exposure to Scenedesmus obliquus and Daphnia magna? J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 383, 121224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turcihan, G.; Isinibilir, M.; Zeybek, Y.G.; Eryalçın, K.M. Effect of different feeds on reproduction performance, nutritional components and fatty acid composition of cladocer water flea (Daphnia magna). Aquac. Res. 2022, 53, 2420–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, D.; Na, J.; Song, J.; Jung, J. Size-dependent chronic toxicity of fragmented polyethylene microplastics to Daphnia magna. Chemosphere 2021, 271, 129591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosker, T.; Olthof, G.; Vijver, M.G.; Baas, J.; Barmentlo, S.H. Significant decline of Daphnia magna population biomass due to microplastic exposure. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 250, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schür, C.; Zipp, S.; Thalau, T.; Wagner, M. Microplastics but not natural particles induce multigenerational effects in Daphnia magna. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 113904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Yu, P.; Cai, M.; Wu, D.; Zhang, M.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Polystyrene nanoplastic exposure induces immobilization, reproduction, and stress defense in the freshwater cladoceran Daphnia pulex. Chemosphere 2019, 215, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljaibachi, R.; Callaghan, A. Impact of polystyrene microplastics on Daphnia magna mortality and reproduction in relation to food availability. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Yan, Z.; Lu, G.; Ji, Y. Single and combined effects of microplastics and roxithromycin on Daphnia magna. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 17010–17020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogonowski, M.; Schür, C.; Jarsén, Å.; Gorokhova, E. The effects of natural and anthropogenic microparticles on individual fitness in Daphnia magna. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhof, H.K.; Rusek, J.; Thiel, M.; Wolinska, J.; Laforsch, C. Do microplastic particles affect Daphnia magna at the morphological, life history and molecular level? PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Felice, B.; Sabatini, V.; Antenucci, S.; Gattoni, G.; Santo, N.; Bacchetta, R.; Ortenzi, M.A.; Parolini, M. Polystyrene microplastics ingestion induced behavioral effects to the cladoceran Daphnia magna. Chemosphere 2019, 231, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Felice, B.; Sugni, M.; Casati, L.; Parolini, M. Molecular, biochemical and behavioral responses of Daphnia magna under long-term exposure to polystyrene nanoplastics. Environ. Int. 2022, 164, 107264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Liu, S.; Tu, J.; Chen, Y.; Zong, Y.; Zhang, P.; Wang, Z.; et al. Influence of microplastics on the growth and the intestinal microbiota composition of brine shrimp. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 717272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Isinibilir, M.; Eryalçın, K.M.; Kideys, A.E. Effect of Polystyrene Microplastics in Different Diet Combinations on Survival, Growth and Reproduction Rates of the Water Flea (Daphnia magna). Microplastics 2023, 2, 27-38. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics2010002
Isinibilir M, Eryalçın KM, Kideys AE. Effect of Polystyrene Microplastics in Different Diet Combinations on Survival, Growth and Reproduction Rates of the Water Flea (Daphnia magna). Microplastics. 2023; 2(1):27-38. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics2010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleIsinibilir, Melek, Kamil Mert Eryalçın, and Ahmet Erkan Kideys. 2023. "Effect of Polystyrene Microplastics in Different Diet Combinations on Survival, Growth and Reproduction Rates of the Water Flea (Daphnia magna)" Microplastics 2, no. 1: 27-38. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics2010002
APA StyleIsinibilir, M., Eryalçın, K. M., & Kideys, A. E. (2023). Effect of Polystyrene Microplastics in Different Diet Combinations on Survival, Growth and Reproduction Rates of the Water Flea (Daphnia magna). Microplastics, 2(1), 27-38. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics2010002