Ingested Microplastics in 18 Local Fish Species from the Northwestern Mediterranean Sea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
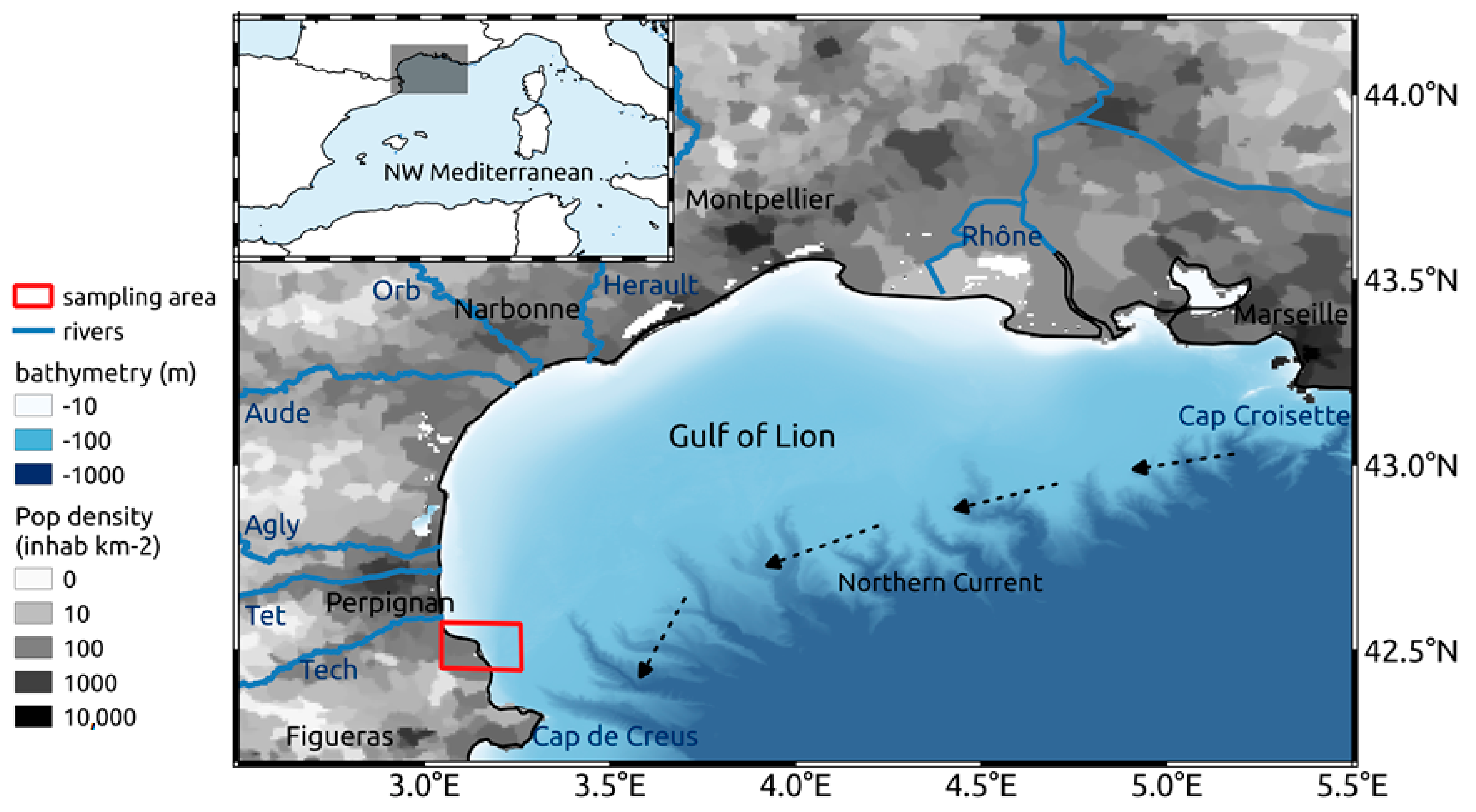
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Extraction of MPs from Fish Tissues
2.4. Polymer Analysis with Fourier Transform InfraRed Spectroscopy
2.5. Data Analysis
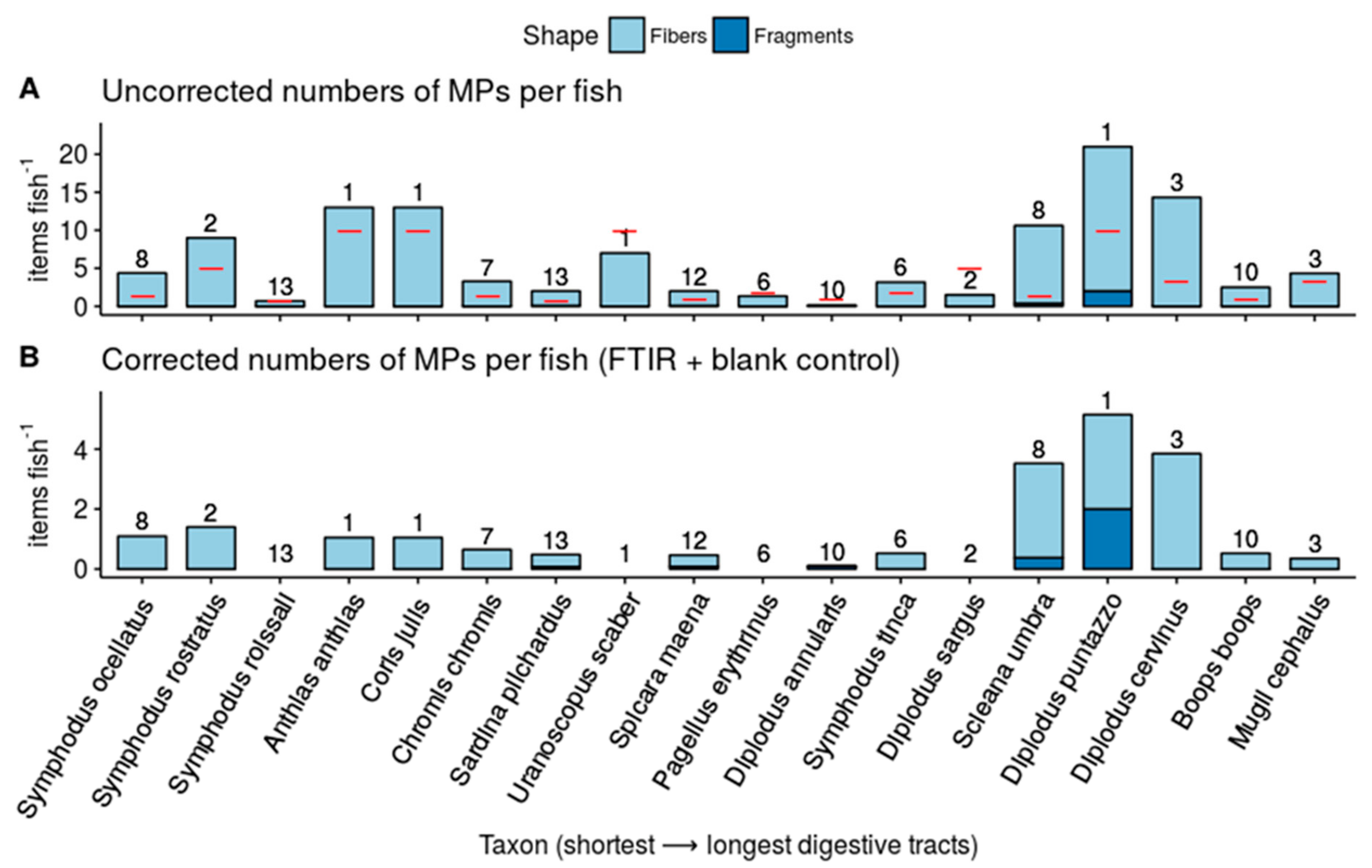
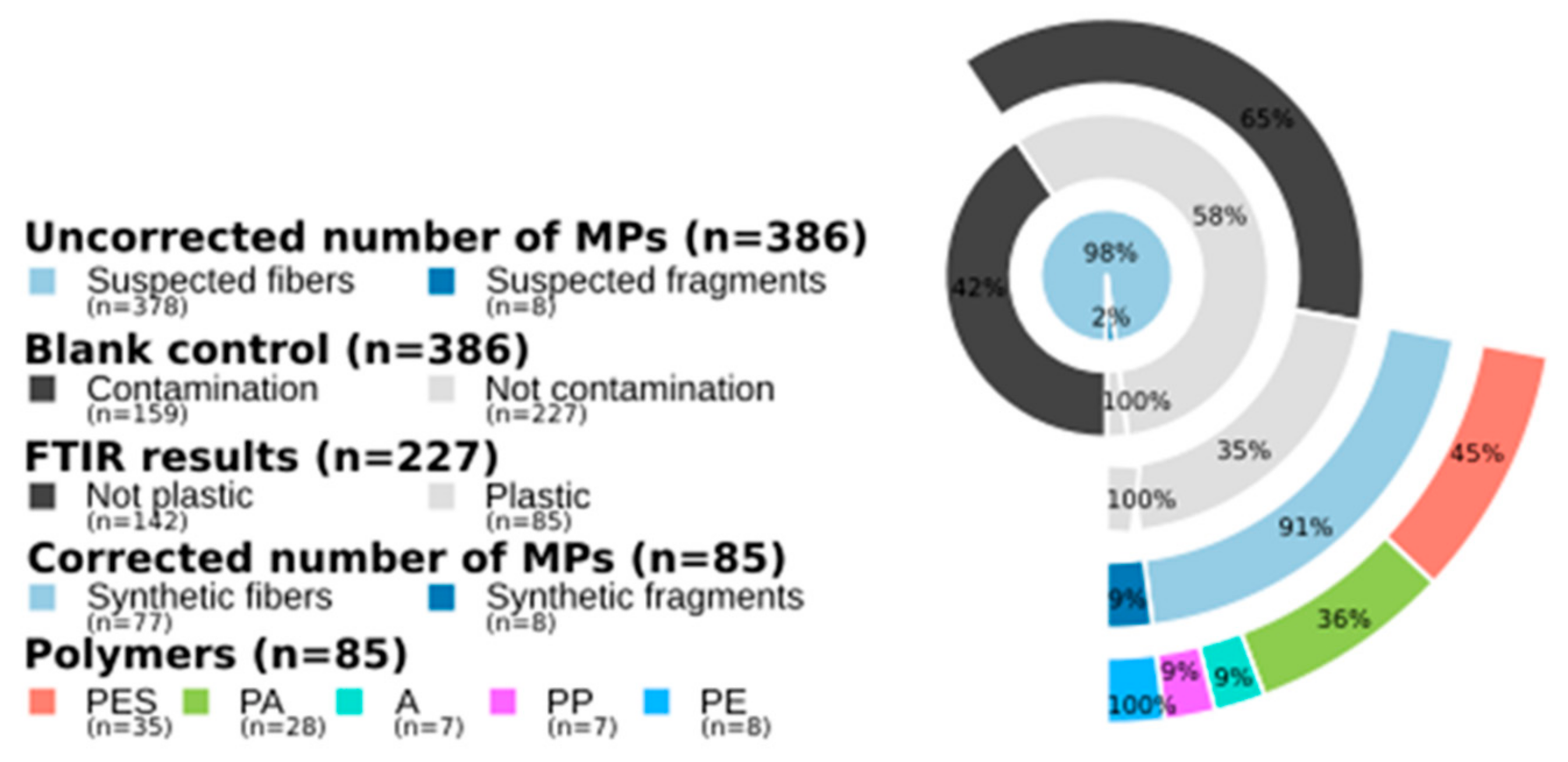
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Mediterranean Fish Species Impacted by MPs
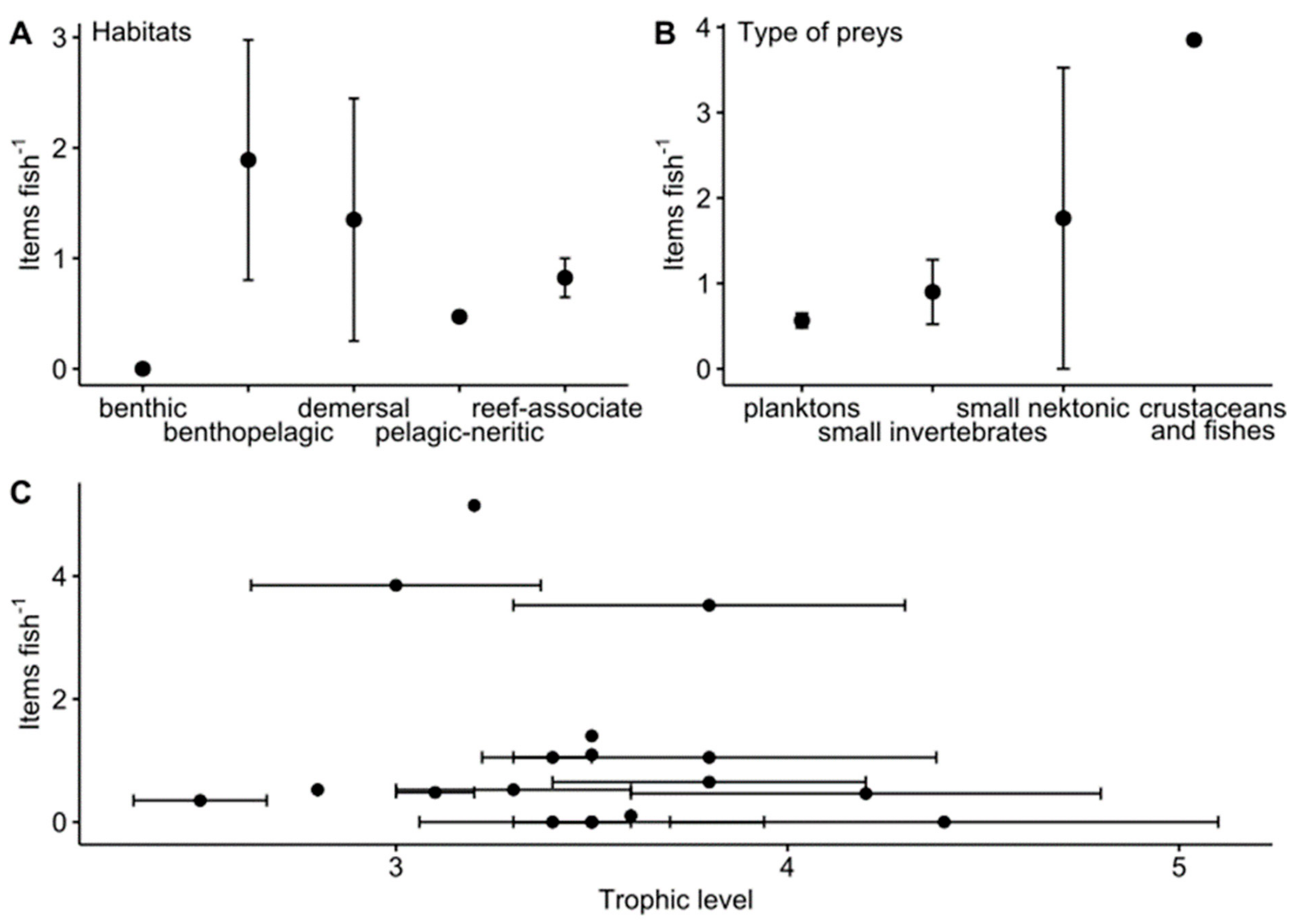
4.2. Impacted Fish Species: Relation with Their Food Supply and Their Habitat
5. Conclusions
- The quantification of MPs in fishes requires high methodological concerns and analytical confirmation. A total of 78% of the suspected plastic particles in our samples were actually not MPs;
- We found that 4 species (D. sargus, P. erythrinus, S. roissali and U. scaber) were not contaminated by MPs and 3 species (D. cervinus, D. puntazzo, S. umbra) were found to have higher than average MP concentrations (>3 MPs per fish). However, the number of investigated fishes per species was low and further investigations are needed to confirm this;
- About 80% of our contaminated species did not exceed the concentration of 2 MPs per fish. A low MP ingestion rate and a rapid egestion through simple digestive tracks can explain this low accumulation;
- Fiber is the main MP shape (91%) found in fish digestive tracts. Their impact on marine life are nearly unknown;
- The length and the morphology of fish digestive tracts, the prey preferences and, with lesser evidence, the habitat may influence the concentration of MPs.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Galgani, F.; Hanke, G.; Maes, T. Global Distribution, Composition and Abundance of Marine Litter. In Marine Anthropogenic Litter; Bergmann, M., Gutow, L., Klages, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin, Germany, 2015; pp. 29–56. ISBN 978-3-319-16509-7. [Google Scholar]
- Kenyon, K.W.; Kridler, E. Laysan Albatrosses Swallow Indigestible Matter. The Auk 1969, 86, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desforges, J.-P.W.; Galbraith, M.; Ross, P.S. Ingestion of Microplastics by Zooplankton in the Northeast Pacific Ocean. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 69, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Digka, N.; Tsangaris, C.; Torre, M.; Anastasopoulou, A.; Zeri, C. Microplastics in Mussels and Fish from the Northern Ionian Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 135, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowler, C.W. Marine Debris and Northern Fur Seals: A Case Study. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1987, 18, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusher, A.L.; Hernandez-Milian, G.; O’Brien, J.; Berrow, S.; O’Connor, I.; Officer, R. Microplastic and Macroplastic Ingestion by a Deep Diving, Oceanic Cetacean: The True’s Beaked Whale Mesoplodon Mirus. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 199, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, P.G. A Brief History of Marine Litter Research. In Marine Anthropogenic Litter; Bergmann, M., Gutow, L., Klages, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin, Germany, 2015; pp. 1–25. ISBN 978-3-319-16509-7. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, P.G.; Connell, A.D.; Gardner, B.D. Plastic Ingestion and PCBs in Seabirds: Is There a Relationship? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1988, 19, 174–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derraik, J.G.B. The Pollution of the Marine Environment by Plastic Debris: A Review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2002, 44, 842–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaughnessy, P.D. Entanglement of Cape Fur Seals with Man-Made Objects. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1980, 11, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisser, J.; Shaw, J.; Hallegraeff, G.; Proietti, M.; Barnes, D.K.A.; Thums, M.; Wilcox, C.; Hardesty, B.D.; Pattiaratchi, C. Millimeter-Sized Marine Plastics: A New Pelagic Habitat for Microorganisms and Invertebrates. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rochman, C.M. The Complex Mixture, Fate and Toxicity of Chemicals Associated with Plastic Debris in the Marine Environment. In Marine Anthropogenic Litter; Bergmann, M., Gutow, L., Klages, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin, Germany, 2015; pp. 117–140. ISBN 978-3-319-16510-3. [Google Scholar]
- Trotter, B.; Ramsperger, A.F.R.M.; Raab, P.; Haberstroh, J.; Laforsch, C. Plastic Waste Interferes with Chemical Communication in Aquatic Ecosystems. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plastics Europe. Plastics-The Facts 2020—An Analysis of European Plastics Production, Demand and Waste Data. Plast. Eur. 2020, 1, 1–64. [Google Scholar]
- GESAMP; IMO/FAO/UNESCO-IOC/UNIDO/WMO/IAEA/UN/UNEP/UNDP Joint Group of Experts on the Scientific Aspects of Marine Environmental Protection. Sources, Fate and Effects of Microplastics in the Marine Environment: A Global Assessment; International Maritime Organization: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Andrady, A.L. Persistence of Plastic Litter in the Oceans. In Marine Anthropogenic Litter; Bergmann, M., Gutow, L., Klages, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin, Germany, 2015; pp. 57–72. ISBN 978-3-319-16509-7. [Google Scholar]
- Napper, I.E.; Bakir, A.; Rowland, S.J.; Thompson, R.C. Characterisation, Quantity and Sorptive Properties of Microplastics Extracted from Cosmetics. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 99, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Albano, M.; Panarello, G.; Di Paola, D.; Capparucci, F.; Crupi, R.; Gugliandolo, E.; Spanò, N.; Capillo, G.; Savoca, S. The Influence of Polystyrene Microspheres Abundance on Development and Feeding Behavior of Artemia Salina (Linnaeus, 1758). Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albano, M.; Panarello, G.; Di Paola, D.; D’Angelo, G.; Granata, A.; Savoca, S.; Capillo, G. The Mauve Stinger Pelagia Noctiluca (Cnidaria, Scyphozoa) Plastics Contamination, the Strait of Messina Case. Int. J. Environ. Stud. 2021, 78, 977–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieczorek, A.M.; Croot, P.L.; Lombard, F.; Sheahan, J.N.; Doyle, T.K. Microplastic Ingestion by Gelatinous Zooplankton May Lower Efficiency of the Biological Pump. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 5387–5395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, P.; Nelson, K. Trophic Level Transfer of Microplastic: Mytilus Edulis (L.) to Carcinus Maenas (L.). Environ. Pollut. 2013, 177, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, E.; Piazza, V.; Lavorano, S.; Faimali, M.; Garaventa, F.; Gambardella, C. Trophic Transfer of Microplastics From Copepods to Jellyfish in the Marine Environment. Front. Environ. Sci. 2020, 8, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galgani, F.; Fleet, D.; Van Franeker, J.; Katsanevakis, S.; Maes, T.; Mouat, J.; Oosterbaan, L.; Poitou, I.; Hanke, G.; Thompson, R.; et al. Marine Strategy Framework Directive Task Group 10 Report: Marine Litter, April 2010; Publications Office: Luxembourg, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi, C.N.; Morri, C. Marine Biodiversity of the Mediterranean Sea: Situation, Problems and Prospects for Future Research. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2000, 40, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cózar, A.; Sanz-Martín, M.; Martí, E.; González-Gordillo, J.I.; Ubeda, B.; Gálvez, J.Á.; Irigoien, X.; Duarte, C.M. Plastic Accumulation in the Mediterranean Sea. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121762. [Google Scholar]
- Tubau, X.; Canals, M.; Lastras, G.; Rayo, X.; Rivera, J.; Amblas, D. Marine Litter on the Floor of Deep Submarine Canyons of the Northwestern Mediterranean Sea: The Role of Hydrodynamic Processes. Prog. Oceanogr. 2015, 134, 379–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deudero, S.; Alomar, C. Mediterranean Marine Biodiversity under Threat: Reviewing Influence of Marine Litter on Species. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 98, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fossi, M.C.; Pedà, C.; Compa, M.; Tsangaris, C.; Alomar, C.; Claro, F.; Ioakeimidis, C.; Galgani, F.; Hema, T.; Deudero, S.; et al. Bioindicators for Monitoring Marine Litter Ingestion and Its Impacts on Mediterranean Biodiversity. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 1023–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galgani, F.; Souplet, A.; Cadiou, Y. Accumulation of Debris on the Deep Sea Floor off the French Mediterranean Coast. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1996, 142, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Durrieu de Madron, X.; Guieu, C.; Sempéré, R.; Conan, P.; Cossa, D.; D’Ortenzio, F.; Estournel, C.; Gazeau, F.; Rabouille, C.; Stemmann, L.; et al. Marine Ecosystems’ Responses to Climatic and Anthropogenic Forcings in the Mediterranean. Prog. Oceanogr. 2011, 91, 97–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collard, F.; Gilbert, B.; Compère, P.; Eppe, G.; Das, K.; Jauniaux, T.; Parmentier, E. Microplastics in Livers of European Anchovies (Engraulis Encrasicolus, L.). Environ. Pollut. 2017, 229, 1000–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collard, F.; Gilbert, B.; Eppe, G.; Parmentier, E.; Das, K. Detection of Anthropogenic Particles in Fish Stomachs: An Isolation Method Adapted to Identification by Raman Spectroscopy. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 69, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collard, F.; Gilbert, B.; Eppe, G.; Roos, L.; Compère, P.; Das, K.; Parmentier, E. Morphology of the Filtration Apparatus of Three Planktivorous Fishes and Relation with Ingested Anthropogenic Particles. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 116, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, C.; Saraux, C.; Heitz, O.; Nowaczyk, A.; Bonnet, D. Microplastics FTIR Characterisation and Distribution in the Water Column and Digestive Tracts of Small Pelagic Fish in the Gulf of Lions. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 142, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennino, M.G.; Bachiller, E.; Lloret-Lloret, E.; Albo-Puigserver, M.; Esteban, A.; Jadaud, A.; Bellido, J.M.; Coll, M. Ingestion of Microplastics and Occurrence of Parasite Association in Mediterranean Anchovy and Sardine. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 158, 111399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durrieu de Madron, X.; Abassi, A.; Heussner, S.; Monaco, A.; Aloisi, J.C.; Radakovitch, O.; Giresse, P.; Buscail, R.; Kerherve, P. Particulate Matter and Organic Carbon Budgets for the Gulf of Lions (NW Mediterranean). Oceanol. Acta 2000, 23, 717–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ludwig, W.; Dumont, E.; Meybeck, M.; Heussner, S. River Discharges of Water and Nutrients to the Mediterranean and Black Sea: Major Drivers for Ecosystem Changes during Past and Future Decades? Prog. Oceanogr. 2009, 80, 199–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouloubassi, I.; Roussiez, V.; Azzoug, M.; Lorre, A. Sources, Dispersal Pathways and Mass Budget of Sedimentary Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAH) in the NW Mediterranean Margin, Gulf of Lions. Mar. Chem. 2012, 142–144, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadaoui, M.; Ludwig, W.; Bourrin, F.; Raimbault, P. Controls, Budgets and Variability of Riverine Sediment Fluxes to the Gulf of Lions (NW Mediterranean Sea). J. Hydrol. 2016, 540, 1002–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courp, T.; Monaco, A. Sediment Dispersal and Accumulation on the Continental Margin of the Gulf of Lions: Sedimentary Budget. Cont. Shelf Res. 1990, 10, 1063–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avio, C.G.; Gorbi, S.; Regoli, F. Experimental Development of a New Protocol for Extraction and Characterization of Microplastics in Fish Tissues: First Observations in Commercial Species from Adriatic Sea. Mar. Environ. Res. 2015, 111, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löder, M.G.J.; Gerdts, G. Methodology Used for the Detection and Identification of Microplastics—A Critical Appraisal. In Marine Anthropogenic Litter; Bergmann, M., Gutow, L., Klages, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin, Germany, 2015; pp. 201–227. ISBN 978-3-319-16509-7. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, R.C.; Olsen, Y.; Mitchell, R.P.; Davis, A.; Rowland, S.J.; John, A.W.G.; McGonigle, D.; Russell, A.E. Lost at Sea: Where Is All the Plastic? Science 2004, 304, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louisy, P. Guide D’identification Des Poissons Marins: Europe De l’ouest et Méditerranée; Editions Eugen Ulmer: Paris, France, 2002; ISBN 2-84138-651-1. [Google Scholar]
- Harmelin, J.-G.; Ruitton, S. Poissons de Méditerranée; Edisud: Biganos, France, 2013; ISBN 978-2-7449-0992-4. [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg, S. Découvrir La Vie Sous-Marine Méditerranée; Guardian Angel Publishing: Saint Louis, MO, USA, 2013; ISBN 2-7417-0533-X. [Google Scholar]
- Froese, R.; Pauly, D. FishBase. Available online: www.fishbase.org (accessed on 13 November 2021).
- Pellini, G.; Gomiero, A.; Fortibuoni, T.; Ferrà, C.; Grati, F.; Tassetti, A.N.; Polidori, P.; Fabi, G.; Scarcella, G. Characterization of Microplastic Litter in the Gastrointestinal Tract of Solea Solea from the Adriatic Sea. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 943–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anastasopoulou, A.; Kovač Viršek, M.; Bojanić Varezić, D.; Digka, N.; Fortibuoni, T.; Koren, Š.; Mandić, M.; Mytilineou, C.; Pešić, A.; Ronchi, F.; et al. Assessment on Marine Litter Ingested by Fish in the Adriatic and NE Ionian Sea Macro-Region (Mediterranean). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 133, 841–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajšt, T.; Bizjak, T.; Palatinus, A.; Liubartseva, S.; Kržan, A. Sea Surface Microplastics in Slovenian Part of the Northern Adriatic. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 113, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constant, M.; Kerhervé, P.; Mino-Vercellio-Verollet, M.; Dumontier, M.; Sànchez Vidal, A.; Canals, M.; Heussner, S. Beached Microplastics in the Northwestern Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 142, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alomar, C.; Deudero, S. Evidence of Microplastic Ingestion in the Shark Galeus Melastomus Rafinesque, 1810 in the Continental Shelf off the Western Mediterranean Sea. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellas, J.; Martínez-Armental, J.; Martínez-Cámara, A.; Besada, V.; Martínez-Gómez, C. Ingestion of Microplastics by Demersal Fish from the Spanish Atlantic and Mediterranean Coasts. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 109, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güven, O.; Gökdağ, K.; Jovanović, B.; Kıdeyş, A.E. Microplastic Litter Composition of the Turkish Territorial Waters of the Mediterranean Sea, and Its Occurrence in the Gastrointestinal Tract of Fish. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compa, M.; Ventero, A.; Iglesias, M.; Deudero, S. Ingestion of Microplastics and Natural Fibres in Sardina Pilchardus (Walbaum, 1792) and Engraulis Encrasicolus (Linnaeus, 1758) along the Spanish Mediterranean Coast. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 128, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadal, M.A.; Alomar, C.; Deudero, S. High Levels of Microplastic Ingestion by the Semipelagic Fish Bogue Boops Boops (L.) around the Balearic Islands. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 214, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alomar, C.; Sureda, A.; Capó, X.; Guijarro, B.; Tejada, S.; Deudero, S. Microplastic Ingestion by Mullus Surmuletus Linnaeus, 1758 Fish and Its Potential for Causing Oxidative Stress. Environ. Res. 2017, 159, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napper, I.E.; Thompson, R.C. Release of Synthetic Microplastic Plastic Fibres from Domestic Washing Machines: Effects of Fabric Type and Washing Conditions. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 112, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Consoli, P.; Andaloro, F.; Altobelli, C.; Battaglia, P.; Campagnuolo, S.; Canese, S.; Castriota, L.; Cillari, T.; Falautano, M.; Pedà, C.; et al. Marine Litter in an EBSA (Ecologically or Biologically Significant Area) of the Central Mediterranean Sea: Abundance, Composition, Impact on Benthic Species and Basis for Monitoring Entanglement. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 236, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, M. A Novel Method for Preparing Microplastic Fibers. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcia-Garin, O.; Vighi, M.; Aguilar, A.; Tsangaris, C.; Digka, N.; Kaberi, H.; Borrell, A. Boops Boops as a Bioindicator of Microplastic Pollution along the Spanish Catalan Coast. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 149, 110648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios-Fuster, B.; Alomar, C.; Compa, M.; Guijarro, B.; Deudero, S. Anthropogenic Particles Ingestion in Fish Species from Two Areas of the Western Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 144, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sbrana, A.; Valente, T.; Scacco, U.; Bianchi, J.; Silvestri, C.; Palazzo, L.; De Lucia, G.A.; Valerani, C.; Ardizzone, G.; Matiddi, M. Spatial Variability and Influence of Biological Parameters on Microplastic Ingestion by Boops Boops (L.) along the Italian Coasts (Western Mediterranean Sea). Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsangaris, C.; Digka, N.; Valente, T.; Aguilar, A.; Borrell, A.; De Lucia, G.A.; Gambaiani, D.; Garcia-Garin, O.; Kaberi, H.; Martin, J.; et al. Using Boops Boops (Osteichthyes) to Assess Microplastic Ingestion in the Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 158, 111397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giani, D.; Baini, M.; Galli, M.; Casini, S.; Fossi, M.C. Microplastics Occurrence in Edible Fish Species (Mullus Barbatus and Merluccius Merluccius) Collected in Three Different Geographical Sub-Areas of the Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 140, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capillo, G.; Savoca, S.; Panarello, G.; Mancuso, M.; Branca, C.; Romano, V.; D’Angelo, G.; Bottari, T.; Spanò, N. Quali-Quantitative Analysis of Plastics and Synthetic Microfibers Found in Demersal Species from Southern Tyrrhenian Sea (Central Mediterranean). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 150, 110596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savoca, S.; Capillo, G.; Mancuso, M.; Bottari, T.; Crupi, R.; Branca, C.; Romano, V.; Faggio, C.; D’Angelo, G.; Spanò, N. Microplastics Occurrence in the Tyrrhenian Waters and in the Gastrointestinal Tract of Two Congener Species of Seabreams. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 67, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avio, C.G.; Cardelli, L.R.; Gorbi, S.; Pellegrini, D.; Regoli, F. Microplastics Pollution after the Removal of the Costa Concordia Wreck: First Evidences from a Biomonitoring Case Study. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 227, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foekema, E.M.; De Gruijter, C.; Mergia, M.T.; Van Franeker, J.A.; Murk, A.J.; Koelmans, A.A. Plastic in North Sea Fish. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 8818–8824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welden, N.A.; Abylkhani, B.; Howarth, L.M. The Effects of Trophic Transfer and Environmental Factors on Microplastic Uptake by Plaice, Pleuronectes Plastessa, and Spider Crab, Maja Squinado. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 239, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romeo, T.; Pietro, B.; Pedà, C.; Consoli, P.; Andaloro, F.; Fossi, M.C. First Evidence of Presence of Plastic Debris in Stomach of Large Pelagic Fish in the Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 95, 358–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, T.; Peda, C.; Fossi, M.C.; Andaloro, F.; Battaglia, P. First Record of Plastic Debris in the Stomach of Mediterranean Lanternfishes. Acta Adriat. 2016, 57, 115–122. [Google Scholar]
| Species | Number of Fish | Size (cm) | Mean Digestive Tract Length (mm) | Habitat | Type of Preys | Trophic Level | Mean MPs Per Fish |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anthias anthias | 1 | 17 | 113 | reef-associated | small nektonic | 3.8 ± 0.6 | 1.05 |
| Boops boops | 10 | 23 | 493 | demersal | small nektonic | 2.8 ± 0.0 | 0.52 |
| Chromis chromis | 7 | 9 | 140 | reef-associated | small nektonic | 3.8 ± 0.4 | 0.65 |
| Coris julis | 1 | 23 | 121 | reef-associated | small nektonic | 3.4 ± 0.1 | 1.05 |
| Diplodus annularis | 10 | 17 | 203 | benthopelagic | small nektonic | 3.6 ± 0.0 | 0.10 |
| Diplodus cervinus | 3 | 43 | 451 | benthopelagic | small nektonic | 3.0 ± 0.4 | 3.85 |
| Diplodus puntazzo | 1 | 35 | 429 | benthopelagic | small nektonic | 3.2 ± 0.0 | 5.15 |
| Diplodus sargus | 2 | 25 | 276 | demersal | small nektonic | 3.4 ± 0.1 | 0.00 |
| Mugil cephalus | 3 | 75 | 1739 | benthopelagic | planktons | 2.5 ± 0.2 | 0.35 |
| Pagellus erythrinus | 6 | 35 | 197 | benthopelagic | small nektonic | 3.5 ± 0.1 | 0.00 |
| Sardina pilchardus | 13 | 19 | 145 | pelagic-neritic | small invertebrates | 3.1 ± 0.1 | 0.48 |
| Scieana umbra | 8 | 38 | 351 | demersal | small nektonic | 3.8 ± 0.5 | 3.52 |
| Spicara maena | 12 | 23 | 179 | pelagic-neritic | small invertebrates | 4.2 ± 0.6 | 0.46 |
| Symphodus ocellatus | 8 | 9 | 66 | reef-associated | small nektonic | 3.5 ± 0.0 | 1.09 |
| Symphodus roissali | 13 | 14 | 95 | reef-associated | small nektonic | 3.5 ± 0.4 | 0.00 |
| Symphodus rostratus | 2 | 9 | 71 | reef-associated | small nektonic | 3.5 ± 0.0 | 1.40 |
| Symphodus tinca | 6 | 28 | 228 | reef-associated | small nektonic | 3.3 ± 0.3 | 0.52 |
| Uranoscopus scaber | 1 | 30 | 175 | benthic | crustaceans and fishes | 4.4 ± 0.7 | 0.00 |
| Species | Number of Fish | Fish with MPs | Concentrations (Items fish−1) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anthias anthias | 1 | 1.1 | This study | |
| Boops Boops | 1750 | 50% | 0.8 | [56,61,62,63,64] |
| 10 | 0.5 | This study | ||
| Chromis chromis | 7 | 0.7 | This study | |
| Coris julis | 1 | 1.1 | This study | |
| Diplodus annularis | 10 | 0.1 | This study | |
| Diplodus cervinus | 3 | 3.85 | This study | |
| Diplodus puntazzo | 1 | 5.2 | This study | |
| Diplodus sargus | 2 | 0 | This study | |
| Mugil cephalus | 3 | 0.35 | This study | |
| Mullus barbatus | 281 | 19% | 1.4 | [53,65,66] |
| Mullus surmuletus | 417 | 27% | 0.4 | [57] |
| Pagellus bogaraveo | 24 | 13% | ND | [67] |
| Pagellus erythrinus | 15 | 6% | ND | [67] |
| 6 | 0% | 0 | This study | |
| Raya miraletus | 1 | 100% | 2.0 | [66] |
| Spondyliosoma cantharus | 3 | 100% | 2.3 ± 1.1 * | [54] |
| Sardina pilchardus | 229 | 35% | 0.8 | [35,62,68] |
| 13 | 0.5 | This study | ||
| Scieana umbra | 8 | 3.5 | This study | |
| Scorpaena sp. | 8 | 63% | 3.2 ± 3.3 * | [54] |
| Spicara maena | 12 | 0.5 | This study | |
| Spondyliosoma cantharus | 3 | 100% | 2.3 ±1.1 * | [54] |
| Symphodus ocellatus | 8 | 1.1 | This study | |
| Symphodus roissali | 13 | 0 | This study | |
| Symphodus rostratus | 2 | 1.4 | This study | |
| Symphodus tinca | 6 | 0.5 | This study | |
| Trigla lyra | 16 | 19% | 0.3 | [66] |
| Uranoscopus scaber | 6 | 83% | 2.4 ± 1.7 * | [54] |
| 1 | 0 | This study |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Constant, M.; Reynaud, M.; Weiss, L.; Ludwig, W.; Kerhervé, P. Ingested Microplastics in 18 Local Fish Species from the Northwestern Mediterranean Sea. Microplastics 2022, 1, 186-197. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics1010012
Constant M, Reynaud M, Weiss L, Ludwig W, Kerhervé P. Ingested Microplastics in 18 Local Fish Species from the Northwestern Mediterranean Sea. Microplastics. 2022; 1(1):186-197. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics1010012
Chicago/Turabian StyleConstant, Mel, Mathieu Reynaud, Lisa Weiss, Wolfgang Ludwig, and Philippe Kerhervé. 2022. "Ingested Microplastics in 18 Local Fish Species from the Northwestern Mediterranean Sea" Microplastics 1, no. 1: 186-197. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics1010012
APA StyleConstant, M., Reynaud, M., Weiss, L., Ludwig, W., & Kerhervé, P. (2022). Ingested Microplastics in 18 Local Fish Species from the Northwestern Mediterranean Sea. Microplastics, 1(1), 186-197. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics1010012






