Microplastics Occurrence in Two Mountainous Rivers in the Lowland Area—A Case Study of the Central Pomeranian Region, Poland
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling Sites
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Microplastic Extraction
2.4. Quality Control and Blind Samples
2.5. Microplastics Identification
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
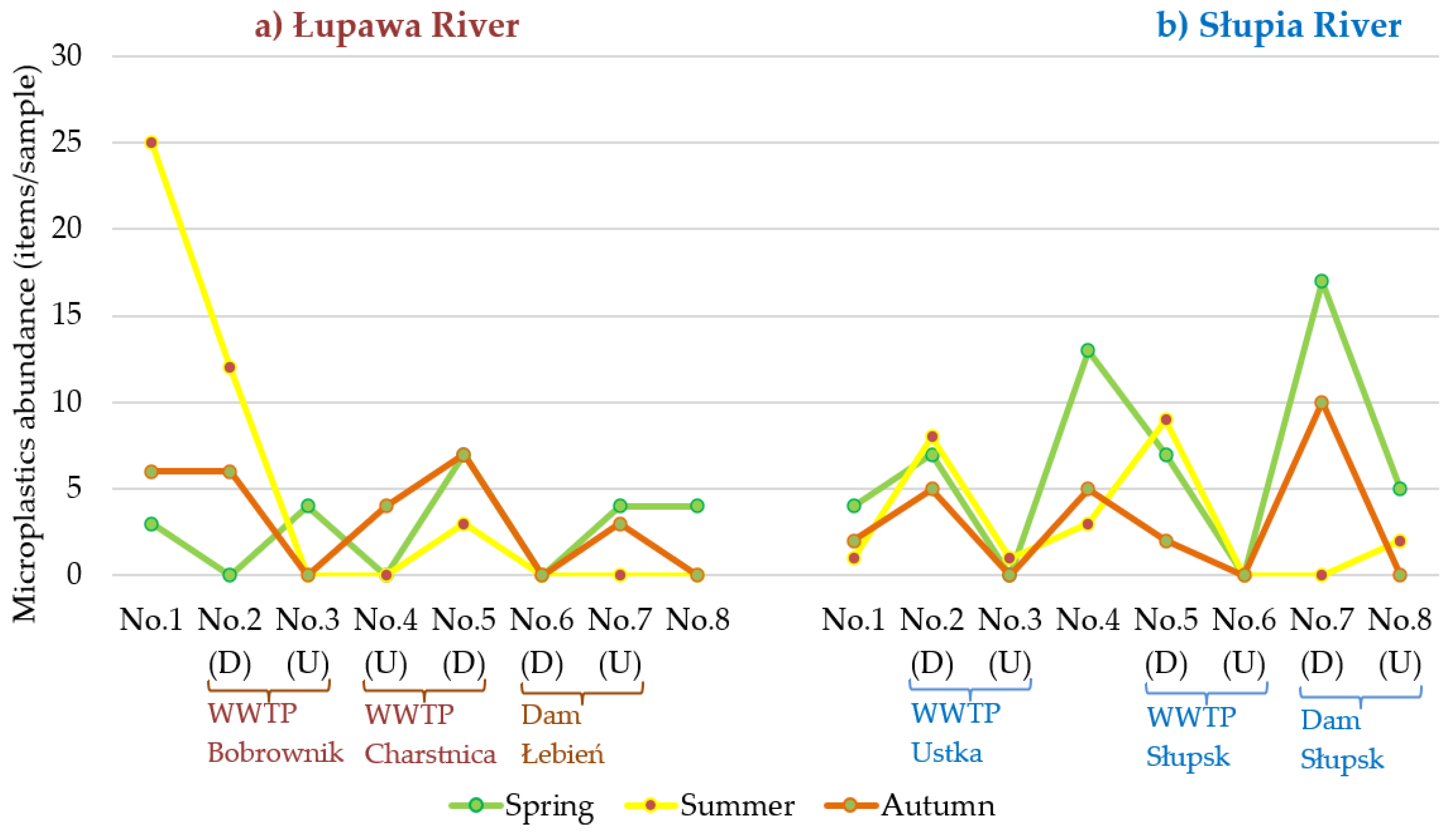
3.1. Abundance and Temporal Variation of MPs
3.2. Comparison of MPs Abundance along the River Course
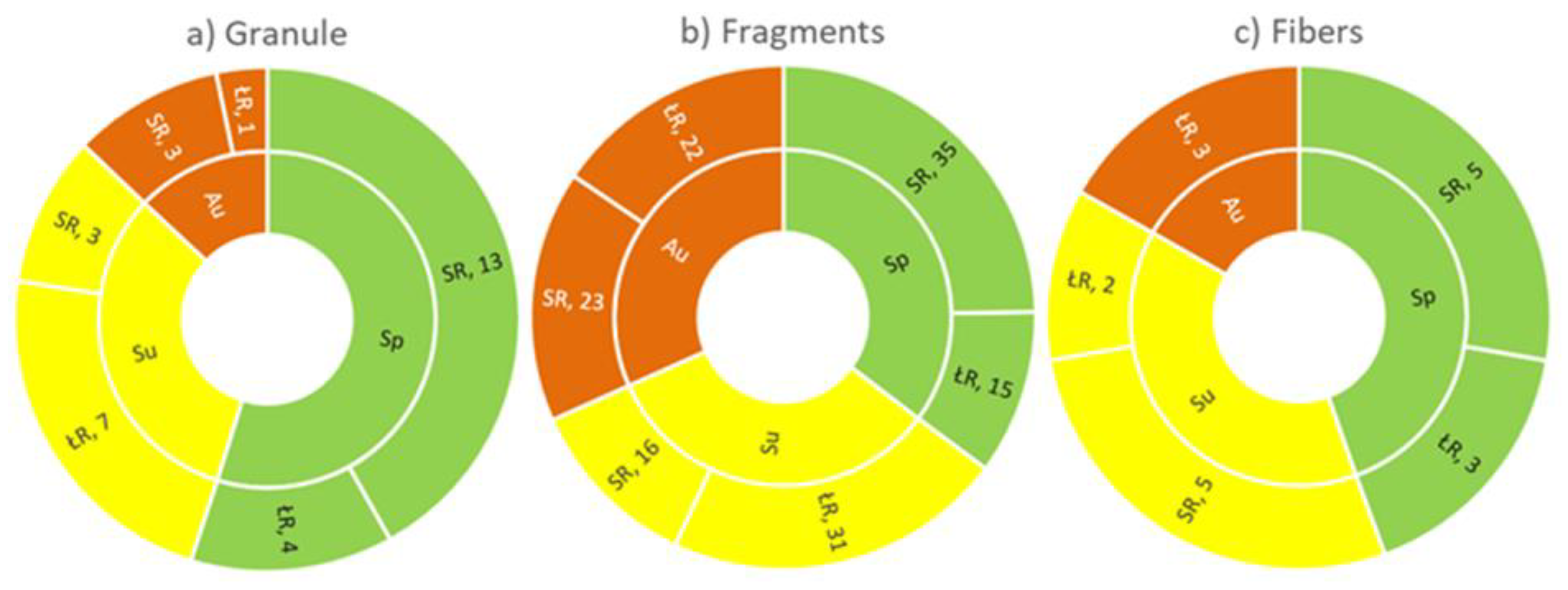
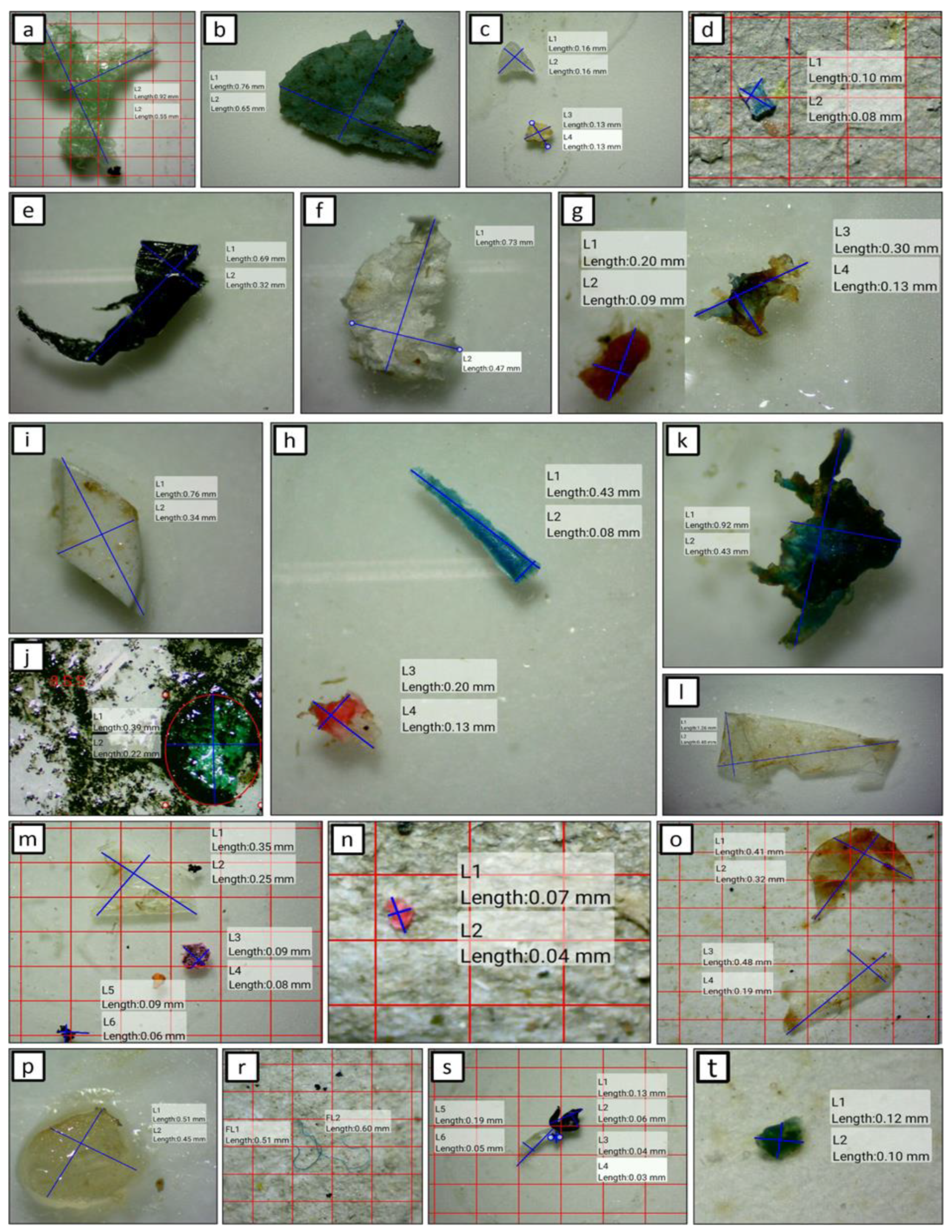
3.3. Morphology Characteristics
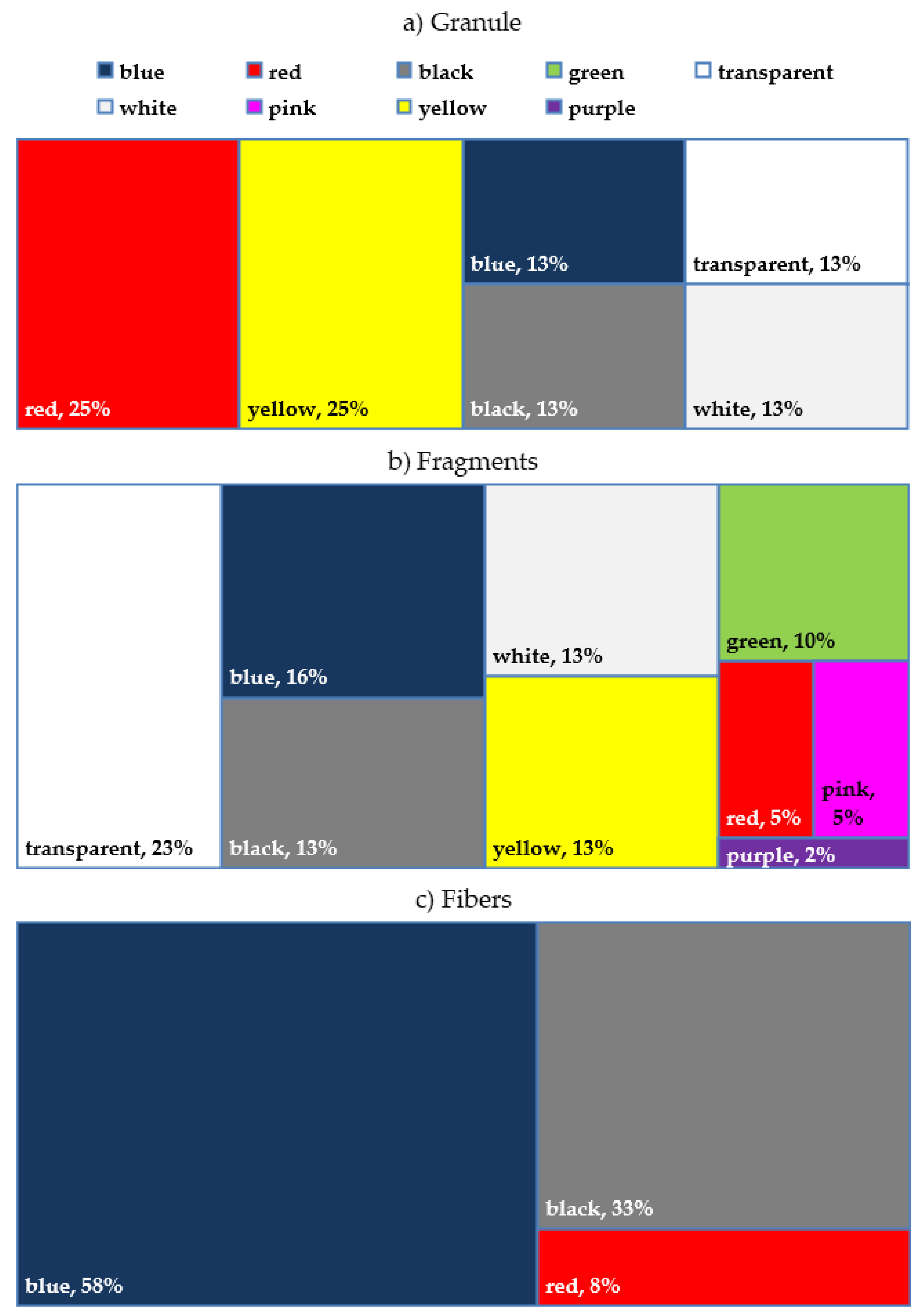
3.4. MPs Composition Assessment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parashar, N.; Hait, S. Plastics in the time of COVID-19 pandemic: Protector or polluter? Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 759, 144274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geyer, R.; Jambeck, J.R.; Law, K.L. Production, use, and fate of all plastics ever made. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1700782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rajmohan, K.V.S.; Ramya, C.; Viswanathan, R.V.; Varjani, S. Plastic pollutants: Effective waste management for pollution control and abatement. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2019, 12, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jambeck, J.R.; Geyer, R.; Wilcox, C.; Siegler, T.R.; Perryman, M.; Andrady, A. Plastic waste in puts from land into the ocean. Science 2015, 347, 769–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, K.L.; Thompson, R.C. Microplastics in the seas. Science 2014, 345, 144–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, A. The Impacts of Microplastics: From Tea Bags and Bottled Water to Salt and Fish. In Environmental Strategy, News, Planet, Pollution, Pollution Management; 2020; Available online: https://youmatter.world/en/microplastics-types-effects-humans-nature/ (accessed on 13 December 2021).
- Browne, M.A.; Crump, P.; Niven, S.J.; Teuten, E.L.; Tonkin, A.; Gallowa, T.; Thompson, R.C. Accumulations of microplastic on shorelines worldwide: Sources and sinks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 9175–9179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrady, A.L. The plastic in microplastics: A review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 119, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, J.; Friot, D. Primary Microplastics in the Oceans: A Global Evaluation of Sources; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kole, P.J.; Löhr, A.J.; Van Belleghem, F.G.A.J.; Ragas, A.M.J. Wear and Tear of Tyres: A Stealthy Source of Microplastics in the Environment. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebreton, L.; Slat, B.; Ferrari, F.; Sainte-Rose, B.; Aitken, J.; Marthouse, R.; Hajbane, S.; Cunsolo, S.; Schwarz, A.; Levivier, A.; et al. Evidence that the Great Pacific Garbage Patch is rapidly accumulating plastic. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takahashi, Y.; Hamanaka, I.; Shimizu, H. Effect of thermal shock on mechanical properties of infection-molded thermoplastic denture base resins. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2012, 70, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnusson, K.; Eliasson, A.; Frane, K.; Haikonen, J.; Hulten, M.; Olshammar, J.; Stadmark, A. Swedish Sources and Pathways for Microplastics to the Marine Environment. Report C183; Swedish Environmental Research Institute: Stokholm, Sweden, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hahladakis, N.J.; Costas, A.V.; Weber, R.; Iacovidou, E.; Purnell, P. An overview of chemical additives present in plastics: Migration, release, fate and environmental impact during their use, disposal and recycling. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 179–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashton, K.; Holmes, L.; Turner, A. Association of metals with plastic production pellets in the marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 2050–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antunes, J.C.; Frias, J.G.L.; Micaelo, A.C.; Sobral, P. Resin pellets from beaches of the Portuguese coast and adsorbed persistent organic pollutants. Estuar. Coast Shelf. 2013, 130, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakir, A.; Rowland, S.J.; Thompson, R.C. Enhanced desorption of persistent organic pollutants from microplastics under simulated physiological conditions. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 185, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joo, S.H.; Liang, Y.; Kim, M.; Byun, J.; Choi, H. Microplastics with adsorber contaminants: Mechanism and Treatment. Environ. Chall. 2021, 3, 100042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zettler, E.R.; Mincer, T.J.; Amaral-Zettler, L.A. Life in the “plastisphere”: Microbial communities on plastic marine debris. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 7137–7146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Salem, S.M.; Al-Hazza’a, A.; Karam, H.J.; Al-Wadi, M.H.; Al-Dhafeeri, A.T.; Al-Rowaih, A.A. Insights into the evaluation of the abiotic and biotic degradation rate of commercial pro-oxidant filled polyethylene (PE) thin films. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 250, 109475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.J.; Moore, S.L.; Weisberg, S.B.; Lattin, G.L.; Zellers, A.F. A comparison of neustonic plastic and zooplankton abundance in southern California’s coastal waters. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2002, 44, 1035–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lestari, P.; Trihadiningrum, Y.; Wijaya, B.I.; Yunus, K.A.; Firdaus, M. Distribution of microplastics in Surabaya River, Indonesia. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 726, 138560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Yin, L.; Li, Z.; Wen, X.; Luo, X.; Hu, Z.; Yang, H.; Long, Y.; Deng, B.; Huang, L.; et al. Microplastic pollution in the rivers of the Tibet Plateau. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xue, N.; Li, W.; Zhang, D.; Pan, X.; Luo, Y. Selectively enrichment of antibiotics and ARGs by microplastics river, estuary and marine waters. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 134594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kay, P.; Hiscoe, R.; Moberley, I.; Bajic, L.; McKenna, N. Wastewater treatment plants as a source of microplastics in river catchments. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 20264–20267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Napper, I.E.; Baroth, A.; Barrett, A.C.; Bhola, S.; Chowdhury, G.W.; Davies, B.F.R.; Duncan, E.M.; Kumar, S.; Nelms, S.E.; Niloy, M.N.H.; et al. The abudance and characteristics of microplastics in surface water in the transboundary Ganges River. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 274, 116348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eo, S.; Hong, S.H.; Song, Y.K.; Han, G.M.; Shim, W.J. Spatiotemporal distribution and annual load of microplastics in the Nakdown River, South Korea. Water Res. 2019, 160, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegfried, M.; Koelmans, A.A.; Besseling, E.; Kroeze, C. Export of microplastics from land to sea. A modeling approach. Water Res. 2017, 127, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannerla, M.; Andersson, M.; Birzaks, J.; Debowski, P.; Degerman, E.; Huhmarniemi, A.; Häggström, H.; Ikonen, E.; Jokikokko, E.; Jutila, E.; et al. Salmon and Sea Trout Populations and Rivers in the Baltic Sea—HELCOM assessment of salmon (Salmo salar) and sea trout (Salmo trutta) populations and habitats in rivers flowing to the Baltic Sea. Balt. Sea Environ. Proc. 2011, 126A, 1–79. [Google Scholar]
- Obolewski, K. Macrozoobenthos patterns along environmental gradients and hydrological connectivity of oxbow lakes. Ecolog. Eng. 2011, 37, 796–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drwal, J.; Cieśliński, R.; Fac-Beneda, J. Geographic record of human impact conformance to different water relationships along a Coastal River (The Łupawa Catchment). Quaest. Geogr. 2011, 30, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cyberski, J.; Jędrasik, J. The exchange and the circulation of waters in the lake Gardno. In Zlewnia Przymorskiej Rzeki Łupawy i Jej Jeziora; Korzeniewski, K., Ed.; WSP: Słupsk, Poland, 1992; pp. 199–220. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Jasińska, E. Motion of salt water and associated fronts in tideless estuaries. Estuaries 1993, 16, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesa, F.S.; Turra, A.; Baruque-Ramos, J. Synthetic fibers as microplastics in the marine environment: A review from textile perspective with a focus on domestic washings. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 598, 1116–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napper, I.E.; Thompson, R.C. Release of synthetic microplastic plastic fibres from domestic washing machines: Effects of fabric type and washing conditions. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 112, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sillanpää, M.; Sainio, P. Release of polyester and cotton fibers from textiles in machine washings. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 19313–19321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Falco, F.; Di Pace, E.; Cocca, M.; Avella, M. The contribution of washing processes of synthetic clothes to microplastic pollution. Sci Rep. 2019, 9, 6633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dris, R.; Gasperi, J.; Rocher, V.; Saad, M.; Renault, N.; Tassin, B. Microplastic contamination in an Urban area: A case study in Greater Paris. Environ. Chem. 2015, 12, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, T.; Nihei, Y.; Kudou, K.; Hinata, H. Assessment of the sources and inflow processes of microplastics in the river environments of Japan. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 958–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Institute of Meteorology and Water Management National Research Institute. Available online: https://hydro.imgw.pl/#map/17.4283,54.4828,11,true,true,0 (accessed on 15 November 2021).
- GeoPortal—Interactive Map. Available online: https://mapy.geoportal.gov.pl/imap/Imgp_2.html?gpmap=gp0 (accessed on 15 November 2021).
- Chen, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Gao, F.; Lan, C.; Yang, B.; Zhang, S.; Gao, Y. pH-responsive catalytic mesocrystals for chemodynamic therapy via ultrasound-assisted Fenton re action. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 369, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, L.; Bao, L.J.; Shi, L.; Wong, C.S.; Zeng, E.Y. A review of methods for measuring microplastics in aquatic environments. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 11319–11332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, J. Investigation of microplastics in aquatic environments: An overview of the methods used, from field sampling to laboratory analysis. TrAC 2018, 108, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avio, C.G.; Gorbi, S.; Regoli, F. Experimental development of a new protocol for extraction and characterization of microplastics in fish tissues: First observations in commercial species from Adriatic Sea. Mar. Environ. Res. 2015, 111, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusher, A.L.; McHugh, M.; Thompson, R.C. Occurrence of microplastics in the gastrointestinal tract of pelagic and demersal fish from the English Channel. Mar. Pollut Bull. 2013, 67, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaliszewicz, A.; Winczek, M.; Karaban, K.; Kurzydłowski, D.; Górska, M.; Koselak, W.; Romanowski, J. The contamination of inland Walters by microplastic fibres under different anthropogenic pressure: Preliminary study in Central Europe (Poland). Waste. Manag. Res. 2020, 38, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, M.O.; Abrantes, N.; Gonçalves, F.J.M.; Nogueira, H.; Marques, J.C.; Gonçalves, A.M.M. Spatial and temporal distribution of microplastics in water and sediments of a freshwater system (Antuã River, Portugal). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 1549–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekudewicz, I.; Dąbrowska, A.M.; Syczewski, M.D. Microplastic pollution in surface water and sediments in the Urban section of the Vistula River (Poland). Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 762, 143111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Xie, Y.; Zhong, S.; Yang, B.; Lu, D.; Zhong, Q. Distribution of microplastics in surface water and sediments of Qin river In Beibu Gulf, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 708, 135176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.; Mao, R.; Guo, X.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, C. Microplastics in surface waters and sediments of the Wei River, in the northwest of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 667, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, M.; Niu, X.; Tang, M.; Zhang, B.T.; Wang, G.; Yue, W.; Kong, X.; Zhu, J. Distribution of microplastics in surface water of the lower Yellow River near estuary. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 707, 135601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Lu, H.; Yao, T.; Liu, Y.; Tian, P.; Lu, J. Microplastic footprints in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and their implications to the Yangtze River Basin. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 407, 124776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, A.; Hoellein, T.J.; Mason, S.S.; Schluep, J.; Kelly, J.J. Microplastic is an Abundant and Distinct Microbial Habitat in an Urban River. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 11863–11871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morritt, D.; Stefanoudis, P.V.; Pearce, D.; Crimmen, O.A.; Clark, P.F. Plastic in the Thames: A river runs through it. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 78, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estahbanati, S.; Fahrenfeld, N.L. Influence of wastewater treatment plant discharges on microplastic concentrations in surface water. Chemosphere 2016, 162, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalčikova, G.; Alič, B.; Skalar, T.; Bundschuh, M.; Žgajnar Gotvajn, A. Wastewater treatment plant effluents as source of cosmetic polyethylene microbeads to freshwater. Chemosphere 2017, 188, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horton, A.A.; Svendsen, C.; Williams, R.J.; Spurgeon, D.J.; Lahive, E. Large microplastic particles in sediments of tributaries of the River Thames, UK e abundance, sources and methods for effective quantification. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 114, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, D.; Li, X.; Ouyang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Wu, R.; Zhang, C.; Lin, C.; Li, Y.; Guo, X. The occurrence and abundance of microplastics in surface water and sediment of theWest River downstream, in the south of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 756, 143857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherer, C.; Weber, A.; Stock, F.; Vurusic, S.; Egerci, H.; Kochleus, C.; Arendt, N.; Foeldi, C.; Dierkes, G.; Wagner, M.; et al. Comparative assessment of microplastics in water and sediment of a large European River. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 738, 139866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issac, M.N.; Kandasubramanian, B. Effect of microplastics in water and aquatic systems. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 19544–19562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazurais, D.; Ernande, B.; Quazuguel, P.; Severe, A.; Huelvan, C.; Madec, L.; Mouchel, O.; Soudant, P.; Robbens, J.; Huvet, A.; et al. Evaluation of the impast of polyethylene microbeads ingestion in European sea bass (Dicentrarchuslabrax) larvae. Mar. Environ. Res. 2015, 112, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lei, L.; Wu, S.; Lu, S.; Liu, M.; Song, Y.; Fu, Z.; Shi, H.; Reley-Susman, K.M.; He, D. Microplastic particles cause intestinal damage and other adverse effects in zebrafishDanio rerio and nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidoo, T.; Glassom, D. Decreased growth and survival in small juvenile fish, after chronic exposure to environmentally relevant concentrations of microplastic. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 145, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greven, A.C.; Merk, T.; Karagöz, F.; Mohr, K.; Klapper, M.; Jovanović, B.; Palić, D. Polycarbonate and polystyrene nanoplastic particles act as stressors to the innate immune system of fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 3093–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Jiang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Geng, J.; Ding, L.; Ren, H. Uptake and accumulation of polystyrene microplastics in zebrafish (Danio rerio) and toxic effectsin liver. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 4054–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Gundlach, M.; Yang, S.; Jiang, J.; Velki, M.; Yin, D.; Hollert, H. Quantitative investigation of the mechanisms of microplastics and nanoplastics toward zebrafishlarvae locomotor activity. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584, 1022–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Zhang, S.; Razanajatovo, R.M.; Zou, H.; Zhu, W. Accumulation, tissue distribution, and biochemical effects of polystyrenemicroplastics in the freshwater fish redtilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Environ. Pollut. 2018, 238, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochman, C.M.; Kurobe, T.; Flores, I.; Teh, S.J. Early warning signs of endocrine disruption in adult fish from the ingestion of polyethylene with and without sorbetchemical pollutants from the marine environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 493, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karami, A.; Romano, N.; Galloway, T.; Hamzah, H. Virgin microplastics cause toxicity andmodulate the impacts of phenanthrene on biomarker responses in African catfish (Clarias gariepinus). Environ. Res. 2016, 151, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, M.; Soliman, H.A.; Osman, A.G.; Sayed, A.E.D.H. Assessment the effect of exposure to microplastics in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) early juvenile: I. Bloodbiomarkers. Chemosphere 2019, 228, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochman, C.M.; Hoh, E.; Kurobe, T.; Teh, S.J. Ingested plastic transfers hazardous chemicals to fish and induces hepatic stress. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.; Ribeiro, A.; Hylland, K.; Guilhermino, L. Single and combined effects of microplastics and pyrene on juveniles (0+ group) of the common gobyPomatoschistus microps (Teleostei, Gobiidae). Ecol. Indic. 2013, 34, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghi, B.N.; Banaee, M. Effects of micro-plastic particles on paraquat toxicity to common carp (Cyprinus carpio): Biochemical changes. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 14, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallik, A.; Xavier, M.; Naidu, B.; Nayak, B. Ecotoxicological and physiological risks of microplastics on fish and their possible mitigation measures. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 779, 146433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanović, B. Ingestion of microplastics by fish and its potential consequences from a physical perspective. Soc. Environ. Tox. Chem. 2017, 13, 510–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakubowska, M.; Białowąs, M.; Stankevičiūtė, M.; Chomiczewska, A.; Pažusienė, J.; Jonko-Sobuś, K.; Hallmann, A.; Urban-Malinga, B. Effects of chronic exposure to microplastics of different polymer types on early life stages of sea trout Salmo trutta. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 139922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huppertsberg, S.; Knepper, T.P. Instrumental analysis of microplastics—benefits and challenges. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 6343–6352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Covernton, G.A.; Pearce, C.M.; Gurney-Smith, H.J.; Chastain, S.G.; Ross, P.S.; Dower, F.F.; Dudas, S.E. Size and shape matter: A preliminary analysis of microplastic sampling technique in seawater studies with implications for ecological risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 667, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, M.; Lindeque, P.; Halsband, C.; Galloway, T.S. Microplastics as contaminants in the marine environment: A review. Mar.Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 2588–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nor, N.H.M.; Obbard, J.P. Microplastics in Singapore’s coastal mangrove ecosystems. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 79, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Morphological Type | Season | The Sum of Ranks ŁR | The Sum of Ranks SR | Mann–Whitney U Statistic | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MPs total | all period | 546.0 | 630.0 | 246.0 | 0.392 |
| granule | 542.0 | 634.0 | 242.0 | 0.348 | |
| fragments | 562.0 | 614.0 | 262.0 | 0.599 | |
| fibers | 585.0 | 591.0 | 285.0 | 0.959 | |
| MPs total | Spring | 53.5 | 82.5 | 17.5 | 0.141 |
| granule | 58.0 | 78.0 | 22.0 | 0.318 | |
| fragments | 58.5 | 77.5 | 22.5 | 0.344 | |
| fibers | 63.5 | 72.5 | 27.5 | 0.674 | |
| MPs total | Summer | 62.5 | 73.5 | 26.5 | 0.599 |
| granule | 67.0 | 69.0 | 31.0 | 0.958 | |
| fragments | 65.5 | 70.5 | 29.5 | 0.833 | |
| fibers | 60.5 | 75.5 | 24.5 | 0.462 | |
| MPs total | Autumn | 71.5 | 64.5 | 28.5 | 0.753 |
| granule | 63.5 | 72.5 | 27.5 | 0.674 | |
| fragments | 70.0 | 66.0 | 30.0 | 0.874 | |
| fibers | 80.0 | 56.0 | 20.0 | 0.227 |
| Dimension | Color | N | Mean [mm] | Median [mm] | Range [mm] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Length [mm] | green | 6 | 0.38 | 0.25 | 0.04–0.92 |
| Width [mm] | 0.27 | 0.16 | 0.03–0.66 | ||
| Area [mm2] | 0.19 | 0.05 | 0.001–0.521 | ||
| Length [mm] | transparent | 15 | 0.43 | 0.34 | 0.13–1.26 |
| Width [mm] | 0.35 | 0.25 | 0.03–1.65 | ||
| Area [mm2] | 0.16 | 0.09 | 0.009–0.605 | ||
| Length [mm] | yellow | 10 | 0.72 | 0.09 | 0.04–6.00 |
| Width [mm] | 0.71 | 0.08 | 0.03–6.100 | ||
| Area [mm2] | 3.68 | 0.01 | 0.001–36.60 | ||
| Length [mm] | blue | 18 | 0.31 | 0.27 | 0.03–0.92 |
| Width [mm] | 11 | 0.12 | 0.09 | 0.04–0.43 | |
| Area [mm2] | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.001–0.396 | ||
| Length [mm] | red | 6 | 0.27 | 0.12 | 0.01–0.75 |
| Width [mm] | 5 | 0.12 | 0.03 | 0.01–0.44 | |
| Area [mm2] | 0.07 | 0.001 | 0.00–0.33 | ||
| Length [mm] | white | 9 | 0.63 | 0.29 | 0.12–3.00 |
| Width [mm] | 0.59 | 0.30 | 0.08–3.10 | ||
| Area [mm2] | 1.13 | 0.09 | 0.01–9.30 | ||
| Length [mm] | black | 13 | 0.23 | 0.22 | 0.03–0.69 |
| Width [mm] | 9 | 0.12 | 0.09 | 0.04–0.32 | |
| Area [mm2] | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.001–0.221 | ||
| Length [mm] | pink | 3 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 0.07–0.13 |
| Width [mm] | 0.10 | 0.060 | 0.04–0.20 | ||
| Area [mm2] | 0.01 | 0.007 | 0.002–0.026 | ||
| Length [mm] | purple | 1 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09 |
| Width [mm] | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 | ||
| Area [mm2] | 0.007 | 0.007 | 0.007 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Piskuła, P.; Astel, A.M. Microplastics Occurrence in Two Mountainous Rivers in the Lowland Area—A Case Study of the Central Pomeranian Region, Poland. Microplastics 2022, 1, 167-185. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics1010011
Piskuła P, Astel AM. Microplastics Occurrence in Two Mountainous Rivers in the Lowland Area—A Case Study of the Central Pomeranian Region, Poland. Microplastics. 2022; 1(1):167-185. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics1010011
Chicago/Turabian StylePiskuła, Paulina, and Aleksander Maria Astel. 2022. "Microplastics Occurrence in Two Mountainous Rivers in the Lowland Area—A Case Study of the Central Pomeranian Region, Poland" Microplastics 1, no. 1: 167-185. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics1010011
APA StylePiskuła, P., & Astel, A. M. (2022). Microplastics Occurrence in Two Mountainous Rivers in the Lowland Area—A Case Study of the Central Pomeranian Region, Poland. Microplastics, 1(1), 167-185. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics1010011





