Abstract
The PowerPlex Fusion 6C PCR™ amplification kit provides a strong discriminatory power for human identification. We have validated the kit with a reduced volume (12.5 µL) and as part of the validation we compared the efficiency of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) prepared manually and on Hamilton Microlab® Autolys STAR Biorobot. Three years of casework data has been also included in the validation. Optimisation was carried out on different types of samples (blood, saliva, semen) and DNA was extracted robotically. Tests were conducted at two different cycle numbers (30;32), followed by analysis on both the Applied BiosystemsTM 3500 and 3500 xL Genetic Analyzer instruments (Applied Biosystems®, Foster City, CA, USA). When the PCR was prepared manually, no allele dropout was observed over 0.15 ng input DNA. Whereas when the PCR was prepared robotically, dropout already appeared at the level of 0.15 ng input DNA. In cases when increased cycle number was utilised, an increasing number of dropouts started to arise from 0.075 ng total input DNA. Despite the fact that robotically prepared PCR produced more missing alleles than the manually prepared PCR, using the optimal 0.5 ng input DNA, both methods proved to be reliable. Based on the results, our half-volume protocol is robust, and after three years of application it has proven to be effective with respect to a large number of casework samples.
1. Introduction
Since the method of DNA profiling was discovered and introduced into forensic science, new technological developments have gradually emerged making individual identification easier and faster [1,2]. Today, next generation sequencing (NGS or MPS) represents a new and promising tool, but short tandem repeats (STRs) still dominate the field [2,3,4,5]. In contrast to the first STR kits, multiplex-fluorescent-labelled STR assays now contain a high number, up to more than 20 loci [6,7,8]. Despite recent advancements, forensic genetics still faces frequent challenges, such as inhibition and degradation, especially when casework samples are analysed. Some of these difficulties are easier to overcome than others, such as degradation, which still poses a severe issue. Kits including more than 20 loci often exhibit loss of data, as longer fragments are more exposed to deteriorating effects than shorter ones. In such cases, a kit such as the NGM Detect PCR Amplification Kit (Applied Biosystems™, Foster City, CA, USA) that contains less loci and produces reduced-size amplicons might perform better [9]. New optimisation protocols such as reduced volume validations are also being introduced into practice. These methods enable reduction of costs and template DNA, as well as in some cases resulting in a better profile. Such findings were already observed in the case of the GlobalFilerTM Amplification Kit (Applied Biosystems™, Foster City, CA, USA) and the VeriFilerTM Express PCR Amplification Kit (Applied Biosystems™) [10,11].
We aimed to pursue the same advantages, and decided to validate in half-volume the PowerPlex® Fusion 6C PCR™ System (Promega Corporation, Madison, WI, USA) (PF6C). The PF6C is a comprehensive kit containing all the necessary components for amplifying and detecting 27 specific genetic markers of the human genome. Among others, these loci can also be found in the European Standard Set (ESS) STR database and among the core loci of the Combined DNA Index System (CODIS). By incorporating information from both CODIS and ESS loci, the system substantially increases the discriminatory power of DNA profiling, minimising the likelihood of coincidental matches, known as adventitious matches. The included markers offer a wide range of information about an unknown person, and its outstanding feature is its exceptional PI (Probability of Identity) value of 9.09 × 10−31 compared to other similar STR kits [12].
A recent publication demonstrates that the PF6C kit is compatible with the half-volume protocol, but does not apply to casework samples [13]. The Scientific Working Group on DNA Analysis Methods (SWIGDAM) and the European Network of Forensic Science Institutes (ENFSI) recommend involving casework samples in validation [14,15]. Here in our half-volume validation, we present three years of real case data processed by the PF6C.
Apart from half volume validations, forensic workflow can be improved with liquid-handling systems by increasing accuracy and traceability, and by reducing processing time and costs [16,17]. Today, many laboratories use robots, and there is a growing interest in reactions that require lower reaction volumes processed by automated systems [16]. However, many concerns need to be considered before adapting new routines. One of them is the pipetting channel, as reduced-volume protocols might display difficulties during robotically prepared PCR [18].
The widely used Hamilton Microlab® Autolys STAR biorobot (Hamilton Bonaduz AG, Bonaduz, Switzerland; Hamilton biorobot) possesses a 1000 µL pipetting channel, and for PCR it uses 50 µL and 300 µL pipette tips; thus, accurate measurement of volumes under 10 µL can be challenging compared to manually prepared PCR [19,20]. However, given the growing demand for forensic genetics, we must focus on prioritizing methods that require less human intervention, even if the pursuit of automation might outweigh the benefits of half-volume validation.
All things considered, our study has three main goals. First, it is the validation of the PF6C for our laboratory in half the volume recommended by the manufacturer. Second, we aim at comparing the effectiveness of the half-volume protocol for both the manually and the robotically prepared PCRs performed with Hamilton biorobot. Third, following the recommendations of the SWIGDAM and the ENFSI, we included three years of data from real crime scene samples degraded to varying degrees. Validation settings were designed to represent the variability between sample types, to simulate the characteristics of samples in which more than one person may be present or contain small amounts of DNA.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
For validation parameters such as reproducibility, repeatability, and sensitivity, five saliva samples were collected with sterile Omni Swab (Qiagen GmbH, Hilden, Germany) from one known male person and diluted into solutions of known concentration. Amplifications were carried out five times in parallel using the following inputs: 1 ng, 0.5 ng, 0.15 ng, 0.075 ng, 0.0375 ng, 0.015 ng, and 0.0075 ng. For testing mixture samples, only the optimal 0.5 ng DNA input was used, and one male and one female saliva sample were mixed in different ratios. Regarding stability, blood and semen samples were collected, too. Each sample type was tested five parallel times. All samples were stored at −20 °C until usage. In the case of degraded casework samples, a total of 201 samples were included, such as on-site wipe samples, hair, bone, blood, semen, saliva, nail scrapping, and cigarette filter.
2.2. DNA Extraction
DNA extraction of all samples (including the casework samples) was done with Qiagen EZ1 Advanced XL robot using EZ1&2 DNA Investigator Kit (48) and DNA Purification (Large-Volume) protocol (Qiagen GmbH, Hilden, Germany) [21]. Following extraction, DNA yield and validation of manually diluted stock concentrations were confirmed with QuantifilerTM Trio DNA Quantification kit (Applied Biosystems™, Foster City, CA, USA) on ABI 7500 Real-time PCR System (Applied Biosystems™, Foster City, CA, USA) following the manufacturer’s instructions.
2.3. PCR Amplification and Settings
Amplifications with the PowerPlex® Fusion 6C PCR™ System were prepared manually and on Hamilton Microlab® Autolys STAR biorobot.
The half-volume validation process was optimised to 0.5 ng DNA in all cases.
For all PCRs, instead of the final volume of 25 µL recommended by the manufacturer, 12.5 μL was used and the reaction mix also contained half amount of the PowerPlex® Fusion 5X Master Mix and Primer Pair Mix (Promega Corporation, Madison, WI, USA) [22]. Aside from the 5 µL reaction mix, negative control contained 7.5 μL Amplification Grade Water, while the positive control included 1 μL DNA Control 2800 M (0.5 ng/μL) and 6.5 μL Amplification Grade Water.
The PCR conditions were 1 min at 96 °C, followed by 30 or 32 cycles of 5 s at 96 °C, 1 min at 60 °C, and a final extension for 20 min at 60 °C. The determination of increased cycle number of 32 was based on the measured allelic dropout.
2.4. Capillary Electrophoresis
Spectral calibration was done for Applied Biosystems™ 3500 and 3500 xL Genetic Analyzer instruments following the PowerPlex 6C Matrix Standard Technical Manual [23]. Electrokinetic injection for ABI 3500 and 3500 xL instruments took 15 s at 1.2 kV and 24 s at 1.2 kV, respectively.
Minimum threshold calculation was done based on the results of five negative control samples after running at 30 and 32 cycles. The evaluation was performed using the GeneMapper® ID-X 1.4 software with a Peak Detection Threshold setting of one relative fluorescent unit (RFU). The validated analytical threshold for the respective instrument was obtained by adding ten times the standard deviation to the average of the detected peak heights of all colours. The highest RFU value, 52, was produced by the green colour and served as the basis for setting the threshold.
PCR ladders were also run five parallel times on the Applied BiosystemsTM 3500 and 3500 xL Genetic Analyzer instruments to exclude the possibility of allele slippage, thus increasing searchability among profiles. Only 0.5 bp difference was allowed.
Results were analysed with GeneMapper® ID-X 1.4. software (Applied Biosystems™, Foster City, CA, USA), with all settings in accordance with the technical manual of the PF6C kit [22]. Data interpretation of the casework samples was done using DNAxs 2.5.8. software (©2017–2022 Netherlands Forensic Institute).
3. Validation
Before using the PF6C, the kit underwent a successful internal validation process in accordance with the Scientific Working Group on DNA Analysis Methods (SWGDAM Interpretation Guidelines for Autosomal STR Typing by Forensic DNA Testing Laboratories, 1 December 2017 Rev 13 July 2021) and the European Network of Forensic Science Institutes (ENFSI, Recommended Minimum Criteria for the Validation of Various Aspects of the DNA Profiling Process, Issue No: 001, November 2010) guidelines to assess its robustness [14,15]. Only the validation parameters affected by the modifications are clarified.
3.1. Repeatability and Reproducibility
The repeatability and reproducibility studies involved five parallel PCRs of each saliva sample with known DNA input: 1 ng, 0.5 ng, 0.15 ng, 0.075 ng, 0.0375 ng, 0.015 ng, and 0.0075 ng. Repeatability was confirmed by PCRs performed three different times, at least one week apart by the same person, while reproducibility was verified by PCRs done by three people. Preparation of PCRs was done both manually and on Hamilton biorobot using the same set of equipment.
3.2. Sensitivity
Representing the properties of low-copy number (LCN) casework samples, we performed a comparative assessment of the half-volume method at various DNA concentration levels (1 ng, 0.5 ng, 0.15 ng, 0.075 ng, 0.0375 ng, 0.015 ng, and 0.0075 ng). On each concentration, five parallel measurements were conducted.
The evaluation included the determination of the average peak height, standard deviation, fragment size (bp), and the percentage of allele dropout in each DNA profile.
3.3. Mixture Samples
Optimisation of the half-volume method involved five parallel tests of mixed female (major) and male (minor) samples in different ratios using samples of two known reference persons. Total input DNA was 0.5 ng again, keeping the ratios of 1:1; 1:4; 1:7; 1:9; 1:19. All PCRs were performed both manually and in the automated way.
3.4. Stability
Tests of three different sample types (blood, saliva, and semen) collected from one male person were carried out to evaluate the stability of the new protocol. Manually prepared PCRs of one sample from each sample type was repeated five times in parallel using the optimal 0.5 ng DNA input, and analysed on Applied BiosystemsTM 3500 and 3500 xL Genetic Analyzer instruments. Stability tests for all sample types incorporated the same parameters as the sensitivity test.
3.5. Degraded Casework Samples
Casework samples degraded to varying levels were analysed after using the newly validated protocol over a three-year period between 2020 and 2022. During this time, a total of 4921 PCRs of casework samples were processed using Hamilton biorobot, and 17,311 PCRs were prepared manually. A total of 201 forensic cases samples were run at least two times either manually (183) or in the automated way (18). Degradation was categorized into three different groups based on the degradation index (DI) obtained with ABI 7500 Real-time PCR System after extraction [24]. Samples with DI of 3–4 were considered as “Low”, samples with a DI of 4–7 were considered as “Medium”, and samples with a DI over >7 were considered as “High”, respectively. Samples with less than 3 (DI) were not considered degraded. DNA input for PCR was 0.5 ng in all cases.
4. Results
4.1. Sensitivity
To assess the acuteness of the half-volume protocol, five parallel measurements were conducted on saliva samples using different DNA inputs (1 ng, 0.5 ng, 0.15 ng, 0.075 ng, 0.0375 ng, 0.015 ng, and 0.0075 ng) both manually and in an automated way. Based on the initial results of manually prepared PCR on default cycle number (30×), we determined which input DNA quantities required more cycles (32×).
Regardless of colours, the average peak height on default cycle number with manually prepared PCR was between 7838 and 13,796.3 RFU (1 ng input DNA) and 79.67 and 136.2 RFU (0.0075 ng input DNA). By raising the cycle number from 30 to 32, average RFU of 0.0075 ng input DNA raised to 273.5–403.67 RFU. Based on these data and allele dropout, automated PCRs on default cycle number were done only in the cases of 0.5 and 0.15 ng DNA. RFUs were 6099.3–3112.1 RFU and 530.11–1808.17 RFU, respectively. As for the raised cycle number, the average was between 9138.77 and 5300.6 RFU (0.15 ng) and 273.5 and 403.67 RFU (0.0075 ng) (Table 1 and Table 2).

Table 1.
Average RFU, standard deviation, and allele dropout for each dye for five parallel manual and automated PCRs on default (30×) cycle number.

Table 2.
Average RFU, standard deviation, and allele dropout for each dye for five manual and automated PCRs on increased (32×) cycle number.
In the case of manually prepared PCR, the first allele dropout appeared from 0.075 ng, but after raising the cycle number it started to decrease. Given the PCR with Hamilton biorobot, out of 0.5 ng and 0.15 ng input DNA, allele dropout appeared only in the case of the purple colour for 0.15 ng. As for the raised cycle number, tests were done below 0.15 ng and dropout started to appear again from 0.075 ng, but in increasing numbers. For example, for 0.015 ng in the case of manually prepared PCR, the dropout was 10–18%, while in the case of automated PCR, it was already 35–46%. In general, manually prepared PCR proved to be more precise, presenting less allele dropout and higher RFUs compared to the automated method (Table 1 and Table 2).
Additionally, detected fragment sizes were compared to the fragment sizes of the PCR ladders that were run five times in parallel. The statistical analysis revealed no slippage in either the manually or the automatically prepared PCR, and the alleles were identical on all loci to the genotype of the known reference person. The balance of allele heights within the loci was not allowed to fall below 60% in at least four out of five parallel measurements. Imbalance values with both PCR preparation methods met this criterion when the optimal 0.5 ng input DNA was used.
4.2. Mixture Analysis
To simulate casework samples, mixtures of female and male saliva samples were created in different ratios: 1:1; 1:4; 1:7; 1:9; and 1:19. Regarding allele dropout, manually prepared PCR performed better than automated PCR with Hamilton biorobot. When PCR was done manually, in the sample containing the least male DNA (1:19) only 14.22% of alleles failed to amplify, compared to 23.11% dropout of the automated method. Incomplete male profiles were obtained under the 1:4 ratio. No dropout was detected in the case of the female/major component for either PCR methods. Results are summarised in Table 3.

Table 3.
Allele dropout in mixture samples for manually prepared and automated PCR.
4.3. Stability Assessment
The stability tests of the five parallel repetitions were successful for all sample types (blood, saliva, semen). PCRs were done using the optimal DNA input of 0.5 ng, and no allele dropout occurred in any sample types.
4.4. Degraded Casework Samples
The successfully validated half-volume protocol has been working reliably in our lab since the end of 2019. Between 2020 and 2022, in 201 cases at least two parallel PCRs of degraded samples using the half-volume optimised PF6C protocol on Hamilton biorobot (18) or manually (183) were done. Given that degradation is a common problem in the casework samples, our laboratory routinely measures it with the QuantifilerTM Trio Kit [16]. Longer fragments are more exposed to detrimental effects and less likely to amplify during PCR, causing a ‘ski slope’ on the electropherogram. Figure 1 presents the difference between a highly, moderately, and lowly degraded profile demonstrating the deterioration of larger markers. In the case of a highly degraded sample (Figure 1a), extreme imbalance can be seen between the smaller and longer loci, leading to allele dropout. Here, we evaluate the protocol taking degradation into consideration and report the results.
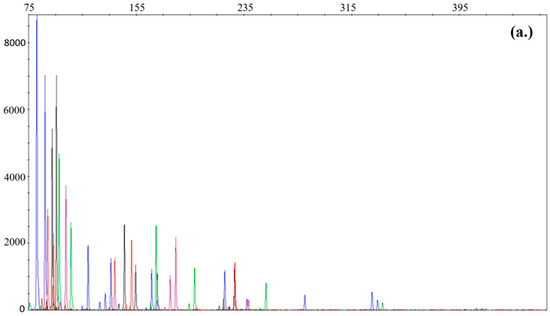
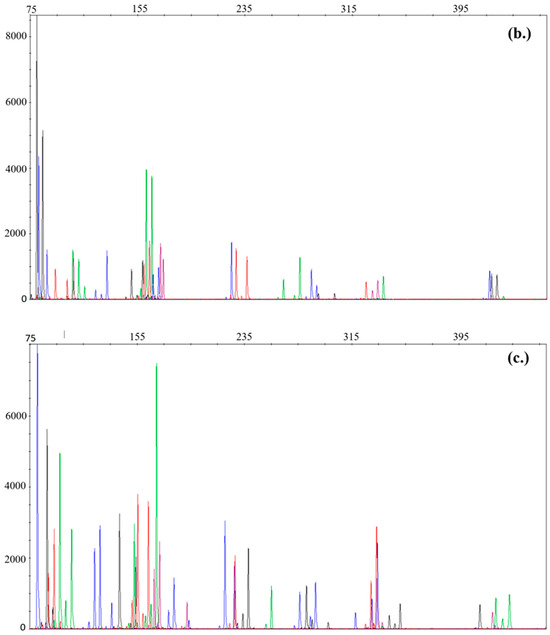
Figure 1.
Profiles with different degradation levels. (a) Profile with high degradation level (DI = 8.74); (b) profile with medium degradation level (DI = 5.84); (c) profile with low degradation level (DI = 3.15). Fragment size can be seen on the x-axis, while RFU is on the y-axis. Electropherograms are reported in raw form in order to respect personal rights.
We found that 61% of slightly degraded and manually processed samples were able to provide a profile suitable for comparison, compared to the 50% success for the Hamilton biorobot. For medium degraded samples, these were 46.7% and 40%, respectively. In the case of highly degraded samples for Hamilton biorobot, no PCR was done. Regardless of the sample types and the PCR preparation methods, we successfully obtained comparable profiles in 60%, 46%, and 24% in the cases of lowly, moderately, and highly degraded samples, respectively. Calculation of allele dropout was not possible due to multiperson casework samples and/or the lack of reference samples. Average locus dropout, initial DNA concentrations, and results are shown in Table 4.

Table 4.
Results of the manual and automated PCRs regarding the degradation index of casework samples.
5. Discussion
In our laboratory, we have previously confirmed the effectiveness of the PowerPlex® Fusion 6C PCR™ System kit by assessing its ability to produce reliable results under various challenging conditions that are typically encountered in forensic casework. These could be degradation, mixture of samples, or low DNA content, all of which have an impact on data interpretation and eventually, on the quality of profiles. Due to its robustness, the kit can overcome these difficulties with a high success rate, though it could be improved further.
In the last few years, several manuscripts about reduced-volume protocols have been published, such as in the case of the GlobalFilerTM kit for half-volume [10], the VeriFilerTM kit, which was validated in even smaller, radically reduced (5 µL instead of 25 µL) volume [11], and even for the PF6C [13]. The authors found that the reduced volume did not impair the reliability of the kit, but in some instances, it even produced better profiles. Shortly, the reduced volume protocols proved to be not only robust and cost efficient, but also enable to save DNA for further amplifications, which is highly important in the case of casework samples.
To integrate these findings into our routine, we also validated the PF6C in half-volume. The assessment involved analysing a diverse set of samples, such as saliva, blood, and semen and the validation embodied the tests of sensitivity, stability, mixture samples, and—in long-term—the degradation of casework samples. In our investigation, we also emphasised comparing the results of manual and automated PCRs, as the automatic liquid handling systems have different abilities. The Hamilton biorobot we use on a daily basis possesses a 1000 µL pipetting channel; for PCR it uses 50 µL and 300 µL pipette tips, so it might have analytical problems when pipetting volumes under 10 µL. This question is not studied in reduced volume validations, although our results showed that in the case of sensitive samples, the preparation method of PCR has its importance. Yet, the growing number of samples and possible mistakes do not allow for an increase in the number of manually prepared PCRs over automated, making it highly important to verify the results of both methods.
First, using five parallel runs of saliva samples, we determined the analytical threshold to precisely discriminate artifacts and allele peaks, then checked the ladder to exclude slippage of alleles.
In the sensitivity test of the saliva samples, we confirmed that the half-volume protocol did not affect the efficacy of the PF6C kit. Interestingly, the manually prepared PCR resulted in fewer null alleles and higher peaks compared to the automated PCR. Based on allelic dropout we decided the input DNA limit, below which increased cycle number (32×) is required. Although the automated PCR produced weaker profiles, the new protocol with the optimal 0.5 ng input DNA proved to be applicable for both methods. The profiles obtained from the sensitivity test were all identical to the ones of known persons.
Regarding the mixture samples containing two contributors (female and male) in different ratios, allele dropout started to appear from the 1:4 dilution in the case of automated PCR, but only from the 1:7 dilution when PCR was prepared manually. For the highest dilution ratio (1:19), PCR prepared with the Hamilton biorobot failed to amplify the 23.11% of male alleles, while this was only 14.22% for manual preparation. Despite the higher difference, a dropout of 23% still serves with manageable profile, especially when the female/major component is reliable.
As for the stability, tests were extended for other types of bodily fluids, such as blood and semen. The reduced volume protocol proved to be appropriate, as presenting no allele dropout in any sample types when the optimal DNA input of 0.5 ng was used. While testing stability, degradation was not considered, but three years of casework data are involved to indicate it.
In conclusion, the results of the validation demonstrated consistency, proving that the protocol with the optimal DNA input worked stable for both manually and robotically prepared PCRs.
To present additional information, we also analysed long-term data of PF6C after using it in half-volume for casework samples, and for a significant time. These samples are often affected by degradation, which is a common problem in forensic investigations, causing a slope on the electropherogram [2,24]. Thus, validations often try to simulate degradation with artificially damaged DNA to assess the robustness of the protocol. Degradation and low template content are problems that often are hand in hand, making it difficult to precisely validate the results. Here we report data of three years of casework samples concerned by both challenges. As part of routine work, between 2020 and 2022, we used the half-volume protocol of PF6C in 201 cases. Samples were run at least twice either prepared manually or in the automated way. Since DNA was isolated by EZ1 minirobot, inhibition could be excluded as an issue, but degradation and low template DNA still posed a problem. Samples were categorized into three groups based on the degradation index measured by the real-time PCR. The initial concentrations ranged between 0.002 ng/µL and 0.1465 ng/µL. By using the optimum DNA input validated through the sensitivity test, we could obtain DNA profiles suitable for comparison in a good rate even for moderately degraded samples. However, out of 201 cases, only 18 were done with Hamilton biorobot. Significance tests between the manually and robotically prepared PCRs cannot be interpreted; however, based on the long-term practice in our laboratory, the difference does not seem to be significant. Since our data are based on real casework samples, tests were not repeatable with the full-volume protocol.
When comparing manually and automated prepared PCR with Hamilton biorobot, our purpose was to understand the effect of the two methods on our protocol and exclude uncertainties. The automated system is a common and fundamental technology in forensic genetics and research to exclude the chances of human error and reduce the workload of employees. Although our results show that both PCR methods are compatible with the half-volume protocol, in the case of degraded and LCN samples, manually prepared PCR performs better and is still in favour.
In summary, the PF6C is a multiplex assay developed for forensic investigations and, due to the wide range of primers, it allows high sensitivity, even in challenging casework and degraded samples. We successfully validated the PF6C for half-volume and optimised it for casework samples using both manually and robotically prepared PCRs to maximise the quality of profiles with the highest reliability. The results of the assessment indicate that our protocol demonstrated a high level of efficiency in handling the challenges of PCR methods, and in reliably analysing the diverse range of samples encountered in casework.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.É.L., A.H. and N.M.; methodology, A.H., N.M., K.A.R. and E.É.L.; data curation, A.H., N.M., K.A.R., E.É.L. and T.C.; writing—original draft preparation, E.É.L., A.H. and N.M.M.; writing—review and editing, N.M.M., A.H., N.M. and E.É.L.; visualization, A.H. and N.M.M.; supervision, A.H. and N.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Hungarian Institute for Forensic Sciences (protocol code 29200-801/99311/2019. ált., date of approval: 11 June 2019).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the internal validation. Regarding casework samples, personality rights were respected by communicating the data in a way that is not suitable for identification and by following the Act of XXIX of 2016 on Judicial Experts as part of the Hungarian criminal law and General Data Protection Regulation (EU) 2016/679 of the European Parliament and of the Council.
Data Availability Statement
All relevant data are placed in the article. Should you be interested, the corresponding author would be glad to provide further information.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the support we received from Ágota Dobos (HIFS, Head of the Department of Genetics) and Márton Lontai (HIFS, General Director, General Counsel) for our research activity. Additionally, we would like to recognize the anonymous colleagues who donated samples for the internal validation. All persons mentioned by name have acknowledged their presence in the section and in the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Haddrill, P.R. Developments in forensic DNA analysis. Emerg. Top Life Sci. 2021, 5, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, P.; Haned, H.; Bleka, O.; Hansson, O.; Dørum, G.; Egeland, T. Genotyping and interpretation of STR-DNA: Low-template, mixtures and database matches—Twenty years of research and development. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2015, 18, 100–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roewer, L. DNA fingerprinting in forensics: Past, present, future. Investig. Genet 2013, 4, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Cubero, M.J.; Saiz, M.; Martínez-García, B.; Sayalero, S.M.; Entrala, C.; Lorente, J.A.; Martinez-Gonzalez, L.J. Next generation sequencing: An application in forensic sciences? Ann. Hum. Biol. 2017, 44, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aalbers, S.E.; Hipp, M.J.; Kennedy, R.S.; Weir, B.S. Analyzing population structure for forensic STR markers in next generation sequencing data. Genetics 2020, 49, 102364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraemer, M.; Prochnow, A.; Bussmann, M.; Scherer, M.; Peist, R.; Steffen, C. Developmental validation of QIAGEN Investigator® 24plex QS Kit and Investigator® 24plex GO! Kit: Two 6-dye multiplex assays for the extended CODIS core loci. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2017, 29, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, G.; Foley, M.M.; Knight, K.L. Applied Biosystems’ GlobalFiler™ PCR Amplification Kit. In Forensic DNA Analysis: Methods and Protocols; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2023; Volume 2685, pp. 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensenberger, M.G.; Lenz, K.A.; Matthies, L.K.; Hadinoto, G.M.; Schienman, J.E.; Przech, A.J.; Morganti, M.W.; Renstrom, D.T.; Baker, V.M.; Gawrys, K.M.; et al. Developmental validation of the PowerPlex(®) Fusion 6C System. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2016, 21, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burch, S.; Sulzer, A.; Voegeli, P.; Morf, N.V.; Gysi, M.; Kratzer, A. The Applied Biosystems™ NGM Detect™ PCR Amplification Kit—As promising as promised? Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. Suppl. Ser. 2017, 6, 504–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Almohammed, E.; Hadi, S. Internal validation of GlobalFilerTM kit using reduced reaction volume. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. Suppl. Ser. 2019, 7, 878–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, J.; Munshi, T.; Haizel, T.; Iyavoo, S. Validation of reduced volume VeriFiler™ Express PCR Amplification Kit for buccal swab samples extracted using Prep-n-Go™ Buffer. J. Forensic Sci. 2022, 67, 1971–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steffen, C.R.; Doble, M.D.; Gettings, K.B.; Vallone, P.M. Corrigendum to ‘U.S. Population Data for 29 Autosomal STR Loci’. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2017, 31, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCaughan, C.; Lenz, K.A. DNA Amplification Using Promega’s PowerPlex® Fusion Systems (5C and 6C). In Forensic DNA Analysis: Methods and Protocols; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2023; Volume 2685, pp. 207–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.swgdam.org/_files/ugd/4344b0_3f94c9a6286048c3924c58e2c230e74e.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2024).
- Available online: https://enfsi.eu/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/minimum_validation_guidelines_in_dna_profiling_-_v2010_0.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2024).
- Tegally, H.; San, J.E.; Giandhari, J.; de Oliveira, T. Unlocking the efficiency of genomics laboratories with robotic liquid-handling. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, J.Y.; Chang-Yen, D.; Blanchard, D.P.; Lam, W.; Searle, P.A. An Automated Tube Labeler for High-Throughput Purification Laboratories. SLAS Technol. 2021, 26, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enoch, E.; Councill, A.W.; Axtell, N.B.; Truong, T.; Liang, Y.; Aposhian, A.L.; Webber, K.G.I.; Zhu, Y.; Cong, Y.; Carson, R.H.; et al. Adapting a Low-Cost and Open-Source Commercial Pipetting Robot for Nanoliter Liquid Handling. SLAS Technol. 2021, 26, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, N.; Gately, R.; Ooi, L. Automated liquid handling for microplate assays: A simplified user interface for the Hamilton Microlab STAR. J. Appl. Bioanal. 2021, 7, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; Yuan, L.; Zheng, Y.F.; Chen, W. Automatic Liquid Handling for Life Science: A Critical Review of the Current State of the Art. J. Lab. Autom 2012, 17, 169–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://www.qiagen.com/us/resources/resourcedetail?id=46064856-1b88-4b27-a825-d3f616e06c08&lang=en (accessed on 20 January 2024).
- Promega Corporation. PowerPlex® Fusion System for Use on the Applied Biosystems® Genetic Analyzers; Instructions for Use of Products DC2402 and DC2408. Technical Manual TMD039, Revised in July 2020; Promega Corporation: Madison, WI, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Promega Corporation. PowerPlex® 6C Matrix Standard, Instructions for Use of Product DG4900; Technical Manual TMD046, Revised in October 2015; Promega Corporation: Madison, WI, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Vernarecci, S.; Ottaviani, E.; Agostino, A.; Mei, E.; Calandro, L.; Montagna, P. Quantifiler® Trio Kit and forensic samples management: A matter of degradation. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2015, 16, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).