W Chromosome Evolution by Repeated Recycling in the Frog Glandirana rugosa
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animals
2.2. Identification of Heterogametic Sex
2.3. Amplification of Mitochondrial DNA and Construction of Phylogenetic Trees
2.4. RT-PCR of Sex-Linked Androgen Receptor
2.5. Microsatellite DNA Amplification of Sex-Linked Sox3 Upstream Region
2.6. Genome Analysis to Determine Population Genetic Structure
2.7. Genome Analysis to Determine the Genome Structure of Sex Chromosomes
3. Results
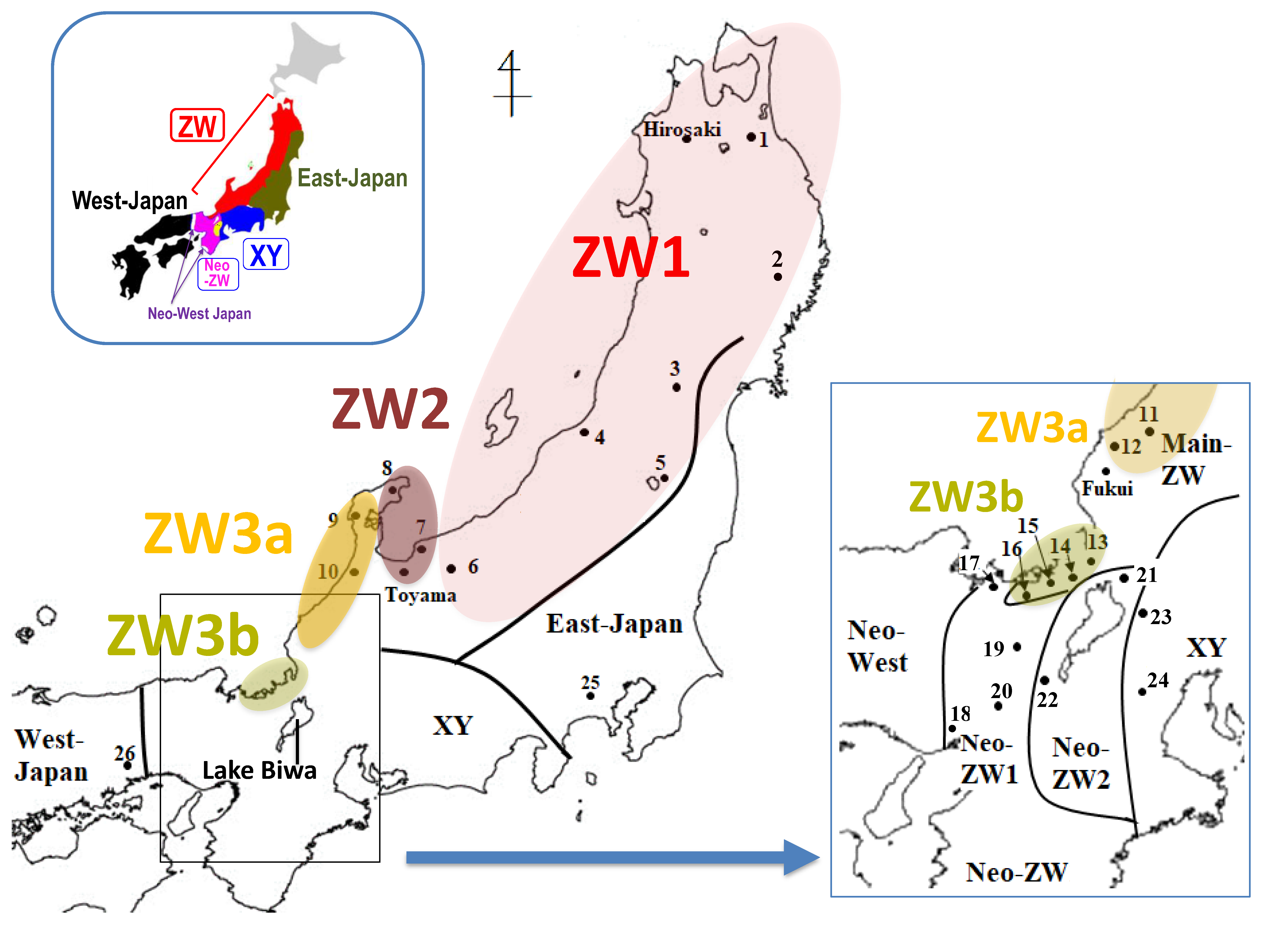
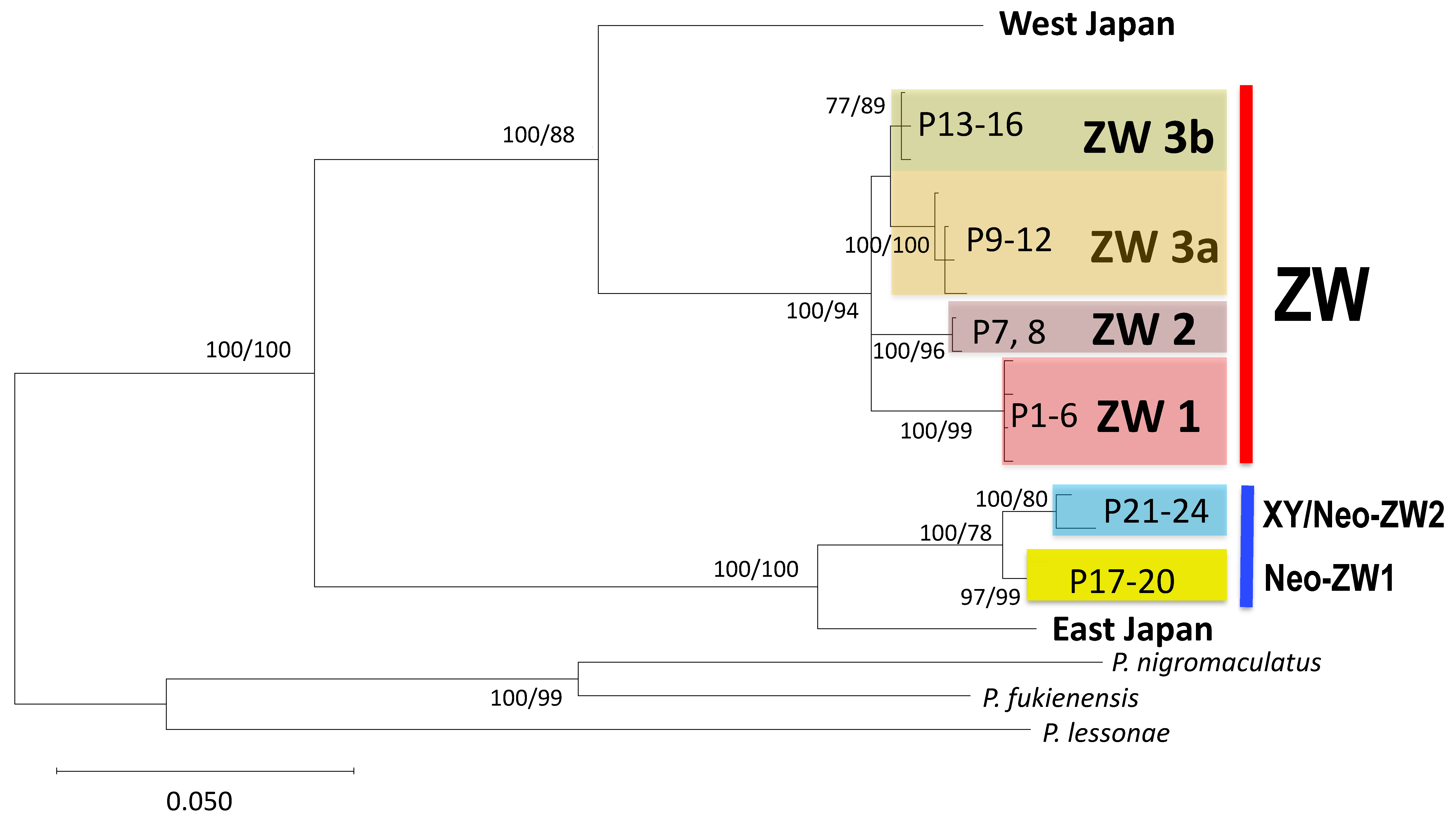
3.1. Identification of Three ZW Sub-Groups Based on Mitochondrial DNA Sequence
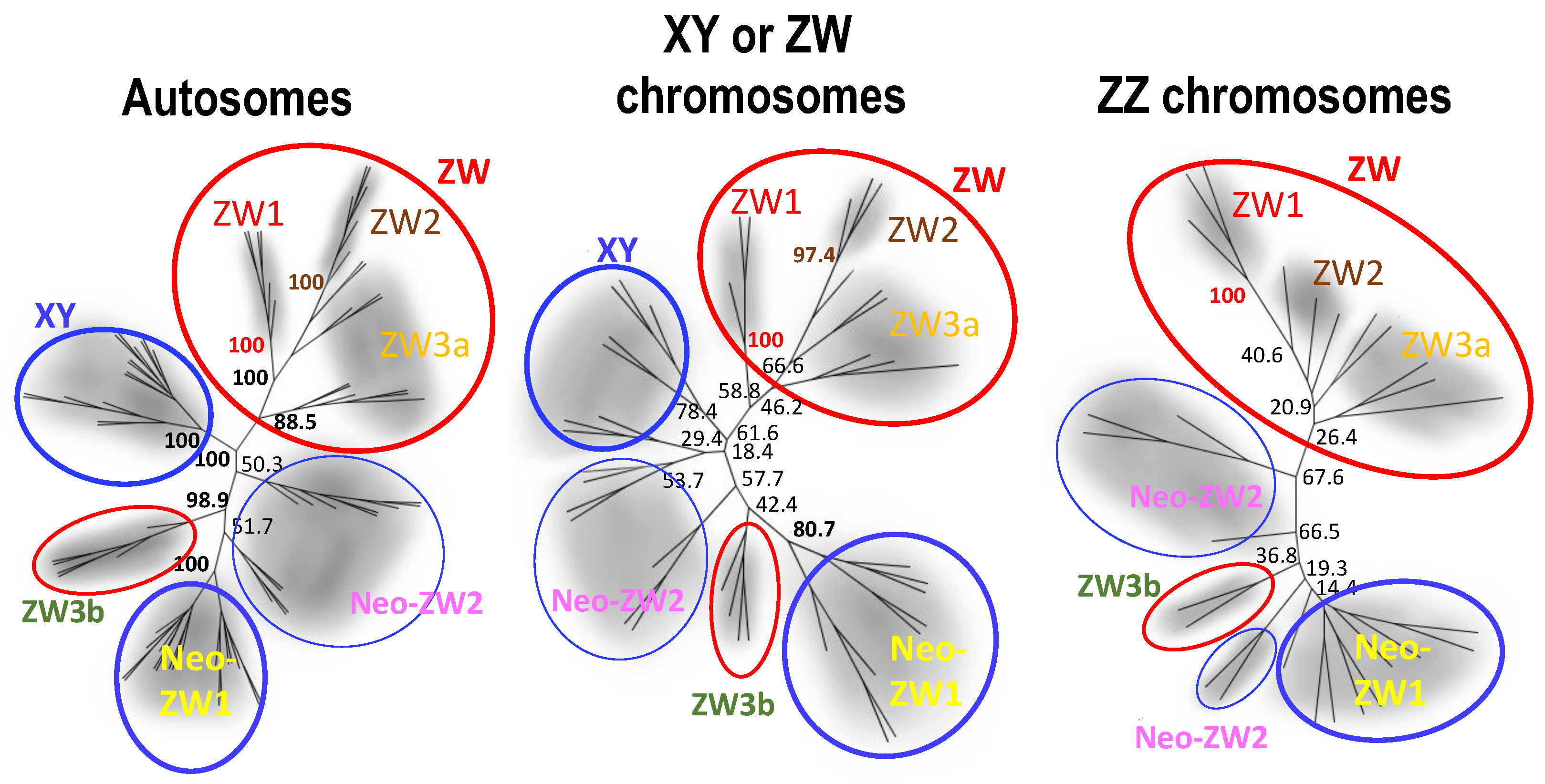
3.2. Three ZW Sub-Groups Based on Nuclear Genomes
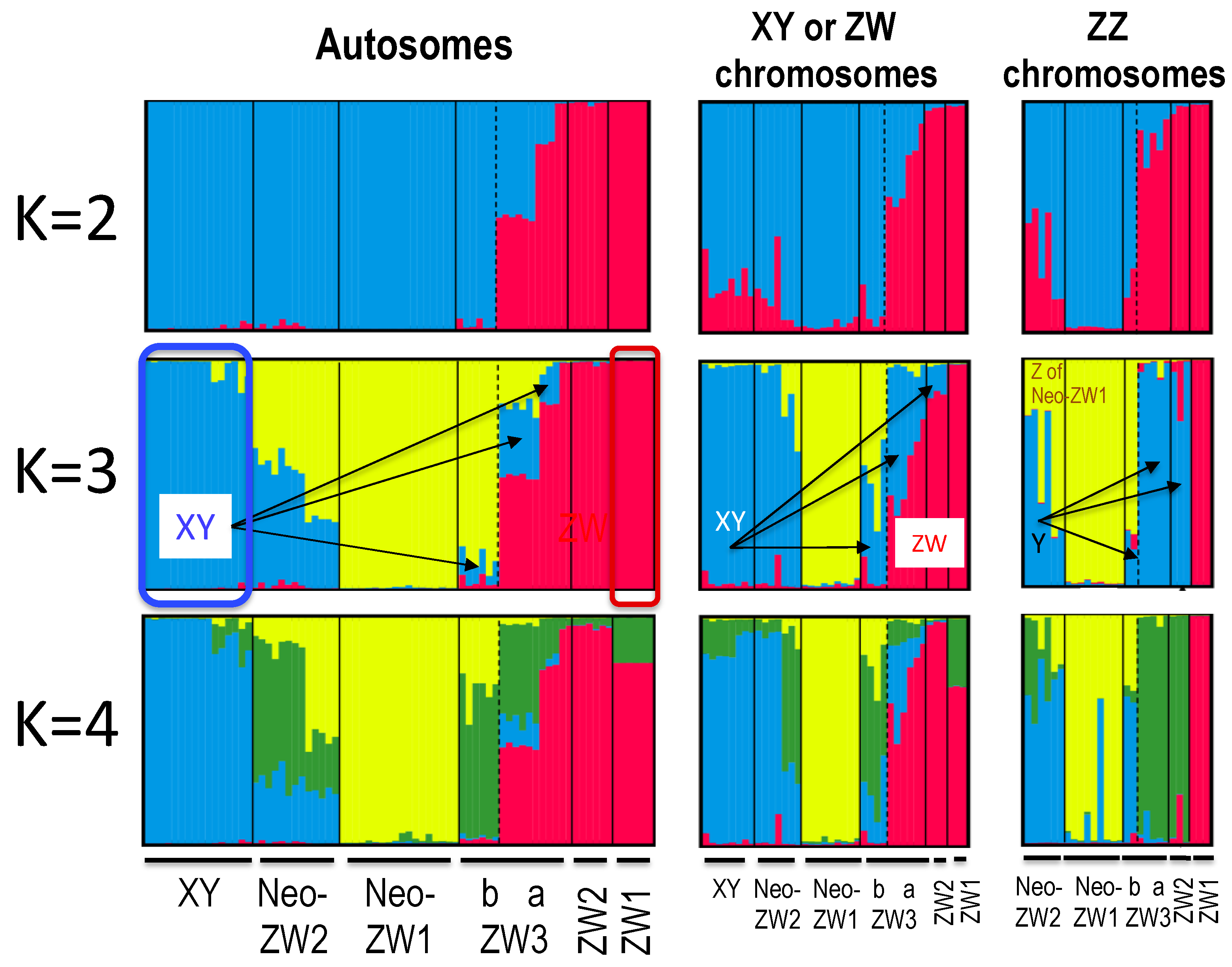
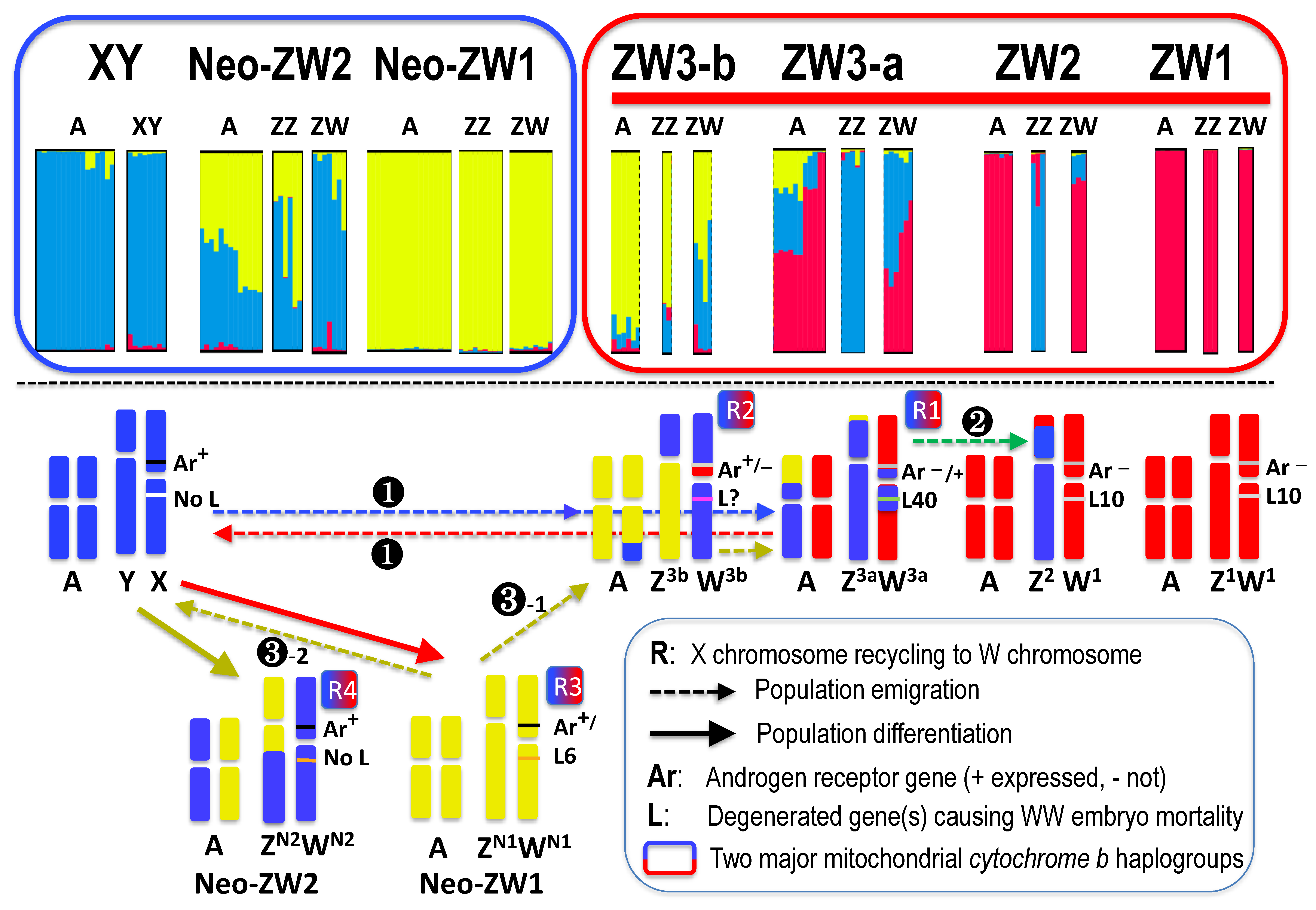
3.3. Population Genetic Structure
3.4. Genomic Structure of Sex Chromosomes
3.5. Expression of the Ar Gene on W Chromosome
3.6. Microsatellite Locus of Sex-Linked Sox3 Upstream Region
4. Discussion
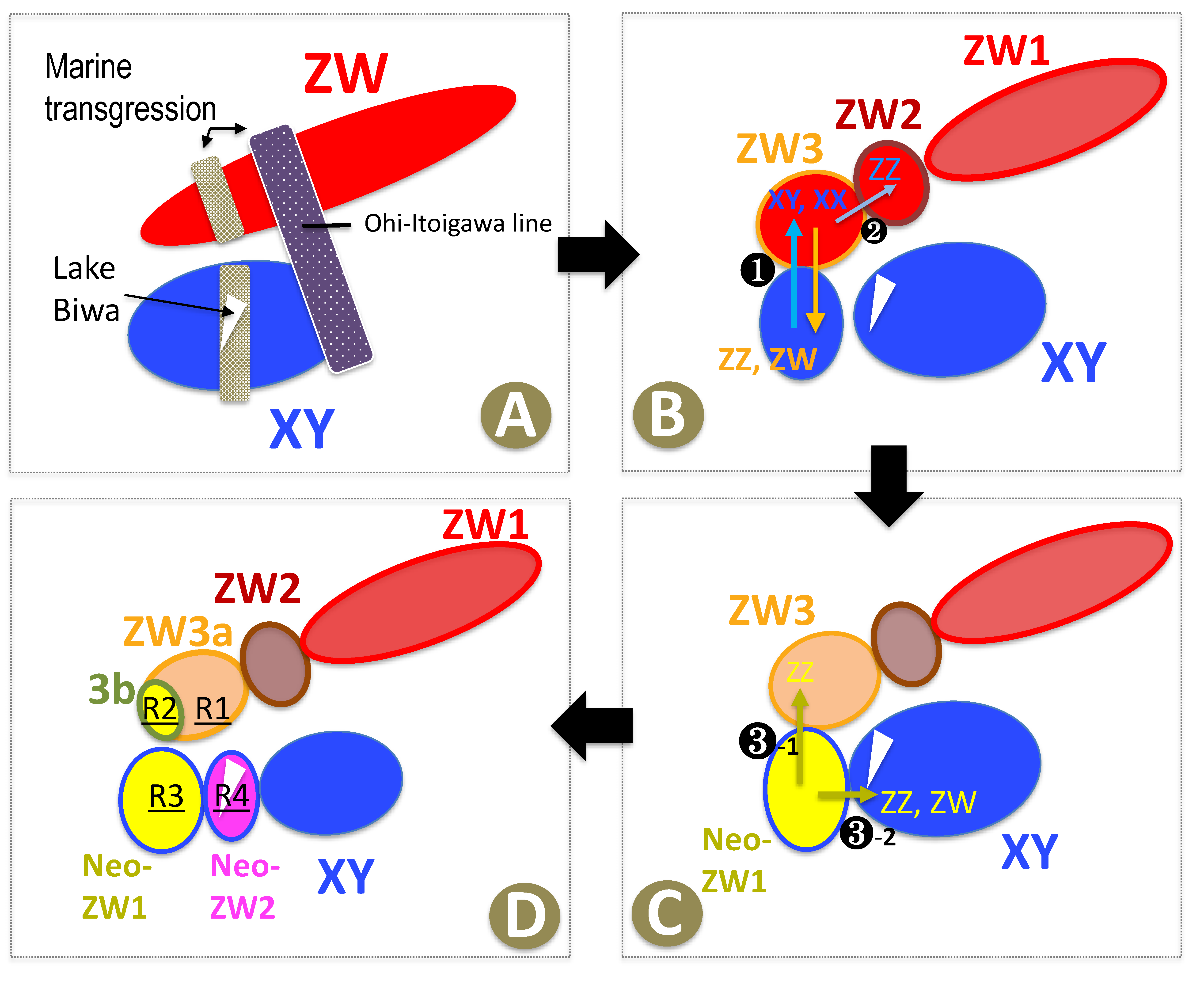
4.1. Geographic Differentiation of the Three ZW Sub-Groups
4.2. W Chromosome Heterogeneity as a Result of Repeated X Chromosome Recycling
4.3. Another Model of the W Chromosome Evolution
4.4. Novel Evolutionary Theory on the Origin of Neo-ZW Group
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Muller, H.J. A gene for the fourth chromosome of Drosophila. J. Exp. Zool. 1914, 17, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, S. Sex Chromosomes and Sex-Linked Genes; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Charlesworth, D.; Charlesworth, B.; Marais, G. Steps in the evolution of heteromorphic sex chromosomes. Heredity 2005, 95, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahn, B.T.; Page, D.C. Four evolutionary strata on the human X chromosome. Science 1999, 286, 964–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, J.F.; Skaletsky, H.; Brown, L.G.; Pyntikova, T.; Graves, T.; Fulton, R.S.; Dugan, S.; Ding, Y.; Buhay, C.J.; Kremitzki, C.; et al. Strict evolutionary conservation followed rapid gene loss on human and rhesus Y chromosomes. Nature 2012, 483, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthey, R. La formule chromosomique et le pro-blème de la détermination sexuelle chez Ellobius lutescens Thomas (Rodentia-Muri- dae-Microtinae). Arch Klaus-Stift VererbForsch 1953, 28, 65–73. (In French) [Google Scholar]
- Just, W.; Rau, W.; Vogel, W.; Akhverdian, M.; Fredga, K.; Graves, J.A.M.; Lyapunova, E. Absence of Sry in species of the vole Ellobius. Nat. Genet. 1995, 11, 117–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honda, T.; Suzuki, H.; Itoh, M. An unusual sex chromosome constitution found in the ama- mi spinous country-rat, Tokudaia osimensis. Jap. J. Genet. 1977, 52, 247–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soullier, S.; Hanni, C.; Catzeflis, F.; Berta, P.; Laudet, V. Male sex determination in the spiny rat Tokudaia osimensis (Rodentia: Muridae) is not Sry dependent. Mamm. Genome 1998, 9, 590–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takagi, N.; Itoh, M.; Sasaki, M. Chromosome studies in four species of Ratitae (Aves). Chromosoma 1972, 36, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, M.; Enderle, E.; Schindler, D.; Schempp, W. Chromosome banding and DNA replication patterns in bird karyotypes. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 1989, 52, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Boer, L.E.M. Do the chromosomes of the kiwi provide evidence for a monophyletic origin of the ratites? Nature 1980, 287, 84–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, H.A.; Takagi, N.; Sasaki, M. Morphological differentiation of sex chromosomes in three species of ratite birds. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 1988, 47, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida-Umehara, C.; Tsuda, Y.; Ishijima, J.; Ando, J.; Fujiwara, A.; Matsuda, Y.; Griffin, D. The molecular basis of chromosome orthologies and sex chromosomal differentiation in palaeognathous birds. Chromosome Res. 2007, 15, 721–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlesworth, D. The timing of genetic degeneration of sex chromosomes. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2021, 376, 20200093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, I.; Ohtani, H.; Ogata, M. Independent degeneration of the W and Y sex chromosomes in frog Rana rugosa. Chromosome Res. 2012, 20, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, I. An evolutionary witness: The frog Rana rugosa underwent change of heterogametic sex from XY male to ZW female. Sex. Dev. 2007, 1, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, I. Sex Determination and Sex Chromosomes in Amphibia. Sex. Dev. 2017, 11, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, M.; Suzuki, K.; Yuasa, Y.; Miura, I. Sex-chromosome evolution from a heteromorphic to a homomorphic system by inter-population hybridization in a frog. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2021, 376, 20200105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, M.; Lambert, M.; Ezaz, T.; Miura, I. Reconstruction of female heterogamety from admixture of XX-XY and ZZ-ZW sex chromosome systems within a frog species. Mol. Ecol. 2018, 27, 4078–4089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, M.; Hasegawa, Y.; Ohtani, H.; Mineyama, M.; Miura, I. The ZZ/ZW sex-determining mechanism originated twice and independently during evolution of the frog, Rana Rugosa. Heredity 2008, 100, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanabe, A. Kakusan and Aminosan: Two programs for comparing nonpartitioned, proportional, and separate models for combined molecular phylogenetic analyses of multilocus sequence data. Mol. Ecol. Res. 2011, 11, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jobb, G. TREEFINDER Version of March 2011. Munich, Germany. Available online: www.treefinder.de (accessed on 25 March 2014).
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; van der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2011, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A. Tracer Ver. 1.5.0; University of Edinburgh: Edinburgh, UK, 2009; Available online: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/tracer/ (accessed on 1 November 2018).
- Kilian, A.; Wenzl, P.; Huttner, E.; Carling, J.; Xia, L.; Blois, H.; Caig, V.; Heller-Uszynska, K.; Jaccoud, D.; Hopper, C. Diversity arrays technology: A generic genome profiling technology on open platforms. In Data Production and Analysis in Population Genomics; Methods in Molecular Biology 888; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 67–89. [Google Scholar]
- Prichard, J. Doculentation for Structure Software: Version 2.3. 2010. Available online: http://pritch.bsd.uchicago.edu/structure.html (accessed on 2 August 2015).
- Earl, D.A.; von Holdt, B.M. STRUCTURE HARVESTER: A website and program for visualizing STRUCTURE output and implementing the Evanno method. Conserv. Genet. Resour. 2012, 4, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, B.; Unmack, P.J.; Berry, O.F.; Georges, A. dartR: An r package to facilitate analysis of SNP data generated from reduced representation genome sequencing. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2018, 18, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felsenstein, J. PHYLIP-Phylogeny Inference Package (Version 3.2). Cladistics 1989, 5, 164–166. [Google Scholar]
- Ohtani, H.; Miura, I.; Ichikawa, Y. Role of aromatase and androgen receptor expression in gonadal sex differentiation of ZW/ZZ-type frogs, Rana rugosa. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C-Tox. Pharm. 2003, 134, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uno, Y.; Nishida, C.; Oshima, Y.; Yokoyama, S.; Miura, I.; Matsuda, Y.; Nakamura, M. Comparative chromosome mapping of sex-linked genes and identification of sex chromosomal rearrangements in the Japanese wrinkled frog (Rana rugosa, Ranidae) with ZW and XY sex chromosome systems. Chromosome Res. 2008, 16, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, I.; Ezaz, T.; Ohtani, H.; Uno, Y.; Nishida, C.; Matsuda, Y.; Graves, J.A.M. The W chromosome evolution and sex-linked gene expression in the Japanese frog Rana rugosa. In Sex Chromosomes: Genetics, Abnormalities and Disorders; Nova Science Publishers Inc.: Weingarten, CN, USA; Jefferson, SE, USA, 2009; pp. 123–140. [Google Scholar]
- Machida, H.; Matsuda, T.; Umitsu, M.; Koizumi, T. Regional Geomorphology of the Japanese Islands; Geomorphology of Chubu region University of Tokyo Press: Tokyo, Japan, 2006; Volume 5, p. 385. [Google Scholar]
- Berlin, S.; Ellegren, H. Clonal inheritance of avian mitochondrial DNA. Nature 2001, 413, 37–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeds, L.; Warmuth, V.; Bolivar, P.; Uebbing, S.; Burri, R.; Suh, A.; Nater, A.; Bureš, S.; Garamszegi, L.Z.; Hogner, S.; et al. Evolutionary analysis of the female-specific avian W chromosome. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishioka, M.; Hanada, H.; Miura, I.; Ryuzaki, M. Four Kinds of Sex Chromosomes in Rana rugosa. Sci. Rep. Lab. Amphib. Biol. Hiroshima Univ. 1994, 13, 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Ohtani, H.; Miura, I.; Hanada, H.; Ichikawa, Y. Alteration of the sex determining system resulting from structural change of the sex chromosomes in the frog Rana rugosa. J. Exp. Zool. 2000, 286, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, D.J.; van Dorp, L.; Falush, D. A tutorial on how not to over-interpret STRUCTURE and ADMIXTURE bar plots. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishioka, M.; Kodama, Y.; Sumida, M.; Ryuzaki, M. Systematic evolution of 40 populations of Rana rugosa distributed in Japan elucidated by electrophoresis. Sci. Rep. Lab. Amphib. Biol. Hiroshima Univ. 1993, 12, 83–131. [Google Scholar]
- Nishioka, M.; Miura, I.; Saitoh, K. Sex chromosomes of Rana rugosa with special reference to local differences in sex determining mechanism. Sci. Rep. Lab. Amphib. Biol. Hiroshima Univ. 1993, 12, 55–81. [Google Scholar]
- Nishioka, M.; Hanada, H. Sex of reciprocal hybrids between the Hamakita (XX-XY type) population and the Murakami (ZW-ZZ type) population of Rana rugosa. Sci. Rep. Lab. Amphib. Biol. Hiroshima Univ. 1994, 13, 35–50. [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa, Y.; Ueda, H.; Sumida, M. Clinal geographic variation in the advertisement call of the wrinkled frog, Rana rugosa. Herpetologica 1999, 55, 318–324. [Google Scholar]
- Takehana, Y.; Sakai, M.; Narita, T.; Sato, T.; Naruse, K.; Sakaizumi, M. Origin of boundary populations in medaka (Oryzias latipes species complex). Zool. Sci. 2016, 33, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennell, M.W.; Mank, J.E.; Peichel, C.L. Transitions in sex determination and sex chromosomes across vertebrate species. Mol. Ecol. 2018, 27, 3950–3963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, B.J.; Alexander, P.R.; Wiens, J.J. Polyploidization and sex chromosome evolution in amphibians. In Polyploidy and Genome Evolution; Soltis, P.S., Soltis, E.E., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 385–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Population Number | Population (City) | Prefecture | No. of Frogs Examined | Heterogametic Sex Based on SF1 Genotype | Microsatellite Allele of Sox3-UTR on W or X Chromosome | Expression of Androgen receptor Gene on W or X Chromosome | Cytochrome b Haplotype (Accession No.) | Cytochrome b Haplogroup | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Female | ||||||||
| 1 | Towada | Aomori | 6 | 8 | Female | 230 | NE | L671792 | ZW1 |
| 2 | Toono | Iwate | 0 | 1 | Female | NE | − | L671793 | ZW1 |
| 3 $ | Yamagata | Yamagata | 7 | 3 | Female | 230 | NE | L671794 | ZW1 |
| 4 * | Niigata | Niigata | 0 | 1 | Female | NE | − * | L671795 | ZW1 |
| 5 | Inawashiro | Fukushima | 4 | 7 | Female | 230 | NE | L671793 | ZW1 |
| 6 | Oomachi | Nagano | 2 | 1 | Female | 230 | NE | L671792 | ZW1 |
| 7 $ | Kurobe | Toyama | 9 | 5 | Female | 223 | − | L671796 | ZW2 |
| 8 | Suzu | Ishikawa | 3 | 4 | Female | 275 | − | L671797 | ZW2 |
| 9 $ | Tomiki | Ishikawa | 1 | 3 | Female | 266/284 | NE | L671798 | ZW3a |
| 10 * | Kanazawa | Ishikawa | 0 | 1 | Female | NE | − * | L671799 | ZW3a |
| 11 $ | Yamanaka | Ishikawa | 1 | 2 | Female | 230 | − | L671800 | ZW3a |
| 12 $ | Awara | Fukui | 3 | 6 | Female | 248 | +3/−3 | L6717801 | ZW3a |
| 13 | Tsuruga | Fukui | 3 | 7 | Female | 240 | +6/−1 | L6717804 | ZW3b |
| 14 $ | Wakasa | Fukui | 2 | 8 | Female | 240 | + | L6717802 | ZW3b |
| 15 | Obama | Fukui | 3 | 7 | Female | 240 | +6/−1 | L6717803 | ZW3b |
| 16 | Kamikato | Fukui | 4 | 6 | Female | 240 | + | L6717804 | ZW3b |
| 17 | Maizuru | Kyoto | 1 | 4 | Female | 240 | +3/−1 | L6717808 | Neo-ZW1 |
| 18 * | Sanda | Hyogo | 0 | 1 | Female | 240 | NE | L6717809 | Neo-ZW1 |
| 19 *$ | Kashiwabara | Kyoto | 8 | 4 | Female | 240 | NE | NE (Neo-ZW1) | |
| 20*$ | Osaka | Osaka | 5 | 6 | Female | 240 | + | NE (Neo-ZW1) | |
| 21 *$ | Kinomoto | Shiga | 4 | 8 | Female | 222/232 | + | L6717805 | Neo-ZW2 |
| 22 *$ | Kyoto | Kyoto | 3 | 3 | Female | 248 | + | L6717807 | Neo-ZW2 |
| 23 *$ | Sekigahara | Gifu | 3 | 3 | Male | 222/232 | + | L6717805 | XY |
| 24 *$ | Kameyama | Mie | 5 | 10 | Male | 222/232/240/248 /250 | + | XY | |
| 25 | Isehara | Kanagawa | 0 | 1 | Homo # | NE | NE | L6717810 | East-J |
| 26 | Kamigoori | Hyogo | 0 | 1 | Homo # | NE | NE | L6717806 | West-J |
| Total | 79 | 116 | |||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ogata, M.; Shams, F.; Yoshimura, Y.; Ezaz, T.; Miura, I. W Chromosome Evolution by Repeated Recycling in the Frog Glandirana rugosa. DNA 2022, 2, 172-184. https://doi.org/10.3390/dna2030012
Ogata M, Shams F, Yoshimura Y, Ezaz T, Miura I. W Chromosome Evolution by Repeated Recycling in the Frog Glandirana rugosa. DNA. 2022; 2(3):172-184. https://doi.org/10.3390/dna2030012
Chicago/Turabian StyleOgata, Mitsuaki, Foyez Shams, Yuri Yoshimura, Tariq Ezaz, and Ikuo Miura. 2022. "W Chromosome Evolution by Repeated Recycling in the Frog Glandirana rugosa" DNA 2, no. 3: 172-184. https://doi.org/10.3390/dna2030012
APA StyleOgata, M., Shams, F., Yoshimura, Y., Ezaz, T., & Miura, I. (2022). W Chromosome Evolution by Repeated Recycling in the Frog Glandirana rugosa. DNA, 2(3), 172-184. https://doi.org/10.3390/dna2030012








