Fed-Batch Cultivation of Microalgae Using Effluent from the Anaerobic Digestion of Cattle Waste and Cultivation Scale-Up in 100 L Raceways
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Effluent Characterization
2.2. Microalgae Cultivation
2.2.1. Cultivation in 10 L Raceways
2.2.2. Pilot-Scale: 100 L-Raceways
2.3. Biomass and Analytical Determinations During Cultivation
2.4. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Cultivation in 10 L Raceways
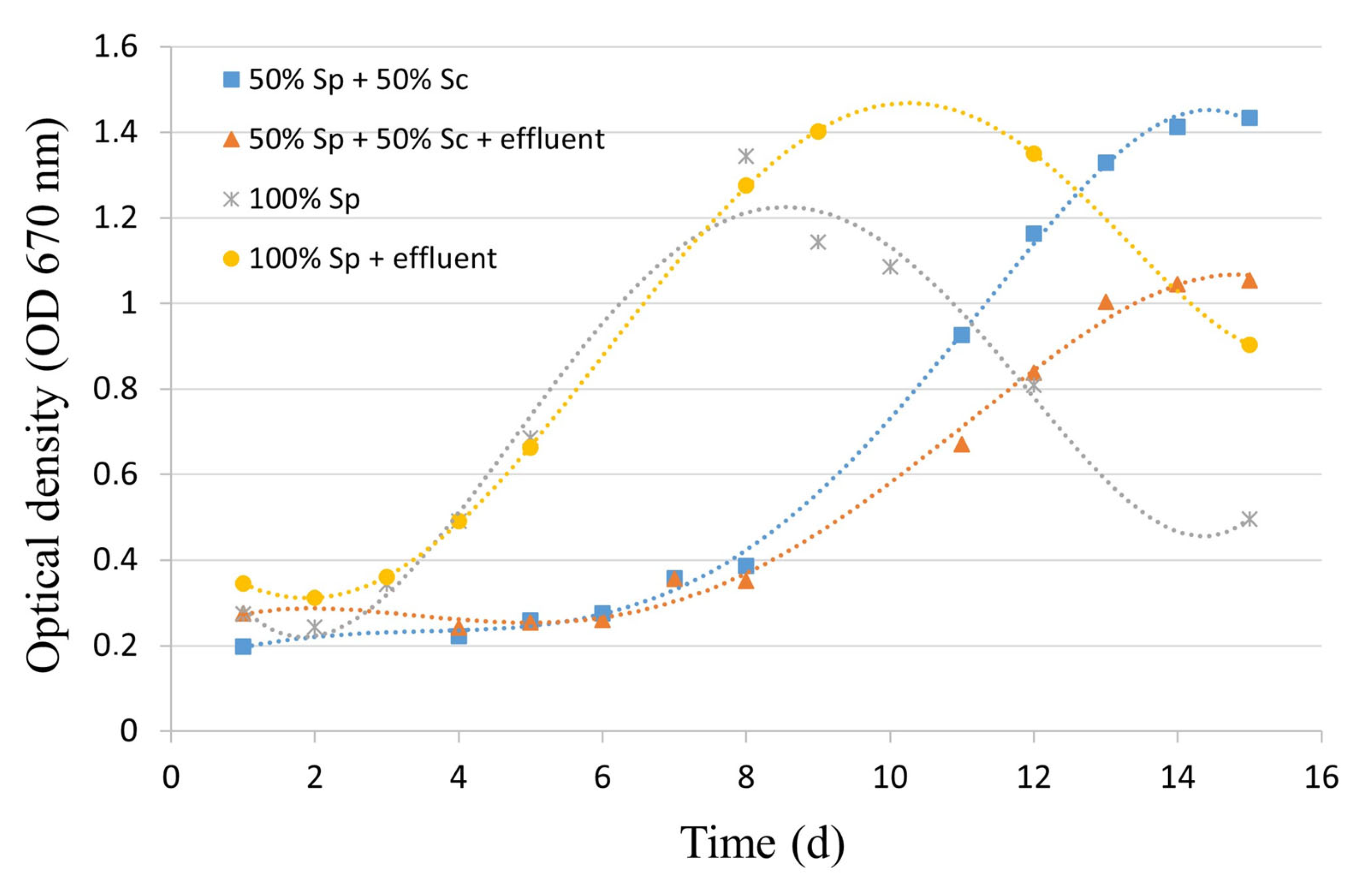
3.1.1. Effects of Cultivation Variables on the Microalgae Growth
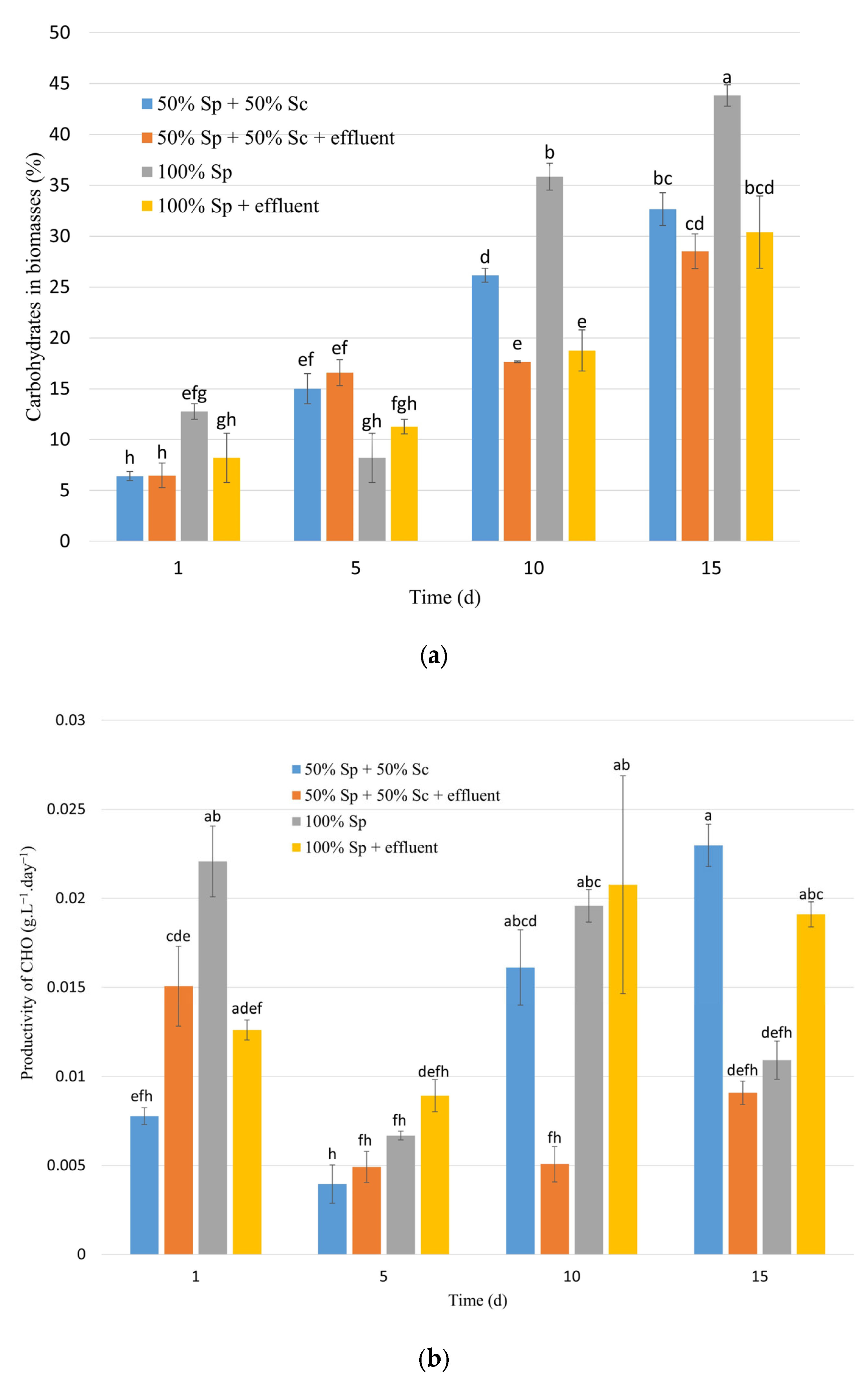
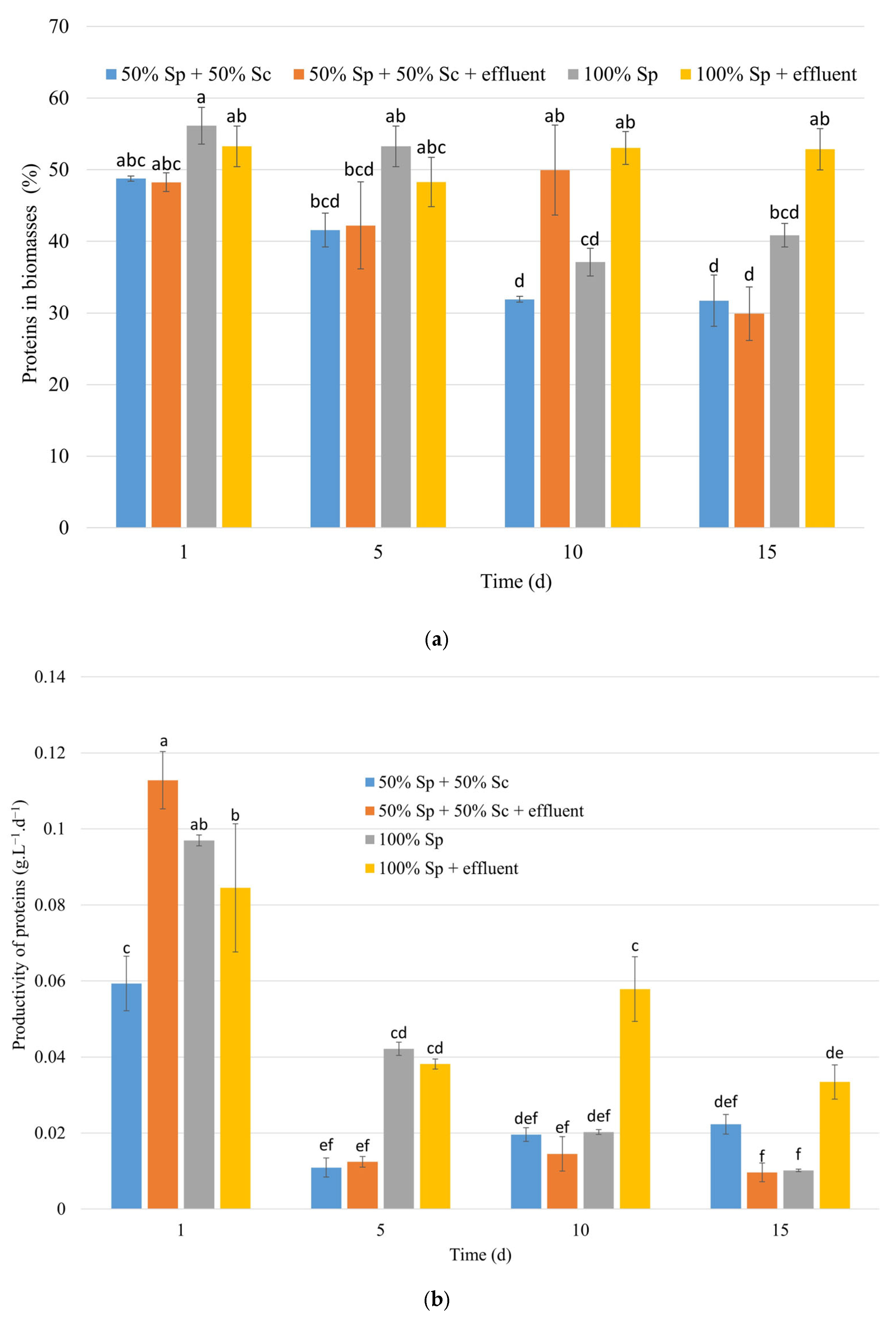
3.1.2. Effects on Biomass Composition
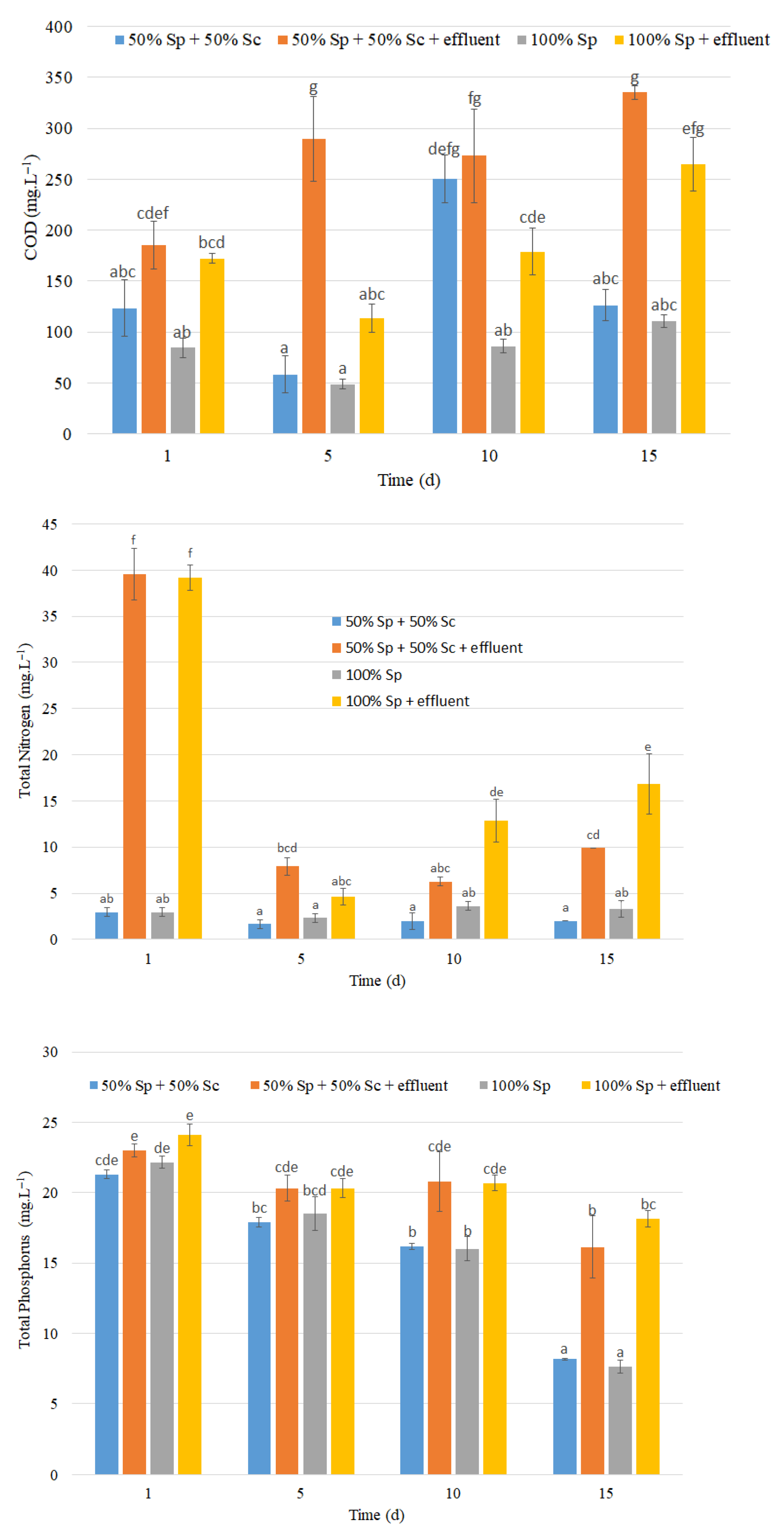
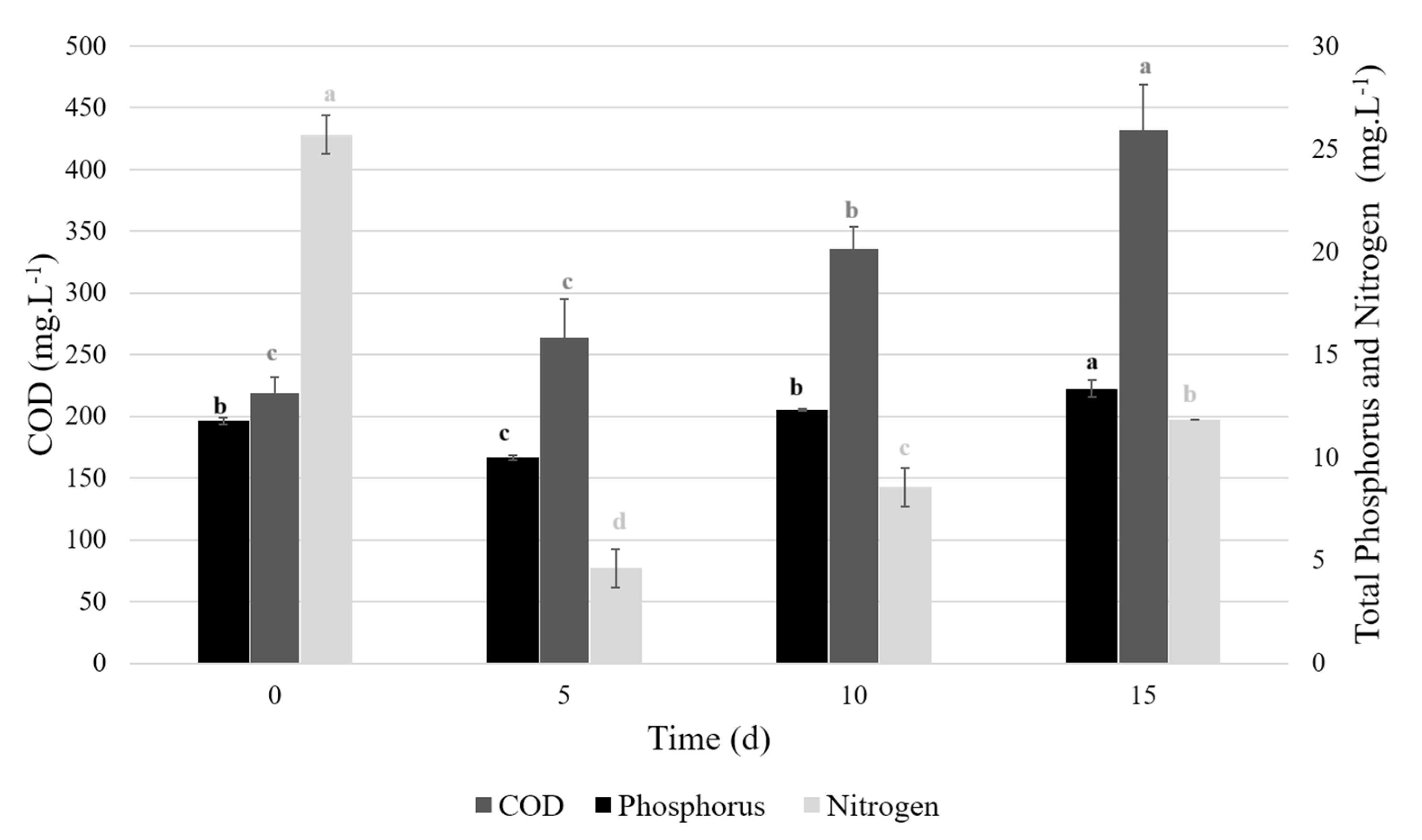
3.1.3. COD, Nitrogen and Phosphorus Concentrations
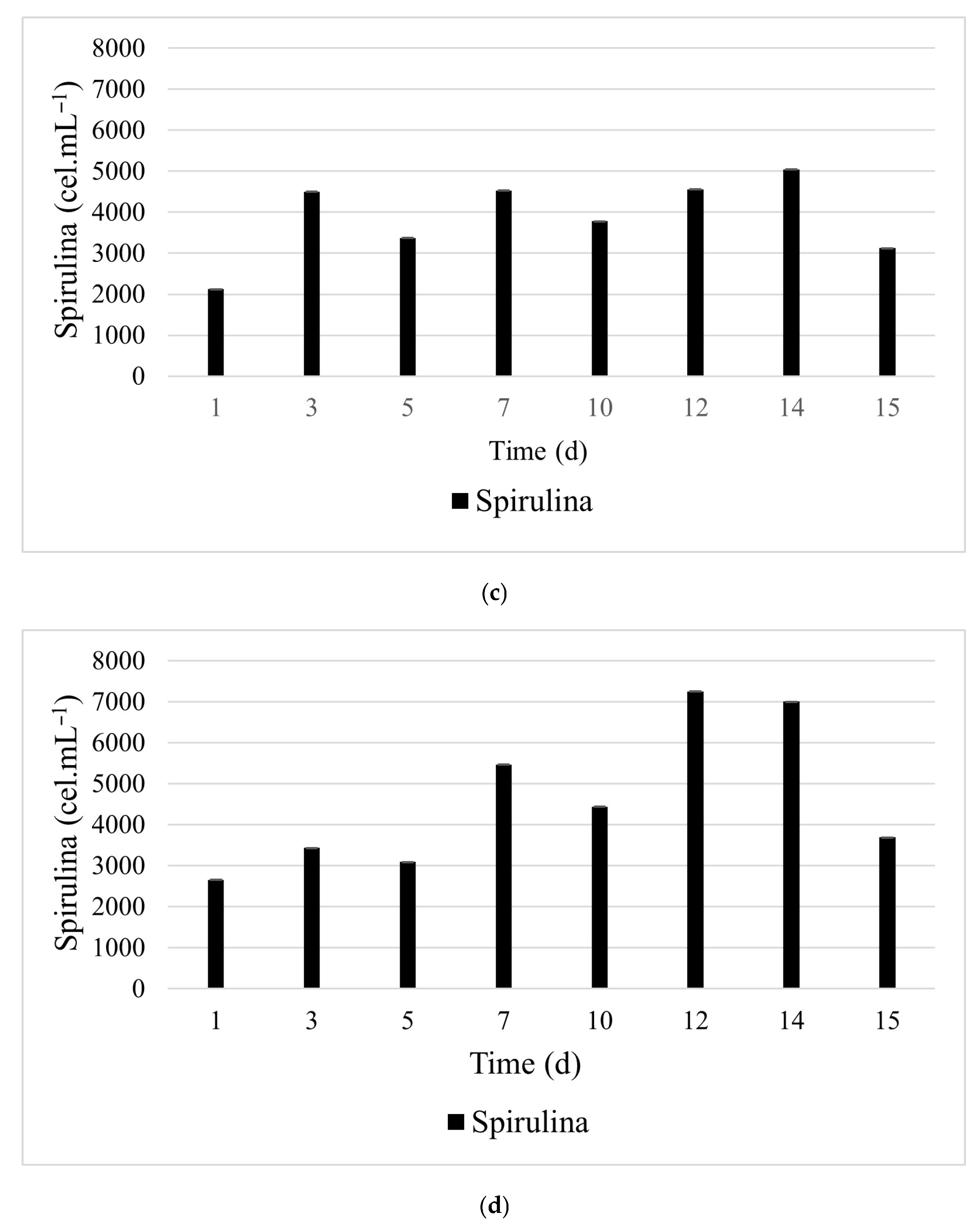
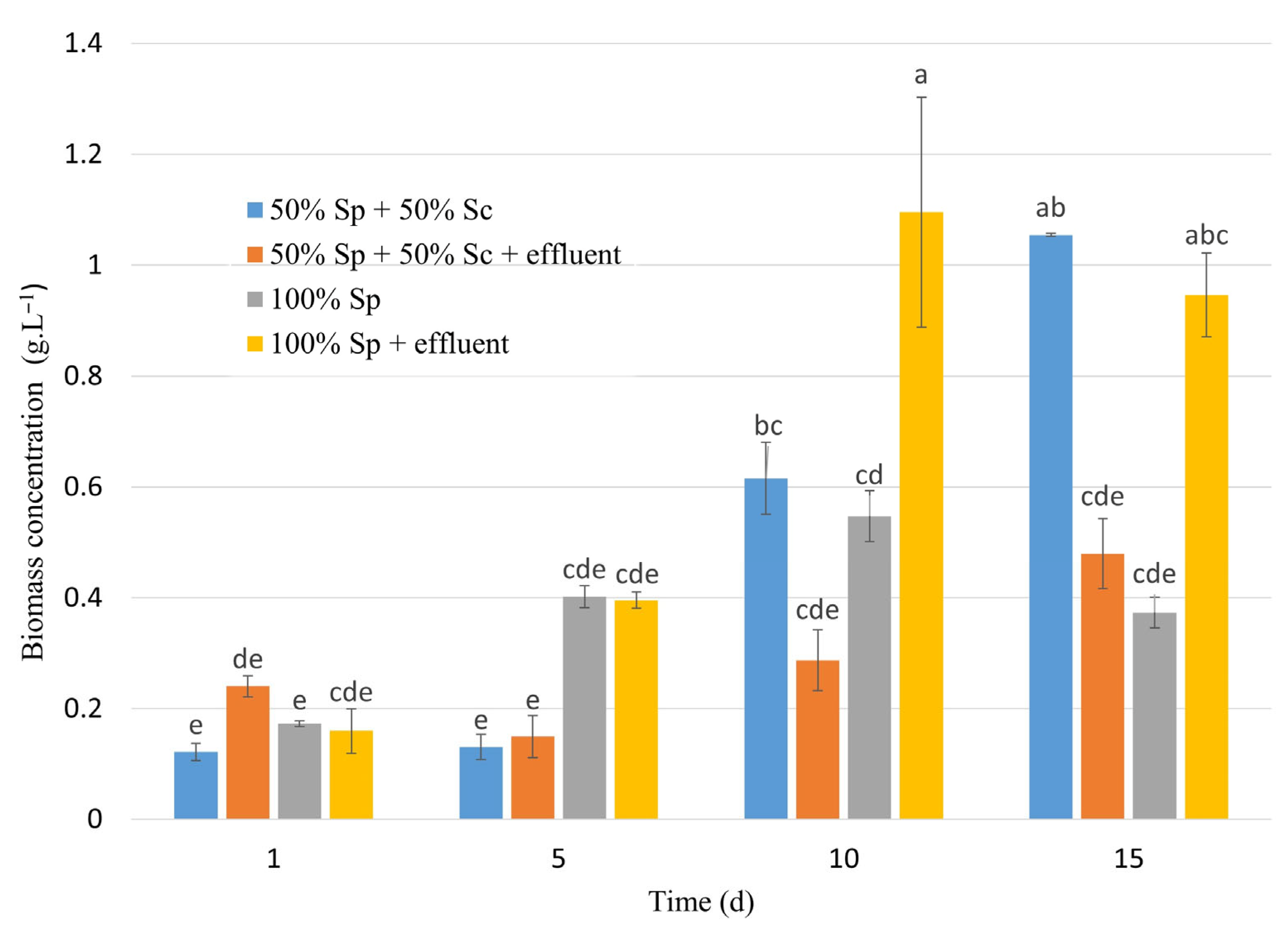
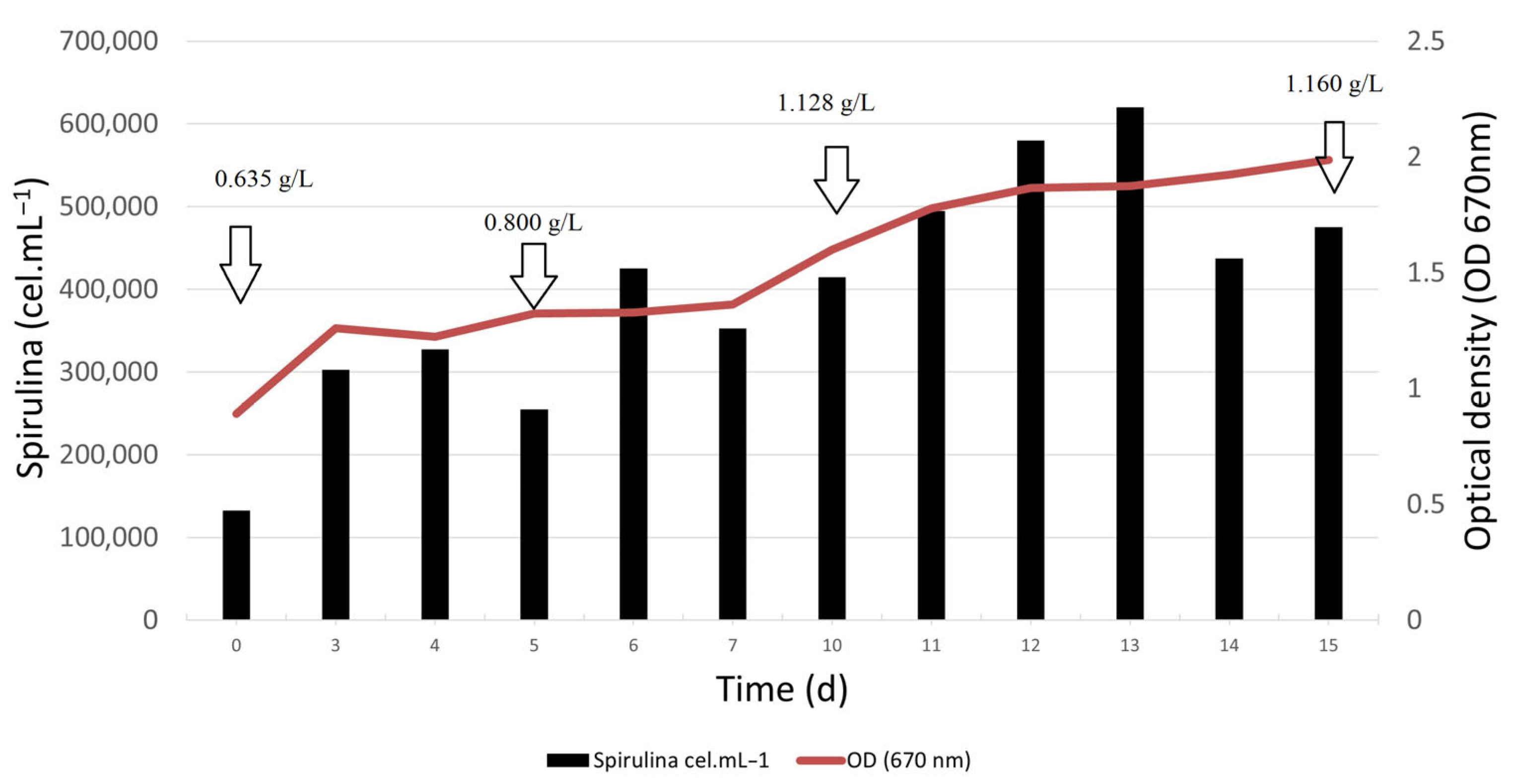
3.2. Pilot-Scale in 100 L Raceway
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Sarwer, A.; Hamed, S.; Osman, A.; Jamil, F.; Al-Muhtaseb, A.H.; Alhajeri, N.S.; Rooney, D.W. Algal biomass valorization for biofuel production and carbon sequestration: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 2797–2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa-Torres, G.; Mahmood, W.; Pittman, J.; Theodoropoulos, C. Microalgal biomass as a biorefinery platform for biobutanol and biodiesel production. Biochem. Eng. J. 2020, 153, 107396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, J.C.A.; Simon, V.; Bortoluzzi, E.C.; Langaro, N.C.; Colla, L.M. Biofertilizers as a potential tool towards sustainable agriculture. Rev. Tecnol. E Soc. 2025, 21, 271–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Khoo, K.; Chew, K.; Tao, Y.; Ho, S.-H.; Show, P.L. Potential utilization of bioproducts from microalgae for the quality enhancement of natural products. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 304, 122997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astolfi, A.L.; Rempel, A.; Cavanhi, V.A.F.; Alves, M.; Deamici, K.M.; Colla, L.M.; Costa, J.A.V. Simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of Spirulina sp. and corn starch for the production of bioethanol and obtaining biopeptides with high antioxidant activity. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 301, 122698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Srivastava, R.; Pal, P.; Mandal, S.; Sahoo, U.K.; Prakash, A.; Sridhar, K.; Sharma, M.; Sarangi, P.K.; Inbaraj, B.S. Microalgal biorefinery as a sustainable and cost-effective platform for co-production of high-value-added products/metabolites: An insight into emerging trends, challenges, and opportunities. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2024, 58, 103192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheirsilp, B.; Maneechote, W.; Srinuanpan, S.; Angelidaki, I. Microalgae as Tools for Bio-Circular-Green Economy: Zero-waste Approaches for Sustainable Production and Biorefineries of Microalgal Biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 387, 129620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitag, J.F.; Fagundes, V.D.; Simon, V.; de Souza Schneider, R.D.C.; Colla, L.M. Life cycle analysis of microalgae bioethanol production scenarios. Biomass Bioenergy 2026, 204, 108398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vendruscolo, L.P.; Rubert, A.; Nazari, M.T.; Sossella, F.d.S.; Colla, L.M.; Costa, J.A.V.; Hemkemeier, M. Simultaneous Biomass Production, Carbohydrate Accumulation, and Contaminants Removal Using Malting Wastewater in Microalgae Cultivation. Bioenergy Res. 2023, 17, 612–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malakar, B.; Das, D.; Mohanty, K. Utilization of waste peel extract for cultivation of microalgal isolates: A study of lipid productivity and growth kinetics. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2023, 13, 17017–17026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beigbeder, J.B.; Lavoie, J.M. Effect of photoperiods and CO2 concentrations on the cultivation of carbohydrate-rich P. kessleri microalgae for the sustainable production of bioethanol. J. CO2 Util. 2022, 58, 101934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hultberg, M.; Lind, O.; Birgersson, G.; Asp, H. Use of the effluent from biogas production for cultivation of Spirulina. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2017, 40, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Guo, X.; Su, G.; Danquah, M.K.; Zhang, S.; Lu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Lin, L. Bioprocess considerations for microalgal-based wastewater treatment and biomass production. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 42, 1385–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jareonsin, S.; Mahanil, K.; Duangjan, K.; Srinuanpan, S.; Pekkoh, J.; Ishii, M.; Pumas, C. Dark mode of microalga—A sustainable and economical solution for microalgal biofuel production and waste treatment. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2023, 23, 101574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, F.A.; Ravindran, B.; Gupta, S.K.; Nasr, M.; Rawat, I.; Bux, F. Techno-economic estimation of wastewater phycoremediation and environmental benefits using Scenedesmus obliquus microalgae. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 240, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markou, G. Fed-batch cultivation of Arthrospira and Chlorella in ammonia-rich wastewater: Optimization of nutrient removal and biomass production. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 193, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paddock, M.B.; Fernández-Bayo, J.D.; VanderGheynst, J.S. The effect of the microalgae-bacteria microbiome on wastewater treatment and biomass production. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 893–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira Salla, A.C.; Margarites, A.C.; Seibel, F.I.; Holz, L.C.; Brião, V.B.; Bertolin, T.E.; Colla, L.M.; Costa, J.A.V. Increase in the carbohydrate content of the microalgae Spirulina in culture by nutrient starvation and the addition of residues of whey protein concentrate. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 209, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magro, F.G.; Freitag, J.F.; Bergoli, A.; Costa, J.A.V.; Colla, L.M. Microalgae Consortia for Post-treating Effluent of Anaerobic Digestion of Cattle Waste and Evaluation of Biochemical Composition of Biomass. BioEnergy Res. 2021, 15, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, R.P.; Anisha, G.S.; Nampoothiri, K.M.; Pandey, A. Micro and macroalgal biomass: A renewable source for bioethanol. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaparoli, M.; Ziemniczak, F.G.; Mantovani, L.; Costa, J.A.V.; Colla, L.M. Cellular Stress Conditions as a Strategy to Increase Carbohydrate Productivity in Spirulina platensis. BioEnergy Res. 2020, 13, 1221–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magro, F.G.; Margarites, A.C.; Reinehr, C.O.; Gonçalves, G.C.; Rodigheri, G.; Costa, J.A.V.; Colla, L.M. Spirulina platensis biomass composition is influenced by the light availability and harvest phase in raceway ponds. Environ. Technol. 2017, 39, 1868–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasapoor, M.; Young, B.; Brar, R.; Sarmah, A.; Zhuang, W.Q.; Baroutian, S. Recognizing the challenges of anaerobic digestion: Critical steps toward improving biogas generation. Fuel 2020, 261, 116497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinbomi, J.G.; Patinvoh, R.J.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Current challenges of high-solid anaerobic digestion and possible measures for its effective applications: A review. Biotechnol. Biofuels Bioprod. 2022, 15, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, J.C.A.; Sommer, F.; Sans, G.A.; Rempel, A.; Lângaro, N.C.; Colla, L.M. Microalgal biomass as a partial replacement for chemical fertilizers in barley cultivation. Cad. Pedagógico 2025, 22, e19372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maschio, L.D.G.; Tonello, C.Z.; Souza, L.C.B.; Colla, L.M.; Lângaro, N.C. Spirulina platensis no tratamento de sementes de cereais. Contrib. A Las Cienc. Soc. 2025, 18, e19709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rempel, A.; de Souza Sossella, F.; Margarites, A.C.; Astolfi, A.L.; Steinmetz, R.L.R.; Kunz, A.; Colla, L.M. Bioethanol from Spirulina platensis biomass and the use of residuals to produce biomethane: An energy efficient approach. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 288, 121588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aditya, L.; Mahlia, T.; Nguyen, L.; Vu, H.P.; Nghiem, L.D. Microalgae-bacteria consortium for wastewater treatment and biomass production. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 155871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Sun, L.; Sun, Z.; Li, D. Screening of a Chlorella-bacteria consortium and research on piggery wastewater purification. Algal Res. 2020, 47, 101840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chieti, M.; Petrucciani, A.; Mollo, L.; Gerotto, C.; Eusebi, A.; Fatone, F.; Norici, A.; González-Camejo, J. Acclimated green microalgae consortium to treat sewage in an alternative urban WWTP in a coastal area of Central Italy. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 945, 174056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huy, M.; Kumar, G.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, S.H. Photoautotrophic cultivation of mixed microalgae consortia using various organic waste streams towards remediation and resource recovery. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 576–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bélanger-Lépine, F.; Lemire-Lamothe, M.; Tremblay, A.; Rondeau, S.; Marchand, P.; Huot, Y.; Barnabé, S. Cultivation of an Algae-Bacteria Consortium in a Mixture of Industrial Wastewater to Obtain Valuable Products for Local Use. Ind. Biotechnol. 2020, 16, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koreiviene, J.; Valčiukas, R.; Karosiene, J.; Baltrenas, P. Testing of Chlorella/Scenedesmus microalgae consortia for remediation of wastewater, CO2 mitigation and algae biomass feasibility for lipid production. J. Environ. Eng. Landsc. Manag. 2014, 22, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Shu, Q.; Feng, P.; Zhu, L.; Xu, J.; Yuan, Z. Microalgae consortia cultivation in dairy wastewater to improve the potential of nutrient removal and biodiesel feedstock production. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 8379–8387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choong, Y.J.; Yokoyama, H.; Matsumura, Y.; Lam, M.K.; Uemura, Y.; Dasan, Y.K.; Kadir, W.N.A.; Lim, J.W. The potential of using microalgae for simultaneous oil removal in wastewater and lipid production. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 17, 2755–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Yuan, Z. Cultivation of Chlorella sp. using raw dairy wastewater for nutrient removal and biodiesel production: Characteristics comparison of indoor bench-scale and outdoor pilot-scale cultures. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 192, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Guo, J.; Feng, J.; Liu, Q.; Xie, S. A comparative study on flocculating ability and growth potential of two microalgae in simulated secondary effluent. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 205, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- APHA American Public Health Association. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 19th ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, WA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 17th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Collaboration (AOAC) International: Rockville, MD, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Serrano, C.; Morales-Amaral, M.M.; Acién, F.G.; Escudero, R.; Fernández-Sevilla, J.M.; Molina-Grima, E. Utilization of secondary-treated wastewater for the production of freshwater microalgae. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 6931–6944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.A.V.; Colla, L.M.; Filho, P.D. Modelling of Spirulina platensis growth in fresh water using response surface methodology. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002, 18, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, M.; Gilles, K.; Hamilton, J.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, O.H. Protein measurement with the Folin-Phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidell, W.; Lima Ude, A.; Aquarone, E.; Borzani, W. Biotecnologia Industrial Vol. 2: Engenharia Bioquímica; Blucher: São Paulo, Brazil, 2001; ISBN 978-85-212-1518-9. [Google Scholar]
- Margarites, A.C.; Volpato, N.; Araújo, E.; Cardoso, L.G.; Bertolin, T.E.; Colla, L.M.; Costa, J.A.V. Spirulina platensis is more efficient than Chlorella homosphaera in carbohydrate productivity. Environ. Technol. 2016, 1, 2209–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabra, M.; Martínez-Sanz, M.; Gómez-Mascaraque, L.G.; Gavara, R.; López-Rubio, A. Structural and physicochemical characterization of thermoplastic corn starch films containing microalgae. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 186, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, S.H.; Chen, C.Y.; Chang, J.S. Effect of light intensity and nitrogen starvation on CO2 fixation and lipid/carbohydrate production of an indigenous microalga Scenedesmus obliquus CNW-N. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 113, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, J.C.A.; Balbinot, L.; Beuter, M.A.; Rempel, A.; Colla, L.M. Mixotrophic cultivation of microalgae using agro-industrial waste: Tolerance level, scale up, perspectives and future use of biomass. Algal Res. 2024, 80, 103554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.; Chagas, B.; Sassi, R.; Medeiros, G.F.; Aguiar, E.M.; Borba, L.H.F.; E Silva, E.P.; Neto, J.C.A.; Rangel, A.H.N. Mixotrophic cultivation of Spirulina platensis in dairy wastewater: Effects on the production of biomass, biochemical composition and antioxidant capacity. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossa, R.; Di Colandrea, M.; Salbitani, G.; Carfagna, S. Phosphorous Utilization in Microalgae: Physiological Aspects and Applied Implications. Plants 2024, 13, 2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Morales-Amaral, M.M.; Gómez-Serrano, C.; Acién, F.G.; Fernández-Sevilla, J.M.; Molina-Grima, E. Outdoor production of Scenedesmus sp. in thin-layer and raceway reactors using centrate from anaerobic digestion as the sole nutrient source. Algal Res. 2015, 12, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, M.D.; de Oliveira, A.C.; Filho, F.J.C.M.; Ugaya, C.M.L.; Mariano, A.B.; Vargas, J.V.C. Environmental study of producing microalgal biomass and bioremediation of cattle manure effluents by microalgae cultivation. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2017, 19, 1745–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hena, S.; Znad, H.; Heong, K.T.; Judd, S. Dairy farm wastewater treatment and lipid accumulation by Arthrospira platensis. Water Res. 2018, 128, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Scenedesmus obliquus | Spirulina platensis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experiments * | Effluent Addition | Xmax (cells mL−1) | µmax (d−1) | Xmax (cells mL−1) | µmax (d−1) |
| (1) 50% Sp + 50% Sc | No | 1.15 × 104 ± 7.51 × 102 a | 0.11 ± 0.01 b | 1.02.104 ± 2.21 × 102 a | 0.40 ± 0.00 a |
| (2) 50% Sp + 50% Sc | Yes | 2.11 × 104 ± 3.89 × 103 a | 0.19 ± 0.02 a | 1.56.103 ± 1.77 × 102 c | 0.25 ± 0.03 b |
| (3) 100% Sp | No | - | - | 5.05.103 ± 2.19 × 102 b | 0.10 ± 0.01 c |
| (4) 100% Sp | Yes | - | - | 8.44.103 ± 8.84 × 102 a | 0.25 ± 0.02 b |
| Time of Cultivation (days) * | Carbohydrates (%) | Proteins (%) | PCHO (g·L−1·day−1) | PPTN (g·L−1·day−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 13.189 ± 0.726 a | 69.380 ± 4.431 a | 0.084 ± 0.005 a | 0.441 ± 0.028 a |
| 5 | 12.731 ± 2.479 a | 51.001 ± 3.989 b | 0.020 ± 0.004 c | 0.081 ± 0.006 b |
| 10 | 25.095 ± 1.353 b | 51.141 ± 2.071 b | 0.028 ± 0.002 bc | 0.058 ± 0.002 b |
| 15 | 28.807 ± 3.912 b | 55.030 ± 2.671 b | 0.032 ± 0.004 b | 0.061 ± 0.003 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Magro, F.G.; Rempel, A.; Reinehr, C.O.; Colla, L.M. Fed-Batch Cultivation of Microalgae Using Effluent from the Anaerobic Digestion of Cattle Waste and Cultivation Scale-Up in 100 L Raceways. Biomass 2025, 5, 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomass5040066
Magro FG, Rempel A, Reinehr CO, Colla LM. Fed-Batch Cultivation of Microalgae Using Effluent from the Anaerobic Digestion of Cattle Waste and Cultivation Scale-Up in 100 L Raceways. Biomass. 2025; 5(4):66. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomass5040066
Chicago/Turabian StyleMagro, Francisco Gerhardt, Alan Rempel, Christian Oliveira Reinehr, and Luciane Maria Colla. 2025. "Fed-Batch Cultivation of Microalgae Using Effluent from the Anaerobic Digestion of Cattle Waste and Cultivation Scale-Up in 100 L Raceways" Biomass 5, no. 4: 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomass5040066
APA StyleMagro, F. G., Rempel, A., Reinehr, C. O., & Colla, L. M. (2025). Fed-Batch Cultivation of Microalgae Using Effluent from the Anaerobic Digestion of Cattle Waste and Cultivation Scale-Up in 100 L Raceways. Biomass, 5(4), 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomass5040066








