Characterization of Spent Mushroom Compost and Evaluation of Its Potential for Thermochemical Valorization through Ash Reduction Treatments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Quartering, Separation, and Selection of Samples
2.2. Characterizations
2.2.1. Lignin, Cellulose, and Hemicellulose Content
2.2.2. Physicochemical Analyses
2.3. Treatments for Ash Reduction
3. Results and Discussion
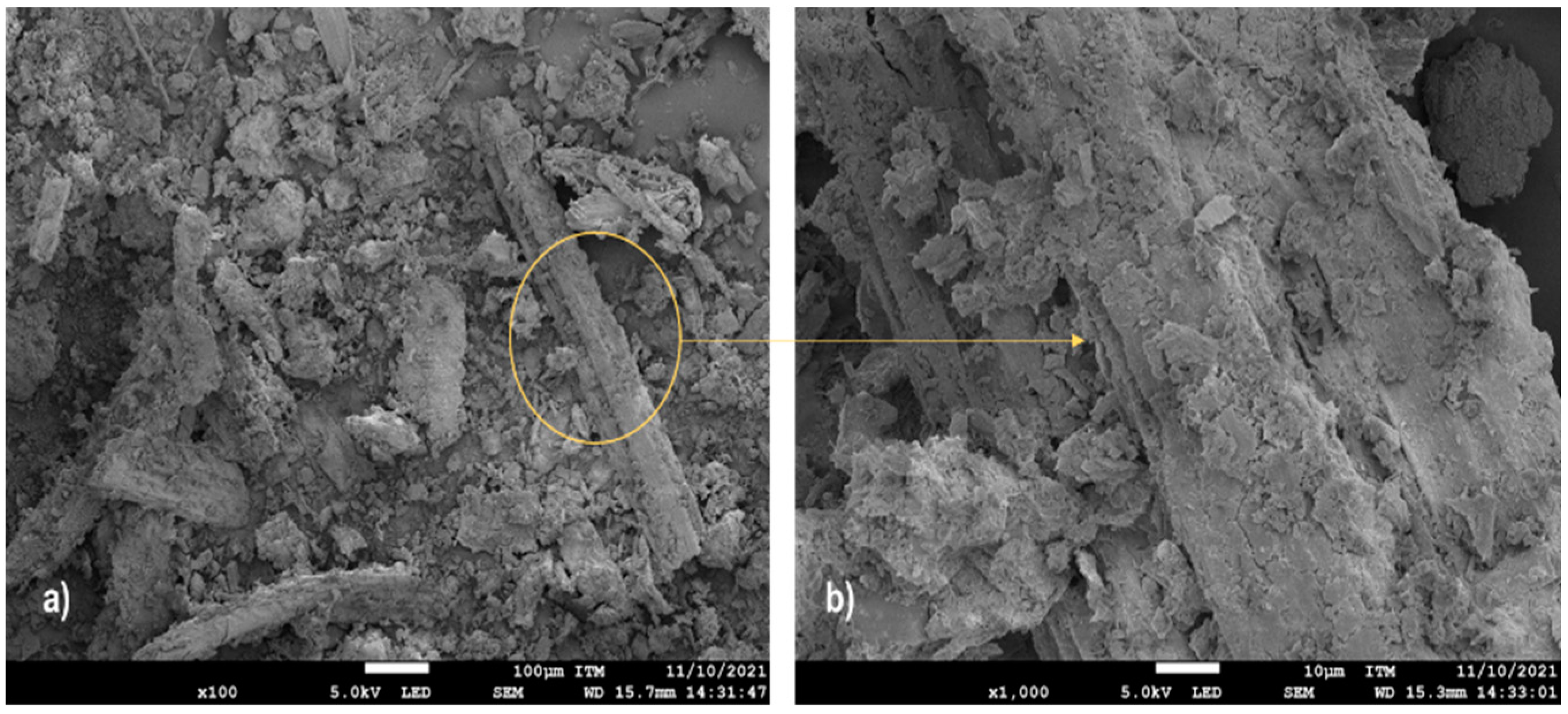
3.1. Characterization of SMC and Heterogeneity Phenomenon
3.2. Effect of Ash Reduction Treatments on the Thermal Behavior of Biomasses
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Cianni, R.; Varese, G.C.; Mancuso, T. A further step toward sustainable development: The case of the edible mushroom supply chain. Foods 2023, 12, 3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leong, Y.K.; Ma, T.-W.; Chang, J.-S.; Yang, F.-C. Recent advances and future directions on the valorization of spent mushroom substrate (SMS): A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 344 Pt A, 126157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leong, Y.K.; Varjani, S.; Lee, D.-J.; Chang, J.-S. Valorization of spent mushroom substrate for low-carbon biofuel production: Recent advances and developments. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 363, 128012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruangjanda, S.; Iwai, C.B.; Greff, B.; Chang, S.W.; Ravindran, B. Valorization of spent mushroom substrate in combination with agro-residues to improve the nutrient and phytohormone contents of vermicompost. Environ. Res. 2022, 214 Pt 1, 113771. [Google Scholar]
- Martín, C.; Zervakis, G.I.; Xiong, S.; Koutrotsios, G.; Strætkvern, K.O. Spent substrate from mushroom cultivation: Exploitation potential toward various applications and value-added products. Bioengineered 2023, 14, 2252138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Bi, X.; Xu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wei, T.; Xi, M.; Li, J.; Chen, L.; Li, H.; Sun, S. Variation in community structure and network characteristics of spent mushroom substrate (SMS) compost microbiota driven by time and environmental conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 364, 127915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atallah, E.; Zeaiter, J.; Ahmad, M.N.; Leahy, J.J.; Kwapinski, W. Hydrothermal carbonization of spent mushroom compost waste compared against torrefaction and pyrolysis. Fuel Process. Technol. 2021, 216, 106795. [Google Scholar]
- Jasińska, A. Spent mushroom compost (SMC)—Retrieved added value product closing loop in agricultural production. Acta Agrar. Debreceniensis 2018, 150, 185–202. [Google Scholar]
- Zakaria, Z.A.; Boopathy, R.; Dib, J.R. (Eds.) Valorisation of Agro-Industrial Residues—Volume I: Biological Approaches, 1st ed.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Van Wyk, L. Potential for use of spent substrate of Pleurotus mushrooms grown on urban waste as feed for dairy cattle. McGill Sci. Undergrad. Res. J. 2022, 17, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuppaladadiyam, A.K.; Vuppaladadiyam, S.S.V.; Sikarwar, V.S.; Ahmad, E.; Pant, K.K.; Murugavelh, S.; Pandey, A.; Bhattacharya, S.; Sarmah, A.; Leu, S.-Y. A critical review on biomass pyrolysis: Reaction mechanisms, process modeling and potential challenges. J. Energy Inst. 2023, 108, 101236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kota, K.B.; Shenbagaraj, S.; Sharma, P.K.; Sharma, A.K.; Ghodke, P.K.; Chen, W.-H. Biomass torrefaction: An overview of process and technology assessment based on global readiness level. Fuel 2022, 324, 124663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojić, M.M.; Petrović, J.T.; Petrović, M.S.; Stanković, S.M.; Porobić, S.J.; Marinović-Cincović, M.T.; Mihajlović, M.L. Hydrothermal carbonization of spent mushroom substrate: Physicochemical characterization, combustion behavior, kinetic and thermodynamic study. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2021, 155, 105028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syguła, E.; Koziel, J.A.; Białowiec, A. Proof-of-Concept of Spent Mushrooms Compost Torrefaction—Studying the Process Kinetics and the Influence of Temperature and Duration on the Calorific Value of the Produced Biocoal. Energies 2019, 12, 3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syguła, E.; Koziel, J.A.; Białowiec, A. Waste to carbon: Preliminary research on mushroom spent compost torrefaction. Preprints 2019, 2019060189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toor, S.S.; Jasiunas, L.; Xu, C.; Sintamarean, I.M.; Yu, D.; Nielsen, A.H.; Rosendahl, L.A. Reduction of inorganics from macroalgae Laminaria digitata and spent mushroom compost (SMC) by acid leaching and selective hydrothermal liquefaction. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2018, 8, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabish, A.N.; Kazmi, M.; Hussain, M.A.; Farhat, I.; Irfan, M.; Zeb, H.; Rafique, U.; Ali, H.; Saddiqi, M.H.; Akram, M.S. Biomass waste valorization by acidic and basic leaching process for thermochemical applications. Waste Biomass Valorization 2021, 12, 6219–6229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D2234/D2234M; Standard Practice for Collection of a Gross Sample of Coal. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- E1757; Standard Practice for Preparation of Biomass for Compositional Analysis. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2019.
- Goering, H.K.; Van Soest, P.J. Forage Fiber Analyses (Apparatus, Reagents, Procedures, and Some Applications); U.S. Agricultural Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.; Han, L.; Liu, X.; Ma, L. The rapid estimation of cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin contents in rice straw by near infrared spectroscopy. Energy Sources Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2010, 33, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Productos para la industria agrícola. Productos orgánicos usados como abonos o fertilizantes y enmiendas o acondicionadores de suelo. Available online: https://tienda.icontec.org/gp-ntc-productos-para-la-industria-agricola-productos-organicos-usados-como-abonos-o-fertilizantes-y-enmiendas-o-acondicionadores-de-suelo-ntc5167-2022.html (accessed on 18 August 2024).
- Saldarriaga, J.F.; Aguado, R.; Pablos, A.; Amutio, M.; Olazar, M.; Bilbao, J. Fast characterization of biomass fuels by thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). Fuel 2015, 140, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandara, Y.W.; Gamage, P.; Gunarathne, D.S. Hot water washing of rice husk for ash removal: The effect of washing temperature, washing time and particle size. Renew. Energy 2020, 153, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, A.; Konttinen, J.; Joronen, T. Effect of different washing parameters on the fuel properties and elemental composition of wheat straw in water-washing pre-treatment. Part 1: Effect of washing duration and biomass size. Fuel 2021, 292, 120206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, A.; Konttinen, J.; Joronen, T. Effect of different washing parameters on the fuel properties and elemental composition of wheat straw in water-washing pre-treatment. Part 2: Effect of washing temperature and solid-to-liquid ratio. Fuel 2021, 292, 120209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Machín, L.; Arteaga-Pérez, L.E.; Pérez-Bermúdez, R.A.; Casas-Ledón, Y.; Prins, W.; Ronsse, F. Effect of citric acid leaching on the demineralization and thermal degradation behavior of sugarcane trash and bagasse. Biomass Bioenergy 2018, 108, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umor, N.A.; Ismail, S.; Abdullah, S.; Huzaifah, M.H.R.; Huzir, N.M.; Mahmood, N.A.N.; Zahrim, A.Y. Zero waste management of spent mushroom compost. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2021, 23, 1726–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, F.R.; Pecchia, J.A. Bacterial Community Patterns in the Agaricus bisporus Cultivation System, from Compost Raw Materials to Mushroom Caps. Microb. Ecol. 2022, 84, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckers, S.J.; Dallo, I.A.; del Campo, I.; Rosenauer, C.; Klein, K.; Wurm, F.R. From Compost to Colloids—Valorization of Spent Mushroom Substrate. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 6991–6998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez Urrego, J.M.; Yepes Jaramillo, S.A. Caracterización nutricional del residuo del cultivo de la seta Agaricus bisporus como alimento potencial para bovinos. CES Med. Vet. Zootec. 2013, 8, 34–56. [Google Scholar]
- Kwak, W.S.; Kim, Y.I.; Seok, J.S.; Oh, Y.K.; Lee, S.M. Molasses and microbial inoculants improve fermentability and silage quality of cotton waste-based spent mushroom substrate. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 1471–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Huang, Q.; Su, Y.; Xue, Q.; Sun, L. Cobalt speciation and phytoavailability in fluvo-aquic soil under treatments of spent mushroom substrate from Pleurotus ostreatus. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 7486–7496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, W.S.; Yoon, J.S. On-site output survey and feed value evaluation on Agro- industrial by-products. J. Anim. Sci. Technol. 2003, 45, 251–264. [Google Scholar]
- Jaramillo, F.E.; Alvarado, P.N. Thermogravimetric evaluation of torrefaction parameters on thermal properties of a Colombian woody biomass. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2020, 80, 133–138. [Google Scholar]
- Jaramillo, F.E.; Alvarado, P.N.; Mazo, R.A. Torrefacción de biomasa en un reactor de tornillo a escala de banco: Efecto de la temperatura y del tipo de biomasa. TecnoLógicas 2022, 25, e2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


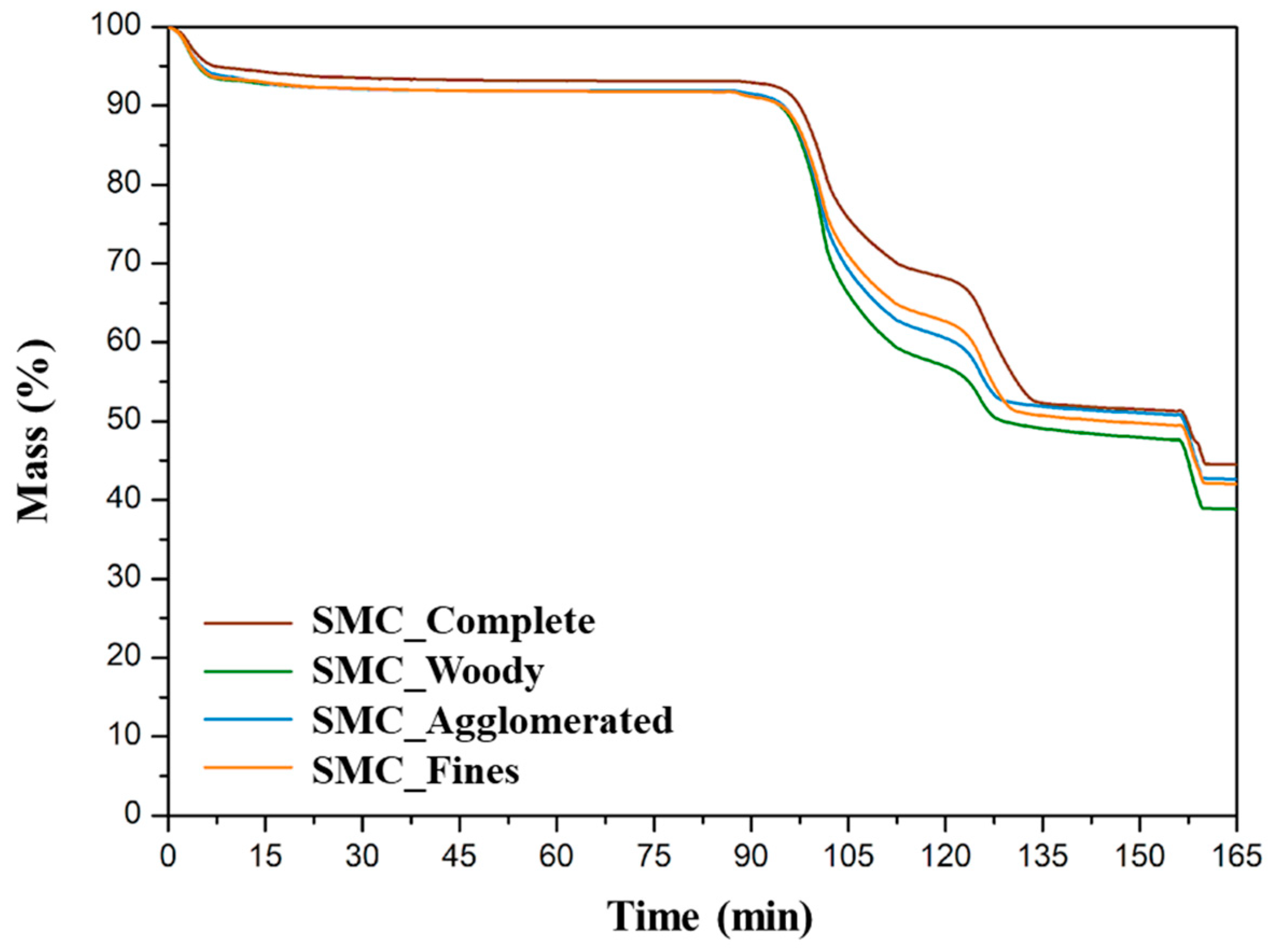
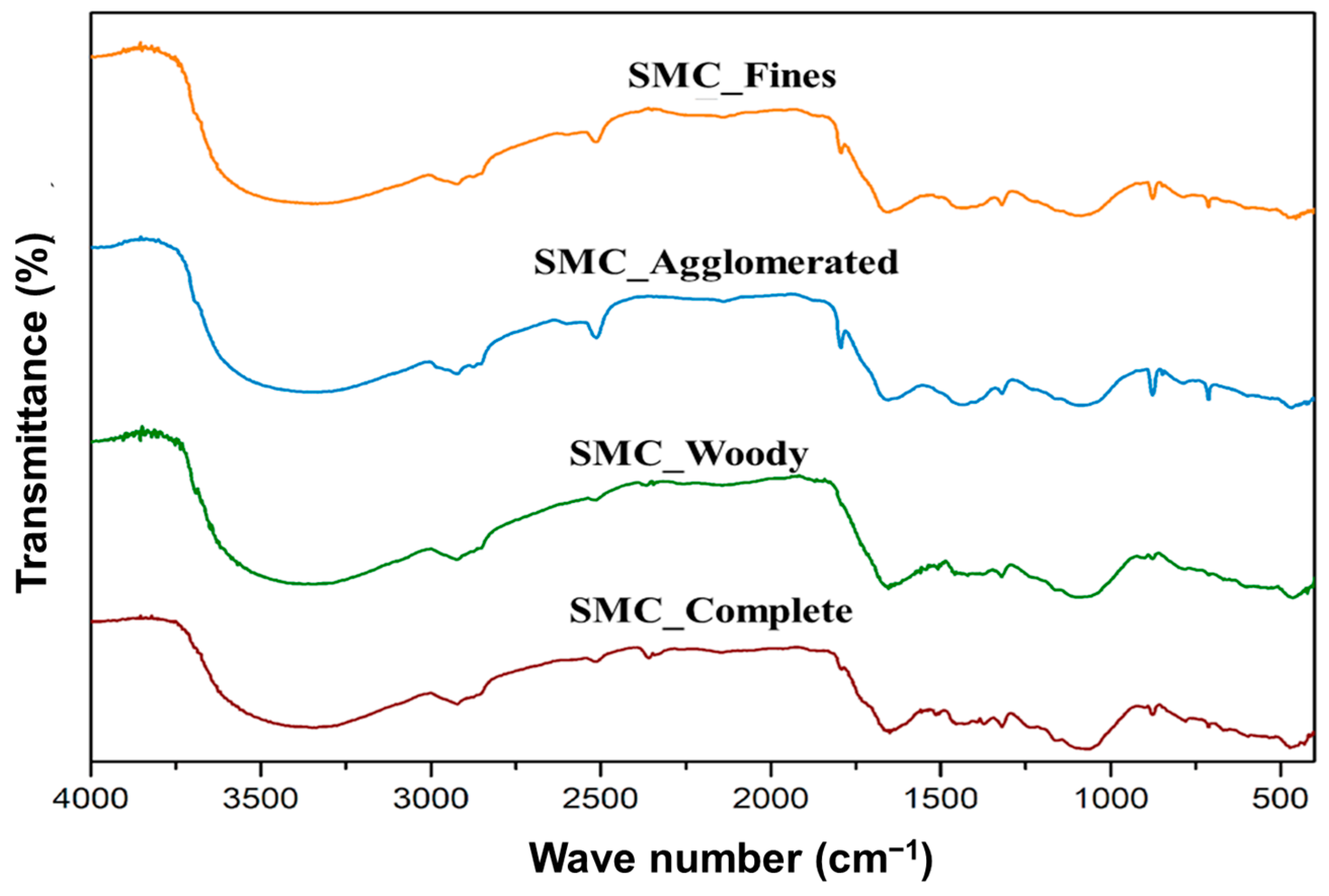
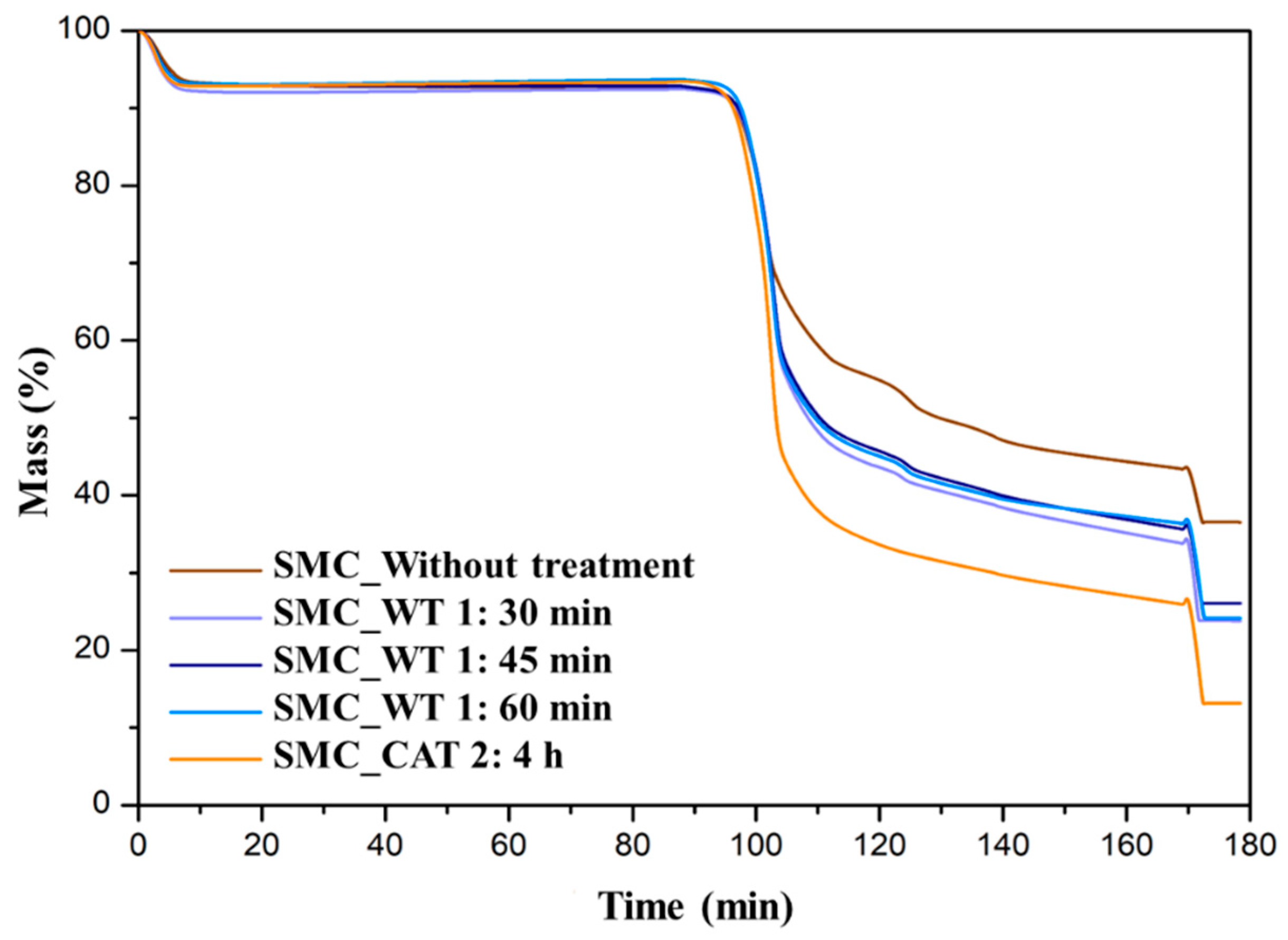
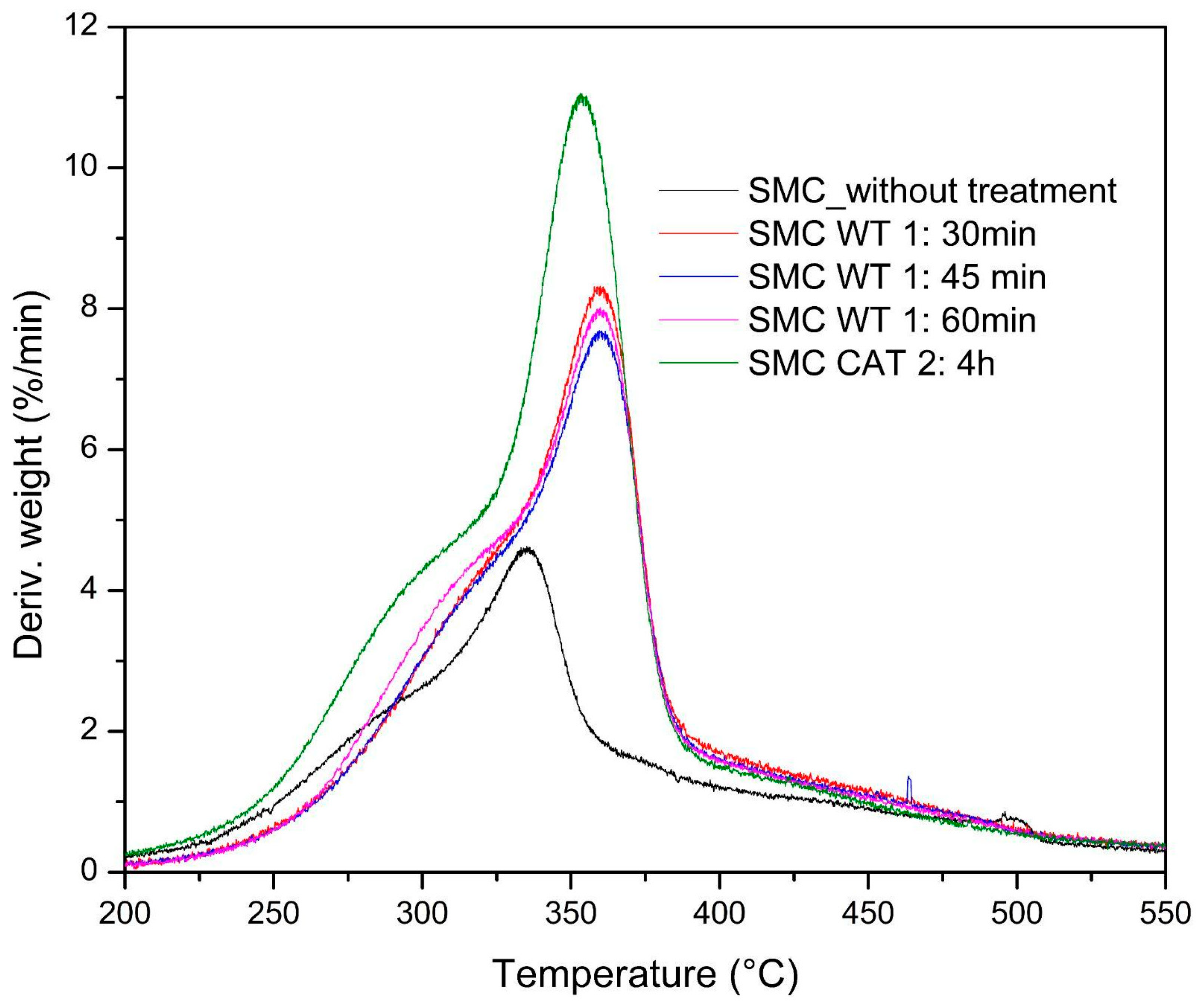
| Acronym | Meaning |
|---|---|
| SMC_Complete | Complete biomass without any physical separation. |
| SMC_Woody | Fraction with woody appearance. |
| SMC_Agglomerated | Fraction of compacted SMC. |
| SMC_Fines | Fraction of SMC with visually small particle sizes. |
| Analysis | Parameter | Symbol or Acronym | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| Proximate analysis a | Moisture | M | 6.9% |
| Volatile matter | VM | 41.7% | |
| Fixed carbon | FC | 6.8% | |
| Ash | Ash | 44.5% | |
| Lignocellulosic components | Hemicellulose | n/a | 9.8% |
| Cellulose | n/a | 8.3% | |
| Lignin | n/a | 34.3% | |
| Inorganics | Cadmium | Cd | <0.10 ppm |
| Chrome | Cr | <1.00 ppm | |
| Nickel | Ni | <0.20 ppm | |
| Lead | Pb | <0.50 ppm | |
| Mercury | Hg | <0.10 ppm | |
| Arsenic | As | <0.10 ppm | |
| Calcium | CaO | 12.68% | |
| Magnesium | MgO | 0.82% | |
| Potassium | K2O | 2.31% | |
| Sodium | Na | 0.11% | |
| Zinc | Zn | 0.007% | |
| Organics | Oxidizable organic carbon | n/a | 42.60% |
| Phosphorus oxide | P2O5 | 0.61% | |
| Organic nitrogen | Total N | 2.88% | |
| C/N ratio | n/a | 14.80 | |
| Physical analysis | pH | n/a | 5.52 |
| WHC b | n/a | 177.80% | |
| Moisture | n/a | 45.30% | |
| CEC c | n/a | 41.60 meq/100 g | |
| Electrical conductivity | n/a | 1.09 dS/m | |
| Density | n/a | 0.24 g/cm3 |
| Sample | Moisture (%) | Volatile Matter (%) | Fixed Carbon (%) | Ash (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMC_Complete | 6.9 ± 0.1 | 41.7 ± 0.8 | 6.8 ± 0.1 | 44.5 ± 0.9 |
| SMC_ Woody | 8.2 ± 0.2 | 44.9 ± 0.9 | 7.7 ± 0.1 | 38.9 ± 0.8 |
| SMC_Agglomerated | 8.1 ± 0.2 | 41.1 ± 0.8 | 8.0 ± 0.2 | 42.6 ± 0.9 |
| SMC_Fines | 8.3 ± 0.2 | 42.2 ± 0.8 | 7.3 ± 0.1 | 42.1 ± 0.8 |
| Sample | Moisture (%) | Volatile Matter (%) | Fixed Carbon (%) | Ash (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMC_ WT 1: 30 min | 7.57 ± 0.15 | 58.08 ± 1.16 | 10.51 ± 0.21 | 23.80 ± 0.47 |
| SMC_ WT 1: 45 min | 7.13 ± 0.14 | 56.72 ± 1.13 | 9.66 ± 0.19 | 26.04 ± 0.52 |
| SMC_ WT 1: 60 min | 6.32 ± 0.13 | 56.78 ± 1.14 | 12.74 ± 0.25 | 24.12 ± 0.48 |
| SMC_ CAT 2: 4 h | 6.63 ± 0.13 | 66.75 ± 1.34 | 13.27 ± 0.26 | 13.15 ± 0.26 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Restrepo Londoño, C.; Alvarado Torres, P.; Moreno, A.; Giraldo Gil, A. Characterization of Spent Mushroom Compost and Evaluation of Its Potential for Thermochemical Valorization through Ash Reduction Treatments. Biomass 2024, 4, 978-989. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomass4030054
Restrepo Londoño C, Alvarado Torres P, Moreno A, Giraldo Gil A. Characterization of Spent Mushroom Compost and Evaluation of Its Potential for Thermochemical Valorization through Ash Reduction Treatments. Biomass. 2024; 4(3):978-989. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomass4030054
Chicago/Turabian StyleRestrepo Londoño, Carolina, Pedro Alvarado Torres, Andrés Moreno, and Alexander Giraldo Gil. 2024. "Characterization of Spent Mushroom Compost and Evaluation of Its Potential for Thermochemical Valorization through Ash Reduction Treatments" Biomass 4, no. 3: 978-989. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomass4030054
APA StyleRestrepo Londoño, C., Alvarado Torres, P., Moreno, A., & Giraldo Gil, A. (2024). Characterization of Spent Mushroom Compost and Evaluation of Its Potential for Thermochemical Valorization through Ash Reduction Treatments. Biomass, 4(3), 978-989. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomass4030054





