Abstract
This work focuses on a culture strategy that combines high biomass production and lipid accumulation in the green microalgae Raphidocelis subcapitata immobilized in alginate gel in order to obtain high lipid productivity for biodiesel production. The study of the effects of nitrogen and phosphorus deficiency on lipid accumulation and biomass production in immobilized microalgae showed that both conditions (N− and P−) promoted lipid accumulation in the microalgae. The lipid contents achieved under nitrogen (31.7% ± 3.2% (dcw)) and phosphorus (19.4% ± 1.9% (dcw)) deficiency conditions were higher than those obtained in the complete medium (control) (14.9% ± 1.5% (dcw)). The highest lipid productivity was recorded under nitrogen deficiency conditions (PL = 11.1 ± 1.1 mg/L/day). This indicated that nitrogen deficiency was more effective than phosphorus deficiency in terms of triggering lipid accumulation in the microalgae. However, the conditions for inducing lipid accumulation (N− or P−) resulted in slower growth. In order to address this issue and achieve high lipid productivity, a two-step culture strategy was used. Immobilized R. subcapitata was cultivated under optimal concentrations of nitrogen and phosphorus to achieve a high biomass concentration. Thereafter, the beads containing the microalgae were transferred to a culture medium under nitrogen deficiency conditions in order to induce lipid accumulation. The concentrations 1.5 g/L of NaNO3 and 20 mg/L of K2HPO4 were determined as being the optimal concentrations for growth, and they produced the highest biomass production rates (µm max = 0.233 ± 0.023 day−1 and µm max = 0.225 ± 0.022 day−1 for NaNO3 and K2HPO4, respectively) from all of the concentrations studied. With the two-step culture strategy, immobilized R. subcapitata accumulated 37.9 ± 3.8% of their dry weight in lipid and reached a lipid productivity value of PL = 40.3 ± 4.0 mg/L/day under nitrogen deficiency conditions. This value was approximately 3.6 times higher than that obtained in the direct culture of cells under nitrogen deficiency conditions (PL = 11.1 ± 1.1 mg/L/day).
1. Introduction
The discovery of oil and coal deposits has served humans well; however, these will eventually be exhausted. In addition, the combustion of fossil fuels generates high greenhouse gas emissions, which are responsible for global warming [1,2,3,4]. Microalgal biomass appears to be a promising solution for the production of renewable fuels, known as “biofuels” [5,6,7]. As compared to higher plants, microalgae have many advantages as a source of biofuels, including biodiesel, for example: (1) their growth is about 50 times faster than that of terrestrial plants [8]; (2) they can produce 10 to 100 times more oil per hectare than oil crops [9,10,11]; (3) they are able to grow in seawater, brackish water, sewage, and on wasteland [12]; (4) their CO2 sequestration is 10 to 50 times greater than that of terrestrial plants [13,14]; (5) their cultivation does not require herbicides or pesticides [15]; (6) after oil extraction, residual biomass can be used as a fertilizer or food, or it can be fermented to produce methane or ethanol [15,16,17,18].
The biodiesel yield of microalgae depends essentially on their lipid content and biomass production. These are influenced by the growing conditions. Nitrogen deficiency is one of the most frequently used strategies to steer the metabolism of microalgae towards lipid accumulation [15,19,20]. Nitrogen is used by microalgae for protein synthesis. Under nitrogen deficiency conditions, the carbon fixed during photosynthesis is converted into lipid rather than proteins [21,22,23]. It has also been shown that phosphorus deficiency can trigger lipid accumulation in microalgae [24,25]. However, the conditions for inducing lipid accumulation generally lead to slower growth [15,26,27]. To address this and achieve high lipid productivity, Rodolfi et al. [15], as well as other researchers [26,27,28,29], proposed a two-step culture strategy. In the first stage, microalgae grow under optimal nitrogen and phosphorus supply conditions to obtain a high biomass concentration. In the second stage, microalgae are transferred to a culture medium under nitrogen or phosphorus deficiency conditions in order to induce lipid accumulation. This strategy has been the subject of many studies using free cultures of microalgae [15,20,28,30]. Although it promotes an increase in lipid production in the microalgae studied, its application with free cultures remains debatable. It should be noted that in the process of producing biodiesel with microalgae, cell harvesting is a limiting step because they are small, light, and diluted in water [8,31]. Centrifugation is the most common method used for harvesting cells, but it is energy-consuming [8,32]. In the two-step culture strategy using free cultures, the microalgae are collected by centrifugation and transferred to a medium deficient in nitrogen or phosphorus to trigger lipid accumulation. They are then collected again at the end of culturing to extract the lipid. This leads to an increase in the energy balance of the process, which drives up the price of the biodiesel produced. In order to increase the economic feasibility of the process, this study proposed the use of immobilized microalgae cultures. The immobilization of microalgae in polymer-based beads, such as alginate, for example, polycarboxylate extracted from brown algae, is a simple, gentle, and economical technique [33]. The beads are large compared to free cells and are easily collected by simple sieving without consuming significant amounts of energy [34].
It is in this context that the present study has been undertaken. Our objective was to use the two-step culture strategy in the green microalgae Raphidocelis subcapitata immobilized in alginate gel in order to obtain high lipid productivity for biodiesel production.
Previous work carried out on Rhaphidocelis subcapitata immobilized in alginate gel and cultured in batch, under standard culture conditions, showed that it had potential for the production of biodiesel. It accumulated 24.7 ± 2.5% of its dry weight in lipid when nitrates and phosphates were exhausted in the culture medium (the stationary phase) [35].
This study was divided into three parts: In the first part, the effects of nitrogen and phosphorus deficiency on lipid accumulation and biomass production in the immobilized microalgae were evaluated in order to determine the most effective trigger (N− or P−) for lipid accumulation in the microalgae. In the second part, the growth of R. subcapitata immobilized under different concentrations of nitrogen and phosphorus was studied in order to determine the optimal concentrations of nitrogen and phosphorus to obtain a high biomass concentration in the first stage of cultivation. In the third part, the two-stage culture strategy was applied. Immobilized R. subcapitata was cultivated under optimal concentrations of nitrogen and phosphorus. Thereafter, the beads containing the microalgae were recovered by sieving and were transferred to a culture medium under nitrogen deficiency conditions (the trigger was chosen based on the results obtained in the first part) in order to induce lipid accumulation.
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to focus on the use of the microalgae Raphidocelis subcapitata immobilized in alginate gel in a two-stage culture process to obtain high lipid productivity for biodiesel production.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microalga and Culture Medium
The green microalgae Raphidocelis subcapitata were obtained from the culture collection of the Environment Canada laboratory (Montréal, QC, Canada). The microalgae culture medium consisted of five nutrient stock solutions. The detailed composition of the medium and its preparation protocol are published on the Environment Canada website [36]. We note that we used 10 mL of each solution for the preparation of the culture medium and not 1 mL as described in the protocol. The pH of the medium was 7.5. The culture medium was sterilized using an autoclave (121 °C, 20 min).
In the experiments related to the growth of R. subcapitata immobilized under different nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations, the volumes taken from the NaNO3 and K2HPO4 stock solutions were adjusted in order to obtain the final concentrations: 0 g/L, 0.25 g/L, 0.5 g/L, 1 g/L, 1.5 g/L, and 2 g/L in NaNO3 and 0 mg/L, 10 mg/L, 20 mg/L, 40 mg/L, and 60 mg/L in K2HPO4.
2.2. Immobilization of R. subcapitata Cells in Alginate Beads
The immobilization of the microalgae in alginate beads was performed aseptically from a suspension of R. subcapitata in the exponential growth phase (biomass concentration of about 1 g/L), sterile sodium alginate solution 2% (w/v) (sodium alginate (No. 71238), Sigma-Aldrich®, Oakville, ON, Canada), and sterile CaCl2 gelling solution 1% (w/v) (CaCl2, 2H2O (No. 700912), Anachemia, Montreal, QC, Canada) [37,38].
The pellet recovered from the centrifugation (4000 rpm for 10 min) of the microalgae suspension (100 mL) was washed three times with sterile saline water (0.85%). The microalgae were then resuspended in 50 mL of sterile saline water. A volume of 50 mL of sodium alginate solution was added to the microalgae suspension. The beads were formed using a sterile 20 mL syringe. The obtained mixture was expelled dropwise into the CaCl2 solution. The beads produced were kept in this solution, under gentle stirring, for 30 min for hardening.
2.3. Culture Conditions for Immobilized Microalgae
The immobilized microalgae cultures were placed in 2 L Erlenmeyer flasks that had previously been sterilized in an autoclave (121 °C, 20 min), containing 1 L of culture medium (sterile). The cultures were placed in a temperature-controlled chamber (INFORS HT Ecotron) to achieve standard culture conditions [35]. They were incubated under a photoperiod of 24 h of light and 0 h of darkness (24/0; L/D).
2.4. Determination of the Biomass of Immobilized Microalgae
The biomass concentrations of immobilized R. subcapitata were determined by measuring the dry weight after the dissolution of the beads in sterile sodium phosphate buffer (pH = 6.0), with a concentration of 50 mM [38,39]. The cells were collected by filtration of the microalgae suspension through pre-weighed glass-fiber filters (Wathman filter, 1.2 μm). They were then washed with sterile distilled water. The filters containing the microalgae were weighed after drying in an oven at 80 °C for 24 h [35,40]. The experiments were performed in duplicate.
2.5. Calculation of Growth Rate, Generation Time, and Biomass Productivity
The maximum biomass production rate (µm max) was calculated during the exponential growth phase, as follows [34]:
where B1 and B2 are the biomass concentrations (g/L) at time t1 and t2, respectively.
The biomass doubling time (Gm) was calculated according to the following formula [41,42]:
The biomass productivity was calculated as follows [43]:
where Bx and B0 are the biomass concentrations (mg/L) at time tx (the final day of cultivation) and t0 (the first day of cultivation), respectively.
2.6. Extraction of Total Lipid from Immobilized Microalgae
Total lipid was extracted according to the “whole-cell analytical method” (WCA) of Van Vooren et al. [35,44]. The extraction was carried out with a mixture of chloroform/methanol solvents (2:1, v/v). Whole R. subcapitata cells were recovered after the beads (10 beads) dissolved in the phosphate buffer, and the suspension was centrifuged (4000 rpm for 10 min). Before adding the solvents, 20 µL of butyl hydroxytoluene (20 µg/µL) were added to the pellet to prevent lipid oxidizing during extraction. The solvent mixture (6 mL) was added three times. After each addition, the tubes were vortexed (10 s) and placed in an ultrasound bath (BRANSON 5200, Fisher Scientific, Montréal, QC, Canada) for 30 s [20]. For complete lipid extraction, the tubes were placed on a pendulum for 6 h in the dark at room temperature. The extracted solvent was evaporated in an oven at 60 °C for 6 h. Finally, the tubes were weighed after cooling in the desiccator. The experiments were performed in duplicate. The rate of total lipid in the biomass was calculated as follows [45]:
2.7. Calculation of Lipid Productivity
The lipid productivity (LP) was calculated using the following formula [45]:
where Cx and C0 are the lipid contents of the microalgae (mg lipid/mg dry weight of cells) at time tx (the final day of cultivation) and t0 (the first day of cultivation), respectively.
Bx is the biomass concentration (mg/L) at tx, and B0 (mg/L) is the biomass concentration at t0.
3. Results
3.1. The Effects of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Deficiency on Lipid Accumulation and Biomass Production in Immobilized R. subcapitata
To assess the effects of nitrogen and phosphorus deficiency on lipid accumulation and biomass production in immobilized R. subcapitata, beads containing microalgae with initial biomass of between 0.082 and 0.09 g/L were inoculated into the following culture media: nitrogen-deficient medium (N−P+) (NaNO3 concentration of 0 g/L; K2HPO4 concentration of 10.44 mg/L); phosphorus-deficient medium (N+P−) (K2HPO4 concentration of 0 mg/L; NaNO3 concentration of 0.255 g/L); and complete medium, which constituted the control (N+P+) (NaNO3 concentration of 0.255 g/L; K2HPO4 concentration of 10.44 mg/L, which are the standard concentrations of the culture medium). The results obtained are presented in Figure 1. The experiments were performed in batch and in duplicate.
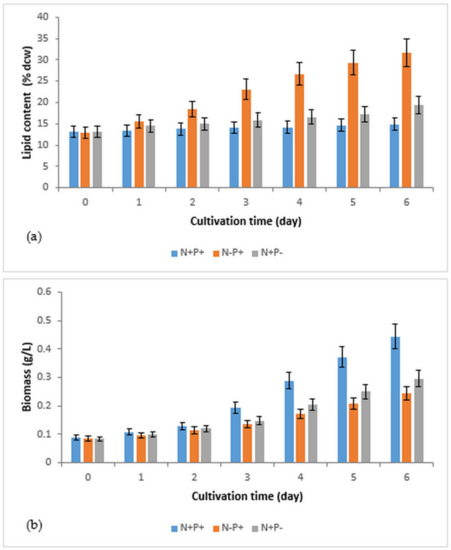
Figure 1.
Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus deficiency on lipid accumulation and biomass production in R. subcapitata immobilized in alginate beads (experiments performed in batch and in duplicate): (a) variations in lipid content per dry weight of cells; (b) variations in biomass; N+P+ (control, complete medium); N−P+ (nitrogen-deficient medium); N+P− (phosphorus-deficient medium). t0 = d1.
The results show that nitrogen deficiency (N−P+) and phosphorus deficiency (N+P−) promoted lipid accumulation in the immobilized R. subcapitata microalgae, unlike the control (N+P+), which produced no significant increase in lipid content (Figure 1a). The latter increased from 13.1% ± 1.3% (dcw) to 14.9 ± 1.5% (dcw) at the end of culture. The highest lipid content (31.7% ± 3.2% (dcw)) was achieved when the microalgae were cultivated in an N-deficient culture medium (Table 1). In the P−deficient medium, the lipid content of 19.4% ± 1.9% (dcw) was obtained (Table 1), which indicates that phosphorus deficiency is also an appropriate stimulant for lipid accumulation in immobilized R. subcapitata but is less effective than nitrogen deficiency.

Table 1.
The lipid content (% dcw), biomass (g/L), biomass productivity (mg/L/day), and lipid productivity (mg/L/day) of immobilized R. subcapitata obtained under different culture conditions.
The lipid productivity recorded under nitrogen deficiency (PL = 11.1 ± 1.1 mg/L/day) (Table 1) was also the highest. However, the lipid productivity value obtained under phosphorus deficiency (PL = 7.7 ± 0.8 mg/L/day) (Table 1) was lower than that obtained in the control medium (N+P+) (PL = 9.1 ± 0.9 mg/ L/day) (Table 1). This can be explained by the low biomass concentration achieved under phosphorus deficiency as compared to the control (Table 1). Indeed, the growth of R. subcapitata immobilized under nitrogen and phosphorus deficiency exhibited a negative trend, which was more pronounced for nitrogen than phosphorus (Figure 1b and Table 1). In the absence of nitrogen or phosphorus in the culture medium, microalgae use their internal reserves in these elements to compensate for this lack and to ensure certain cell divisions; photosynthesis then occurs but at a reduced rhythm compared to a culture where N and P are present in sufficient quantity. The rate of growth of microalgae in a medium deficient in nitrogen or phosphorus depends on the intracellular level of these elements [15].
Our results are in accordance with other studies on various microalgae that demonstrate a high lipid content resulting from nitrogen deficiency conditions [26,29,46,47]. Nitrogen is involved in the synthesis of essential cell structures and proteins. Nitrogen deficiency conditions cause an imbalance in the ratio of nitrogen and carbon. This imbalance results in the storage of excess carbon, which is fixed during photosynthesis as lipid or carbohydrates rather than as proteins [23].
Lipid accumulation under phosphorus deficiency conditions has also been observed in several species of microalgae, such as Scenedesmus obliquus [26], Monodus subterraneus [24], and Isochrysis galbana U4 [25].
Various studies report that these high lipid production conditions (nitrogen and phosphorus deficiency) generally lead to slower growth [15,26,27].
To address this and obtain high lipid productivity, we recall that the authors of [15,26,27,28,29] suggested a two-step culture strategy. This involves an initial stage of biomass production under the conditions of optimal N and P supply, followed by a second stage inducing the accumulation of lipid under N or P deficiency conditions. It is this strategy that the present study aimed to utilize in order to increase lipid production in immobilized R. subcapitata. In view of the obtained results, nitrogen deficiency was determined to be the most effective trigger for lipid accumulation in immobilized microalgae.
In the following, the studied growth of immobilized R. subcapitata under different concentrations of nitrogen and phosphorus in order to determine the optimal concentrations of nitrogen and phosphorus in order to obtain a high biomass concentration in the first stage of cultivation is presented.
3.2. Growth of R. subcapitata Immobilized under Different Concentrations of Nitrogen and Phosphorus
Figure 2 shows the growth curves of R. subcapitata immobilized in alginate beads under different concentrations of nitrogen and phosphorus.
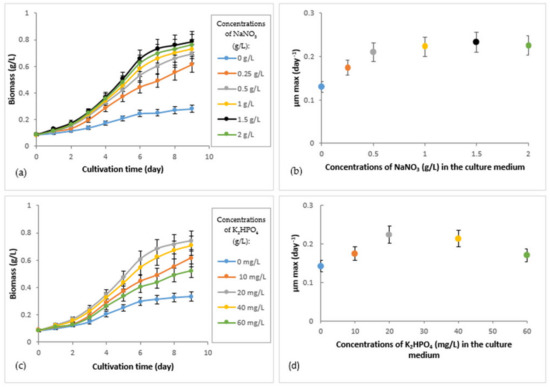
Figure 2.
Growth of R. subcapitata immobilized in alginate beads under different concentrations of nitrogen and phosphorus, over a period of 10 days (experiments performed in batch and in duplicate): (a) production of biomass under different concentrations of NaNO3 (the concentration of K2HPO4 was 10.44 mg/L, which was the standard concentration of the culture medium); (b) production of biomass under different concentrations of K2HPO4 (the concentration of NaNO3 was 0.255 g/L, which was the standard concentration of the culture medium); (c) maximum biomass production rate (µm max) of immobilized R. subcapitata as a function of different concentrations of NaNO3; (d) maximum biomass production rate (µm max) of immobilized R. subcapitata as a function of different concentrations of K2HPO4. t0 = d1.
The results of biomass production under different concentrations of NaNO3 (Figure 2a) show that the lowest biomass was obtained with a concentration of 0 g/L of NaNO3 (µm max = 0.13 ± 0.01 day−1) (Figure 2a,b). Biomass production improved as the NaNO3 concentration increased (0.25, 0.5, 1, and 1.5 g/L). However, a further increase in biomass was not obtained with a NaNO3 concentration of 2 g/L (Figure 2a,b). The immobilized R. subcapitata produced the highest biomass production rate (µm max = 0.233 ± 0.023 day−1) (Figure 2b) with a NaNO3 concentration of 1.5 g/L.
Figure 2c shows the biomass production of R. subcapitata immobilized under different K2HPO4 concentrations. An increase in the biomass concentration was observed with all concentrations of K2HPO4 used. The highest production rate was obtained with a concentration of 20 mg/L (µm max = 0.225 ± 0.022 day−1), and the lowest (µm max = 0.143 ± 0.014 day−1) was obtained with a concentration of 0 g/L (Figure 2d). For the 40 mg/L and 60 mg/L K2HPO4 concentrations, a decrease in the µm max was observed.
Our results are consistent with other studies in that increasing the concentration of nitrogen and phosphorus in the culture medium stimulates the growth of microalgae. However, too high concentrations of these elements appear to inhibit growth [42,48]. One study showed that excess nitrogen could have a toxic effect, leading to a decline in microalgae [49].
Considering the results obtained, the concentrations of 1.5 g/L of NaNO3 and 20 mg/L of K2HPO4 were determined as the optimal concentrations and were used in the remainder of the study to obtain the maximum biomass production.
3.3. Two-Step Culture of Immobilized R. subcapitata
A two-step cultivation strategy was applied to increase the microalgae lipid productivity. The immobilized microalgae were cultivated under optimal growth conditions (concentrations of NaNO3 and K2HPO4 were 1.5 and 20 mg/L, respectively) for 7 days to obtain the maximum biomass production, and then they were transferred to the N-deficient culture medium to trigger lipid accumulation. The results obtained are presented in Figure 3.
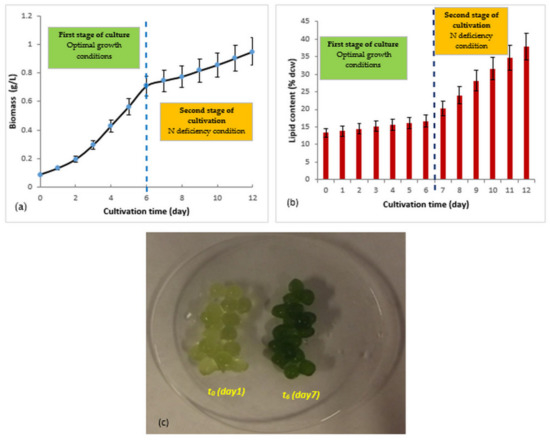
Figure 3.
Two-step culture of R. subcapitata immobilized in alginate beads (experiments performed in duplicate): (a) biomass production; (b) accumulation of total lipid; (c) appearance of alginate beads containing R. subcapitata cells at the beginning and end of the first stage of culture; at t6 (d7), the immobilized microalgae were transferred to the N-deficient medium. t0 = d1.
During the first culture step (optimal growth conditions), an increase in the quantity of biomass produced was observed from the first days (Figure 3a). A biomass production rate of µm max = 0.288 ± 0.028 day−1 was recorded during the exponential growth phase, which corresponded to a doubling time of Gm = 2.40 ± 0.24 days. The microalgae achieved biomass productivity of PB = 103.0 ± 10.3 mg/L/day. This value was approximately 1.7 times higher than that recorded under standard culture conditions (PB = 59.3 ± 5.9 mg/L/day) (Table 1 (N+P+)). Figure 3c shows the appearance of the alginate beads containing the R. subcapitata cells at the beginning and end of this step. With regard to lipid production in this first culture step (Figure 3b), a slight increase in the lipid content was observed, increasing from approximately 13.3% ± 1.3% (dcw) (1er day) to 16.7% ± 1.7% (dcw) (7th day), with a lipid productivity value of PL = 17.7 ± 1.7 mg/L/day. This lipid productivity value was approximately 1.9 times higher than that obtained under standard culture conditions (PL = 9.1 ± 0.9 mg/L/day) (Table 1 (N+P+)). This increase was due to the high biomass concentration achieved under optimal growth conditions.
When the beads containing the microalgae were transferred to the N-deficient culture medium (7th day), a slowing of the growth was observed for the first 3 days (Figure 3a, second culture step). This can be explained by the fact that the immobilized microalgae suffered a shock (sudden nitrogen deficiency), and thus they needed time to adapt to the new growing conditions. After this adaptation period, an increase in biomass production was noted. With regard to lipid production, their accumulation was triggered from the onset of N deficiency (Figure 3b, second step). The immobilized R. subcapitata accumulated 37.9 ± 3.8% of their dry weight in lipid and reached a lipid productivity value of PL = 40.3 ± 4.0 mg/L/day, under nitrogen deficiency.
Using this two-step culture strategy, the lipid productivity of immobilized R. subca-pitata (under nitrogen deficiency) increased by a factor of 3.6 as compared to the direct culture of cells under nitrogen deficiency (PL = 11.1 ± 1.1 mg/L/d) (Table 1 (N−P+)).
Our results are superior to those obtained from other microalgae species, such as Tetraselmis suecica, in which the two-step culture strategy provided a lipid productivity PL = 18.1 mg/L/d [50]. This shows that the immobilized R. subcapitata is a promising candidate for biodiesel production.
4. Conclusions
In the present study, a culture strategy combining high biomass production and lipid accumulation was applied to the immobilized microalgae R. subcapitata in order to achieve high lipid productivity for biodiesel production. In the first step, the immobilized microalgae were cultivated under optimal nitrogen and phosphorus supply conditions (1.5 g/L NaNO3, 20 mg/L K2HPO4) in order to achieve a high biomass concentration. Then, the beads containing the microalgae were transferred to an N-deficient culture medium (the most effective trigger) to induce lipid accumulation.
As a result of the two-step culture strategy, immobilized R. subcapitata accumulated 37.9 ± 3.8% of their dry weight in lipid and reached a lipid productivity value of PL = 40.3 ± 4.0 mg/L/day, under nitrogen deficiency. This value was approximately 3.6 times higher than that obtained from the direct culture of cells under nitrogen deficiency (PL = 11.1 ± 1.1 mg/L/day). The results obtained show that immobilized R. subcapitata is a promising candidate for biodiesel production. This work is the first step in the process of optimizing the lipid productivity of immobilized microalgae. Additional experiments are needed to optimize other growing parameters, such as lighting. Indeed, light plays an important role in the culture of microalgae. Therefore, determining the optimal light intensity and appropriate light cycles for immobilized R. subcapitata would improve its biomass yield and lipid productivity.
Author Contributions
A.B. and R.H. designed and developed the study. A.B. performed the experiments, collected and analyzed the data, and drafted the manuscript. R.H. supervised the work, provided advice on the methodology and results, and revised the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Government of Canada grant number RGPIN 157382-11, and the APC was funded by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We thank the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) for funding this research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bobin, J.-L.; Nifenecker, H.; Stéphan, C. 2. Les combustibles fossiles. In L’Énergie Dans le Monde; EDP Sciences: Les Ulis, France, 2021; pp. 21–36. [Google Scholar]
- Favennec, J.-P. L’avenir du pétrole. Available online: https://www.sciencespo.fr/ceri/sites/sciencespo.fr.ceri/files/art_jpf.pdf (accessed on 20 September 2021).
- Fritz, D. The Costs and Implications of Our Demand for Energy: A Comparative and Comprehensive Analysis of the Available Energy Resources. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3189719 (accessed on 20 September 2021).
- Le Treut, H. Changement climatique et gaz à effet de serre: Un problème ancien qui évolue de manière extrêmement rapide. Cites 2015, 63, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnefond, H.; Combe, C.; Cadoret, J.-P.; Sciandra, A.; Bernard, O. Potentiel des Microalgues; Lavoisier: Inria, France, 2020; Available online: https://hal.inria.fr/hal-02421830/document (accessed on 20 September 2021).
- Bougaran, G.; Saint-Jean, B. Microalgues: De petits végétaux aux grandes promesses! Biofutur 2014, 33, 28–31. [Google Scholar]
- Nafe Aziz, R.P.; Ibrahim, A.I.; Ahmed, A.I. Promising Applications for the Production of Biofuels Through Algae. Microb.Biotechnol. Appl. Agric. Environ. 2018, 1, 81–103. [Google Scholar]
- Suali, E.; Sarbatly, R. Conversion of microalgae to biofuel. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 4316–4342. [Google Scholar]
- Demirbas, A.; Demirbas, M.F. Algae Energy: Algae as a New Source of Biodiesel; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Chisti, Y. Biodiesel from microalgae. Biotechnol. Adv. 2007, 25, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Doré-Deschênes, F. Utilisation des microalgues comme source d’énergie durable. Available online: https://savoirs.usherbrooke.ca/bitstream/handle/11143/7149/cufe_Deschenes_essai80.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 18 September 2021).
- Gouveia, L. Microalgae as a Feedstock for Biofuels. In Microalgae as a Feedstock for Biofuels; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 1–69. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.A.; Rashmi; Hussain, M.Z.; Prasad, S.; Banerjee, U.C. Prospects of biodiesel production from microalgae in India. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2009, 13, 2361–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Horsman, M.; Wu, N.; Lan, C.Q.; Dubois-Calero, N. Biocatalysts and bioreactor design. Biotechnol. Prog. 2008, 24, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rodolfi, L.; Chini Zittelli, G.; Bassi, N.; Padovani, G.; Biondi, N.; Bonini, G.; Tredici, M.R. Microalgae for oil: Strain selection, induction of lipid synthesis and outdoor mass cultivation in a low-cost photobioreactor. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2009, 102, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mata, T.M.; Martins, A.A.; Caetano, N.S. Microalgae for biodiesel production and other applications: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cardozo, K.H.; Guaratini, T.; Barros, M.P.; Falcão, V.R.; Tonon, A.P.; Lopes, N.P.; Campos, S.; Torres, M.A.; Souza, A.O.; Colepicolo, P. Metabolites from algae with economical impact. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2007, 146, 60–78. [Google Scholar]
- Sialve, B.; Bernet, N.; Bernard, O. Anaerobic digestion of microalgae as a necessary step to make microalgal biodiesel sustainable. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 409–416. [Google Scholar]
- Jenck, J.; Lépine, O.; Legrand, J.; Dreno, P.; Grizeau, D.; Dupré, C. Valorisation industrielle des microalgues photosynthétiques. Available online: https://www.techniques-ingenieur.fr/base-documentaire/archives-th12/archives-plastiques-et-composites-tiaam/archive-1/valorisation-industrielle-des-microalgues-photosynthetiques-in201/perspectives-de-developpement-in201niv10003.html#3.1.1 (accessed on 17 September 2021).
- Taleb, A. Production de Biodiesel à Partir des Microalgues: Recherche des Souches Accumulatrices des Lipides et Optimisation des Conditions de Culture en Photobioréacteurs. Ph.D. Thesis, Angers Le Mans University, Nantes, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Falkowski, P.G.; Raven, J.A. Aquatic Photosynthesis; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Boileau, M.-È. Évaluation du potentiel d’utilisation d’une eau usée industrielle comme substrat de culture pour des microalgues d’eau douce dans une optique de production de biocarburants de 3e génération. Available online: https://savoirs.usherbrooke.ca/bitstream/handle/11143/6068/Boileau_Marie_Eve_MEnv_2015.pdf?sequence=3&isAllowed=y (accessed on 5 September 2021).
- Richardson, B.; Orcutt, D.; Schwertner, H.; Martinez, C.L.; Wickline, H.E. Effects of nitrogen limitation on the growth and composition of unicellular algae in continuous culture. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1969, 18, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khozin-Goldberg, I.; Cohen, Z. The effect of phosphate starvation on the lipid and fatty acid composition of the fresh water eustigmatophyte Monodus subterraneus. Phytochemistry 2006, 67, 696–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roopnarain, A.; Gray, V.; Sym, S. Phosphorus limitation and starvation effects on cell growth and lipid accumulation in Isochrysis galbana U4 for biodiesel production. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 156, 408–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Mallick, N. Microalga Scenedesmus obliquus as a potential source for biodiesel production. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 84, 281–291. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, L.; Hong-Ying, H.; Ke, G.; Ying-Xue, S. Effects of different nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations on the growth, nutrient uptake, and lipid accumulation of a freshwater microalga Scenedesmus sp. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 5494–5500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntley, M.E.; Redalje, D.G. CO2 mitigation and renewable oil from photosynthetic microbes: A new appraisal. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Chang. 2007, 12, 573–608. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, P.; Deng, Z.; Fan, L.; Hu, Z. Lipid accumulation and growth characteristics of Chlorella zofingiensis under different nitrate and phosphate concentrations. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2012, 114, 405–410. [Google Scholar]
- Massart, A.; Aubry, É.; Hantson, A.-L. Étude de stratégies de culture de Dunaliella tertiolecta combinant haute densité cellulaire et accumulation de lipides en vue de produire du biodiesel. BASE 2010, 14, 567–572. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.-Y.; Yoo, C.; Jun, S.-Y.; Ahn, C.-Y.; Oh, H.-M. Comparison of several methods for effective lipid extraction from microalgae. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, S75–S77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sander, K.; Murthy, G.S. Life cycle analysis of algae biodiesel. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2010, 15, 704–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulieu, C.; Poncelet, D.; Neufeld, R.J. Encapsulation and immobilization techniques. Birkhauser/Springer 1999, 1, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Lam, M.K.; Lee, K.T. Immobilization as a feasible method to simplify the separation of microalgae from water for biodiesel production. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 191, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benasla, A.; Hausler, R. Growth and production of lipids in Raphidocelis subcapitata immobilized in sodium alginate beads. Energies 2020, 13, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Environnement et changement climatique Canada. Méthode d’essai biologique: Essai d’inhibition de la croissance d’une algue d’eau douce. Available online: https://www.canada.ca/fr/environnement-changement-climatique/services/recherche-faune-science-paysage/publications-methodes-essai-biologique/inhibition-croissance-macroscopique-dulcicole-algue-eau-douce.html#toc23 (accessed on 10 September 2021).
- Santos, M.M.D.; Moreno-Garrido, I.; Gonçalves, F.; Soares, A.M.; Ribeiro, R. An in situ bioassay for estuarine environments using the microalga Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2002, 21, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benasla, A.; Hausler, R. Optimisation of growth of Raphidocelis subcapitata immobilised for biofuel production: Influence of alginate and CaCl2 concentrations on growth. Environments 2018, 5, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Voo, W.-P.; Lee, B.-B.; Idris, A.; Islam, A.; Tey, B.-T.; Chan, E.-S. Production of ultra-high concentration calcium alginate beads with prolonged dissolution profile. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 36687–36695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Río, E.; Armendáriz, A.; García-Gómez, E.; García-González, M.; Guerrero, M.G. Continuous culture methodology for the screening of microalgae for oil. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 195, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richmond, A. Handbook of Microalgal Culture: Biotechnology and Applied Phycology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Clément-Larosière, B. Etude de la Croissance de Chlorella Vulgaris en Photobioréacteur Batch et Continu, en Présence de Concentrations Élevées de CO2. Ph.D. Thesis, Ecole centrale de Paris, Châtenay-Malabry, France, 2012. Available online: https://tel.archives-ouvertes.fr/tel-00697006/document (accessed on 19 September 2021).
- Gonçalves, A.L.; Pires, J.C.; Simões, M. Biotechnological potential of Synechocystis salina co-cultures with selected microalgae and cyanobacteria: Nutrients removal, biomass and lipid production. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 200, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Vooren, G.; Le Grand, F.; Legrand, J.; Cuiné, S.; Peltier, G.; Pruvost, J. Investigation of fatty acids accumulation in Nannochloropsis oculata for biodiesel application. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 124, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alam, M.M.; Mumtaz, A.S.; Russell, M.; Grogger, M.; Veverka, D.; Hallenbeck, P.C. Isolation and Characterization of Microalgae from Diverse Pakistani Habitats: Exploring Third-Generation Biofuel Potential. Energies 2019, 12, 2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shifrin, N.S.; Chisholm, S.W. Phytoplankton Lipids: Interspecific differences and effets of nitrate, silicate and light-dark cycles 1. J. Phycol. 1981, 17, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Sommerfeld, M.; Jarvis, E.; Ghirardi, M.; Posewitz, M.; Seibert, M.; Darzins, A. Microalgal triacylglycerols as feedstocks for biofuel production: Perspectives and advances. Plant J. 2008, 54, 621–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhola, V.; Desikan, R.; Santosh, S.K.; Subburamu, K.; Sanniyasi, E.; Bux, F. Effects of parameters affecting biomass yield and thermal behaviour of Chlorella vulgaris. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2011, 111, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golueke, C.G.; Oswald, W.J.; Gee, H.K. Effect of nitrogen additives on algal yield. J. Water Pollut. Control. Fed. 1967, 39, 823–834. [Google Scholar]
- Go, S.; Lee, S.-J.; Jeong, G.-T.; Kim, S.-K. Factors affecting the growth and the oil accumulation of marine microalgae, Tetraselmis suecica. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2012, 35, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).