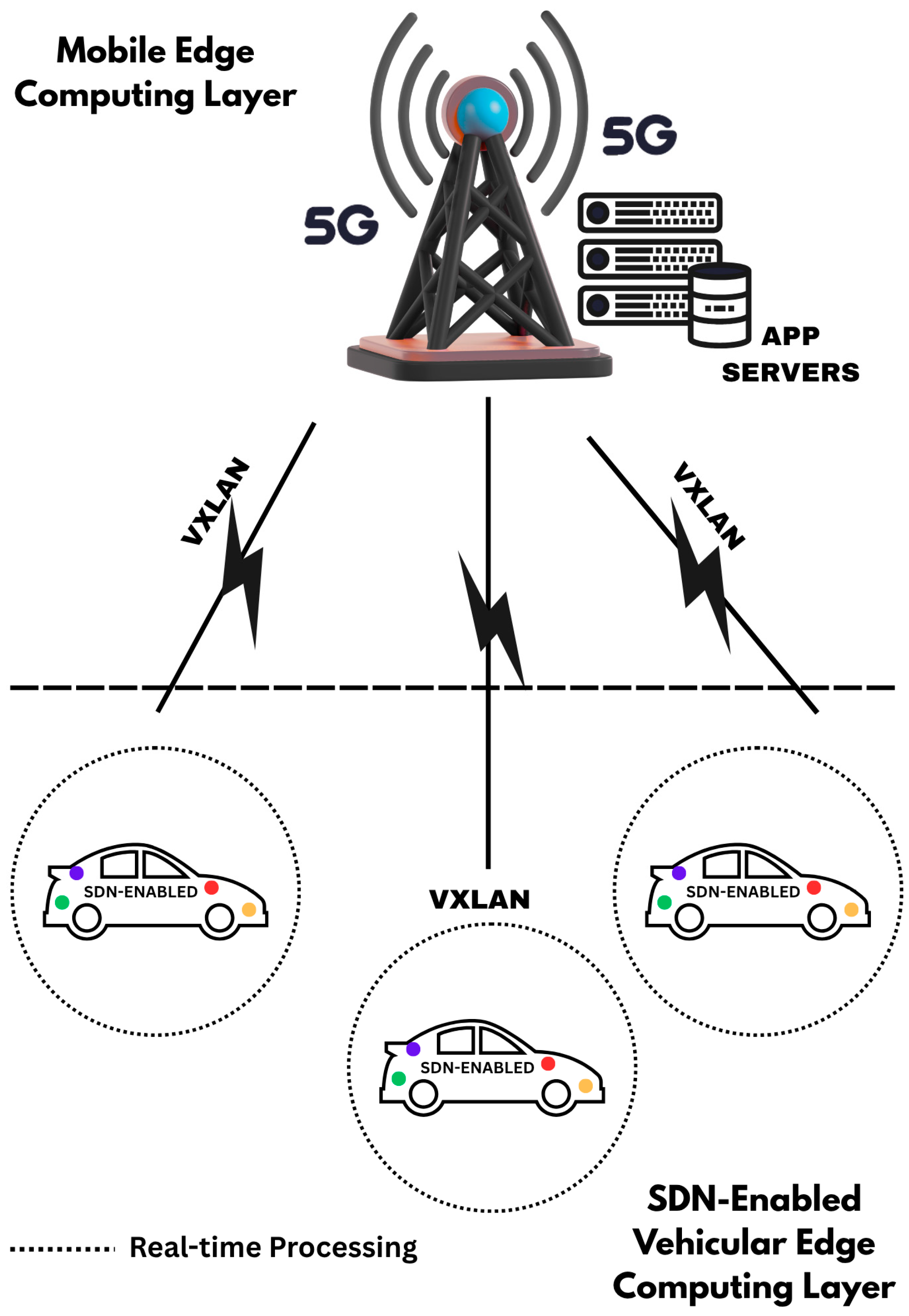
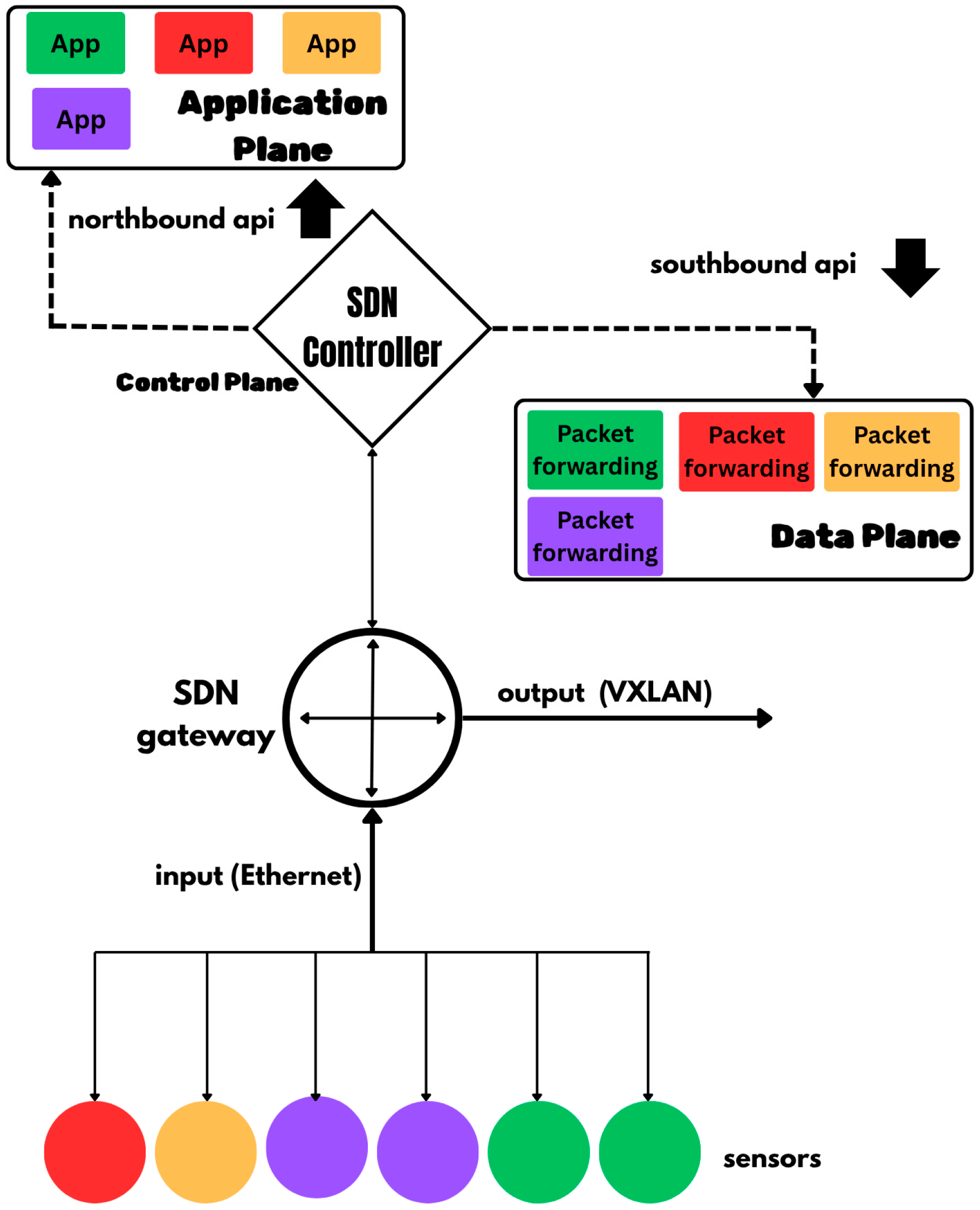
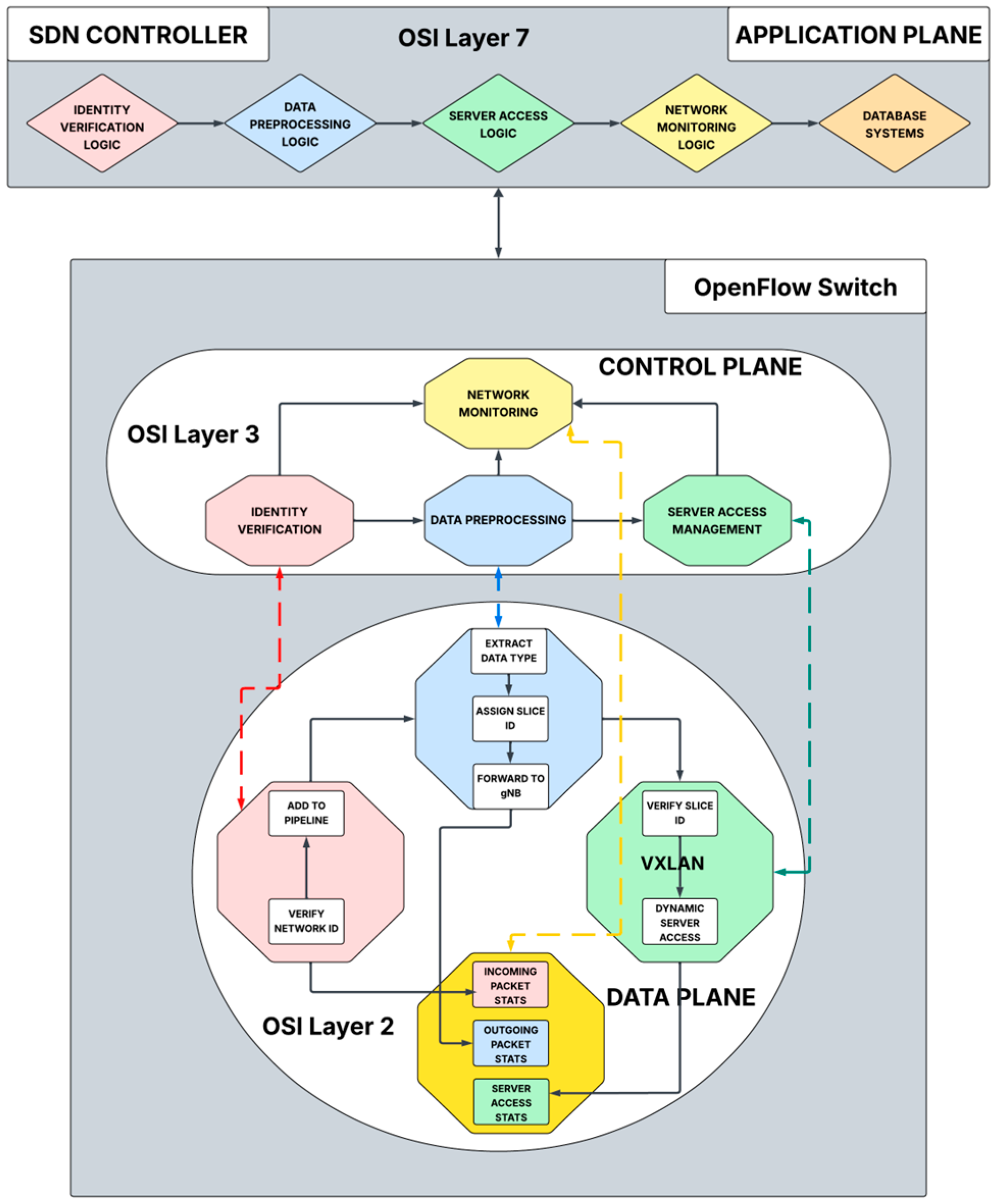
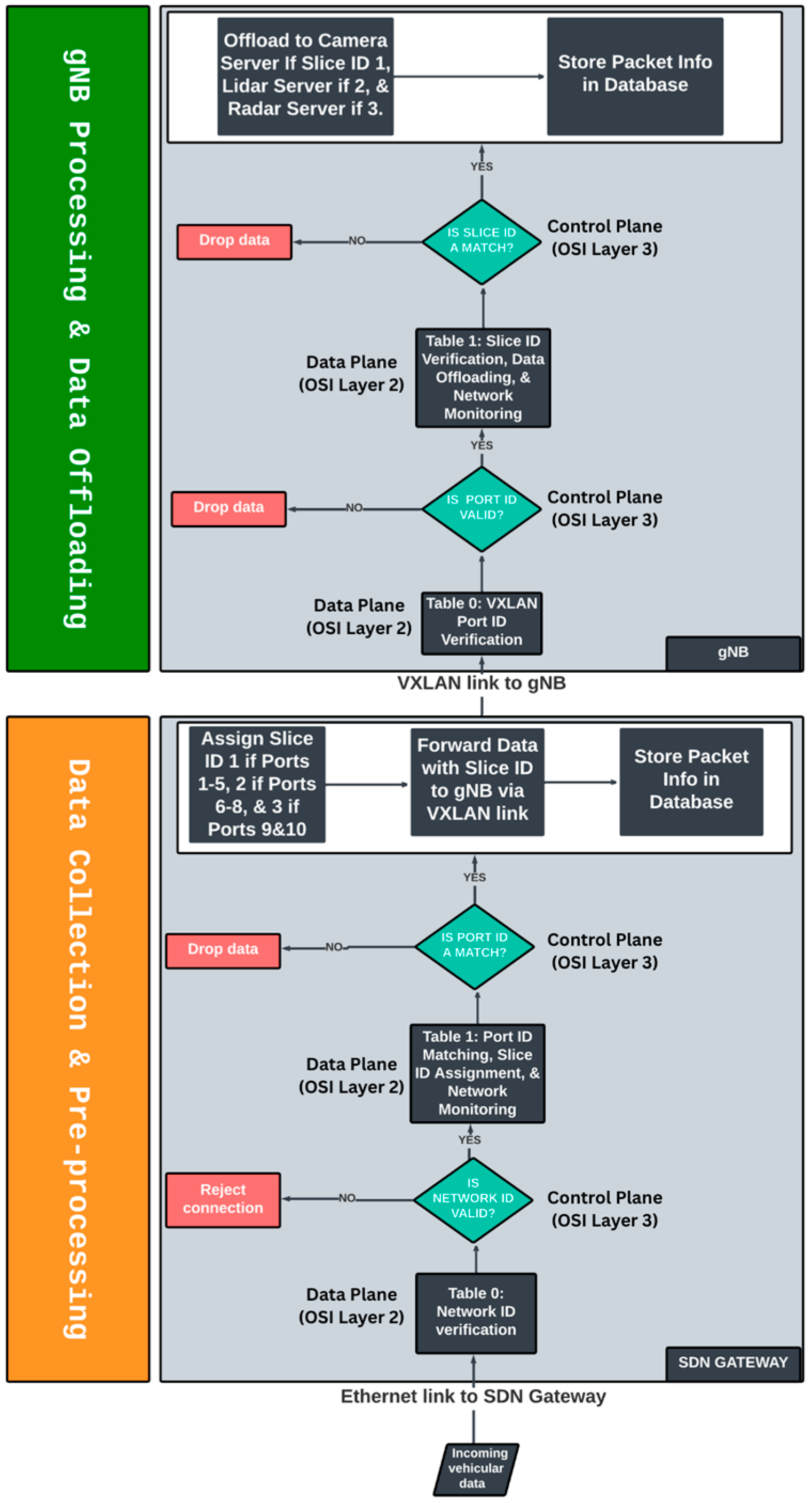
In 5G VANETs, where network resources including hardware and software are distributed across different geographical locations, it is imperative to match vehicular requests to the right resources that can guarantee the required QoS. Furthermore, in a fully virtualised 5G communication infrastructure for critical VANETs applications, where network resources including the virtual Radio Access Network (vRAN) are collectively managed by the SDN Controller, the granular matching of vehicular requests to network functions presents novel opportunities for ensuring optimal QoS for critical operations. The disintegration of the application, control, and user planes in SDN enables the seamless matching of network functions across the three planes.
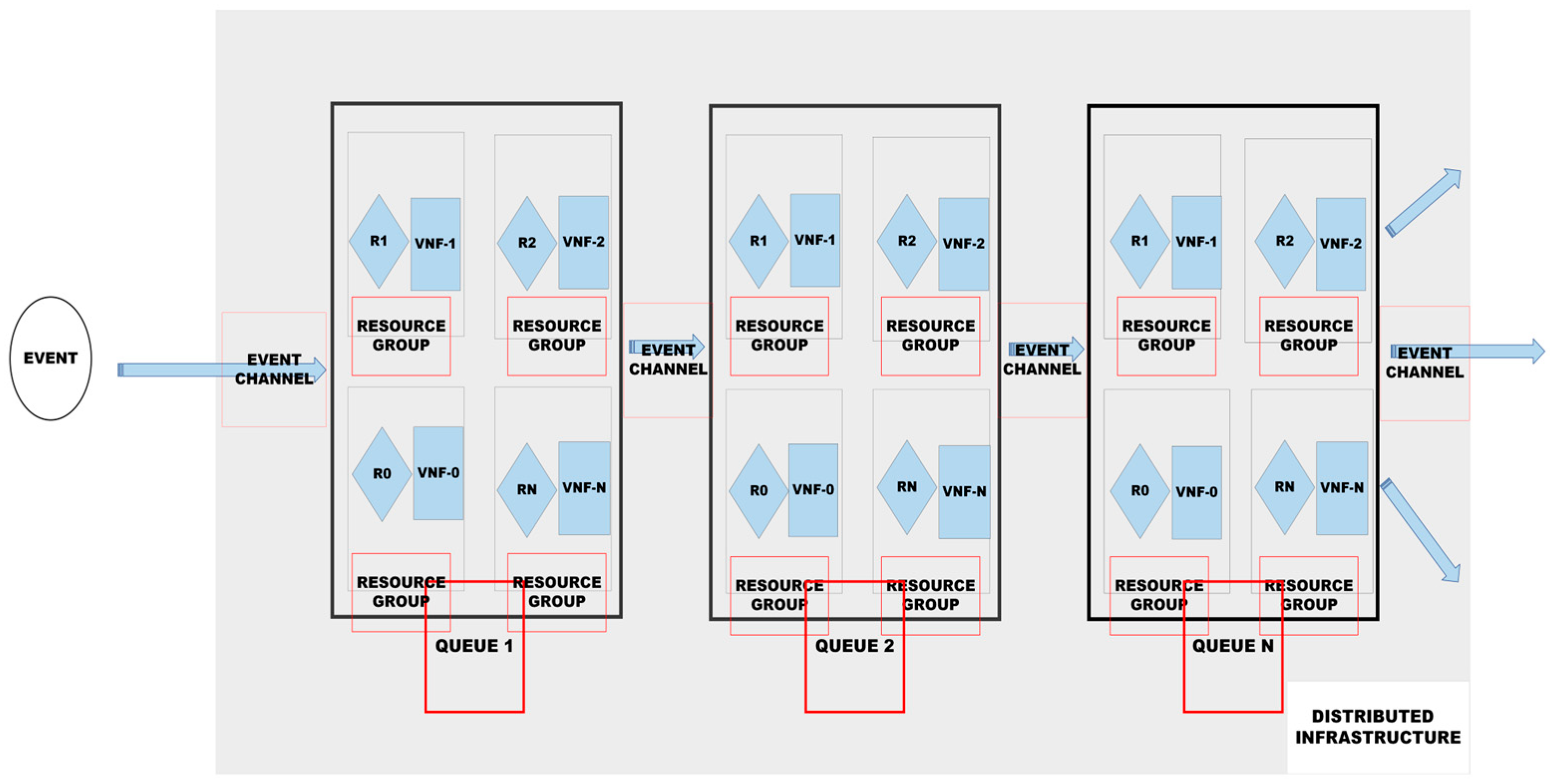
To evaluate the performance of the proposed framework, we applied queueing and delay theories to queue vehicular data (events) across a chain of distributed and virtualised network resources (queues), including communication links. The proposed event-driven multi-queue and delay broker framework (
Figure 12) employs a broker (SDN controller flow rules, R1-RN) to process vehicular data on a chain of queues (VNFs) including the SDN gateway, VXLAN links to gNB, gNB, and links to edge application servers.
Traditionally, VANET frameworks rely on layered communication architectures that apply a fixed set of rules at each layer. This rigid structure limits scalability and dynamic access, making it difficult to achieve optimal QoS in 5G VANETs. In contrast, event-driven software architectures are distributed and asynchronous, offering high scalability and adaptability to single-purpose event-processing components [
21]. Event-driven software models consist of highly decoupled processing units that enable the granular and strategic management of processing units using pre-defined sets of rules.
5.1. Performance Evaluation
We considered M/M/1/K queueing systems where the arrival and services processes are (M)emoryless, there is only one server within a single queue, and K represents the system capacity. Each queue is modelled as a single M/M/1 queue with K capacity. The processing of critical vehicular data, including Camera, LiDAR, and RADAR, with similar QoS requirements but varying transmission rates and packet sizes, creates the problem of service differentiation to ensure optimal QoS. The proposed model follows the FIFO (First-In-First-Out) packet processing methodology.
From our analysis, the management of diverse critical vehicular data on distributed and shared resources creates the problem of longer delays, particularly for sensors with lower transmission rates and packet sizes, like RADAR. Considering the observed results in
Table 1, where the arrival rates are consistently equivalent to the service rates observed at the SDN gateway and VXLAN link to gNB.
The queue-utilisation function
) is approximately equal to 1 across the three tests. This implies that the SDN gateway and VXLAN link to gNB were operating at full utilisation across the three tests. The arrival rate at the gNB is the rate on VXLAN links. Therefore, the relatively higher service rates observed at the gNB (as illustrated in
Table 2) indicate
< 1 at the gNB for all test scenarios.
At the gNB, the system utilisation increased by a small margin between test 1 and test 3 (as illustrated in
Table 3), possibly due to increasing arrival rates. However, the maximum utilisation (
) of approximately 36% suggests that the gNB is far from full utilisation. For queueing systems with finite capacity,
K is the maximum number of packets that can be in the system. Calculating the average number of packets in the system and the waiting time often involves state probabilities and considering the probability of packet loss due to full utilisation. Assuming a
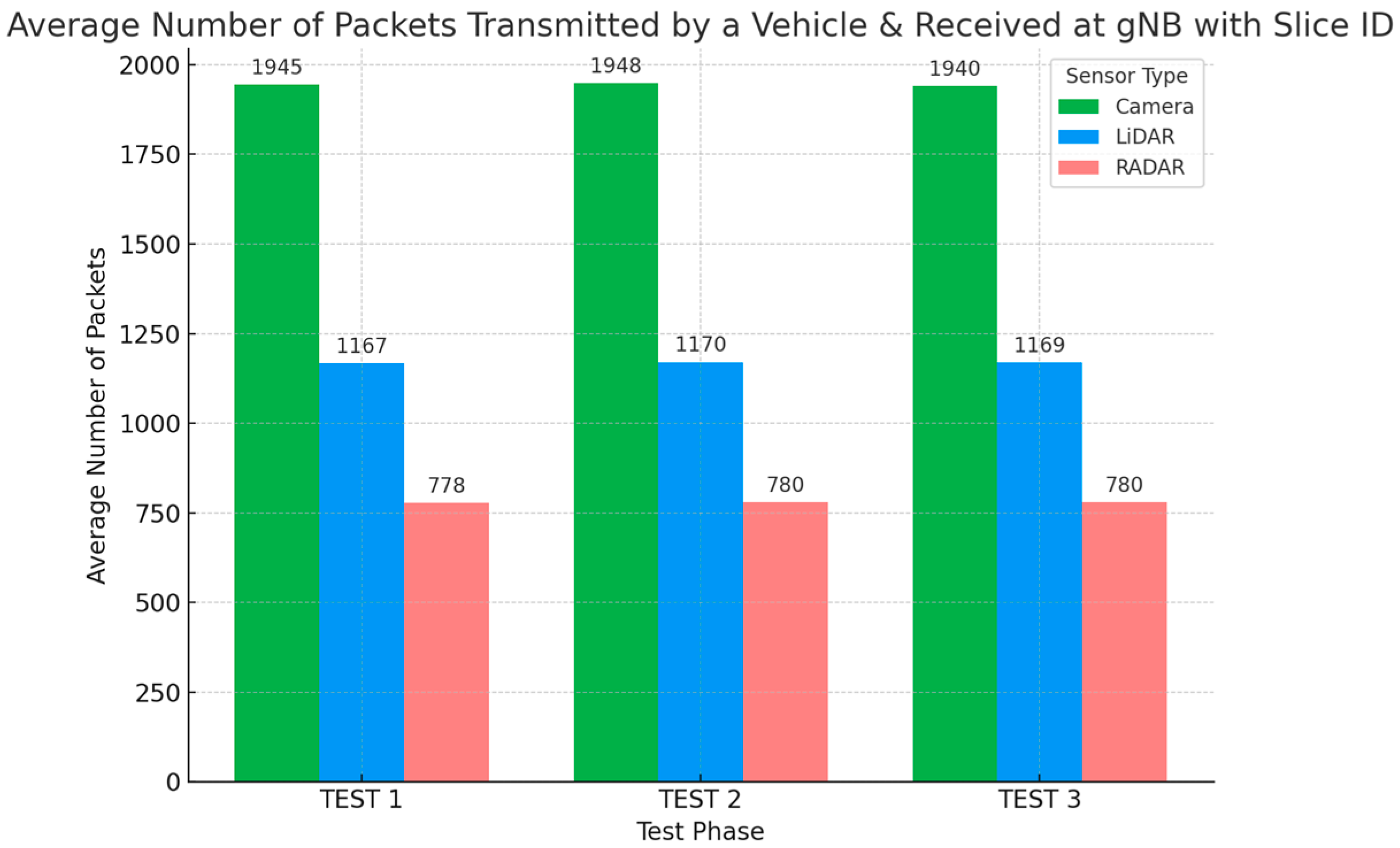
K of 1940, 1169, and 780 for Camera, LiDAR, and RADAR, respectively, during the third test (as illustrated in
Table 4), we can calculate the probability of the system being full
P(K) when
= 1 as follows:
where
K is the number of packets the system can hold, excluding the one currently being served. The probabilities that the system is full for the Camera, LiDAR, and RADAR queues formed in the system are therefore approximately 0.0005%, 0.0009%, and 0.0013%, respectively, during the third test. These low probabilities imply that even though the SDN gateway and VXLAN links currently operate at near full utility, it is unlikely that their performance will deteriorate under the current system dynamics.
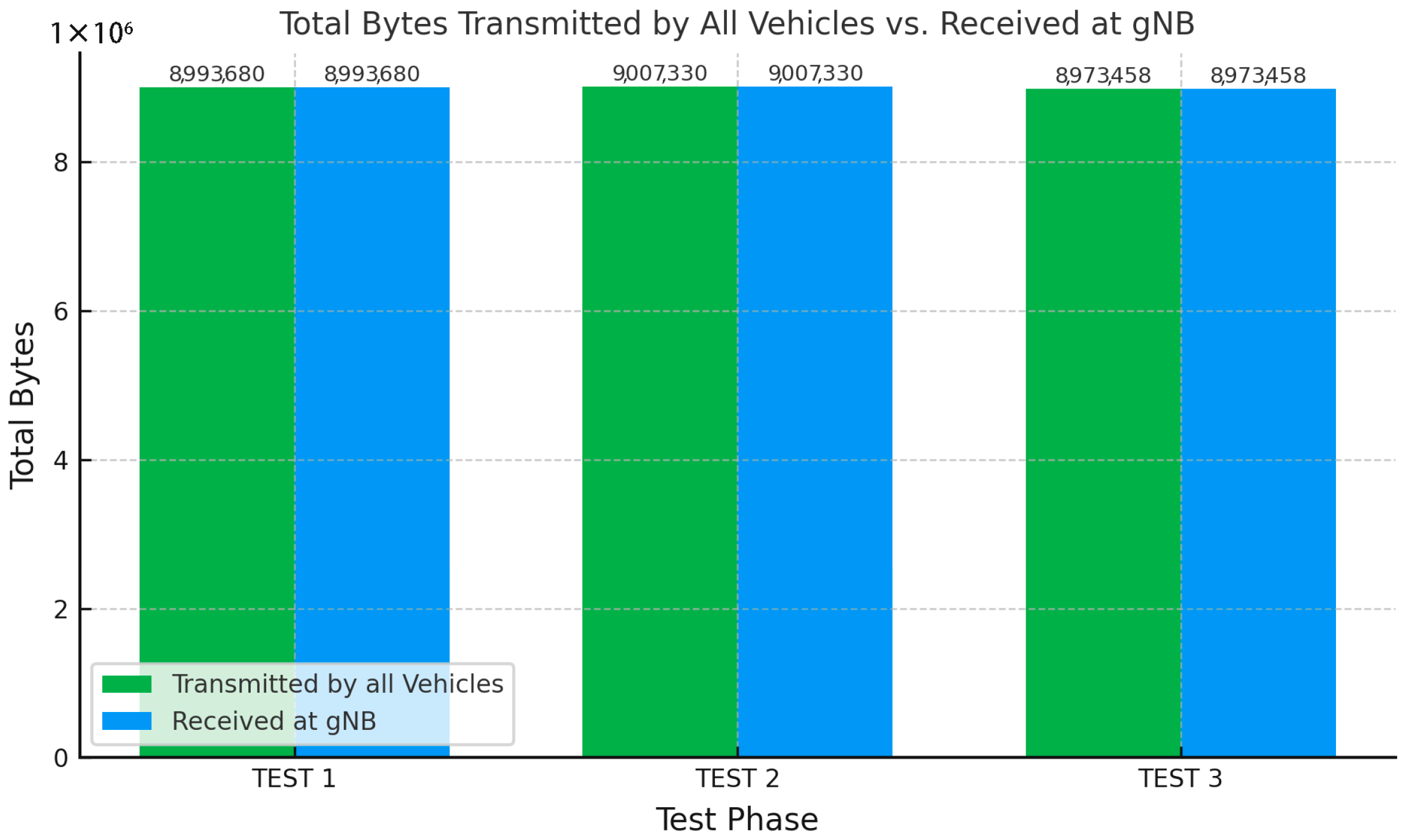
Taking into consideration the above low probabilities and the 100% packet delivery rate observed across all tests, we can assume that the current capacity
K is the average number of packets processed in a queue (
Lq). Therefore, the average waiting time for a packet in a queue (
Wq) is as follows:
Assume
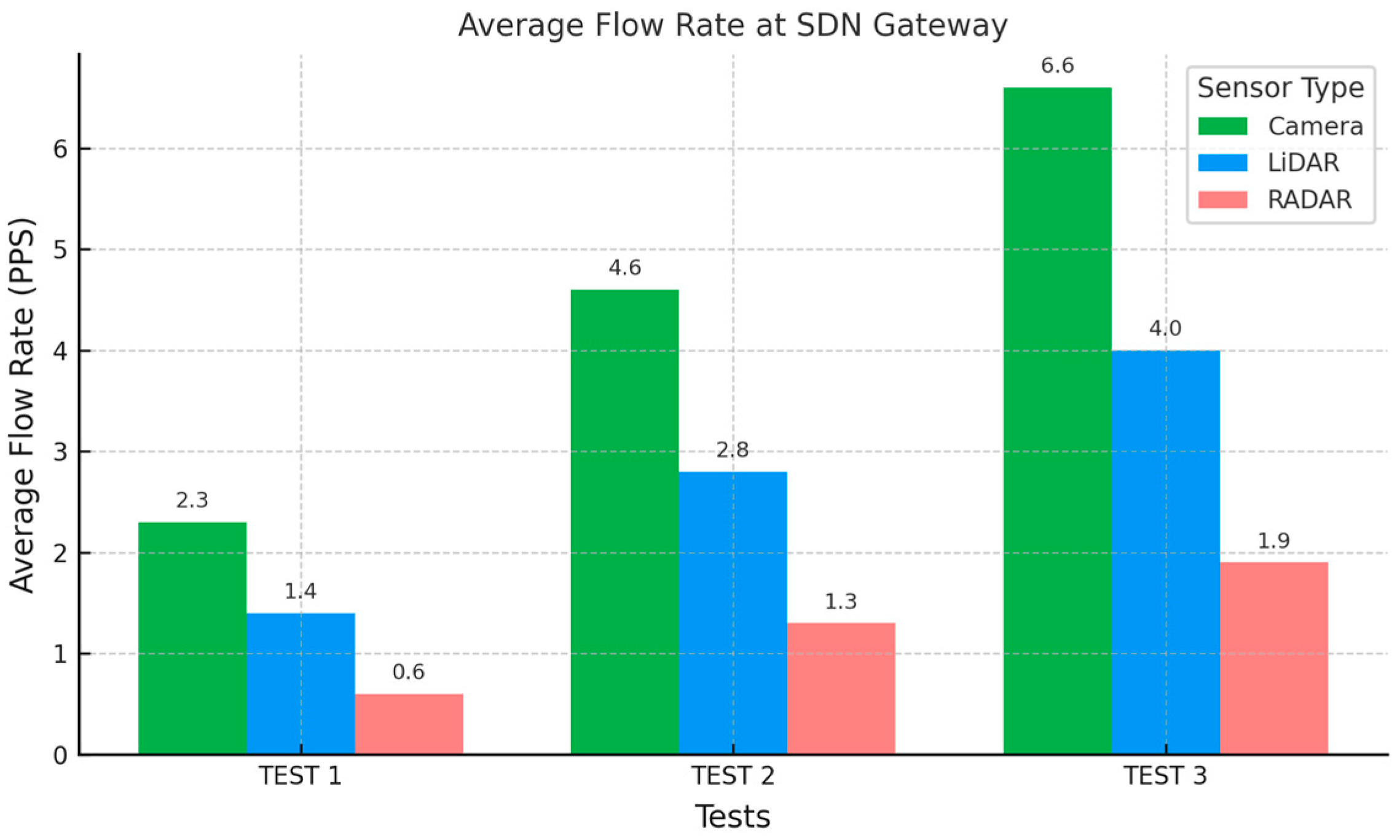
Lq is 1940, 1169, and 780 for the arrival rates (
) of 6.6, 4.0, and 1.9, respectively, observed for Camera, LiDAR, and RADAR sensors at the SDN gateway during the third test.
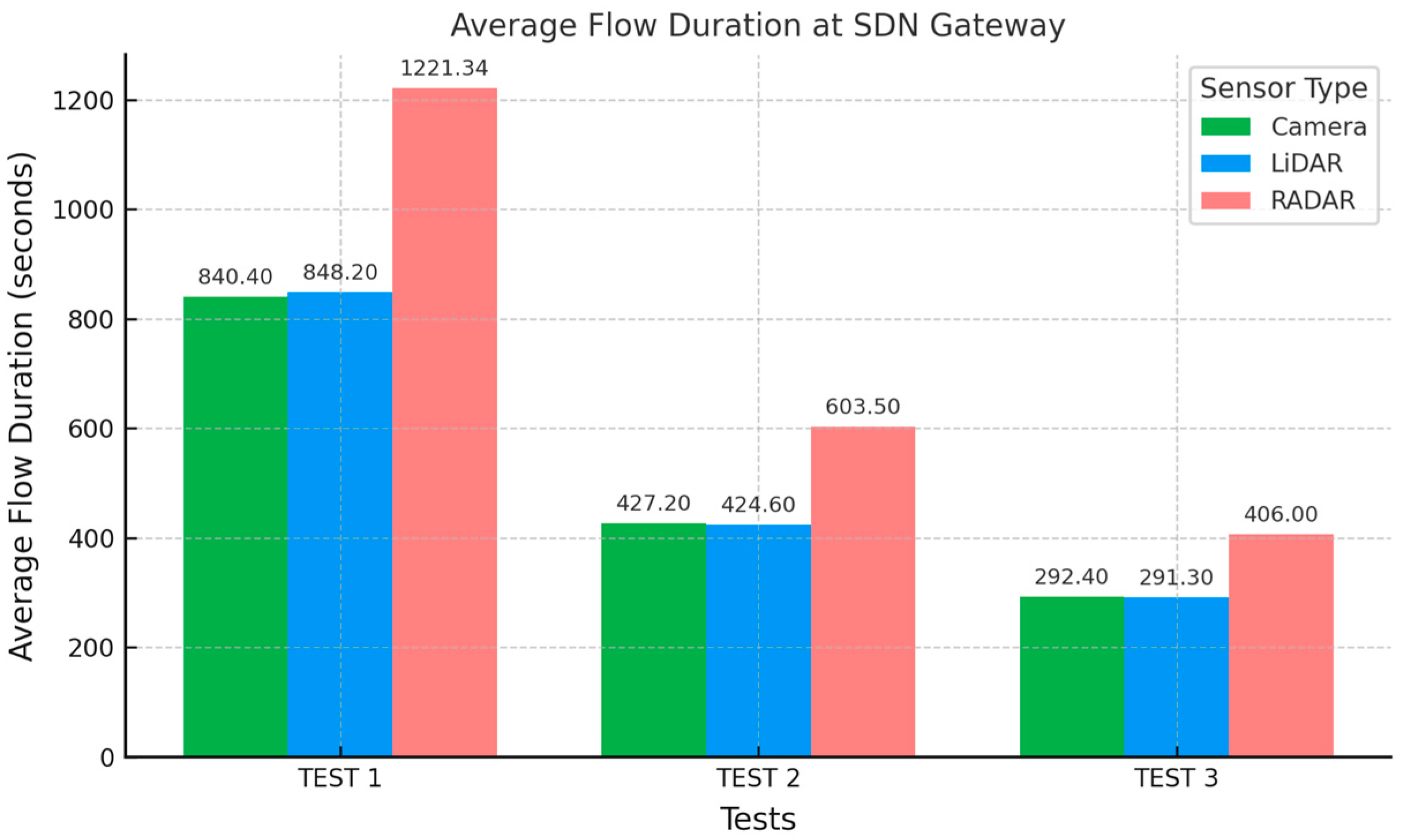
Wq is approximately 294, 292.3, and 410.5 s, respectively (as illustrated in
Table 5). This is the total time taken (average flow duration) by the SDN gateway to pre-process and transmit all vehicular traffic to the gNB for dynamic offloading.
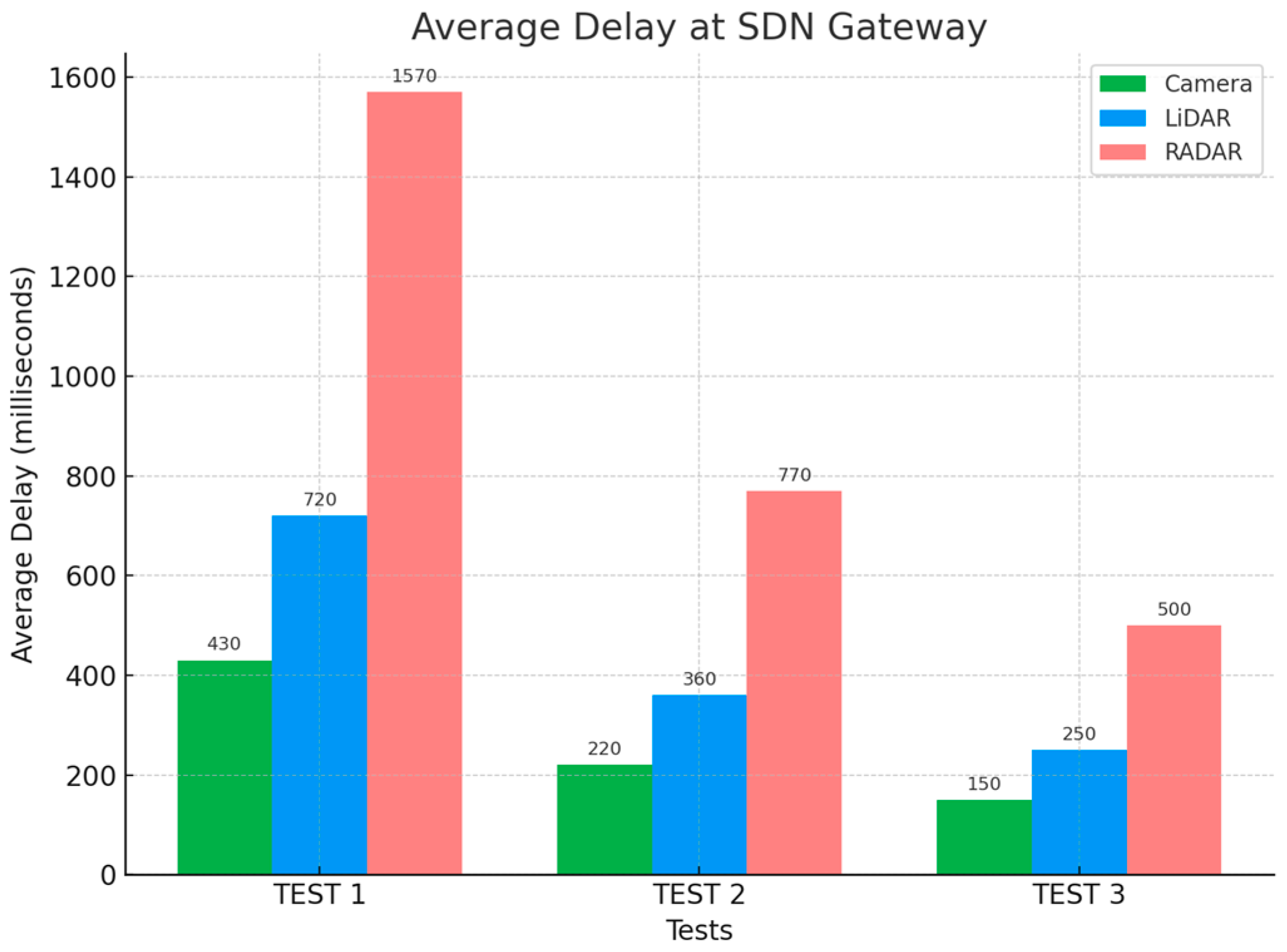
Using the equation below, the average delay (
Li) at the SDN gateway is approximately 0.15, 0.25, and 0.5 s/packet, respectively, during the third test. This implies an average delay per packet of approximately 150, 250, and 500 milliseconds, respectively, for Camera, LiDAR, and RADAR sensors at the SDN gateway (as illustrated in
Table 6). This corresponds with the observed delay per packet observed during our simulations.
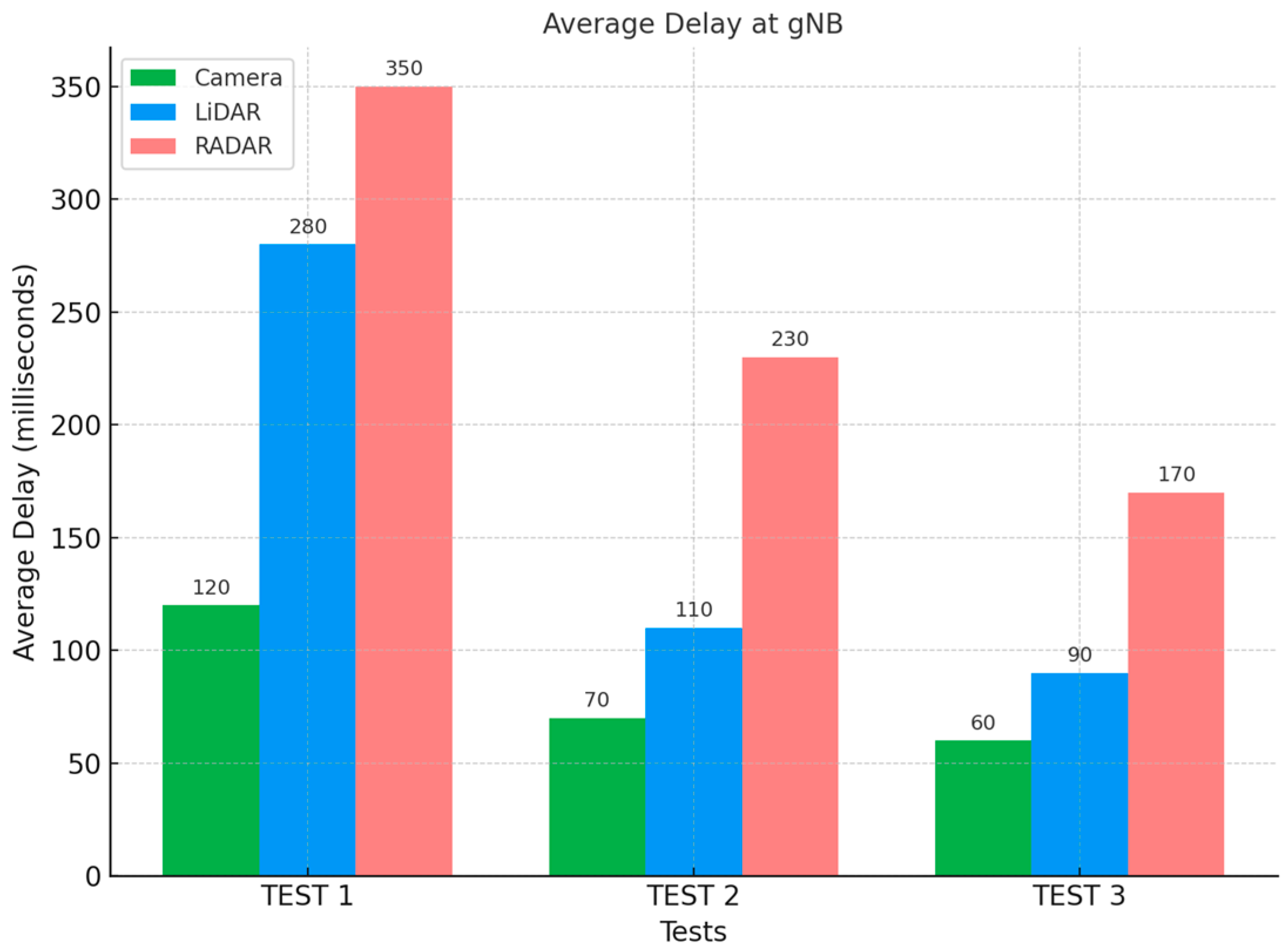
Applying the same formula and considering the average number of packets offloaded at the gNB for all four vehicles (as illustrated in
Table 7) and the average delay observed at gNB during offloading (as illustrated in
Table 8), the average delay per packet (
Li) at the gNB during the third test is approximately 60, 90, and 170 milliseconds for Camera, LiDAR, and RADAR sensors, respectively (as illustrated in
Table 9).
The overall delay per packet for pre-processing vehicular traffic at the SDN gateway, using vehicle on-board resources and dynamically offloading to edge application servers during the third test phase, where the best overall performance was observed, is approximately 210, 340, and 670 milliseconds for Camera, LiDAR, and RADAR, respectively (as illustrated in
Table 10).
5.2. Comparative Analysis
The proposed framework demonstrated superior performance across multiple metrics when compared to existing frameworks in the literature. Notably, it explored interference mitigation via the SDN underlay network, which aligns with the theoretical framework presented in [
12]. In comparison to the SDN overlay model proposed in [
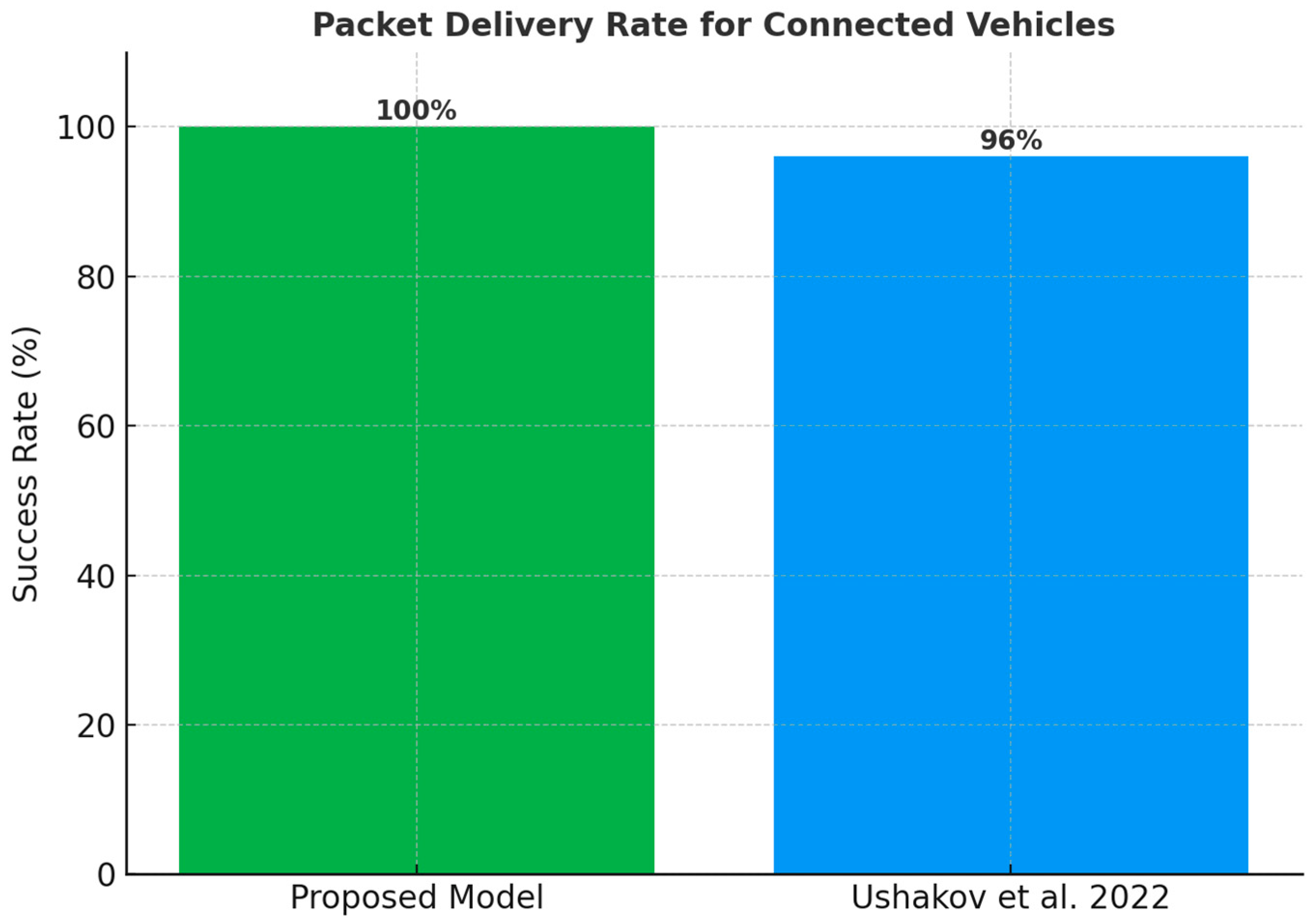
14], which achieved a maximum packet delivery rate of approximately 96% and dropped to as low as 81% under some test conditions, our framework consistently achieved 100% packet delivery rate across all tests (
Figure 13). This confirms its enhanced reliability. In terms of resource management, the proposed framework also performed better than the RAN slicing model proposed in [
22], which supported only two classes of IoT—massive IoT and URLLC. Unlike [
22], our framework provides more granular classification for critical vehicular data types within the URLLC class. At an average flow rate of 2.3, 1.4, and 0.6 PPS for Camera, LiDAR, and RADAR sensors, respectively, our framework maintained a system utilisation of approximately 1; in contrast, they reported less efficient system utilisation values of 1.3, 1.4, and 1.5 at the same flow rates. In addition, our in-vehicle traffic classification model achieved 100% accuracy, outperforming the in-network ML classifier proposed in [
23], which reported an average accuracy of 93.5%. Furthermore, it exceeded Deep Learning (DL) models, Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM), Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), and Deep Neural Network (DNN) when applied for flow-based classification in [
18] (
Figure 14). Whilst AI models offer significant flexibility for dynamic network management in next-generation networks, we recommend that such approaches are reserved for complex, multi-factor resource management tasks. Fundamental network operations, such as traffic classification, can be handled more efficiently using pro-active SDN controller algorithms (as demonstrated in this study) or direct configuration on OpenFlow switches.