Abstract
The essence of the stochastic processes behind the empirical data on infection and fatality during pandemics is the complex interdependence between biological and social factors. Their balance can be checked on the data of new virus outbreaks, where the population is unprepared to fight the viral biology and social measures and healthcare systems adjust with a delay. Using a complex systems perspective, we combine network mapping with K-means clustering and multifractal detrended fluctuations analysis to identify typical trends in fatality rate data. We analyse global data of (normalised) fatality time series recorded during the first two years of the recent pandemic caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 as an appropriate example. Our results reveal six clusters with robust patterns of mortality progression that represent specific adaptations to prevailing biological factors. They make up two significant groups that coincide with the topological communities of the correlation network, with stabilising (group g1) and continuously increasing rates (group g2). Strong cyclic trends and multifractal small-scale fluctuations around them characterise these patterns. The rigorous analysis and the proposed methodology shed more light on the complex nonlinear shapes of the pandemic’s main characteristic curves, which have been discussed extensively in the literature regarding the global infectious diseases that have affected humanity throughout its history. In addition to better pandemic preparedness in the future, the presented methodology can also help to differentiate and predict other trends in pandemics, such as fatality rates, caused simultaneously by different viruses in particular geographic locations.
1. Introduction
Preventing mortality among infected individuals is one of the critical goals in combating pandemics [1] and other high-health-risk situations. Long-term pandemic control and management is another feature that rose to prominence during the COVID-19 pandemic and will be necessary for years to come [2]. While, now, there is a greater appreciation of the role of social, environmental, and biological factors in shaping the dynamics of infection, the likelihood of disease and mortality rates during pandemics throughout human history (see, e.g., Refs. [3,4] and references therein), a rigorous quantitative analysis of these factors’ intrinsic interactions is still visibly lacking [5,6]. Thus, understanding the big picture behind the underlying stochastic processes of infection progression [7] and the impact of fatality resulting during such events and post-infection [8] is vital. In contrast to many other stochastic processes in physics, biology and society, the evolution of epidemics occurs at the interplay of crucial biological and social factors, which are governed by their own (natural) laws. Consequently, the analysis of infectious diseases comprises data at multiple scales, from bio-molecular to global social dynamics, thus making epidemic data rather specific [9] in the era of big data science. In this respect, theoretical concepts developed in complex systems physics can help to recognise properties that emerge at a larger scale [10,11]. In particular, collective dynamic effects occurring in the nonlinear systems under different constraints, driving modes and self-organisation often lead to certain regularities and typical patterns that can be revealed using a complex systems perspective in analysing pertinent empirical data. This work tackles these issues by appropriately analysing global fatality data collected during the first two years of the recent pandemic caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 as a suitable example. (For a recent review on the progress in biomedical research, challenges, diagnostic tools and treatments, see [12] and the annual review article collection [13] for the year 2022).
Regarding the data analysis and modelling of epidemic processes, different approaches are employed depending on specific goals; see a recent overview of models in Ref. [14]. Innovative integrations of methodologies in data analysis are developed—for example, for data clustering [15,16,17], applying systems biology approaches [18] similar to coarse-grained gene expression data along the cell cycle [19], ideas of phase synchronisation [20] and others. In addition, the epidemic modelling and simulations have two primary goals. On one hand, model calibration is used for predictions and practical purposes—for example, to help immediate healthcare measures and assess applied policies [21,22,23,24,25] or to measure economic impacts and socioeconomic consequences [26,27,28,29,30]. More generally, the theoretical line of research by advanced mathematical modelling and theoretical concepts strives to understand the nature of processes and identify specific universal growth signatures [31] underlying epidemic progression and its outcomes. In this context, agent-based modelling enables the adequate inclusion of both biological and social factors through the specific features of viruses and agents’ susceptibility in the model, driven by realistic agents’ activity levels motivated, for example, by transportation and other general needs [32,33] or the prevention of economic damage [34]. (A theoretical overview of economic agents’ behaviours during the recent pandemic can be found in [35]). Another striking feature of such processes is the occurrence of epidemic cycles. Global data analysis of infection rates shows recurrent infection waves that characterise individual countries and survive as a dominant feature of the coarse-grained communities consisting of countries at different geographic locations [36]. Similar waves, on different time scales, characterise earlier epidemic outbreaks—for example, influenza cycles [37] and others. Different theoretical approaches have attempted to model the emergence of epidemic cycles—for example, incorporating certain agent-based features [38] or spatial locality [39] into compartmental models, using reaction-diffusion processes to describe cholera cycles [40] or other “nonstandard” models for the influenza virus cycles [41]. The phenomenology behind these irregular cycles consists of persistent spreading based on the virus biology on one side and human reactions that grow from recognising individual threats to collective behaviour on the other [42]. Naturally, human perceptions of threats differ when the infection cycle grows, increasing the mortality rates in the human population [43], and, when a process is at its bottom, releasing the threat. The natural human reactions in both cases can be further influenced by different local measures, economic security, collective information, the properties of the healthcare system and other factors characteristic of a given location. Recently, while analysing data on online social dynamics with emotional content [44], we have shown that ubiquitous cycles in human dynamics appear based on the natural activity day–night cycle, which is modified mainly by the self-organised collective dynamics. However, a larger time scale characterises the epidemic cycles, which suggests the dominant role of the virus features (infectiveness, virulence, incubation time) and human–virus interactions enabled by social dynamics.
In this work, we use a complex systems perspective to analyse fatality data to reveal potential universal patterns that emerge at the interplay of these biological factors and human dynamics. As a representative example, we download global data on fatality caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 recorded in different countries during the first two years of the pandemic. With network mapping combined with K-means clustering, we could detect six robust clusters with similar fatality rates belonging to two major groups (constantly increasing and stabilising mortality). Each cluster is characterised by its cyclical trend and the multifractal features of the fluctuations around these trends. The identified cyclical trends and the multifractality measures of these clusters suggest six prototypal patterns that the global human population adapts to the prevailing biology factors; meanwhile, additional social efforts lead to minor corrections captured by the features of multifractality spectra. The presented methodology applies to similar epidemiology data caused by different virus strains and time scales and can help to construct the appropriate models.
2. Structure of Infection and Fatality Rate Time Series
Considering a single country, a typical fatality rate time series exhibits cycles mainly induced by primary cycles in the infection rate time series. To elucidate their sequences, here, we show an example of the recorded infection and fatality rates in Serbia; the data are available at https://github.com/CSSEGISandData/COVID-19/ (accessed 19 January 2023). These time series for the entire period of the pandemic are shown in Figure 1a, together with the corresponding cyclical trends. We calculate the cross-correlation between signals and representing the cycles of fatality and infection rates, respectively. The cycle signal for the number of infected is divided by 100, so it has the same scale as . The cross-correlation as a function of time lag d is shown in Figure 1b; the cycle for the number of fatalities is following the infection cycle, with pronounced similarities between them occurring at . The highest cross-correlation appears for time lag .
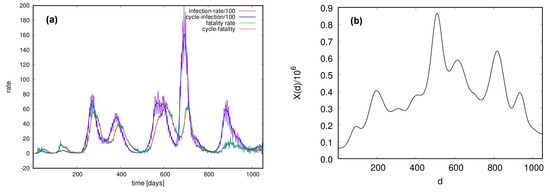
Figure 1.
(a) The infection rate (divided by 100) and fatality rate of COVID-19 in Serbia during the pandemic. Waves in the fatality rate are closely related to the infection cycle. Cyclical trends of both time series, indicated by thick lines, are determined; see text. (b) Cross-correlation between the infection and fatality cycles as a function of time lag d.
Cyclical trends are determined by applying the local adaptive algorithm with overlapping time intervals [44,45,46]. The time series of the total length is divided into overlapping segments of length , which overlap over points. These segments are enumerated as ; the polynomial fits over points in each segment are determined. Then, balancing the contribution of the polynomial in segment k with the one of segment , the local trend over the overlapping points is determined; here, and . Thus, the contribution of the fitted polynomial to the trend in the overlapped region decreases linearly with the distance from the segment’s centre. This rule excludes the initial points in and the final points in where the trend coincides with the actual polynomial fit.
As Figure 1 shows, both time series exhibit cyclical trends that are slightly delayed in the fatality time series. Moreover, it is worth noting the relative height of the fatality time series compared to 1% of the respective infection series (close to the estimated natural fatality for the considered virus strain [47]). In this example, we note that in the first and second infection waves, the fatality rate exceeds the margin of 1%, progressively lowering and stabilising to a low value over time. A similar feature was detected in data from several other countries, in contrast to a continuous increase in fatality rates (in the considered period) recorded in several other countries. These features of the recorded time series of individual countries will influence the appearance of universal patterns, as shown in the following.
3. Finding Typical Fatality Rates in Global Data
Data. We downloaded the publicly available data on the number of fatalities for 265 countries and regions from https://github.com/CSSEGISandData/COVID-19/ (accessed 24 March 2022). The period is approximately two years, i.e., from the day of the first registered casualty, which is different for each country or region, until 24 March 2022. However, the number of time series is significantly shorter. For these reasons, we select countries and regions with a length of at least 500 days, i.e., 228 time series. The shortest time series has a length of 511 days. Thus, we cut all other time series to 511 days starting from their beginning. Moreover, a considerable number of time series out of 228 selected ones have a large number of days with zero casualties; they are less suitable for analysis, and thus we choose ones with at least 60% non-zero entries. In the end, we have a set of 96 different time series with a length of 511 days.
Methodology overview. To find patterns of similar fatality rates in the above-described data, we first normalise these fatality time series of different countries to the equal range . The methodology consists of mapping these normalised time series onto a correlation network by a well-established procedure [48,49,50], where nodes represent different time series (i.e., countries), and the links between them are correlation coefficients that exceed a given threshold, as described below. The next step is finding the topologically distinct communities [51] on the network. These are the groups of nodes that have more connections with the nodes inside the group than with the nodes outside it; in the present context, a node within a given community has a correlation coefficient above the threshold with a more significant number of nodes within the same community than with the nodes belonging to different communities. To identify these communities, we use the Laplacian operator’s eigenvector localisation [52,53]. Then, the time series within each community are further partitioned according to the time series similarity by applying the appropriate K-means clustering algorithms [54]. The centroids of these identified clusters are then analysed using detrended multifractal methods [55,56,57]. A more detailed description of each step is given below regarding the results.
3.1. The Correlation Network and Its Communities
The selected set of suitable time series are mapped to the correlation network; the nodes represent the normalised time series , , where we have ; the links are determined from the Pearson’s correlation coefficients between pairs of time series , i.e., , where and are the average and standard deviation of time series . To enhance the strong positive correlations between time series and remove the false ones, we apply the filtering procedure typically used for this task [48,49,50]. Specifically, we transform each matrix element so that it takes values between by the following formula: . Then, we transform the rows i and j by removing elements and and putting the elements and at the beginning of the rows, respectively. We then calculate the correlation Pearson’s coefficient between rows i and j of the length . The correlation coefficient is positive and has high values for the rows, and thus the time series, that have a similar correlation with the rest of the time series. In contrast, it is close to zero or even negative for the ones that are not correlated similarly. We multiply the transformed correlation coefficient with to obtain filtered correlation matrix , i.e., . The elements of the filtered correlation matrix take values between and 1; see Figure 2a.
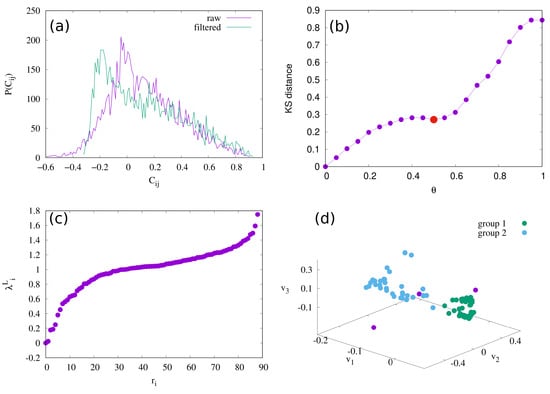
Figure 2.
(a) Probability density distribution of correlation coefficients and filtered correlation coefficient ; (b) dependence of KS distance on threshold value ; (c) eigenvalue spectrum; and (d) scatter plot of the eigenvectors of the three smallest non-zero eigenvalues of the normalized Laplacian (1).
The elements of the adjacency matrix of this undirected unweighted correlation network are defined as when , and zero otherwise. The threshold parameter is determined based on the spectral properties of the two cut matrices and . In particular, we calculate the eigenvalue problem of the matrices for values of with step and determine the Kolmogorov–Smirnov (KS) distance between the spectra of each of these matrices and the spectrum of matrix ; see Figure 2b. A non-zero value of for which we observe a local minimum of the KS distance curve—here, , indicated by the red dot in Figure 2b—is elected as a suitable threshold.
We use the spectral method to obtain the community structure of the network. Previous research [52,53] has shown that the number of smallest non-zero eigenvalues of the Laplacian matrix is a good indicator of the number of communities. Here, we use the spectral properties of the normalised Laplacian to find the community structure. The elements of normalised Laplacian are calculated using the following formula
where is the element adjacency matrix and and are the number of links (degrees) of the nodes i and j. We solve the eigenvalue problem of the normalised Laplacian given in Equation (1), , and obtain eigenvalues and eigenvectors with of the normalised Laplacian. If a network is connected, the normalised Laplacian has one zero eigenvalue with the eigenvector that has all positive components [52]. Meanwhile, the eigenvectors corresponding to the smallest non-zero eigenvalues are orthogonal and localised to the network communities; see Figure 2c. The scatter plot of these three eigenvectors, where each point represents one node in the network, exhibits a branchlike structure with branches corresponding to communities [53]. As shown in Figure 2d, we identify two large communities, here termed group g1 and group g2, containing 97.6% of all time series to be considered in the following, and the remaining small fraction, 2.4%, corresponding to the third eigenvalue.
3.2. Clustering of Time Series within Communities
To further explore the clustering of the time series, we use the implementation of the K-means algorithm for the clustering of time series in Python, known as tslearn [54]. The K-means algorithm represents a standard procedure for data clustering. The algorithm aggregates data points in n dimensions according to their similarities measured by distance metrics. The algorithm starts with K randomly positioned centroids. A data point is assigned to a centroid whose centre is the closest to it according to the distance metric. After the initial grouping of points into K clusters, the new positions or centroids of these K clusters are calculated. The described procedures are repeated in several iterative steps until the optimal positions of centroids are found. In this case, a time series of the length N is considered a data point in the dimension . We use the Dynamic Time Wrapping (DTW) algorithm to calculate the distances between pairs of time series. DTW is widely used for time series comparison and classification. Unlike the Euclidean distance, which only allows comparison between time series of the same length and only considers the distance between the entries at the same position of the two analysed time series, DTW allows the comparison of time series of different lengths and considering the series that are only slightly similar. DTW gives the optimal alignment between two time series by matching the indices from the first to the second time series by considering several constraints. Specifically, the mapping of indices from the first series to the second series must be monotonically increasing. For the two indices i and j from the first time series with , there must be two indices from the second series l and k with such that i is matched with l and j is matched with k. The first and last indices from these time series match with each other. However, these indices may have more other matches. The optimal alignment is the one that satisfies all of these restrictions with a minimal cost, where the cost is the sum of the absolute differences in values for each matched pair of indices. The cost function of the DTW algorithm is the metric distance used to measure the similarity between time series in the K-means algorithm.
We use the silhouette coefficient to determine the optimal number of clusters. The silhouette coefficient, or silhouette score, is a metric used to measure the goodness of clustering. It takes values between and 1, where 1 means that the found clusters are well separated, 0 means that the distance between clusters is not significant, and means that the clusters are assigned in incorrectly. The silhouette value of a data point i is given by , where is the average distance of point i from all other points in the cluster to which point i is assigned, and is the minimal distance between point i and all other nodes that do not belong to the same cluster as point i. The silhouette coefficient for a given number of clusters K is the maximum value of for all data points. The silhouette coefficient is a function of K and has a maximum for the optimal value of K. Figure 3 shows vs. K for the considered sets of time series belonging to the above-determined two groups. In both groups, the maximum of occurs at , which indicates the optimal partitioning of each group into three distinct clusters.
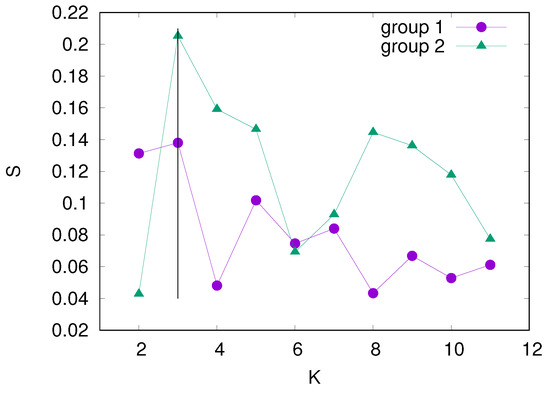
Figure 3.
Silhouette coefficient S vs. the number of clusters K in two groups of time series, described in the text. The vertical line at indicates the optimal partitioning of each group into three clusters.
The typical series, as centroids of each cluster identified by K-means, are depicted in Figure 4 as the black line in each panel. The determined cyclical trends are shown as a red line; meanwhile, the green line represents the corresponding fluctuations around the trend. Notably, these identified typical fatality rates differ in their cyclical trends and the structure of the fluctuations around them, as shown in the next section. The significant difference between the clusters belonging to the two groups is that, in the group , the cycles are superimposed onto an overall increasing trend, as shown in the three panels on the right side of Figure 4. Meanwhile, the centroids comprising the group , shown on the left panels of Figure 4, exhibit a decreasing or stabilising trend behind the pronounced cycles. The multifractal analysis of the fluctuations around these cyclical trends reveals certain similarities across the clusters, as shown in the following section.
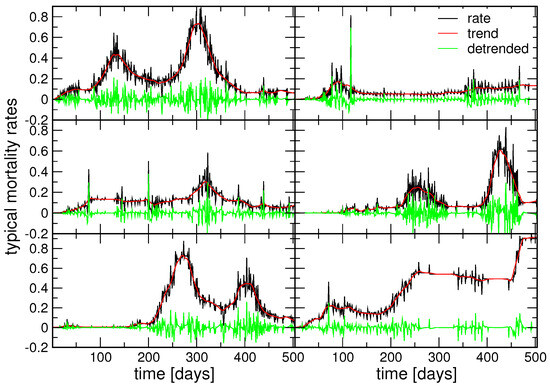
Figure 4.
Six typical fatality rate time series, centroids, shown by black lines, their cyclic trends in red, and fluctuations around cycles in green, for three clusters of the groups g1 (left) and g2 (right); top to bottom panels: g1c1 (25.8%), g1c2 (11.2%), g1c3 (20.2%) for group g1, and similarly g2c1 (10.1%), g2c2 (25.8%), g2c3 (4.5%) for g2; the fraction of time series belonging to the cluster is given in the brackets.
4. Multifractal Fluctuations around Typical Cycles
We use the detrended multifractal analysis of time series [55,56,57] to compute the generalised fluctuation function for varied segment length n. The methodology consists of constructing the profile of the series , which is then divided into segments of length n, starting from the beginning and repeating from the end of the time series ; in total, the number of segments is .
Then, the local trend is determined at each segment by polynomial fitting; the standard deviation around is computed, and, similarly, for . The generalised fluctuation function for the segment length n is obtained as
where and different positive and negative values of the exponent are used. The generalised Hurst exponent , defined in Equation (2), is extracted by fitting the power-law regions on the lines for different q; in the case of monofractality, all lines are parallel, leading to a single exponent coinciding with the standard Hurst exponent for all q values. From the spectrum of the generalised Hurst exponents, we determine other multifractality measures using theoretical relationships [55]—in particular, the exponent related to the box probability measure, . Then, the singularity spectrum is obtained, where . Thus [55,56], represents the fractal dimension of the time series points that have the singularity exponent , according to at different data points t.
Considering the fluctuations around cyclical trends for these six centroids, we determine the fluctuation function vs. time interval n, defined in Equation (2), and extract its apparent scaling properties to determine the spectrum of generalised Hurst exponents for a range of values of q. As stated above, in the case , the function describes the standard deviations with the common Hurst exponent . In Figure 5, we first show that for the cycles with an ascending trend, in the case of the cluster g2c3, the standard Hurst exponent , and the fluctuation function is monofractal. Similarly, this applies to the trends of other centroids in the group g2; meanwhile, is found for the strongly irregular cycles in the centroids of g1; see the inset in Figure 5. The multifractal measures of the fluctuations around these cycles are discussed in the following; see Figure 6 and Figure 7.
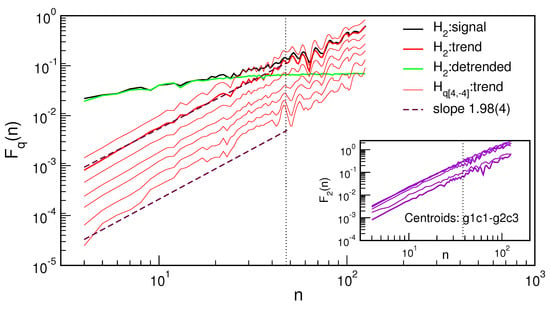
Figure 5.
Fluctuation function vs. time interval length n for the ascending trend (red lines) of the centroid g2c3, indicating its monofractality; for the standard deviation case, also shown are the corresponding lines for the whole signal (black) and the detrended signal (green), which saturates at . Inset: standard deviation function vs. n for trends of all six centroids.
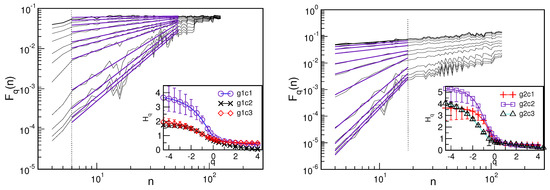
Figure 6.
The function vs. n for different q for the fluctuations around cyclical trends for two representative cases with a diverse range of scales indicated by thick purple lines: g1c2 (main panel left) and g2c2 (right). Insets show the spectrum of generalised Hurst exponents vs. q for three clusters in each group, as indicated in the legend.
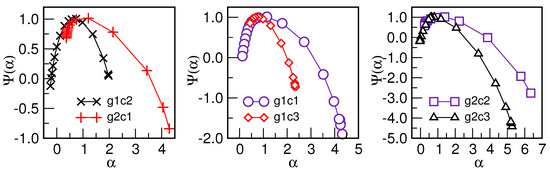
Figure 7.
Singularity spectrum vs. for detrended fluctuations in six centroids; the legend in each panel indicates two centroids where the spectra show certain similarities in the large-scale fluctuations (left side of the spectra); meanwhile, they differ significantly in the small-scale fluctuations, depicted on the right side of the spectra.
In Figure 6, we show the fluctuation function vs. n for two representative cases, indicating different ranges of time scales where multifractality occurs—in particular, a broad range , as for the cluster g1c2, and a narrow range , as for the case g2c2. The corresponding spectra of the generalised Hurst exponents for all clusters are given in the insets, as indicated in the legend. They differ significantly for , corresponding to small-scale fluctuations, whereas they have similar values for , indicating similarity in the large-scale fluctuations. These features are further demonstrated in the corresponding singularity spectra vs. , shown in Figure 7. They are grouped into pairs according to the overlapping in the left parts of the spectra (i.e., large-scale fluctuations). Notably, significant differences occur on the right side of the spectra, which are the critical differences between these pairs of patterns.
5. Discussion and Conclusions
With the complex systems perspective of data analysis, we have shown how to identify specific universal patterns that describe the typical evolution of fatality rates during epidemics. The methodology includes mapping the source time series data onto a correlation network and detecting its topological communities as sets of data with similar correlations; the subsequent partitioning of these sets into clusters with similar temporal behaviour is achieved by the K-means clustering of time series. Finally, the typical time series (centroids) of the identified clusters are characterised by detecting the trends and performing a multifractal analysis of the time series.
The methodology is demonstrated using the available global data on fatality rates caused by COVID-19. The data are properly normalised for the present analysis. In this case, we have identified and characterised six different patterns. The occurrence of irregular cycles is a prominent feature of all identified patterns. In three clusters, comprising group 2, these cycles are superimposed onto overall increasing trends; meanwhile, decreasing or stationary trends apply to the patterns in group 1. The occurrence of cyclical trends in the fatality time series in the data for individual countries can be related to similar waves in the infection rate time series; we have demonstrated this by considering an example, shown in Figure 1, which shows how the infection waves induce oscillations in the fatality time series with the same cycle duration but a changing height over time. The infection waves are understood as a result of the interplay of nonlinear dynamics governing the virus–host biology and the adaptation of social behaviours that can affect infection progression. Beyond the waves, the differences between the number of infections and fatalities indicate that several other factors play a role in the medical treatment of infected individuals.
The well-pronounced sequences of waves appearing in the clusters’ centroids characterise groups of different countries with similar epidemic progression. Fluctuations around these dominant cyclical trends are multifractal; the corresponding singularity spectra differ between the clusters, particularly at the side describing the small-scale changes. Moreover, the clusters with well-pronounced waves exhibit multifractality in a short time interval days; meanwhile, a milder cyclic trend occurring in two centroids (one in each group) allows for multifractality in a broader time scale of days, suggesting potentially different mechanisms behind the small-scale fluctuations.
Based on the complex systems perspective of data analysis, our approach identifies universal patterns of mortality progression that reveal the crucial role of biosocial processes giving rise to dominant cycles and additional factors leading to multifractal fluctuations around them. In this way, it complements other, more standard methods of time series clustering. These findings shed new light on the underlying stochastic processes leading to the observed global empirical data and can help to develop appropriate models and predict outcomes. The presented methodology can be applied to analyse the proper data for epidemics caused by other pathogens. Given the option to keep the identity of the input data as the network nodes, one can use it to identify clusters with different trends, such as fatality rates, related to different virus types simultaneously present in epidemics at a particular geographical location. Furthermore, our results may encourage more investigations on the (dis)similarities between the countries that make up each defined cluster by considering other types of data—for example, on economic development or adapted policies and other pandemic drivers [58]—to assess their potential in shaping the pattern of mortality rates. Finally, the analysis of biosocial interdependence via the technique presented here should assist in developing prevention strategies and contribute to better preparedness for possible pandemic outbreaks in the future.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.T., M.M.D. and R.M.; methodology and software, M.M.D. and B.T.; validation, B.T., M.M.D. and R.M.; formal analysis and visualization, M.M.D. and B.T.; writing—original draft preparation, B.T.; writing—review and editing, R.M., M.M.D. and B.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Slovenian Research Agency under the program P1-0044. M.M.D. acknowledges funding provided by the Institute of Physics Belgrade, through the grant by the Ministry of Science, Technological Development and Innovation of the Republic of Serbia. Numerical simulations were run on the PARADOX-IV supercomputing facility at the Scientific Computing Laboratory, National Center of Excellence for the Study of Complex Systems, Institute of Physics Belgrade. R.M. is grateful to the NSERC and the CRC Program for their support, and he also acknowledges the support of the BERC 2022-2025 program and the Spanish Ministry of Science, Innovation, and Universities through the Agencia Estatal de Investigacion (AEI) BCAM Severo Ochoa excellence accreditation SEV-2017-0718.
Data Availability Statement
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available in the article and provide references and links to the publicly available data used.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Piret, J.; Boivin, G. Pandemics Throughout History. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 631736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contreras, S.; Iftekhar, E.N.; Priesemann, V. From emergency response to long-term management: The many faces of the endemic state of COVID-19. Lancet Reg. Health 2023, 30, 100664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wissler, A.; DeWitte, S.N. Frailty and survival in the 1918 influenza pandemic. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2304545120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T. The socioeconomic and environmental drivers of the COVID-19 pandemic: A review. Ambio 2021, 50, 822–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, E.T.; Barrie, M.B.; Kelly, J.D.; Dibba, Y.; Koedoyoma, S.; Farmer, P.E. Biosocial Approaches to the 2013–2016 Ebola Pandemic. Health Hum. Rights 2016, 18, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fronteira, I.; Sidat, M.; Magalhães, J.P.; de Barros, F.P.C.; Delgado, A.P.; Correia, T.; Daniel-Ribeiro, C.T.; Ferrinho, P. The SARS-CoV-2 pandemic: A syndemic perspective. ONE Health 2021, 12, 100228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilic, B.; Salom, I.; Djordjevic, M.; Djordjevic, M. An analytical framework for understanding infection progression under social mitigation measures. Nonlinear Dyn. 2023, s11071, 08692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad-Roy, C.M.; Levin, S.A.; Grenfell, B.T.; Boots, M. Epidemiological impacts of post-infection mortality. Proc. R. Soc. B 2023, 290, 20230343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasson, P.M. Infectious disease research in the era of big data. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Data Sci. 2020, 3, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadić, B.; Melnik, R. Self-organised critical dynamics as a key to fundamental features of complexity in physical, biological, and social networks. Dynamics 2021, 1, 181–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, J.; Bauer, S.; Contreras, S.; Fleddermann, L.; Parlitz, U.; Priesemann, V. Societal feedback induces complex and chaotic dynamics in endemic infectious diseases. MedRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, H.E.; McCorkell, L.; Vogel, J.M.; Topol, E.J. Long covid: Major findings, mechanisms and recommendations. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annual Reviews Artice Collection Corrona Virus Reasearch. Available online: https://www.annualreviews.org/page/corona-virus-research (accessed on 31 October 2023).
- Zhang, W.; Liu, S.; Osgood, N.; Zhu, H.; Qian, Y.; Jia, P. Using simulation modelling and systems science to help contain COVID-19: A systematic review. Syst. Res. Behav. Sci. 2023, 40, 207–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilbeigipour, S.; Albadvi, A.; Akhondzadeh Noughabi, E. Cluster-based analysis of COVID-19 cases using self-organizing map neural network and k-means methods to improve medical decision-making. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2022, 32, 101005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohari, K.; Kazemnejad, A.; Sheidaei, A.; Hajari, S. Clustering of countries according to the COVID-19 incidence and mortality rates. BMC Public Health 2022, 12, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Zhang, L.; Liu, N.; Wu, Y. Time series clustering of COVID-19 pandemic-related data. Data Sci. Manag. 2023, 6, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djordjevic, M.; Rodic, A.; Salom, I.; Zigic, D.; Milicevic, O.; Ilic, B.; Djordjevic, M. A systems biology approach to COVID-19 progression in population. Adv. Protein Chem. Struct. Biol. 2021, 127, 291–314. [Google Scholar]
- Živković, J.; Tadić, B.; Wick, N.; Thurner, S. Statistical indicators of collective behavior and functional clusters in gene networks of yeast. Eur. Phys. J. -Condens. Matter Complex Syst. 2006, 50, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Borrego-Salcido, C.; Juarez-Del-Toro, R.; Fonseca-Zendejas, A.S. The waves and cycles of COVID-19 pandemic: A phase synchronization approach. Austrian J. Stat. 2023, 52, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Li, M.; Haimabo, N.; Babuna, P.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, X.; Jaeger, C.; Li, Y.; Yang, S. Mechanisms of recurrent outbreak of COVID-19: A model-based study. Nonlinear Dyn. 2021, 106, 1169–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido, J.M.; Martínez-Rodríguez, D.; Rodríguez-Serrano, F.; Pérez-Villares, J.M.; Ferreiro-Marzal, A.; Jiménez-Quintana, M.M.; Villanueva, R.J. Mathematical model optimized for prediction and health care planning for COVID-19. Med. Intensiv. 2022, 46, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haug, N.; Geyrhofer, L.; Londei, A.; Dervic, E.; Desvars-Larrive, A.; Loreto, V.; Pinior, B.; Thurner, S.; Klimek, P. Ranking the effectiveness of worldwide COVID-19 government interventions. Nat. Hum. Behav. 2020, 4, 1303–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgos, C.; Cortes, J.C.; Pinto, C.; Villanueva, R.J. Computing the probability density function of a random compartmental model to describe the dynamics of hiv. Application to real-world data. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Fractional Differentiation and Its Applications (ICFDA), Ajman, United Arab Emirates, 14–16 March 2023; p. 10153250. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Q.; Heydari, B. Micro-level social structures and the success of COVID-19 national policies. Nat. Comput. Sci. 2022, 2, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.K.; Machalaba, C.C.; Seifman, R.; Feferholtz, Y.; Karesh, W.B. Infectious disease and economics: The case for considering multi-sectorial impact. ONE Health 2019, 7, 100080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamelund, S.-E.; Shelley-Egan, C.; Rogeberg, O. The association between socioeconomic status and pandemic influenza: Systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0244346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goenka, A.; Liu, L. Infectious deseases, human capital and economic growth. Econ. Theory 2020, 70, 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COVID-19 Socio-Economic Impact, United Nations Development Programme. Available online: https://www.undp.org/coronavirus/socio-economic-impact-covid-19 (accessed on 26 October 2023).
- Tang, J.W.; Caniza, M.A.; Dinn, M.; Dwyer, D.E.; Heraud, J.M.; Jennings, L.C.; Kok, J.; Kwok, K.O.; Li, Y.; Loh, T.P.; et al. An exploration of the political, social, economic and cultural factors affecting how different global regions reacted to the COVID-19 pandemic. Interface Focus 2022, 12, 20210079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djordjevic, M.; Djordjevic, M.; Ilic, B.; Stojku, S.; Salom, I. Understanding infection progression under strong control measures through universal COVID-19 growth signatures. Glob. Chall. 2021, 5, 2000101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadić, B.; Melnik, R. Modeling latent infection transmissions through biosocial stochastic dynamics. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0241163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadić, B.; Melnik, R. Microscopic dynamics modeling unravels the role of asymptomatic virus carriers in SARS-CoV-2 epidemics at the interplay between biological and social factors. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 133, 104422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kano, T.; Yasui, K.; Mikami, T.; Asally, M.; Ishiguro, A. An agent-based model of the interrelation between the COVID-19 outbreak and economic activities. Proceed. Roy Soc. A 2020, 477, 20200604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jemli, R.; Chtourou, N. Economic Agents’ Behaviors during the Coronavirus Pandemic: Theoretical Overview and Prospective Approach. J. Knowl. Econ. 2022, s13132, 01027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadić, B.; Dankulov, M.M.; Melnik, R. Analysis of worldwide time-series data reveals some universal patterns of evolution of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic. Front. Phys. 2022, 10, 936618. [Google Scholar]
- Juanico, D.E.O. Recurrent epidemic cycles driven by intervention in a population of two susceptibility types. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2014, 490, 012188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkachenko, A.V.; Maslov, S.; Wang, T.; Elbana, A.; Wong, G.N.; Goldenfeld, N. Stochastic social behavior coupled to COVID-19 dynamics leads to waves, plateaus, and an endemic state. eLife 2021, 10, e68341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gostiaux, L.; Bos, W.J.T.; Bertoglio, J.-P. Periodic epidemic outbursts explained by local saturation of clusters. Phys. Rev. E 2023, 107, L012201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wu, G.; Wang, X.; Feng, Z. Dynamics of a reaction-advection-diffusion model for cholera transmission with human behavior change. J. Differ. Equ. 2023, 373, 176–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jódar, L.; Villanueva, R.J.; Arenas, A.J.; González, G.C. Nonstandard numerical methods for a mathematical model for influenza disease. Math. Comput. Simul. 2008, 79, 622–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S. Newblock The Psychology of Pandemics. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 2022, 18, 581–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Msemburi, W.; Karlinsky, A.; Knutson, V.; Aleshin-Guendel, S.; Chatterji, S.; Wakefield, J. The WHO estimates of excess mortality associated with the COVID-19 pandemic. Nature 2023, 613, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadić, B.; Dankulov, M.M.; Melnik, R. Evolving cycles and self-organised criticality in social dynamics. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2023, 171, 113459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Gao, J.; Wang, X. Multifractal analysis of sunspot time series: The effects of the 11-year cycle and fourier truncation. J. Stat. Mech. Theory Exp. 2009, 2009, P02066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šuvakov, M.; Mitrović, M.; Gligorijević, V.; Tadić, B. How the online social networks are used: Dialogues-based structure of myspace. J. R. Soc. Interface 2013, 10, 20120819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alimohamadi, Y.; Tola, H.H.; Abbasi-Ghahramanloo, A.; Janani, M.; Sepandi, M. Case fatality rate of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Prev. Med. Hyg. 2021, 62, E311. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tadić, B.; Mitrović, M. Jamming and correlation patterns in traffic of information on sparse modular networks. Eur. Phys. J. 2009, 71, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruchi, I.; Ben-Jacob, E. Functional holography of recorded neuronal networks activity. Neuroinformatics 2004, 2, 333–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madi, A.; Friedman, Y.; Roth, D.; Regev, T.; Bransburg-Zabary, S.; Jacob, E.B. Genome holography: Deciphering function-form motifs from gene expression data. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorogovtsev, S.N. Lectures on Complex Networks; Oxford Master Series in Statistical, Computational, and Theoretical Physics; Oxford University Press Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Biyikoglu, T.; Leydold, J.; Stadler, P.F. Laplacian Eigenvectors of Graphs: Perron-Frobenius and Faber-Krahn Type Theorems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Mitrović, M.; Tadić, B. Spectral and dynamical properties in classes of sparse networks with mesoscopic inhomogeneities. Phys. Rev. E 2009, 80, 026123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavenard, R.; Faouzi, J.; Vandewiele, G.; Divo, F.; Androz, G.; Holtz, C.; Payne, M.; Yurchak, R.; Rußwurm, M.; Kolar, K.; et al. Tslearn, a machine learning toolkit for time series data. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2020, 21, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kantelhardt, J.W.; Zschiegner, S.A.; Koscielny-Bunde, E.; Havlin, S.; Bunde, A.; Stanley, H.E. Multifractal detrended fluctuation analysis of nonstationary time series. Phys. Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2002, 316, 87–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlov, A.N.; Anishchenko, V.S. Multifractal analysis of complex signals. Phys.-Uspekhi 2007, 50, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadić, B. Multifractal analysis of barkhausen noise reveals the dynamic nature of criticality at hysteresis loop. J. Stat. Mech. Theory Exp. 2016, 2016, 063305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djordjević, M.; Salom, I.; Markovic, S.; Rodic, A.; Milicevic, O.; Djordjevic, M. Inferring the Main Drivers of SARS-CoV-2 Global Transmissibility by Feature Selection Methods. GeoHealth 2021, 5, e2021GH000432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).