Surface EMG in Subacute and Chronic Care after Traumatic Spinal Cord Injuries
Abstract
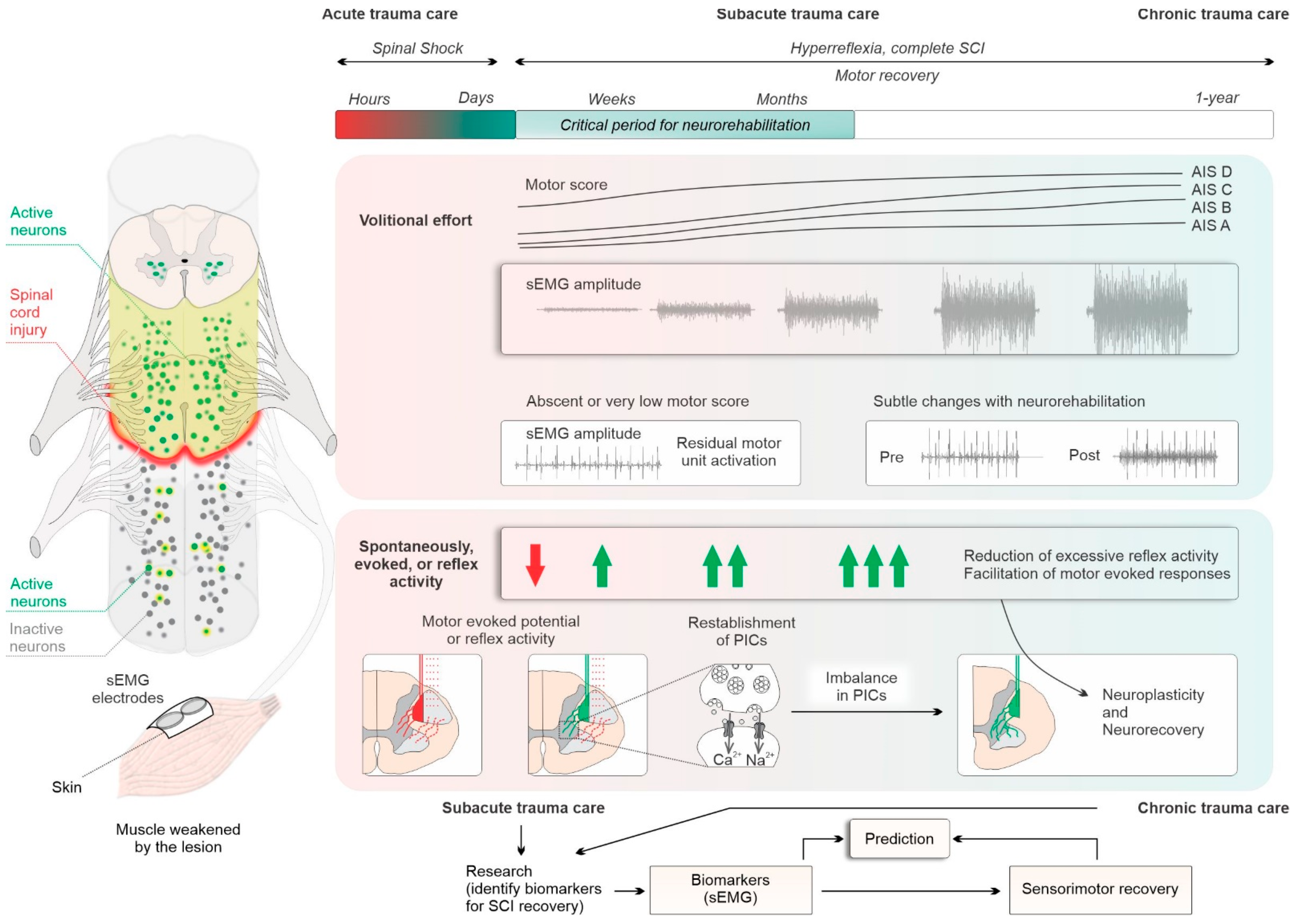
:1. Introduction
2. Subacute Care: Monitoring and Classifying the Lesion Severity and Tracking of the Natural Recovery Process
3. Chronic Care: Tracking Persistent Impairments and the Effects of Neurorehabilitation
4. Future Directions and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Balbinot, G.; Li, G.; Wiest, M.J.; Pakosh, M.; Furlan, J.C.; Kalsi-Ryan, S.; Zariffa, J. Properties of the Surface Electromyogram Following Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury: A Scoping Review. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2021, 18, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ASIA; ISCoS. The 2019 revision of the International Standards for Neurological Classification of Spinal Cord Injury (ISNCSCI)—What’s new? Spinal Cord 2019, 57, 815–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furlan, J.C.; Fehlings, M.G.; Tator, C.H.; Davis, A.M. Motor and sensory assessment of patients in clinical trials for pharmacological therapy of acute spinal cord injury: Psychometric properties of the ASIA standards. J. Neurotrauma 2008, 25, 1273–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furlan, J.C.; Noonan, V.; Singh, A.; Fehlings, M.G. Assessment of impairment in patients with acute traumatic spinal cord injury: A systematic review of the literature. J. Neurotrauma 2011, 28, 1445–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, A.S.; Marino, R.J.; Kalsi-Ryan, S.; Middleton, J.W.; Tetreault, L.A.; Dettori, J.R.; Mihalovich, K.E.; Fehlings, M.G. Type and Timing of Rehabilitation Following Acute and Subacute Spinal Cord Injury: A Systematic Review. Glob. Spine J. 2017, 7 (Suppl. 3), 175S–194S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawcett, J.W.; Curt, A.; Steeves, J.D.; Coleman, W.P.; Tuszynski, M.H.; Lammertse, D.; Bartlett, P.F.; Blight, A.R.; Dietz, V.; Ditunno, J.; et al. Guidelines for the conduct of clinical trials for spinal cord injury as developed by the ICCP panel: Spontaneous recovery after spinal cord injury and statistical power needed for therapeutic clinical trials. Spinal Cord 2007, 45, 190–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steeves, J.D.; Lammertse, D.; Curt, A.; Fawcett, J.W.; Tuszynski, M.H.; Ditunno, J.F.; Ellaway, P.H.; Fehlings, M.G.; Guest, J.D.; Kleitman, N.; et al. Guidelines for the conduct of clinical trials for spinal cord injury (SCI) as developed by the ICCP panel: Clinical trial outcome measures. Spinal Cord 2007, 45, 206–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balbinot, G.; Li, G.; Kalsi-Ryan, S.; Abel, R.; Maier, D.; Kalke, Y.B.; Weidner, N.; Rupp, R.; Schubert, M.; Curt, A.; et al. Segmental Analysis in Cervical Spinal Cord Injury Reveals the Recovery Potential of Hand Muscles with Preserved Corticospinal Tract: Insights beyond Impairment Scales. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korupolu, R.; Stampas, A.; Singh, M.; Zhou, P.; Francisco, G. Electrophysiological Outcome Measures in Spinal Cord Injury Clinical Trials: A Systematic Review. Top. Spinal Cord Inj. Rehabil. 2019, 25, 340–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calancie, B.; Del Rosario Molano, M.; Broton, J.G.; Bean, J.A.; Alexeeva, N. Relationship between EMG and Muscle Force after Spinal Cord Injury. J. Spinal Cord Med. 2001, 24, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merletti, R.; Disselhorst-Klug, C.; Rymer, W.Z.; Campanini, I. (Eds.) Surface Electromyography: Barriers Limiting Widespread Use of sEMG in Clinical Assessment and Neurorehabilitation; Frontiers Media SA: Lausanne, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Balbinot, G.; Wiest, M.J.; Li, G.; Pakosh, M.; Furlan, J.C.; Kalsi-Ryan, S.; Zariffa, J. The Use of Surface EMG in Neurorehabilitation Following Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury: A Scoping Review. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2022, 138, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badhiwala, J.H.; Wilson, J.R.; Witiw, C.D.; Harrop, J.S.; Vaccaro, A.R.; Aarabi, B.; Grossman, R.G.; Geisler, F.H.; Fehlings, M.G. The influence of timing of surgical decompression for acute spinal cord injury: A pooled analysis of individual patient data. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elizei, S.S.; Kwon, B.K. The translational importance of establishing biomarkers of human spinal cord injury. Neural Regen. Res. 2017, 12, 385–388. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, B.K.; Bloom, O.; Wang, K.K.; Armin, I.W.; Jan, C. Neurochemical biomarkers in spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 2019, 57, 819–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leister, I.; Haider, T.; Mattiassich, G.; Kramer, J.L.; Linde, L.D.; Pajalic, A.; Grassner, L.; Altendorfer, B.; Resch, H.; Aschauer-Wallner, S.; et al. Biomarkers in Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury—Technical and Clinical Considerations: A Systematic Review. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2020, 34, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chay, W.; Kirshblum, S. Predicting Outcomes after Spinal Cord Injury. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 31, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorasanizadeh, M.; Yousefifard, M.; Eskian, M.; Lu, Y.; Chalangari, M.; Harrop, J.S.; Jazayeri, S.B.; Seyedpour, S.; Khodaei, B.; Hosseini, M.; et al. Neurological recovery following traumatic spinal cord injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2019, 30, 683–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirshblum, S.; Schmidt Read, M.; Rupp, R. Classification challenges of the 2019 revised International Standards for Neurological Classification of Spinal Cord Injury (ISNCSCI). Spinal Cord 2021, 60, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaja, B.N.R.; Badhiwala, J.; Guest, J.; Harrop, J.; Shaffrey, C.; Boakye, M.; Kurpad, S.; Grossman, R.; Toups, E.; Geisler, F.; et al. Trajectory-Based Classification of Recovery in Sensorimotor Complete Traumatic Cervical Spinal Cord Injury. Neurology 2021, 96, e2736–e2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherwood, A.M.; Dimitrijevic, M.R.; McKay, W.B. Evidence of Subclinical Brain Influence in Clinically Complete Spinal Cord Injury: Discomplete SCI. J. Neurol. Sci. 1992, 110, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.K.; Zaidner, E.Y.; Calancie, B.; Broton, J.G.; Bigland-Ritchie, B.R. Muscle Weakness, Paralysis, and Atrophy after Human Cervical Spinal Cord Injury. Exp. Neurol. 1997, 148, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, C.K. Contractile properties of human thenar muscles paralyzed by spinal cord injury. Muscle Nerve 1997, 20, 788–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, G.X.; Zhang, J.W.; Hong, Y.; Guan, Y.; Guan, H. Motor unit number estimation of the tibialis anterior muscle in spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 2008, 46, 696–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartori, A.M.; Hofer, A.S.; Schwab, M.E. Recovery after spinal cord injury is enhanced by anti-Nogo-A antibody therapy—From animal models to clinical trials. Curr. Opin. Physiol. 2020, 14, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Y.T.; Alam, M.; Zheng, Y.P. Spinal Cord Injury: Lessons about Neuroplasticity from Paired Associative Stimulation. Neuroscientist 2020, 26, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, V.; Wirz, M.; Colombo, G.; Curt, A. Locomotor Capacity and Recovery of Spinal Cord Function in Paraplegic Patients: A Clinical and Electrophysiological Evaluation. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1998, 109, 140–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, V.; Wirz, M.; Curt, A.; Colombo, G. Locomotor Pattern in Paraplegic Patients: Training Effects and Recovery of Spinal Cord Function. Spinal Cord 1998, 36, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangari, S.; Kirshblum, S.; Guest, J.D.; Oudega, M.; Perez, M.A. Distinct Patterns of Spasticity and Corticospinal Connectivity Following Complete Spinal Cord Injury. J. Physiol. 2021, 599, 4441–4454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangari, S.; Lundell, H.; Kirshblum, S.; Perez, M.A. Residual descending motor pathways influence spasticity after spinal cord injury. Ann. Neurol. 2019, 86, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, J.M.; Condliffe, E.G.; Martins, K.J.B.; Bennett, D.J.; Gorassini, M.A. Recovery of neuronal and network excitability after spinal cord injury and implications for spasticity. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scelsi, R.; Marchetti, C.; Poggi, P.; Lotta, S.; Lommi, G. Muscle Fiber Type Morphology and Distribution in Paraplegic Patients with Traumatic Cord Lesion. Acta Neuropathol. 1982, 57, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biering-Sørensen, B.; Kristensen, I.B.; Kjaer, M.; Biering-Sørensen, F. Muscle after spinal cord injury. Muscle Nerve 2009, 40, 499–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimby, G.; Broberg, C.; Krotkiewska, I.; Krotkiewski, M. Muscle Fiber Composition in Patients with Traumatic Cord Lesion. Scand. J. Rehabil. Med. 1976, 8, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Lu, Z.; Wang, I.; Li, L.; Stampas, A.; Zhou, P. Assessing redistribution of muscle innervation zones after spinal cord injuries. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2021, 59, 10255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, J.W.; Ditunno, J.F., Jr.; Stiens, S.A.; Harris, R.M. Incomplete Spinal Cord Injury: Recovery and Hyperreflexia Neuronal Mechanisms of Motor. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1999, 80, 587–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiersemenzel, L.; Curt, A.; Dietz, V. From spinal shock to spasticity Neuronal adaptations to a spinal cord injury. Neurology 2000, 58, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, J.A.; Spiess, M.; Curt, A.; Dietz, V.; Schubert, M.N. Spinal cord injury: One-year evolution of motor-evoked potentials and recovery of leg motor function in 255 patients. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2012, 26, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, A.J.; Walsh, E.G.; Wright, G.W.; Edmond, P. Muscle Tone around the Human Knee in Paraplegia. Q. J. Exp. Physiol. Transl. Integr. 1989, 74, 897–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calancie, B.; Lutton, S.; Broton, J.G. Central Nervous System Plasticity after Spinal Cord Injury in Man: Interlimb Reflexes and the Influence of Cutaneous Stimulation. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1996, 101, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawashima, N.; Nozaki, D.; Abe, M.O.; Nakazawa, K. Shaping appropriate locomotive motor output through interlimb neural pathway within spinal cord in humans. J. Neurophysiol. 2008, 99, 2946–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onushko, T.; Schmit, B.D. Coordinated muscle activity of the legs during assisted bilateral hip scillation in human spinal cord injury. Biomed. Sci. Instrum. 2008, 44, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Onushko, T.; Hyngstrom, A.; Schmit, B.D. Effects of multijoint spastic reflexes of the legs during assisted bilateral hip oscillations in human spinal cord injury. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2010, 91, 1225–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, D.M.; Ross, B.H.; Thomas, C.K. Characteristics of lower extremity clonus after human cervical spinal cord injury. J. Neurotrauma 2012, 29, 915–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Kahn, J.H.; Hornby, T.G.; Schmit, B.D. Rebound Responses to Prolonged Flexor Reflex Stimuli in Human Spinal Cord Injury. Exp. Brain Res. 2009, 193, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornby, T.G.; Kahn, J.H.; Wu, M.; Schmit, B.D. Temporal facilitation of spastic stretch reflexes following human spinal cord injury. J Physiol. 2006, 571, 593–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sköld, C.; Harms-Ringdahl, K.; Seiger, Å. Movement-provoked muscle torque and EMG activity in longstanding motor complete spinal cord injured individuals. J. Rehabil. Med. 2002, 34, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, J.E.; Del Vecchio, A.; Sarma, D.; Verma, N.; Colachis, S.C., 4th; Annetta, N.V.; Collinger, J.L.; Farina, D.; Weber, D.J. Sensing and decoding the neural drive to paralyzed muscles during attempted movements of a person with tetraplegia using a sleeve array. J. Neurophysiol. 2021, 126, 2104–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunday, K.L.; Perez, M.A. Motor Recovery after Spinal Cord Injury Enhanced by Strengthening Corticospinal Synaptic Transmission. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, 2355–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, H.J.; Perez, M.A. Corticospinal-Motor Neuronal Plasticity Promotes Exercise-Mediated Recovery in Humans with Spinal Cord Injury. Brain 2020, 143, 1368–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.K.; Dididze, M.; Martinez, A.; Morris, R.W. Identification and Classification of Involuntary Leg Muscle Contractions in Electromyographic Records from Individuals with Spinal Cord Injury. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2014, 24, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winslow, J.; Martinez, A.; Thomas, C.K. Automatic Identification and Classification of Muscle Spasms in Long-Term EMG Recordings. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2015, 19, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mummidisetty, C.K.; Bohorquez, J.; Thomas, C.K. Automatic Analysis of EMG during Clonus. J. Neurosci. Methods 2012, 204, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zijdewind, I.; Gant, K.; Bakels, R.; Thomas, C.K. Do Additional Inputs Change Maximal Voluntary Motor Unit Firing Rates after Spinal Cord Injury? Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2012, 26, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zijdewind, I.; Thomas, C.K. Motor unit firing during and after voluntary contractions of human thenar muscles weakened by spinal cord injury. J. Neurophysiol. 2003, 89, 2065–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zijdewind, I.; Bakels, R.; Thomas, C.K. Motor Unit firing Rates during Spasms in Thenar Muscles of Spinal Cord Injured Subjects. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, S.A.; Baker, S.N.; Gant, K.; Bohorquez, J.; Thomas, C.K. Spasms after spinal cord injury show low-frequency intermuscular coherence. J. Neurophysiol. 2018, 120, 1765–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesquita, R.; Taylor, J.L.; Trajano, G.S.; Holobar, A.; Gonçalves, B.A.M.; Blazevich, A.J. Effects of reciprocal inhibition and whole-body relaxation on persistent inward currents estimated by two different methods. J. Physiol. 2022, 600, 2765–2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapadia, N.; Moineau, B.; Popovic, M.R. Functional Electrical Stimulation Therapy for Retraining Reaching and Grasping After Spinal Cord Injury and Stroke. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovic, M.R.; Kapadia, N.; Zivanovic, V.; Furlan, J.C.; Craven, B.C.; Mcgillivray, C. Functional Electrical Stimulation Therapy of Voluntary Grasping Versus Only Conventional Rehabilitation for Patients with Subacute Incomplete Tetraplegia: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2011, 25, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heald, E.; Hart, R.; Kilgore, K.; Peckham, P.H. Characterization of Volitional Electromyographic Signals in the Lower Extremity after Motor Complete Spinal Cord Injury. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2017, 31, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandeville, R.M.; Brown, J.M.; Sheean, G.L. A neurophysiological approach to nerve transfer to restore upper limb function in cervical spinal cord injury. Neurosurg. Focus 2017, 43, E6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverman, J.D.; Balbinot, G.; Masani, K.; Zariffa, J. Validity and Reliability of Surface Electromyography Features in Lower Extremity Muscle Contraction in Healthy and Spinal Cord–Injured Participants. Top. Spinal Cord Inj. Rehabil. 2021, 27, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, T.; Potter-Baker, K.; O’Laughlin, K.; Li, M.; Wang, X.; Cunningham, D.; Bethoux, F.; Frost, F.; Plow, E.B. Measurement error and reliability of TMS metrics collected from biceps and triceps in individuals with chronic incomplete tetraplegia. Exp. Brain Res. 2021, 239, 3077–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Balbinot, G. Surface EMG in Subacute and Chronic Care after Traumatic Spinal Cord Injuries. Trauma Care 2022, 2, 381-391. https://doi.org/10.3390/traumacare2020031
Balbinot G. Surface EMG in Subacute and Chronic Care after Traumatic Spinal Cord Injuries. Trauma Care. 2022; 2(2):381-391. https://doi.org/10.3390/traumacare2020031
Chicago/Turabian StyleBalbinot, Gustavo. 2022. "Surface EMG in Subacute and Chronic Care after Traumatic Spinal Cord Injuries" Trauma Care 2, no. 2: 381-391. https://doi.org/10.3390/traumacare2020031
APA StyleBalbinot, G. (2022). Surface EMG in Subacute and Chronic Care after Traumatic Spinal Cord Injuries. Trauma Care, 2(2), 381-391. https://doi.org/10.3390/traumacare2020031





