Hydrolysates of Chicken Byproducts and Their Effect on the Histological and Histopathological Analysis of Liver and Kidney in a Murine Model of Induced Metabolic Syndrome
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Obtention of Chicken Byproduct Hydrolysates (HPO)
2.2. Animals and Diet Administered for the Induction of Metabolic Syndrome (MS)
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Histological Analysis
2.4.1. Sample Processing
2.4.2. Final Fixation
2.4.3. Sectioning
2.4.4. Floating and Adhesion
2.4.5. Dewaxing and Hydration
2.4.6. Histochemical Stains
Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E)
Masson’s Trichrome Stain (MTS)
Periodic Acid–Schiff (PAS)
2.5. Morphometrical Analysis of the Histopathological
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
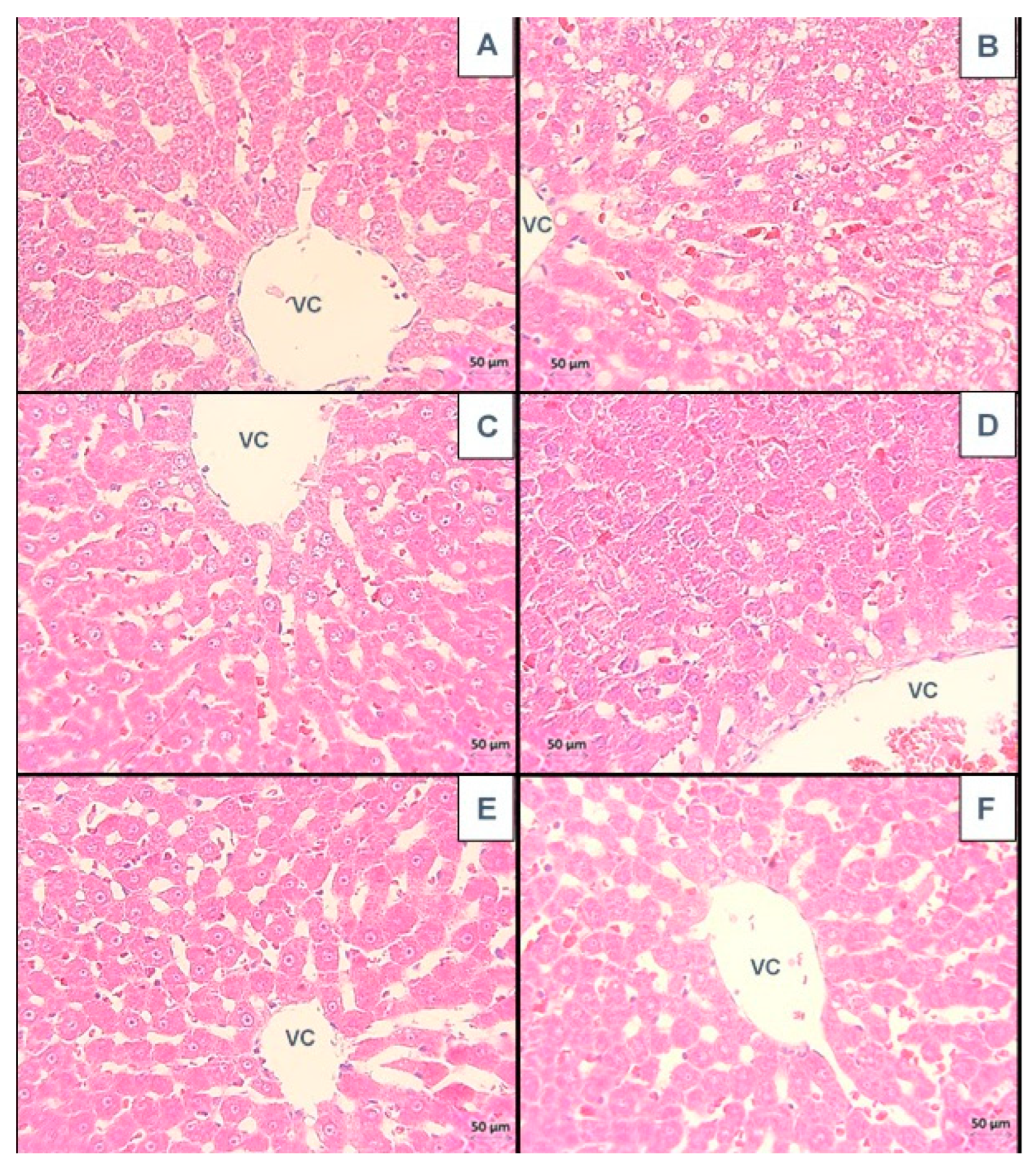
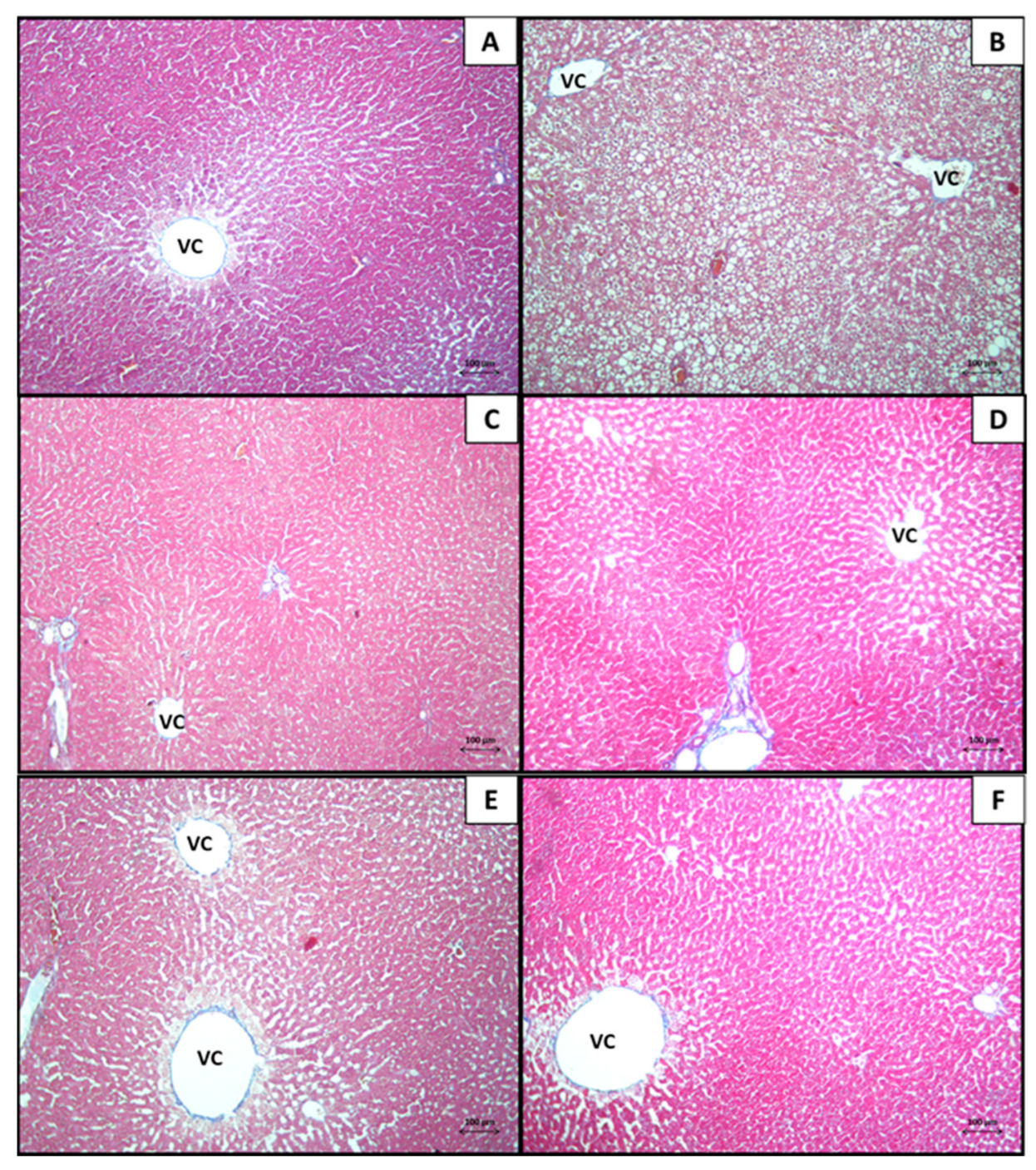
3.1. Liver
3.1.1. Histological Analysis
3.1.2. Morphometrical Analysis of the Histopathological Findings in the Liver
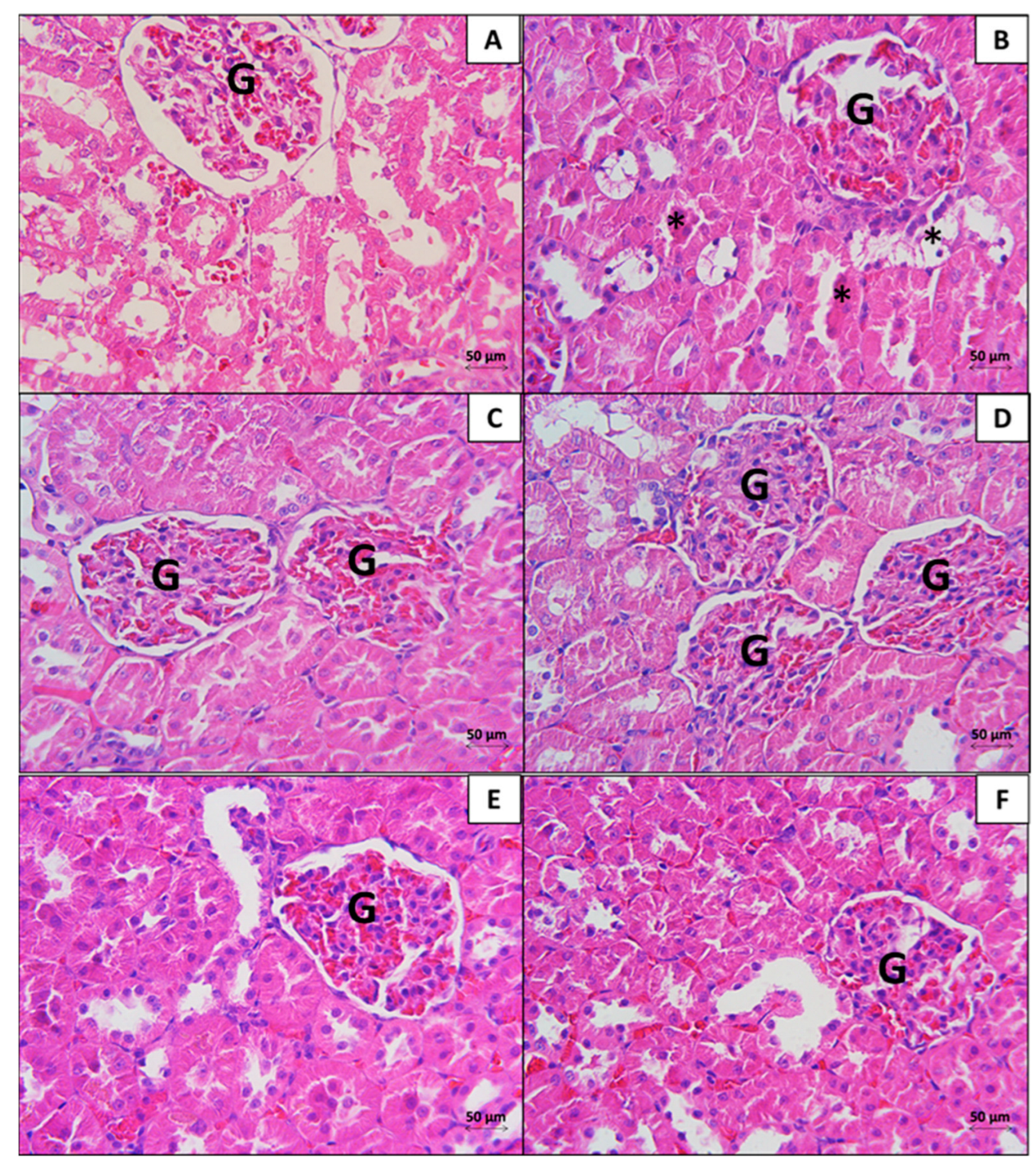
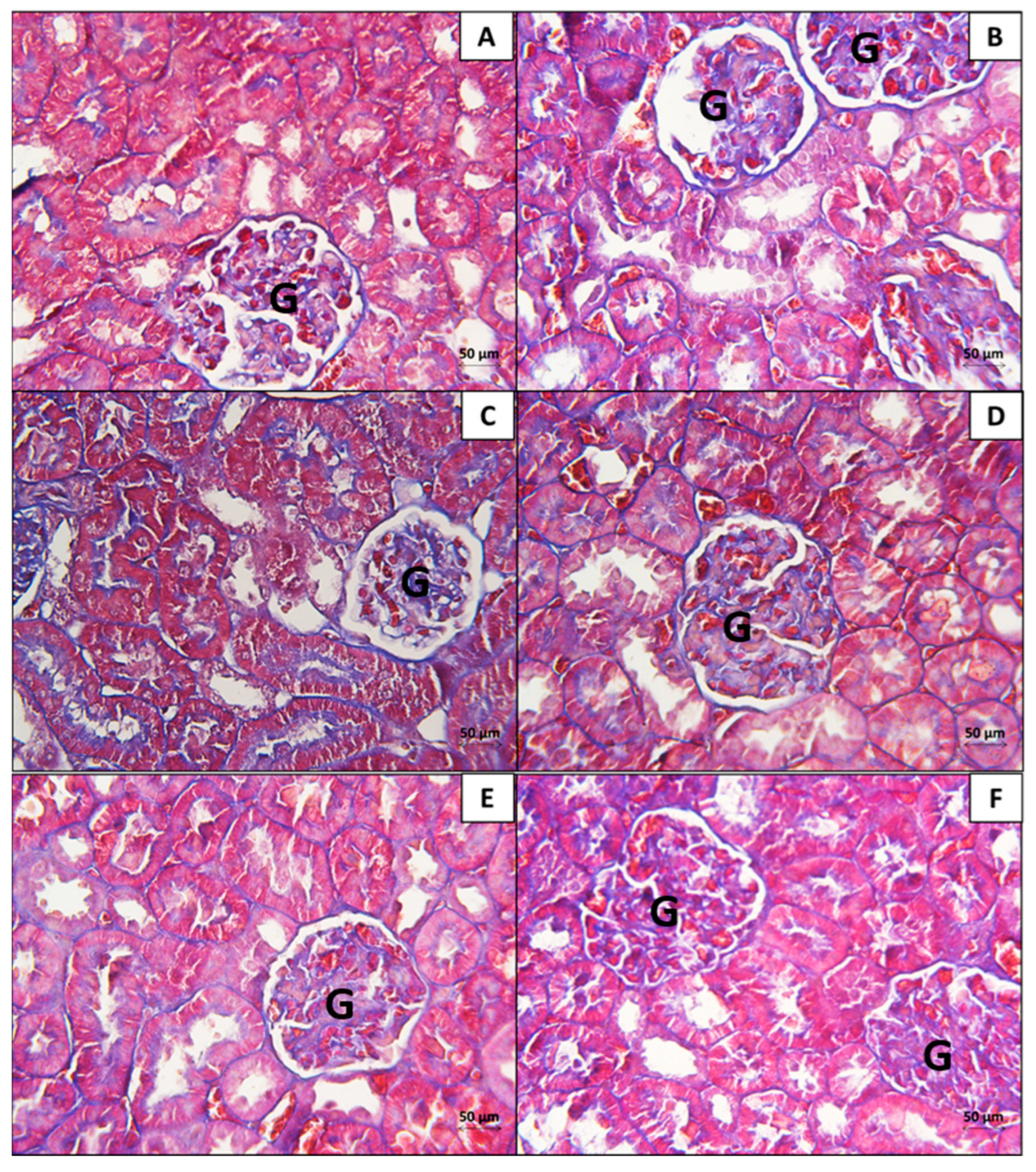
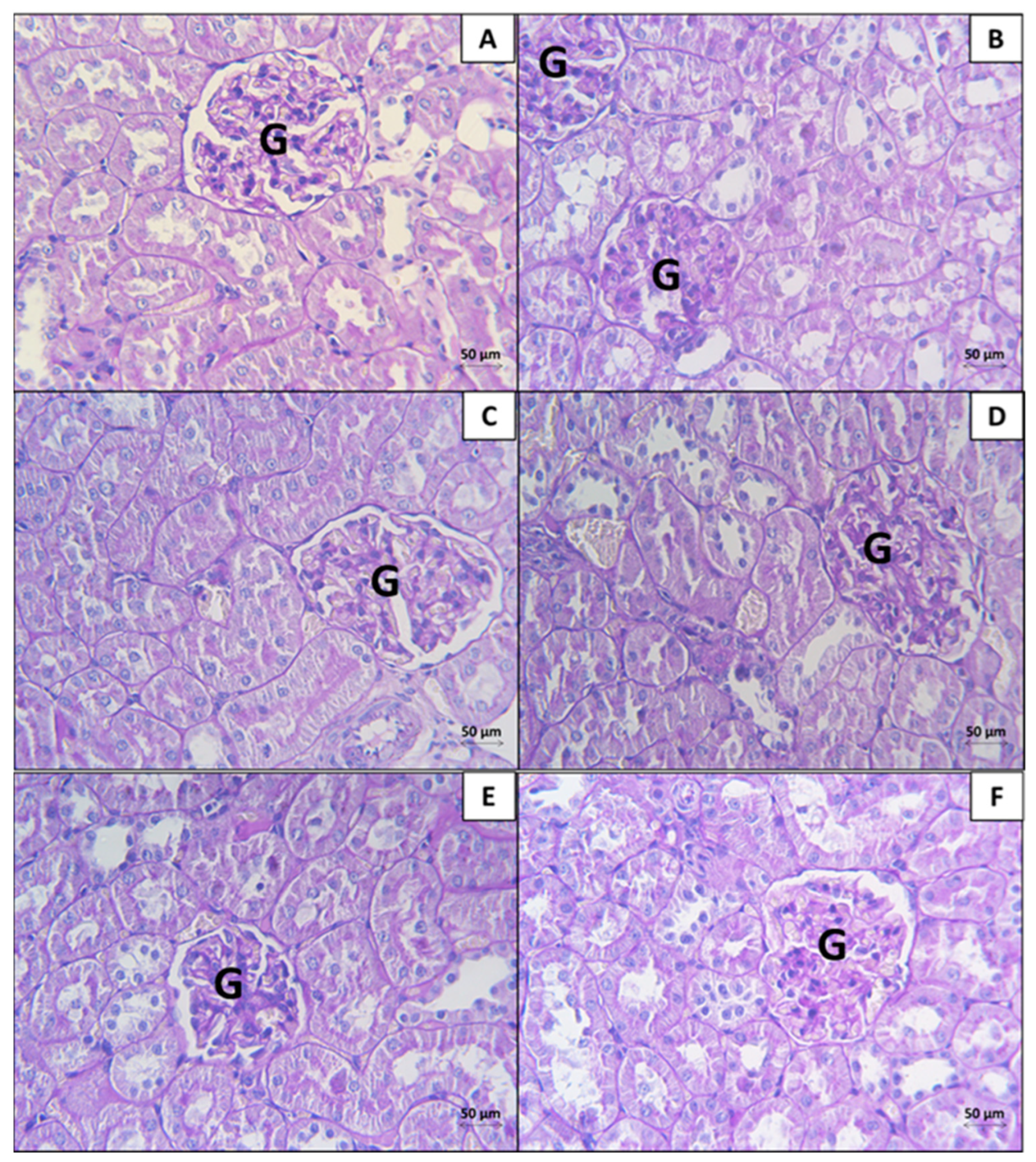
3.2. Kidney
3.2.1. Histopathological Analysis
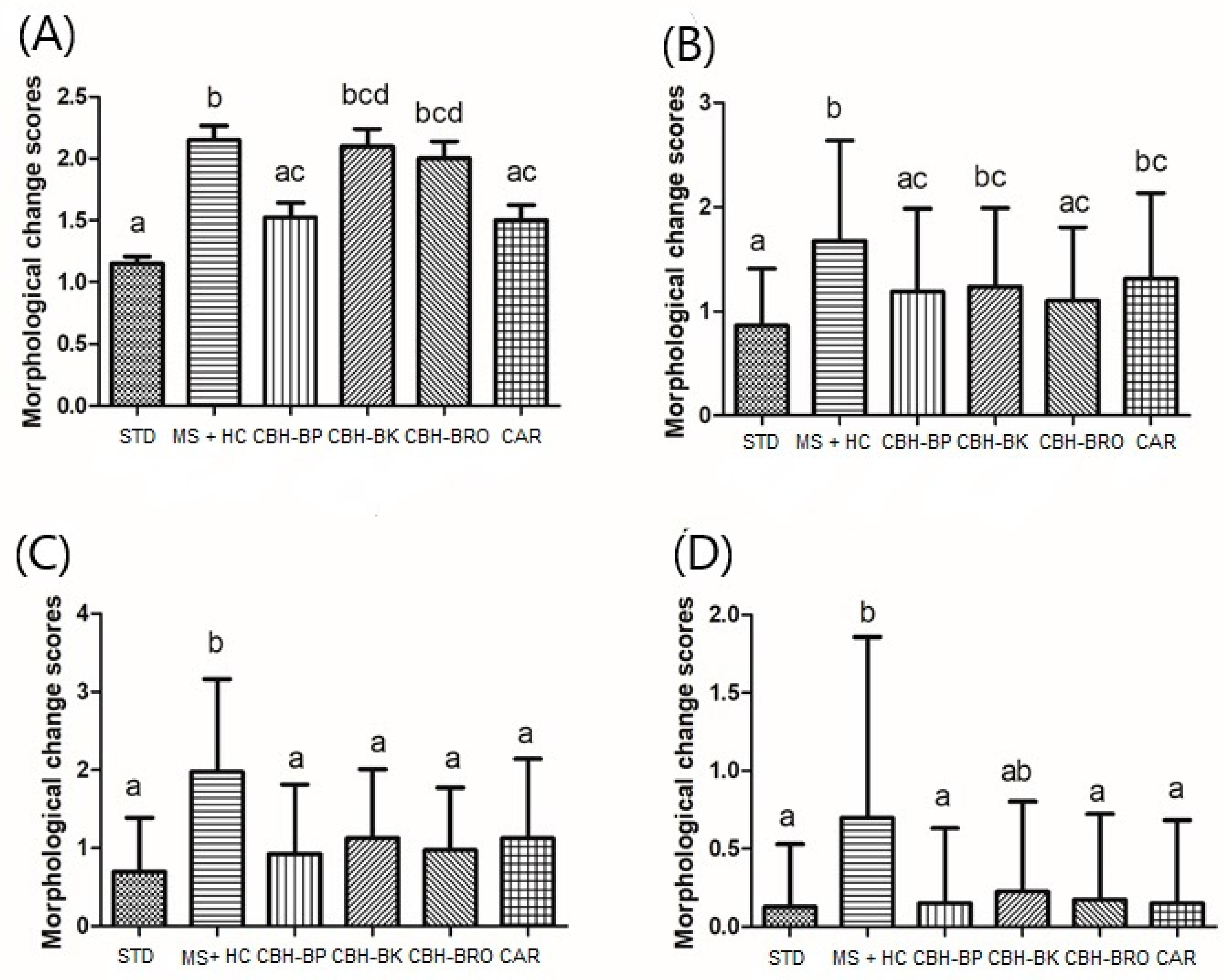
3.2.2. Morphometrical Analysis of the Histopathological Findings in the Kidney
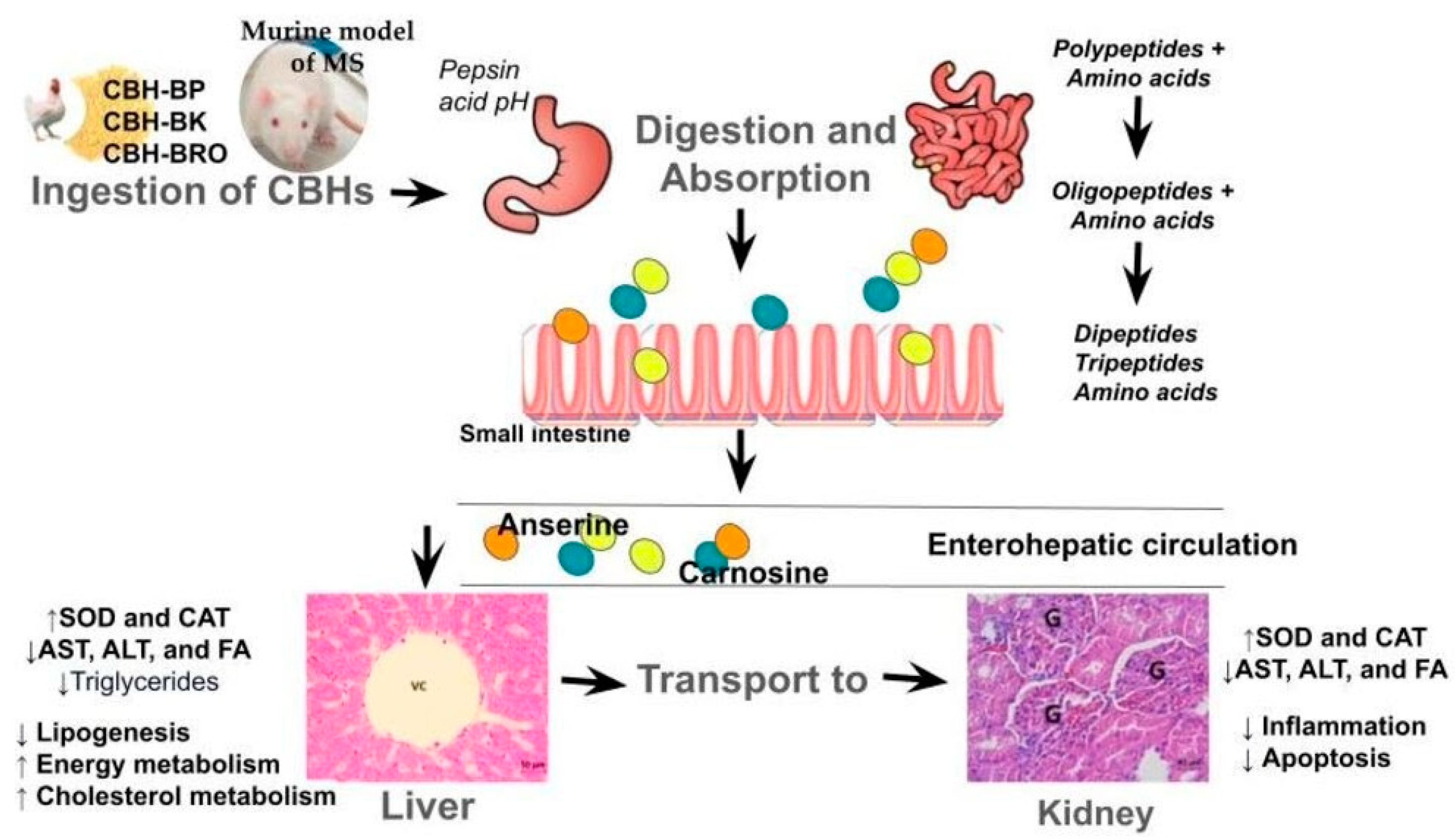
4. Discussion
4.1. Liver
4.2. Kidney
4.3. Limitations of This Study
4.3.1. Generalization of the Animal Model
4.3.2. Technical Limitations of Histological Analysis
4.3.3. Potential Clinical Applications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Suman, R.K.; Mohanty, I.R.; Borde, M.K.; Maheshwari, U.; Deshmukh, Y.A. Development of an experimental model of diabetes co-existing with metabolic syndrome in rats. Adv. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 2016, 9463476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvan, K.T.; Goon, J.A.; Makpol, S.; Tan, J.K. Effects of Microalgae on Metabolic Syndrome. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahima, R.S. Overview of metabolic syndrome. In Metabolic Syndrome: A Comprehensive Textbook; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, A.D.; Majzoub, A.; Agawal, A. Metabolic syndrome, and male fertility. World J. Mens. Health 2019, 37, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidigal, F.d.C.; Bressan, J.; Babio, N.; Salas-Salvadó, J. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome in Brazilian adults: A systematic review. BMC Public Health 2013, 13, 1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntamo, Y.; Jack, B.; Ziqubu, K.; Mazibuko-Mbeje, S.E.; Nkambule, B.B.; Nyambuya, T.M.; Mabhida, S.E.; Hanser, S.; Orlando, P.; Tiano, L.; et al. Epigallocatechin gallate as a nutraceutical to potentially target the metabolic syndrome: Novel insights into therapeutic effects beyond its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 64, 87–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, J.H.; Kang, D.R.; Kim, J.Y.; Koh, K.K. Metabolic syndrome fact sheet 2021: Executive report. Cardiometab. Syndr. J. 2021, 1, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, N.-Y.; Jang, S. Effects of mHealth Practice Patterns on Improving Metabolic Syndrome Using the Information–Motivation–Behavioral Skills Model. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, A.; Vázquez, A. Bioactive peptides: A review. Food Qual. Saf. 2017, 1, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahdatpour, T.; Valizadeh, H.; Mirzakhani, N.; Mesgari-Abbasi, M. Renoprotective Effects of Di- and Tri-peptides Containing Proline, Glycine and Leucine in Diabetes Model of Adult Mice: Enzymology and Histopathology. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2020, 26, 2345–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Garay, M.G.; Montalvo-González, E.; Hernández-González, C.; Soto-Domínguez, A.; Becerra-Verdín, E.M.; García-Magaña, M.D.L. Bioactivity of peptides obtained from poultry by-products: A review. Food Chem. X 2021, 13, 100181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarz-Blanch, N.; Alcaide-Hidalgo, J.M.; Cortés-Espinar, A.J.; Albi-Puig, J.; Suárez, M.; Mulero, M.; Morales, D.; Bravo, F.I. Chicken slaughterhouse by-products: A source of protein hydrolysates to manage non-communicable diseases. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 139, 104125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Garay, M.G.; Martínez-Montaño, E.; Hernández-Mendoza, A.; Vallejo-Cordoba, B.; González-Córdova, A.F.; Montalvo-González, E.; García-Magaña, M.d.L. Bromelia karatas and Bromelia pinguin: Sources of plant proteases used for obtaining antioxidant hydrolysates from chicken and fish by-products. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2020, 63, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-L.; Chen, C.Y.; Yang, D.J.; Wu, Y.H.S.; Lee, Y.J.; Chen, Y.C.; Chen, Y.C. Hepatic-Modulatory Effects of Chicken Liver Hydrolysate-Based Supplement on Autophagy Regulation against Liver Fibrogenesis. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.H.S.; Lin, Y.L.; Yang, W.Y.; Wang, S.Y.; Chen, Y.C. Pepsin-digested chicken-liver hydrolysate attenuates hepatosteatosis by relieving hepatic and peripheral insulin resistance in long-term high-fat dietary habit. J. Food Drug Anal. 2021, 29, 376–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.S.; Lin, Y.; Huang, C.; Chiu, C.; Nakthong, S.; Chen, Y. Cardiac protection of functional chicken-liver hydrolysates on the high-fat diet induced cardio-renal damages via sustaining autophagy homeostasis. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 2443–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.L.; Tai, S.Y.; Chen, J.W.; Chou, C.H.; Fu, S.G.; Chen, Y.C. Ameliorative effects of pepsin-digested chicken liver hydrolysates on development of alcoholic fatty livers in mice. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 1763–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.J.; Tseng, J.K.; Lin, Y.L.; Wu, Y.H.S.; Hsiao, Y.T.; Chen, J.W.; Chen, Y.C. Protective Effects of Functional Chicken Liver Hydrolysates against Liver Fibrogenesis: Antioxidation, Anti-inflammation, and Antifibrosis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 4961–4969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.; Wang, S.; Lin, Y.; Chen, Y. Antioxidant activities of chicken liver hydrolysates by pepsin treatment. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 49, 1654–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.T.; Lin, C.; Liu, C.W.; Chen, Y.C. Effects of chicken-liver hydrolysates on lipid metabolism in a high-fat diet. Food Chem. 2014, 160, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Garay, M.G.; Becerra-Verdín, E.M.; Soto-Domínguez, A.; Montalvo-González, E.; García-Magaña, M.L. Health effects of peptides obtained from hydrolysed chicken by-products by the action of Bromelia pinguin and B. karatas proteases in Wistar rats induced with metabolic syndrome. Int. Food Res. J. 2022, 29, 1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Magaña, M.d.L.; González-Borrayo, J.; Montalvo-González, E.; Rudiño-Piñera, E.; Sáyago-Ayerdi, S.G.; Salazar-Leyva, J.A. Isoelectric focusing, effect of reducing agents and inhibitors: Partial characterization of proteases extracted from Bromelia karatas. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2018, 61, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, M.; Naqvi, S.N.U.; Ahmed, M.; Kaimkhani, Z.A. Altered Kidney Morphology and Enzymes in Streptozotocin Induced Diabetic Rats. Int. J. Morphol. 2009, 27, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mitchell, J.C.; Kumar, R.N.; Abbas, V.; Aster, A.K.; de Robbins y Cotran, C. Patologia Estructural y Funcional; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Chen, X.; Huang, J.; Zhou, X.; Huang, M.; Zhou, G. Stability of antioxidant peptides from duck meat after post-mortem ageing. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 52, 2513–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mong, M.-C.; Chao, C.-Y.; Yin, M.-C. Histidine and carnosine alleviated hepatic steatosis in mice consumed high saturated fat diet. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 653, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Hong, H.; Wu, J.; Yan, X. Bioavailability of bioactive peptides derived from food proteins across the intestinal epithelial membrane: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 86, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.A.; Fadda, L.M.; Elebiary, H.; Soliman, M. Evaluation of the radioprotective action of anserine along with zinc in albino rats exposed to gamma-radiation. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 2, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peverill, W.; Powell, L.W.; Skoien, R. Evolving concepts in the pathogenesis of NASH: Beyond steatosis and inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 8591–8638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizardo, M.E.; del Pilar Navarro, M.; Camacho, M.; Magallanes-Hernández, M.A.; Pacheco-Gutiérrez, R.G.; López-Bordones, M.; Dorta, L. Estimación de la tasa de filtración glomerular en personas con y sin síndrome metabólico. Rev. Fac. Ciencias Salud UDES 2016, 3, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letelier, C.E.M.; Ojeda, C.A.S.M.; Provoste, J.J.R.; Zaror, C.J.F. Fisiopatología de la nefropatía diabética: Una revisión de la literatura. Medwave 2017, 17, 6839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carracedo, J.; Ramírez, R. Fisiología Renal. 2020, pp. 1–20. Available online: http://www.nefrologiaaldia.org/ (accessed on 5 June 2024).
- Ganapathy, V.; Leibach, F.H. Carrier-mediated reabsorption of small peptides in renal proximal tubule. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 1986, 251, F945–F953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitada, M.; Ogura, Y.; Koya, D. Rodent models of diabetic nephropathy: Their utility and limitations. Int. J. Nephrol. Renov. Dis. 2016, 9, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.; Li, B. Beneficial effects of collagen hydrolysate: A review on recent developments. Biomed. J. Sci. Tech. Res. 2017, 1, 458–461. [Google Scholar]
- Vahdatpour, T.; Nokhodchi, A.; Zakeri-Milani, P.; Mesgari-Abbasi, M.; Ahmadi-Asl, N.; Valizadeh, H. Leucine–glycine and carnosine dipeptides prevent diabetes induced by multiple low-doses of streptozotocin in an experimental model of adult mice. J. Diabetes Investig. 2019, 10, 1177–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.T.; Hsu, C.C.; Lin, M.H.; Liu, K.S.; Yin, M.C. Histidine and carnosine delay diabetic deterioration in mice and protect human low density lipoprotein against oxidation and glycation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 513, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, B.C.K.; Kuo, W.W.; Day, C.H.; Hsieh, D.J.Y.; Kuo, C.H.; Daddam, J.; Chen, R.J.; Padma, V.V.; Wang, G.; Huang, C.Y. The soybean bioactive peptide VHVV alleviates hypertension-induced renal damage in hypertensive rats via the SIRT1-PGC1α/Nrf2 pathway. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 75, 104255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Romero-Garay, M.G.; Montalvo-González, E.; Saucedo-Cárdenas, O.; Becerra-Verdín, E.M.; Soto-Domínguez, A.; Rodríguez-Aguayo, C.; García-Magaña, M.d.L. Hydrolysates of Chicken Byproducts and Their Effect on the Histological and Histopathological Analysis of Liver and Kidney in a Murine Model of Induced Metabolic Syndrome. Biologics 2024, 4, 345-363. https://doi.org/10.3390/biologics4030021
Romero-Garay MG, Montalvo-González E, Saucedo-Cárdenas O, Becerra-Verdín EM, Soto-Domínguez A, Rodríguez-Aguayo C, García-Magaña MdL. Hydrolysates of Chicken Byproducts and Their Effect on the Histological and Histopathological Analysis of Liver and Kidney in a Murine Model of Induced Metabolic Syndrome. Biologics. 2024; 4(3):345-363. https://doi.org/10.3390/biologics4030021
Chicago/Turabian StyleRomero-Garay, Martha Guillermina, Efigenia Montalvo-González, Odila Saucedo-Cárdenas, Eduardo Mendeleev Becerra-Verdín, Adolfo Soto-Domínguez, Cristian Rodríguez-Aguayo, and María de Lourdes García-Magaña. 2024. "Hydrolysates of Chicken Byproducts and Their Effect on the Histological and Histopathological Analysis of Liver and Kidney in a Murine Model of Induced Metabolic Syndrome" Biologics 4, no. 3: 345-363. https://doi.org/10.3390/biologics4030021
APA StyleRomero-Garay, M. G., Montalvo-González, E., Saucedo-Cárdenas, O., Becerra-Verdín, E. M., Soto-Domínguez, A., Rodríguez-Aguayo, C., & García-Magaña, M. d. L. (2024). Hydrolysates of Chicken Byproducts and Their Effect on the Histological and Histopathological Analysis of Liver and Kidney in a Murine Model of Induced Metabolic Syndrome. Biologics, 4(3), 345-363. https://doi.org/10.3390/biologics4030021







