Gene Therapy for Hypertension, Atherosclerosis, and Familial Hypercholesterolemia: The Old Concepts and the New Era
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Gene Therapy for EH
3.1. Targeting the RAAS
3.2. Targeting the β1-Rs
3.3. Targeting Kallikrein
3.4. Targeting Nitric Oxide Synthetase (NOS)
3.5. Targeting Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP)
3.6. Targeting Brain Natriuretic Peptide (BNP)
3.7. Targeting Adrenomedullin (ADM)
3.8. Clinical Trials Developed Evaluating the Pharmacological Correspondence and Clinical Characteristics Based on the Personal Gene Polymorphisms
4. Gene Therapy for Atherosclerosis
4.1. Targeting Lipoprotein Metabolism
4.2. Targeting Inflammation
5. Gene Therapy for FH
5.1. Animal Models for FH Gene Therapy
5.2. FH Gene Therapy Studies in Humans
6. Limitations of the Clinical Implications of Gene Therapy
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AAV | Adeno-associated virus |
| ACE | Angiotensin-converting enzyme |
| AdeNOS | Ad-encoding endothelial nitric oxide synthase |
| ADM | Adrenomedullin |
| AmiRNA | Artificial microribonucleic acid |
| AngI | Angiotensin I |
| AngII | Angiotensin II |
| ANP | Atrial natriuretic peptide |
| AOGEN | Precursor hormone angiotensinogen gene |
| AP | Arterial pressure |
| ApoA-I | Apolipoprotein AI |
| ApoA-IM | Apolipoprotein A-I Milano |
| APOA-V | Apolipoprotein A-V |
| ApoB | Apolipoprotein B |
| APOC3 | Apolipoprotein C3 |
| ApoE | Apolipoprotein E |
| AS-ODNs | Antisense synthetic oligodeoxynucleotides |
| AT1R | Angiotensin II type 1 receptor |
| AT2R | Angiotensin II type 2 receptor |
| BNP | Brain natriuretic peptide |
| Cdna | Complementary deoxyribonucleic acid |
| CMV | Cytomegalovirus |
| CVD | Cardiovascular disease |
| DBP | Diastolic blood pressure |
| DOCA-HR | Deoxycorticosterone acetate-salt hypertensive rats |
| EH | Essential hypertension |
| eNOS | Endothelial nitric oxide synthase |
| FH | Familial hypercholesterolemia |
| HDL | High-density lipoprotein |
| He | Heterozygous |
| HMG-CoA | Β-Hydroxy Β-Methylglutaryl-CoA |
| Ho | Homozygous |
| IL-10 | Intereukin-10 |
| JGCs | Juxtaglomerular cells |
| LDL | Low-Density lipoprotein |
| LDLR | Low-Density lipoprotein receptor |
| Lp(a) | Lipoprotein a |
| LPL | Lipoprotein lipase |
| LVH | Left ventricular hypertrophy |
| MESH | Medical subject headings |
| MR | Mineralocorticoid receptor |
| mRNA | Messenger ribonucleic acid |
| nNOS | Neuronal nitric oxide synthase |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| NOS | Nitric oxide synthetase |
| PCKS9 | Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 |
| PVN | Paraventricular nucleus |
| RAAS | Renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system |
| RNAi | Ribonucleic acid interference |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| RSV | Rous sarcoma virus |
| SBP | Systolic blood pressure |
| SHR | Spontaneously hypertensive rats |
| shRNA | Short hairpin ribonucleic acid |
| siRNA | Small interfering ribonucleic acid |
| STAT3 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 |
| TGF-β | Transforming growth factor beta |
| TGs | Triglycerides |
| TIMP-1 | Tissue metallopeptidase inhibitor- 1 |
| TiO2 | Titanium dioxide |
| VCAM-1 | Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 |
| VLDL | Very low-density lipoprotein |
| β1-Rs | B-1-adrenergic receptors |
References
- Roth, G.A.; Mensah, G.A.; Johnson, C.O.; Addolorato, G.; Ammirati, E.; Baddour, L.M.; Barengo, N.C.; Beaton, A.Z.; Benjamin, E.J.; Benziger, C.P.; et al. Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors, 1990–2019: Update from the GBD 2019 Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 2982–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, K.T.; Stefanescu, A.; He, J. The Global Epidemiology of Hypertension. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appleton, S.L.; Neo, C.; Hill, C.L.; Douglas, K.A.; Adams, R.J. Untreated Hypertension: Prevalence and Patient Factors and Beliefs Associated with under-Treatment in a Population Sample. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2013, 27, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulis, L.; Franke, H.; Simko, F. Gene Therapy for Hypertension. Expert. Opin. Biol. Ther. 2017, 17, 1345–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, M.I. Is Gene Therapy for Hypertension Possible? Hypertension 1999, 33, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gluba, A.; Banach, M.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Rysz, J. Genetic Determinants of Cardiovascular Disease: The Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System, Paraoxonases, Endothelin-1, Nitric Oxide Synthase and Adrenergic Receptors. In Vivo 2009, 23, 797–812. [Google Scholar]
- Dichgans, M.; Pulit, S.L.; Rosand, J. Stroke Genetics: Discovery, Biology, and Clinical Applications. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 587–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahwa, R.; Jialal, I. Atherosclerosis; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Jebari-Benslaiman, S.; Galicia-García, U.; Larrea-Sebal, A.; Olaetxea, J.R.; Alloza, I.; Vandenbroeck, K.; Benito-Vicente, A.; Martín, C. Pathophysiology of Atherosclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacic, S.; Bakran, M. Genetic Susceptibility to Atherosclerosis. Stroke Res. Treat. 2012, 2012, 362941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ison, H.E.; Clarke, S.L.; Knowles, J.W. Familial Hypercholesterolemia; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, G.; Xuan, X.; Zhang, R.; Hu, J.; Dong, H. Gene Therapy for Cardiovascular Disease: Basic Research and Clinical Prospects. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 760140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheller, E.L.; Krebsbach, P.H. Gene Therapy: Design and Prospects for Craniofacial Regeneration. J. Dent. Res. 2009, 88, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, T.; Ali, A.O.; Saxena, M. Pathophysiology of Essential Hypertension: An Update. Expert. Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2018, 16, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beevers, G.; Lip, G.Y.; O’Brien, E. ABC of Hypertension: The Pathophysiology of Hypertension. BMJ 2001, 322, 912–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Lee, C.H. The Roles of Sodium and Volume Overload on Hypertension in Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 2021, 40, 542–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-H.; Mohammadmoradi, S.; Chen, J.Z.; Sawada, H.; Daugherty, A.; Lu, H.S. Renin-Angiotensin System and Cardiovascular Functions. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2018, 38, e108–e116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sequeira-Lopez, M.L.S.; Gomez, R.A. Renin Cells, the Kidney, and Hypertension. Circ. Res. 2021, 128, 887–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benetos, A.; Gautier, S.; Ricard, S.; Topouchian, J.; Asmar, R.; Poirier, O.; Larosa, E.; Guize, L.; Safar, M.; Soubrier, F.; et al. Influence of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme and Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor Gene Polymorphisms on Aortic Stiffness in Normotensive and Hypertensive Patients. Circulation 1996, 94, 698–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caulfield, M.; Lavender, P.; Farrall, M.; Munroe, P.; Lawson, M.; Turner, P.; Clark, A.J. Linkage of the Angiotensinogen Gene to Essential Hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994, 330, 1629–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloem, L.J.; Foroud, T.M.; Ambrosius, W.T.; Hanna, M.P.; Tewksbury, D.A.; Pratt, J.H. Association of the Angiotensinogen Gene to Serum Angiotensinogen in Blacks and Whites. Hypertension 1997, 29, 1078–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davisson, R.L.; Ding, Y.; Stec, D.E.; Catterall, J.F.; Sigmund, C.D. Novel Mechanism of Hypertension Revealed by Cell-Specific Targeting of Human Angiotensinogen in Transgenic Mice. Physiol. Genom. 1999, 1, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danigo, A.; Rovini, A.; Bessaguet, F.; Bouchenaki, H.; Bernard, A.; Sturtz, F.; Bourthoumieu, S.; Desmoulière, A.; Magy, L.; Demiot, C. The Angiotensin II Type 2 Receptor, a Target for Protection and Regeneration of the Peripheral Nervous System? Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janc, J.; Suchański, M.; Mierzchała-Pasierb, M.; Woźnica-Niesobska, E.; Łysenko, L.; Leśnik, P. Does the Serum Concentration of Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor Have an Effect on the Severity of COVID-19? A Prospective Preliminary Observational Study among Healthcare Professionals. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, M.I.; Kimura, B. Gene Therapy for Hypertension: Antisense Inhibition of the Renin-Angiotensin System. Methods Mol. Med. 2005, 108, 363–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- St Paul, A.; Corbett, C.B.; Okune, R.; Autieri, M. V Angiotensin II, Hypercholesterolemia, and Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells: A Perfect Trio for Vascular Pathology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaspari, T.A.; Vinh, A.; Jones, E.S.; Widdop, R.E. Ganging up on Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptors in Vascular Remodeling. Hypertension 2012, 60, 17–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Morimoto, S.; Ichihara, A. Management of Primary Aldosteronism and Mineralocorticoid Receptor-Associated Hypertension. Hypertens. Res. 2020, 43, 744–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, W.; Shibata, S. Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonists for Preventing Chronic Kidney Disease Progression: Current Evidence and Future Challenges. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gyurko, R.; Wielbo, D.; Phillips, M.I. Antisense Inhibition of AT1 Receptor MRNA and Angiotensinogen MRNA in the Brain of Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats Reduces Hypertension of Neurogenic Origin. Regul. Pept. 1993, 49, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, M.I.; Wielbo, D.; Gyurko, R. Antisense Inhibition of Hypertension: A New Strategy for Renin-Angiotensin Candidate Genes. Kidney Int. 1994, 46, 1554–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wielbo, D.; Sernia, C.; Gyurko, R.; Phillips, M.I. Antisense Inhibition of Hypertension in the Spontaneously Hypertensive Rat. Hypertension 1995, 25, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wielbo, D.; Simon, A.; Phillips, M.I.; Toffolo, S. Inhibition of Hypertension by Peripheral Administration of Antisense Oligodeoxynucleotides. Hypertension 1996, 28, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomita, N.; Morishita, R.; Higaki, J.; Aoki, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Mikami, H.; Fukamizu, A.; Murakami, K.; Kaneda, Y.; Ogihara, T. Transient Decrease in High Blood Pressure by In Vivo Transfer of Antisense Oligodeoxynucleotides against Rat Angiotensinogen. Hypertension 1995, 26, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, D.; Yu, K.; Raizada, M.K. Retrovirus-Mediated Transfer of an Angiotensin Type I Receptor (AT1-R) Antisense Sequence Decreases AT1-Rs and Angiotensin II Action in Astroglial and Neuronal Cells in Primary Cultures from the Brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 1162–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schinke, M.; Böhm, M.; Bricca, G.; Ganten, D.; Bader, M. Permanent Inhibition of Angiotensinogen Synthesis by Antisense RNA Expression. Hypertension 1996, 27, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, M.I.; Mohuczy-Dominiak, D.; Coffey, M.; Galli, S.M.; Kimura, B.; Wu, P.; Zelles, T. Prolonged Reduction of High Blood Pressure with an In Vivo, Nonpathogenic, Adeno-Associated Viral Vector Delivery of AT1-R MRNA Antisense. Hypertension 1997, 29, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, M.I. Antisense Inhibition and Adeno-Associated Viral Vector Delivery for Reducing Hypertension. Hypertension 1997, 29, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gyurko, R.; Tran, D.; Phillips, M.I. Time Course of Inhibition of Hypertension by Antisense Oligonucleotides Targeted to AT1 Angiotensin Receptor MRNA in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Am. J. Hypertens. 1997, 10, 56S–62S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyer, S.N.; Lu, D.; Katovich, M.J.; Raizada, M.K. Chronic Control of High Blood Pressure in the Spontaneously Hypertensive Rat by Delivery of Angiotensin Type 1 Receptor Antisense. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 9960–9965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makino, N.; Sugano, M.; Ohtsuka, S.; Sawada, S. Intravenous Injection with Antisense Oligodeoxynucleotides against Angiotensinogen Decreases Blood Pressure in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Hypertension 1998, 31, 1166–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lu, D.; Yang, H.; Raizada, M.K. Attenuation of ANG II Actions by Adenovirus Delivery of AT1 Receptor Antisense in Neurons and SMC. Am. J. Physiol. 1998, 274, H719–H727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Mohuczy, D.; Zhang, Y.C.; Kimura, B.; Galli, S.M.; Phillips, M.I. Intravenous Angiotensinogen Antisense in AAV-Based Vector Decreases Hypertension. Am. J. Physiol. 1999, 277, H2392–H2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachori, A.S.; Wang, H.; Gelband, C.H.; Ferrario, C.M.; Katovich, M.J.; Raizada, M.K. Inability to Induce Hypertension in Normotensive Rat Expressing AT(1) Receptor Antisense. Circ. Res. 2000, 86, 1167–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, B.; Mohuczy, D.; Tang, X.; Phillips, M.I. Attenuation of Hypertension and Heart Hypertrophy by Adeno-Associated Virus Delivering Angiotensinogen Antisense. Hypertension 2001, 37, 376–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Katovich, M.J.; Reaves, P.Y.; Francis, S.C.; Pachori, A.S.; Wang, H.W.; Raizada, M.K. Gene Therapy Attenuates the Elevated Blood Pressure and Glucose Intolerance in an Insulin-Resistant Model of Hypertension. J. Hypertens. 2001, 19, 1553–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pachori, A.S.; Numan, M.T.; Ferrario, C.M.; Diz, D.M.; Raizada, M.K.; Katovich, M.J. Blood Pressure-Independent Attenuation of Cardiac Hypertrophy by AT(1)R-AS Gene Therapy. Hypertension 2002, 39, 969–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reaves, P.Y.; Beck, C.R.; Wang, H.-W.; Raizada, M.K.; Katovich, M.J. Endothelial-Independent Prevention of High Blood Pressure in L-NAME-Treated Rats by Angiotensin II Type I Receptor Antisense Gene Therapy. Exp. Physiol. 2003, 88, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.-D.; Zhang, L.; Shi, Z.; Gan, X.-B.; Gao, X.-Y.; Zhu, G.-Q. Artificial MicroRNA Interference Targeting AT(1a) Receptors in Paraventricular Nucleus Attenuates Hypertension in Rats. Gene Ther. 2012, 19, 810–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Huang, B.S.; Wang, H.-W.; Ahmad, M.; Leenen, F.H.H. Knockdown of Mineralocorticoid or Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor Gene Expression in the Paraventricular Nucleus Prevents Angiotensin II Hypertension in Rats. J. Physiol. 2014, 592, 3523–3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Repkova, M.N.; Levina, A.S.; Seryapina, A.A.; Shikina, N.V.; Bessudnova, E.V.; Zarytova, V.F.; Markel, A.L. Toward Gene Therapy of Hypertension: Experimental Study on Hypertensive ISIAH Rats. Biochemistry 2017, 82, 454–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Hodgkinson, C.P.; Pratt, R.E.; Dzau, V.J. CRISPR/Cas9 Mediated Deletion of the Angiotensinogen Gene Reduces Hypertension: A Potential for Cure? Hypertension 2021, 77, 1990–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanton, A.M.; Heydarpour, M.; Williams, J.S.; Williams, G.H.; Adler, G.K. CACNA1D Gene Polymorphisms Associate with Increased Blood Pressure and Salt Sensitivity of Blood Pressure in White Individuals. Hypertension 2023, 80, 2665–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruchaya, P.J.; Speretta, G.F.; Blanch, G.T.; Li, H.; Sumners, C.; Menani, J.V.; Colombari, E.; Colombari, D.S.A. Overexpression of AT2R in the Solitary-Vagal Complex Improves Baroreflex in the Spontaneously Hypertensive Rat. Neuropeptides 2016, 60, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhayek, S.; Preuss, C.V. Beta 1 Receptors; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Clare Zhang, Y.; Kimura, B.; Shen, L.; Phillips, M.I. New Beta-Blocker: Prolonged Reduction in High Blood Pressure with Beta(1) Antisense Oligodeoxynucleotides. Hypertension 2000, 35, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Lin, S.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, J.; Yu, X. Beta-1 Adrenergic Receptor Antisense-Oligodeoxynucleotides Ameliorates Left Ventricular Remodeling in 2-Kidney, 1-Clip Rats. J. Biomed. Sci. 2007, 14, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, X.-L.; Wen, J.; Huang, L.-H.; Lu, Y.; Miao, R.-J.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Xing, X.-W.; Yuan, H. Downregulation of the Β1 Adrenergic Receptor in the Myocardium Results in Insensitivity to Metoprolol and Reduces Blood Pressure in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 15, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagnino, A.P.A.; Campos, M.M.; Silva, R.B.M. Kinins and Their Receptors in Infectious Diseases. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Chao, L.; Chao, J. Direct Gene Delivery of Human Tissue Kallikrein Reduces Blood Pressure in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 95, 1710–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yayama, K.; Wang, C.; Chao, L.; Chao, J. Kallikrein Gene Delivery Attenuates Hypertension and Cardiac Hypertrophy and Enhances Renal Function in Goldblatt Hypertensive Rats. Hypertension 1998, 31, 1104–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.J.; Wang, C.; Lin, K.F.; Chao, L.; Chao, J. Human Tissue Kallikrein Attenuates Hypertension and Secretes into Circulation and Urine after Intramuscular Gene Delivery in Hypertensive Rats. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 1999, 21, 1145–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrzynski, E.; Yoshida, H.; Chao, J.; Chao, L. Adenovirus-Mediated Kallikrein Gene Delivery Attenuates Hypertension and Protects against Renal Injury in Deoxycorticosterone-Salt Rats. Immunopharmacology 1999, 44, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, P.; Xiao, X.; Chao, J.; Chao, L.; Wang, D.W.; Zeldin, D.C. Gene Therapy with Human Tissue Kallikrein Reduces Hypertension and Hyperinsulinemia in Fructose-Induced Hypertensive Rats. Hypertension 2003, 42, 1026–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wang, T.; Li, H.; Zhao, C.; Chen, C.; Li, J.; Chao, J.; Chao, L.; Xiao, X.; Wang, D.W. Recombinant Adeno-Associated Virus-Mediated Kallikrein Gene Therapy Reduces Hypertension and Attenuates Its Cardiovascular Injuries. Gene Ther. 2004, 11, 1342–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Hou, L.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, C.; Xiao, X.; Wang, D. Intramuscular Delivery of RAAV-Mediated Kallikrein Gene Reduces Hypertension and Prevents Cardiovascular Injuries in Model Rats. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2007, 28, 1898–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Yan, J.; Wang, T.; Li, J.; Xiao, X.; Wang, D. Recombinant Adeno-Associated Virus-Mediated Human Kallikrein Gene Therapy Prevents High-Salt Diet-Induced Hypertension without Effect on Basal Blood Pressure. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2008, 29, 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valerieva, A.; Longhurst, H.J. Treatment of Hereditary Angioedema-Single or Multiple Pathways to the Rescue. Front. Allergy 2022, 3, 952233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marceau, F. Correction: Marceau, F. Drugs of the Kallikrein–Kinin System: An Overview. Drugs Drug Candidates 2023, 2, 538–553. Drugs Drug Candidates 2024, 3, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrone, J.D.; Bhattacharjee, G.; Revenko, A.S.; Zanardi, T.A.; Warren, M.S.; Derosier, F.J.; Viney, N.J.; Pham, N.C.; Kaeser, G.E.; Baker, B.F.; et al. IONIS-PKKRx a Novel Antisense Inhibitor of Prekallikrein and Bradykinin Production. Nucleic Acid. Ther. 2019, 29, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://www.intelliatx.com/Our-Science/Publications-and-Presentations/ (accessed on 26 February 2024).
- Shehjar, F.; Maktabi, B.; Rahman, Z.A.; Bahader, G.A.; James, A.W.; Naqvi, A.; Mahajan, R.; Shah, Z.A. Stroke: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapies: Update on Recent Developments. Neurochem. Int. 2023, 162, 105458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander-Curtis, M.; Pauls, R.; Chao, J.; Volpi, J.J.; Bath, P.M.; Verdoorn, T.A. Human Tissue Kallikrein in the Treatment of Acute Ischemic Stroke. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2019, 12, 1756286418821918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulloh, R. Etiology, Diagnosis, and Pharmacologic Treatment of Pediatric Pulmonary Hypertension. Paediatr. Drugs 2009, 11, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, G.; da Silva, M.; Nascimento, D.; Lima Silva, E.; Gouvêa, F.; de França Lopes, L.; Araújo, A.; Ferraz Pereira, K.; de Queiroz, T. Nitric Oxide as a Central Molecule in Hypertension: Focus on the Vasorelaxant Activity of New Nitric Oxide Donors. Biology 2021, 10, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, N.S. Nitric Oxide Deficiency Is a Primary Driver of Hypertension. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2022, 206, 115325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, J.; Zhang, J.J.; Lin, K.F.; Chao, L. Human Kallikrein Gene Delivery Attenuates Hypertension, Cardiac Hypertrophy, and Renal Injury in Dahl Salt-Sensitive Rats. Hum. Gene Ther. 1998, 9, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, W.H.; Brosnan, M.J.; Graham, D.; Nicol, C.G.; Morecroft, I.; Channon, K.M.; Danilov, S.M.; Reynolds, P.N.; Baker, A.H.; Dominiczak, A.F. Targeting Endothelial Cells with Adenovirus Expressing Nitric Oxide Synthase Prevents Elevation of Blood Pressure in Stroke-Prone Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Mol. Ther. 2005, 12, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gava, A.L.; Peotta, V.A.; Cabral, A.M.; Vasquez, E.C.; Meyrelles, S.S. Overexpression of ENOS Prevents the Development of Renovascular Hypertension in Mice. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2008, 86, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.X.; Xu, X.; Cui, Y.; Wang, P.; Wei, X.; Yang, S.; Edin, M.L.; Zeldin, D.C.; Wang, D.W. Increased Endothelial Nitric-Oxide Synthase Expression Reduces Hypertension and Hyperinsulinemia in Fructose-Treated Rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2009, 328, 610–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannone, V.; Cabassi, A.; Volpi, R.; Burnett, J.C., Jr. Atrial Natriuretic Peptide: A Molecular Target of Novel Therapeutic Approaches to Cardio-Metabolic Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.F.; Chao, J.; Chao, L. Atrial Natriuretic Peptide Gene Delivery Attenuates Hypertension, Cardiac Hypertrophy, and Renal Injury in Salt-Sensitive Rats. Hum. Gene Ther. 1998, 9, 1429–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therrien, J.-P.; Kim, S.M.; Terunuma, A.; Qin, Y.; Tock, C.L.; Pfützner, W.; Ohyama, M.; Schnermann, J.; Vogel, J.C. A Gene Therapy Approach for Long-Term Normalization of Blood Pressure in Hypertensive Mice by ANP-Secreting Human Skin Grafts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 1178–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzetta, L.; Orlandi, A.; Page, C.; Rogliani, P.; Rinaldi, B.; Rosano, G.; Cazzola, M.; Matera, M.G. Brain Natriuretic Peptide: Much More than a Biomarker. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 221, 1031–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataliotti, A.; Tonne, J.M.; Bellavia, D.; Martin, F.L.; Oehler, E.A.; Harders, G.E.; Campbell, J.M.; Peng, K.-W.; Russell, S.J.; Malatino, L.S.; et al. Long-Term Cardiac pro-B-Type Natriuretic Peptide Gene Delivery Prevents the Development of Hypertensive Heart Disease in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Circulation 2011, 123, 1297–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonne, J.M.; Holditch, S.J.; Oehler, E.A.; Schreiber, C.A.; Ikeda, Y.; Cataliotti, A. Cardiac BNP Gene Delivery Prolongs Survival in Aged Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats with Overt Hypertensive Heart Disease. Aging 2014, 6, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, P.; Wang, Q.; Wang, F.-Z.; Dai, H.-B.; Wang, H.-Y.; Gao, Q.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, Y.-B. Adrenomedullin Improves Cardiac Remodeling and Function in Obese Rats with Hypertension. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, J.; Jin, L.; Lin, K.F.; Chao, L. Adrenomedullin Gene Delivery Reduces Blood Pressure in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Hypertens. Res. 1997, 20, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.J.; Yoshida, H.; Chao, L.; Chao, J. Human Adrenomedullin Gene Delivery Protects against Cardiac Hypertrophy, Fibrosis, and Renal Damage in Hypertensive Dahl Salt-Sensitive Rats. Hum. Gene Ther. 2000, 11, 1817–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phelps, P.K.; Kelley, E.F.; Walla, D.M.; Ross, J.K.; Simmons, J.J.; Bulock, E.K.; Ayres, A.; Akre, M.K.; Sprissler, R.; Olson, T.P.; et al. Relationship between a Weighted Multi-Gene Algorithm and Blood Pressure Control in Hypertension. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05349825 (accessed on 10 April 2024).
- Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04660630?Cond=Hypertension&intr=therapy%20gene&rank=1 (accessed on 10 April 2024).
- Chiesa, G.; Sirtori, C.R. Apolipoprotein A-I(Milano): Current Perspectives. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2003, 14, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanllorente, A.; Lassale, C.; Soria-Florido, M.T.; Castañer, O.; Fitó, M.; Hernáez, Á. Modification of High-Density Lipoprotein Functions by Diet and Other Lifestyle Changes: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pászty, C.; Maeda, N.; Verstuyft, J.; Rubin, E.M. Apolipoprotein AI Transgene Corrects Apolipoprotein E Deficiency-Induced Atherosclerosis in Mice. J. Clin. Investig. 1994, 94, 899–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soma, M.R.; Donetti, E.; Parolini, C.; Sirtori, C.R.; Fumagalli, R.; Franceschini, G. Recombinant Apolipoprotein A-I Milano Dimer Inhibits Carotid Intimal Thickening Induced by Perivascular Manipulation in Rabbits. Circ. Res. 1995, 76, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangirala, R.K.; Tsukamoto, K.; Chun, S.H.; Usher, D.; Puré, E.; Rader, D.J. Regression of Atherosclerosis Induced by Liver-Directed Gene Transfer of Apolipoprotein A-I in Mice. Circulation 1999, 100, 1816–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishiguro, H.; Yoshida, H.; Major, A.S.; Zhu, T.; Babaev, V.R.; Linton, M.F.; Fazio, S. Retrovirus-Mediated Expression of Apolipoprotein A-I in the Macrophage Protects against Atherosclerosis In Vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 36742–36748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitajima, K.; Marchadier, D.H.L.; Miller, G.C.; Gao, G.; Wilson, J.M.; Rader, D.J. Complete Prevention of Atherosclerosis in ApoE-Deficient Mice by Hepatic Human ApoE Gene Transfer with Adeno-Associated Virus Serotypes 7 and 8. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2006, 26, 1852–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebherz, C.; Sanmiguel, J.; Wilson, J.M.; Rader, D.J. Gene Transfer of Wild-Type ApoA-I and ApoA-I Milano Reduce Atherosclerosis to a Similar Extent. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2007, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, V.; Foster, H.; Graham, I.R.; Foster, K.; Athanasopoulos, T.; Simons, J.P.; Dickson, G.; Owen, J.S. Human Apolipoprotein E Expression from Mouse Skeletal Muscle by Electrotransfer of Nonviral DNA (Plasmid) and Pseudotyped Recombinant Adeno-Associated Virus (AAV2/7). Hum. Gene Ther. 2008, 19, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Van Craeyveld, E.; Jacobs, F.; Lievens, J.; Snoeys, J.; De Geest, B. Wild-Type Apo A-I and Apo A-I (Milano) Gene Transfer Reduce Native and Transplant Arteriosclerosis to a Similar Extent. J. Mol. Med. 2009, 87, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaessen, S.F.C.; Veldman, R.J.; Comijn, E.M.; Snapper, J.; Sierts, J.A.; van den Oever, K.; Beattie, S.G.; Twisk, J.; Kuivenhoven, J.A. AAV Gene Therapy as a Means to Increase Apolipoprotein (Apo) A-I and High-Density Lipoprotein-Cholesterol Levels: Correction of Murine ApoA-I Deficiency. J. Gene Med. 2009, 11, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koornneef, A.; Maczuga, P.; van Logtenstein, R.; Borel, F.; Blits, B.; Ritsema, T.; van Deventer, S.; Petry, H.; Konstantinova, P. Apolipoprotein B Knockdown by AAV-Delivered ShRNA Lowers Plasma Cholesterol in Mice. Mol. Ther. 2011, 19, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Beckstead, J.A.; Simonsen, J.B.; Nelbach, L.; Watson, G.; Forte, T.M.; Ryan, R.O. Gene Transfer of Apolipoprotein A-V Improves the Hypertriglyceridemic Phenotype of Apoa5 (−/−) Mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2013, 33, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Wang, L.; Arias, A.; Yang, M.; Sharifi, B.G.; Shah, P.K. Comparative Antiatherogenic Effects of Intravenous AAV8- and AAV2-Mediated ApoA-IMilano Gene Transfer in Hypercholesterolemic Mice. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 20, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wacker, B.K.; Dronadula, N.; Bi, L.; Stamatikos, A.; Dichek, D.A. Apo A-I (Apolipoprotein A-I) Vascular Gene Therapy Provides Durable Protection Against Atherosclerosis in Hyperlipidemic Rabbits. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2018, 38, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, L.; Wacker, B.K.; Komandur, K.; Sanford, N.; Dichek, D.A. Apolipoprotein A-I Vascular Gene Therapy Reduces Vein-Graft Atherosclerosis. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2023, 30, 558–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, V.; Twisk, J.; Kwikkers, K.; Aronica, E.; Brisson, D.; Methot, J.; Petry, H.; Gaudet, D. Immune Responses to Intramuscular Administration of Alipogene Tiparvovec (AAV1-LPL(S447X)) in a Phase II Clinical Trial of Lipoprotein Lipase Deficiency Gene Therapy. Hum. Gene Ther. 2014, 25, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaudet, D.; Méthot, J.; Déry, S.; Brisson, D.; Essiembre, C.; Tremblay, G.; Tremblay, K.; de Wal, J.; Twisk, J.; van den Bulk, N.; et al. Efficacy and Long-Term Safety of Alipogene Tiparvovec (AAV1-LPLS447X) Gene Therapy for Lipoprotein Lipase Deficiency: An Open-Label Trial. Gene Ther. 2013, 20, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossman, P.M.; Mendelsohn, F.; Henry, T.D.; Hermiller, J.B.; Litt, M.; Saucedo, J.F.; Weiss, R.J.; Kandzari, D.E.; Kleiman, N.; Anderson, R.D.; et al. Results from a Phase II Multicenter, Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Study of Del-1 (VLTS-589) for Intermittent Claudication in Subjects with Peripheral Arterial Disease. Am. Heart J. 2007, 153, 874–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT00696124?Cond=Atherosclerosis&intr=gene%20therapy&page=2&rank=13 (accessed on 10 April 2024).
- Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02144610?Cond=Atherosclerosis&intr=gene%20therapy&page=2&rank=12 (accessed on 10 April 2024).
- Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT01064440?Cond=Atherosclerosis&intr=gene%20therapy&page=2&rank=11 (accessed on 10 April 2024).
- Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02016755?Cond=Atherosclerosis&intr=gene%20therapy&page=3&rank=21 (accessed on 10 April 2024).
- Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT06112327 (accessed on 10 April 2024).
- Rouis, M.; Adamy, C.; Duverger, N.; Lesnik, P.; Horellou, P.; Moreau, M.; Emmanuel, F.; Caillaud, J.M.; Laplaud, P.M.; Dachet, C.; et al. Adenovirus-Mediated Overexpression of Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase-1 Reduces Atherosclerotic Lesions in Apolipoprotein E-Deficient Mice. Circulation 1999, 100, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, H.; Neplioueva, V.; Shetty, G.A.; Channon, K.M.; George, S.E. Nitric Oxide Synthase Gene Therapy Rapidly Reduces Adhesion Molecule Expression and Inflammatory Cell Infiltration in Carotid Arteries of Cholesterol-Fed Rabbits. Circulation 1999, 99, 2979–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Von Der Thüsen, J.H.; Kuiper, J.; Fekkes, M.L.; De Vos, P.; Van Berkel, T.J.; Biessen, E.A. Attenuation of Atherogenesis by Systemic and Local Adenovirus-Mediated Gene Transfer of Interleukin-10 in LDLr−/− Mice. FASEB J. 2001, 15, 2730–2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshioka, T.; Okada, T.; Maeda, Y.; Ikeda, U.; Shimpo, M.; Nomoto, T.; Takeuchi, K.; Nonaka-Sarukawa, M.; Ito, T.; Takahashi, M.; et al. Adeno-Associated Virus Vector-Mediated Interleukin-10 Gene Transfer Inhibits Atherosclerosis in Apolipoprotein E-Deficient Mice. Gene Ther. 2004, 11, 1772–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, D.; Chen, J.; Xie, J.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Zhang, D.; Nemarkommula, A.R.; Liu, H.; Mehta, J.L.; Hermonat, P.L. Inhibition of Atherogenesis in LDLR Knockout Mice by Systemic Delivery of Adeno-Associated Virus Type 2-HIL-10. Atherosclerosis 2006, 188, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namiki, M.; Kawashima, S.; Yamashita, T.; Ozaki, M.; Sakoda, T.; Inoue, N.; Hirata, K.-I.; Morishita, R.; Kaneda, Y.; Yokoyama, M. Intramuscular Gene Transfer of Interleukin-10 CDNA Reduces Atherosclerosis in Apolipoprotein E-Knockout Mice. Atherosclerosis 2004, 172, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Velchala, N.; Amani, F.; Nemarkommula, A.; Chen, K.; Rayaz, H.; Zhang, D.; Liu, H.; et al. Suppression of Atherogenesis by Delivery of TGFbeta1ACT Using Adeno-Associated Virus Type 2 in LDLR Knockout Mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 344, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, J.A.; Cao, M.; Kang, B.-Y.; Liu, Y.; Mehta, J.L.; Hermonat, P.L. AAV/HSTAT3-Gene Delivery Lowers Aortic Inflammatory Cell Infiltration in LDLR KO Mice on High Cholesterol. Atherosclerosis 2010, 213, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, M.; Khan, J.A.; Kang, B.-Y.; Mehta, J.L.; Hermonat, P.L. Dual AAV/IL-10 Plus STAT3 Anti-Inflammatory Gene Delivery Lowers Atherosclerosis in LDLR KO Mice, but without Increased Benefit. Int. J. Vasc. Med. 2012, 2012, 524235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, L.; Wacker, B.K.; Bueren, E.; Ham, E.; Dronadula, N.; Dichek, D.A. A Rabbit Model for Testing Helper-Dependent Adenovirus-Mediated Gene Therapy for Vein Graft Atherosclerosis. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2017, 7, 96–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, R.; O’Kane, M.; McGilligan, V.; Watterson, S. The Genetics and Screening of Familial Hypercholesterolaemia. J. Biomed. Sci. 2016, 23, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, N.P.; Ahmed, H.M.; Wilson Tang, W.H. Familial Hypercholesterolemia: Detect, Treat, and Ask about Family. Cleve Clin. J. Med. 2020, 87, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, J.R.; Grossman, M.; Gupta, S.; Chowdhury, N.R.; Baker, J.R.; Wilson, J.M. Long-Term Improvement of Hypercholesterolemia after Ex Vivo Gene Therapy in LDLR-Deficient Rabbits. Science 1991, 254, 1802–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.J.; Rader, D.J.; Tazelaar, J.; Kawashiri, M.; Gao, G.; Wilson, J.M. Prolonged Correction of Hyperlipidemia in Mice with Familial Hypercholesterolemia Using an Adeno-Associated Viral Vector Expressing Very-Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor. Mol. Ther. 2000, 2, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kankkonen, H.M.; Vähäkangas, E.; Marr, R.A.; Pakkanen, T.; Laurema, A.; Leppänen, P.; Jalkanen, J.; Verma, I.M.; Ylä-Herttuala, S. Long-Term Lowering of Plasma Cholesterol Levels in LDL-Receptor-Deficient WHHL Rabbits by Gene Therapy. Mol. Ther. 2004, 9, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassim, S.H.; Li, H.; Vandenberghe, L.H.; Hinderer, C.; Bell, P.; Marchadier, D.; Wilson, A.; Cromley, D.; Redon, V.; Yu, H.; et al. Gene Therapy in a Humanized Mouse Model of Familial Hypercholesterolemia Leads to Marked Regression of Atherosclerosis. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibbitt, O.; Agkatsev, S.; Owen, C.; Cioroch, M.; Seymour, L.; Channon, K.; Wade-Martins, R. RNAi-Mediated Knockdown of HMG CoA Reductase Enhances Gene Expression from Physiologically Regulated Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor Therapeutic Vectors In Vivo. Gene Ther. 2012, 19, 463–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kassim, S.H.; Li, H.; Bell, P.; Somanathan, S.; Lagor, W.; Jacobs, F.; Billheimer, J.; Wilson, J.M.; Rader, D.J. Adeno-Associated Virus Serotype 8 Gene Therapy Leads to Significant Lowering of Plasma Cholesterol Levels in Humanized Mouse Models of Homozygous and Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia. Hum. Gene Ther. 2013, 24, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somanathan, S.; Jacobs, F.; Wang, Q.; Hanlon, A.L.; Wilson, J.M.; Rader, D.J. AAV Vectors Expressing LDLR Gain-of-Function Variants Demonstrate Increased Efficacy in Mouse Models of Familial Hypercholesterolemia. Circ. Res. 2014, 115, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Muthuramu, I.; Somanathan, S.; Zhang, H.; Bell, P.; He, Z.; Yu, H.; Zhu, Y.; Tretiakova, A.P.; Wilson, J.M. Developing a Second-Generation Clinical Candidate AAV Vector for Gene Therapy of Familial Hypercholesterolemia. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2021, 22, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Yang, G.; Yuan, L. Exosome-Based Ldlr Gene Therapy for Familial Hypercholesterolemia in a Mouse Model. Theranostics 2021, 11, 2953–2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, M.; Raper, S.E.; Kozarsky, K.; Stein, E.A.; Engelhardt, J.F.; Muller, D.; Lupien, P.J.; Wilson, J.M. Successful Ex Vivo Gene Therapy Directed to Liver in a Patient with Familial Hypercholesterolaemia. Nat. Genet. 1994, 6, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossman, M.; Rader, D.J.; Muller, D.W.; Kolansky, D.M.; Kozarsky, K.; Clark, B.J.; Stein, E.A.; Lupien, P.J.; Brewer, H.B.; Raper, S.E. A Pilot Study of Ex Vivo Gene Therapy for Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolaemia. Nat. Med. 1995, 1, 1148–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/Study/NCT02651675 (accessed on 27 February 2024).
- Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05043181 (accessed on 27 February 2024).
- Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03400800 (accessed on 27 February 2024).
- Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03747224 (accessed on 27 February 2024).
- Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04606602 (accessed on 27 February 2024).
- Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04270760 (accessed on 27 February 2024).
- Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03626662 (accessed on 27 February 2024).
- Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/Ct2/Show/NCT02900027 (accessed on 27 February 2024).
- Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03385239 (accessed on 27 February 2024).
- Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02211209 (accessed on 27 February 2024).
- O’Donoghue, M.L.; Rosenson, R.S.; Gencer, B.; López, J.A.G.; Lepor, N.E.; Baum, S.J.; Stout, E.; Gaudet, D.; Knusel, B.; Kuder, J.F.; et al. Small Interfering RNA to Reduce Lipoprotein(a) in Cardiovascular Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 1855–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, W.F. September 14, 1990: The Beginning. Hum. Gene Ther. 1990, 1, 371–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabi, F.; Mansouri, V.; Ahmadbeigi, N. Gene Therapy Clinical Trials, Where Do We Go? An Overview. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 153, 113324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardin, A.; Ronzitti, G. Current Limitations of Gene Therapy for Rare Pediatric Diseases: Lessons Learned from Clinical Experience with AAV Vectors. Arch. Pédiatrie 2023, 30, 8S46–8S52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grieger, J.C.; Samulski, R.J. Packaging Capacity of Adeno-Associated Virus Serotypes: Impact of Larger Genomes on Infectivity and Postentry Steps. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 9933–9944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athanasopoulos, T.; Munye, M.M.; Yáñez-Muñoz, R.J. Nonintegrating Gene Therapy Vectors. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 31, 753–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, M.; Zaman, M.; Ahmad, A.; Khan, R.; Mallhi, T.; Hasan, M.; Khan, Y.; Hafeez, S.; Massoud, E.; Rahman, M.; et al. Appraisal for the Potential of Viral and Nonviral Vectors in Gene Therapy: A Review. Genes 2022, 13, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, F.; Rudin, C.M.; Sen, T. CRISPR Gene Therapy: Applications, Limitations, and Implications for the Future. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
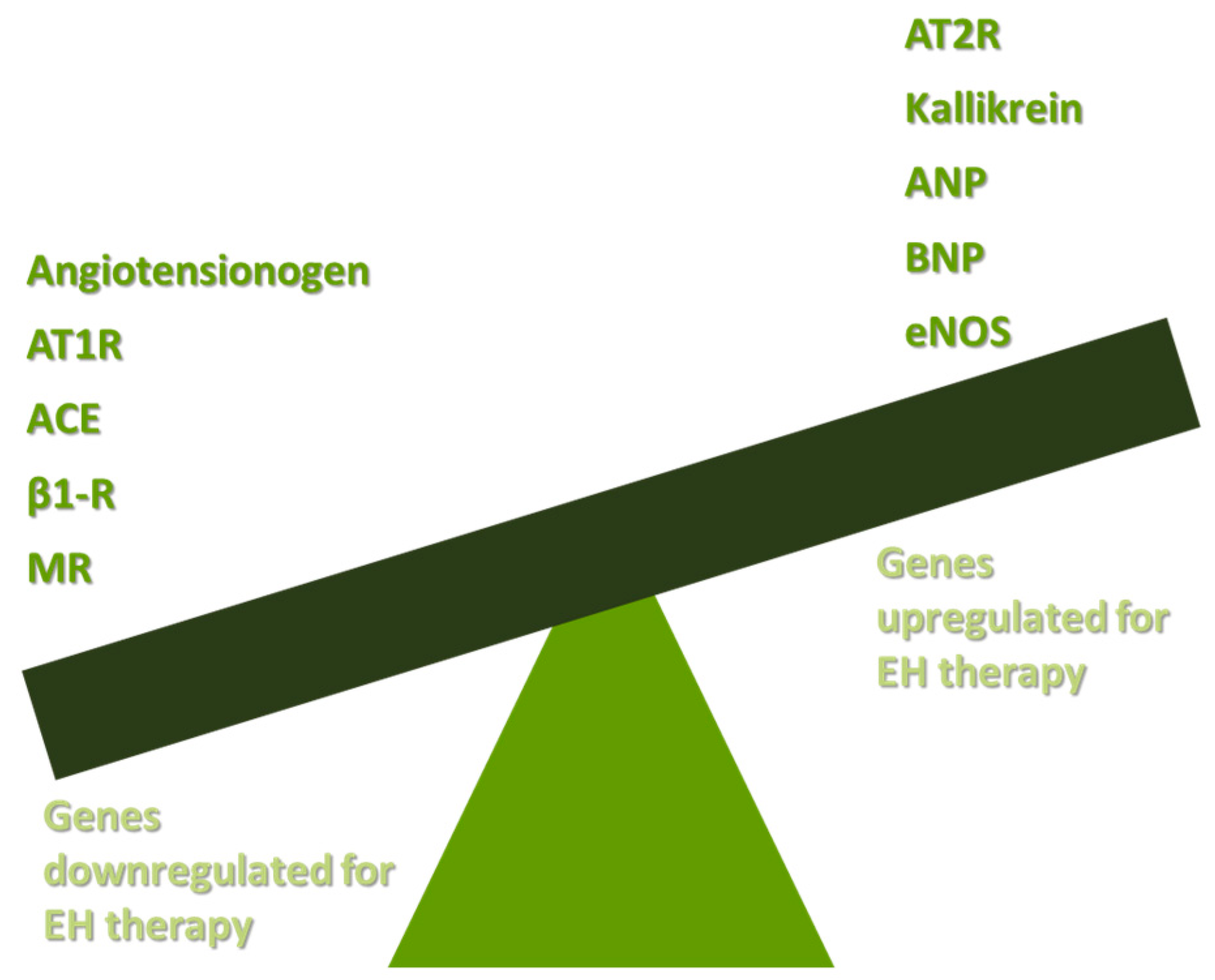
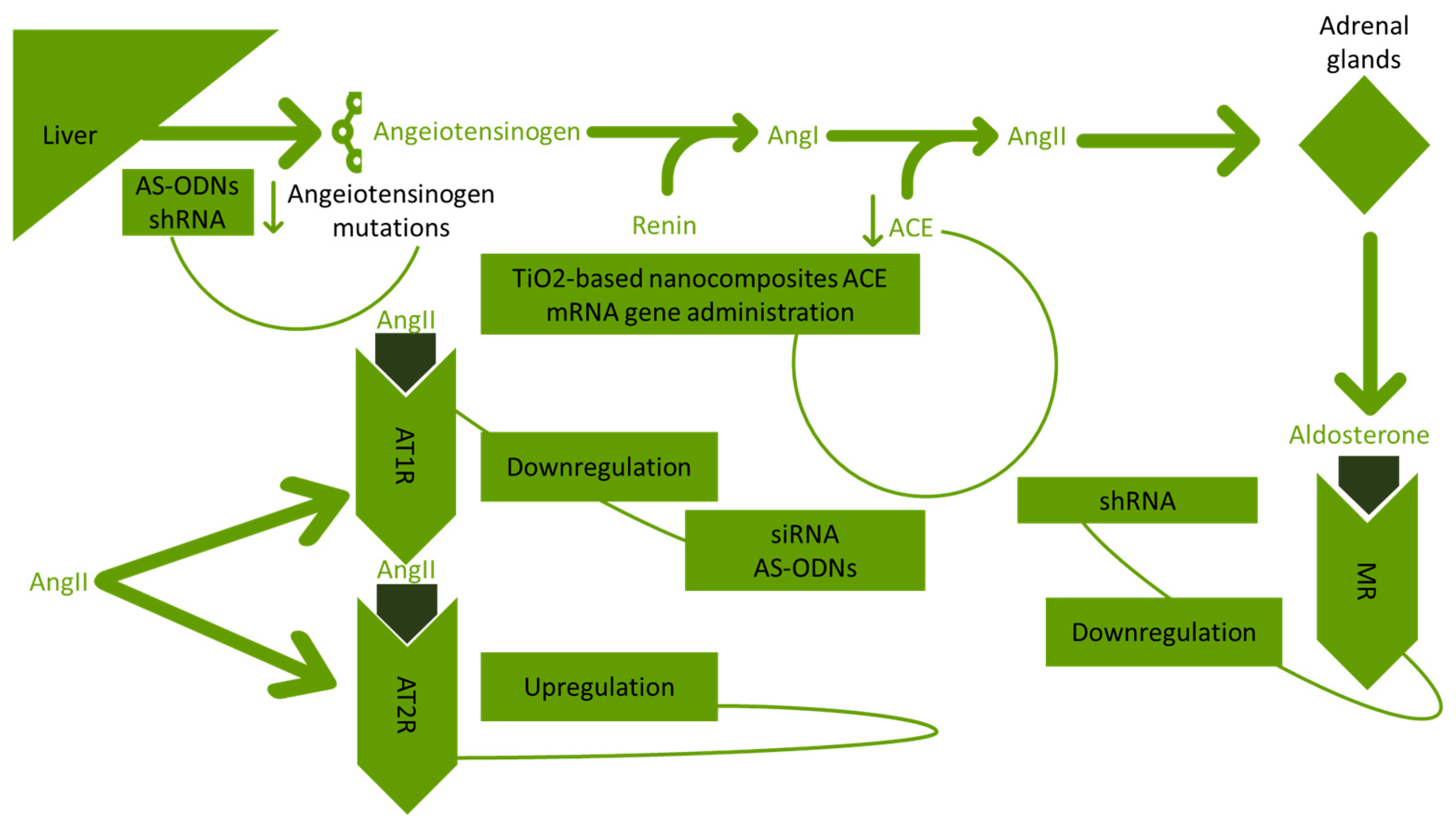
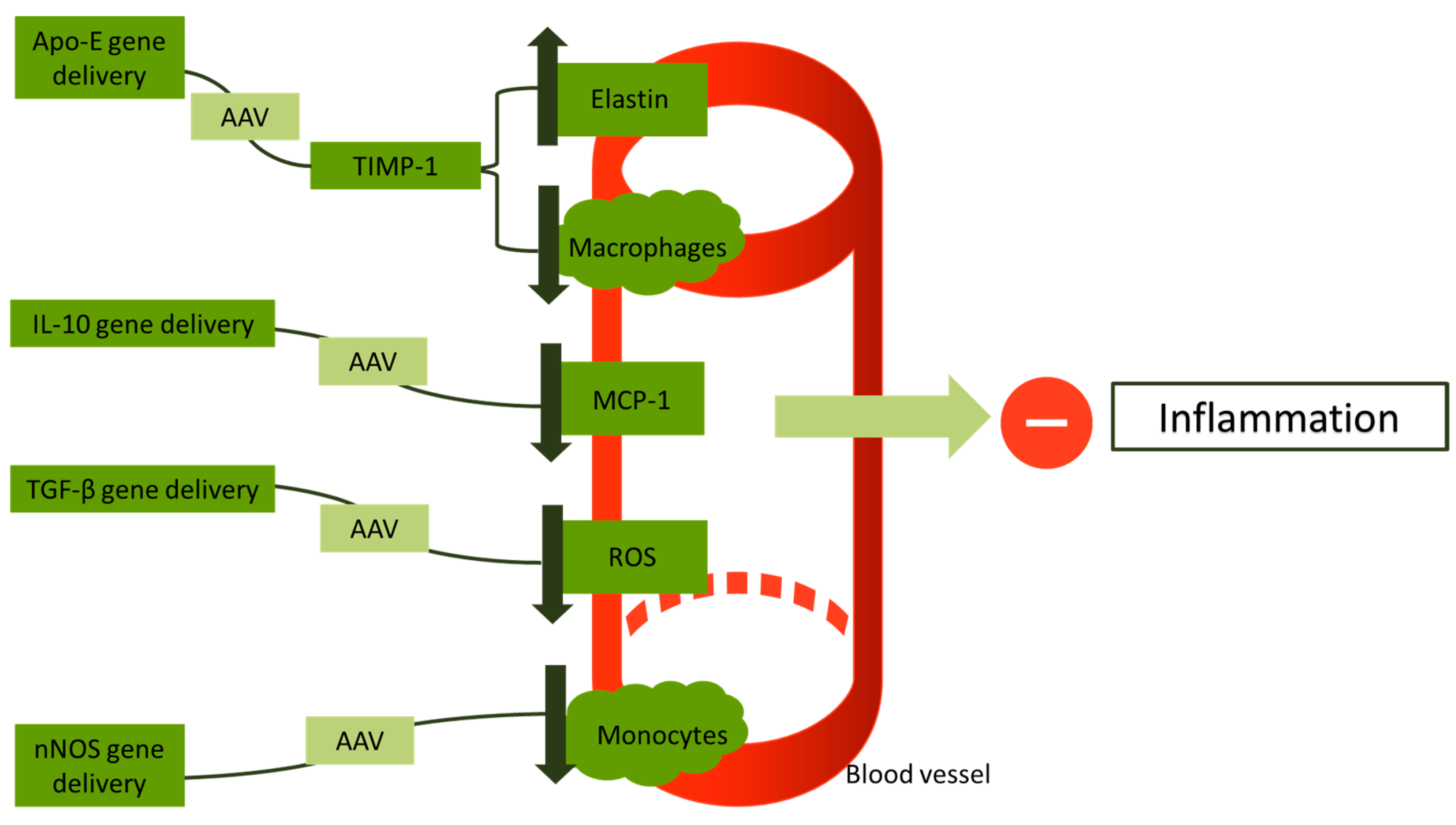
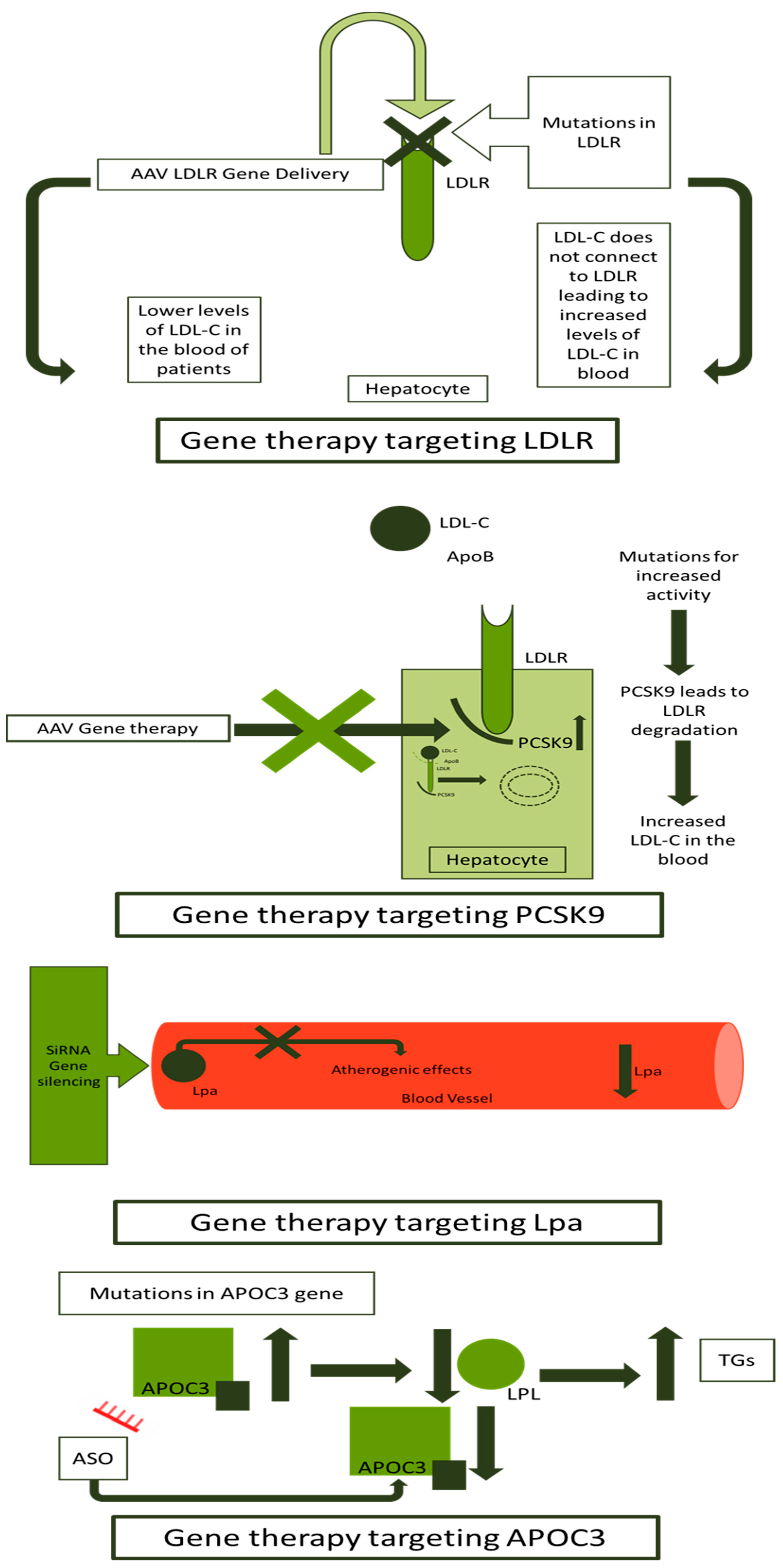
| Study | Method of Gene Administration | Outcome | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chao et al. | eNOS gene direct administration | Decrease in SBP and DBP | [77] |
| Miller et al. | eNOS gene via AAV vector | Decrease in SBP and DBP | [78] |
| Gava et al. | eNOS gene via AAV vector | Prevention of renovascular hypertension | [79] |
| Zhao et al. | eNOS cDNA | Decrease in SBP and DBP in hyperglycemic rats | [80] |
| Trial Number | Method of Gene Administration | Target | Effect | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FH | ||||
| CT-AMT-011-01 | AAV | LPL Deficiency | 40% decrease in TGs in three to 12 weeks | [110] |
| NCT02651675 | AAV8 | LDLR | No clinical outcome | [140] |
| NCT05043181 | AAV | LDLR | Decrease in TC, TGs, LDL-C, and HDL-C | [141] |
| NCT03400800 | AAV | PCSK9 | A 50% decrease in LDL-C | [142] |
| NCT03747224 | AAV | PCSK9 | A 42% decrease in LDL-C | [143] |
| NCT04606602 | SiRNA | Lp(a) | Dose-dependent decrease in Lp(a) 70% (300 mg) or 80% (600 mg) | [146] |
| NCT04270760 | SiRNA | Lp(a) | Lower levels of Lp(a) | [150] |
| NCT03626662 | SiRNA | Lp(a) | A 76–91% decrease in Lp(a) levels | [144] |
| NCT02900027 | ASO | ApoC3 | A 93% decrease in ApoC3 | [147] |
| NCT03385239 | ASO | ApoC3 | Reduction in TG levels | [148] |
| NCT02211209 | ASO | ApoC3 | A decrease 84% of ApoC3 | [149] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Evangelidis, N.; Evangelidis, P. Gene Therapy for Hypertension, Atherosclerosis, and Familial Hypercholesterolemia: The Old Concepts and the New Era. Biologics 2024, 4, 143-160. https://doi.org/10.3390/biologics4020010
Evangelidis N, Evangelidis P. Gene Therapy for Hypertension, Atherosclerosis, and Familial Hypercholesterolemia: The Old Concepts and the New Era. Biologics. 2024; 4(2):143-160. https://doi.org/10.3390/biologics4020010
Chicago/Turabian StyleEvangelidis, Nikolaos, and Paschalis Evangelidis. 2024. "Gene Therapy for Hypertension, Atherosclerosis, and Familial Hypercholesterolemia: The Old Concepts and the New Era" Biologics 4, no. 2: 143-160. https://doi.org/10.3390/biologics4020010
APA StyleEvangelidis, N., & Evangelidis, P. (2024). Gene Therapy for Hypertension, Atherosclerosis, and Familial Hypercholesterolemia: The Old Concepts and the New Era. Biologics, 4(2), 143-160. https://doi.org/10.3390/biologics4020010







