Identification and Effects of Skim Milk-Derived Bioactive Antihypertensive Peptides
Abstract
:1. Introduction
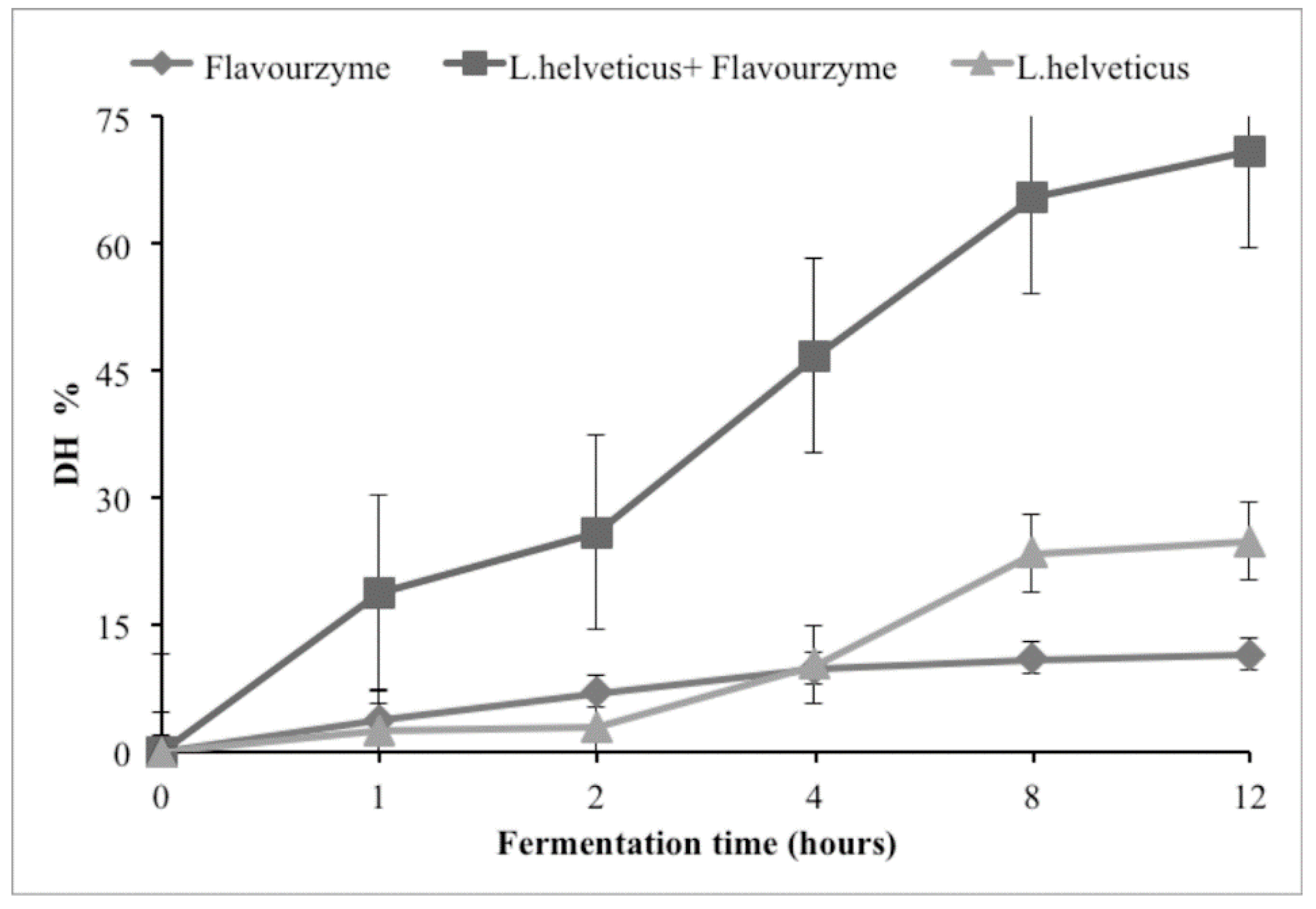
2. Results and Discussion
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Propagation of Cultures and Preparation of Fermented RSM
4.3. Bioreactor Assay of RSM
4.4. Determination of Hydrolysis and ACE-I Activity
4.5. Micro-Fluidic Lab-on-a-Chip Electrophoresis
4.6. Isolation and Characterization of Peptides
4.7. ACE-I Peptide Identification
4.8. Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization (MALDI)-MS/MS Analysis
4.9. Animal Experiments
4.10. Statistical Analyses
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sultan, S.; Huma, N.; Butt, M.S.; Aleem, M.; Abbas, M. Therapeutic Potential of Dairy Bioactive Peptides: A Contemporary Perspective. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, R.J.; Murray, B.A. Bioactive Peptides and Lactic Fermentations. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2006, 59, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raveschot, C.; Deracinois, B.; Bertrand, E.; Flahaut, C.; Frémont, M.; Drider, D.; Dhulster, P.; Cudennec, B.; Coutte, F.J.F.I.B. Biotechnology. Integrated Continuous Bioprocess Development for ACE-Inhibitory Peptide Production by Lactobacillus Helveticus Strains in Membrane Bioreactor. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otte, J.; Shalaby, S.M.; Zakora, M.; Nielsen, M.S. Fractionation and Identification of ACE-Inhibitory Peptides from α-Lactalbumin and β-Casein Produced by Thermolysin-Catalysed Hydrolysis. Int. Dairy J. 2007, 17, 1460–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearney, P.M.; Whelton, M.; Reynolds, K.; Muntner, P.; Whelton, P.K.; He, J. Global Burden of Hypertension: Analysis of Worldwide Data. Lancet 2005, 365, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Hypertension. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hypertension (accessed on 12 November 2021).
- Ramchandran, L.; Shah, N.P.J. Yogurt can Beneficially Affect Blood Contributors of Cardiovascular Health Status in Hypertensive Rats. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, H131–H136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Cheng, X.; Zhou, J.; Tang, X.; Mao, X.-Y. Hypertension-Attenuating Effect of Whey Protein Hydrolysate on Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 122–126. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Musoles, R.; Manzanares, P.; Burguete, M.C.; Alborch, E.; Salom, J.B. In Vivo Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme Inhibition by Long-Term Intake of Antihypertensive Lactoferrin Hydrolysate in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Food Res. Int. 2013, 54, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauzin, J.; Miclo, L.; Gaillard, J.-L. Angiotensin-I-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides from Tryptic Hydrolysate of Bovine αS2-Casein. FEBS Lett. 2002, 531, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hernández-Ledesma, B.; del Mar Contreras, M.; Recio, I. Antihypertensive Peptides: Production, Bioavailability and Incorporation into Foods. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 165, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hernández-Ledesma, B.; García-Nebot, M.J.; Fernández-Tomé, S.; Amigo, L.; Recio, I. Dairy Protein Hydrolysates: Peptides for Health Benefits. Int. Dairy J. 2014, 38, 82–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pihlanto-Leppälä, A. Bioactive Peptides Derived from Bovine Whey Proteins: Opioid and Ace-Inhibitory Peptides. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2000, 11, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauregi, P.; Welderufael, F.T. Added-Value Protein Products from Whey. Nutrafoods 2010, 9, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Fang, M.; Wu, H.; Xie, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, P.; Zhang, D.; Huang, Z.; Xia, Y.; Zhou, L.J. A Novel Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptide from Phascolosoma Esculenta Water-Soluble Protein Hydrolysate. J. Funct. Foods 2013, 5, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisele, T.; Stressler, T.; Kranz, B.; Fischer, L. Bioactive Peptides Generated in an Enzyme Membrane Reactor Using Bacillus Lentus Alkaline Peptidase. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2013, 236, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahtesh, F.; Stojanovska, L.; Shah, N.; Mishra, V.K. Effect of Flavourzyme® on Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides Formed in Skim Milk and Whey Protein Concentrate during Fermentation by Lactobacillus Helveticus. J. Food Sci. 2016, 81, M135–M143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahtesh, F.B.; Stojanovska, L.; Mathai, M.L.; Apostolopoulos, V.; Mishra, V.K. Proteolytic and Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme-Inhibitory Activities of Selected Probiotic Bacteria. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 865–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Ahtesh, F.; Mathai, M.; McAinch, A.J.; Su, X.Q. Effects of Fermentation Conditions on the Potential Anti-Hypertensive Peptides Released from Yogurt Fermented by Lactobacillus Helveticus and Flavourzyme®. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 52, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Narva, M.; Collin, M.; Jauhiainen, T.; Vapaatalo, H.; Korpela, R. Effects of Lactobacillus Helveticus Fermented Milk and Its Bioactive Peptides on Bone Parameters in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Milchwissenschaft 2004, 59, 359–363. [Google Scholar]
- Expósito, I.L.; Recio, I. Antibacterial Activity of Peptides and Folding Variants from Milk Proteins. Int. Dairy J. 2006, 16, 1294–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtinen, R.; Jauhiainen, T.; Kankuri, E.; Lindstedt, K.; Kovanen, P.T.; Kerojoki, O.; Korpela, R.; Vapaatalo, H. Effects of Milk Casein-Derived Tripeptides Ile-Pro-Pro, Val-Pro-Pro, and Leu-Pro-Pro on Enzymes Processing Vasoactive Precursors In Vitro. Arzneimittelforschung 2010, 60, 182–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.; Cheung, H.S.; Wang, F.L.; Ma, O.; Ef, S. Binding of Peptide Substrates and Inhibitors of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme: Importance of the Cooh-Terminal Dipeptide Sequence. J. Biol. Chem. 1980, 25, 401–407. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, Y.; Yamamoto, N.; Sakai, K.; Okubo, A.; Yamazaki, S.; Takano, T. Purification and Characterization of Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors from Sour Milk. J. Dairy Sci. 1995, 78, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Aluko, R.E.; Nakai, S. Structural Requirements of Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides: Quantitative Structure—Activity Relationship Study of Di-and Tripeptides. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welderufael, F.T.; Gibson, T.; Jauregi, P. Production of Angiotensin-I-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides from β-Lactoglobulin-and Casein-Derived Peptides: An Integrative Approach. Biotechnol. Prog. 2012, 28, 746–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahtesh, F.B.; Stojanovska, L.; Apostolopoulos, V. Processing and Sensory Characteristics of a Fermented Low-Fat Skim Milk Drink Containing Bioactive Antihypertensive Peptides, a Functional Milk Product. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2018, 71, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauhiainen, T.; Pilvi, T.; Cheng, Z.J.; Kautiainen, H.; Müller, D.N.; Vapaatalo, H.; Korpela, R.; Mervaala, E. Milk Products Containing Bioactive Tripeptides Have an Antihypertensive Effect in Double Transgenic Rats (dTGR) Harbouring Human Renin and Human Angiotensinogen Genes. J. Nutr. Metab. 2010, 2010, 287030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jauhiainen, T.; Vapaatalo, H.; Poussa, T.; Kyrönpalo, S.; Rasmussen, M.; Korpela, R. Lactobacillus Helveticus Fermented Milk Lowers Blood Pressure in Hypertensive Subjects in 24-H Ambulatory Blood Pressure Measurement. Am. J. Hypertens. 2005, 18, 1600–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nikolić, Z.; Đorđević, V.; Torbica, A.; Mikić, A. Legumes Seed Storage Proteins Characterization by SDS-PAGE and Lab-on-a-Chip Electrophoresis. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2012, 28, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anema, S.G. The Use of “Lab-on-a-Chip” Microfluidic SDS Electrophoresis Technology for the Separation and Quantification of Milk Proteins. Int. Dairy J. 2009, 19, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Pan, D.; Tanokura, M. Optimisation of Hydrolysis Conditions for the Production of the Angiotensin-I Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitory Peptides from Whey Protein Using Response Surface Methodology. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahtesh, F.B.; Stojanovska, L.; Apostolopoulos, V. Anti-Hypertensive Peptides Released from Milk Proteins by Probiotics. Maturitas 2018, 115, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pihlanto, A.; Virtanen, T.; Korhonen, H. Angiotensin I Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitory Activity and Antihypertensive Effect of Fermented Milk. Int. Dairy J. 2010, 20, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutrou, R.; Gaudichon, C.; Dupont, D.; Jardin, J.; Airinei, G.; Marsset-Baglieri, A.; Benamouzig, R.; Tome, D.; Leonil, J. Sequential Release of Milk Protein-Derived Bioactive Peptides in the Jejunum in Healthy Humans. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 97, 1314–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quirós, A.; Ramos, M.; Muguerza, B.; Delgado, M.A.; Miguel, M.; Aleixandre, A.; Recio, I. Identification of Novel Antihypertensive Peptides in Milk Fermented with Enterococcus Faecalis. Int. Dairy J. 2007, 17, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaki, H.; Sugano, S.; Uchiwa, H.; Sugai, R.; Murakami, U.; Takemoto, S. Antihypertensive Effect of Tryptic Hydrolysate of Milk Casein in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Comp. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1990, 96, 367–371. [Google Scholar]
- Sah, B.N.P.; Vasiljevic, T.; McKechnie, S.; Donkor, O. Antioxidative and Antibacterial Peptides Derived from Bovine Milk Proteins. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 726–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Tang, S.; He, Q.; Hu, J.; Zheng, J. In Vitro Antioxidant and Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Activity of Fermented Milk with Different Culture Combinations. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 1120–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Mar Contreras, M.; Carrón, R.; Montero, M.J.; Ramos, M.; Recio, I. Novel Casein-Derived Peptides with Antihypertensive Activity. Int. Dairy J. 2009, 19, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshii, H.; Tachi, N.; Ohba, R.; Sakamura, O.; Takeyama, H.; Itani, T. Antihypertensive Effect of ACE Inhibitory Oligopeptides from Chicken Egg Yolks. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2001, 128, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madureira, A.; Tavares, T.; Gomes, A.; Pintado, M.; Malcata, F.X. Invited Review: Physiological Properties of Bioactive Peptides Obtained from Whey Proteins. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 437–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, Z.; Liu, B.; Zhao, W.; Yin, Y.; Liu, J.; Chen, F. Primary and Secondary Structure of Novel ACE-Inhibitory Peptides from Egg White Protein. Food Chem. 2012, 133, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; Zhang, W.; He, R.; Xiong, F.; Ma, H. Protein Breakdown and Release of Antioxidant Peptides during Simulated Gastrointestinal Digestion and the Absorption by Everted Intestinal Sac of Rapeseed Proteins. LWT 2017, 86, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, N.; Maeno, M.; Takano, T. Purification and Characterization of an Antihypertensive Peptide from a Yogurt-Like Product Fermented by Lactobacillus Helveticus CPN4. J. Dairy Sci. 1999, 82, 1388–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seppo, L.; Jauhiainen, T.; Poussa, T.; Korpela, R. A Fermented Milk High in Bioactive Peptides Has a Blood Pressure–Lowering Effect in Hypertensive Subjects. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 77, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adibi, S.A.; Morse, E.L. Intestinal Transport of Dipeptides in Man: Relative Importance of Hydrolysis and Intact Absorption. J. Clin. Investig. 1971, 50, 2266–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.; Birtwhistle, W.; Kim, Y.J. Peptide Hydrolases in the Brush Border and Soluble Fractions of Small Intestinal Mucosa of Rat and Man. J. Clin. Investig. 1972, 51, 1419–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, T.; Zhu, X.L.; Watanabe, K.; Tanaka, K.; Kusano, Y.; Matsumoto, K. Combined Administration of Captopril with an Antihypertensive Val–Tyr Di-Peptide to Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats Attenuates the Blood Pressure Lowering Effect. Life Sci. 2006, 79, 2492–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleeson, J.P.; Heade, J.; Ryan, S.M.; Brayden, D.J. Stability, Toxicity and Intestinal Permeation Enhancement of Two Food-Derived Antihypertensive Tripeptides, Ile-Pro-Pro and Leu-Lys-Pro. Peptides 2015, 71, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regazzo, D. Bioactive Peptides from Milk Proteins: Focusing on Peptides Displaying Immunomodulatory Activity. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Padua, Padova, Italy, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Sipola, M.; Finckenberg, P.; Korpela, R.; Vapaatalo, H.; Nurminen, M.-L. Effect of Long-Term Intake of Milk Products on Blood Pressure in Hypertensive Rats. J. Dairy Res. 2002, 69, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuglsang, A.; Nilsson, D.; Nyborg, N.C. Cardiovascular Effects of Fermented Milk Containing Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors Evaluated in Permanently Catheterized, Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 3566–3569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fuglsang, A.; Rattray, F.P.; Nilsson, D.; Nyborg, N.C. Lactic Acid Bacteria: Inhibition of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme In Vitro and In Vivo. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2003, 83, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravallec-Plé, R.; Gilmartin, L.; Van Wormhoudt, A.; Le Gal, Y. Influence of the Hydrolysis Process on the Biological Activities of Protein Hydrolysates From Cod (Gadus morhua) Muscle. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2000, 80, 2176–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
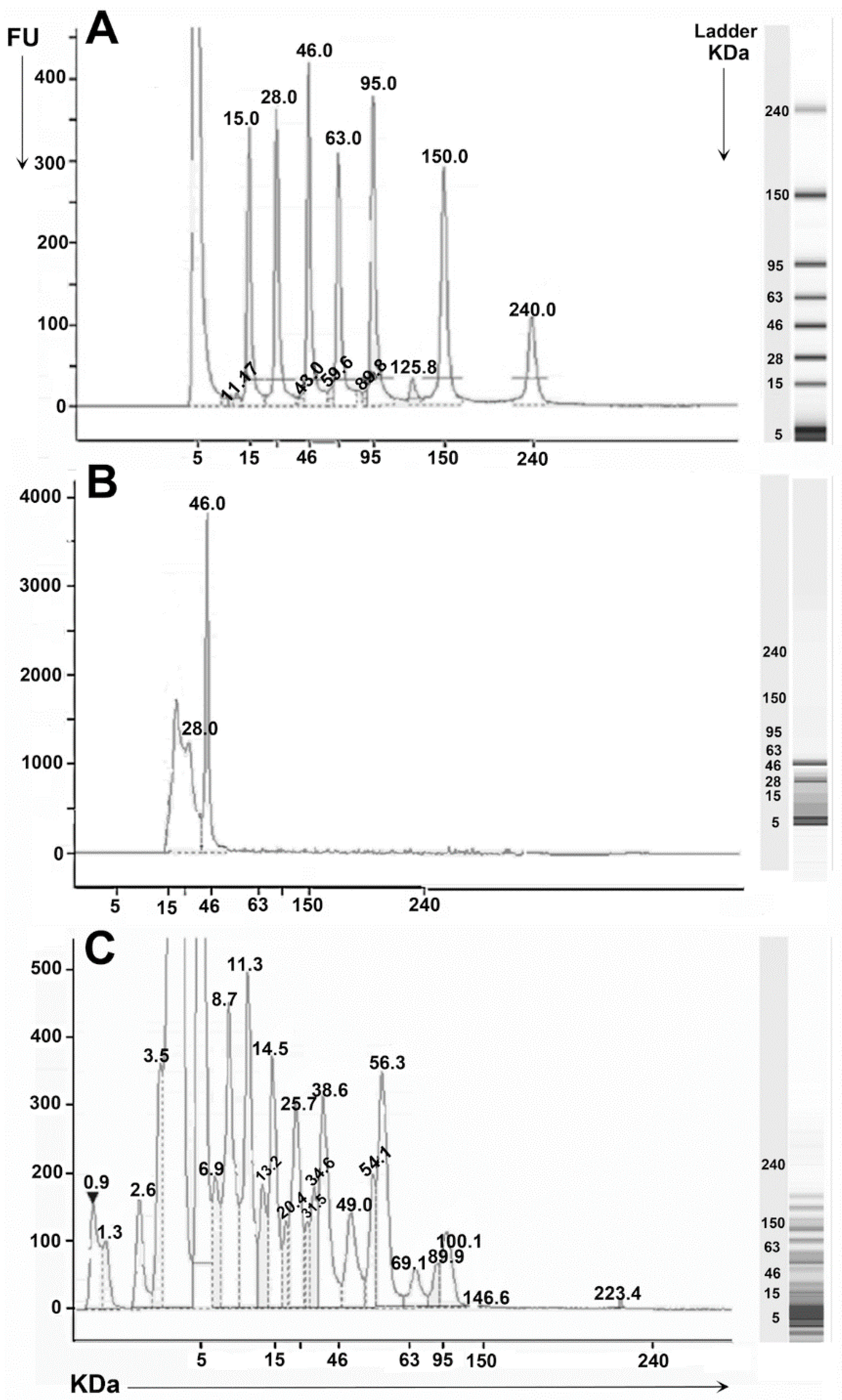


| Fractions | ACE-I % | IC50 mg/mL |
|---|---|---|
| F1 | 85.40 ± 0.32 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 d |
| F2 | 72.04 ± 0.91 b | 0.34 ± 0.03 cd |
| F3 | 42.39 ± 1.20 c | 0.47 ± 0.09 bc |
| F4 | 17.31 ± 2.21 d | 1.18 ± 0.16 a |
| F5 | 27.91 ± 5.30 d | 0.78 ± 0.11 b |
| F6 | 95.51 ± 0.21 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 d |
| Protein Family | Mass (Da) | Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction 1 (F1) | ||
| CASB_BOVIN | 25,091 | Beta-casein |
| CASA1_BOVIN | 24,513 | Alpha-S1-casein |
| CASA1_BUBBU | 24,311 | Alpha-S1-casein |
| LACB_BOVIN | 19,870 | Beta-lacto globulin |
| CAC1E_RABIT | 254,089 | Voltage-dependent R-type calcium channel subunit alpha |
| CASA2_CAPHI | 26,372 | Alpha-S2-casein |
| LALBA_BOSMU | 16,237 | Alpha-lactoalbumin |
| Fraction 6 (F6) | ||
| CASB_BOVIN | 25,091 | Beta-casein |
| CASA1_BOVIN | 24,513 | Alpha-S1-casein |
| CASA1_BUBBU | 24,311 | Alpha-S1-casein |
| LACB_BOVIN | 19,870 | Beta-lacto globulin |
| CASA2_BOVIN | 26,002 | Alpha-S2-casein |
| LALBA_BOSMU | 16,237 | Alpha-lactoalbumin |
| CASK_BOVIN | 21,256 | Kappa-casein OS |
| FETUA_BOVIN | 38,394 | Alpha-2-HS-glycoprotein |
| GLCM1_BOVIN | 17,141 | Glycosylation-dependent cell adhesion molecule |
| DDX56_BOVIN | 61,216 | Probable ATP-dependent RNA helicase |
| BRAT1_AILME | 88,137 | BRCA1-associated ATM activator |
| NIF3L_BOVIN | 41,880 | NIF3-like protein |
| Protein Accession | Protein Description | Peptide, m/z (Experimental) | Peptide Mass, Da (Experimental) | Peptide Mass, Da (Calculated) | Peptide Sequence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fraction 6 (F6) CASB_BOVIN | Beta-casein | 458.3093 | 914.6041 | 914.5953 | LHLPLPLL |
| CASB_BOVIN | Beta-casein | 522.3336 | 1042.6526 | 1042.6539 | LHLPLPLLQ |
| CASB_BOVIN | Beta-casein | 576.3528 | 1150.691 | 1150.6863 | GPVRGPFPIIV |
| CASA1_BOVIN | Alpha-S1-casein | 552.8222 | 1103.6299 | 1103.6339 | LGYLEQLLR |
| CASA1_BOVIN | Alpha-S1-casein | 559.3271 | 1116.6396 | 1116.6291 | VLNENLLRF |
| CASA1_BOVIN | Alpha-S1-casein | 571.7766 | 1141.5387 | 1141.5251 | SDIPNPIGSEN |
| CASA1_BOVIN | Alpha-S1-casein | 609.3681 | 1216.7216 | 1216.7179 | LGYLEQLLRL |
| CASA1_BOVIN | Alpha-S1-casein | 610.3212 | 1218.6279 | 1218.6285 | VAPFPEVFGKE |
| CASA1_BOVIN | Alpha-S1-casein | 669.8782 | 1337.7419 | 1337.7191 | GLPQEVLNENLL |
| CASA1_BOVIN | Alpha-S1-casein | 683.8746 | 1365.7347 | 1365.6969 | FFVAPFPEVFGKE |
| CASA1_BUBBU | Alpha-S1-casein | 559.3271 | 1116.6396 | 1116.6291 | VLNENLLRF |
| CASA1_BUBBU | Alpha-S1-casein | 571.7766 | 1141.5387 | 1141.5251 | SDIPNPIGSEN |
| CASA1_BUBBU | Alpha-S1-casein | 609.3681 | 1216.7216 | 1216.7179 | LGYLEQLLRL |
| CASA1_BUBBU | Alpha-S1-casein | 610.3212 | 1218.6279 | 1218.6285 | VAPFPEVFGKE |
| CASA1_BUBBU | Alpha-S1-casein | 683.8746 | 1365.7347 | 1365.6969 | FVAPFPEVFGKE |
| Fraction 1 (F1) CASA1_BOVIN | Alpha-S1-casein | 24,513 | 1828.8711 | 1828.8513 | DIPNPIGSENSEKTTMP |
| CASA1_BOVIN | Alpha-S1-casein | 24,513 | 997.5195 | 997.508 | GLPQEVLNE |
| CASB_BOVIN | Beta-casein | 25,091 | 1258.6949 | 1258.6921 | DVENLHLPLPL |
| CASB_BOVIN | Beta-casein | 25,091 | 1332.6589 | 1332.6424 | EMPFPKYPVEP |
| CASB_BOVIN | Beta-casein | 25,091 | 1150.691 | 1150.6863 | GPVRGPFPIIV |
| CASB_BOVIN | Beta-casein | 25,091 | 1356.8285 | 1356.8017 | IPPLTQTPVVVPP |
| CASB_BOVIN | Beta-casein | 25,091 | 1503.8765 | 1503.8701 | IPPLTQTPVVVPPF |
| CASB_BOVIN | Beta-casein | 25,091 | 1503.8817 | 1503.8701 | IPPLTQTPVVVPPF |
| CASB_BOVIN | Beta-casein | 25,091 | 1363.7167 | 1363.6846 | KEMPFPKYPVE |
| CASB_BOVIN | Beta-casein | 25,091 | 1380.7026 | 1380.6972 | MHQPHQPLPPTV |
| CASB_BOVIN | Beta-casein | 25,091 | 1219.619 | 1219.5947 | MPFPKYPVEP |
| CASB_BOVIN | Beta-casein | 25,091 | 1319.7531 | 1307.7085 | PVVVPPFLQPEV |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahtesh, F.B.; Stojanovska, L.; Mishra, V.; Donkor, O.; Feehan, J.; Bosevski, M.; Mathai, M.; Apostolopoulos, V. Identification and Effects of Skim Milk-Derived Bioactive Antihypertensive Peptides. Biologics 2022, 2, 1-14. https://doi.org/10.3390/biologics2010001
Ahtesh FB, Stojanovska L, Mishra V, Donkor O, Feehan J, Bosevski M, Mathai M, Apostolopoulos V. Identification and Effects of Skim Milk-Derived Bioactive Antihypertensive Peptides. Biologics. 2022; 2(1):1-14. https://doi.org/10.3390/biologics2010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhtesh, Fatah B., Lily Stojanovska, Vijay Mishra, Osaana Donkor, Jack Feehan, Marijan Bosevski, Michael Mathai, and Vasso Apostolopoulos. 2022. "Identification and Effects of Skim Milk-Derived Bioactive Antihypertensive Peptides" Biologics 2, no. 1: 1-14. https://doi.org/10.3390/biologics2010001
APA StyleAhtesh, F. B., Stojanovska, L., Mishra, V., Donkor, O., Feehan, J., Bosevski, M., Mathai, M., & Apostolopoulos, V. (2022). Identification and Effects of Skim Milk-Derived Bioactive Antihypertensive Peptides. Biologics, 2(1), 1-14. https://doi.org/10.3390/biologics2010001









