Methods to Diagnose Adiposity (Overweight/Obesity) in Children and Avoid Misdiagnosis: Relative Fat Mass vs. Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Design
2.2. Subjects
Ethical Approval
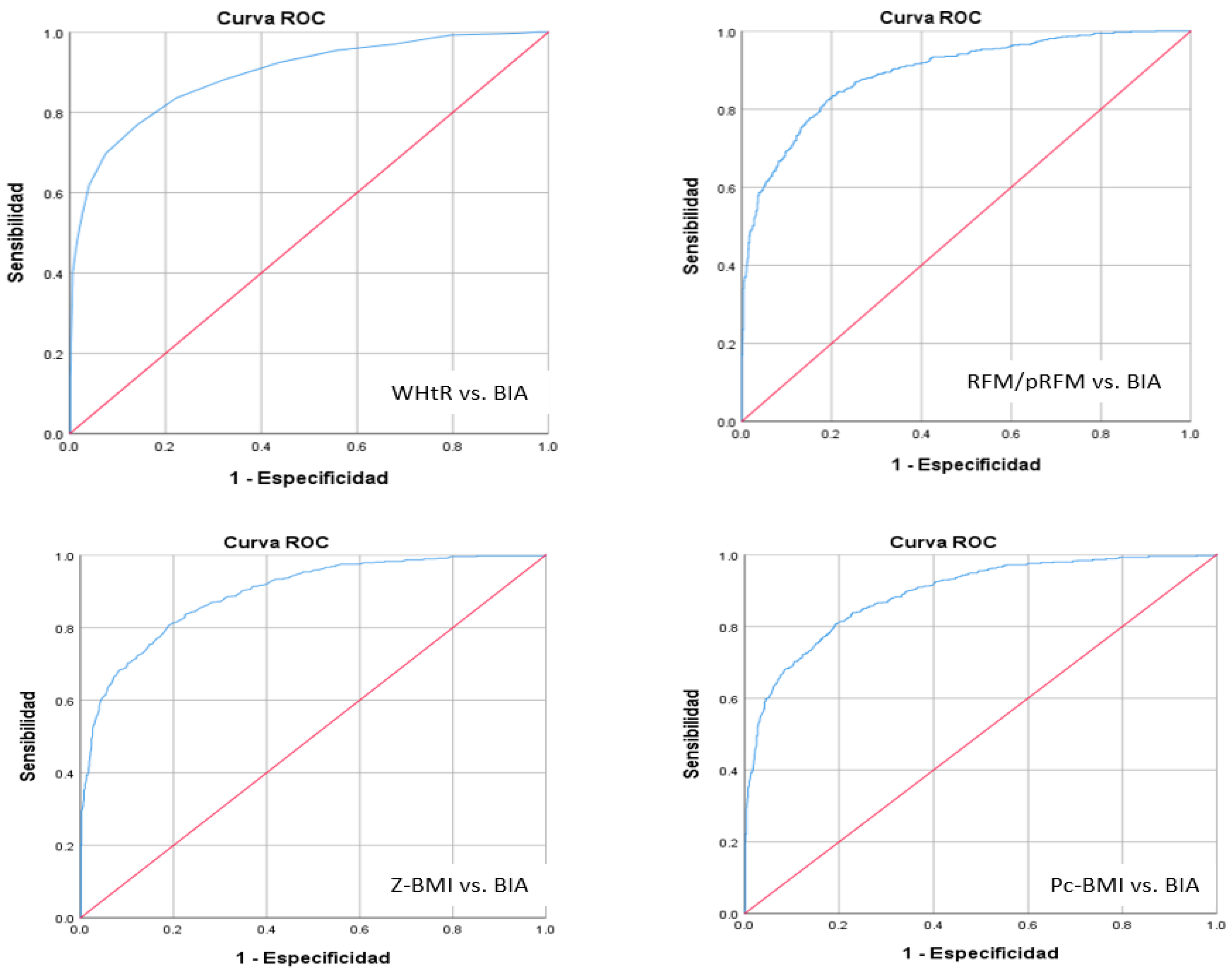
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Ni, Y.; Yi, C.; Fang, Y.; Qingyng, N.; Shen, B.; Zhang, K.; Liu, Y.; Yang, L.; et al. Global Prevalence of Overweight and Obesity in Children and Adolescents A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Pediatr. 2024, 178, 800–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamah-Levy, T.; Cuevas-Nasu, L.; Gaona-Pineda, E.B.; Valenzuela-Bravo, D.G.; Méndez Gómez-Humarán, I.; Ávila-Arcos, M.A. Childhood obesity in Mexico: Influencing factors and prevention strategies. Front Public Health 2022, 10, 949893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shamah-Levy, T.; Gaona-Pineda, E.B.; Cuevas-Nasu, L.; Morales-Ruan, C.; Valenzuela-Bravo, D.G.; Méndez-Gómez Humaran, I.; Ávila-Arcos, M.A. Prevalence of overweight and obesity in the school-age and adolescent population in Mexico. Ensanut Continua 2020–2022. Public Health Mex. 2023, 65, s218–s224. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llorca-Colomer, F.; Murillo-Llorente, M.T.; Legidos-García, M.E.; Palau-Ferré, A.; Pérez-Bermejo, M. Differences in Classification Standards For the Prevalence of Overweight and Obesity in Children. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Epidemiol. 2022, 14, 1031–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque, V.; Closa-Monasterolo, R.; Rubio-Torrents, C.; Zaragoza-Jordana, M.; Ferré, N.; Gispert-Llauradó, M.; Escribano, J. Bioimpedance in 7-year-old children: Validation by dual X-ray absorptiometry—Part 1: Assessment of whole body composition. Ann Nutr Metab. 2014, 64, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Xanthakos, S.A.; Hornung, L.; Arce-Clachar, C.; Siegel, R.; Kalkwarf, H.J. Relative Accuracy of Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis for Assessing Body Composition in Children With Severe Obesity. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol Nutr. 2020, 70, e129–e135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Woolcott, O.O.; Bergman, R.N. Relative Fat Mass as an estimator of whole-body fat percentage among children and adolescents: A cross-sectional study using NHANES. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Costa-Urrutia, P.; Vizuet-Gámez, A.; Ramirez-Alcántara, M.; Guillen-González, M.Á.; Medina-Contreras, O.; Valdes-Moreno, M.; Musalem-Younes, C.; Solares-Tlapechco, J.; Granados, J.; Franco-Trecu, V.; et al. Obesity measured as percent body fat, relationship with body mass index, and percentile curves for Mexican pediatric population. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Styne, D.M.; Arslanian, S.A.; Connor, E.L.; Farooqi, I.S.; Murad, M.H.; Silverstein, J.H.; Yanovski, J.A. Pediatric Obesity—Assessment, Treatment, and Prevention: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metabolism. 2017, 102, 709–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monasor-Ortolá, D.; Quesada-Rico, J.A.; Nso-Roca, A.P.; Rizo-Baeza, M.; Cortés-Castell, E.; Martínez-Segura, A.; Sánchez-Ferrer, F. Degree of Accuracy of the BMI Z-Score to Determine Excess Fat Mass Using DXA in Children and Adolescents. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hampl, S.E.; Hassink, S.G.; Skinner, A.C.; Armstrong, S.C.; Barlow, S.E.; Bolling, C.F.; Avila Edwards, K.C.; Eneli, I.; Hamre, R.; Joseph, M.M.; et al. Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Treatment of Children and Adolescents With Obesity. Pediatrics 2023, 151, e2022060640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilly, J.; Kelly, J. Long-term impact of overweight and obesity in childhood and adolescence on morbidity and premature mortality in adulthood: Systematic review. Int. J. Obes. 2011, 35, 891–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, L.L.; Mihrshahi, S.; Gale, J.; Drayton, B.; Bauman, A.; Mitchell, J. 30-year trends in overweight, obesity and waist-to-height ratio by socioeconomic status in Australian children, 1985 to 2015. Int. J. Obes. 2017, 41, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, H.; Ribas, L.; Koebnick, C.; Funtikova, A.; Gomez, S.F.; Fíto, M.; Perez-Rodrigo, C.; Serra-Majem, L. Prevalence of Abdominal Obesity in Spanish Children and Adolescents. Do We Need Waist Circumference Measurements in Pediatric Practice? PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamliel, A.; Ziv-Baran, T.; Siegel, R.M.; Fogelman, Y.; Dubnov-Raz, G. Using weight-for-age percentiles to screen for overweight and obese children and adolescents. Prev. Med. 2015, 81, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Ventura, A.L.; Pelaez-Ballestas, I.; Sámano-Sámano, R.; Jimenez-Gutierrez, C.; Aguilar-Salinas, C. Barriers to lose weight from the perspective of children with overweight/obesity and their parents: A sociocultural approach. J. Obes. 2014, 2014, 575184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samano, R.; Rodríguez-Ventura, A.L.; Sanchez-Jimenez, B.; Martinez, E.Y.G.; Noriega, A.; Zelonka, R.; Garza, M.; Nieto, J. Body image satisfaction in mexican adolescents and adults and its relation with body selfperception and real body mass index. Nutr. Hosp. 2015, 31, 1082–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavira-Suarez, E.; Rosel-Pech, C.; Polo-Oteyza, E.; Ancira-Moreno, M.; Ibarra-Gonzalez, I.; Vela-Amieva, M.; Meraz-Cruz, N.; Aguilar-Salinas, C.; Vadillo-Ortega, F. Simultaneous evaluation of metabolomic and inflammatory biomarkers in children with different body mass index (BMI) and waist-to height ratio (WHtR). PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Waist Circumference and Waist-Hip Ratio: Report of a WHO Expert Consultation, Geneva, 8–11 December 2008; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011; Available online: https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/44583 (accessed on 8 June 2025).
- GBD 2021 Adolescent BMI Collaboraters. Global, regional, and national prevalence of child and adolescent overweight and obesity, 1990–2021, with forecasts to 2050: A forecasting study for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet 2025, 405, 785–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garvey, W.T.; Mechanick, J.I.; Brett, E.M.; Garber, A.J.; Hurley, D.L.; Jastreboff, A.M.; Nadolsky, K.; Pessah-Pollack, R.; Plodkowski, R. Reviewers of AACE/ACE Clinical Practice Guidelines for Obesity. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologist and American College of Endocrinology: Comprehensive Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Medical Care of patients with obesity. Endocr. Pract. Off. J. Am. Coll. Endocrinol. Am. Assoc. Clin. Endocrinol. 2016, 22 (Suppl. S3), 1–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, M.W.; Kallapur, S.G.; Jobe, A.H.; Newnham, J.P. Obesity and the developmental origins of health and disease. J. Pediatr. Child Health 2012, 48, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zambrano, E.; Ibáñez, C.; Martinez-Samayoa, P.; Lomas-Soria, C.; Durand-Carbajal Rodríguez-Gonzalez, G.L. Maternal Obesity: Lifelong Metabolic Outcomes for Offspring from Poor Developmental Trajectories During the Perinatal Period. Arch. Clin. Res. 2016, 47, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giza, S.A.; Sethi, S.; Smit, L.M.; Empey, M.E.E.T.; Morris, L.E.; McKenzie, C.A. The application of in utero magnetic resonance imaging in the study of the metabolic and cardiovascular consequences of the developmental origins of health and disease. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2021, 12, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubino, F.; Cummings, D.E.; Eckel, R.H.; Cohen, R.V.; Wilding, J.P.H.; Brown, W.A.; Stanford, F.C.; Batterham, R.L.; Farooqi, I.S.; Farpour-Lambert, N.J.; et al. Definition and diagnostic criteria of clinical obesity. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2025, 13, 221–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.K.; Metzger, D.L.; Daymont, C.; Hadjiyannakis, S.; Rodd, C.J. LMS tables for waist-circumference and waist-height ratio Z-scores in children aged 5–19 y in NHANES III: Association with cardio-metabolic risks. Pediatr. Res. 2015, 78, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindholm, A.; Roswall, J.; Alm, B.; Almquist-Tangen, G.; Bremander, A.; Dahlgren, J.; Staland-Nyman, C.; Bergman, S. Body Mass Index Classification Misses to Identify Children With an Elevated Waist-to-Height Ratio at 5 Years of Age. Pediatr. Res. 2019, 85, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sijtsma, A.; Bocca, G.; L’Abée, C.; Liem, E.T.; Sauer, P.J.; Corpeleijn, E. Waist-to-Height Ratio, Waist Circumference and BMI as Indicators of Percentage Fat Mass and Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Children Aged 3-7 Years. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 33, 3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Ventura, A.; Parra-Solano, A.; Illescas-Zárate, D.; Hernández-Flores, M.; Paredes, C.; Flores-Cisneros, C.; Sánchez, B.; Tolentino, M.; Sámano, R.; Chinchilla, D. “Sacbe”, a Comprehensive Intervention to Decrease Body Mass Index in Children with Adiposity: A Pilot Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra-Solano, A.; Hernández-Flores, M.; Sánchez, B.; Paredes, C.; Monroy, L.; Palacios, F.; Almaguer, L.; Rodriguez-Ventura, A. Reducing the Number of Times Eating Out Helps to Decrease Adiposity (Overweight/Obesity) in Children. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| RFM = 64−(20 × height/waist circumference) + 12 for women −0 for men− (≥15 years old) |
| pRFM = 74−(22 × height/waist circumference) + 5 for women −0 for men− (8–14 years old) |
| Different Diagnostic Methods | Basal Visit n = 531 | Basal Fem. n = 278 | Basal Male n = 253 | Visit 1 Total n = 475 | V1 Fem n = 258 | V1 Male n = 217 | Visit 2 Total n = 476 | V2 Fem n = 260 | V2 Male n = 216 | Visit 3 Total n = 444 | V3 Fem n = 243 | V3 Male n = 201 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overweight Z-BMI | 23.2 | 24.1 | 20.5 | 23.6 | 26.3 | 20.3 | 23.1 | 28.4 | 16.6 | 23 | 30 | 14.9 |
| Obesity Z-BMI | 11.3 | 11.5 | 11.4 | 10.5 | 9.3 | 12.3 | 9.4 | 9.2 | 10.1 | 9.2 | 9 | 9.4 |
| Ow and Ob Z-BMI | 34.5 | 35.6 | 31.9 | 34.1 | 35.6 | 32.6 | 32.5 | 37.6 | 36.7 | 32.2 | 39 | 24.3 |
| Overweight Pc BMI | 16.1 | 17.6 | 14.6 | 15.7 | 18.3 | 12.5 | 14.3 | 18.4 | 9.2 | 16.2 | 20.6 | 10.9 |
| Obesity Pc BMI | 17.1 | 16.9 | 17.3 | 15.8 | 14.7 | 17.1 | 16 | 15.7 | 16.2 | 15.7 | 17.3 | 13.9 |
| Ow and Ob Pc BMI | 33.2 | 34.5 | 31.9 | 31.5 | 33 | 29.6 | 30.3 | 34.1 | 25.4 | 31.9 | 37.9 | 24.8 |
| Obesity -BIA- | 43.5 | 50 | 36.7 | 38.6 | 44.5 | 31.3 | 41.8 | 52.7 | 28.7 | 40.8 | 48.8 | 30.8 |
| WHtR ≥0.5 | 21.5 | 21.1 | 22 | 23.5 | 24.8 | 22.1 | 21.2 | 22.6 | 22.8 | 23.6 | 26.3 | 20.4 |
| n = 1500 | WHtR | BIA | RFM-pRFM | Z-BMI | BMI Pc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WHtR | 1 | 0.305 * | 0.443 * | 0.358 * | 0.331 * |
| BIA | 0.305 * | 1 | 0.848 * | 0.735 * | 0.686 * |
| RFM-pRFM | 0.443 * | 0.848 * | 1 | 0.721 * | 0.684 * |
| Z-BMI | 0.358 * | 0.735 * | 0.721 * | 1 | 0.943 * |
| BMI Pc | 0.331 * | 0.686 * | 0.684 * | 0.943 * | 1 |
| Area | Diagnostic Method | p | Inferior Limit | Superior Limit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.894 | RFM/pRFM | 0.000 | 0.877 | 0.91 |
| 0.893 | WHtR | 0.000 | 0.877 | 0.909 |
| 0.893 | Z-BMI | 0.000 | 0.877 | 0.909 |
| 0.89 | Pc-BMI | 0.000 | 0.874 | 0.907 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodriguez-Ventura, A.; Zuñiga-Puente, N.; Figueroa-Sanchez, L.F.; Guerrero, J.; Sánchez, E.; Perez, T.; Calzad, F.; Peña, D. Methods to Diagnose Adiposity (Overweight/Obesity) in Children and Avoid Misdiagnosis: Relative Fat Mass vs. Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis. BioMed 2025, 5, 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomed5040029
Rodriguez-Ventura A, Zuñiga-Puente N, Figueroa-Sanchez LF, Guerrero J, Sánchez E, Perez T, Calzad F, Peña D. Methods to Diagnose Adiposity (Overweight/Obesity) in Children and Avoid Misdiagnosis: Relative Fat Mass vs. Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis. BioMed. 2025; 5(4):29. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomed5040029
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodriguez-Ventura, Ana, Nayeli Zuñiga-Puente, Luis F. Figueroa-Sanchez, Jessica Guerrero, Esveidy Sánchez, Tanya Perez, Fernanda Calzad, and Diana Peña. 2025. "Methods to Diagnose Adiposity (Overweight/Obesity) in Children and Avoid Misdiagnosis: Relative Fat Mass vs. Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis" BioMed 5, no. 4: 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomed5040029
APA StyleRodriguez-Ventura, A., Zuñiga-Puente, N., Figueroa-Sanchez, L. F., Guerrero, J., Sánchez, E., Perez, T., Calzad, F., & Peña, D. (2025). Methods to Diagnose Adiposity (Overweight/Obesity) in Children and Avoid Misdiagnosis: Relative Fat Mass vs. Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis. BioMed, 5(4), 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomed5040029






