Biological Reference Intervals for 17α-Hydroxyprogesterone Immunoreactive Trypsinogen, and Biotinidase in Indian Newborns
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection and Analysis of 17-OHP, IRT, and Biotinidase Samples
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
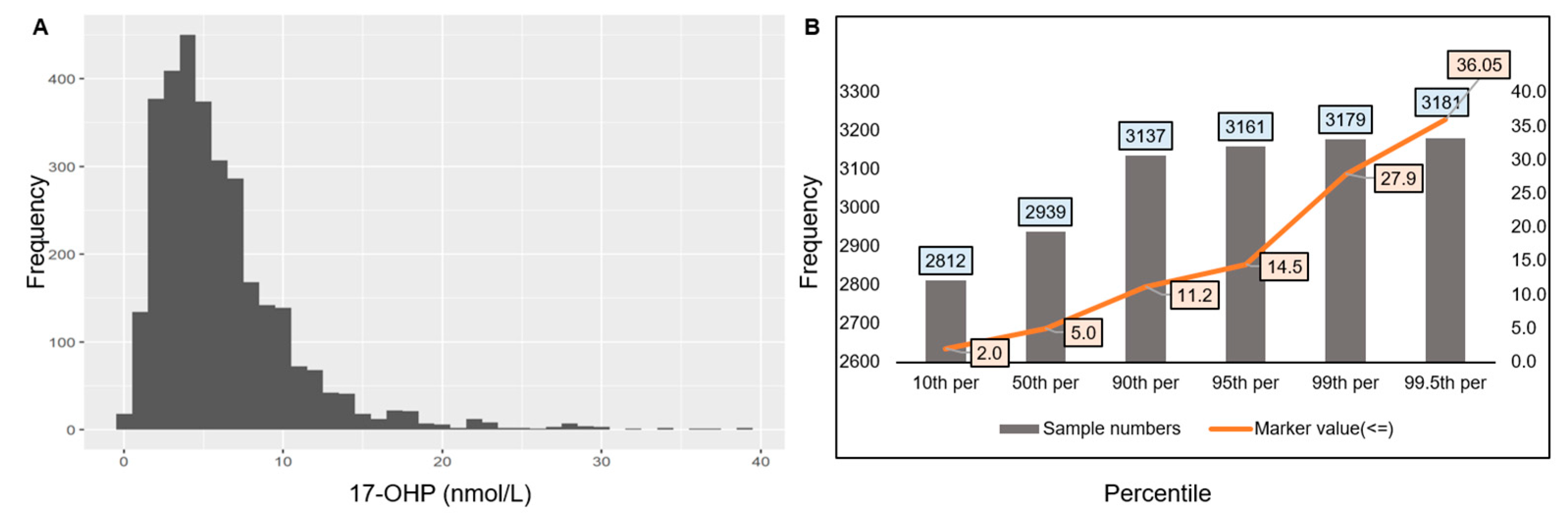
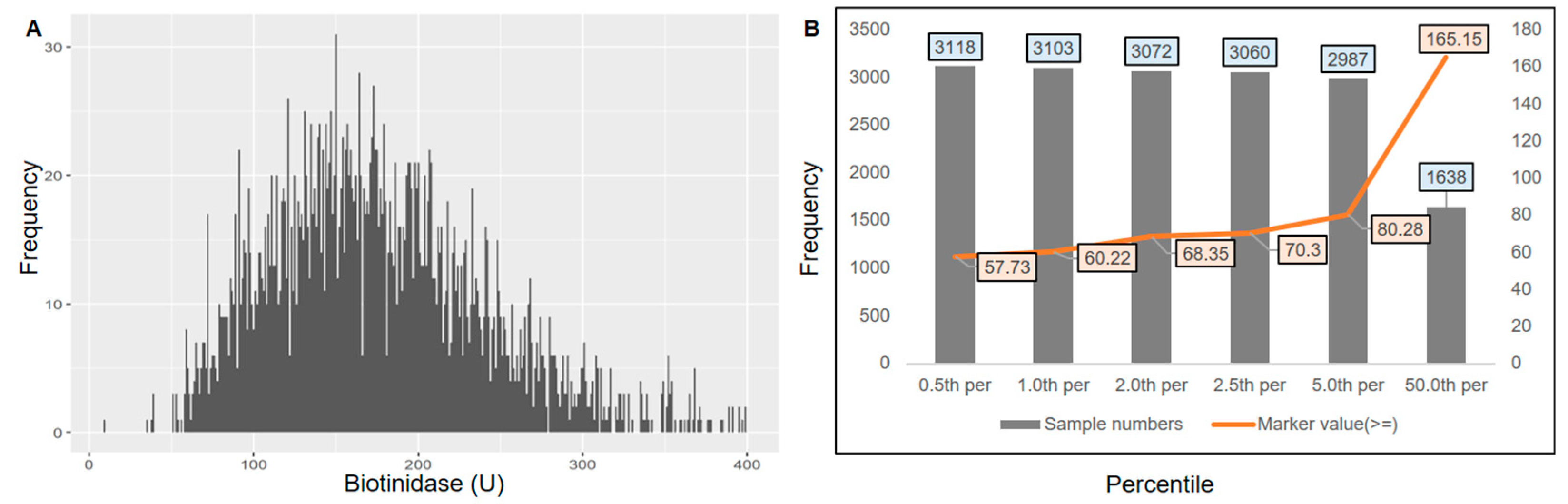
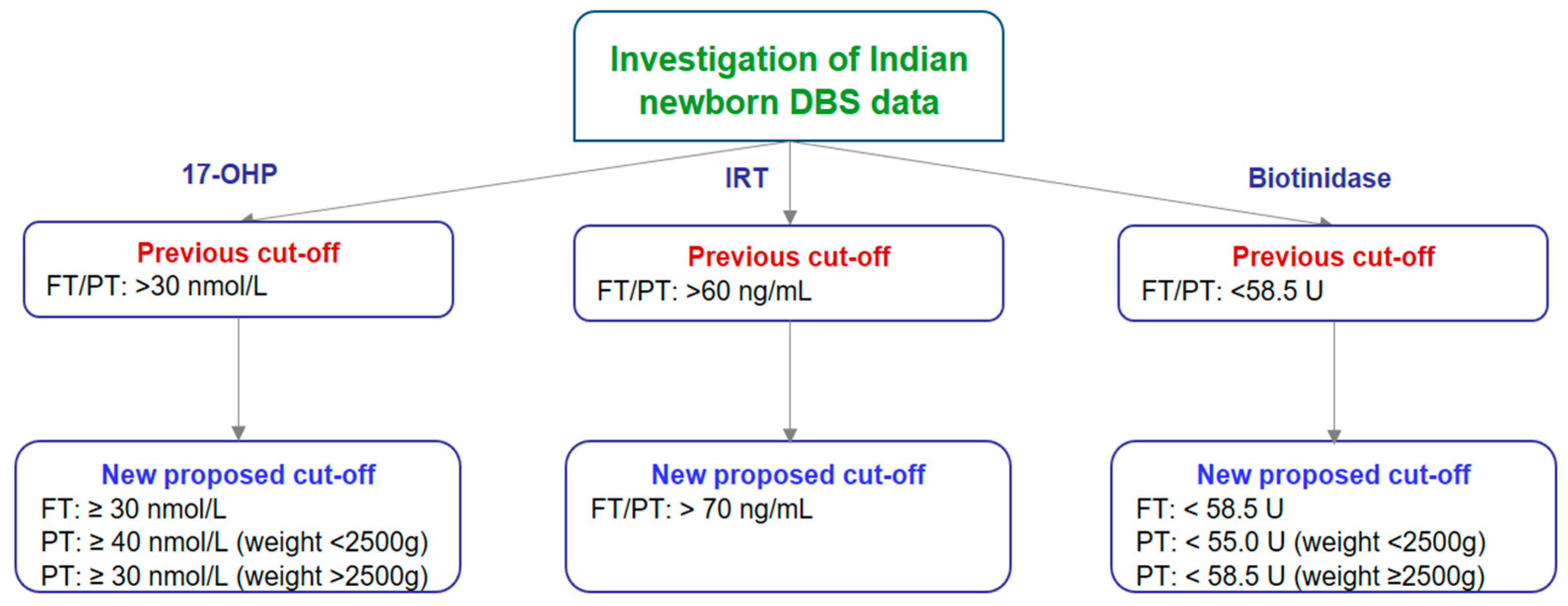
3.1. Cut-Off Establishment for 17-OHP, IRT, and Biotinidase in Indian Newborns
3.1.1. Cut-Off Establishment for 17-OHP
3.1.2. Cut-Off Establishment for IRT
3.1.3. Cut-Off Establishment for Biotinidase
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FDA-NIH Biomarker Working Group. Diagnostic Biomarker. In BEST (Biomarkers, Endpoints, and Other Tools) Resource; Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bodaghi, A.; Fattahi, N.; Ramazani, A. Biomarkers: Promising and Valuable Tools towards Diagnosis, Prognosis and Treatment of COVID-19 and Other Diseases. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Imran, M.; Ahsan, H. Biomarkers as Biomedical Bioindicators: Approaches and Techniques for the Detection, Analysis, and Validation of Novel Biomarkers of Diseases. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa-Mangeret, F.; Benski, A.-C.; Golaz, A.; Zala, P.Z.; Kyokan, M.; Wagner, N.; Muhe, L.M.; Pfister, R.E. 2.5 Million Annual Deaths—Are Neonates in Low- and Middle-Income Countries Too Small to Be Seen? A Bottom-Up Overview on Neonatal Morbi-Mortality. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2022, 7, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsden, D.; Bedrosian, C.L.; Vockley, J. Impact of Newborn Screening on the Reported Incidence and Clinical Outcomes Associated with Medium- and Long-Chain Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders. Genet. Med. 2021, 23, 816–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, J.C.; MacDonald, A. Dietary Intervention in the Management of Phenylketonuria: Current Perspectives. Pediatr. Health Med. Ther. 2016, 7, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widaman, K.F. Phenylketonuria in Children and Mothers: Genes, Environments, Behavior. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 2009, 18, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrman, R.E.; Butler, A.S.; Healthy Outcomes (Eds.) Mortality and Acute Complications in Preterm Infants. In Preterm Birth: Causes, Consequences, and Prevention; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Pitt, J.J. Newborn Screening. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2010, 31, 57. [Google Scholar]
- Crump, C. Preterm Birth and Mortality in Adulthood: A Systematic Review. J. Perinatol. 2020, 40, 833–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy-Shraga, Y.; Pinhas-Hamiel, O. High 17-Hydroxyprogesterone Level in Newborn Screening Test for Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia. BMJ Case Rep. 2016, bcr2015213939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdea, L.; Mendez, M.D. 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Jha, S.; Turcu, A.F. Non-Classic Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia: What Do Endocrinologists Need to Know? Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 50, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momodu, I.I.; Lee, B.; Singh, G. Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Wróbel, T.M.; Jørgensen, F.S.; Pandey, A.V.; Grudzińska, A.; Sharma, K.; Yakubu, J.; Björkling, F. Non-Steroidal CYP17A1 Inhibitors: Discovery and Assessment. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 6542–6566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newborn Screening for Cystic Fibrosis: Do We Need a Second IRT?—PMC. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2065957/ (accessed on 14 August 2024).
- Ooi, C.Y.; Sutherland, R.; Castellani, C.; Keenan, K.; Boland, M.; Reisman, J.; Bjornson, C.; Chilvers, M.A.; van Wylick, R.; Kent, S.; et al. Immunoreactive Trypsinogen Levels in Newborn Screened Infants with an Inconclusive Diagnosis of Cystic Fibrosis. BMC Pediatr. 2019, 19, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, C.B.; Markovetz, M.R.; Ehre, C. Mucus, Mucins and Cystic Fibrosis. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2019, 54, S84–S96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canda, E.; Kalkan Uçar, S.; Çoker, M. Biotinidase Deficiency: Prevalence, Impact And Management Strategies. Pediatr. Health Med. Ther. 2020, 11, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hymes, J.; Wolf, B. Biotinidase and Its Roles in Biotin Metabolism. Clin. Chim. Acta 1996, 255, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L. Structure and Function of Biotin-Dependent Carboxylases. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2012, 70, 863–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tippabathani, J.; Seenappa, V.; Murugan, A.; Phani, N.M.; Hampe, M.H.; Appaswamy, G.; Sadashiv Gambhir, P. Neonatal Screening for Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia in Indian Newborns with Reflex Genetic Analysis of 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency. Int. J. Neonatal Screen 2023, 9, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-F.; Rose, A.M.; Waisbren, S.; Ahmad, A.; Prosser, L.A. Newborn Screening and Treatment of Phenylketonuria: Projected Health Outcomes and Cost-Effectiveness. Children 2021, 8, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Held, P.K.; Bird, I.M.; Heather, N.L. Newborn Screening for Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia: Review of Factors Affecting Screening Accuracy. Int. J. Neonatal Screen 2020, 6, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bereket, A. Editorial: Neonatal Screening for Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia in Turkey. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2019, 11, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaye, C.I.; The Committee on Genetics. Newborn Screening Fact Sheets. Pediatrics 2006, 118, e934–e963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torresani, T.; Grüters, A.; Scherz, R.; Burckhardt, J.J.; Harras, A.; Zachmann, M. Improving the Efficacy of Newborn Screening for Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia by Adjusting the Cut-off Level of 17α-Hydroxyprogesterone to Gestational Age. Screening 1994, 3, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmilä, I.; Dakubu, S.; Mukkala, V.-M.; Siitari, H.; Lövgren, T. Europium as a Label in Time-Resolved Immunofluorometric Assays. Anal. Biochem. 1984, 137, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rock, M.J.; Mischler, E.H.; Farrell, P.M.; Bruns, W.T.; Hassemer, D.J.; Laessig, R.H. Immunoreactive Trypsinogen Screening for Cystic Fibrosis: Characterization of Infants with a False-Positive Screening Test. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 1989, 6, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, L.T.; Applegarth, D.A.; Davidson, A.G.; Wong, L.T.; Hardwick, D.F. Use of a Dried Blood Spot in Immunoreactive-Trypsin Assay for Detection of Cystic Fibrosis in Infants. Clin. Chem. 1981, 27, 678–680. Available online: https://academic.oup.com/clinchem/article-abstract/27/5/678/5666531 (accessed on 14 August 2024).
- Hart, P.S.; Hymes, J.; Wolf, B. Biochemical and Immunologic Characterization of Serum Biotinidase in Partial Biotinidase. Pediatr. Res. 1992, 31, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wolf, B.; Heard, G.S.; Jefferson, L.G.; Proud, V.K.; Nance, W.E.; Weissbecker, K.A. Clinical Findings in Four Children with Biotinidase Deficiency Detected through a Statewide Neonatal Screening Program. N. Engl. J. Med. 1985, 313, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, M.; Khattab, A.; Yuen, T.; New, M. Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia. In Endotext; Feingold, K.R., Anawalt, B., Blackman, M.R., Boyce, A., Chrousos, G., Corpas, E., de Herder, W.W., Dhatariya, K., Dungan, K., Hofland, J., et al., Eds.; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Nimkarn, S.; Gangishetti, P.K.; Yau, M.; New, M.I. 21-Hydroxylase-Deficient Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia. In GeneReviews®; Adam, M.P., Feldman, J., Mirzaa, G.M., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Bean, L.J., Gripp, K.W., Amemiya, A., Eds.; University of Washington, Seattle: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Southern, K.W.; Mérelle, M.M.E.; Dankert-Roelse, J.E.; Nagelkerke, A. Newborn Screening for Cystic Fibrosis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2009, CD001402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patadia, C.; Desai, D. A Child Born Late: Neonatal and Paediatric Compilations Related to Post-Dated Pregnancy. preprint 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, S.; Aiken, C. Prolonged Pregnancy: Balancing Risks and Interventions for Post-Term Gestations. Obstet. Gynaecol. Reprod. Med. 2024, 34, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neggers, Y.H. Gestational Age and Pregnancy Outcomes. In Pregnancy and Birth Outcomes; Intech: London, UK, 2018; ISBN 978-1-78923-243-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akanmode, A.M.; Mahdy, H. Macrosomia. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Fallah, S.; Chen, X.-K.; Lefebvre, D.; Kurji, J.; Hader, J.; Leeb, K. Babies Admitted to NICU/ICU: Province of Birth and Mode of Delivery Matter. Healthc. Q. 2011, 14, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woldeamanuel, G.G.; Geta, T.G.; Mohammed, T.P.; Shuba, M.B.; Bafa, T.A. Effect of Nutritional Status of Pregnant Women on Birth Weight of Newborns at Butajira Referral Hospital, Butajira, Ethiopia. SAGE Open Med. 2019, 7, 2050312119827096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seghieri, G.; Anichini, R.; De Bellis, A.; Alviggi, L.; Franconi, F.; Breschi, M.C. Relationship between Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Low Maternal Birth Weight. Diabetes Care 2002, 25, 1761–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandowska, M. Maternal Obesity and Risk of Low Birth Weight, Fetal Growth Restriction, and Macrosomia: Multiple Analyses. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ornoy, A.; Becker, M.; Weinstein-Fudim, L.; Ergaz, Z. Diabetes during Pregnancy: A Maternal Disease Complicating the Course of Pregnancy with Long-Term Deleterious Effects on the Offspring. A Clinical Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honour, J.W. 17-Hydroxyprogesterone in Children, Adolescents and Adults. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2014, 51, 424–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, N.A.; Sharma, S.; Das, M.; Kapoor, A.; Maskey, U. Devastating Salt-Wasting Crisis in a Four-Month-Old Male Child with Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia, Highlighting the Essence of Neonatal Screening. Clin. Case Rep. 2022, 10, e6010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waugh, N.; Royle, P.; Craigie, I.; Ho, V.; Pandit, L.; Ewings, P.; Adler, A.; Helms, P.; Sheldon, C. Screening for Cystic Fibrosis-Related Diabetes: A Systematic Review. Health Technol. Assess. 2012, 16, 1–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, P.M.; Rosenstein, B.J.; White, T.B.; Accurso, F.J.; Castellani, C.; Cutting, G.R.; Durie, P.R.; Legrys, V.A.; Massie, J.; Parad, R.B.; et al. Guidelines for Diagnosis of Cystic Fibrosis in Newborns through Older Adults: Cystic Fibrosis Foundation Consensus Report. J. Pediatr. 2008, 153, S4–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, T.M.; Blitzer, M.G.; Wolf, B. Technical Standards and Guidelines for the Diagnosis of Biotinidase Deficiency. Genet. Med. 2010, 12, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, H.; Simpson, B. Biotinidase Deficiency. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Kannan, B.; Navamani, H.K.; Jayaseelan, V.P.; Arumugam, P. A Rare Biotinidase Deficiency in the Pediatrics Population: Genotype–Phenotype Analysis. J. Pediatr. Genet. 2022, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prasad, E.M.; Kinha, R.; Bendre, R. Biological Reference Intervals for 17α-Hydroxyprogesterone Immunoreactive Trypsinogen, and Biotinidase in Indian Newborns. BioMed 2024, 4, 268-276. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomed4030021
Prasad EM, Kinha R, Bendre R. Biological Reference Intervals for 17α-Hydroxyprogesterone Immunoreactive Trypsinogen, and Biotinidase in Indian Newborns. BioMed. 2024; 4(3):268-276. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomed4030021
Chicago/Turabian StylePrasad, E. Maruthi, Ramesh Kinha, and Rajesh Bendre. 2024. "Biological Reference Intervals for 17α-Hydroxyprogesterone Immunoreactive Trypsinogen, and Biotinidase in Indian Newborns" BioMed 4, no. 3: 268-276. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomed4030021
APA StylePrasad, E. M., Kinha, R., & Bendre, R. (2024). Biological Reference Intervals for 17α-Hydroxyprogesterone Immunoreactive Trypsinogen, and Biotinidase in Indian Newborns. BioMed, 4(3), 268-276. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomed4030021






