The Application of NMR-Based Metabolomics in the Field of Nutritional Studies
Definition
1. Introduction
2. Biomarkers of Food Intake
2.1. NMR in the Identification of BFIs
2.2. NMR in Dietary Pattern Recognition
| Food | Application | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Fruits and Vegetables | ||
| Citrus fruit | Proline and betaine detected in urine, and serum. | Mitry [48]; Heinzmann, et al. [44]. |
| Tomatoes | Trans-lycopene, cis-lycopene in plasma and serum. | Chiva-Blanch, et al. [49]. |
| Cruciferous vegetables | S-methyl cysteine sulfoxide, sulforaphane metabolites in urine. | Edmands, et al. [50]. |
| Carrots | α- and β-carotene in plasma, and serum. | Arathi, et al. [51]. |
| Whole Grains, Cereals and Legumes | ||
| Whole-grain wheat and rye | Alkylresorcinols in plasma, urine, and red blood cells. | Landberg, et al. [52]; Chelladurai, et al. [53]. |
| Oats and barley | Avenanthramides, β-glucan metabolites in plasma, and urine. | Wang, et al. [54]. |
| Lentils, Chickpeas, and Beans | 2-hydroxybutyric acid, lysine, trigonelline in serum, and urine. | Madrid-Gambin, et al. [55]. |
| Animal Products | ||
| Fish and seafood | Trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO), ω-3 fatty acids (EPA, DHA), in plasma, and urine. | Lemos [56]; Hanhineva [57]; Lombardo, et al. [58]; Burton, et al. [59]; Xyda, et al. [60]. |
| Red meat | Carnitine, creatine, creatinine, anserine in urine, and plasma. | Carrizo, et al. [61]; Pan, et al. [62]; |
| Dairy products | Odd-chain fatty acids (C15:0, C17:0), trans-palmitoleic acid in serum, and urine. | Trimigno, et al. [40]; Münger, et al. [63]; Correia, et al. [64]. |
| Beverages | ||
| Coffee | Trigonelline, caffeine, paraxanthine, 3-hydroxyhippuric acid in urine, and plasma. | Rådjursöga, et al. [65]; Rothwell, et al. [66]. |
| Tea | Catechins, theaflavins, 4-O-methylgallic acid in plasma, and urine. | Rothwell, et al. [66]; Law, et al. [67]; Madrid-Gambin, et al. [68]; Daykin, et al. [69]. |
| Wine | Tartaric acid, ethyl glucuronide, resveratrol metabolites in urine, and plasma. | van Dorsten, et al. [70]; Vázquez-Fresno, et al. [71]; Hong [72]. |
2.2.1. Mediterranean Diet
2.2.2. Vegetarian and Vegan Diet
2.2.3. Western Diet
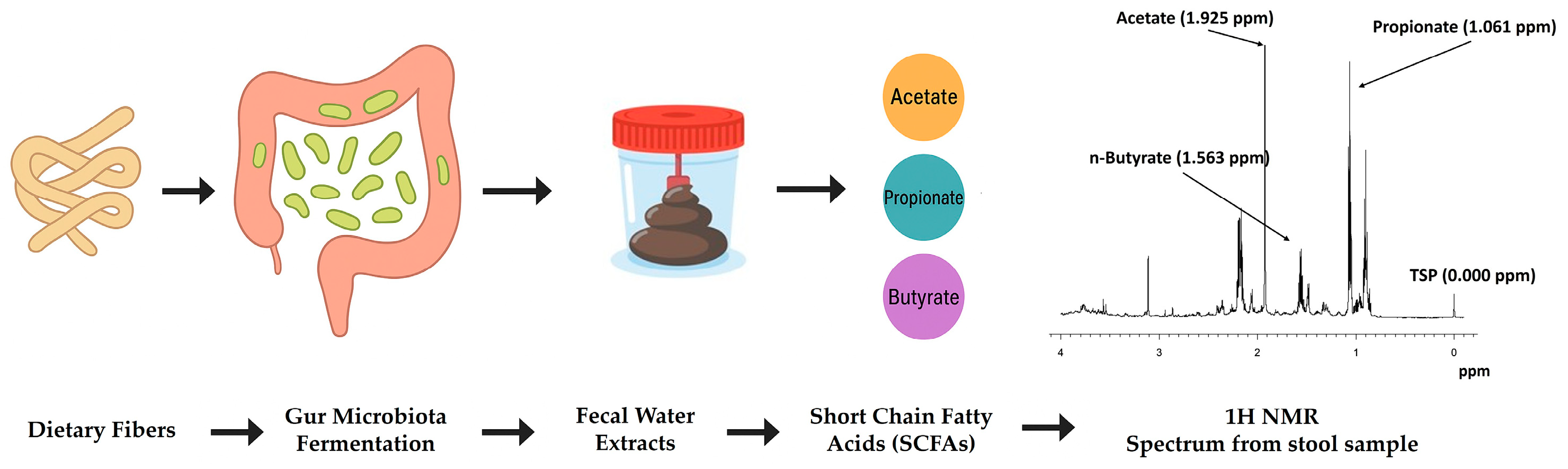
3. NMR Metabolomics and Gut Microbiota–Diet Interactions
4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DSS | Trimethylsilylpropane sulfonic acid |
| FFQs | Food Frequency Questionnaires |
| GC | Gas Chromatography |
| LC | Liquid Chromatography |
| LDL | Low-Density Lipoproteins |
| MD | Mediterranean Diet |
| MS | Mass Spectrometry |
| NMR | Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |
| NAFLD | Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease |
| OPLS | Orthogonal Partial Least Squares |
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
| PLS-DA | Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis |
| SCFAs | Short Chain Fatty Acids |
| TMAO | Trimethylamine-N-oxide |
| TSP | 2,2,3,3-tetradeutero-3-trimethylsilylpropionic acid |
| VD | Vegetarian and Vegan Diet |
| WD | Wester Diet |
References
- Klassen, A.; Faccio, A.T.; Canuto, G.A.B.; da Cruz, P.L.R.; Ribeiro, H.C.; Tavares, M.F.M.; Sussulini, A. Metabolomics: Definitions and significance in systems biology. In Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, J.K.; Lindon, J.C. Metabonomics. Nature 2008, 455, 1054–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer-Brolsma, E.M.; Brennan, L.; Drevon, C.A.; van Kranen, H.; Manach, C.; Dragsted, L.O.; Roche, H.M.; Andres-Lacueva, C.; Bakker, S.J.L.; Bouwman, J.; et al. Combining traditional dietary assessment methods with novel metabolomics techniques: Present efforts by the Food Biomarker Alliance. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2017, 76, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajnajafi, K.; Iqbal, M.A. Mass-spectrometry based metabolomics: An overview of workflows, strategies, data analysis and applications. Proteome Sci. 2025, 23, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, J.K.; Lindon, J.C.; Holmes, E. ‘Metabonomics’: Understanding the metabolic responses of living systems to pathophysiological stimuli via multivariate statistical analysis of biological NMR spectroscopic data. Xenobiotica 1999, 29, 1181–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbons, H.; O’Gorman, A.; Brennan, L. Metabolomics as a tool in nutritional research. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2015, 26, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guasch-Ferré, M.; Bhupathiraju, S.N.; Hu, F.B. Use of metabolomics in improving assessment of dietary intake. Clin. Chem. 2018, 64, 82–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulaszewska, M.M.; Weinert, C.H.; Trimigno, A.; Portmann, R.; Andres Lacueva, C.; Badertscher, R.; Brennan, L.; Brunius, C.; Bub, A.; Capozzi, F.; et al. Nutrimetabolomics: An Integrative Action for Metabolomic Analyses in Human Nutritional Studies. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, 1800384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.P.; Park, Y.; Ziegler, T.R. Nutritional metabolomics: Progress in addressing complexity in diet and health. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2012, 32, 183–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vimaleswaran, K.S.; Le Roy, C.I.; Claus, S.P. Foodomics for personalized nutrition: How far are we? Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2015, 4, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Jia, W. Toward personalized nutrition: Comprehensive phytoprofiling and metabotyping. J. Proteome Res. 2013, 12, 1547–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bervoets, L.; Adriaensens, P. Metabolomics in Nutritional Metabolism, Obesity, and Diabetes. In Nutritional Signaling Pathway Activities in Obesity and Diabetes; Cheng, Z., Ed.; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Catussi, B.L.C.; Lo Turco, E.G.; Pereira, D.M.; Teixeira, R.M.N.; Castro, B.P.; Massaia, I.F.D. Metabolomics: Unveiling biological matrices in precision nutrition and health. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2024, 64, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortesniemi, M.; Noerman, S.; Kårlund, A.; Raita, J.; Meuronen, T.; Koistinen, V.; Landberg, R.; Hanhineva, K. Nutritional metabolomics: Recent developments and future needs. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2023, 77, 102400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emwas, A.-H.; Roy, R.; McKay, R.T.; Tenori, L.; Saccenti, E.; Gowda, G.N.; Raftery, D.; Alahmari, F.; Jaremko, L.; Jaremko, M. NMR spectroscopy for metabolomics research. Metabolites 2019, 9, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dona, A.C.; Jiménez, B.; Schäfer, H.; Humpfer, E.; Spraul, M.; Lewis, M.R.; Pearce, J.T.; Holmes, E.; Lindon, J.C.; Nicholson, J.K. Precision high-throughput proton NMR spectroscopy of human urine, serum, and plasma for large-scale metabolic phenotyping. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 9887–9894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wishart, D.S. Metabolomics for investigating physiological and pathophysiological processes. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 1819–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Psychogios, N.; Hau, D.D.; Peng, J.; Guo, A.C.; Mandal, R.; Bouatra, S.; Sinelnikov, I.; Krishnamurthy, R.; Eisner, R.; Gautam, B. The human serum metabolome. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moosmang, S.; Pitscheider, M.; Sturm, S.; Seger, C.; Tilg, H.; Halabalaki, M.; Stuppner, H. Metabolomic analysis—Addressing NMR and LC-MS related problems in human feces sample preparation. Clin. Chim. Acta 2019, 489, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Liu, Y.; Xu, S.; Yang, L.; Yin, R. Review on analytical technologies and applications in metabolomics. Biocell 2024, 48, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emwas, A.-H.M. The strengths and weaknesses of NMR spectroscopy and mass spectrometry with particular focus on metabolomics research. In Metabonomics: Methods and Protocols; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 161–193. [Google Scholar]
- Ciampa, A.; Danesi, F.; Picone, G. NMR-based metabolomics for a more holistic and sustainable research in food quality assessment: A narrative review. Appl. Sci. 2022, 13, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, L. NMR-based metabolomics: From sample preparation to applications in nutrition research. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 2014, 83, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picone, G. The 1H HR-NMR Methods for the Evaluation of the Stability, Quality, Authenticity, and Shelf Life of Foods. Encyclopedia 2024, 5, 1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasso, D.; Geminiani, M.; Galderisi, S.; Iacomelli, G.; Peruzzi, L.; Marzocchi, B.; Santucci, A.; Bernini, A. Untargeted NMR Metabolomics Reveals Alternative Biomarkers and Pathways in Alkaptonuria. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Laghi, L.; Zhang, Z.; He, Y.; Wu, D.; Zhang, H.; Huang, Y.; Li, C.; Zou, L. First Steps toward the Giant Panda Metabolome Database: Untargeted Metabolomics of Feces, Urine, Serum, and Saliva by 1H NMR. J. Proteome Res. 2020, 19, 1052–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martias, C.; Baroukh, N.; Mavel, S.; Blasco, H.; Lefèvre, A.; Roch, L.; Montigny, F.; Gatien, J.; Schibler, L.; Dufour-Rainfray, D.; et al. Optimization of Sample Preparation for Metabolomics Exploration of Urine, Feces, Blood and Saliva in Humans Using Combined NMR and UHPLC-HRMS Platforms. Molecules 2021, 26, 4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomášová, P.; Procházková, P.; Roubalová, R.; Dvořák, J.I.; Tlaskalová-Hogenová, H.; Čermáková, M.; Pelantová, H.; Šedivá, B.; Vecka, M.; Papežová, H. NMR-and MS-based untargeted metabolomic study of stool and serum samples from patients with anorexia nervosa. J. Proteome Res. 2021, 21, 778–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravanbakhsh, S.; Liu, P.; Bjordahl, T.C.; Mandal, R.; Grant, J.R.; Wilson, M.; Eisner, R.; Sinelnikov, I.; Hu, X.; Luchinat, C. Accurate, fully-automated NMR spectral profiling for metabolomics. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, A.; Ikeguchi, M.; Sugai, S. Appropriateness of DSS and TSP as internal references for 1H NMR studies of molten globule proteins in aqueous media. J. Biomol. NMR 1994, 4, 859–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savorani, F.; Rasmussen, M.A.; Mikkelsen, M.S.; Engelsen, S.B. A primer to nutritional metabolomics by NMR spectroscopy and chemometrics. Food Res. Int. 2013, 54, 1131–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsaro, C.; Vasi, S.; Neri, F.; Mezzasalma, A.M.; Neri, G.; Fazio, E. NMR in metabolomics: From conventional statistics to machine learning and neural network approaches. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picone, G.; Mengucci, C.; Capozzi, F. The NMR added value to the green foodomics perspective: Advances by machine learning to the holistic view on food and nutrition. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2022, 60, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, R.L. Overview of dietary assessment methods for measuring intakes of foods, beverages, and dietary supplements in research studies. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2021, 70, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravelli, M.N.; Schoeller, D.A. Traditional Self-Reported Dietary Instruments Are Prone to Inaccuracies and New Approaches Are Needed. Front. Nutr. 2020, 7, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrows, T.L.; Ho, Y.Y.; Rollo, M.E.; Collins, C.E. Validity of Dietary Assessment Methods When Compared to the Method of Doubly Labeled Water: A Systematic Review in Adults. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamara, A.E.; Brennan, L. Potential of food intake biomarkers in nutrition research. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2020, 79, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafiq, T.; Azab, S.M.; Teo, K.K.; Thabane, L.; Anand, S.S.; Morrison, K.M.; de Souza, R.J.; Britz-McKibbin, P. Nutritional Metabolomics and the Classification of Dietary Biomarker Candidates: A Critical Review. Adv. Nutr. 2021, 12, 2333–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, C.; McNamara, A.E.; Brennan, L. Role of metabolomics in identification of biomarkers related to food intake. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2019, 78, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trimigno, A.; Münger, L.; Picone, G.; Freiburghaus, C.; Pimentel, G.; Vionnet, N.; Pralong, F.; Capozzi, F.; Badertscher, R.; Vergères, G. GC-MS Based Metabolomics and NMR Spectroscopy Investigation of Food Intake Biomarkers for Milk and Cheese in Serum of Healthy Humans. Metabolites 2018, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchsmann, P.; Tena Stern, M.; Münger, L.H.; Pimentel, G.; Burton, K.J.; Vionnet, N.; Vergères, G. Nutrivolatilomics of Urinary and Plasma Samples to Identify Candidate Biomarkers after Cheese, Milk, and Soy-Based Drink Intake in Healthy Humans. J. Proteome Res. 2020, 19, 4019–4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano Escuder, P. Statistical Methods for Intake Prediction and Biological Significance Analysis in Nutrimetabolomic Studies. Ph.D. Thesis, Universitat de Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich, N.; Pietzner, M.; Cannet, C.; Thuesen, B.H.; Hansen, T.; Wallaschofski, H.; Grarup, N.; Skaaby, T.; Budde, K.; Pedersen, O. Urinary metabolomics reveals glycemic and coffee associated signatures of thyroid function in two population-based cohorts. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinzmann, S.S.; Brown, I.J.; Chan, Q.; Bictash, M.; Dumas, M.-E.; Kochhar, S.; Stamler, J.; Holmes, E.; Elliott, P.; Nicholson, J.K. Metabolic profiling strategy for discovery of nutritional biomarkers: Proline betaine as a marker of citrus consumption. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 92, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.-H.; Sun, H.; Qiu, S.; Wang, X.-J. NMR-based metabolomics coupled with pattern recognition methods in biomarker discovery and disease diagnosis. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2013, 51, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Baixauli, J.; Quesada-Vázquez, S.; Mariné-Casadó, R.; Gil Cardoso, K.; Caimari, A.; Del Bas, J.M.; Escoté, X.; Baselga-Escudero, L. Detection of early disease risk factors associated with metabolic syndrome: A new era with the NMR metabolomics assessment. Nutrients 2020, 12, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, C.A.; Oluwagbemigun, K.; Nöthlings, U. Advances in dietary pattern analysis in nutritional epidemiology. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 4115–4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitry, P.A.R. New Biomarkers of Habitual Dietary Intake in Observational Studies. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universität München, Munich, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Chiva-Blanch, G.; Jiménez, C.; Pinyol, M.; Herreras, Z.; Catalán, M.; Martínez-Huélamo, M.; Lamuela-Raventos, R.M.; Sala-Vila, A.; Cofán, M.; Gilabert, R. 5-CIS-, trans-and total lycopene plasma concentrations inversely relate to atherosclerotic plaque burden in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes subjects. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmands, W.M.; Beckonert, O.P.; Stella, C.; Campbell, A.; Lake, B.G.; Lindon, J.C.; Holmes, E.; Gooderham, N.J. Identification of human urinary biomarkers of cruciferous vegetable consumption by metabonomic profiling. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 4513–4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arathi, B.P.; Sowmya, P.R.-R.; Vijay, K.; Baskaran, V.; Lakshminarayana, R. Biofunctionality of carotenoid metabolites: An insight into qualitative and quantitative analysis. In Metabolomics-Fundamentals and Applications; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016; p. 19. [Google Scholar]
- Landberg, R.; Hanhineva, K.; Tuohy, K.; Garcia-Aloy, M.; Biskup, I.; Llorach, R.; Yin, X.; Brennan, L.; Kolehmainen, M. Biomarkers of cereal food intake. Genes Nutr. 2019, 14, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelladurai, P.K.; Pandey, A.; Swamy, C.T.; Govindarajan, N.; Ravichandran, L.; Anbu, K.; Shiddamallayya, N.; Singh Purewal, S. Rye Phenolics: Extraction, Identification, Structure and Health Benefits. In Rye: Processing, Nutritional Profile and Commercial Uses; Singh Purewal, S., Ed.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; pp. 117–156. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Chen, H.; Zhu, Y.; McBride, J.; Fu, J.; Sang, S. Oat avenanthramide-C (2c) is biotransformed by mice and the human microbiota into bioactive metabolites. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madrid-Gambin, F.; Brunius, C.; Garcia-Aloy, M.; Estruel-Amades, S.; Landberg, R.; Andres-Lacueva, C. Untargeted 1H NMR-based metabolomics analysis of urine and serum profiles after consumption of lentils, chickpeas, and beans: An extended meal study to discover dietary biomarkers of pulses. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 6997–7005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos, M.T.O. Urinary Biomarkers of Biofortified Beef in Healthy Women Explored by Untargeted Metabolomics; Universidade NOVA de Lisboa: Lisbon, Portugal, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Hanhineva, K. Application of metabolomics to assess effects of controlled dietary interventions. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2015, 4, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, M.; Aulisa, G.; Marcon, D.; Rizzo, G.; Tarsisano, M.G.; Di Renzo, L.; Federici, M.; Caprio, M.; De Lorenzo, A. Association of urinary and plasma levels of trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) with foods. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, K.J.; Krüger, R.; Scherz, V.; Münger, L.H.; Picone, G.; Vionnet, N.; Bertelli, C.; Greub, G.; Capozzi, F.; Vergères, G. Trimethylamine-N-oxide postprandial response in plasma and urine is lower after fermented compared to non-fermented dairy consumption in healthy adults. Nutrients 2020, 12, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xyda, S.-E.; Vuckovic, I.; Petterson, X.-M.; Dasari, S.; Lalia, A.Z.; Parvizi, M.; Macura, S.I.; Lanza, I.R. Distinct influence of omega-3 fatty acids on the plasma metabolome of healthy older adults. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2020, 75, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrizo, D.; Chevallier, O.P.; Woodside, J.V.; Brennan, S.F.; Cantwell, M.M.; Cuskelly, G.; Elliott, C.T. Untargeted metabolomic analysis of human serum samples associated with different levels of red meat consumption: A possible indicator of type 2 diabetes? Food Chem. 2017, 221, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, L.; Chen, L.; Lv, J.; Pang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Pei, P.; Du, H.; Yang, L.; Millwood, I.Y.; Walters, R.G. Association of red meat consumption, metabolic markers, and risk of cardiovascular diseases. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 833271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Münger, L.H.; Trimigno, A.; Picone, G.; Freiburghaus, C.; Pimentel, G.; Burton, K.J.; Pralong, F.P.; Vionnet, N.; Capozzi, F.; Badertscher, R. Identification of urinary food intake biomarkers for milk, cheese, and soy-based drink by untargeted GC-MS and NMR in healthy humans. J. Proteome Res. 2017, 16, 3321–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, B.S.; Sandby, K.; Krarup, T.; Magkos, F.; Geiker, N.R.; Bertram, H.C. Changes in Plasma, Urine, and Fecal Metabolome after 16 Weeks of Consuming Dairy With Different Food Matrixes–A Randomized Controlled Trial. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2024, 68, 2300363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rådjursöga, M.; Karlsson, G.B.; Lindqvist, H.M.; Pedersen, A.; Persson, C.; Pinto, R.C.; Ellegård, L.; Winkvist, A. Metabolic profiles from two different breakfast meals characterized by 1H NMR-based metabolomics. Food Chem. 2017, 231, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothwell, J.A.; Madrid-Gambin, F.; Garcia-Aloy, M.; Andres-Lacueva, C.; Logue, C.; Gallagher, A.M.; Mack, C.; Kulling, S.E.; Gao, Q.; Praticò, G. Biomarkers of intake for coffee, tea, and sweetened beverages. Genes Nutr. 2018, 13, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, W.S.; Huang, P.Y.; Ong, E.S.; Ong, C.N.; Li, S.F.Y.; Pasikanti, K.K.; Chan, E.C.Y. Metabonomics investigation of human urine after ingestion of green tea with gas chromatography/mass spectrometry, liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry and 1H NMR spectroscopy. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2008, 22, 2436–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madrid-Gambin, F.; Garcia-Aloy, M.; Vazquez-Fresno, R.; Vegas-Lozano, E.; Sanchez-Pla, A.; Misawa, K.; Hase, T.; Shimotoyodome, A.; Andres-Lacueva, C. Metabolic signature of a functional high-catechin tea after acute and sustained consumption in healthy volunteers through 1H NMR based metabolomics analysis of urine. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 67, 3118–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daykin, C.A.; Duynhoven, J.P.V.; Groenewegen, A.; Dachtler, M.; Amelsvoort, J.M.V.; Mulder, T.P. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopic based studies of the metabolism of black tea polyphenols in humans. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 1428–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dorsten, F.A.; Grün, C.H.; van Velzen, E.J.; Jacobs, D.M.; Draijer, R.; van Duynhoven, J.P. The metabolic fate of red wine and grape juice polyphenols in humans assessed by metabolomics. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2010, 54, 897–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Fresno, R.; Llorach, R.; Alcaro, F.; Rodríguez, M.Á.; Vinaixa, M.; Chiva-Blanch, G.; Estruch, R.; Correig, X.; Andrés-Lacueva, C. 1H-NMR-based metabolomic analysis of the effect of moderate wine consumption on subjects with cardiovascular risk factors. Electrophoresis 2012, 33, 2345–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.S. NMR-based metabolomics in wine science. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2011, 49, S13–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macias, S.; Kirma, J.; Yilmaz, A.; Moore, S.E.; McKinley, M.C.; McKeown, P.P.; Woodside, J.V.; Graham, S.F.; Green, B.D. Application of 1H-NMR Metabolomics for the Discovery of Blood Plasma Biomarkers of a Mediterranean Diet. Metabolites 2019, 9, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vázquez-Fresno, R.; Llorach, R.; Urpi-Sarda, M.; Lupianez-Barbero, A.; Estruch, R.; Corella, D.; Fitó, M.; Arós, F.; Ruiz-Canela, M.; Salas-Salvado, J. Metabolomic pattern analysis after mediterranean diet intervention in a nondiabetic population: A 1-and 3-year follow-up in the PREDIMED study. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarys, P.; Deliens, T.; Huybrechts, I.; Deriemaeker, P.; Vanaelst, B.; De Keyzer, W.; Hebbelinck, M.; Mullie, P. Comparison of Nutritional Quality of the Vegan, Vegetarian, Semi-Vegetarian, Pesco-Vegetarian and Omnivorous Diet. Nutrients 2014, 6, 1318–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, W.J. Health effects of vegan diets2. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 89, 1627S–1633S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satija, A.; Hu, F.B. Plant-based diets and cardiovascular health. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2018, 28, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Yang, S.; Cai, S.; Dong, J.; Li, X.; Chen, Z. Identification of biochemical changes in lactovegetarian urine using 1H NMR spectroscopy and pattern recognition. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 396, 1451–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordain, L.; Eaton, S.B.; Sebastian, A.; Mann, N.; Lindeberg, S.; Watkins, B.A.; O’Keefe, J.H.; Brand-Miller, J. Origins and evolution of the Western diet: Health implications for the 21st century. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 81, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente-Suárez, V.J.; Beltrán-Velasco, A.I.; Redondo-Flórez, L.; Martín-Rodríguez, A.; Tornero-Aguilera, J.F. Global impacts of western diet and its effects on metabolism and health: A narrative review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabek, A.; Paslawski, R.; Paslawska, U.; Wojtowicz, W.; Drozdz, K.; Polakof, S.; Podhorska, M.; Dziegiel, P.; Mlynarz, P.; Szuba, A. The influence of different diets on metabolism and atherosclerosis processes—A porcine model: Blood serum, urine and tissues 1H NMR metabolomics targeted analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newgard, C.B.; An, J.; Bain, J.R.; Muehlbauer, M.J.; Stevens, R.D.; Lien, L.F.; Haqq, A.M.; Shah, S.H.; Arlotto, M.; Slentz, C.A.; et al. A Branched-Chain Amino Acid-Related Metabolic Signature that Differentiates Obese and Lean Humans and Contributes to Insulin Resistance. Cell Metab. 2009, 9, 311–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guasch-Ferré, M.; Hruby, A.; Toledo, E.; Clish, C.B.; Martínez-González, M.A.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Hu, F.B. Metabolomics in Prediabetes and Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 833–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Wang, Z.; Lee, Y.; Lai, H.T.; de Oliveira Otto, M.C.; Lemaitre, R.N.; Fretts, A.; Sotoodehnia, N.; Budoff, M.; DiDonato, J.A. Dietary meat, trimethylamine N-oxide-related metabolites, and incident cardiovascular disease among older adults: The cardiovascular health study. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2022, 42, e273–e288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.S.; Fernandez, M.L. Trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO), diet and cardiovascular disease. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2021, 23, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallister, T.; Jackson, M.A.; Martin, T.C.; Zierer, J.; Jennings, A.; Mohney, R.P.; MacGregor, A.; Steves, C.J.; Cassidy, A.; Spector, T.D. Hippurate as a metabolomic marker of gut microbiome diversity: Modulation by diet and relationship to metabolic syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brial, F.; Chilloux, J.; Nielsen, T.; Vieira-Silva, S.; Falony, G.; Andrikopoulos, P.; Olanipekun, M.; Hoyles, L.; Djouadi, F.; Neves, A.L. Human and preclinical studies of the host–gut microbiome co-metabolite hippurate as a marker and mediator of metabolic health. Gut 2021, 70, 2105–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfora, E.E.; Meex, R.C.; Venema, K.; Blaak, E.E. Gut microbial metabolites in obesity, NAFLD and T2DM. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shimizu, Y.; Kimura, I. Gut microbial metabolite short-chain fatty acids and obesity. Biosci. Microbiota Food Health 2017, 36, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prendiville, O.; Walton, J.; Flynn, A.; Nugent, A.P.; McNulty, B.A.; Brennan, L. Classifying Individuals Into a Dietary Pattern Based on Metabolomic Data. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2021, 65, 2001183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, I.; Gibson, G.; Heinken, A.; Scott, K.; Swann, J.; Thiele, I.; Tuohy, K. Gut microbiota functions: Metabolism of nutrients and other food components. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernocchi, P.; Del Chierico, F.; Putignani, L. Gut microbiota metabolism and interaction with food components. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Tan, Y.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, D.; Feng, W.; Peng, C. Functions of gut microbiota metabolites, current status and future perspectives. Aging Dis. 2022, 13, 1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, D.M.; Deltimple, N.; van Velzen, E.; van Dorsten, F.A.; Bingham, M.; Vaughan, E.E.; van Duynhoven, J. 1H NMR metabolite profiling of feces as a tool to assess the impact of nutrition on the human microbiome. NMR Biomed. 2008, 21, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almanza-Aguilera, E.; Urpi-Sarda, M.; Llorach, R.; Vázquez-Fresno, R.; Garcia-Aloy, M.; Carmona, F.; Sanchez, A.; Madrid-Gambin, F.; Estruch, R.; Corella, D. Microbial metabolites are associated with a high adherence to a Mediterranean dietary pattern using a 1H-NMR-based untargeted metabolomics approach. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2017, 48, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinde, Y.; Deokar, G. Regulation of Gut Microbiota by Herbal Medicines. Curr. Drug Metab. 2024, 25, 110–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, A.; Akhter, S.; Kabir, Y. Diet, Microbiome, and Human Health. In Health Benefits of Fermented Foods and Beverages; Dhaka University: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2015; pp. 212–245. [Google Scholar]
- Trimigno, A.; Łoniewska, B.; Skonieczna-Żydecka, K.; Kaczmarczyk, M.; Łoniewski, I.; Picone, G. The application of High-Resolution Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (HR NMR) in metabolomic analyses of meconium and stool in newborns. A preliminary pilot study of MABEL project: Metabolomics approach for the assessment of Baby-Mother Enteric Microbiota Legacy. PharmaNutrition 2024, 27, 100378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C. 1H-NMR Spectroscopy to Investigate the Effects of Food on Animals and Humans Through Metabolomics. Ph.D. Thesis, Universitat de Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Li, Y.; Nie, X.; Zhu, C.; Luo, Q.; Laghi, L.; Picone, G. Metabolomic Analysis of Feces vs. Cecum Content in Animals: A Comparative Study Investigated by 1H-NMR. Metabolites 2025, 15, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanden Bussche, J.; Marzorati, M.; Laukens, D.; Vanhaecke, L. Validated High Resolution Mass Spectrometry-Based Approach for Metabolomic Fingerprinting of the Human Gut Phenotype. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 10927–10934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, B.; Schwerdtfeger, L.A.; Richardson, A.; Tobet, S.A.; Henry, C.S. 1H-NMR Profiling of Short-Chain Fatty Acid Content from a Physiologically Accurate Gut-on-a-Chip Device. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 9987–9992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization; World Health Organization. Probiotics in Food: Health and Nutritional Properties and Guidelines for Evaluation; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Poulsen, K.O. The Use of Metabolomics for Studying the Effects of Pre-and Probiotics. Bachelor’s Thesis, Aarhus University, Aarhus, Denmark, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen, S.M.M.; Nielsen, N.C.; Andersen, H.J.; Olsson, J.; Simrén, M.; Öhman, L.; Svensson, U.; Malmendal, A.; Bertram, H.C. The Serum Metabolite Response to Diet Intervention with Probiotic Acidified Milk in Irritable Bowel Syndrome Patients Is Indistinguishable from that of Non-Probiotic Acidified Milk by 1H NMR-Based Metabonomic Analysis. Nutrients 2010, 2, 1141–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brasili, E.; Mengheri, E.; Tomassini, A.; Capuani, G.; Roselli, M.; Finamore, A.; Sciubba, F.; Marini, F.; Miccheli, A. Lactobacillus acidophilus La5 and Bifidobacterium lactis Bb12 Induce Different Age-Related Metabolic Profiles Revealed by 1H-NMR Spectroscopy in Urine and Feces of Mice. J. Nutr. 2013, 143, 1549–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, H.; Ma, F.; Ma, C.W.; Lu, B.; Xie, Z. Metabonomic strategy for the detection of metabolic effects of probiotics combined with prebiotic supplementation in weaned rats. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 5042–5057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cesare, F.; Calgaro, M.; Ghini, V.; Squarzanti, D.F.; De Prisco, A.; Visciglia, A.; Zanetta, P.; Rolla, R.; Savoia, P.; Amoruso, A. Exploring the Effects of Probiotic Treatment on Urinary and Serum Metabolic Profiles in Healthy Individuals. J. Proteome Res. 2023, 22, 3866–3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowiak, P.; Śliżewska, K. Effects of probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics on human health. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vulevic, J.; Juric, A.; Walton, G.E.; Claus, S.P.; Tzortzis, G.; Toward, R.E.; Gibson, G.R. Influence of galacto-oligosaccharide mixture (B-GOS) on gut microbiota, immune parameters and metabonomics in elderly persons. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 114, 586–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, G.R.; Hutkins, R.W.; Sanders, M.E.; Prescott, S.L.; Reimer, R.A.; Salminen, S.J.; Scott, K.; Stanton, C.; Swanson, K.S.; Cani, P.D. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) Consensus Statement on the Definition and Scope of Prebiotics; University of Nebraska-Lincoln: Lincoln, NE, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
| Metabolite | Trend in Vegetarians/Vegans 1 | Biological/Dietary Source |
|---|---|---|
| BCAAs: leucine, isoleucine, valine | ↓ Decreased | Mainly from animal protein (meat, dairy) |
| Methionine | ↓ Decreased | Animal protein (meat, eggs, dairy) |
| Taurine | ↓ Decreased | Animal tissue (meat, seafood) |
| Creatine/Creatinine | ↓ Decreased | Animal muscle, absent in plants |
| TMAO | ↓ Decreased | Produced from choline/carnitine in animal foods |
| Glycine | ↑ Increased | Plant proteins, conjugation of polyphenols |
| Citrate, Succinate, Malate | ↑ Increased | Organic acids from fruits/vegetables, TCA intermediates |
| Pyruvate, Lactate | ↑Variable | Altered glycolytic flux, fiber fermentation |
| SCFAs: acetate, propionate, butyrate | ↑ Increased | Microbial fermentation of dietary fiber |
| Formate | ↑ Increased | Microbial fermentation by gut microbiota |
| Hippurate | ↑ Increased | Polyphenol metabolism (fruits, vegetables, tea) |
| Phenylacetylglutamine | ↑ Increased | Microbial metabolism of aromatic polyphenols |
| Cinnamoylglycine | ↑ Increased | Polyphenol-rich foods |
| Betaine | ↑ Increased | Whole grains, beets, spinach |
| Myo-inositol | ↑ Increased | Legumes, cereals, nuts |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Picone, G. The Application of NMR-Based Metabolomics in the Field of Nutritional Studies. Encyclopedia 2025, 5, 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia5040174
Picone G. The Application of NMR-Based Metabolomics in the Field of Nutritional Studies. Encyclopedia. 2025; 5(4):174. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia5040174
Chicago/Turabian StylePicone, Gianfranco. 2025. "The Application of NMR-Based Metabolomics in the Field of Nutritional Studies" Encyclopedia 5, no. 4: 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia5040174
APA StylePicone, G. (2025). The Application of NMR-Based Metabolomics in the Field of Nutritional Studies. Encyclopedia, 5(4), 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia5040174






