Abstract
Circular economy marketing (CEM) represents an innovative approach to aligning business strategies with sustainability objectives. This paper explores the role of CEM as a driver of green marketing innovation, emphasising strategies that minimise environmental impact on business competitiveness while enhancing consumer engagement. Using a systematic literature review based on the PRISMA methodology, we identified 39 high-impact studies across multiple industries, categorising findings into key themes, theoretical frameworks, and marketing strategies. The analysis highlights emerging trends, including the shift toward product-service systems (PSSs), behavioural nudging, transparent sustainability branding, and integration of digital technologies such as AI and blockchain to enhance traceability and consumer trust. Findings reveal that while circular economy marketing presents opportunities for businesses to differentiate themselves and build long-term sustainability strategies, significant challenges remain, including scalability issues, consumer scepticism, and risks of greenwashing. Moreover, gaps in standardising impact measurement and industry-specific adaptation hinder wider implementation. Business model innovation, policy support, and collaborative efforts are crucial in overcoming these barriers. This study provides insights for businesses, policymakers, and researchers, highlighting how CEM fosters green innovation and competitiveness. Future research should compare the effectiveness of various strategies to accelerate the transition toward sustainable marketing practices through regulation and interdisciplinary collaboration.
1. Introduction
The increasing emphasis on sustainability has led businesses to integrate circular economy (CE) principles into marketing strategies, creating a new paradigm known as circular economy marketing (CEM) (e.g., [1,2,3,4,5]). This concept represents a transformative approach to aligning business practices with sustainability goals, offering innovative strategies to address pressing environmental challenges such as resource depletion, climate change, and pollution [3,5,6,7,8,9]. By integrating principles of waste reduction, material reuse, and ecosystem regeneration, CEM goes beyond promoting eco-friendly products—it redefines how businesses create and communicate value throughout the product lifecycle [10,11,12,13,14].
Studies have emphasised the role of green marketing in promoting eco-friendly practices and influencing consumer behaviour [15,16]. Environmental education has been shown to impact students’ sustainable consumption habits, offering insights into green marketing strategies [17]. The intersection of CE and marketing spans themes such as green marketing, remanufacturing, product-service systems, and neuromarketing tools [18]. Design frameworks can be used to analyse and develop marketing strategies for circular products and services [1]. Sustainable marketing aligned with CE principles faces challenges in implementation, particularly in avoiding greenwashing accusations [19]. Innovation in sustainability marketing is crucial, focusing on creating value across the value chain and aligning with societal expectations [20]. Therefore, based on the extended literature review, several research questions guided this study:
- R1: How does CEM contribute to sustainability and green marketing innovation?
- R2: What key marketing strategies are used to integrate circular economy principles across different industries?
- R3: What are the main challenges businesses face when implementing circular economy marketing, and how can they be addressed?
- R4: How do consumer perceptions and behavioural changes influence the success of circular economy marketing initiatives?
- R5: What roles do digital technologies (e.g., AI, blockchain, IoT) play in enhancing transparency and effectiveness in circular economy marketing?
- R6: What are the gaps in current research and policy frameworks related to circular economy marketing, and how can they be bridged?
Key strategies in CEM include product life extension through repair and resale, design for recyclability, closed-loop systems, and collaborative consumption models like leasing and sharing platforms [6,21,22]. These approaches minimise environmental impact and enhance consumer engagement through transparency and sustainability storytelling [23,24]. As consumer demand for ethical consumption grows, businesses adopting these strategies are poised to gain competitive advantages and unlock new market opportunities [25]. Integrating advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, and the Internet of Things (IoT) further drives innovation in CEM by enabling enhanced traceability, personalisation, and efficiency [26]. However, businesses face challenges, including greenwashing risks, scaling sustainable solutions, and transitioning traditional supply chains to circular models [8,22].
The answers to the research questions are crucial due to their profound implications for sustainability, business transformation, and global environmental challenges.
This paper explores the role of circular economy marketing as a catalyst for green innovation, examining emerging trends, challenges, and actionable strategies. This research addresses the pressing need to transition from a linear economy (take–make–dispose) to a circular economy (reduce–reuse–recycle) by integrating marketing strategies that promote sustainability.
A systematic literature review analyses the theoretical frameworks, case studies, and practical applications to provide valuable insights for businesses, policymakers, and researchers aiming to drive sustainability and accelerate the shift toward circular economy marketing [6,27].
2. Methodology
This research employed the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) [28] framework to ensure a rigorous and transparent review 98 process. The methodology involved the following steps:
Identification—Databases searched: Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar using the following keywords: “circular economy marketing”, “green marketing innovation”, “sustainability strategies”, and “eco-friendly marketing”. And reached an initial record of 259 studies.
Screening—After analysing the first set of studies, the duplicates (50 studies) were removed (see Figure 1).
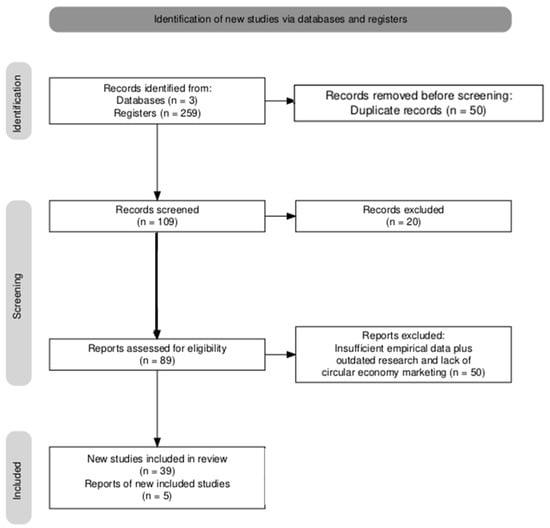
Figure 1.
PRISMA Flow Diagram, using the tool of Haddaway et al. [29].
Eligibility—In a complete assessment analysis, 20 studies with insufficient empirical data, outdated research, or a lack of clear circular economy marketing implications were excluded. Therefore, 89 studies were chosen for their quality and alignment with the research goals.
Inclusion—The studies included in this set underwent data extraction and thematic coding to categorise key insights and strategies, and a final selection of 30 high-impact studies that met all criteria was reached.
Examining business models emphasising access over ownership; Remanufacturing and Recycling Practices (5 studies)—Investigating strategies for product life extension and waste minimisation; Consumer Engagement and Behavioural Change (10 studies)—Understanding how messaging and incentives influence sustainable purchasing; technology-driven Circular Economy Innovations (9 studies)—Highlighting the role of AI, blockchain, and IoT in improving CE adoption.
The studies employed various theoretical perspectives, including the Theory of Planned Behaviour (TPB) (5 studies)—Explaining consumer adoption of circular products; Stakeholder Theory (4 studies)—Analysing the role of multi-stakeholder collaboration in CE marketing; Institutional Theory (3 studies)—Investigating how regulatory and societal norms shape CE marketing strategies; Value-Belief-Norm (VBN) Theory (3 studies)—Understanding moral and ethical consumer decision-making; Innovation Diffusion Theory (9 studies)—Assessing the adoption of circular business models; Other interdisciplinary approaches (15 studies)—Including behavioural economics, macro marketing, and sustainable supply chain management.
The marketing strategies extracted from the studies fall into five key categories: Sustainability Communication and Branding (10 studies)—Focusing on transparency, storytelling, and green advertising effectiveness; Consumer Incentives and Nudging (6 studies)– Investigating price incentives, product labelling, and behavioural nudges; Business. Model Innovation (6 studies)—Covering subscription-based models, leasing, and sharing economy strategies; Design for Circularity (9 studies)—Addressing product durability, modularity, and recyclability as marketing advantages; Technology Integration for Market Competitiveness (8 studies)—Exploring the role of data-driven marketing, AI, and blockchains to enhance consumer trust and circularity adoption.
By structuring the analysis across these dimensions, it was possible to provide a comprehensive understanding of how circular economy marketing strategies are developed, applied and theorised within the academic literature.
3. Results
3.1. Marketing Strategies for the Circular Economy
The extant literature (see Appendix A) consistently demonstrates a strong integration between circular economy principles and green marketing strategies, suggesting a broader trend in business practices (Table 1). Chamberlain and Boks [1] highlighted how design frameworks can be used to analyse and recommend marketing strategies for circular products and services, demonstrating the potential for adapting existing tools from other disciplines to address the unique challenges of marketing in a circular economy context. Lu et al. and Sachi et al. [3,30] emphasised the need for businesses to adapt their marketing strategies and consider how these strategies can drive fundamental changes in consumer behaviour and business operations. They then discuss the importance of advantage acquisition and behaviour transition through green marketing in the circular economy transition.

Table 1.
Marketing strategies for the circular economy.
An integrated model for marketing strategies within the green circular bioeconomy highlights [31] how these strategies are integral to both sectoral and regional approaches [6,22]. This perspective emphasises the importance of considering broader economic and geographic contexts when developing circular economy marketing strategies. Rejeb et al. [18] systematically reviewed the intersection of circular economy and marketing, identifying four main themes: green marketing, remanufacturing marketing, product-service systems, and neuro-marketing tools.
From a different angle [21], those who have a macro marketing perspective reveal inefficiency in supply and procurement processes, highlighting areas where business model innovation is needed to fully realise the potential of circular economy principles in this industry [32]. Ranta et al. [2] identified four alternative value creation logics (resurrect, share, optimise, and replace value) that suppliers use to articulate customer value propositions in the circular economy context. This framework provides insights into how businesses can innovate their models to align with circular economy principles while creating and communicating value to customers [22,33]. Using social and sustainability marketing within a sharing economy model for reusable products demonstrates how circular economy principles can transform traditional business models in everyday consumer contexts [25].
Adapting established marketing frameworks to circular economy principles suggests a practical approach for businesses looking to implement these strategies [34]. Research findings indicate that these approaches can effectively communicate circularity to consumers, emphasising simplicity, transparency, and effectiveness. This suggests that integrating circular economy principles into established marketing frameworks can effectively drive consumer engagement and behaviour change [24,34]. Ranta et al. [10] demonstrated that circular economy message framing enhances the effectiveness of green advertising, reducing its abstractness, and several authors further explored language use in luxury marketing, showing that progress-focused language increases consumer engagement with circular products [35]. It is possible to summarise the emerging key trends in CE marketing and sustainability (see Figure 2). Innovative green marketing strategies in circular economy marketing have emerged as essential tools for promoting sustainability while maintaining business competitiveness. One of the most impactful strategies is the Product-Service Systems (PSS) and subscription models, which shift the focus from product ownership to access-based services. Companies like Philips Lighting have successfully implemented this model, which offers lighting as a service, and BMW’s DriveNow. This car-sharing initiative reduces waste by optimising vehicle usage [2]. These approaches minimise resource consumption and encourage businesses to design durable and maintainable products, extending their lifecycle and reducing environmental impact [7].

Figure 2.
Emerging key trends in CE marketing and sustainability.
Another key strategy is “sustainability storytelling and transparent branding”, which communicates a product’s circular lifecycle and enhances consumer trust [36]. Companies increasingly leverage transparency in their marketing messages to prevent greenwashing and align with consumer demand for ethical and sustainable consumption. Brands can strengthen their market positioning by showcasing their products’ environmental benefits and providing verifiable information on sourcing, production, and recyclability [23,36]. Sustainability storytelling is vital in engaging consumers, making sustainability more relatable and tangible through compelling narratives [10].
Another strategy has also proven effective in driving circular consumption (behavioural nudging and consumer incentives), as many companies now offer trade-in programs, discounts for returning used products, and eco-labels that guide purchasing decisions. Businesses encourage sustainable behaviour without coercion by integrating behavioural economics into marketing strategies. Rainatto ei al., [34] highlighted how the beauty sector has successfully adapted traditional marketing frameworks, such as the 7Ps, to incorporate nudges that make sustainability an attractive choice.
The “integration of digital technologies” such as artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, and the Internet of Things (IoT) further enhances the effectiveness of circular economy marketing. These technologies improve transparency, traceability, and efficiency, ensuring that sustainability claims are verifiable and credible [5]. Blockchain, in particular, has been employed to create immutable records of a product’s lifecycle, fostering consumer trust and regulatory compliance. AI-driven personalisation also enables companies to offer tailored sustainability experiences, guiding consumers toward eco-friendly choices based on their preferences and past behaviours [13].
These key trends demonstrate how businesses are evolving to integrate sustainability and circular economy principles into their marketing strategies while addressing consumer preferences and regulatory shifts. By continuing to refine green marketing strategies, businesses can enhance their sustainability efforts while gaining a competitive edge in an increasingly eco-conscious market.
Despite these innovations, several challenges persist. One of the most pressing issues is “measuring the real impact of circular marketing strategies”. The lack of standardised metrics to evaluate how these strategies influence consumer behaviour, business performance, and environmental outcomes makes it difficult to assess their long-term effectiveness [33]. Additionally, “scalability and economic viability” remains a concern, particularly for small and medium enterprises (SMEs) that face high initial investment costs when transitioning to circular business models [3,32].
Consumer perception also presents a significant challenge. While sustainability awareness is growing, many consumers still associate circular products with lower quality or inconvenience compared with traditional alternatives [11,12]. Overcoming these biases requires a combination of strategic messaging, incentives, and education to reshape consumer attitudes. This scepticism can undermine efforts to promote circular consumption, requiring businesses to invest heavily in educational campaigns, transparency, and branding to shift consumer attitudes [10]. The challenge is creating circular products and communicating their value effectively, ensuring consumers recognise the sustainable alternatives’ economic and environmental benefits. The threat of greenwashing and regulatory uncertainty also pose a considerable risk to circular economy marketing. Some businesses exploit sustainability trends by making misleading claims about their environmental impact, eroding consumer trust in green marketing [23]. Furthermore, “the rise of greenwashing and regulatory uncertainty” threatens to undermine genuine circular economy efforts. The absence of clear regulatory frameworks and standardised third-party certifications makes it challenging to differentiate truly sustainable businesses from those engaging in deceptive marketing practices [23]. Without explicit regulatory guidelines and standardised third-party certifications, it becomes difficult to distinguish genuine circular economy efforts from deceptive marketing practices. Policymakers must establish stricter regulations to ensure accountability and prevent companies from misleading consumers with vague or exaggerated sustainability claims [18].
While some industries, such as fashion, electronics, and automotive, have made significant strides in implementing circular economy marketing, other sectors, including food and pharmaceuticals, lag. More research is needed to explore how circular strategies can effectively adapt to diverse industries with unique regulatory and operational constraints [18]. Moreover, industry-specific challenges hinder the widespread adoption of circular economy marketing. While the fashion, electronics, and automotive sectors have made significant strides in implementing circular strategies, other industries, such as food and pharmaceuticals, face unique regulatory and operational constraints that limit their ability to transition to circular models [2]. Perishable goods, health and safety regulations, and complex supply chains make applying circular economy principles in these industries more complex, requiring sector-specific solutions and innovations [7].
Notwithstanding the promising advancements in circular economy marketing, several challenges hinder its full-scale implementation across industries. One of the most pressing issues is measuring and evaluating circular marketing effectiveness. While many companies are integrating sustainability into their marketing strategies, there is a lack of standardised metrics to assess their impact on consumer behaviour, business performance, and environmental benefits [35]. Without consistent and reliable assessment frameworks, businesses struggle to quantify the return on investment of circular initiatives, making it harder to justify long-term commitments to sustainability.
Another significant challenge lies in the circular economy models’ scalability and economic viability, particularly for small and medium enterprises (SMEs). While larger corporations often have the resources to invest in sustainable infrastructure and innovation, SMEs face financial and logistical constraints that make transitioning to circular models more difficult [3]. High initial costs, limited access to sustainable supply chains, and the complexity of integrating circular business models into existing operations can deter companies from fully embracing circular economy principles [5].
Addressing these challenges requires a multi-faceted approach that includes better measurement frameworks, financial support for SMEs, consumer education, stricter regulations against greenwashing, and industry-specific circular solutions. By overcoming these barriers, businesses and policymakers can accelerate the transition toward a genuinely circular economy while maintaining trust, competitiveness, and long-term sustainability [37].
These challenges seem to be unanswered by research since, while circular economy marketing has gained traction as a key strategy for sustainability, several gaps in the studies remain, limiting its widespread adoption and effectiveness. One of the most significant gaps is the lack of comprehensive impact assessment models. Although many businesses incorporate circular principles into their marketing strategies, no universally accepted framework measures their long-term environmental, economic, and social benefits [35]. Existing evaluation methods often focus on short-term consumer behaviour rather than the broader systemic changes required to transition to a fully circular economy. Another key gap is the limited research on consumer behaviour and engagement in circular economy marketing. While studies have highlighted the importance of sustainability messaging and behavioural nudges, more empirical research is needed to understand how consumer segments respond to circular economy initiatives [10]. Psychological barriers, such as perceived inconvenience and product scepticism, are not yet fully understood, making it difficult for businesses to design effective marketing strategies that encourage the widespread adoption of circular products [11,12].
Moreover, the role of digital technologies in enabling circular economy marketing remains underexplored. While blockchain, AI, and IoT have been identified as tools for improving traceability and transparency, limited research exists on how these technologies can be effectively integrated into marketing strategies to enhance consumer trust and engagement [13]. Businesses need more precise guidelines on leveraging digital innovations to support circular economy objectives, from personalised sustainability recommendations to real-time tracking of product lifecycles [5].
Another gap lies in the fragmented policy and regulatory landscape surrounding circular economy marketing. Many countries and industries lack consistent guidelines on how businesses should communicate sustainability efforts, leading to confusion and greenwashing concerns [23]. The absence of standardised certification schemes makes it challenging for consumers to distinguish between genuinely sustainable products and those marketed with misleading claims. Future research should explore how regulatory frameworks can be harmonised to provide clear and enforceable guidelines for circular marketing practices [18].
Additionally, the application of circular economy marketing across different industries remains uneven. While the fashion, electronics, and automotive sectors have seen significant innovations, industries such as food, pharmaceuticals, and heavy manufacturing face unique challenges that hinder their transition to circular models [2]. Research is needed to explore how circular principles can be adapted to sectors where factors like perishability, health regulations, and high production costs pose additional barriers [7,37,38].
Lastly, interdisciplinary research on circular economy marketing is still in its early stages. Many studies focus on business strategies or sustainability impacts but fail to integrate behavioural psychology, data science, and environmental economics insights to create a holistic understanding of circular marketing [3]. Future research should bridge these gaps by fostering cross-disciplinary collaboration to develop more effective and scalable circular economy marketing models.
By addressing these research gaps, scholars and practitioners can strengthen circular economy marketing’s impact, ensuring businesses can effectively transition to sustainable models while gaining consumer trust and regulatory support models while gaining consumer trust and regulatory support.
3.2. Business Implications of Circular Economy Marketing
The transition toward circular economy marketing presents significant business implications, requiring companies to rethink their strategies, business models, and market engagement, which are summarised in Table 2.

Table 2.
Business implementation implications when adopting circular economy marketing.
A key aspect of this transformation is the shift from traditional product-based models to product-service systems (PSSs), where businesses prioritise access over ownership. By offering leasing, rental, and pay-per-use options, companies can enhance lifecycle management, improve customer satisfaction, and ensure compliance with sustainability goals [2]. However, initial investment costs and restructuring existing business models remain key obstacles [7,38].
A crucial component of effective circular economy marketing is message framing, where businesses use clear, concrete language to communicate sustainability efforts. Studies indicate that adopting circular economy-based narratives reduces the perceived abstractness of green advertising and increases consumer willingness to pay for sustainable products [10]. However, this approach is not without its challenges, as consumer understanding and message complexity can hinder the effectiveness of such communication [35,39].
Eco-innovation is another important factor in circular marketing, which involves integrating sustainability principles into product and service development. Companies leveraging eco-innovation benefit from enhanced market competitiveness and the ability to develop sustainable products that appeal to environmentally conscious consumers [12]. Still, the high research and development costs and technological limitations hinder widespread adoption [5,38]. Businesses must carefully balance the financial feasibility of these innovations with their long-term sustainability objectives.
Transparency plays a vital role in circular economy marketing, with honest and transparent sustainability communication proving essential in building consumer trust [39]. Companies that provide detailed information about their environmental efforts can increase engagement and encourage responsible consumer behaviour [23]. However, the risk of greenwashing remains a significant concern, as misleading claims can erode credibility and lead to competitive disadvantages [18]. Businesses must adopt verifiable sustainability metrics to ensure authenticity and protect their reputations.
Consumer behaviour is a significant determinant of circular economy success, and behavioural nudging has emerged as an effective strategy to guide consumers toward sustainable choices [34]. Subtle prompts like sustainability labels and default green options encourage environmentally friendly behaviour. However, businesses must navigate ethical considerations and develop accurate methods for measuring the impact of these nudges.
To fully integrate circular economy principles, businesses must adopt a triple-bottom-line approach, aligning economic, environmental, and social goals [5]. This holistic strategy enhances sustainability performance and market competitiveness but introduces complexities, such as trade-offs between profitability and long-term sustainability commitments. Companies must carefully manage these tensions to balance financial success and environmental responsibility effectively.
Green branding is another critical aspect of circular economy marketing, with companies increasingly positioning themselves as sustainability leaders [11,36]. A strong sustainability-focused brand identity helps differentiate businesses and foster consumer loyalty. However, authenticity remains challenging, as market scepticism toward green claims necessitates concrete proof of sustainability efforts [23]. To maintain credibility, businesses must ensure their branding aligns with real, measurable impacts.
Efficient circular supply chain management is fundamental to achieving sustainability goals, requiring businesses to implement closed-loop systems for materials and products [21]. Companies focusing on resource efficiency and waste reduction benefit from cost savings and enhanced sustainability performance. However, logistical challenges and the need for supplier cooperation often hinder the seamless integration of circular supply chains. Collaborative partnerships and open innovation frameworks can help address these barriers [26].
Consumer education is an often-overlooked component of circular economy marketing, which is crucial in promoting sustainable purchasing decisions [11]. Providing accessible information and resources helps improve consumer understanding and encourages the adoption of circular products. However, businesses face the challenge of allocating resources effectively and measuring the impact of educational campaigns on consumer behaviour [35].
While circular economy strategies can be broadly applied, sector-specific adaptations are necessary to ensure relevance and effectiveness [2]. Different industries require tailored approaches due to varying regulations, consumer expectations, and operational constraints. However, a lack of industry-specific research limits businesses’ ability to implement highly customised circular strategies [7]. Further studies are needed to develop frameworks that cater to diverse market contexts.
Long-term studies [9] show that circular business models generate revenue, enhance resource productivity, and ensure business continuity. Collaboration across industries and value chains is a significant enabler of circular economy marketing success. Inter-organisational collaboration has been shown to accelerate the implementation of circular economy practices, particularly in industries such as food and beverage [26]. Open innovation is key in enabling information exchange, ensuring that knowledge-sharing facilitates the extension of product lifecycles [8]. Successful case studies highlight the importance of partnerships built on mutual trust and economic viability, particularly in sectors focused on waste valorisation [14,27]. Cross-industry collaborations further enhance circular economy implementation by allowing companies to pool resources, optimise logistics, and streamline sustainability efforts [4].
The transition to circular economy marketing is not without challenges (see Table 3). Technical knowledge gaps require businesses to invest in employee engagement and continuous learning initiatives [34]. Training programs and knowledge-sharing platforms are essential in developing the necessary skills to support circular economy implementation. High-tech solutions can be beneficial; studies indicate that simple, cost-effective technologies are often just as effective in enabling circular practices [5].

Table 3.
Business implementation challenges and success factors.
Regulatory barriers also impede circular economy adoption, necessitating supportive policies that incentivise sustainable practices. Engagement with policymakers and advocacy for favourable regulations can help create an environment where businesses can successfully implement circular economy models [18].
Another significant challenge is the complexity of the supply chain, which can be mitigated through collaboration and open innovation. Developing closed-loop supply chains requires businesses to work closely with suppliers and partners to optimise material reuse and minimise waste. Market volatility also impacts circular economy strategies, making it essential for companies to develop flexible, adaptive models that balance linear and circular systems.
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Research on circular economy marketing has increasingly demonstrated the potential for businesses to align sustainability with competitive advantage. Integrating circular economy principles into marketing strategies enables companies to implement product-service systems, behavioural nudging, transparent branding, and digital innovations such as AI and blockchain [13,21]. This study’s application of the PRISMA methodology provided a structured framework for analysing key strategies, success factors, and challenges within circular economy marketing [9,28,40].
One of the central insights from this research is that circular economy marketing enhances business resilience and consumer engagement by integrating sustainability into branding, communication, and supply chain strategies [23,24,39]. However, challenges such as greenwashing risks, scalability issues, regulatory inconsistencies, and the complexity of shifting to circular business models remain significant barriers [18,37]. Addressing these issues requires a multi-stakeholder approach, combining business innovation, regulatory support, and consumer education [8,26] (see Table 4).

Table 4.
Stakeholder’s insights.
From a research perspective, this study underscores the need for further interdisciplinary investigations to assess the long-term impact of circular marketing strategies. More empirical studies comparing sector-specific adaptations and measuring the effectiveness of different approaches would strengthen the field [35]. Additionally, exploring the role of behavioural science in influencing sustainable consumption could offer new insights into consumer engagement strategies [10,24]. Further research should also focus on developing standardised impact measurement frameworks that evaluate circular economy marketing initiatives’ economic, environmental, and social benefits [34].
For management, the findings indicate that businesses must adopt a holistic view of circular economy marketing by integrating lifecycle thinking, stakeholder collaboration, and innovative financial models to overcome economic and operational barriers [25,37]. Firms that successfully align circular economy principles with consumer values and technological advancements will be better positioned to thrive in an increasingly sustainability-driven market. Research should explore best practices for scaling circular economy marketing initiatives, particularly in small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), to ensure broader adoption across industries [32].
From a policy standpoint, the study emphasised the importance of regulatory frameworks that encourage circular innovation while preventing misleading sustainability claims [11,41]. Governments and international organisations should promote standardisation in sustainability reporting, provide financial incentives for businesses transitioning to circular models, and facilitate collaboration between industries to optimise resource efficiency [3]. Further research should investigate the role of policy interventions in accelerating circular economy adoption and identify the most effective mechanisms for supporting businesses in this transition [4].
As sustainability becomes an urgent global priority, businesses and policymakers seek innovative strategies to reduce environmental impact while maintaining economic viability. Circular economy marketing (CEM) emerges as a transformative approach that aligns business practices with sustainability goals by promoting resource efficiency, waste reduction, and product lifecycle extension. Unlike traditional marketing, which often drives excessive consumption, CEM shifts the focus toward regenerative models, fostering green marketing innovation and sustainable business growth (Answer to R1: How does CEM contribute to sustainability and green marketing innovation?).
A key aspect of this transformation lies in the strategic integration of circular economy principles across diverse industries. Companies leverage various marketing strategies, including product-as-a-service models, eco-design, and reverse logistics, to create sustainable value propositions. These strategies not only drive environmental benefits but also enhance brand loyalty by appealing to increasingly eco-conscious consumers. Understanding the best practices in implementing these strategies across different sectors is crucial for scaling the circular economy (Answer to R2: What key marketing strategies are used to integrate circular economy principles across different industries?).
Despite its potential, businesses face significant challenges in adopting circular economy marketing. These include high initial investment costs, supply chain complexities, and the difficulty of reshaping consumer behaviour. Additionally, companies must navigate regulatory uncertainties and ensure that sustainability claims are credible to avoid greenwashing. Identifying these challenges and proposing actionable solutions will help businesses transition more effectively to circular models (Answer to R3: What are the main challenges businesses face when implementing circular economy marketing, and how can they be addressed?).
Consumer behaviour plays a critical role in the success of circular economy initiatives. While there is growing awareness of sustainability, actual purchasing decisions often do not align with environmentally friendly intentions. Psychological factors, perceived inconvenience, and price sensitivity can act as barriers to adopting circular products and services. Researching how to influence consumer perceptions and foster behavioural shifts will be key to ensuring long-term success in CEM (Answer to R4: How do consumer perceptions and behavioural changes influence the success of circular economy marketing initiatives?).
Technology serves as a vital enabler in advancing circular economy marketing. Digital tools such as artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, and the Internet of Things (IoT) enhance transparency, improve supply chain traceability, and facilitate data-driven decision-making. For instance, blockchain technology can verify product authenticity and sustainability claims, while AI-driven analytics help optimise resource use. Exploring the role of these technologies will provide insights into how businesses can maximise efficiency and accountability in circular economy marketing (Answer to R5: What roles do digital technologies (e.g., AI, blockchain, IoT) play in enhancing transparency and effectiveness in circular economy marketing?).
Finally, the evolution of CEM requires a solid foundation of academic research and supportive policy frameworks. However, significant gaps remain, particularly in terms of standardised impact assessment methods, cross-industry collaboration, and regulatory alignment across regions. Bridging these gaps will require a combination of scholarly research, policy innovation, and industry-driven initiatives. Addressing these issues will not only strengthen CEM’s credibility but also accelerate its widespread adoption (Answer to R6: What are the gaps in current research and policy frameworks related to circular economy marketing, and how can they be bridged?).
While this study provides valuable insights into circular economy marketing (CEM) and its role in driving sustainability, several limitations must be acknowledged. One significant weakness is the lack of empirical data that could offer another perspective and understanding within the systematic literature review framework. Theoretical discussions and conceptual models dominate the existing body of research, often resulting in overgeneralisation across industries. This broad approach, while useful for identifying overarching trends, overlooks the nuanced challenges and opportunities that specific sectors may face in implementing circular marketing strategies.
Another limitation is the insufficient analysis of consumer behaviour within the context of circular economy initiatives. While consumer engagement is a crucial component of sustainable marketing, many studies fail to provide comprehensive behavioural insights into how individuals perceive, adopt, and remain loyal to circular brands. Without this perspective, businesses may struggle to develop effective marketing strategies that align with consumer expectations and drive meaningful change.
Moreover, the absence of standardised impact metrics further complicates the evaluation of circular economy marketing strategies. Companies and researchers alike face difficulties in measuring the true effectiveness of these initiatives due to a lack of universally accepted benchmarks. This gap not only affects academic discourse but also creates challenges for businesses trying to assess their sustainability performance and communicate their progress transparently.
Beyond these academic and methodological concerns, practical challenges hinder the widespread adoption of CEM. Scalability remains a key issue, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) that may lack the financial and operational resources to transition toward circular business models. Additionally, the persistent risk of greenwashing—where companies exaggerate or misrepresent their sustainability efforts—threatens to undermine consumer trust and the credibility of circular economy practices. This challenge is exacerbated by fragmented regulatory frameworks, which vary significantly across regions and industries, creating inconsistencies in enforcement and compliance.
Addressing these limitations requires targeted research efforts that prioritise empirical case studies, industry-specific investigations, and a stronger focus on consumer behaviour analysis. Additionally, developing standardised impact metrics and enhancing regulatory support will be essential in ensuring the long-term success of CEM. By overcoming these challenges, circular economy marketing can evolve into a more effective and credible strategy for driving sustainability in the business world.
Overall, and despite its limitations, this study contributes to the growing discourse on circular economy marketing by identifying key strategies, trends, and challenges while offering a roadmap for businesses, policymakers, and researchers to drive sustainability through innovative marketing approaches. Future research should continue exploring emerging technologies, consumer behaviour shifts, cross-industry collaborations, and policy interventions to further advance the field of circular economy marketing and ensure its long-term success. Future research should explore comparative studies on the effectiveness of different marketing strategies and their impact on consumer behaviour. Policymakers must also facilitate industry-wide transitions through supportive regulations and collaboration incentives, ensuring the longevity and success of circular economy marketing strategies.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A. List of Authors and Main Papers’ Contribution and Characteristics
| Authors | Methodology | Industry/Market Context | Focus Area | Key Variables Examined and Outcomes |
| Camargo Hermosilla, C., 2024 [12] | Systematic literature review | No mention found | Green and circular marketing strategies are crucial for transitioning to a sustainable economy. | Importance of sustainable marketing practices in promoting circular products |
| Chabowski et al., 2023 [22] | Literature review and synthesis | No mention found/transversal to various global sectors | International firms’ response to major threats (environmental, social, and economic problems) arising from ecological destruction, population growth, and economic activity. | International resource design influences marketing capabilities adaptation, which, in turn, impacts international performance. |
| Chamberlin and Boks, 2018 [1] | An exploratory study using design frameworks | Retail sector, focusing on circular products and services | Design frameworks (Dimensions of Behaviour Change and Design with Intent) | Design frameworks provide comprehensive means to analyse and develop marketing strategies for the circular economy Consumer acceptance of circular value propositions |
| Cui et al., 2025 [11] | Systematic review | Textile and apparel industry | Green marketing and branding | Consumer understanding and corporate green branding are the key success factors. |
| De Jesus and Mendonna 2017 [37] | Literature review that comprises academic literature and policy reports | No mention found | Drivers and Barriers in the Eco-Innovation for the circular economy | Drivers and barriers identification. The innovation systems view is an appropriate perspective for understanding the transition to a CE. Policy implications. |
| de Jesus et al., 2021 [41] | (systematic) review of (systematic) reviews | No mention found | Eco-innovation Diversity in a Circular Economy | A framework for understanding pro-circular innovation strategies and enhancing the need to advance “circular innovation studies” as an agenda. |
| Fargnoli et al., 2024 [7] | Case study | Photovoltaic systems | Decision-making framework for green marketing | Shift towards a Product-Service System (PSS) approach |
| Gutentag and Russell, 2024 [7] | Quantitative Experimental 9 studies | Consumer goods (laundry detergent) | Circular economy message framing in green advertising | Reduced the perceived abstractness of green advertising. Perceived abstractness, willingness to pay, and sustainable consumption behaviours |
| Hamouda, H.N., 2024 [6] | Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analysis | No mention found | Relationship between corporate sustainability and circular economy (CE) methods | The circular economy methods affect financial, social, and environmental performance metrics used in business sustainability assessments. Advantages of switching to circular business models and management practices. Relationship between CE strategies and firm performance |
| Hopkinson et al., 2018 [9] | Single in-depth case study | Electronic products industry | Global business model for over 30 years | Circular economy business practices, resource productivity, and business continuity Marketing is crucial to influence change in the culture of consumers (including business users). |
| Joenpolvi et al., 2024 [35] | Field study, empirical research | Luxury goods | Language effects in marketing communications | Predominant locomotion and progress-focused language increase consumer engagement with circular luxury products. |
| Jørgensen and Scarso, 2023 [8] | case study approach, collecting data through semi-structured interviews and questionnaire | No mention | Circular economy business model offering services with embedded information exchange capabilities | Information exchange has been identified as a critical factor in advancing the principles of a circular economy in order to extend product life through maintenance and repair. |
| Kalverkamp and Raabe, 2018 [21] | Theoretical analysis, exploratory study | Automotive re-manufacturing | Macromarketing perspective | The Macromarketing perspective reveals inefficiencies in supply and procurement processes for automotive remanufacturing |
| Kanchana, P., 2024 [15] | Literature review | No mention found | Consumer Perceptions and Brand Strategy | Roadmap for leveraging green marketing as a transformative tool in driving sustainable consumerism and achieving environmental stewardship. |
| Kouser et al., 2024 [13] | Empirical survey study | General market | Eco-innovation in green marketing | Impact of strategic green marketing on sustainable product creation |
| Lopes et al., 2023 [23] | Empirical survey study | Portuguese consumer market | Greenwashing and circular consumption | Paradoxical positive effect of greenwashing on circular consumption intentions |
| Lu et al., 2023 [3] | Mixed methods approach | Hospitality Industry | Circular economy transition through green marketing | Green marketing implementation and circular economy transition process. Advantage acquisition and behaviour transition as key factors in circular economy transition through green marketing |
| Lyubenov, L., 2021 [31] | Theoretical/conceptual paper | Marketing strategies in the green circular bioeconomy | Integral marketing strategies to sectoral and regional strategies in the green circular bioeconomy | |
| Maher et al., 2023 [27] | Multiple case studies | Organics, textiles, packaging, and construction materials | Government-funded training and pilot program | Circular business models, government support for SMEs |
| Mai and Day, 2023 [33] | Qualitative content analysis | Automotive sector, specifically B2C car-sharing | Online marketing communications of car-sharing firms | Consumer adoption factors, marketing communications. |
| Pereira et al., 2024 [24] | Exploratory multiple case study | Manufacturing sector, focusing on industries using recycled materials | Knowledge brokerage for consumer engagement in a circular economy | Knowledge exchange, green Marketing campaigns, consumer engagement |
| Perotti et al., 2024 [26] | Two case studies on collaborative networks | Food and Beverage industry waste | Collaborative networks for upcycling practices in food and beverage | Open innovation, circular supply chain, circular ecosystem |
| Prieto-Sandoval et al., 2022 [17] | Quantitative empirical work | Higher Education Institutions | Opportunities from an Environmental Education Analysis in Young Consumers | Green marketing strategy development focused on engaging in green education, creating community, being aware of consumer diversity, and not differentiating by gender. |
| Proszowska et al., 2024 [19] | Exploratory study, empirical research, theoretical analysis | Multiple sectors | Sustainable marketing strategies and Circular economy | Challenges in aligning marketing strategies with the circular economy framework; recommendations for avoiding greenwashing. Identifies key concepts and strategies of sustainable marketing, providing examples and recommendations |
Rainatto et al., 2023 [34] | Exploratory multiple case studies | Beauty sector | Circular business models adoption through Marketing mix, and nudges for circularity | Adaptations in the 7Ps of the marketing mix to support circularity Circular economy business practices, resource productivity, and business continuity |
| Ranta et al., 2020 [2] | Theoretical analysis, empirical research (multiple-case study) | Multiple industries within the Finnish B2B market | Customer Value Propositions (CVPs) | Identifies four value creation logics for articulating customer value propositions in a circular economy |
| Rao et al., 2024 [14] | Single case study company | Citrus industry | Citrus peel valorising company | Waste Valorisation Regulatory context, partnerships, stakeholder communication, and employee adaptability |
| Ravichandran, S.S., 2023 [16] | Opinion perspective based on a thorough review of the literature | No mention found | Circular Economy Elements in Marketing Communications | Guidance to policymakers and marketers in promoting sustainable thinking among consumers and encouraging circular consumption patterns |
| Rehman et al., 2023 [5] | Empirical survey study | SMEs in emerging economies | Circular economy innovation | Enhanced market competitiveness and Triple Bottom Line efficiencies |
| Rejeb et al., 2022 [18] | Systematic literature review through a qualitative analysis of content | Multiple sectors: Manufacturing, Agri-food, ICT, Hospitality, Textile, Wood | Circular economy and marketing intersection Green marketing, Remanufacturing marketing, Product-service systems, Neuromarketing tools | Identification of four key research themes in CE marketing: green marketing, remanufacturing marketing, product-service systems, and neuromarketing tools |
| Romero-Luis et al., 2022 [39] | Qualitative content analysis using Grounded Theory | Sustainability and Circular Economy, Biotechnology, Communication | Communication effectiveness in social marketing campaigns for the circular economy | Barriers and enablers in communication, sustainable behaviour change |
| Sarkar, A.N., 2012 [36] | Literature review | No mention found | Green Branding and Eco-Innovations for Evolving a Sustainable Green Marketing Strategy | Green branding and green marketing opportunities intimately linked with national and international environmental policy Green marketing and advertising are important for communication to consumers and their scrutiny in seeking validation of such products |
| Shashi et al., 2023 [30] | Quantitative study using structural equation modelling | No mention found | Consumer behaviour in circular economy contexts | Perceived risk, marketing mix, cost, inconvenience, and purchase intention, actual purchase behaviour, circular disposal |
| Stempfle et al., 2022 [40] | Single case study company | Olive oil supply chain | By-product management (olive pomace), Circular Business Model Canvas | Identify the interplaying elements to capture, create, and deliver value, as well as the relationships with the broader economic system. Particularly enhances two distinctive components of CBMC: material loops and adoption factors. Internal and external barriers to the adoption of the new circular business model. |
| Supanut et al., 2024 [4] | Qualitative, multiple-case study design | Companies across various industries | Circular economy strategies, drivers, practices, challenges, enablers, outcomes | Drivers and barriers to adopting circular economy strategies. |
| Ünal et al., 2019 [32] | Qualitative single case study | Office supply industry | Management practices to design a circular economy business model through three dimensions: value network, customer value proposition, and managerial commitment | Managerial practices for circular economy business models to embrace in practice circular economy principles to support the design, change, or upgrade of the business model. |
| Venkatesan, M., 2021 [25] | Theoretical analysis | Coffee shop culture | Social and sustainability marketing within the sharing economy model | Highlights the use of social and sustainability marketing within the sharing economy model for reusable products |
| Verma and Diwan, 2024 [20] | Quantitative performance analysis and qualitative intellectual structure analysis | No mention found | Marketing Innovation for Sustainability | Sustainability and conducive marketing strategies, co-creation to provide tangible and non-tangible corporate advantages. Corporate or macro-level policies align with the dynamic market/stakeholder expectations. |
| Vogtlander et al., 2017 [38] | Theoretical framework development | The remanufacturing industry within the circular economy, focusing on various sectors | Eco-efficient value creation method | Costs, market value, eco-costs, circular business models Marketing strategies for remanufactured products should focus on personal benefits rather than solely on environmental benefits. |
References
- Chamberlin, L.; Boks, C. Marketing Approaches for a Circular Economy: Using Design Frameworks to Interpret Online Communications. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranta, V.; Keränen, J.; Aarikka-Stenroos, L. How B2B Suppliers Articulate Customer Value Propositions in the Circular Economy: Four Innovation-Driven Value Creation Logics. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2020, 87, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Ngo, T.; Tran, H.T.T. Exploring a Hierarchical Model for Circular Economy Transition through Launching Green Marketing. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 32, 2119–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supanut, A.; Maisak, R.; Ratchatakulpat, T. Circular Economy Strategies in Practice: A Qualitative Examination of Industry Adaptation and Innovation. Rev. Gestão Soc. E Ambient. 2024, 18, e06723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, F.U.; Gyamfi, S.; Rasool, S.F.; Akbar, F.; Hussain, K.; Prokop, V. The Nexus between Circular Economy Innovation, Market Competitiveness, and Triple Bottom Lines Efficiencies among SMEs: Evidence from Emerging Economies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 122274–122292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamouda, H.N. Circular Economy Strategies for Business Sustainability: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Green. Manag. Bus. Stud. 2024, 4, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fargnoli, M.; Salvatori, E.; Tronci, M. A Green Marketing and Operations Management Decision-Making Approach Based on QFDE for Photovoltaic Systems. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, R.; Scarso, E. Information as a Circular Resource—Facilitating Information Exchange to Extend Product-Life. Meas. Bus. Excell. 2023, 27, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkinson, P.; Zils, M.; Hawkins, P.; Roper, S. Managing a Complex Global Circular Economy Business Model: Opportunities and Challenges. Calif. Manag. Rev. 2018, 60, 71–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutentag, J.; Antonia Russell, C. Selling Sustainability: Making Green Advertising More Concrete with Circular Economy Message Framing. Int. J. Advert. 2025, 44, 47–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Shaari, N.; Zainal Abidin, S.; Mohd Ali, N.A. Sustainable Style: Unraveling the Trends and Future of Green Marketing in the Textile and Apparel Industry. Sustainability 2025, 17, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermosillas, C.; Moises, R. Impact of Marketing strategies in the promotion of circular products: A systematic review. Gestión En El Tercer Milenio 2024, 27, 461–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouser, R.; Zahra, K.A.; Memon, M.A.B.; Mahmood, G. A Comprehensive Analysis of Role of Eco-Innovation in Linking Strategic Green Marketing and Service Innovation to Sustainable Products. Sustain. Bus. Soc. Emerg. Econ. 2024, 6, 227–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.; Bilić, L.; Bast, A.; de Boer, A. What Does It Take to Close the Loop? Lessons from a Successful Citrus Waste Valorisation Business. Br. Food J. 2024, 126, 143–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanchana, P. Green Marketing in the Age of Sustainability: Consumer Perceptions and Brand Strategy. Nanotechnol. Percept. 2024, 20, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravichandran, S.S. Circular Economy Elements in Marketing Communications: An Opinion Perspective for a Sustainable Future. Prabandhan Indian J. Manag. 2023, 16, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto-Sandoval, V.; Torres-Guevara, L.E.; García-Díaz, C. Green Marketing Innovation: Opportunities from an Environmental Education Analysis in Young Consumers. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 363, 132509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejeb, A.; Rejeb, K.; Keogh, J.G. The Circular Economy and Marketing: A Literature Review. ETIKONOMI 2022, 21, 153–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proszowska, A.; Prymon-Ryś, E.; Dubel, A.; Kondak, A.; Wilk, A. Sustainable Marketing and the Circular Economy in Poland; Routledge: London, UK, 2024; ISBN 9781003408642. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, S.; Diwan, H. Marketing Innovation for Sustainability: Review, Trends, and Way Forward. Bus. Ethics Environ. Responsib. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalverkamp, M.; Raabe, T. Automotive Remanufacturing in the Circular Economy in Europe: Marketing System Challenges. J. Macromark. 2018, 38, 112–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabowski, B.R.; Gabrielsson, P.; Hult, G.T.M.; Morgeson, F.V. Sustainable International Business Model Innovations for a Globalizing Circular Economy: A Review and Synthesis, Integrative Framework, and Opportunities for Future Research. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2023, 56, 383–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, J.M.; Gomes, S.; Trancoso, T. The Dark Side of Green Marketing: How Greenwashing Affects Circular Consumption? Sustainability 2023, 15, 11649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, G.M.; Borchardt, M.; Viegas, C.V.; Bond, A.J.; Vendrametto, O.; Milan, G.S. Facilitating Most Population Engagement with the Circular Economy: Challenges for Academics and (as) Social Media Influencers. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 463, 142765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, M. Social and Sustainability Marketing and the Sharing Economy in the Coffee Shop Culture. In Social and Sustainability Marketing: A Casebook for Reaching Your Socially Responsible Consumers Through Marketing Science; Taylor and Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2021; pp. 839–862. ISBN 9781000408027. [Google Scholar]
- Perotti, F.A.; Bargoni, A.; De Bernardi, P.; Rozsa, Z. Fostering Circular Economy through Open Innovation: Insights from Multiple Case Studies. In Proceedings of the Business Ethics, the Environment and Responsibility; John Wiley and Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Maher, R.; Yarnold, J.; Pushpamali, N.N.C. Circular Economy 4 Business: A Program and Framework for Small-to-Medium Enterprises (SMEs) with Three Case Studies. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 412, 137114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. Rev. Panam. Salud Publica/Pan Am. J. Public Health 2022, 46, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddaway, N.R.; Page, M.J.; Pritchard, C.C.; McGuinness, L.A. PRISMA2020: An R Package and Shiny App for Producing PRISMA 2020-Compliant Flow Diagrams, with Interactivity for Optimised Digital Transparency and Open Synthesis. Campbell Syst. Rev. 2022, 18, e1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shashi; Centobelli, P.; Cerchione, R.; Jhamb, D. What Makes People Hesitant from Circularity: An Analysis of Risk, Marketing Mix, Cost and Inconvenience. J. Consum. Behav. 2024, 23, 43–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyubenov, L. Marketing strategies at sectoral and regional level in the context of the green circular bioeconomy. Econ. Thought J. 2021, 5, 39–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ünal, E.; Urbinati, A.; Chiaroni, D. Managerial Practices for Designing Circular Economy Business Models: The Case of an Italian SME in the Office Supply Industry. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2019, 30, 561–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, P.; Day, S.J. Persuading Reluctant Customers: The Online Marketing Communications of Car Sharing Firms. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainatto, G.M.; Lopes de Sousa Jabbour, A.B.; Cardoso Machado, M.; Chiappetta Jabbour, C.J.; Tiwari, S. How Can Companies Better Engage Consumers in the Transition towards Circularity? Case Studies on the Role of the Marketing Mix and Nudges. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 434, 139779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joenpolvi, E.; Mortimer, G.; Mathmann, F. Driving Consumer Engagement for Circular Luxury Products: Two Large Field Studies on the Role of Regulatory Mode Language. J. Consum. Behav. 2024, 24, 886–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.N. Green Branding and Eco-Innovations for Evolving a Sustainable Green Marketing Strategy. Asia-Pac. J. Manag. Res. Innov. 2012, 8, 39–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jesus, A.; Mendonna, S. Lost in Transition? Drivers and Barriers in the Eco-Innovation Road to the Circular Economy. SSRN Electron. J. 2017, 24, 886–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogtlander, J.G.; Scheepens, A.E.; Bocken, N.M.P.; Peck, D. Combined Analyses of Costs, Market Value and Eco-Costs in Circular Business Models: Eco-Efficient Value Creation in Remanufacturing. J. Remanuf. 2017, 7, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Luis, J.; Carbonell-Alcocer, A.; Gertrudix, M.; Gertrudis Casado, M.D.C.; Giardullo, P.; Wuebben, D. Recommendations to Improve Communication Effectiveness in Social Marketing Campaigns: Boosting Behavior Change to Foster a Circular Economy. Cogent Soc. Sci. 2022, 8, 2147265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stempfle, S.; Roselli, L.; Carlucci, D.; Leone, A.; de Gennaro, B.; Giannoccaro, G. Toward the Circular Economy into the Olive Oil Supply Chain: A Case Study Analysis of a Vertically Integrated Firm. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2022, 6, 1005604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jesus, A.; Lammi, M.; Domenech, T.; Vanhuyse, F.; Mendonça, S. Eco-Innovation Diversity in a Circular Economy: Towards Circular Innovation Studies. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).