Interleukin-33 and Obesity-Related Inflammation and Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Biology of IL-33 and Its Receptors
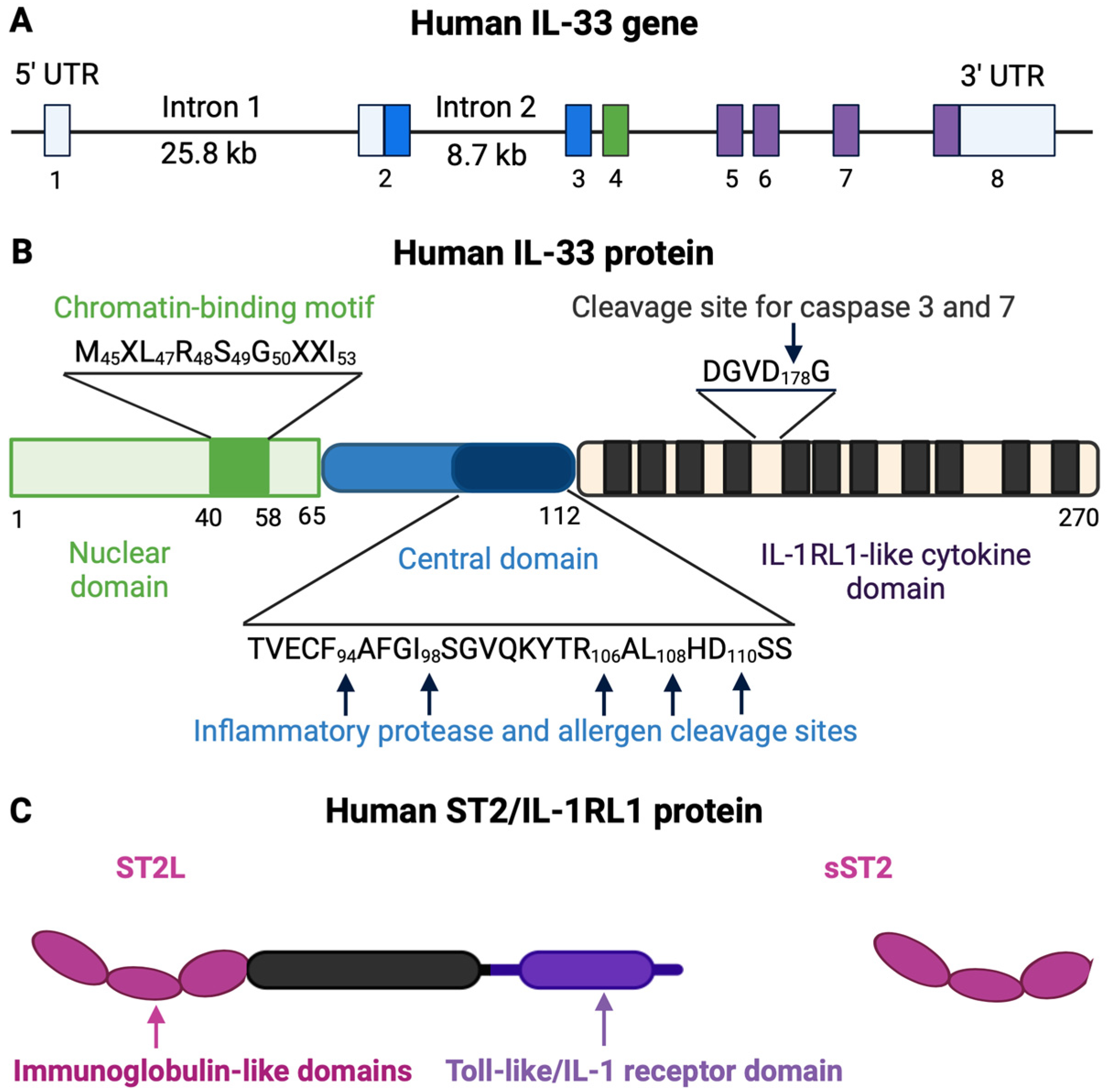
2.1. IL-33
2.2. IL-33 Receptor
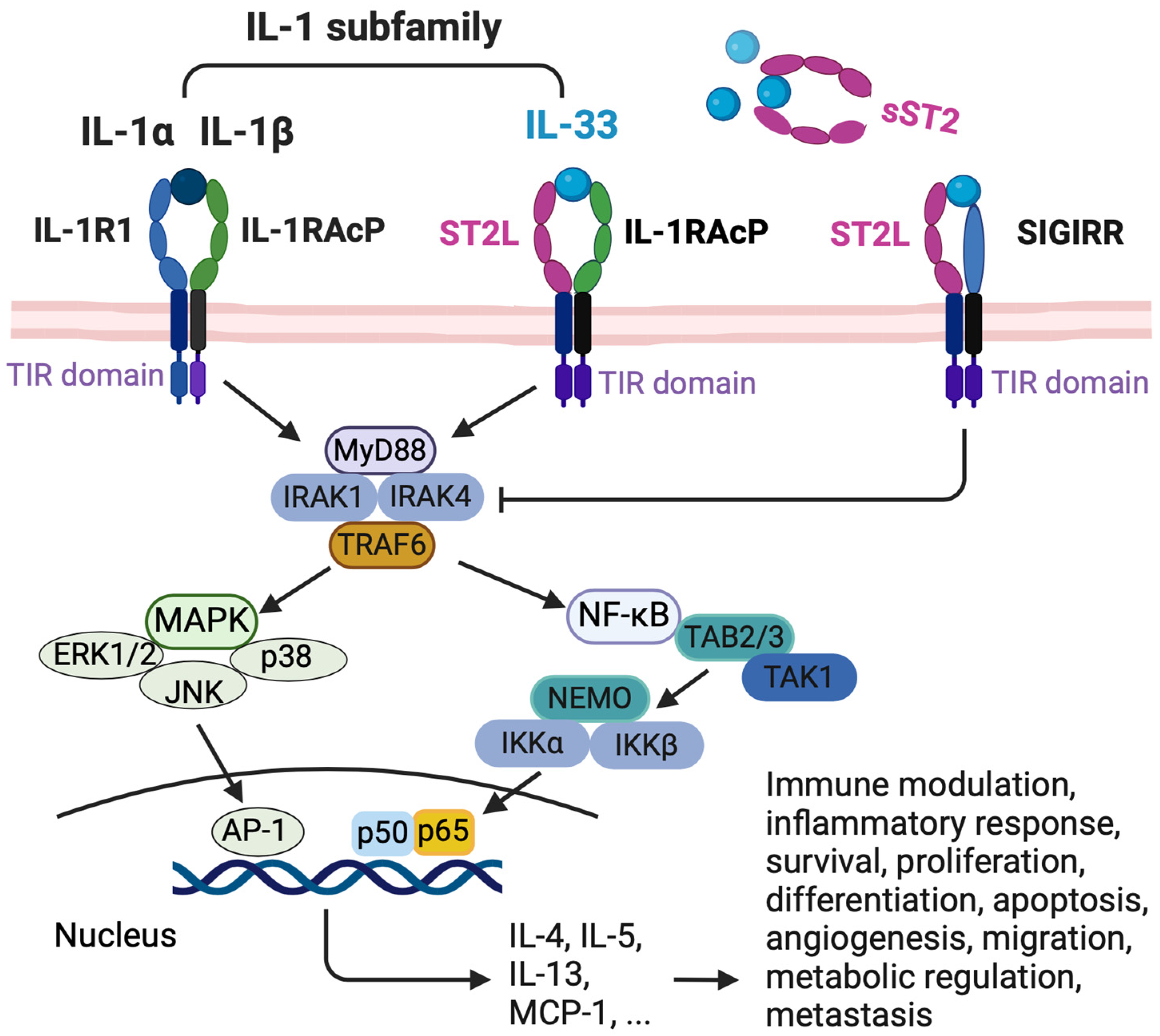
2.3. IL-33/ST2 Signaling Pathway
3. The Role of IL-33 in Immune Responses
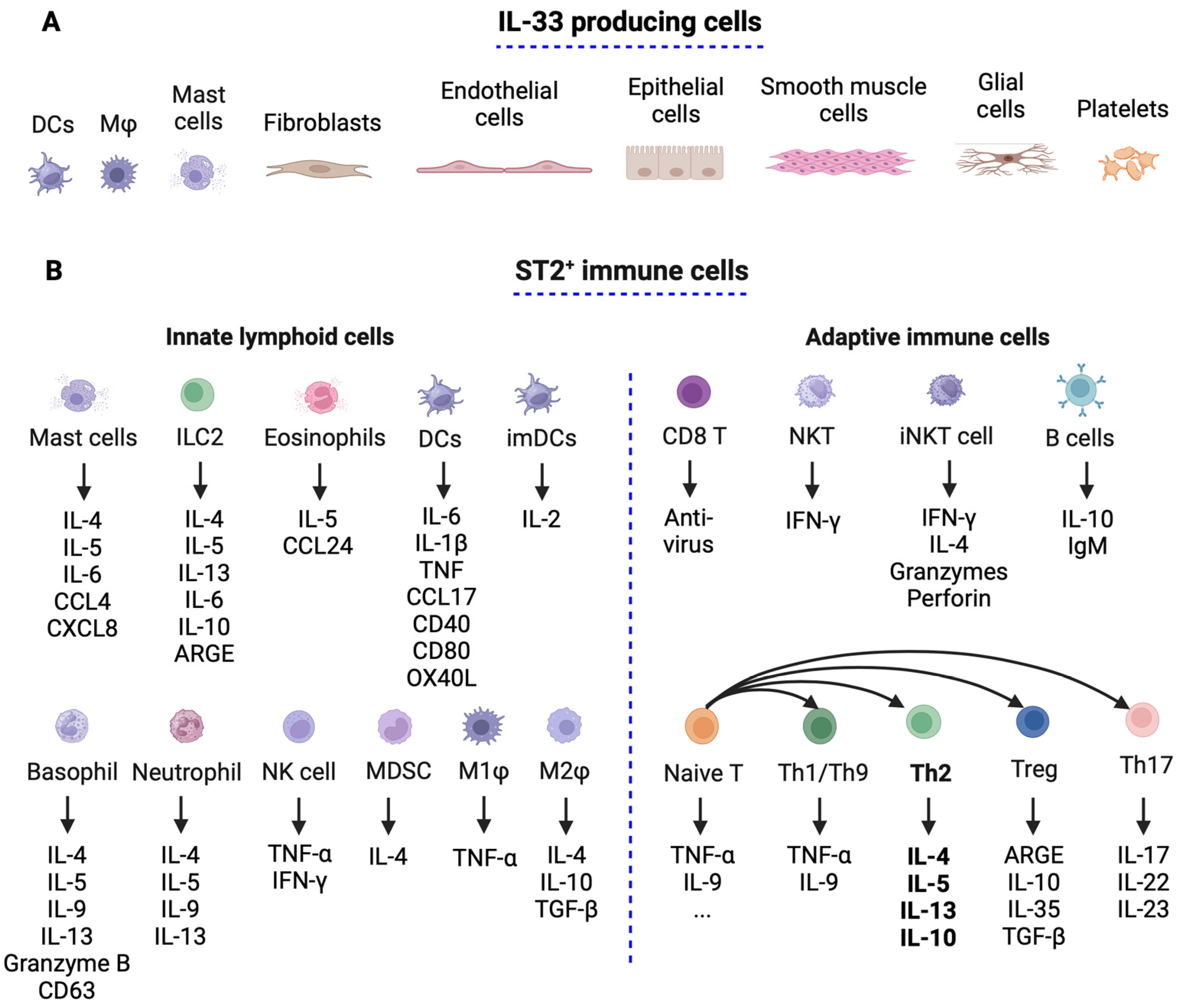
3.1. IL-33 and ST2 Expression in Immune Cells
3.2. Il-33’s Role in Immune Responses
4. IL-33 in Obesity
4.1. IL-33 and ST2 Immune Cell Distribution in Adipose Tissue
4.2. Effect of IL-33 in Adipose Tissue During Obesity

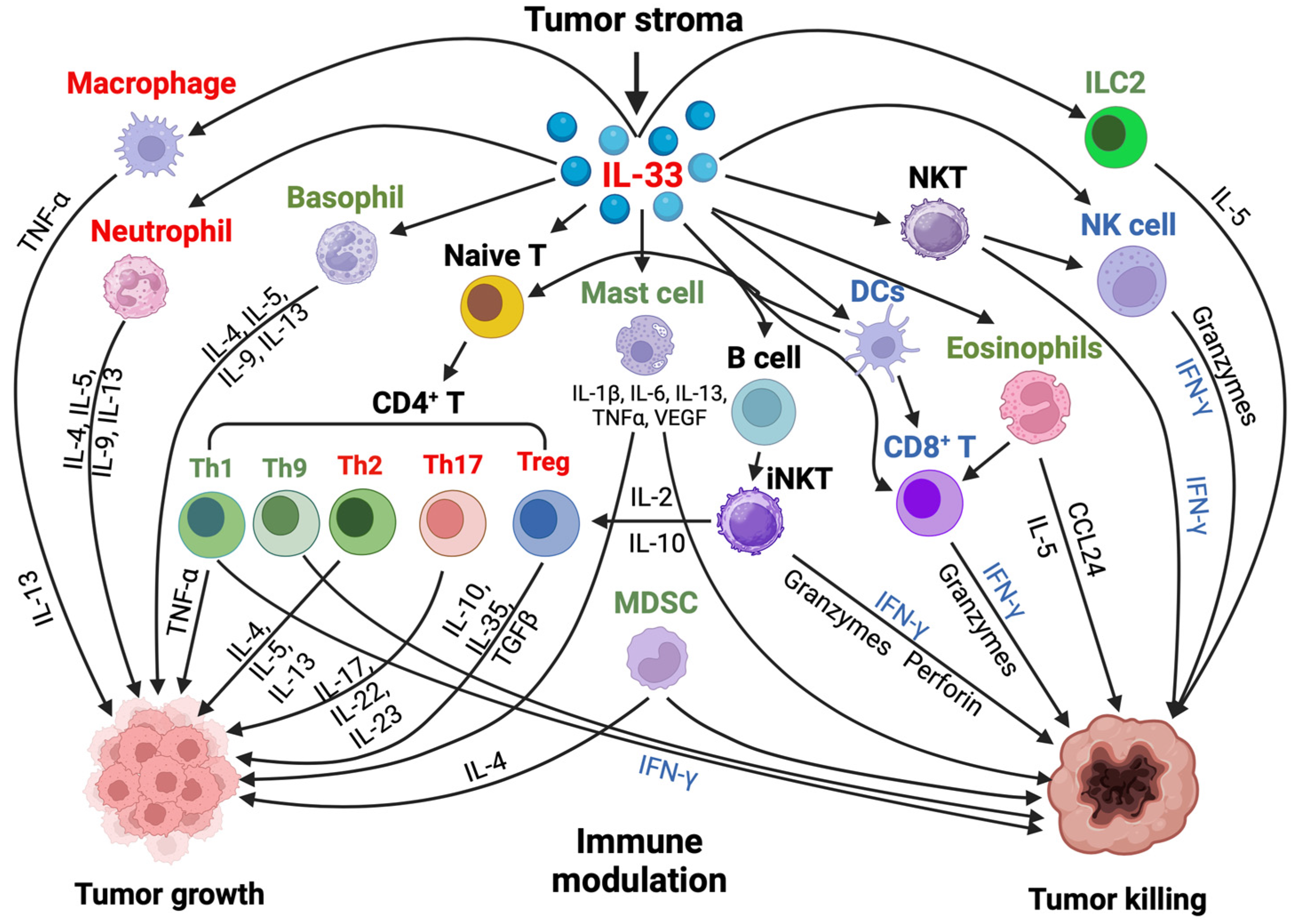
5. Effect of Il-33 in the Tumor Microenvironment
5.1. IL-33 and ST2 Immune Cell Distribution in the Tumor Microenvironment (TME)
5.2. Effect of Il-33 on Neutrophils, Eosinophils, Mast Cells, and Basophils
5.3. Effect of Il-33 on Macrophages and Dendritic Cells
5.4. Effect of Il-33 on CD8+ T, NK, and NKT Cells
5.5. Effect of Il-33 on Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells
5.6. Effect of Il-33 on T Helper Cells
5.7. Effect of Il-33 on CD4+ Treg Cells and in Tumor Immunity
5.8. IL-33-Expressing Cells and the Effects of IL-33 on Non-Immune Cells in the TME
6. Discussion of IL-33 and Obesity-Associated Cancer
7. Conclusions and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Takeuchi, T. Cytokines and cytokine receptors as targets of immune-mediated inflammatory diseases-RA as a role model. Inflamm. Regen. 2022, 42, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, M.D.; Nedjai, B.; Hurst, T.; Pennington, D.J. Cytokines and chemokines: At the crossroads of cell signalling and inflammatory disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1843, 2563–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samadi, M.; Kamrani, A.; Nasiri, H.; Shomali, N.; Heris, J.A.; Shahabi, P.; Ghahremanzadeh, K.; Mohammadinasab, R.; Sadeghi, M.; Sadeghvand, S.; et al. Cancer immunotherapy focusing on the role of interleukins: A comprehensive and updated study. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2023, 249, 154732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brocker, C.; Thompson, D.; Matsumoto, A.; Nebert, D.W.; Vasiliou, V. Evolutionary divergence and functions of the human interleukin (IL) gene family. Hum. Genomics 2010, 5, 30–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsutsui, H.; Cai, X.; Hayashi, S. Interleukin-1 Family Cytokines in Liver Diseases. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 630265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, J.; Owyang, A.; Oldham, E.; Song, Y.; Murphy, E.; McClanahan, T.K.; Zurawski, G.; Moshrefi, M.; Qin, J.; Li, X.; et al. IL-33, an interleukin-1-like cytokine that signals via the IL-1 receptor-related protein ST2 and induces T helper type 2-associated cytokines. Immunity 2005, 23, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baekkevold, E.S.; Roussigné, M.; Yamanaka, T.; Johansen, F.E.; Jahnsen, F.L.; Amalric, F.; Brandtzaeg, P.; Erard, M.; Haraldsen, G.; Girard, J.P. Molecular characterization of NF-HEV, a nuclear factor preferentially expressed in human high endothelial venules. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 163, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaurav, R.; Poole, J.A. Interleukin (IL)-33 immunobiology in asthma and airway inflammatory diseases. J. Asthma 2022, 59, 2530–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Carmine, S.; Scott, M.M.; McLean, M.H.; McSorley, H.J. The role of interleukin-33 in organ fibrosis. Discov. Immunol. 2022, 1, kyac006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.Y.; Li, L.C.; Wu, Y.H.; Yang, J.L.; Tzeng, H.T. Emerging Roles of Interleukin-33-responsive Kidney Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells in Acute Kidney Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, G.; Barile, B.; Nicchia, G.P.; Onorati, F.; Luciani, G.B.; Galeone, A. The ST2/IL-33 Pathway in Adult and Paediatric Heart Disease and Transplantation. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Fuente, M.; MacDonald, T.T.; Hermoso, M.A. The IL-33/ST2 axis: Role in health and disease. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015, 26, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, X.M.; Lian, H.; Li, S. Signaling and functions of interleukin-33 in immune regulation and diseases. Cell Insight 2022, 1, 100042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Z.; Guo, M.; Ge, X.; Chen, F.; Lei, P. IL-33/ST2 Axis: A Potential Therapeutic Target in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, D.; Yu, Z.; Ning, Y.; Tan, Z. Knowledge mapping of interleukin-33: A bibliometric study. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2023, 15, 914–931. [Google Scholar]
- Okunogbe, A.; Nugent, R.; Spencer, G.; Powis, J.; Ralston, J.; Wilding, J. Economic impacts of overweight and obesity: Current and future estimates for 161 countries. BMJ Glob. Health 2022, 7, e009773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. World Health Statitiscs 2024: Monitoring Health for the SDGs, Sustainable Development Goals; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- United States Cancer Statistics. 2024. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/dataviz (accessed on 28 August 2024).
- Arnold, M.; Pandeya, N.; Byrnes, G.; Renehan, P.A.G.; Stevens, G.A.; Ezzati, P.M.; Ferlay, J.; Miranda, J.J.; Romieu, I.; Dikshit, R.; et al. Global burden of cancer attributable to high body-mass index in 2012: A population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, A.; Kochumon, S.; Al-Ozairi, E.; Tuomilehto, J.; Ahmad, R. Association between Adipose Tissue Interleukin-33 and Immunometabolic Markers in Individuals with Varying Degrees of Glycemia. Dis. Markers 2019, 2019, 7901062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrante, A.W. The immune cells in adipose tissue. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2013, 15 (Suppl. S3), S34–S38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, M.F.A.; Talvani, A.; Rocha-Vieira, E. IL-33 in obesity: Where do we go from here? Inflamm. Res. 2019, 68, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, P.; Wan, X.; Cui, B.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, C.; Rong, J.; Zheng, M.; Song, Y.; Chen, L.; He, J.; et al. Interleukin 33 in tumor microenvironment is crucial for the accumulation and function of myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Oncoimmunology 2016, 5, e1063772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allegra, A.; Innao, V.; Tartarisco, G.; Pioggia, G.; Casciaro, M.; Musolino, C.; Gangemi, S. The ST2/Interleukin-33 Axis in Hematologic Malignancies: The IL-33 Paradox. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.; Yang, J.; Di, M.; Hong, Y.; Pan, Q.; Du, Y.; Xiang, T.; Liu, J.; Tang, Y.; Wang, Q.; et al. Alarmin IL-33 orchestrates antitumoral T cell responses to enhance sensitivity to 5-fluorouracil in colorectal cancer. Theranostics 2023, 13, 1649–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatrabnous, N.; Jafarzadeh, A.; Ghaderi, A.; Ariafar, A.; Aminizadeh, N.; Ghassabi, F.; Nemati, M. Association of elevated interleukin-33 serum levels with tumorstages in patients with prostate cancer. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2019, 30, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanovic, B.; Gajovic, N.; Jurisevic, M.; Stojanovic, M.D.; Jovanovic, M.; Jovanovic, I.; Stojanovic, B.S.; Milosevic, B. Decoding the IL-33/ST2 Axis: Its Impact on the Immune Landscape of Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Chen, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Piao, L.; Wang, S.; Yue, Y. Role of the IL-33/ST2 receptor axis in ovarian cancer progression. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 22, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borovcanin, M.M.; Vesic, K. Breast cancer in schizophrenia could be interleukin-33-mediated. World J. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 1065–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pati, S.; Irfan, W.; Jameel, A.; Ahmed, S.; Shahid, R.K. Obesity and Cancer: A Current Overview of Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, Outcomes, and Management. Cancers 2023, 15, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garlanda, C.; Dinarello, C.A.; Mantovani, A. The interleukin-1 family: Back to the future. Immunity 2013, 39, 1003–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carriere, V.; Roussel, L.; Ortega, N.; Lacorre, D.A.; Americh, L.; Aguilar, L.; Bouche, G.; Girard, J.P. IL-33, the IL-1-like cytokine ligand for ST2 receptor, is a chromatin-associated nuclear factor in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayrol, C.; Girard, J.P. Interleukin-33 (IL-33): A nuclear cytokine from the IL-1 family. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 281, 154–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liew, F.Y.; Girard, J.P.; Turnquist, H.R. Interleukin-33 in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 676–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luzina, I.G.; Clerman, A.; Fishelevich, R.; Todd, N.W.; Lockatell, V.; Atamas, S.P. Identification of the IL-33 protein segment that controls subcellular localization, extracellular secretion, and functional maturation. Cytokine 2019, 119, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cayrol, C.; Girard, J.P. The IL-1-like cytokine IL-33 is inactivated after maturation by caspase-1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 9021–9026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Hammel, M.; He, Y.; Tainer, J.A.; Jeng, U.S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, X. Structural insights into the interaction of IL-33 with its receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 14918–14923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingel, A.; Weiss, T.M.; Niebuhr, M.; Pan, B.; Appleton, B.A.; Wiesmann, C.; Bazan, J.F.; Fairbrother, W.J. Structure of IL-33 and its interaction with the ST2 and IL-1RAcP receptors--insight into heterotrimeric IL-1 signaling complexes. Structure 2009, 17, 1398–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwahana, H.; Yanagisawa, K.; Ito-Kosaka, A.; Kuroiwa, K.; Tago, K.; Komatsu, N.; Katashima, R.; Itakura, M.; Tominaga, S. Different promoter usage and multiple transcription initiation sites of the interleukin-1 receptor-related human ST2 gene in UT-7 and TM12 cells. Eur. J. Biochem. 1999, 264, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemenz, R.; Hoffmann, S.; Werenskiold, A.K. Serum- and oncoprotein-mediated induction of a gene with sequence similarity to the gene encoding carcinoembryonic antigen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 5708–5712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominaga, S. A putative protein of a growth specific cDNA from BALB/c-3T3 cells is highly similar to the extracellular portion of mouse interleukin 1 receptor. FEBS Lett. 1989, 258, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gächter, T.; Werenskiold, A.K.; Klemenz, R. Transcription of the interleukin-1 receptor-related T1 gene is initiated at different promoters in mast cells and fibroblasts. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakkar, R.; Lee, R.T. The IL-33/ST2 pathway: Therapeutic target and novel biomarker. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 827–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariotti, F.R.; Supino, D.; Landolina, N.; Garlanda, C.; Mantovani, A.; Moretta, L.; Maggi, E. IL-1R8: A molecular brake of anti-tumor and anti-viral activity of NK cells and ILC. Semin. Immunol. 2023, 66, 101712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulek, K.; Swaidani, S.; Qin, J.; Lu, Y.; Gulen, M.F.; Herjan, T.; Min, B.; Kastelein, R.A.; Aronica, M.; Kosz-Vnenchak, M.; et al. The essential role of single Ig IL-1 receptor-related molecule/Toll IL-1R8 in regulation of Th2 immune response. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 2601–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Chan, W.L.; Leung, B.P.; Huang, F.; Wheeler, R.; Piedrafita, D.; Robinson, J.H.; Liew, F.Y. Selective expression of a stable cell surface molecule on type 2 but not type 1 helper T cells. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 187, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.; Huber, M.; Kollewe, C.; Bischoff, S.C.; Falk, W.; Martin, M.U. IL-1 receptor accessory protein is essential for IL-33-induced activation of T lymphocytes and mast cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 18660–18665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chackerian, A.A.; Oldham, E.R.; Murphy, E.E.; Schmitz, J.; Pflanz, S.; Kastelein, R.A. IL-1 receptor accessory protein and ST2 comprise the IL-33 receptor complex. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 2551–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayrol, C.; Girard, J.P. IL-33: An alarmin cytokine with crucial roles in innate immunity, inflammation and allergy. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2014, 31, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.Y.; Wu, M.Y.; Zheng, L.Y.; Duan, Y.; Fan, Q.; Zhu, X.M.; Yao, Y.M. Interleukin-33/serum stimulation-2 pathway: Regulatory mechanisms and emerging implications in immune and inflammatory diseases. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2024, 76, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, K.; Sanada, S.; Kudinova, A.Y.; Steinhauser, M.L.; Handa, V.; Gannon, J.; Lee, R.T. Interleukin-33 prevents apoptosis and improves survival after experimental myocardial infarction through ST2 signaling. Circ. Heart Fail. 2009, 2, 684–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarezadeh Mehrabadi, A.; Shahba, F.; Khorramdelazad, H.; Aghamohammadi, N.; Karimi, M.; Bagherzadeh, K.; Khoshmirsafa, M.; Massoumi, R.; Falak, R. Interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein (IL-1RAP): A magic bullet candidate for immunotherapy of human malignancies. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2024, 193, 104200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.S.; Choi, H.J.; Min, J.K.; Pyun, B.J.; Maeng, Y.S.; Park, H.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y.M.; Kwon, Y.G. Interleukin-33 induces angiogenesis and vascular permeability through ST2/TRAF6-mediated endothelial nitric oxide production. Blood 2009, 114, 3117–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artru, F.; Bou Saleh, M.; Maggiotto, F.; Lassailly, G.; Ningarhari, M.; Demaret, J.; Ntandja-Wandji, L.C.; Pais de Barros, J.P.; Labreuche, J.; Drumez, E.; et al. IL-33/ST2 pathway regulates neutrophil migration and predicts outcome in patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 1052–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeyda, M.; Wernly, B.; Demyanets, S.; Kaun, C.; Hämmerle, M.; Hantusch, B.; Schranz, M.; Neuhofer, A.; Itariu, B.K.; Keck, M.; et al. Severe obesity increases adipose tissue expression of interleukin-33 and its receptor ST2, both predominantly detectable in endothelial cells of human adipose tissue. Int. J. Obes. 2013, 37, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, J.W.; Seok, S.H.; Kim, S.; An, H.W.; Choudhury, A.D.; Woo, S.H.; Oh, J.S.; Kim, J.K.; Voon, D.C.; Kim, D.Y.; et al. A synergistic partnership between IL-33/ST2 and Wnt pathway through Bcl-xL drives gastric cancer stemness and metastasis. Oncogene 2023, 42, 501–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cayrol, C.; Girard, J.P. Interleukin-33 (IL-33): A critical review of its biology and the mechanisms involved in its release as a potent extracellular cytokine. Cytokine 2022, 156, 155891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göpfert, C.; Andreas, N.; Weber, F.; Häfner, N.; Yakovleva, T.; Gaestel, M.; Kamradt, T.; Drube, S. The p38-MK2/3 Module Is Critical for IL-33-Induced Signaling and Cytokine Production in Dendritic Cells. J. Immunol. 2018, 200, 1198–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiguro, N.; Moriyama, M.; Furusho, K.; Furukawa, S.; Shibata, T.; Murakami, Y.; Chinju, A.; Haque, A.S.M.R.; Gion, Y.; Ohta, M.; et al. Activated M2 Macrophages Contribute to the Pathogenesis of IgG4-Related Disease via Toll-like Receptor 7/Interleukin-33 Signaling. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020, 72, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löhning, M.; Stroehmann, A.; Coyle, A.J.; Grogan, J.L.; Lin, S.; Gutierrez-Ramos, J.C.; Levinson, D.; Radbruch, A.; Kamradt, T. T1/ST2 is preferentially expressed on murine Th2 cells, independent of interleukin 4, interleukin 5, and interleukin 10, and important for Th2 effector function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 6930–6935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, E.O.; Shimpo, M.; De Keulenaer, G.W.; MacGillivray, C.; Tominaga, S.; Solomon, S.D.; Rouleau, J.L.; Lee, R.T. Expression and regulation of ST2, an interleukin-1 receptor family member, in cardiomyocytes and myocardial infarction. Circulation 2002, 106, 2961–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griesenauer, B.; Paczesny, S. The ST2/IL-33 Axis in Immune Cells during Inflammatory Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neill, D.R.; Wong, S.H.; Bellosi, A.; Flynn, R.J.; Daly, M.; Langford, T.K.; Bucks, C.; Kane, C.M.; Fallon, P.G.; Pannell, R.; et al. Nuocytes represent a new innate effector leukocyte that mediates type-2 immunity. Nature 2010, 464, 1367–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiering, C.; Krausgruber, T.; Chomka, A.; Fröhlich, A.; Adelmann, K.; Wohlfert, E.A.; Pott, J.; Griseri, T.; Bollrath, J.; Hegazy, A.N.; et al. The alarmin IL-33 promotes regulatory T-cell function in the intestine. Nature 2014, 513, 564–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastille, E.; Wasmer, M.H.; Adamczyk, A.; Vu, V.P.; Mager, L.F.; Phuong, N.N.T.; Palmieri, V.; Simillion, C.; Hansen, W.; Kasper, S.; et al. The IL-33/ST2 pathway shapes the regulatory T cell phenotype to promote intestinal cancer. Mucosal Immunol. 2019, 12, 990–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourgeois, E.; Van, L.P.; Samson, M.; Diem, S.; Barra, A.; Roga, S.; Gombert, M.; Schneider, E.; Dy, M.; Gourdy, P.; et al. The pro-Th2 cytokine IL-33 directly interacts with invariant NKT and NK cells to induce IFN-γ production. Eur. J. Immunol. 2009, 39, 1046–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Dang, W.; Tao, Y.; Zhao, H.; Yang, B.; Xu, X.; Li, Y. THE IL-33/ST2 Axis Promotes Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome by Natural Killer T Cells. Shock 2023, 59, 902–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, C.; Bonilla, W.V.; Fröhlich, A.; Helmstetter, C.; Peine, M.; Hegazy, A.N.; Pinschewer, D.D.; Löhning, M. T-bet- and STAT4-dependent IL-33 receptor expression directly promotes antiviral Th1 cell responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 4056–4061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, G.K.; D’Cruz, L.M.; Turnquist, H.R. Emerging Functions of IL-33 in Homeostasis and Immunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 40, 15–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, T.M.; Serve, S.; Marx, A.F.; Fadejeva, J.; Saikali, P.; Dzamukova, M.; Durán-Hernández, N.; Kommer, C.; Heinrich, F.; Durek, P.; et al. A type 1 immunity-restricted promoter of the IL-33 receptor gene directs antiviral T-cell responses. Nat. Immunol. 2024, 25, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milovanovic, M.; Volarevic, V.; Radosavljevic, G.; Jovanovic, I.; Pejnovic, N.; Arsenijevic, N.; Lukic, M.L. IL-33/ST2 axis in inflammation and immunopathology. Immunol. Res. 2012, 52, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, C.; Mahmoud, A.; Keane, J.; Murphy, C.; White, D.; Carey, S.; O’Riordain, M.; Bennett, M.W.; Brint, E.; Houston, A. An antitumorigenic role for the IL-33 receptor, ST2L, in colon cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 114, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurowska-Stolarska, M.; Kewin, P.; Murphy, G.; Russo, R.C.; Stolarski, B.; Garcia, C.C.; Komai-Koma, M.; Pitman, N.; Li, Y.; Niedbala, W.; et al. IL-33 induces antigen-specific IL-5+ T cells and promotes allergic-induced airway inflammation independent of IL-4. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 4780–4790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokubo, K.; Onodera, A.; Kiuchi, M.; Tsuji, K.; Hirahara, K.; Nakayama, T. Conventional and pathogenic Th2 cells in inflammation, tissue repair, and fibrosis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 945063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stark, J.M.; Tibbitt, C.A.; Coquet, J.M. The Metabolic Requirements of Th2 Cell Differentiation. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 02318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setrerrahmane, S.; Xu, H. Tumor-related interleukins: Old validated targets for new anti-cancer drug development. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, B.H.; Leland, P.; Lababidi, S.; Varrichio, F.; Puri, R.K. Interleukin-4 receptor alpha overexpression in human bladder cancer correlates with the pathological grade and stage of the disease. Cancer Med. 2014, 3, 1615–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokopchuk, O.; Liu, Y.; Henne-Bruns, D.; Kornmann, M. Interleukin-4 enhances proliferation of human pancreatic cancer cells: Evidence for autocrine and paracrine actions. Br. J. Cancer 2005, 92, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todaro, M.; Lombardo, Y.; Francipane, M.G.; Alea, M.P.; Cammareri, P.; Iovino, F.; Di Stefano, A.B.; Di Bernardo, C.; Agrusa, A.; Condorelli, G.; et al. Apoptosis resistance in epithelial tumors is mediated by tumor-cell-derived interleukin-4. Cell Death Differ. 2008, 15, 762–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brightling, C.E.; Desai, D.; Pavord, I.D. Cytokine-Specific Therapy in Asthma. In Middleton’s Allergy, 8th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 1491–1502. [Google Scholar]
- Pelaia, C.; Paoletti, G.; Puggioni, F.; Racca, F.; Pelaia, G.; Canonica, G.W.; Heffler, E. Interleukin-5 in the Pathophysiology of Severe Asthma. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gour, N.; Wills-Karp, M. IL-4 and IL-13 signaling in allergic airway disease. Cytokine 2015, 75, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibold, M.A. Interleukin-13 Stimulation Reveals the Cellular and Functional Plasticity of the Airway Epithelium. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2018, 15 (Suppl. S2), S98–S102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doran, E.; Cai, F.; Holweg, C.T.J.; Wong, K.; Brumm, J.; Arron, J.R. Interleukin-13 in Asthma and Other Eosinophilic Disorders. Front. Med. 2017, 4, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knudson, K.M.; Hwang, S.; McCann, M.S.; Joshi, B.H.; Husain, S.R.; Puri, R.K. Recent Advances in IL-13Rα2-Directed Cancer Immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 878365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirichenko, T.V.; Markina, Y.V.; Bogatyreva, A.I.; Tolstik, T.V.; Varaeva, Y.R.; Starodubova, A.V. The Role of Adipokines in Inflammatory Mechanisms of Obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, F.M.; Weschenfelder, J.; Sander, C.; Minkwitz, J.; Thormann, J.; Chittka, T.; Mergl, R.; Kirkby, K.C.; Faßhauer, M.; Stumvoll, M.; et al. Inflammatory Cytokines in General and Central Obesity and Modulating Effects of Physical Activity. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, Y.J. The Role of Adipokines in Tumor Progression and Its Association with Obesity. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gesta, S.; Tseng, Y.H.; Kahn, C.R. Developmental origin of fat: Tracking obesity to its source. Cell 2007, 131, 242–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frontini, A.; Cinti, S. Distribution and development of brown adipocytes in the murine and human adipose organ. Cell Metab. 2010, 11, 253–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, E.D.; Spiegelman, B.M. What we talk about when we talk about fat. Cell 2014, 156, 20–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.J.; Wu, Y.; Fried, S.K. Adipose tissue heterogeneity: Implication of depot differences in adipose tissue for obesity complications. Mol. Asp. Med. 2013, 34, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michailidou, Z.; Gomez-Salazar, M.; Alexaki, V.I. Innate Immune Cells in the Adipose Tissue in Health and Metabolic Disease. J. Innate Immun. 2022, 14, 4–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, K.; Kallies, A.; Vasanthakumar, A. Resident and migratory adipose immune cells control systemic metabolism and thermogenesis. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2022, 19, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathis, D. Immunological goings-on in visceral adipose tissue. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deiuliis, J.; Shah, Z.; Shah, N.; Needleman, B.; Mikami, D.; Narula, V.; Perry, K.; Hazey, J.; Kampfrath, T.; Kollengode, M.; et al. Visceral adipose inflammation in obesity is associated with critical alterations in tregulatory cell numbers. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molofsky, A.B.; Van Gool, F.; Liang, H.E.; Van Dyken, S.J.; Nussbaum, J.C.; Lee, J.; Bluestone, J.A.; Locksley, R.M. Interleukin-33 and Interferon-γ Counter-Regulate Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cell Activation during Immune Perturbation. Immunity 2015, 43, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odegaard, J.I.; Lee, M.W.; Sogawa, Y.; Bertholet, A.M.; Locksley, R.M.; Weinberg, D.E.; Kirichok, Y.; Deo, R.C.; Chawla, A. Perinatal Licensing of Thermogenesis by IL-33 and ST2. Cell 2016, 166, 841–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, D.; Zhang, X.; Wan, Q.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, M.; Zou, L.; Elly, C.; Lee, J.H.; Liu, Y.C. E3 Ligase VHL Promotes Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cell Maturation and Function via Glycolysis Inhibition and Induction of Interleukin-33 Receptor. Immunity 2018, 48, 258–270.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.M.; Asquith, D.L.; Hueber, A.J.; Anderson, L.A.; Holmes, W.M.; McKenzie, A.N.; Xu, D.; Sattar, N.; McInnes, I.B.; Liew, F.Y. Interleukin-33 induces protective effects in adipose tissue inflammation during obesity in mice. Circ. Res. 2010, 107, 650–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlakõiv, T.; Flamar, A.L.; Johnston, L.K.; Moriyama, S.; Putzel, G.G.; Bryce, P.J.; Artis, D. Stromal cells maintain immune cell homeostasis in adipose tissue via production of interleukin-33. Sci. Immunol. 2019, 4, eaax0416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brestoff, J.R.; Kim, B.S.; Saenz, S.A.; Stine, R.R.; Monticelli, L.A.; Sonnenberg, G.F.; Thome, J.J.; Farber, D.L.; Lutfy, K.; Seale, P.; et al. Group 2 innate lymphoid cells promote beiging of white adipose tissue and limit obesity. Nature 2015, 519, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.W.; Odegaard, J.I.; Mukundan, L.; Qiu, Y.; Molofsky, A.B.; Nussbaum, J.C.; Yun, K.; Locksley, R.M.; Chawla, A. Activated type 2 innate lymphoid cells regulate beige fat biogenesis. Cell 2015, 160, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Luo, Y.; Luo, L.; Wu, D.; Ding, X.; Zheng, H.; Wu, H.; Liu, B.; Yang, X.; Silva, F.; et al. Adiponectin restrains ILC2 activation by AMPK-mediated feedback inhibition of IL-33 signaling. J. Exp. Med. 2021, 218, e20191054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Gang, X.; Yang, S.; Cui, M.; Sun, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, G. The Alterations in and the Role of the Th17/Treg Balance in Metabolic Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 678355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Xu, D. The roles of T cells in obese adipose tissue inflammation. Adipocyte 2021, 10, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, V.; Hogan, A.E.; Fallon, P.G.; Schwartz, C. Obesity-Mediated Immune Modulation: One Step Forward, (Th)2 Steps Back. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 932893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.Y.; Zhou, L.; Chen, Z.; Ji, Y.; Peng, X.; Qi, L.; Li, S.; Lin, J.D. The obesity-induced adipokine sST2 exacerbates adipose T. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaay6191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Li, G.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, L.; Chen, E.; Turnquist, H.; Zhang, X.; Finn, O.J.; Chen, X.; Lu, B. IL-33 synergizes with TCR and IL-12 signaling to promote the effector function of CD8+ T cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2011, 41, 3351–3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smithgall, M.D.; Comeau, M.R.; Yoon, B.R.; Kaufman, D.; Armitage, R.; Smith, D.E. IL-33 amplifies both Th1- and Th2-type responses through its activity on human basophils, allergen-reactive Th2 cells, iNKT and NK cells. Int. Immunol. 2008, 20, 1019–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrizabalaga, L.; Risson, A.; Ezcurra-Hualde, M.; Aranda, F.; Berraondo, P. Unveiling the multifaceted antitumor effects of interleukin 33. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1425282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, N.M.; Simon, M.C. The tumor microenvironment. Curr. Biol. 2020, 30, R921–R925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truffi, M.; Sorrentino, L.; Corsi, F. Fibroblasts in the Tumor Microenvironment. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1234, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Yang, M.; Wang, Q. Interleukin-33 in tumorigenesis, tumor immune evasion, and cancer immunotherapy. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 94, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, L.; Sun, W.; Wei, F.; Chen, L.; Wen, W. Interleukin-33 modulates immune responses in cutaneous melanoma in a context-specific way. Aging 2021, 13, 6740–6751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuijs, M.J.; Png, S.; Richard, A.C.; Tsyben, A.; Hamm, G.; Stockis, J.; Garcia, C.; Pinaud, S.; Nicholls, A.; Ros, X.R.; et al. ILC2-driven innate immune checkpoint mechanism antagonizes NK cell antimetastatic function in the lung. Nat. Immunol. 2020, 21, 998–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, K.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Bai, L.; Dong, W.; Shi, G.; Xia, X.; Wu, L. Transgenic expression of IL-33 activates CD8(+) T cells and NK cells and inhibits tumor growth and metastasis in mice. Cancer Lett. 2013, 335, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, Q.; Zhao, X.; Wen, W.; Li, G.; Lu, J.; Qin, W.; Qi, Y.; Xie, F.; et al. Tumoral expression of IL-33 inhibits tumor growth and modifies the tumor microenvironment through CD8+ T and NK cells. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucarini, V.; Ziccheddu, G.; Macchia, I.; La Sorsa, V.; Peschiaroli, F.; Buccione, C.; Sistigu, A.; Sanchez, M.; Andreone, S.; D’Urso, M.T.; et al. IL-33 restricts tumor growth and inhibits pulmonary metastasis in melanoma-bearing mice through eosinophils. Oncoimmunology 2017, 6, e1317420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, D.; Ye, C.; Geng, Z.; Chen, S.; Fan, J.; Qin, L.; Long, A.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Exogenous IL-33 Restores Dendritic Cell Activation and Maturation in Established Cancer. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 1365–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briukhovetska, D.; Dörr, J.; Endres, S.; Libby, P.; Dinarello, C.A.; Kobold, S. Interleukins in cancer: From biology to therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2021, 21, 481–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatzioannou, A.; Banos, A.; Sakelaropoulos, T.; Fedonidis, C.; Vidali, M.S.; Köhne, M.; Händler, K.; Boon, L.; Henriques, A.; Koliaraki, V.; et al. An intrinsic role of IL-33 in T. Nat. Immunol. 2020, 21, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeoh, W.J.; Vu, V.P.; Krebs, P. IL-33 biology in cancer: An update and future perspectives. Cytokine 2022, 157, 155961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, F.; Fritz, J.H.; Piccirillo, C.A. Pleiotropic Effects of IL-33 on CD4+ T Cell Differentiation and Effector Functions. Rontiers Immunol. 2019, 10, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Yan, F.; Liu, O. Interleukin (IL)-33: An orchestrator of immunity from host defence to tissue homeostasis. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2020, 9, e1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreone, S.; Spadaro, F.; Buccione, C.; Mancini, J.; Tinari, A.; Sestili, P.; Gambardella, A.R.; Lucarini, V.; Ziccheddu, G.; Parolini, I.; et al. IL-33 Promotes CD11b/CD18-Mediated Adhesion of Eosinophils to Cancer Cells and Synapse-Polarized Degranulation Leading to Tumor Cell Killing. Cancers 2019, 11, 1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marichal, T.; Tsai, M.; Galli, S.J. Mast cells: Potential positive and negative roles in tumor biology. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2013, 1, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribatti, D. Mast Cells and Resistance to Immunotherapy in Cancer. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2023, 71, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Tian, W.; Teng, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Z.; Tang, S.; Chen, W.; Xie, R.; Lü, M.; et al. Tumor-infiltrating mast cells stimulate ICOS. J. Adv. Res. 2024, 57, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreone, S.; Gambardella, A.R.; Mancini, J.; Loffredo, S.; Marcella, S.; La Sorsa, V.; Varricchi, G.; Schiavoni, G.; Mattei, F. Anti-Tumorigenic Activities of IL-33: A Mechanistic Insight. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 571593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, E.; Petit-Bertron, A.F.; Bricard, R.; Levasseur, M.; Ramadan, A.; Girard, J.P.; Herbelin, A.; Dy, M. IL-33 activates unprimed murine basophils directly in vitro and induces their in vivo expansion indirectly by promoting hematopoietic growth factor production. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 3591–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecaric-Petkovic, T.; Didichenko, S.A.; Kaempfer, S.; Spiegl, N.; Dahinden, C.A. Human basophils and eosinophils are the direct target leukocytes of the novel IL-1 family member IL-33. Blood 2009, 113, 1526–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivellese, F.; Suurmond, J.; de Paulis, A.; Marone, G.; Huizinga, T.W.; Toes, R.E. IgE and IL-33-mediated triggering of human basophils inhibits TLR4-induced monocyte activation. Eur. J. Immunol. 2014, 44, 3045–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afferni, C.; Buccione, C.; Andreone, S.; Galdiero, M.R.; Varricchi, G.; Marone, G.; Mattei, F.; Schiavoni, G. The Pleiotropic Immunomodulatory Functions of IL-33 and Its Implications in Tumor Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prete, A.D.; Salvi, V.; Soriani, A.; Laffranchi, M.; Sozio, F.; Bosisio, D.; Sozzani, S. Dendritic cell subsets in cancer immunity and tumor antigen sensing. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2023, 20, 432–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Li, D.; Ma, J.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, L.; Tian, R.; Liu, Y.; Sun, L.; Su, J. The IL-33/ST2 axis affects tumor growth by regulating mitophagy in macrophages and reprogramming their polarization. Cancer Biol. Med. 2021, 18, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, A.; Yi, H.; Gu, R.; Yi, Q.; et al. Interleukin-33 Contributes to the Induction of Th9 Cells and Antitumor Efficacy by Dectin-1-Activated Dendritic Cells. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, W.; Zeng, P.; Xu, J.; Diao, H. The Contradictory Role of Interleukin-33 in Immune Cells and Tumor Immunity. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 7527–7537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, L.; Si, F.; Huang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Hoft, D.F.; Peng, G. NK and NKT cells have distinct properties and functions in cancer. Oncogene 2021, 40, 4521–4537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.R.; Sosman, J.A.; Zhang, B. The Janus Face of IL-33 Signaling in Tumor Development and Immune Escape. Cancers 2021, 13, 3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komai-Koma, M.; Wang, E.; Kurowska-Stolarska, M.; Li, D.; McSharry, C.; Xu, D. Interleukin-33 promoting Th1 lymphocyte differentiation dependents on IL-12. Immunobiology 2016, 221, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Tian, J.; Wang, S. Insight Into Non-Pathogenic Th17 Cells in Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.; Man, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Peng, H. Factors impacting the benefits and pathogenicity of Th17 cells in the tumor microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1224269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual-Reguant, A.; Bayat Sarmadi, J.; Baumann, C.; Noster, R.; Cirera-Salinas, D.; Curato, C.; Pelczar, P.; Huber, S.; Zielinski, C.E.; Löhning, M.; et al. TH17 cells express ST2 and are controlled by the alarmin IL-33 in the small intestine. Mucosal Immunol. 2017, 10, 1431–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Bossila, E.A.; Ma, X.; Zhao, C.; Zhao, Y. Dual Immune Regulatory Roles of Interleukin-33 in Pathological Conditions. Cells 2022, 11, 3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, S.; Jin, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, L.; Qi, G.; Yang, J. The role of IL-33/ST2 signaling in the tumor microenvironment and Treg immunotherapy. Exp. Biol. Med. 2022, 247, 1810–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.C.; Kobayashi, T.; Iijima, K.; Hsu, F.C.; Kita, H. IL-33 dysregulates regulatory T cells and impairs established immunologic tolerance in the lungs. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 140, 1351–1363.e1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shani, O.; Vorobyov, T.; Monteran, L.; Lavie, D.; Cohen, N.; Raz, Y.; Tsarfaty, G.; Avivi, C.; Barshack, I.; Erez, N. Fibroblast-Derived IL33 Facilitates Breast Cancer Metastasis by Modifying the Immune Microenvironment and Driving Type 2 Immunity. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 5317–5329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteran, L.; Erez, N. The Dark Side of Fibroblasts: Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts as Mediators of Immunosuppression in the Tumor Microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.F.; Nieh, S.; Jao, S.W.; Wu, M.Z.; Liu, C.L.; Chang, Y.C.; Lin, Y.S. The paracrine effect of cancer-associated fibroblast-induced interleukin-33 regulates the invasiveness of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J. Pathol. 2013, 231, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Sun, W.; Chen, L.; Wen, W.P. The Role of Interleukin-33 in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Is Determined by Its Cellular Sources in the Tumor Microenvironment. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 588454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, P.; Yang, Y.; Hosaka, K.; Zhang, Y.; Fischer, C.; Braun, H.; Liu, S.; Yu, G.; Beyaert, R.; Chang, M.; et al. Molecular mechanisms of IL-33-mediated stromal interactions in cancer metastasis. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e122375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Chen, L.; Souto, F.O.; Canasto-Chibuque, C.; Bongers, G.; Deshpande, M.; Harpaz, N.; Ko, H.M.; Kelley, K.; Furtado, G.C.; et al. Epithelial-derived IL-33 promotes intestinal tumorigenesis in Apc. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Sun, R.; Xu, J.; Zhai, W.; Zhang, D.; Yang, M.; Yue, C.; Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Turnquist, H.; et al. Tumor-Derived IL33 Promotes Tissue-Resident CD8. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2020, 8, 1381–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Feng, Y.; Yue, C.; Xu, B.; Chen, L.; Jiang, J.; Lu, B.; Zhu, Y. Lower expression level of IL-33 is associated with poor prognosis of pulmonary adenocarcinoma. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Shen, J.X.; Hu, J.L.; Huang, W.H.; Zhang, G.J. Significance of interleukin-33 and its related cytokines in patients with breast cancers. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Kim, G.; Lim, S.C.; Choi, H.S. IL-33-Induced Transcriptional Activation of LPIN1 Accelerates Breast Tumorigenesis. Cancers 2021, 13, 2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, R.; Sutterwala, F.S.; Zhang, W. Obesity and cancer: Inflammation bridges the two. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2016, 29, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kowitt, C.; Zhang, Q. Interleukin-33 and Obesity-Related Inflammation and Cancer. Encyclopedia 2024, 4, 1770-1789. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia4040117
Kowitt C, Zhang Q. Interleukin-33 and Obesity-Related Inflammation and Cancer. Encyclopedia. 2024; 4(4):1770-1789. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia4040117
Chicago/Turabian StyleKowitt, Cameron, and Qiuyang Zhang. 2024. "Interleukin-33 and Obesity-Related Inflammation and Cancer" Encyclopedia 4, no. 4: 1770-1789. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia4040117
APA StyleKowitt, C., & Zhang, Q. (2024). Interleukin-33 and Obesity-Related Inflammation and Cancer. Encyclopedia, 4(4), 1770-1789. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia4040117





