Nuclear Magnetic Resonance and Artificial Intelligence
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Databases and Data Standards
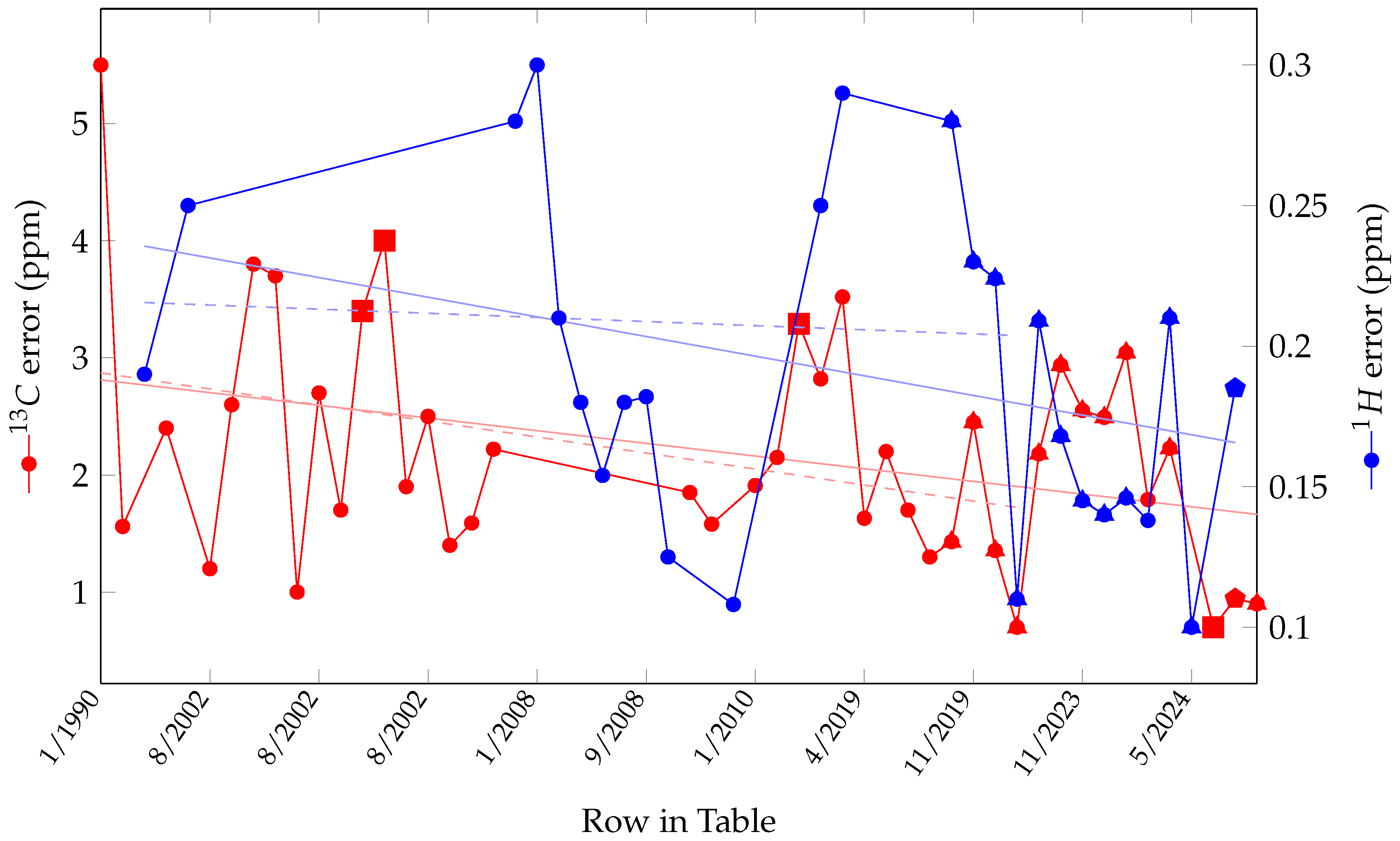
3. Chemical Shift Prediction
| Date | 1H MAE (ppm) | 13C MAE (ppm) | Method | Training | Test Dataset | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9/2023 | 0.209 | 2.18 | FullSSPrUCe (GNN) | nmrshiftdb2 | nmrshiftdb2 | [28] |
| 11/2023 | 0.168 | 2.938 | ComENet | GlycoNMR 80% | GlycoNMR 10% | [29] |
| 11/2023 | 0.145 | 2.550 | DimeNet++ | GlycoNMR 80% | GlycoNMR 10% | [29] |
| 11/2023 | 0.140 | 2.492 | SchNet | GlycoNMR 80% | GlycoNMR 10% | [29] |
| 11/2023 | 0.146 | 3.044 | SphereNet | GlycoNMR 80% | GlycoNMR 10% | [29] |
| 12/2023 | 0.138 | 1.79 | fragment-based | COLMAR | 768 COLMAR Metabolites | [23] |
| 3/2024 | 0.210 | 2.228 | GNN | nmrshiftdb2 subset | HMDB and CH-NMR-NP | [30] |
| 5/2024 | 0.10 | - | GNN | PROSPRE 3755 compounds | PROSPRE 272 compounds | [22] |
| 5/2024 | - | 0.7 | DFT | - | 132 shifts | [31] |
| 6/2024 | 0.185 | 0.944 | DFT+3D GNN | nmrshiftdb2 80% | nmrshiftdb2 20% | [32] |
| 6/2024 | - | 0.9 *** | GNN | 2026 organic molecules | 171 benzenic structures | [33] |
4. Spectral Simulations
5. Spectral Processing and Peak Picking
6. (Pure Compound) Structure Elucidation
7. Mixtures and Metabolomics
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial intelligence |
| CNN | Convolutional neural network |
| DL | Deep learning |
| ML | Machine learning |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| MRS | In vivo magnetic resonance spectroscopy |
| NMR | Nuclear magnetic resonance |
| RNN | Recurrent neural network |
References
- Borges, R.M.; Ferreira, G.A.; Campos, M.M.; Teixeira, A.M.; Costa, F.D.N.; das Chagas, F.O.; Colonna, M. NMR as a tool for compound identification in mixtures. Phytochem. Anal. 2023, 34, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wishart, D.S.; Cheng, L.L.; Copie, V.; Edison, A.S.; Eghbalnia, H.R.; Hoch, J.C.; Gouveia, G.J.; Pathmasiri, W.; Powers, R.; Schock, T.B.; et al. NMR and Metabolomics-A Roadmap for the Future. Metabolites 2022, 12, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Journal of Magnetic Resonance. Special Issue: Artificial Intelligence in NMR, EPR, and MRI; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/special-issue/106L0B084H8 (accessed on 17 October 2024).
- Magnetic Resonance in Chemistry. Special Issue: Applications of Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence in NMR; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022; Volume 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.Y.; Wu, H.P.; Ma, H.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.T.; Pan, Z.Y.; Xie, Y.; Wang, L.; Ren, B.; et al. Deep Learning-Assisted Spectrum–Structure Correlation: State-of-the-Art and Perspectives. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 7959–7975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, V.K.; Heller, G.T.; Hansen, D.F. Biomolecular NMR spectroscopy in the era of artificial intelligence. Structure 2023, 31, 1360–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamanos, T.K.; Matthews, S. Biomolecular NMR in the AI-assisted structural biology era: Old tricks and new opportunities. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Proteins Proteom. 2024, 1872, 140949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés, I.; Cuadrado, C.; Hernández Daranas, A.; Sarotti, A.M. Machine learning in computational NMR-aided structural elucidation. Front. Nat. Prod. 2023, 2, 1122426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, S.; Borges, R.M.; Venturini, F.; Sansotera, M. Dataset Size and Machine Learning-Open NMR Databases as a Case Study. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 46th Annual Computers, Software, and Applications Conference (COMPSAC), Online, 27 June–1 July 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- For chemists, the AI revolution has yet to happen. Nature 2023, 617, 438. [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, M.D.; Dumontier, M.; Aalbersberg, I.J.; Appleton, G.; Axton, M.; Baak, A.; Blomberg, N.; Boiten, J.W.; da Silva Santos, L.B.; Bourne, P.E.; et al. The FAIR Guiding Principles for scientific data management and stewardship. Sci Data 2016, 3, 160018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, S.; Kolshorn, H.; Steinbeck, C.; Schlörer, N. Twenty years of nmrshiftdb2: A case study of an open database for analytical chemistry. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2024, 62, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guitton, Y.; Tremblay-Franco, M.; Le Corguillé, G.; Martin, J.F.; Pétéra, M.; Roger-Mele, P.; Delabrière, A.; Goulitquer, S.; Monsoor, M.; Duperier, C.; et al. Create, run, share, publish, and reference your LC–MS, FIA–MS, GC–MS, and NMR data analysis workflows with the Workflow4Metabolomics 3.0 Galaxy online infrastructure for metabolomics. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2017, 93, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NP-MRD: The Natural Products Magnetic Resonance Database. Available online: https://pubpeer.com/publications/C08A991740F8D3D70C95F7CDE904C8 (accessed on 10 August 2024).
- Kuhn, S.; Wieske, L.H.E.; Trevorrow, P.; Schober, D.; Schlörer, N.E.; Nuzillard, J.M.; Kessler, P.; Junker, J.; Herráez, A.; Farès, C.; et al. NMReDATA: Tools and applications. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2021, 59, 792–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, A.N.; Lampen, P. JCAMP-DX for NMR. Appl. Spectrosc. 1993, 47, 1093–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, S.; Helmus, T.; Lancashire, R.J.; Murray-Rust, P.; Rzepa, H.S.; Steinbeck, C.; Willighagen, E.L. Chemical Markup, XML, and the World Wide Web. 7. CMLSpect, an XML Vocabulary for Spectral Data. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2007, 47, 2015–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schober, D.; Jacob, D.; Wilson, M.; Cruz, J.A.; Marcu, A.; Grant, J.R.; Moing, A.; Deborde, C.; de Figueiredo, L.F.; Haug, K.; et al. nmrML: A Community Supported Open Data Standard for the Description, Storage, and Exchange of NMR Data. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayya, N. A New NMR MI Standard–Feedback Welcome. Available online: https://www.nfdi4chem.de/a-new-nmr-mi-standard-from-nfdi4chem/ (accessed on 10 August 2024).
- Wenk, M.; Nuzillard, J.M.; Steinbeck, C. Sherlock—A Free and Open-Source System for the Computer-Assisted Structure Elucidation of Organic Compounds from NMR Data. Molecules 2023, 28, 1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonas, E.; Kuhn, S.; Schlörer, N. Prediction of chemical shift in NMR: A review. Magn. Reson. Chem. MRC 2022, 60, 1021–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajed, T.; Sayeeda, Z.; Lee, B.L.; Berjanskii, M.; Wang, F.; Gautam, V.; Wishart, D.S. Accurate Prediction of 1H NMR Chemical Shifts of Small Molecules Using Machine Learning. Metabolites 2024, 14, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigel, N.; Li, D.W.; Brüschweiler, R. COLMARppm: A Web Server Tool for the Accurate and Rapid Prediction of 1H and 13C NMR Chemical Shifts of Organic Molecules and Metabolites. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rull, H.; Fischer, M.; Kuhn, S. NMR shift prediction from small data quantities. J. Cheminform. 2023, 15, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerrard, W.; Bratholm, L.A.; Packer, M.J.; Mulholland, A.J.; Glowacki, D.R.; Butts, C.P. IMPRESSION—Prediction of NMR parameters for 3-dimensional chemical structures using machine learning with near quantum chemical accuracy. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanemura, K.A.; Das, S.; Merz, K.M., Jr. AutoGraph: Autonomous Graph-Based Clustering of Small-Molecule Conformations. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2021, 61, 1647–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Edison, A.S.; Merz, K.M.J. Metabolite Structure Assignment Using In Silico NMR Techniques. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 10412–10419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, J.; Jonas, E. Rapid prediction of full spin systems using uncertainty-aware machine learning. Chem. Sci. 2023, 14, 10902–10913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Badman, R.P.; Foley, L.; Woods, R.; Hong, P. GlycoNMR: Dataset and benchmarks for NMR chemical shift prediction of carbohydrates with graph neural networks. arXiv 2023, arXiv:cs.LG/2311.17134. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Xu, H.; Hong, P. AI-enabled prediction of NMR spectroscopy: Deducing 2-D NMR of carbohydrate. arXiv 2024, arXiv:cs.LG/2403.11353. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos, S.A.; Mueller, L.J.; Beran, G.J.O. The interplay of density functional selection and crystal structure for accurate NMR chemical shift predictions. Faraday Discuss. 2024. advance article. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Zhang, D.; Xia, S.; Zhang, Y. Accurate Prediction of NMR Chemical Shifts: Integrating DFT Calculations with Three-Dimensional Graph Neural Networks. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2024, 20, 5250–5258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duprat, F.; Ploix, J.L.; Dreyfus, G. Can Graph Machines Accurately Estimate 13C NMR Chemical Shifts of Benzenic Compounds? Prepr. Mol. 2024, 29, 3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogben, H.; Krzystyniak, M.; Charnock, G.; Hore, P.; Kuprov, I. Spinach—A software library for simulation of spin dynamics in large spin systems. J. Magn. Reson. 2011, 208, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worswick, S.G.; Spencer, J.A.; Jeschke, G.; Kuprov, I. Deep neural network processing of DEER data. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaat5218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protein NMR Assignment with AI. Available online: https://spindynamics.org/wiki/index.php?title=Protein_NMR_Assignment_with_AI (accessed on 3 July 2024).
- Kuhn, S.; Cobas, C.; Barba, A.; Colreavy-Donnelly, S.; Caraffini, F.; Borges, R.M. Direct deduction of chemical class from NMR spectra. J. Magn. Reson. 2023, 348, 107381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.W.; Hansen, A.L.; Yuan, C.; Bruschweiler-Li, L.; Bruschweiler, R. DEEP picker is a deep neural network for accurate deconvolution of complex two-dimensional NMR spectra. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, N.; Bruderer, S.; Paruzzo, F.; Fischetti, G.; Toscano, G.; Graf, D.; Fey, M.; Henrici, A.; Ziebart, V.; Heitmann, B.; et al. Deconvolution of 1D NMR spectra: A deep learning-based approach. J. Magn. Reson. 2023, 347, 107357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Meyer, T.; Sinnaeve, D.; Van Gasse, B.; Tsiporkova, E.; Rietzschel, E.R.; De Buyzere, M.L.; Gillebert, T.C.; Bekaert, S.; Martins, J.C.; Van Criekinge, W. NMR-Based Characterization of Metabolic Alterations in Hypertension Using an Adaptive, Intelligent Binning Algorithm. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 3783–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, P.E.; Reo, N.V.; DelRaso, N.J.; Doom, T.E.; Raymer, M.L. Gaussian binning: A new kernel-based method for processing NMR spectroscopic data for metabolomics. Metabolomics 2008, 4, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleif, F.M.; Riemer, T.; Börner, U.; Schnapka-Hille, L.; Cross, M. Genetic algorithm for shift-uncertainty correction in 1-D NMR-based metabolite identifications and quantifications. Bioinformatics 2010, 27, 524–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Burns, D.C.; Mazzola, E.P.; Reynolds, W.F. The role of computer-assisted structure elucidation (CASE) programs in the structure elucidation of complex natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2019, 36, 919–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milanowski, D.J.; Oku, N.; Cartner, L.K.; Bokesch, H.R.; Williamson, R.T.; Saurí, J.; Liu, Y.; Blinov, K.A.; Ding, Y.; Li, X.C.; et al. Unequivocal determination of caulamidines A and B: Application and validation of new tools in the structure elucidation tool box. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbeck, C. SENECA: A Platform-Independent, Distributed, and Parallel System for Computer-Assisted Structure Elucidation in Organic Chemistry. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2001, 41, 1500–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meiler, J.; Will, M. Genius: A Genetic Algorithm for Automated Structure Elucidation from 13C NMR Spectra. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 1868–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrelly, C.; Kell, D.B.; Knowles, J. Molecular Structure Elucidation Using Ant Colony Optimization: A Preliminary Study. In International Conference on Ant Colony Optimization and Swarm Intelligence; Dorigo, M., Birattari, M., Blum, C., Clerc, M., Stützle, T., Winfield, A.F.T., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 120–131. [Google Scholar]
- Pritišanac, I.; Degiacomi, M.T.; Alderson, T.R.; Carneiro, M.G.; AB, E.; Siegal, G.; Baldwin, A.J. Automatic Assignment of Methyl-NMR Spectra of Supramolecular Machines Using Graph Theory. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 9523–9533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.W.; Zhang, C.; Reher, R.; Wang, M.; Alexander, K.L.; Nothias, L.F.; Han, Y.K.; Shin, H.; Lee, K.Y.; Lee, K.H.; et al. DeepSAT: Learning Molecular Structures from Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Data. J. Cheminform. 2023, 15, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, M.; Zhao, W.Y.; Zhang, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Huang, X.X.; Song, S.J. The identification of alkaloids from the stems of Picrasma quassioides via computer-assisted structure elucidation and quantum chemical calculations. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 23, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutateladze, A.G.; Kuznetsov, D.M.; Beloglazkina, A.A.; Holt, T. Addressing the Challenges of Structure Elucidation in Natural Products Possessing the Oxirane Moiety. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 83, 8341–8352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elyashberg, M.; Argyropoulos, D. Computer Assisted Structure Elucidation (CASE): Current and future perspectives. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2021, 59, 669–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Saurí, J.; Mevers, E.; Peczuh, M.W.; Hiemstra, H.; Clardy, J.; Martin, G.E.; Williamson, R.T. Unequivocal determination of complex molecular structures using anisotropic NMR measurements. Science 2017, 356, eaam5349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howarth, A.; Ermanis, K.; Goodman, J.M. DP4-AI automated NMR data analysis: Straight from spectrometer to structure. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 4351–4359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberts, M.; Zipoli, F.; Vaucher, A.C. Learning the Language of NMR: Structure Elucidation from NMR spectra using Transformer Models. ChemRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Chen, M.S.; Rotskoff, G.M.; Kanan, M.W.; Markland, T.E. Accurate and efficient structure elucidation from routine one-dimensional NMR spectra using multitask machine learning. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.08284. [Google Scholar]
- Borges, R.M.; Colby, S.M.; Das, S.; Edison, A.S.; Fiehn, O.; Kind, T.; Lee, J.; Merrill, A.T.; Merz, K.M.J.; Metz, T.O.; et al. Quantum Chemistry Calculations for Metabolomics. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 5633–5670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruguière, A.; Derbré, S.; Dietsch, J.; Leguy, J.; Rahier, V.; Pottier, Q.; Bréard, D.; Suor-Cherer, S.; Viault, G.; Le Ray, A.M.; et al. MixONat, a Software for the Dereplication of Mixtures Based on 13C NMR Spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 8793–8801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bingol, K.; Li, D.W.; Zhang, B.; Brüschweiler, R. Comprehensive Metabolite Identification Strategy Using Multiple Two-Dimensional NMR Spectra of a Complex Mixture Implemented in the COLMARm Web Server. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 12411–12418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Tayyari, F.; Edison, A.S.; Su, Z.; Gu, L. NMR-based metabolomics reveals urinary metabolome modifications in female Sprague–Dawley rats by cranberry procyanidins. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2016, 34, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borchert, A.J.; Gouveia, G.J.; Edison, A.S.; Downs, D.M.; Pupo, M.T. Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Metabolomics Corroborates Serine Hydroxymethyltransferase as the Primary Target of 2-Aminoacrylate in a ridA Mutant of Salmonella enterica. mSystems 2020, 5, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maughon, T.S.; Shen, X.; Huang, D.; Michael, A.O.A.; Shockey, W.A.; Andrews, S.H.; McRae, J.M.; Platt, M.O.; Fernández, F.M.; Edison, A.S.; et al. Metabolomics and cytokine profiling of mesenchymal stromal cells identify markers predictive of T-cell suppression. Cytotherapy 2022, 24, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeRatt, B.N.; Ralat, M.A.; Lysne, V.; Tayyari, F.; Dhar, I.; Edison, A.S.; Garrett, T.J.; Øivind, M.; Ueland, P.M.; Nygård, O.K.; et al. Metabolomic Evaluation of the Consequences of Plasma Cystathionine Elevation in Adults with Stable Angina Pectoris. J. Nutr. 2017, 147, 1658–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakiri, A.; Hubert, J.; Reynaud, R.; Lambert, C.; Martinez, A.; Renault, J.H.; Nuzillard, J.M. Reconstruction of HMBC Correlation Networks: A Novel NMR-Based Contribution to Metabolite Mixture Analysis. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2018, 58, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, S.; Colreavy-Donnelly, S.; Santana de Souza, J.; Borges, R.M. An integrated approach for mixture analysis using MS and NMR techniques. Faraday Discuss. 2019, 218, 339–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubert, J.; Nuzillard, J.M.; Purson, S.; Hamzaoui, M.; Borie, N.; Reynaud, R.; Renault, J.H. Identification of Natural Metabolites in Mixture: A Pattern Recognition Strategy Based on 13C NMR. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 2955–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, S.; Colreavy-Donnelly, S.; de Andrade Silva Quaresma, L.E.; de Andrade Silva Quaresma, E.; Borges, R.M. Applying NMR compound identification using NMRfilter to match predicted to experimental data. Metabolomics 2020, 16, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza Wuillda, A.C.J.; das Neves Costa, F.; Garrett, R.; dos Santos de Carvalho, M.; Borges, R.M. High-speed countercurrent chromatography with offline detection by electrospray mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance detection as a tool to resolve complex mixtures: A practical approach using leaf extract. Phytochem. Anal. 2024, 35, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watermann, S.; Bode, M.C.; Hackl, T. Identification of metabolites from complex mixtures by 3D correlation of 1H NMR, MS and LC data using the SCORE-metabolite-ID approach. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 15834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, R.M.; das Neves Costa, F.; Chagas, F.O.; Teixeira, A.M.; Yoon, J.; Weiss, M.B.; Crnkovic, C.M.; Pilon, A.C.; Garrido, B.C.; Betancur, L.A.; et al. Data Fusion-based Discovery (DAFdiscovery) pipeline to aid compound annotation and bioactive compound discovery across diverse spectral data. Phytochem. Anal. 2023, 34, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, S.; Tumer, E.; Colreavy-Donnelly, S.; Moreira Borges, R. A pilot study for fragment identification using 2D NMR and deep learning. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2022, 60, 1052–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.W.; Zhang, C.; Cottrell, G.W.; Gerwick, W.H. SMART-Miner: A convolutional neural network-based metabolite identification from 1H-13C HSQC spectra. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2022, 60, 1070–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Cong, Y.; Deng, W. Identifying molecular functional groups of organic compounds by deep learning of NMR data. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2022, 60, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, J.; Shu, J.; Li, M.; Mudappathi, R.; Jin, Y.; Lewis, F.; Boon, A.; Qin, X.; Liu, L.; Gu, H. Artificial intelligence in metabolomics: A current review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2024, 178, 117852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debik, J.; Sangermani, M.; Wang, F.; Madssen, T.S.; Giskeødegård, G.F. Multivariate analysis of NMR-based metabolomic data. NMR Biomed. 2022, 35, e4638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buergel, T.; Steinfeldt, J.; Ruyoga, G.; Pietzner, M.; Bizzarri, D.; Vojinovic, D.; Upmeier zu Belzen, J.; Loock, L.; Kittner, P.; Christmann, L.; et al. Metabolomic profiles predict individual multidisease outcomes. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 2309–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bifarin, O.O.; Gaul, D.A.; Sah, S.; Arnold, R.S.; Ogan, K.; Master, V.A.; Roberts, D.L.; Bergquist, S.H.; Petros, J.A.; Fernández, F.M.; et al. Machine Learning-Enabled Renal Cell Carcinoma Status Prediction Using Multiplatform Urine-Based Metabolomics. J. Proteome Res. 2021, 20, 3629–3641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundekilde, U.K.; Eggers, N.; Bertram, H.C. NMR-Based Metabolomics of Food. In NMR-Based Metabolomics: Methods and Protocols; Gowda, G.A.N., Raftery, D., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, P.; Viereck, N.; Bro, R.; Engelsen, S.B. Chemometric Analysis of NMR Spectra. In Modern Magnetic Resonance; Webb, G.A., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Xu, Y.; Jin, G.; Zong, J.; Peng, C.; Cai, H.; Hou, R. Machine learning applications for identify the geographical origin, variety and processing of black tea using 1H NMR chemical fingerprinting. Food Control 2023, 148, 109686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, M.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Ryu, J.E.; Ko, J.; Zaidi, S.F.A.; Seo, J.A.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, D.Y.; Choi, H.K. Differentiation of Geographical Origin of White and Brown Rice Samples Using NMR Spectroscopy Coupled with Machine Learning Techniques. Metabolites 2022, 12, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, S.; Reitel, K.; Homapour, E.; Kork, K.; Vaino, V.; Arula, T.; Bernotas, P.; Reile, I. Discriminating the origin of fish from closely related water bodies by combining NMR spectroscopy with statistical analysis and machine learning. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 83, 102753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khakimov, B.; Mobaraki, N.; Trimigno, A.; Aru, V.; Engelsen, S.B. Signature Mapping (SigMa): An efficient approach for processing complex human urine 1H NMR metabolomics data. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1108, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiopoulou, P.D.; Chasapi, S.A.; Christopoulou, I.; Varvarigou, A.; Spyroulias, G.A. Untargeted 1H-NMR Urine Metabolomic Analysis of Preterm Infants with Neonatal Sepsis. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, L.; Godejohann, M.; Martin, F.P.J.; Collino, S.; Bürkle, A.; Moreno-Villanueva, M.; Bernhardt, J.; Toussaint, O.; Grubeck-Loebenstein, B.; Gonos, E.S.; et al. High-Resolution Quantitative Metabolome Analysis of Urine by Automated Flow Injection NMR. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 5801–5809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, J.; Aaryani, T.S. Explainable AI to Facilitate Understanding of Neural Network-Based Metabolite Profiling Using NMR Spectroscopy. Metabolites 2024, 14, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otvos, J.D.; Jeyarajah, E.J.; Bennett, D.W. Quantification of plasma lipoproteins by proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Clin. Chem. 1991, 37, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daiana, I.; Dídac, L.; Cèlia, R.B.; Natalia, A.; Núria, P.; Roberto, S.; Ana, G.L.; Núria, A.; Josefa, G.; Lluí, M. The Lipoprotein Profile Evaluated by 1H-NMR Improves the Performance of Genetic Testing in Familial Hypercholesterolemia. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 109, e2090–e2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markley, J.L.; Brüschweiler, R.; Edison, A.S.; Eghbalnia, H.R.; Powers, R.; Raftery, D.; Wishart, D.S. The future of NMR-based metabolomics. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2017, 43, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ma, L.H.; Maletic-Savatic, M.; Liu, Z. NMRQNet: A deep learning approach for automatic identification and quantification of metabolites using Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) in human plasma samples. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Embade, N.; Cannet, C.; Diercks, T.; Gil-Redondo, R.; Bruzzone, C.; Ansó, S.; Echevarría, L.R.; Ayucar, M.M.M.; Collazos, L.; Lodoso, B.; et al. NMR-based newborn urine screening for optimized detection of inherited errors of metabolism. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuhn, S.; de Jesus, R.P.; Borges, R.M. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance and Artificial Intelligence. Encyclopedia 2024, 4, 1568-1580. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia4040102
Kuhn S, de Jesus RP, Borges RM. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance and Artificial Intelligence. Encyclopedia. 2024; 4(4):1568-1580. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia4040102
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuhn, Stefan, Rômulo Pereira de Jesus, and Ricardo Moreira Borges. 2024. "Nuclear Magnetic Resonance and Artificial Intelligence" Encyclopedia 4, no. 4: 1568-1580. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia4040102
APA StyleKuhn, S., de Jesus, R. P., & Borges, R. M. (2024). Nuclear Magnetic Resonance and Artificial Intelligence. Encyclopedia, 4(4), 1568-1580. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia4040102









