Phosphatidyl Inositol 4-Kinases
Definition
1. Introduction
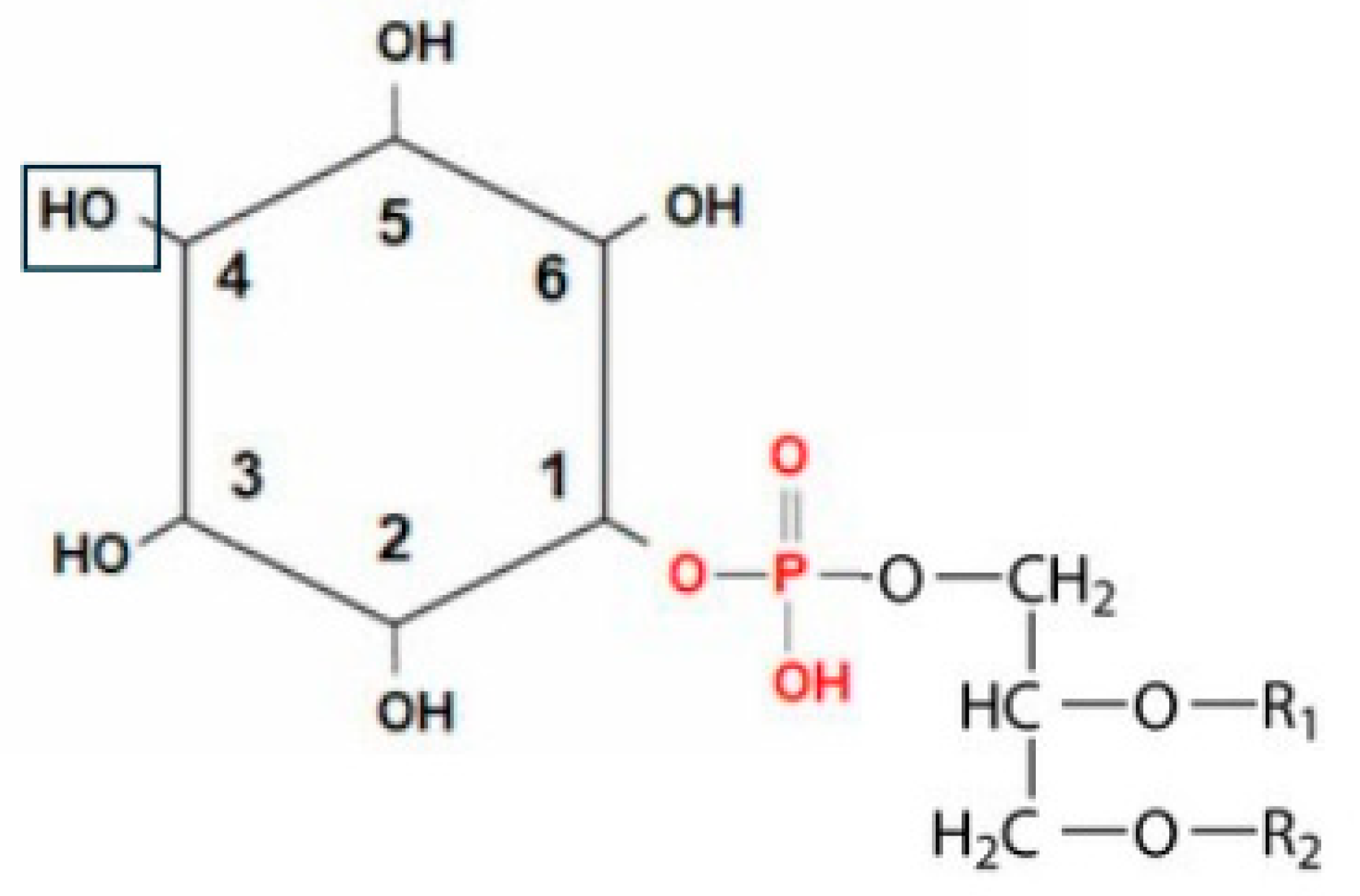
2. Phosphatidylinositol
3. Phosphatidyl Inositol 4-Kinases (PtdIns 4-Kinase)
4. Type-II PtdIns 4-Kinases
5. Type-III PtdIns 4-Kinases
6. Structure and Domains of PtdIns 4-Kinases
7. Localization of Different PtdIns 4-Kinases
7.1. Localization of Type-II Phosphatidylinositol 4-Kinase
7.2. Localization of Type-III Phosphatidylinositol 4-Kinase
8. Phosphoinositide 4-Phosphatases
9. Regulation of Phosphatidylinositol 4-Kinases
9.1. Effect of Polycations
9.2. Effect of Phosphorylation
9.3. Regulation by Small Molecules
9.4. Divalent Cations and Detergents
10. PtdIns 4-Kinase Involved in Cell Signaling
11. Proteins Interacting with Phosphoinositides
11.1. Gelsolin
11.2. CapZ
11.3. α-Actinin
11.4. Profilin
11.5. Vinculin
12. Protein Interactors of Phosphatidylinositol 4-Kinases
13. Functions of Phosphatidylinositol 4-Kinases
14. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sasaki, T.; Takasuga, S.; Sasaki, J.; Kofuji, S.; Eguchi, S.; Yamazaki, M.; Suzuki, A. Mammalian phosphoinositide kinases and phosphatases. Prog. Lipid Res. 2009, 48, 307–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tom, D.B.; Katan, M. Phosphoinositide signaling in cancer: Beyond PI3K and PTEN. Nat. Rev. 2010, 10, 342–352. [Google Scholar]
- De Matteis, M.A.; Godi, A. PI-loting membrane traffic. Nat. Cell Biol. 2004, 6, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopher, L.C.; Lewis, C.C. Phosphoinositide kinases. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1996, 8, 153–158. [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa, T.; Goto, K.; Konda, H. Cloning, expression and localization of 230 kDa phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 12088–12094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, T.; Goto, K.; Konda, H. Cloning and characterization of a 92kDa soluble phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase. Biochem. J. 1996, 320, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracia-Bustos, J.F.; Marini, F.; Stevenson, I.; Feri, C.; Hall, M.N. PIK1, an essential phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase associated with the yeast nucleus. EMBO J. 1994, 13, 2352–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, S.; Ohya, Y.; Giebl, M.; Nakano, A.; Anraku, Y.J. A novel gene STT4 encodes a phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase in the PKC1 protein kinase pathway of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 1166–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balla, T.; Downing, G.J.; Jaffe, H.; Kim, S.; Zolyomi, A. Isolation and molecular cloning of wortmannin-sensitive bovine type III phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 18358–18366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehrmann, T.; Vereb, G.; Schimdt, M.; Klix, D.; Meyer, H.E.; Varsanyi, M.; Heilmeyer, L.M.G., Jr. Identification of 200 kDa polypeptide as type 3 phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase from bovine brain by partial protein and cDNA sequencing. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1996, 1311, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endemann, G.C.; Graziani, A.; Cantley, L.C. A monoclonal antibody distinguishes two types of phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase. Biochem.J. 1991, 273 Pt 1, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barylko, B.; Gerber, S.H.; Binns, D.D.; Grichine, N.; Khvotchev, M.; Sudhof, T.C.; Albanesi, J.P. A novel family of phosphatidylinositol 4-kinases conserved from yeast to humans. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 7705–7708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minogue, S.; Anderson, J.S.; Waugh, M.G.; dos Santos, M.; Corless, S.; Cramer, R.; Hsuan, J.J. Cloning of a human type II phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase reveals a novel lipid kinase family. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 16635–16640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balla, A.; Tuymetova, G.; Barshishat, M.; Geiszt, M.; Balla, T. Characterization of type II phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase isoforms reveals association of the enzyme with endosomal vesicular compartment. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 20041–20050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flanagan, C.A.; Thorner, J. Purification and characterization of a soluble phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 24117–24125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, S.; Catt, J.K.; Balla, T. A wortmannin—sensitive phosphatidylinositol 4—kinase that regulates hormone sensitive pools of inositolphospholipids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 5317–5321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zólyomi, A.; Zhao, X.; Downing, G.J.; Balla, T. Localization of two distinct type III phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase enzyme mRNAs in the rat. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2000, 278, C914–C920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Wenk, M.R.; Pellegrini, L.; Onofri, F.; Benfenati, F.; De Camilli, P. Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase type IIalpha is responsible for the phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase activity associated with synaptic vesicles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 3995–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivetac, I.; Munday, A.D.; Kisseleva, M.V.; Zhang, X.M.; Luff, S.; Tiganis, T.; Whisstock, J.C.; Rowe, T.; Majerus, P.W.; Mitchell, C.A. The type I alpha inositol polyphosphate 4-phosphatase generates and terminates phosphoinositide 3-kinase signals on endosomes and the plasma membrane. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2005, 16, 2218–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boura, E.; Nencka, R. Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinases: Function, structure, and inhibition. Exp. Cell Res. 2015, 337, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumlova, A.; Chalupska, D.; Róźycki, B.; Jovic, M.; Wisniewski, E.; Klima, M.; Dubankova, A.; Kloer, D.P.; Nencka, R.; Balla, T.; et al. The crystal structure of the phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase IIα. EMBO Rep. 2014, 15, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klima, M.; Baumlova, A.; Chalupska, D.; Hřebabecký, H.; Dejmek, M.; Nencka, R.; Boura, E. The high-resolution crystal structure of phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase IIβ and the crystal structure of phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase IIα containing a nucleoside analogue provide a structural basis for isoform-specific inhibitor design. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2015, 71, 1555–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misehe, M.; Klima, M.; Matoušová, M.; Chalupská, D.; Dejmek, M.; Šála, M.; Mertlíková-Kaiserová, H.; Boura, E.; Nencka, R. Structure-based design and modular synthesis of novel PI4K class II inhibitors bearing a 4-aminoquinazoline scaffold. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2022, 76, 129010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fienberg, S.; Eyermann, C.J.; Arendse, L.B.; Basarab, G.S.; McPhail, J.A.; Burke, J.E.; Chibale, K. Structural Basis for Inhibitor Potency and Selectivity of Plasmodium falciparum Phosphatidylinositol 4-Kinase Inhibitors. ACS Infect. Dis. 2020, 6, 3048–3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Wang, J.; Sun, H.Q.; Martinez, M.; Sun, Y.X.; Macia, E.; Kirchhausen, T.; Albanesi, J.P.; Roth, M.G.; Yin, H.L. Phosphatidylinositol 4 phosphate regulates targeting of clathrin adaptorAP-1 complexes to the Golgi. Cell 2003, 114, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waugh, M.G.; Minogue, S.; Anderson, J.S.; Balinger, A.; Blumenkrantz, D.; Calnan, D.P.; Cramer, R.; Hsuan, J.J. Localization of a highly active pool of type II phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase in a p97/valosin-containing-protein-rich fraction of the endoplasmicreticulum. Biochem. J. 2003, 373, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakuk, A.; Friedländer, E.; Vereb, G., Jr.; Kása, A.; Balla, A.; Balla, T.; Heilmeyer, L.M., Jr.; Gergely, P.; Vereb, G. Nucleolar localization of phosphatidyl inositol 4-kinasePI4K230 in various mammalian cells. Cytometry A 2006, 69, 1174–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balla, A.; Vereb, G.; Gülkan, H.; Gehrmann, T.; Gergely, P.; Heilmeyer, L.M., Jr.; Antal, M. Immunohistochemical localization of two phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase Isoforms, PI4K230 and PI4K92, in the central nervous system of rats. Exp. Brain. Res. 2000, 134, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szivak, I.; Lamb, N.; Heilmeyer, L.M. Subcellular localization and structural function of endogenous phosphorylated phos-phatidylinositol 4-kinase (PI4K92). J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 16740–16749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, A.; Reghellin, V.; Donnici, L.; Fenu, S.; Alvarez, R.; Baruffa, C.; Peri, F.; Pagani, M.; Abrignani, S.; Neddermann, P.; et al. Metabolism of phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase IIIα-dependent PI4P Is subverted by HCV and is targeted by a 4-anilino quinazoline with antiviral activity. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.; Yamori, T. Advances in development of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitors. Curr. Med. Chem. 2009, 16, 2839–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thor, G.; Gulkan, H.; Suer, S.; Herberg, F.W.; Balla, A.; Vereb, G.; Mayer, G.W.; Heilmeyer, L.M.G., Jr. Functional expression and characterisation of new human phosphatidylinositol 4- kinase PI4K230. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1437, 341–356. [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco, D.; Jacob, G.; Allende, C.C.; Allende, J.E. Polylysine and polyamine stimulation of the phosphatidylinositol kinases of amphibian oocytes membranes. Biochem. Int. 1988, 17, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vogel, S.; Hoppe, J. Polyamines stimulate the phosphorylation of phosphatidylinositol in membranes from A431 cells. Europ. J. Biochem. 1986, 154, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.D.; Synderman, R. Modulation of inositol phospholipid metabolism by polyamines. Biochem. J. 1988, 256, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundberg, G.A.; Sundler, R.; Jergil, B. Activation of phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate kinase in rat liver plasma membranes by polyamines. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1987, 922, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, T.N.; Eng, S.P.; Jaseph, L.A.; Beaven, M.A.; Lo, C.S. Cardiotoxin from cobra venom increases the level of phosphatidylinositol 4-monophosphate and phosphatidylinositol kinase activity in two cell lines. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1988, 970, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, D.H.; Pike, L.J. Stimulation of purified phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase by cobra venom cardiotoxin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1990, 1055, 295–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eng, S.P.; Lo, C.S. Mastoparan increases membrane bound phosphatidylinositol kinase and phosphatidylinositol 4-monophosphate kinase activities in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. Life Sci. 1990, 46, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, D.C.; Brown, A.B.; Jeng, Y.; Tatoyan, A.; Chan, T.M. Activation of a membrane associated phosphatidylinositol kinase through tyrosine-protein phosphorylation by naphthoquinones and orthovandate. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1990, 283, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, G.K.; Dodson, J.M.; Montogomery, P.A.; Johnson, R.M.; Sarup, J.C.; Wong, W.L.; Ullrich, A.; Sheperd, H.M.; Benz, C.C. p185HER2 signal transduction in breast cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 14300–14305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, D.H.; Pike, L.J. Phosphatidylinositol kinase is activated in membranes derived from cells treated with epidermal growth factor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 7513–7517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Einicker-Lamas, M.; Wenceslau, L.D.; Bernardo, R.; Nogaroli, L.; Guilheme, A.; Oliveria, M.M.; Vieyra, A. Sphingosine 1-phosphate formation activates phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase in blasolateral membranes from kidney cells: Crosstalk in cell signalling through sphingolipids and phospholipids. J. Biochem. 2003, 134, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, G.H.; Subrahmanyam, G.; Anderson, R.A. Purification and reconstitution of phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase from human erythrocytes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1991, 1080, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naito, T.; Nakagawa, S.; Okita, T.A.; Yamashita, H.; Yamashita, T.; Kamei, H.; Tomatsu, K.; Imanishi, H.; Kawaguchi, H. Synthesis and bronchodilating activity of 2, 9 disubstituted adenine derivatives BB-1502 (9-cyclohexyl-2-n-propoxy-9H- adenine) and its analogs. Chem. Parm. Bull. 1982, 30, 2011–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishioka, H.; Imoto, M.; Sawa, T.; Hamada, M.; Naganawa, H.; Takeuchi, T.; Umezawa, K. Screening of phosphatidylinositol kinase inhibitors from Streptomyces. J. Antibiot. 1989, 42, 823–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Porter, F.D.; Li, Y.-S.; Deuel, T.F. Purification and characterization of a phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase from bovine uteri. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 8989–8995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashizume, T.; Nakao, M.; Sato, T. Sphingosine enhances phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase activity in rabbit platelets. J. Biochem. 1996, 120, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholz, G.; Baritt, G.J.; Kwok, F. Purification and chemical modification of a phosphatidylinositol kinase from sheep brain. Eur. J. Biochem. 1991, 201, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzker, R.; Klinger, R.; Hsuan, J.; Fry, M.J.; Kauffnmann-Zeh, A.; Muller, E.; Frunder, H.; Waterfield, M. Purification and characterization of phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase from human erythrocyte membranes. Eur. J. Bioch. 1991, 200, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katso, R.; Okkenhaug, K.; Ahmadi, K.; White, S.; Timms, J.; Waterfield, M.D. Cellular function of phosphoinositide 3-kinases; implications for development, homeostasis and cancer. Annu. Rev. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2001, 17, 615–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelman, J.A.; Luo, J.; Cantley, L.C. The evolution of phosphoinositide 3-kinases as regulators of growth and metabolism. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2006, 6, 606–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datta, S.R.; Brunet, A.; Greenberg, M.E. Cellular survival: A play in three Akts. Genes. Dev. 1999, 13, 2905–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brazil, D.P.; Yang, Z.; Hemmings, B.A. Advances in protein kinase B signalling: AKT action on multiple fronts. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2004, 29, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brugge, J.; Hung, M.C.; Mills, G.B. A new mutational AKT activation in the PI3K pathway. Cancer Cell 2007, 12, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardone, M.H.; Roy, N.; Stennicke, H.R.; Salvesen, G.S.; Franke, T.F.; Stanbridge, E.; Frisch, S.; Reed, J.C. Regulation of cell death protease caspase-9 by phosphorylation. Science 1988, 282, 1318–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, M.; He, D.; Guan, W.; Yao, H. Research progress on phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase inhibitors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2024, 220, 115993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aberle, H.; Bauer, A.; Stappert, J.; Kispert, A.; Kemler, R. β-catenin is a target for the ubiquitin proteasome pathway. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 3797–3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nteliopoulos, G.; Marley, S.B.; Gordon, M.Y. Influence of PI-3K/Akt pathway on Wnt signalling in regulating myeloid progenitor cell proliferation. Evidence for a role of autocrine/paracrine Wnt regulation. Br. J. Haematol. Res. Pap.
- Xu, L.; Corcoran, R.B.; Welsh, J.W.; Pennica, D.; Levine, A.J. WISP-1 is a Wnt-1- and beta-catenin-responsive oncogene. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, T.C.; Sparks, A.B.; Rago, C.; Hermeking, H.; Zawel, L.; da Costa, L.T.; Morin, P.J.; Vogelstein, B.; Kinzler, K.W. Identification of c-MYC as a target of the APC pathway. Science 1998, 281, 1509–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roose, J.; Clevers, H. TCF transcription factors: Molecular switches in carcinogenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1424, M23–M37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, B.; Gelos, M.; Siedow, A.; Hansk, I.M.; Gratchev, A.; Ilyas, M.; Bodmer, W.; Moyer, M.; Riecken, E.; Buhr, H. Target genes of betacatenin-T cell-factor/lymphoid-enhancer-factor signaling in human colorectal carcinomas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 1603–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, M.; Concordet, J.; Lassot, I.; Albert, I.; del los Santos, R.; Durand, H.; Perret, C.; Rubinfeld, B.; Margottin, F.; Benarous, R.; et al. The F-box protein beta-TrCP associates with phosphorylated beta-catenin and regulates its activity in the cell. Curr. Biol. 1999, 9, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, T.F.; El-Deiry, W.S. The p53 pathway and apoptosis. J. Cell. Physiol. 1999, 181, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- el-Deiry, W.S. Regulation of p53 downstream genes. Semin. Cancer Biol. 1998, 8, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berridge, M.J.; Irvine, R.F. Inositol phosphates and cell signalling. Nature 1989, 21, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brian, C.; Vogel, V.G.; Singletary, S.E.; Ward, N.E. Elevated protein kinase C expression in human breast tumor biopsies relative to normal breast tissue. Cancer Res. 1989, 49, 3215–3217. [Google Scholar]
- Kopp, R.; Noelke, B.; Sauter, G.; Schildberg, F.W.; Paumgartner, G.; Pfeiffer, A. Altered protein kinase C activity in biopsies of human colonic adenomas and carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1991, 51, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stossel, T.P. On the crawling of animal cells. Science 1993, 260, 1086–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schafer, D.A.; Jennings, P.B.; Cooper, J.A. Dynamics of capping protein and actin assembly in vitro: Uncapping barbed ends by polyphosphoinositides. J. Cell Biol. 1996, 135, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carol, O.A.; Carpen, O. A actinin revisited: A fresh look at an old player. Cell Motil. Cytoskelet. 2004, 58, 104–111. [Google Scholar]
- Yarmola, G.E.; Bubb, M.R. How depolymerization can promote polymerization: The case of actin and profilin. Bioassays 2009, 31, 1150–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilmore, A.P.; Burridge, K. Regulation of vinculin binding to talin and actin by phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. Nature 1996, 381, 531–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Paolo, G.; De Camilli, P. Phosphoinositides in cell regulation and membrane dynamics. Nature 2006, 443, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hausser, A.; Link, G.; Hoene, M.; Russo, C.; Selchow, O.; Pfizenmaier, K. Phospho-specific binding of 14-3-3 proteins to phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase III beta protects from dephosphorylation and stabilizes lipid kinase activity. J. Cell Sci. 2006, 119 Pt 17, 3613–3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalupska, D.; Eisenreichova, A.; Różycki, B.; Rezabkova, L.; Humpolickova, J.; Klima, M.; Boura, E. Structural analysis of phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase IIIβ (PI4KB)—14-3-3 protein complex reveals internal flexibility and explains 14-3-3 mediated protection from degradation in vitro. J. Struct. Biol. 2017, 200, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demmel, L.; Beck, M.; Klose, C.; Schlaitz, A.L.; Gloor, Y.; Hsu, P.P.; Havlis, J.; Shevchenko, A.; Krause, E.; Kalaidzidis, Y.; et al. Nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of the Golgi phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase Pik1 is regulated by 14-3-3 proteins and coordinates Golgi function with cell growth. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2008, 19, 1046–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R. Differential abundance and transcription of 14-3-3 proteins during vegetative growth and sexual reproduction in budding yeast. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R. An account of fungal 14-3-3 proteins. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2017, 96, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- STT4/YLR305C Interactions, 2024. Available online: https://www.yeastgenome.org/locus/S000004296/interaction (accessed on 28 May 2024).
- PIK1/YNL267W Interactions, 2024. Available online: https://www.yeastgenome.org/locus/S000005211/interaction (accessed on 28 May 2024).
- Anne, S.; Wurmser, A.E.; Emr, S.D.; Stenmark, H. The role of phosphoinositides in membrane transport. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2001, 13, 485–492. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.; Blake, T.; Chitnis, A.; Liu, P.; Balla, T. Crucial role of phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase III α in development of zebrafish pectoral fin is linked to phosphoinositide 3-kinase FGF signaling. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 4303–4310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balla, A.; Kim, Y.J.; Varni, P.; Szentpetery, Z.; Knight, Z.; Shokat, K.M.; Balla, T. Maintenance of hormone—Sensitive phosphoinositide pools in the plasma membrane require phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase III alpha. Mol. Biol. Cell 2008, 19, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, K.L.; Cooper, J.D.; Heaton, N.S.; Yoon, R.; Oakland, T.E.; Jordan, T.X.; Mateu, G.; Grakoui, A.; Randall, G. Roles for endocytic trafficking and phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase III alpha in hepatitis C virus replication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 75577–75582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simons, J.P.; Al-Shwai, R.; Miongue, S.; Waugh, M.; Wiedmenn, C.; Evangelou, S.; Loesch, A.; Sihra, T.S.; King, R.; Warner, T.T.; et al. Loss of phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase 2 alpha activity cause late onset degeneration of spinal cord axons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 11535–11539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Kan, G.H.; Qin, Z.; Chen, C. PI4KIIα is a novel regulator of tumor growth by its action on angiogenesis and HIF-1α regulation. Oncogene 2010, 29, 2550–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, W.; Choi, S.C.; Wang, H.; Qin, Y.; Volpicelli-Daley, L.; Swan, L.; Lucast, L.; Khoo, C.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.; et al. Wnt 3a mediated formation of phosphatidylinositol 4, 5-bisphosphate regulates LRP6 phosphorylation. Science 2008, 321, 1350–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Li, L.; Pan, W.; Wu, D. Regulation of phosphatidylinositol kinases and metabolism by Wnt3a and Dvl2. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 22544–222548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Huang, G.; Kandror, K.V. Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase type II alpha is targeted specifically to cellugyrin-positive glucose transporter 4 vesicles. Mol. Endocrinol. 2006, 20, 2890–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minogue, S.; Waugh, M.G.; De Matteis, M.A.; Stephens, D.J.; Berditchevski, F.; Hsuan, J.J. Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase is required for endosomal trafficking and degradation of the EGF receptor. J. Cell Sci. 2006, 119, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craige, B.; Salazar, G.; Faundez, V. Phosphatidylinositol-4-kinase type II alpha contains an AP-3-sorting motif and a kinase domain that are both required for endosome traffic. Mol. Biol. Cell 2008, 19, 1415–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liscovitch, M. Phospholipase D: Role in signal transduction and membrane traffic. J. Lipid Mediat. Signal. 1996, 14, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F.S.; Han, G.S.; Carman, G.S.; Blumer, K.J. A WASp binding type II phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase required for actin polymerization driven endosome motility. J. Cell. Biol. 2005, 171, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, R.; Ratheesh, A.; Gude, R.K.; Roa, K.V.; Panda, D.; Subrahmanyam, G. Resveratol inhibits type II phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase: A key component in pathways of phosphoinositide turnover. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2005, 70, 1048–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizarro-Cerda, J.; Payrastre, B.; Wang, Y.J.; Veiga, E.; Yin, H.L.; Cossart, P. Type II phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase promotes Listeria monocytogenes entry into target cells. Cell Microbiol. 2007, 9, 2381–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, J.; Liu, J.; Shen, X. Inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase results in a significant reduced respiratory brust in formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine-stimulated human Neutrophils. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 49093–49099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naveen, B.; Shanker, B.S.; Subrahmanyam, G. Fcepsilon RI crossliking activates a type II phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase in RBL2H3cells. Mol. Immunol. 2005, 42, 1541–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, Y.; Furuno, T.; Nakanishi, M. The role of phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase II alpha in degranulation of RBL2H3 cells. Inflamm. Res. 2006, 55, 465–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiedemann, C.; Schafer, T.; Burger, M.M. Chromaffin granule-associated phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase activity is required for stimulated secretion. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 2094–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibon, J.; Buckley, S.M.; Unsain, N.; Kaartinen, V.; Séguéla, P.; Barker, P.A. proBDNF and p75NTR Control Excitability and Persistent Firing of Cortical Pyramidal Neurons. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 9741–9753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhter, S.; Uddin, M.N.; Jeong, I.S.; Kim, D.W.; Liu, X.M.; Bahk, J.D. Role of Arabidopsis AtPI4Kγ3, a type II phosphoinositide 4-kinase, in abiotic stress responses and floral transition. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2015, 14, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okazaki, K.; Miyagishima, S.Y.; Wada, H. Phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate negatively regulates chloroplast division in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2015, 27, 663–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antignani, V.; Klocko, A.L.; Bak, G.; Chandrasekaran, S.D.; Dunivin, T.; Nielsen, E. Recruitment of PLANT U-BOX13 and the PI4Kβ1/β2 phosphatidylinositol-4 kinases by the small GTPase RabA4B plays important roles during salicylic acid-mediated plant defense signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2015, 27, 243–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Yang, Z.; Liu, X.; Mao, K.; Nair, U.; Klionsky, D.J. Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinases are required for autophagic membrane trafficking. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 37964–37972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhry, S.; Joshi, V.; Bojjireddy, N.; Thoh, M.; Sandur, S.K.; Subrahmanyam, G. Silencing of type II phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase β stabilizes prostate apoptosis response-4 and induces apoptosis in cancer cells. Biochem. J. 2019, 476, 405–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Kong, F.; Yu, W.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, J.; Meng, X. Locational and functional characterization of PI4KB in the mouse embryo. J. Cell Physiol. 2024, 239, e31195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koester, A.M.; Geiser, A.; Laidlaw, K.M.E.; Morris, S.; Cutiongco, M.F.A.; Stirrat, L.; Gadegaard, N.; Boles, E.; Black, H.L.; Bryant, N.J.; et al. EFR3 and phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase IIIα regulate insulin-stimulated glucose transport and GLUT4 dispersal in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Biosci. Rep. 2022, 42, BSR20221181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delang, L.; Harak, C.; Benkheil, M.; Khan, H.; Leyssen, P.; Andrews, M.; Lohmann, V.; Neyts, J. PI4KIII inhibitor enviroxime impedes the replication of the hepatitis C virus by inhibiting PI3 kinases. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 3375–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Highland, C.M.; Fromme, J.C. Arf1 directly recruits the Pik1-Frq1 PI4K complex to regulate the final stages of Golgi maturation. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2021, 32, 1064–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, L.; Mei, X.; Wang, C.; Guo, Z.; Li, L.; Li, B.; Liang, Y.; Zou, S.; Dong, H. The type II phosphoinositide 4-kinase FgLsb6 is important for the development and virulence of Fusarium graminearum. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2020, 144, 103443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansi Kushwaha, N.K.; Singh, A.K.; Karim, M.J.; Chakraborty, S. Nicotiana benthamiana phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase type II regulates chilli leaf curl virus pathogenesis. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2019, 20, 1408–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Krishnamoorthy, P.; Schubert, V.; Hause, G.; Heilmann, M.; Heilmann, I. A dual role for cell plate-associated PI4Kβ in endocytosis and phragmoplast dynamics during plant somatic cytokinesis. EMBO J. 2019, 38, e100303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| S. No. | Species | Function/Role in different cellular process | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| 01 | Mus musculus | Persistent Firing of Cortical Pyramidal Neurons | [102] |
| 02 | Arabidopsis thaliana | Resistant against abiotic stress and delay of floral transition | [103] |
| 03 | Arabidopsis thaliana | Regulation of chloroplast division | [104] |
| 04 | Arabidopsis thaliana | Plant defense mechanism | [105] |
| 05 | S. cerevisiae | Autophagy | [106] |
| 06 | MCF-7 cell line | Apoptosis | [107] |
| 07 | Mus musculus | Embryo development | [108] |
| 08 | 3T3-L1 adipocytes | Glucose transporters mobilization | [109] |
| 09 | HPV-C | Viral replication | [110] |
| 10 | Pichia pastoris | Golgi maturation/formation | [111] |
| 12 | Fusarium graminearum | Fungal infection/pathogenesis in plants | [112] |
| 13 | Nicotiana benthamiana | Viral infection in plants | [113] |
| 14 | Arabidopsis thaliana | Cytokinesis | [114] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kumar, R.; Kumar, P. Phosphatidyl Inositol 4-Kinases. Encyclopedia 2024, 4, 1062-1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia4030068
Kumar R, Kumar P. Phosphatidyl Inositol 4-Kinases. Encyclopedia. 2024; 4(3):1062-1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia4030068
Chicago/Turabian StyleKumar, Ravinder, and Piyush Kumar. 2024. "Phosphatidyl Inositol 4-Kinases" Encyclopedia 4, no. 3: 1062-1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia4030068
APA StyleKumar, R., & Kumar, P. (2024). Phosphatidyl Inositol 4-Kinases. Encyclopedia, 4(3), 1062-1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia4030068






