Solid Lipid Nanoparticles
Definition
:1. Introduction
2. Features of SLNs
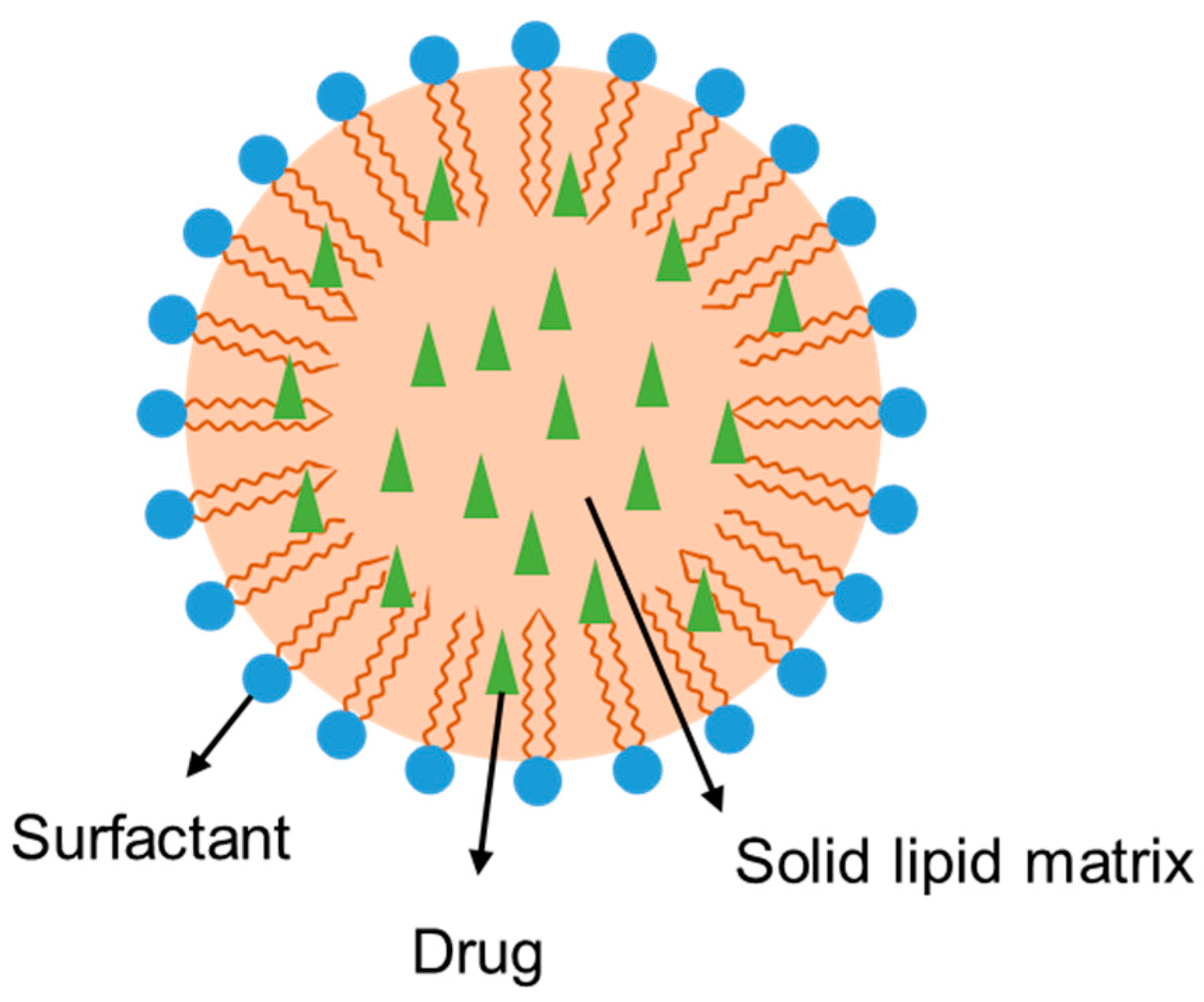
2.1. Structural Features and General Components of SLNs
| Ingredient | Examples | References |
|---|---|---|
| Solid lipid | Glyceryl palmitostearate (Precirol®® ATO 5) | [37,38,39] |
| Glyceryl behenate (Compritol®® 888 ATO) | [37,40] | |
| Stearic acid | [41] | |
| Palmitic acid | [42] | |
| Tristearin | [39,43,44] | |
| Tripalmitin (Dynasan®® 116) | [45] | |
| Trimyristin (Dynasan®® 114) | [20] | |
| Cetyl palmitate | [46] | |
| Cholesterol | [47] | |
| Triolein | [44] | |
| Tricaprylin | [44] | |
| Liquid lipid | MCT (Miglyol®® 812) | [37,48] |
| Propylene glycol dicaprylocaprate (Labrafac®®) | [40] | |
| Caprylocaproyl Polyoxyl-8 glycerides (Labrasol®®) | [38] | |
| Propylene glycol monocaprylate (Capryol™ 90) | [39] | |
| Isopropyl myristate | [39] | |
| Oleic acid | [42,43,44] | |
| Squalene | [49,50] | |
| α-tocopherol | [51] | |
| Emulsifier | Poloxamer 188 | [37,40,47,50] |
| Poloxamer 407 | [39] | |
| Soybean lecithin, phosphatidylcholine | [20,43] | |
| Polysorbate 80 | [20,42,43] | |
| Polysorbate 60 | [44] | |
| PEG-40 castor oil (Cremophor®® RH40) | [38] | |
| Sodium deoxycholate | [51] | |
| Sodium dodecyl sulfate | [41] |
2.2. Physicochemical Characterization
2.2.1. Particle Size and Polydispersity Index
2.2.2. Zeta Potential
2.2.3. Entrapment Efficiency
2.2.4. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) and X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.2.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM), and Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
2.3. Drug Incorporation Models and Drug Release
2.4. Stability and Safety
3. Methods for SLNs Preparation
3.1. Solvent-Based Methods
3.1.1. Solvent Emulsification-Evaporation Method
3.1.2. Solvent Emulsification-Diffusion Method
3.1.3. Solvent Injection Method
3.2. Non-Solvent Methods
3.2.1. High-Pressure Homogenization Method
3.2.2. High-Speed Stirring and Ultra-Sonication Methods
3.2.3. Microemulsion Method
3.2.4. Phase Inversion Temperature (PIT) Method
3.2.5. Membrane Contactor Method
3.2.6. Coacervation Method
3.3. Other Methods
3.3.1. Double Emulsion Method
3.3.2. Supercritical-Fluid-Based Methods
4. Recent Applications of SLNs in Drug Delivery
4.1. Oral Delivery
4.2. Parenteral Delivery
4.3. Transdermal Delivery
4.4. Intranasal Delivery
4.5. Ocular Delivery
4.6. Pulmonary Delivery
4.7. Clinical Application State
5. Conclusions and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, C.; Gao, H.; Ouyang, L. Advance cardiac nanomedicine by targeting the pathophysiological characteristics of heart failure. J. Control. Release 2021, 337, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastegari, E.; Hsiao, Y.-J.; Lai, W.-Y.; Lai, Y.-H.; Yang, T.-C.; Chen, S.-J.; Huang, P.-I.; Chiou, S.-H.; Mou, C.-Y.; Chien, Y. An update on mesoporous silica nanoparticle applications in nanomedicine. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Alem, C.M.A.; Metselaar, J.M.; van Kooten, C.; Rotmans, J.I. Recent advances in liposomal-based anti-inflammatory therapy. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Wilson, R.; Hui, Y.; Yu, L.; Wibowo, D.; Zhang, C.; Whittaker, A.K.; Middelberg AP, J.; et al. Bioinspired core–shell nanoparticles for hydrophobic drug delivery. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 14357–14364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, M.J.; Billingsley, M.M.; Haley, R.M.; Wechsler, M.E.; Peppas, N.A.; Langer, R. Engineering precision nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 101–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, J.K.; Das, G.; Fraceto, L.F.; Campos, E.V.R.; del Pilar Rodriguez-Torres, M.; Acosta-Torres, L.S.; Diaz-Torres, L.A.; Grillo, R.; Swamy, M.K.; Sharma, S.; et al. Nano based drug delivery systems: Recent developments and future prospects. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, Q.-V.; Choi, J.; Oh, Y.-K. Nano delivery systems and cancer immunotherapy. J. Pharm. Investig. 2018, 48, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, T.; Liu, J.; Zhao, H. Multifunctional gold nanoparticles: A novel nanomaterial for various medical applications and biological activities. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Yang, T.; Liu, S.; Du, L.; Chen, Q.; Li, X.; Dong, J.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, S.; Gong, Y.; et al. Insights into the Synthesis, types and application of iron Nanoparticles: The overlooked significance of environmental effects. Environ. Int. 2022, 158, 106980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, L.S.; Pessan, J.P.; Vieira, A.P.M.; Lima, T.M.T.D.; Monteiro, D.R. Iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications: A perspective on synthesis, drugs, antimicrobial activity, and toxicity. Antibiotics 2018, 7, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosn, Y.; Kamareddine, M.H.; Tawk, A.; Elia, C.; El Mahmoud, A.; Terro, K.; El Harake, N.; El-Baba, B.; Makdessi, J.; Farhat, S. Inorganic nanoparticles as drug delivery systems and their potential role in the treatment of chronic myelogenous leukaemia. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 18, 1533033819853241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldorera-Moore, M.; Vela Ramirez, J.E.; Peppas, N.A. Transport and delivery of interferon-α through epithelial tight junctions via pH-responsive poly(methacrylic acid-grafted-ethylene glycol) nanoparticles. J. Drug Target. 2019, 27, 582–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valcourt, D.M.; Dang, M.N.; Scully, M.A.; Day, E.S. Nanoparticle-mediated co-delivery of Notch-1 antibodies and ABT-737 as a potent treatment strategy for triple-negative breast cancer. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 3378–3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, Q.-V.; Suh, J.; Choi, J.J.; Park, G.T.; Lee, J.W.; Shim, G.; Oh, Y.-K. In situ nanoadjuvant-assembled tumor vaccine for preventing long-term recurrence. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 7442–7462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.V.; Campbell, K.; Painter, G.F.; Young, S.L.; Walker, G.F. Nanoparticle system based on amino-dextran as a drug delivery vehicle: Immune-stimulatory cpg-oligonucleotide loading and delivery. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorente, C.; Cabeza, L.; Clares, B.; Ortiz, R.; Halbaut, L.; Delgado, Á.V.; Perazzoli, G.; Prados, J.; Arias, J.L.; Melguizo, C. Formulation and in vitro evaluation of magnetoliposomes as a potential nanotool in colorectal cancer therapy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 171, 553–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hammadi, M.M.; Delgado, Á.V.; Melguizo, C.; Prados, J.C.; Arias, J.L. Folic acid-decorated and PEGylated PLGA nanoparticles for improving the antitumour activity of 5-fluorouracil. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 516, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehnert, W.; Mäder, K. Solid lipid nanoparticles: Production, characterization and applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. 2001, 47, 165–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardeike, J.; Hommoss, A.; Müller, R.H. Lipid nanoparticles (SLN, NLC) in cosmetic and pharmaceutical dermal products. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 366, 170–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskar, K.; Anbu, J.; Ravichandiran, V.; Venkateswarlu, V.; Rao, Y.M. Lipid nanoparticles for transdermal delivery of flurbiprofen: Formulation, in vitro, ex vivo and in vivo studies. Lipids Health Dis. 2009, 8, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qushawy, M.; Prabahar, K.; Abd-Alhaseeb, M.; Swidan, S.; Nasr, A. Preparation and evaluation of carbamazepine solid lipid nanoparticle for alleviating seizure activity in pentylenetetrazole-kindled mice. Molecules 2019, 24, 3971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, M.D.; Müller, R.H. Lipid nanoparticles for parenteral delivery of actives. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2009, 71, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, R.H.; Mäder, K.; Gohla, S. Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) for controlled drug delivery—A review of the state of the art. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2000, 50, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wissing, S.A.; Kayser, O.; Müller, R.H. Solid lipid nanoparticles for parenteral drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2004, 56, 1257–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, J.-S.; Cho, C.-W. Surface modification of solid lipid nanoparticles for oral delivery of curcumin: Improvement of bioavailability through enhanced cellular uptake, and lymphatic uptake. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 117, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, H.; Chokshi, N.; Rawal, S.; Patel, B.M.; Badanthadka, M.; Patel, M.M. Fabrication and in vivo evaluation of ligand appended paclitaxel and artemether loaded lipid nanoparticulate systems for the treatment of NSCLC: A nanoparticle assisted combination oncotherapy. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 583, 119386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhiman, N.; Awasthi, R.; Sharma, B.; Kharkwal, H.; Kulkarni, G.T. Lipid nanoparticles as carriers for bioactive delivery. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 580118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scioli Montoto, S.; Muraca, G.; Ruiz, M.E. Solid lipid nanoparticles for drug delivery: Pharmacological and biopharmaceutical aspects. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 587997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taratula, O.; Kuzmov, A.; Shah, M.; Garbuzenko, O.B.; Minko, T. Nanostructured lipid carriers as multifunctional nanomedicine platform for pulmonary co-delivery of anticancer drugs and siRNA. J. Control. Release 2013, 171, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, H.A.; Allam, A.; Elsabahy, M.; Fetih, G.; El-Badry, M. Nanostructured lipid carriers for improved oral delivery and prolonged antihyperlipidemic effect of simvastatin. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 162, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R.H.; Radtke, M.; Wissing, S.A. Nanostructured lipid matrices for improved microencapsulation of drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 242, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westesen, K.; Bunjes, H.; Koch, M.H.J. Physicochemical characterization of lipid nanoparticles and evaluation of their drug loading capacity and sustained release potential. J. Control. Release 1997, 48, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, J.; Zheng, F.; Yang, X.; Yu, A.; Zhai, G. Nanostructured lipid carriers for oral delivery of baicalin: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 466, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, J.; Nikolic, S.; Egea, M.A.; Souto, E.B.; Garcia, M.L. Nanostructured lipid carriers for triamcinolone acetonide delivery to the posterior segment of the eye. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 88, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.-W.; Sweeney, C.; Dudhipala, N.; Lakhani, P.; Chaurasiya, N.D.; Tekwani, B.L.; Majumdar, S. Primaquine loaded solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN), nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC), and nanoemulsion (NE): Effect of lipid matrix and surfactant on drug entrapment, in vitro release, and ex vivo hemolysis. AAPS PharmSciTech 2021, 22, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, J.-S.; Pham, C.V.; Myung, C.-S.; Cho, C.-W. Tadalafil-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers using permeation enhancers. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 495, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, R.M.; Abd-Elbary, A.; Kassem, M.A.; Ghorab, M.M.; Basha, M. Nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) versus solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) for topical delivery of meloxicam. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2014, 19, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, C.; Feng, N. Nanostructured lipid carriers for percutaneous administration of alkaloids isolated from Aconitum sinomontanum. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2015, 13, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Salam, F.S.; Mahmoud, A.A.; Ammar, H.O.; Elkheshen, S.A. Nanostructured lipid carriers as semisolid topical delivery formulations for diflucortolone valerate. J. Liposome Res. 2017, 27, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirri, M.; Bragagni, M.; Mennini, N.; Mura, P. Development of a new delivery system consisting in “drug—In cyclodextrin—In nanostructured lipid carriers” for ketoprofen topical delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 80, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.-Q.; Jiang, S.-P.; Du, Y.-Z.; Yuan, H.; Ye, Y.-Q.; Zeng, S. Preparation and characterization of stearic acid nanostructured lipid carriers by solvent diffusion method in an aqueous system. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2005, 45, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tetyczka, C.; Griesbacher, M.; Absenger-Novak, M.; Fröhlich, E.; Roblegg, E. Development of nanostructured lipid carriers for intraoral delivery of Domperidone. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 526, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uprit, S.; Kumar Sahu, R.; Roy, A.; Pare, A. Preparation and characterization of minoxidil loaded nanostructured lipid carrier gel for effective treatment of alopecia. Saudi Pharm. J. 2013, 21, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Corona, A.; Schubert, B.; Reeder, R.; Henson, M.A. The effect of oil type on the aggregation stability of nanostructured lipid carriers. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 418, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, E.B.; Wissing, S.A.; Barbosa, C.M.; Müller, R.H. Evaluation of the physical stability of SLN and NLC before and after incorporation into hydrogel formulations. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2004, 58, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teeranachaideekul, V.; Souto, E.B.; Junyaprasert, V.B.; Müller, R.H. Cetyl palmitate-based NLC for topical delivery of Coenzyme Q10—Development, physicochemical characterization and in vitro release studies. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2007, 67, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami, J.; Rezazadeh, M.; Varshosaz, J.; Tabbakhian, M.; Aslani, A. formulation of ldl targeted nanostructured lipid carriers loaded with paclitaxel: A detailed study of preparation, freeze drying condition, and in vitro cytotoxicity. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štecová, J.; Mehnert, W.; Blaschke, T.; Kleuser, B.; Sivaramakrishnan, R.; Zouboulis, C.C.; Seltmann, H.; Korting, H.C.; Kramer, K.D.; Schäfer-Korting, M. Cyproterone acetate loading to lipid nanoparticles for topical acne treatment: Particle characterisation and skin uptake. Pharm. Res. 2007, 24, 991–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.-Y.; Fang, C.-L.; Liu, C.-H.; Su, Y.-H. Lipid nanoparticles as vehicles for topical psoralen delivery: Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) versus nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC). Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 70, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-C.; Tsai, T.-H.; Huang, Z.-R.; Fang, J.-Y. Effects of lipophilic emulsifiers on the oral administration of lovastatin from nanostructured lipid carriers: Physicochemical characterization and pharmacokinetics. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2010, 74, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, E.B.; Mehnert, W.; Müller, R.H. Polymorphic behaviour of Compritol®888 ATO as bulk lipid and as SLN and NLC. J. Microencapsul. 2006, 23, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Chaudhury, A. Recent advances in lipid nanoparticle formulations with solid matrix for oral drug delivery. AAPS PharmSciTech 2011, 12, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R.H.; Runge, S.; Ravelli, V.; Mehnert, W.; Thünemann, A.F.; Souto, E.B. Oral bioavailability of cyclosporine: Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN®) versus drug nanocrystals. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 317, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, R.H.; Runge, S.A.; Ravelli, V.; Thünemann, A.F.; Mehnert, W.; Souto, E.B. Cyclosporine-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN®): Drug–lipid physicochemical interactions and characterization of drug incorporation. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 68, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, M.A.; Md, S.; Sahni, J.K.; Baboota, S.; Dang, S.; Ali, J. Nanostructured lipid carriers system: Recent advances in drug delivery. J. Drug Target. 2012, 20, 813–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anton, N.; Benoit, J.-P.; Saulnier, P. Design and production of nanoparticles formulated from nano-emulsion templates—A review. J. Control. Release 2008, 128, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Fan, Y.; Smith, E. Experimental design for the optimization of lipid nanoparticles. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 98, 1813–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjula, B.; Shah, F.M.; Javed, A.; Alka, A. Effect of poloxamer 188 on lymphatic uptake of carvedilol-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles for bioavailability enhancement. J. Drug Target. 2009, 17, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paliwal, R.; Rai, S.; Vaidya, B.; Khatri, K.; Goyal, A.K.; Mishra, N.; Mehta, A.; Vyas, S.P. Effect of lipid core material on characteristics of solid lipid nanoparticles designed for oral lymphatic delivery. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2009, 5, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Jiang, S.; Shen, H.; Qin, S.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, R.; Xu, Q. Diclofenac sodium-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles prepared by emulsion/solvent evaporation method. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2011, 13, 2375–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, W.; Gao, X.; Li, T. Solvent injection-lyophilization of tert-butyl alcohol/water cosolvent systems for the preparation of drug-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 79, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duong, V.-A.; Nguyen, T.-T.-L.; Maeng, H.-J. Preparation of solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers for drug delivery and the effects of preparation parameters of solvent injection method. Molecules 2020, 25, 4781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingling, G.; Yuan, Z.; Weigen, L. Preparation, optimization, characterization and in vivo pharmacokinetic study of asiatic acid tromethamine salt-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2016, 42, 1325–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanwar, R.; Gradzielski, M.; Mehta, S.K. Biomimetic Solid lipid nanoparticles of sophorolipids designed for antileprosy drugs. J. Phys. Chem. B 2018, 122, 6837–6845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansraj, G.P.; Singh, S.K.; Kumar, P. Sumatriptan succinate loaded chitosan solid lipid nanoparticles for enhanced anti-migraine potential. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 81, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafique, H.; Ahad, A.; Khan, W.; Want, M.Y.; Bhatt, P.C.; Ahmad, S.; Panda, B.P.; Mujeeb, M. Ganoderic acid -loaded solid lipid nanoparticles ameliorate d-galactosamine induced hepatotoxicity in Wistar rats. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 50, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, V.-A.; Nguyen, T.-T.-L.; Maeng, H.-J.; Chi, S.-C. Preparation of ondansetron hydrochloride-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers using solvent injection method for enhancement of pharmacokinetic properties. Pharm. Res. 2019, 36, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Ahmad, I.; Akhter, S.; Jain, G.K.; Iqbal, Z.; Talegaonkar, S.; Ahmad, F.J. Nanocarrier based formulation of Thymoquinone improves oral delivery: Stability assessment, in vitro and in vivo studies. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 102, 822–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estella-Hermoso de Mendoza, A.; Rayo, M.; Mollinedo, F.; Blanco-Prieto, M.J. Lipid nanoparticles for alkyl lysophospholipid edelfosine encapsulation: Development and in vitro characterization. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 68, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mühlen A z Mühlen E z Niehus, H.; Mehnert, W. Atomic force microscopy studies of solid lipid nanoparticles. Pharm. Res. 1996, 13, 1411–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubes, A.; Parrot-Lopez, H.; Abdelwahed, W.; Degobert, G.; Fessi, H.; Shahgaldian, P.; Coleman, A.W. Scanning electron microscopy and atomic force microscopy imaging of solid lipid nanoparticles derived from amphiphilic cyclodextrins. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2003, 55, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- zur Mühlen, A.; Schwarz, C.; Mehnert, W. Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) for controlled drug delivery—Drug release and release mechanism. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 1998, 45, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wissing, S.A.; Müller, R.H. Solid lipid nanoparticles as carrier for sunscreens: In vitro release and in vivo skin penetration. J. Control. Release 2002, 81, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Jain, S.; Khare, P.; Gulbake, A.; Bansal, D.; Jain, S.K. Design and development of solid lipid nanoparticles for topical delivery of an anti-fungal agent. Drug Deliv. 2010, 17, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castelli, F.; Puglia, C.; Sarpietro, M.G.; Rizza, L.; Bonina, F. Characterization of indomethacin-loaded lipid nanoparticles by differential scanning calorimetry. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 304, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R.H.; Radtke, M.; Wissing, S.A. Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) and nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) in cosmetic and dermatological preparations. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2002, 54, S131–S155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, C.; Müller, R.H. Effect of light and temperature on zeta potential and physical stability in solid lipid nanoparticle (SLN™) dispersions. Int. J. Pharm. 1998, 168, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakkar, V.; Singh, S.; Singla, D.; Kaur, I.P. Exploring solid lipid nanoparticles to enhance the oral bioavailability of curcumin. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2011, 55, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahgaldian, P.; Da Silva, E.; Coleman, A.W.; Rather, B.; Zaworotko, M.J. Para-acyl-calix-arene based solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs): A detailed study of preparation and stability parameters. Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 253, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degobert, G.; Aydin, D. Lyophilization of nanocapsules: Instability sources, formulation and process parameters. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satari, N.; Taymouri, S.; Varshosaz, J.; Rostami, M.; Mirian, M. Preparation and evaluation of inhalable dry powder containing glucosamine-conjugated gefitinib SLNs for lung cancer therapy. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2020, 46, 1265–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.-T.-L.; Duong, V.-A.; Maeng, H.-J.; Chi, S.-C. Development of an oil suspension containing granisetron hydrochloride as a sustained-release parenteral formulation for enhancement of pharmacokinetic properties. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 51, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.-T.-L.; Duong, V.-A.; Maeng, H.-J.; Chi, S.-C. Preparation of an oil suspension containing ondansetron hydrochloride as a sustained release parenteral formulation. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2019, 10, 282–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gualbert, J.; Shahgaldian, P.; Coleman, A.W. Interactions of amphiphilic calix[4]arene-based solid lipid nanoparticles with bovine serum albumin. Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 257, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Shi, S.; Zhang, Z.; Gong, T.; Sun, X. Coating solid lipid nanoparticles with hyaluronic acid enhances antitumor activity against melanoma stem-like cells. Theranostics 2015, 5, 755–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.H.; Choi, J.Y.; Ramasamy, T.; Truong, D.H.; Nguyen, C.N.; Choi, H.-G.; Yong, C.S.; Kim, J.O. Hyaluronic acid-coated solid lipid nanoparticles for targeted delivery of vorinostat to CD44 overexpressing cancer cells. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 114, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R.H.; Maaβen, S.; Weyhers, H.; Specht, F.; Lucks, J.S. Cytotoxicity of magnetite-loaded polylactide, polylactide/glycolide particles and solid lipid nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 1996, 138, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pooja, D.; Tunki, L.; Kulhari, H.; Reddy, B.B.; Sistla, R. Characterization, biorecognitive activity and stability of WGA grafted lipid nanostructures for the controlled delivery of Rifampicin. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2015, 193, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, K. Decapeptide modified doxorubicin loaded solid lipid nanoparticles as targeted drug delivery system against prostate cancer. Langmuir 2021, 37, 13194–13207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farsani, P.A.; Mahjub, R.; Mohammadi, M.; Oliaei, S.S.; Mahboobian, M.M. Development of perphenazine-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles: Statistical optimization and cytotoxicity studies. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 6619195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musika, J.; Chudapongse, N. Development of lipid-based nanocarriers for increasing gastrointestinal absorption of lupinifolin. Planta. Med. 2020, 86, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, D.; Sonar, P.K.; Parashar, P.; Chaudhary, S.K.; Upadhyay, S.; Saraf, S.K. Augmented brain delivery of cinnarizine through nanostructured lipid carriers loaded in situ gel: In vitro and pharmacokinetic evaluation. Bionanoscience 2021, 11, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, N.; Imran, M.; Kesharwani, P.; Khanna, K.; Karwasra, R.; Sharma, N.; Rawat, S.; Sharma, D.; Ahmad, F.J.; Jain, G.K.; et al. Intranasal delivery of Naloxone-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles as a promising simple and non-invasive approach for the management of opioid overdose. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 599, 120428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranizadeh, K.; Mahboobian, M.M.; Amiri, I.; Tavilani, H.; Shafiee, G. Effects of progesterone nanoparticles on the sperm capacitation and acrosome reaction in asthenozoospermia men. Andrologia 2022, 54, e14258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelhakeem, E.; El-Nabarawi, M.; Shamma, R. Lipid-based nano-formulation platform for eplerenone oral delivery as a potential treatment of chronic central serous chorioretinopathy: In-vitro optimization and ex-vivo assessment. Drug Deliv. 2021, 28, 642–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, P.; Mahjub, R.; Mohammadi, M.; Derakhshandeh, K.; Ghaleiha, A.; Mahboobian, M.M. Pharmacokinetics and brain distribution studies of perphenazine-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2021, 47, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotta, M.; Debernardi, F.; Caputo, O. Preparation of solid lipid nanoparticles by a solvent emulsification–diffusion technique. Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 257, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.Q.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, H.H.; Fang, M. Preparation of solid lipid nanoparticles with clobetasol propionate by a novel solvent diffusion method in aqueous system and physicochemical characterization. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 239, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-algaleel, S.A.; Metwally, A.A.; Abdel-Bar, H.M.; Kassem, D.H.; Hathout, R.M. Synchronizing in silico, in vitro, and in vivo studies for the successful nose to brain delivery of an anticancer molecule. Mol. Pharm. 2021, 18, 3763–3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patravale, V.B.; Mirani, A.G. Pharmaceutical Nanotechnology: Basic Protocols; Weissig, V., Elbayoumi, T., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 293–302. [Google Scholar]
- Taymouri, S.; Minaiyan, M.; Ebrahimi, F.; Tavakoli, N. In-vitro and in-vivo evaluation of chitosan-based thermosensitive gel containing lorazepam NLCs for the treatment of status epilepticus. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 14, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, A.; Das, M.K.; Chakraborty, T.; Das, S. Nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs)-based intranasal Drug Delivery System of Tenofovir disoproxil fumerate (TDF) for brain targeting. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2020, 13, 5411–5424. [Google Scholar]
- Masjedi, M.; Azadi, A.; Heidari, R.; Mohammadi-Samani, S. Nose-to-brain delivery of sumatriptan-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers: Preparation, optimization, characterization and pharmacokinetic evaluation. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2020, 72, 1341–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noorulla, K.M.; Yasir, M.; Muzaffar, F.; Roshan, S.; Ghoneim, M.M.; Almurshedi, A.S.; Tura, A.J.; Alshehri, S.; Gebissa, T.; Mekit, S.; et al. Intranasal delivery of chitosan decorated nanostructured lipid carriers of Buspirone for brain targeting: Formulation development, optimization and In-Vivo preclinical evaluation. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 67, 102939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, M.A.; Müller-Goymann, C.C. Solvent injection as a new approach for manufacturing lipid nanoparticles—Evaluation of the method and process parameters. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2003, 55, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yun, J.; Shen, S.; Chen, Z.; Yao, K.; Chen, J.; Chen, B. Formation of solid lipid nanoparticles in a microchannel system with a cross-shaped junction. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2008, 63, 5600–5605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.-H.; Shen, S.-C.; Chen, Z.; Yun, J.-X.; Yao, K.-J.; Chen, B.-B.; Chen, J.-Z. Preparation of solid lipid nanoparticles in co-flowing microchannels. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 144, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, X.; Du, J.; Liu, M.; Feng, J.; Hu, K. Improved brain delivery of pueraria flavones via intranasal administration of borneol-modified solid lipid nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 2019, 14, 2105–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, K.; Sharma, N.; Rawat, S.; Khan, N.; Karwasra, R.; Hasan, N.; Kumar, A.; Jain, G.K.; Nishad, D.K.; Khanna, S.; et al. Intranasal solid lipid nanoparticles for management of pain: A full factorial design approach, characterization & Gamma Scintigraphy. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2021, 236, 105060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhou, M.; Xu, Y.; Peng, W.; Zhang, S.; Li, R.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, S.; Wang, Y.; et al. Resveratrol-loaded TPGS-resveratrol-solid lipid nanoparticles for multidrug-resistant therapy of breast cancer: In vivo and in vitro study. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 762489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calva-Estrada, S.J.; García, O.; Mendoza, M.R.; Jiménez, M. Characterization of O/W emulsions of carotenes in blackberry juice performed by ultrasound and high-pressure homogenization. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2018, 39, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvão, K.C.S.; Vicente, A.A.; Sobral, P.J.A. Development, characterization, and stability of O/W pepper nanoemulsions produced by high-pressure homogenization. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2018, 11, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amasya, G.; Aksu, B.; Badilli, U.; Onay-Besikci, A.; Tarimci, N. QbD guided early pharmaceutical development study: Production of lipid nanoparticles by high pressure homogenization for skin cancer treatment. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 563, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, S.; Bicker, J.; Fonseca, C.; Ferreira, N.R.; Vitorino, C.; Alves, G.; Falcão, A.; Fortuna, A. Encapsulated Escitalopram and paroxetine intranasal co-administration: In vitro/in vivo evaluation. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 751321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Qian, A.; Wang, Q.; Xu, F.; He, Y.; Xu, J.; Xia, Y.; Xia, Q. Industrialization of lipid nanoparticles: From laboratory-scale to large-scale production line. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 109, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shegokar, R.; Singh, K.K.; Müller, R.H. Production & stability of stavudine solid lipid nanoparticles—From lab to industrial scale. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 416, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madane, R.G.; Mahajan, H.S. Curcumin-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) for nasal administration: Design, characterization, and in vivo study. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 1326–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Kesarla, R.; Chotai, N.; Misra, A.; Omri, A. Systematic Approach for the formulation and optimization of solid lipid nanoparticles of efavirenz by high pressure homogenization using design of experiments for brain targeting and enhanced bioavailability. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 5984014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, E.; Sguizzato, M.; Drechsler, M.; Mariani, P.; Carducci, F.; Nastruzzi, C.; Cortesi, R. Progesterone lipid nanoparticles: Scaling up and in vivo human study. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 119, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Üner, M.; Yener, G.; Ergüven, M. Design of colloidal drug carriers of celecoxib for use in treatment of breast cancer and leukemia. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 103, 109874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, M.; Schiavone, N.; Guzman-Aranguez, A.; Giansanti, F.; Papucci, L.; Perez de Lara, M.J.; Singh, M.; Kaur, I.P. Atorvastatin-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles as eye drops: Proposed treatment option for age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2020, 10, 919–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Li, H.; Tian, B.; Sai, S.; Gao, Y.; Lan, T.; Meng, Y.; Ding, C. Development of nose-to-brain delivery of ketoconazole by nanostructured lipid carriers against cryptococcal meningoencephalitis in mice. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 183, 110446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitorino, C.; Silva, S.; Gouveia, F.; Bicker, J.; Falcão, A.; Fortuna, A. QbD-driven development of intranasal lipid nanoparticles for depression treatment. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2020, 153, 106–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardeshi, C.V.; Belgamwar, V.S. Improved brain pharmacokinetics following intranasal administration of N,N,N-trimethyl chitosan tailored mucoadhesive NLCs. Mater. Technol. 2020, 35, 249–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Dhar, A.; Patel, C.; Khimani, M.; Neogi, S.; Sharma, P.; Siva Kumar, N.; Vekariya, R.L. A brief review on solid lipid nanoparticles: Part and parcel of contemporary drug delivery systems. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 26777–26791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, V.-A.; Nguyen, T.-T.-L.; Maeng, H.-J.; Chi, S.-C. Nanostructured lipid carriers containing ondansetron hydrochloride by cold high-pressure homogenization method: Preparation, characterization, and pharmacokinetic evaluation. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 101185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, V.-A.; Nguyen, T.-T.-L.; Maeng, H.-J.; Chi, S.-C. Data on optimization and drug release kinetics of nanostructured lipid carriers containing ondansetron hydrochloride prepared by cold high-pressure homogenization method. Data Brief 2019, 26, 104475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neupane, Y.R.; Sabir, M.D.; Ahmad, N.; Ali, M.; Kohli, K. Lipid drug conjugate nanoparticle as a novel lipid nanocarrier for the oral delivery of decitabine: Ex vivo gut permeation studies. Nanotechnology 2013, 24, 415102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.-J.; Zhang, Y.-T.; Zhao, J.-H.; Shen, L.-N.; Shi, F.; Feng, N.-P. Preparation and in vitro anti-tumor properties of toad venom extract-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles. Die Pharm. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 68, 653–660. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, G.; Chopra, K.; Puri, S.; Bishnoi, M.; Rishi, P.; Kaur, I.P. Topical delivery of TRPsiRNA-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles confer reduced pain sensation via TRPV1 silencing, in rats. J. Drug Target. 2018, 26, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, E.B.; Doktorovova, S.; Zielinska, A.; Silva, A.M. Key production parameters for the development of solid lipid nanoparticles by high shear homogenization. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2019, 24, 1181–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severino, P.; Santana, M.H.A.; Souto, E.B. Optimizing SLN and NLC by 22 full factorial design: Effect of homogenization technique. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2012, 32, 1375–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel Hady, M.; Sayed, O.M.; Akl, M.A. Brain uptake and accumulation of new levofloxacin-doxycycline combination through the use of solid lipid nanoparticles: Formulation; Optimization and in-vivo evaluation. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 193, 111076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Zhu, L.; Dong, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhou, W. Preparation, characterization and pharmacokinetics of enrofloxacin-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles: Influences of fatty acids. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 83, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abourehab, M.A.S.; Khames, A.; Genedy, S.; Mostafa, S.; Khaleel, M.A.; Omar, M.M.; El Sisi, A.M. Sesame oil-based nanostructured lipid carriers of nicergoline, intranasal delivery system for brain targeting of synergistic cerebrovascular protection. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jannin, V.; Blas, L.; Chevrier, S.; Miolane, C.; Demarne, F.; Spitzer, D. Evaluation of the digestibility of solid lipid nanoparticles of glyceryl dibehenate produced by two techniques: Ultrasonication and spray-flash evaporation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 111, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortesi, R.; Esposito, E.; Luca, G.; Nastruzzi, C. Production of lipospheres as carriers for bioactive compounds. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 2283–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.; Chavda, K.; Vyas, B.; Patel, S. Formulation development of linagliptin solid lipid nanoparticles for oral bioavailability enhancement: Role of P-gp inhibition. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2020, 11, 1166–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.; Iqubal, M.K.; Imtiyaz, K.; Saleem, S.; Mittal, S.; Rizvi, M.M.A.; Ali, J.; Baboota, S. Topical nanostructured lipid carrier gel of quercetin and resveratrol: Formulation, optimization, in vitro and ex vivo study for the treatment of skin cancer. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 587, 119705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.S.L.; Roberts, C.; Billa, N. Pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution of an orally administered mucoadhesive chitosan-coated amphotericin B-Loaded nanostructured lipid carrier (NLC) in rats. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2020, 31, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasir, M.; Chauhan, I.; Zafar, A.; Verma, M.; Noorulla, K.M.; Tura, A.J.; Alruwaili, N.K.; Haji, M.J.; Puri, D.; Gobena, W.G.; et al. Buspirone loaded solid lipid nanoparticles for amplification of nose to brain efficacy: Formulation development, optimization by Box-Behnken design, in-vitro characterization and in-vivo biological evaluation. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 61, 102164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, H.P.; Gandhi, P.A.; Chaudhari, P.S.; Desai, B.V.; Desai, D.T.; Dedhiya, P.P.; Maulvi, F.A.; Vyas, B.A. Clozapine loaded nanostructured lipid carriers engineered for brain targeting via nose-to-brain delivery: Optimization and in vivo pharmacokinetic studies. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 64, 102533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uppuluri, C.T.; Ravi, P.R.; Dalvi, A.V. Design, optimization and pharmacokinetic evaluation of Piribedil loaded solid lipid nanoparticles dispersed in nasal in situ gelling system for effective management of Parkinson’s disease. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 606, 120881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautam, D.; Singh, S.; Maurya, P.; Singh, M.; Kushwaha, S.; Saraf, A.S. Appraisal of nano-lipidic astaxanthin cum thermoreversible gel and its efficacy in haloperidol induced parkinsonism. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2021, 18, 1515–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohd, Y.; Praveen Kumar, G.; Dinesh, P.; Preeti, S.; Shanmugam Sadish, K. Solid lipid nanoparticles approach for lymphatic targeting through intraduodenal delivery of quetiapine fumarate. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2018, 15, 818–828. [Google Scholar]
- Masiiwa, W.L.; Gadaga, L.L. Intestinal permeability of artesunate-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles using the everted gut method. J. Drug Deliv. 2018, 2018, 3021738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathy Abd-Ellatef, G.-E.; Gazzano, E.; Chirio, D.; Ragab Hamed, A.; Belisario, D.C.; Zuddas, C.; Peira, E.; Rolando, B.; Kopecka, J.; Assem Said Marie, M.; et al. Curcumin-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles bypass p-glycoprotein mediated doxorubicin resistance in triple negative breast cancer cells. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igartua, M.; Saulnier, P.; Heurtault, B.; Pech, B.; Proust, J.E.; Pedraz, J.L.; Benoit, J.P. Development and characterization of solid lipid nanoparticles loaded with magnetite. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 233, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Wairkar, S.; Bhatt, L.K. Isotretinoin and α-tocopherol acetate-loaded solid lipid nanoparticle topical gel for the treatment of acne. J. Microencapsul. 2020, 37, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshkar, S.S.; Jadhav, M.S.; Shirolkar, S.V. Development of carbamazepine nanostructured lipid carrier loaded thermosensitive gel for intranasal delivery. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2021, 11, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Gorki, V.; Singh, G.; Kaur, R.; Katare, O.P.; Nirmalan, N.; Singh, B. Intranasal delivery of polymer-anchored lipid nanoconstructs of artemether-lumefantrine in Plasmodium berghei ANKA murine model. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 61, 102114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matarazzo, A.P.; Elisei, L.M.S.; Carvalho, F.C.; Bonfílio, R.; Ruela, A.L.M.; Galdino, G.; Pereira, G.R. Mucoadhesive nanostructured lipid carriers as a cannabidiol nasal delivery system for the treatment of neuropathic pain. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 159, 105698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heurtault, B.; Saulnier, P.; Pech, B.; Proust, J.-E.; Benoit, J.-P. A novel phase inversion-based process for the preparation of lipid nanocarriers. Pharm. Res. 2002, 19, 875–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montenegro, L.; Sarpietro, M.G.; Ottimo, S.; Puglisi, G.; Castelli, F. Differential scanning calorimetry studies on sunscreen loaded solid lipid nanoparticles prepared by the phase inversion temperature method. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 415, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montenegro, L.; Sinico, C.; Castangia, I.; Carbone, C.; Puglisi, G. Idebenone-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles for drug delivery to the skin: In vitro evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 434, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, C.; Tomasello, B.; Ruozi, B.; Renis, M.; Puglisi, G. Preparation and optimization of PIT solid lipid nanoparticles via statistical factorial design. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 49, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo, P.; Feng, J.; Esquena, J.; Tadros, T.F.; Dederen, J.C.; Garcia, M.J.; Azemar, N.; Solans, C. The influence of surfactant mixing ratio on nano-emulsion formation by the pit method. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 285, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarpietro, M.G.; Accolla, M.L.; Puglisi, G.; Castelli, F.; Montenegro, L. Idebenone loaded solid lipid nanoparticles: Calorimetric studies on surfactant and drug loading effects. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 471, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, U.A.; Parmar, S.J.; Easwaran, S. Metronidazole-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers to improve skin deposition and retention in the treatment of rosacea. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2019, 45, 1039–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarheed, O.; Shouqair, D.; Ramesh, K.; Amin, M.; Boateng, J.; Drechsler, M. Physicochemical characteristics and in vitro permeation of loratadine solid lipid nanoparticles for transdermal delivery. Ther. Deliv. 2020, 11, 685–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charcosset, C.; El-Harati, A.; Fessi, H. Preparation of solid lipid nanoparticles using a membrane contactor. J. Control. Release 2005, 108, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayata, N.; Abdelwahed, W.; Chehna, M.F.; Charcosset, C.; Fessi, H. Preparation of vitamin E loaded nanocapsules by the nanoprecipitation method: From laboratory scale to large scale using a membrane contactor. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 423, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’oria, C.; Charcosset, C.; Barresi, A.A.; Fessi, H. Preparation of solid lipid particles by membrane emulsification—Influence of process parameters. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2009, 338, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laouini, A.; Andrieu, V.; Vecellio, L.; Fessi, H.; Charcosset, C. Characterization of different vitamin E carriers intended for pulmonary drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 471, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battaglia, L.; Gallarate, M.; Cavalli, R.; Trotta, M. Solid lipid nanoparticles produced through a coacervation method. J. Microencapsul. 2010, 27, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglia, L.; Muntoni, E.; Chirio, D.; Peira, E.; Annovazzi, L.; Schiffer, D.; Mellai, M.; Riganti, C.; Salaroglio, I.C.; Lanotte, M.; et al. Solid lipid nanoparticles by coacervation loaded with a methotrexate prodrug: Preliminary study for glioma treatment. Nanomedicine 2017, 12, 639–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglia, L.; Gallarate, M.; Peira, E.; Chirio, D.; Solazzi, I.; Giordano, S.M.A.; Gigliotti, C.L.; Riganti, C.; Dianzani, C. Bevacizumab loaded solid lipid nanoparticles prepared by the coacervation technique: Preliminary in vitro studies. Nanotechnology 2015, 26, 255102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente, N.; Ferrara, B.; Gigliotti, C.L.; Boggio, E.; Capucchio, M.T.; Biasibetti, E.; Schiffer, D.; Mellai, M.; Annovazzi, L.; Cangemi, L.; et al. Solid lipid nanoparticles carrying temozolomide for melanoma treatment. preliminary in vitro and in vivo studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muntoni, E.; Marini, E.; Ahmadi, N.; Milla, P.; Ghè, C.; Bargoni, A.; Capucchio, M.T.; Biasibetti, E.; Battaglia, L. Lipid nanoparticles as vehicles for oral delivery of insulin and insulin analogs: Preliminary ex vivo and in vivo studies. Acta Diabetol. 2019, 56, 1283–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.U.; Razzaq, A.; Khan, A.; Rehman, N.U.; Khan, H.; Khan, T.; Khan, A.U.; Althobaiti, N.A.; Menaa, F.; Iqbal, H.; et al. Physicochemical characterizations and pharmacokinetic evaluation of pentazocine solid lipid nanoparticles against inflammatory pain model. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz de Escalona, M.; Sáez-Fernández, E.; Prados, J.C.; Melguizo, C.; Arias, J.L. Magnetic solid lipid nanoparticles in hyperthermia against colon cancer. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 504, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazur, K.L.; Feuser, P.E.; Valério, A.; Poester Cordeiro, A.; de Oliveira, C.I.; Assolini, J.P.; Pavanelli, W.R.; Sayer, C.; Araújo, P.H.H. Diethyldithiocarbamate loaded in beeswax-copaiba oil nanoparticles obtained by solventless double emulsion technique promote promastigote death in vitro. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 176, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker Peres, L.; Becker Peres, L.; de Araújo, P.H.H.; Sayer, C. Solid lipid nanoparticles for encapsulation of hydrophilic drugs by an organic solvent free double emulsion technique. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 140, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, N.A.H.A.; Kassem, A.A.; Farid, R.M.; Ismail, F.A.; El-Massik, M.A.E.; Boraie, N.A. A novel nasal almotriptan loaded solid lipid nanoparticles in mucoadhesive in situ gel formulation for brain targeting: Preparation, characterization and in vivo evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 548, 609–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yu, L.; Zheng, L.; Geng, F. Studies on crystallinity state of puerarin loaded solid lipid nanoparticles prepared by double emulsion method. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2010, 99, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonte, P.; Nogueira, T.; Gehm, C.; Ferreira, D.; Sarmento, B. Chitosan-coated solid lipid nanoparticles enhance the oral absorption of insulin. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2011, 1, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallarate, M.; Trotta, M.; Battaglia, L.; Chirio, D. Preparation of solid lipid nanoparticles from W/O/W emulsions: Preliminary studies on insulin encapsulation. J. Microencapsul. 2009, 26, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabi-Meibodi, M.; Vatanara, A.; Najafabadi, A.R.; Rouini, M.R.; Ramezani, V.; Gilani, K.; Etemadzadeh, S.M.H.; Azadmanesh, K. The effective encapsulation of a hydrophobic lipid-insoluble drug in solid lipid nanoparticles using a modified double emulsion solvent evaporation method. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 112, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trucillo, P.; Campardelli, R. Production of solid lipid nanoparticles with a supercritical fluid assisted process. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2019, 143, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo-Morantes, C.Y.; Acevedo-Morantes, M.T.; Suleiman-Rosado, D.; Ramírez-Vick, J.E. Evaluation of the cytotoxic effect of camptothecin solid lipid nanoparticles on MCF7 cells. Drug Deliv. 2013, 20, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, P.; Shekunov, B.Y.; Yim, D.; Cipolla, D.; Boyd, B.; Farr, S. Production of solid lipid nanoparticle suspensions using supercritical fluid extraction of emulsions (SFEE) for pulmonary delivery using the AERx system. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campardelli, R.; Cherain, M.; Perfetti, C.; Iorio, C.; Scognamiglio, M.; Reverchon, E.; Della Porta, G. Lipid nanoparticles production by supercritical fluid assisted emulsion–diffusion. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2013, 82, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, L.N.; Oliveira, D.M.L.; Chaud, M.V.; Alves, T.F.R.; Nery, M.; da Silva, C.F.; Gonsalves, J.K.C.; Nunes, R.S.; Corrêa, C.B.; Amaral, R.G.; et al. Praziquantel-solid lipid nanoparticles produced by supercritical carbon dioxide extraction: Physicochemical characterization, release profile, and cytotoxicity. Molecules 2019, 24, 3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trevaskis, N.L.; Charman, W.N.; Porter, C.J.H. Lipid-based delivery systems and intestinal lymphatic drug transport: A mechanistic update. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 702–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalikwar, S.S.; Belgamwar, V.S.; Talele, V.R.; Surana, S.J.; Patil, M.U. Formulation and evaluation of Nimodipine-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles delivered via lymphatic transport system. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2012, 97, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, M.; McClements, D.J.; Xiao, H. Improving oral bioavailability of nutraceuticals by engineered nanoparticle-based delivery systems. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2015, 2, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roger, E.; Lagarce, F.; Garcion, E.; Benoit, J.P. Lipid nanocarriers improve paclitaxel transport throughout human intestinal epithelial cells by using vesicle-mediated transcytosis. J. Control. Release 2009, 140, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beloqui, A.; Solinís, M.Á.; Gascón, A.R.; del Pozo-Rodríguez, A.; des Rieux, A.; Préat, V. Mechanism of transport of saquinavir-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers across the intestinal barrier. J. Control. Release 2013, 166, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.-T.-L.; Duong, V.-A.; Maeng, H.-J. Pharmaceutical formulations with p-glycoprotein inhibitory effect as promising approaches for enhancing oral drug absorption and bioavailability. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.; Affram, K.; Nottingham, E.L.; Han, B.; Amissah, F.; Krishnan, S.; Trevino, J.; Agyare, E. Application of smart solid lipid nanoparticles to enhance the efficacy of 5-fluorouracil in the treatment of colorectal cancer. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sguizzato, M.; Esposito, E.; Cortesi, R. Lipid-based nanosystems as a tool to overcome skin barrier. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.S.; Shah, K.U.; Mohaini, M.A.; Alsalman, A.J.; Hawaj, M.A.A.; Alhashem, Y.N.; Ghazanfar, S.; Khan, K.A.; Niazi, Z.R.; Farid, A. Tacrolimus-loaded solid lipid nanoparticle gel: Formulation development and in vitro assessment for topical applications. Gels 2022, 8, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.-H.; Chon, J.; Kim, Y.-I.; Lee, H.-J.; Oh, D.-W.; Lee, H.-G.; Han, C.-S.; Kim, D.-W.; Park, C.-W. Preparation and evaluation of tacrolimus-loaded thermosensitive solid lipid nanoparticles for improved dermal distribution. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 5381–5396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.-T.-L.; Maeng, H.-J. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of intranasal solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers for nose-to-brain delivery. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadhave, D.G.; Tagalpallewar, A.A.; Kokare, C.R. Agranulocytosis-protective olanzapine-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers engineered for CNS delivery: Optimization and hematological toxicity studies. AAPS PharmSciTech 2019, 20, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Praveen, S.; Gowda, D.; Siddaramaiah, H.; Hemalatha, S. Ziprasidone hydrochloride loaded nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCS) for intranasal delivery: Optimization and in vivo studies. Int. J. Appl. Pharm. 2020, 12, 31–41. [Google Scholar]
- de Oliveira, I.F.; Barbosa, E.J.; Peters, M.C.C.; Henostroza, M.A.B.; Yukuyama, M.N.; dos Santos Neto, E.; Löbenberg, R.; Bou-Chacra, N. Cutting-edge advances in therapy for the posterior segment of the eye: Solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 589, 119831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platania, C.B.M.; Dei Cas, M.; Cianciolo, S.; Fidilio, A.; Lazzara, F.; Paroni, R.; Pignatello, R.; Strettoi, E.; Ghidoni, R.; Drago, F.; et al. Novel ophthalmic formulation of myriocin: Implications in retinitis pigmentosa. Drug Deliv. 2019, 26, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Sheng, Y. Sustained delivery of epalrestat to the retina using PEGylated solid lipid nanoparticles laden contact lens. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 587, 119688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, A.B.; Shah, J.; Al-Dhubiab, B.E.; Jacob, S.; Patel, S.S.; Venugopala, K.N.; Morsy, M.A.; Gupta, S.; Attimarad, M.; Sreeharsha, N.; et al. Clarithromycin solid lipid nanoparticles for topical ocular therapy: Optimization, Evaluation and in vivo studies. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Wu, M.; Ye, W.; Huang, Z.; Ma, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, W.; Huang, Y.; Pan, X.; Wu, C. Inhalable solid lipid nanoparticles for intracellular tuberculosis infection therapy: Macrophage-targeting and pH-sensitive properties. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2021, 11, 1218–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landh, E.; Moir, L.M.; Traini, D.; Young, P.M.; Ong, H.X. Properties of rapamycin solid lipid nanoparticles for lymphatic access through the lungs & part II: The effect of nanoparticle charge. Nanomedicine 2020, 15, 1947–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto Bárbara, F.; Ribeiro Lorena Natasha, B.; da Silva Gisela Bevilacqua Rolfsen, F.; Freitas Camila, S.; Kraemer, L.; Oliveira Fabrício Marcus, S.; Clímaco Marianna, C.; Mourão Flávio Afonso, G.; Santos Gabryella Soares Pinheiro d Béla Samantha, R.; Gurgel Isabella Luísa da, S.; et al. Inhalation of dimethyl fumarate-encapsulated solid lipid nanoparticles attenuate clinical signs of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and pulmonary inflammatory dysfunction in mice. Clin. Sci. 2022, 136, 81–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Pérez Marc, G.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baden, L.R.; El Sahly, H.M.; Essink, B.; Kotloff, K.; Frey, S.; Novak, R.; Diemert, D.; Spector, S.A.; Rouphael, N.; Creech, C.B.; et al. Efficacy and safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 384, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameters | Characterization | References |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | Dynamic light scattering and laser diffraction | [52] |
| Polydispersit index | Dynamic light scattering and laser diffraction | [52] |
| Zeta potential | Dynamic light scattering | [58,59] |
| Entrapment efficiency | Gel filtration chromatography | [63] |
| Dialysis | [64] | |
| Ultracentrifugation | [65,66] | |
| Filter membrane | [67] | |
| Crystallinity | Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and X-ray diffraction (XRD) | [35] |
| Shape and morphology | Scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and atomic force microscopy (AFM) | [52,55,70,71] |
| Method | Features | References |
|---|---|---|
| Solvent emulsification-evaporation | Suitable for highly thermo-labile drugs, no high temperatures and physical stress Toxic organic solvent removal | [91,92,93,94,95] |
| Solvent emulsification-diffusion | Suitable for highly thermo-labile drugs, does not require high temperatures and physical stress Toxic organic solvent removal, high water amount, and low SLN concentration | [101,102,103,104] |
| Solvent injection | Simple, fast production, no complicated instruments Toxic organic solvent removal | [67,108,109,110] |
| Hot high-pressure homogenization | Organic-solvent-free operation, short production time, and scale-up feasibility Unsuitable for heat-sensitive or hydrophilic drugs | [120,121,122,123,124] |
| Cold high-pressure homogenization | Suitable for water-soluble drugs to prevent drug loss Large particles and laborious processes | [126,129,130] |
| High-speed stirring and ultra-sonication | Organic-solvent-free operation and ease of implementation High surfactant amounts, exposal of drugs to high temperatures, and metal contamination | [138,139,140,141,142,143] |
| Microemulsion | Simple, reproducible, solvent-free, and feasible to scale up Large amount of surfactant and water | [149,150,151,152] |
| Phase inversion temperature | Based on non-ionic polyoxyethylated surfactants Solvent-free, little energy input Low stability of the nanoemulsion | [158,159,160] |
| Membrane contactor | Use of a specific membrane contactor Scale-up feasibility and particle-size controllability Sophisticated system and clogging risk of the membrane | [164] |
| Coacervation | Use of alkaline salts of fatty acids Straightforward and solvent-free Unsuitable for pH-sensitive drugs, only applicable to alkaline salt lipids | [168,169] |
| Double emulsion | Preparation of a water/oi/water double emulsion Suitable for hydrophilic drugs High drug loss and large particle size | [172,173,177,178] |
| Supercritical fluid | Uniform-particle-size distributions and high solvent-extraction efficiencies Use of organic solvents and expensive supercritical fluids | [180,183] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, T.-T.-L.; Duong, V.-A. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles. Encyclopedia 2022, 2, 952-973. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia2020063
Nguyen T-T-L, Duong V-A. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles. Encyclopedia. 2022; 2(2):952-973. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia2020063
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Thi-Thao-Linh, and Van-An Duong. 2022. "Solid Lipid Nanoparticles" Encyclopedia 2, no. 2: 952-973. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia2020063
APA StyleNguyen, T.-T.-L., & Duong, V.-A. (2022). Solid Lipid Nanoparticles. Encyclopedia, 2(2), 952-973. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia2020063







