Definition
Toxoplasma gondii is a ubiquitous zoonotic parasite with an obligatory intracellular lifestyle. It relies on a specialized set of cytoskeletal and secretory organelles for host cell invasion. When infecting its felid definitive host, T. gondii undergoes sexual reproduction in the intestinal epithelium, producing oocysts that are excreted with the feces and sporulate in the environment. In other hosts and/or tissues, T. gondii multiplies by asexual reproduction. Rapidly dividing tachyzoites expand through multiple tissues, particularly nervous and muscular tissues, and eventually convert to slowly dividing bradyzoites which produce tissue cysts, structures that evade the immune system and remain infective within the host. Infection normally occurs through ingestion of sporulated oocysts or tissue cysts. While T. gondii is able to infect virtually all warm-blooded animals, most infections in humans are asymptomatic, with clinical disease occurring most often in immunocompromised hosts or fetuses carried by seronegative mothers that are infected during pregnancy.
Keywords:
Toxoplasma gondii; toxoplasmosis; parasite; tissue cyst; endodyogeny; lytic cycle; life cycle; oocyst; Apicomplexa 1. Toxoplasma gondii: A Successful Parasite
Toxoplasma gondii is frequently described as one of the most successful parasites, due to its ubiquitous distribution, the wide range of host species it is able to infect and its high prevalence rates around the world. The amenability of T. gondii to laboratory conservation and propagation both in vivo and in vitro as well as to genetic manipulation have made this parasite a widely used biological model for the study of conserved biological processes in closely related parasites more challenging to manipulate in a laboratory setting [1].
T. gondii was initially observed in the tissues of the rodent Ctenodactylus gundi by Nicolle and Manceaux (1908) [2] and in the tissues of a rabbit by Splendore (1908) [3]. At the time, the host Ctenodactylus gundi was erroneously identified as Ctenodactylus gondi, which resulted in the specific epithet of T. gondii. The name of the genus was given as a reference to the shape of the parasite, from the Greek tóxon meaning arc or bow [4]. T. gondii is an obligate intracellular parasite and is the causative agent of toxoplasmosis in humans and animals. T. gondii has a worldwide distribution and infects a wide variety of animals, although only a fraction develop disease [5,6]. Toxoplasmosis is usually acquired through ingestion of either sporulated oocysts that are shed by the felid definitive host and found in food and water supplies, or through consumption of contaminated meat products containing tissue cysts. Rapidly dividing tachyzoites readily invade and replicate in many tissues and cell types and, if not kept in check by the host’s immune system, extensive proliferation then causes acute disease and severe tissue pathology in multiple organs [7]. Thus, toxoplasmosis represents a health risk mainly for immunocompromised individuals and for fetuses upon primary infection during pregnancy [8]. Therapeutic and prophylactic options currently available are either insufficient, or cause severe adverse side effects in both humans and animals [9].
2. A Prevalent and Silent Infection
Apicomplexan parasites are responsible for several diseases of veterinary and medical relevance, including zoonotic diseases. Mosquito-borne hematozoan parasites of the genus Plasmodium are the causative agents of malaria, a life-threatening disease with over 200 million cases estimated in 2019 [10]. The tick-borne Babesia spp. piroplasms cause hemolysis related disease and present zoonotic potential [11,12]. Cryptosporidium spp., also zoonotic parasites, are a major cause of gastrointestinal disease in non-immunocompetent hosts [13]. Cyst-forming Coccidia include the stenoxenous Neospora caninum and Besnoitia besnoiti, which are major sources of economic loss in animal production [14,15]. Toxoplasma gondii and Sarcocystis spp. are cyst-forming Coccidia as well; however, they do not present host specificity with regard to the intermediate host. T. gondii is exceptional in the variety of intermediate hosts it can infect, assumed to be all warm-blooded animals.
2.1. Epidemiology and Transmission
Infection by T. gondii has been described in over 350 different host species, most of which inhabit wild environments, including 31 felid species [16]. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that over 60 million people are chronically infected with T. gondii in the United States, and considers this one of five neglected tropical parasitic diseases deserving public health action [17]. In the European Union, only congenital toxoplasmosis is officially reported, with 208 cases communicated in 2018 [18]. However, only three countries have both mandatory screening programs of pregnant women and report screening data to the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC), with cases being reported from 22 countries, of which France accounts for 72.6% of the cases. Therefore, the actual number of cases is likely higher than the reported. T. gondii seroprevalence varies widely among regions. In humans, seroprevalences have been estimated at 8%–76% in different countries [19]. Similar variations ranging from very low to high seroprevalence rates have been reported for various animal species around the world [20,21,22,23,24,25,26]. Felids, particularly wild species, tend to have high seroprevalence rates [27].
Infection can occur through horizontal and vertical transmission and may originate in three different infective stages: sporozoites, bradyzoites, and tachyzoites. The parasite is able to bypass the definitive or the intermediate host, providing further possibilities for perpetuating its cycle. The sporozoites, enclosed in the sporulated oocyst, are resistance stages that remain viable and accumulate in the environment. This stage is strongly linked to the ubiquitous distribution and parasitic success of T. gondii [28]. Oocyst ingestion explains infections in vegetarians and herbivore species, however, this transmission route is not limited to these groups. A recent meta-analysis study reported a mean pooled prevalence of T. gondii oocysts in public environments of 16%, ranging from 8% to 23% in the sampled continents, North America, Asia, South America and Europe [29]. Felids are able to shed millions of oocysts upon infection, acting as disseminators of the sporozoite infective stage. Risk factors for exposure to T. gondii in farm animals include the presence of cats, rodents, and birds, access to pastures, farm type, and water quality [28,30,31]. Direct contact with cats is not significantly associated with increased risk of exposure to T. gondii in humans [16]. This is likely due to the short period of oocyst shedding after infection and to the fact that environmental sporulation is needed for the oocyst to become infectious, which takes one to five days. There is evidence that cats shed fewer total oocysts upon re-shedding [32]. Human infection caused by oocysts is associated with ingestion of shallow well water, uncooked vegetables, fruit, uncooked shellfish, and contact with soil [16,33,34,35,36]. Sporulated oocysts are highly resistant in the environment and to chemical inactivation agents; therefore, prevention of oocyst shedding is a major factor in lowering possible infection sources [28]. Vaccination of cats stands as an effective means of achieving this, with a recent work by Ramakrishnan et al. (2019) [37] showing a live-attenuated vaccine that resulted in no oocyst shedding upon challenge with a wild-type T. gondii strain. Ingestion of tissue cysts harboring bradyzoites is another important route of transmission. Within the tissue cyst, bradyzoites are protected from digestive proteolytic enzymes, and thus are much more likely to successfully infect a host through ingestion as compared to tachyzoites [38]. Furthermore, tissue cysts harbor viable bradyzoites indefinitely, and are able to cause infection in both definitive hosts and intermediate hosts, where new tissue cysts may develop. Therefore, bradyzoites enclosed in tissue cysts are resistant parasitic stages in host tissues [38]. Intermediate or definitive hosts are infected through carnivorism. Ingestion of undercooked meat has been consistently identified as a risk factor for exposure to T. gondii in humans [33,34,36,39]. Furthermore, a study published in 1965 by Desmonts and colleagues demonstrated that T. gondii seroprevalence was associated with the ingestion of raw meat [40]. The relative importance of T. gondii transmission through tissue cyst or oocyst ingestion in humans is still uncertain [28]. However, the recent development of a western blot assay that specifically detects anti-T. gondii antibodies generated from oocyst infection may allow for differentiation between transmission routes [41]. The tachyzoite, although not a resistant stage, plays an important role in Toxoplasma epidemiology if primary infection occurs during gestation, in which case there is a high probability of transmission to the fetus. Toxoplasmosis acquired through vertical transmission is of great importance in humans and in domestic animals, particularly in small ruminants [16,24,42]. Solid organ transplantation is recognized as a route of infection in humans, while raw milk may transmit T. gondii; however, these routes are not considered epidemiologically relevant [43,44,45,46].
2.2. Infection and Disease
Toxoplasmosis is frequently a silent infection, causing mild or no signs in immunocompetent hosts upon primary infection. Tachyzoite–bradyzoite conversion privileges the formation of tissue cysts that remain viable in the host; however, these do not cause disease unless the host immune system becomes compromised. Persistent infection is a concern mainly due to the risk of recrudescence. However, different studies have shown an association between chronic infection and a range of neuropsychiatric and behavioral disorders [47]. Very rarely, severe clinical disease may occur upon primary infection of immunocompetent hosts [24,48]. Ocular toxoplasmosis is the most frequent manifestation recorded in humans, while other consequences of generalized toxoplasmosis such as pneumonia, hepatitis and encephalitis have been reported in both humans and other species [48,49]. If primary toxoplasmosis occurs during pregnancy the parasite may be transmitted to the fetus, causing abortion or congenital infection, possibly leading to severe generalized toxoplasmosis and death. In immunocompromised hosts, severe disease occurs mostly due to recrudescence of a chronic infection [48]. Acute toxoplasmosis is usually treated with a combination of drugs, with pyrimethamine and sulfadiazine currently considered the most effective treatment [50]. Therapeutic options available at present fail to eliminate tissue cysts that may reactivate at a later stage, usually when the immune system is compromised, leading to manifestations of acute toxoplasmosis. A new compound, the tetrahydroquinolone JAG21, has recently been reported as a promising treatment for acute and chronic toxoplasmosis [51].
Primary infection was previously thought to induce an immune state that impaired re-shedding of oocysts by felids, and to protect intermediate hosts from disease and congenital transmission upon re-infection. However, several reports show that this is not always the case. Re-infection with a different T. gondii strain along with factors related to host-specific biology such as time post-primary infection seem to bypass this protection [52,53,54]. Although T. gondii is able to infect a great variety of animal species, susceptibility to infection and parasite resistance in tissues vary among species. Sheep and goats are among the most affected domesticated species, with toxoplasmosis causing frequent reproductive disorders, abortion, and neonatal death [24,42]. Goats appear to be particularly susceptible to acute infection by T. gondii according to existing reports of clinical toxoplasmosis outbreaks affecting adults [24], and in sheep T. gondii is considered one of the main causes of infective abortion. In fact, the only commercially available vaccine against T. gondii is approved for the reduction of embryonic death, infertility and abortion in sheep [42]. Cattle are considered to be mostly resistant to clinical disease, including abortion and congenital infection, presenting low levels of tissues cysts in muscle tissues [26,55]. Although tissue cysts are more easily detected in pigs, clinical toxoplasmosis is very rare, with occasional reproductive-related issues occurring [56,57]. An exception to the low rate of clinical toxoplasmosis in pigs has been reported in China, where several recent outbreaks have been recorded. This is thought to be related to the genotypes most prevalent in this area, namely genotypes Toxoplasma Database (ToxoDB) #9 and #10 [57]. Chickens are mostly resistant to clinical toxoplasmosis and frequently present high prevalence rates [58]. As ground feeders, free range chickens can act as sentinels of environmental contamination with oocysts, and are therefore useful for studying the epidemiology of T. gondii [58]. Marine mammals frequently exhibit clinical toxoplasmosis. This is thought to be associated with high levels of exposure to oocysts due to land-to-sea transport and oocyst accumulation in marine ecosystems, where they remain viable for years [28]. Sea otters are at particularly high risk of acquiring T. gondii, with a prevalence as high as 70% in the Monterey Bay area in California, and high mortality rates correlated with atypical strains [59,60,61]. Toxoplasmosis presents a low morbidity in cats and dogs, with clinical disease often associated with immunosuppression or congenital infection [49]. When present, clinical signs may be diverse, including respiratory, nervous, cutaneous, and ocular manifestations along with more general signs, which lead to a challenging diagnosis [49].
3. An Apicomplexa Parasite
T. gondii features the defining hallmarks of Apicomplexa, namely, an intracellular parasitic life style, an apical complex, a glideosome and an apicomplexan plastid, or apicoplast [62,63]. Apicomplexa, Dinoflagellata and Ciliata include the majority of alveolates, unicellular eukaryotes that present very diverse life styles including phototrophy, predation, and intracellular parasitism [64]. The Alveolata are named for the contiguous membranous vesicles or alveoli located immediately below the plasma membrane (PM). While previous taxonomic classifications included Alveolata within the kingdom Protozoa, recent analyses taking advantage of technological progress in electron microscopy and gene sequencing have re-assigned Alveolata to the kingdom Chromista (Table 1). Cilliata and Dinoflagellata are mostly free-living or commensal organisms, while Apicomplexa are obligate intracellular parasites [64]. Apicomplexa include the invertebrate parasites Gregarina, the blood parasites Hematozoa, the Coccidia, containing cyst-forming and non-cyst forming genera, and the more divergent and harder to classify Cryptosporidia [65]. Although Cryptosporidia were previously considered part of Coccidia, phylogenetic analyses have shown that these parasites are more closely related to Gregarina [65]. Both Gregarina and Cryptosporidia have suffered loss of the apicoplast. It was initially thought that Hematozoa had largely lost the invasion-related structure conoid, however, recent research showed that the conoid structures are conserved among all Apicomplexa clades and that the conoid is present throughout the life cycle of the hematozoan Plasmodium berghei [66].

Table 1.
Comparison of classical and updated taxonomic classifications of Toxoplasma gondii.
4. Genetic Diversity: One Species, Many Strains
Several T. gondii strains presenting genotypic and phenotypic differences have been isolated. Strain nomenclature is not consensual. Designations of genotype, haplogroup, Toxoplasma Biological Resource Centre code, and conventional type designation are attributed according to the method used for characterization, and matches between the different designations are not always available. The initial characterization of the T. gondii population was based on samples from Europe and North America. This identified a highly clonal population structure grouped in three strain types, designated types I, II, and III, with very low genetic divergence among types at the DNA sequence level [72]. These clonal lines are contemporary to agricultural expansion and to the domestication of the cat, having emerged around 104 years ago, and are associated with an increased oral infectivity that allowed the bypassing of sexual reproduction [73]. Conversely, T. gondii isolates from South America, Africa, and Asia are much more divergent. South America is particularly rich in divergent strains, with 88 genotypes having been isolated in Brazil alone [74,75]. Molecular phylogenetic analysis suggests that the North and South American strains diverged from a common ancestor over 106 years ago [74]. Type II strains predominate in Europe and North America, while the less frequent type III strains have a worldwide distribution [16]. Type I strains are the least abundant of the clonal lineages, being mostly found in Europe and America. Strains vary in virulence, which is frequently defined using the T. gondii mouse model. Type I strains (e.g., RH and GT1) are more virulent and present higher morbidity and mortality when infecting mice [16]; this is coupled to lower rates of tissue cyst formation. South American strains frequently show type I strain-like virulence and have the ability to form tissue cysts, a characteristic associated with a reduced potential for oral transmission that seems to be exclusive to these clonal lines [76]. Type II strains (e.g., ME49 and Prugniaud) and type III strains (e.g., CTG and VEG) tend to be avirulent, presenting low morbidity and high rates of chronic infection with tissue cyst formation [16]. Type III strains are slightly more virulent than type II strains. Genotyping analyses show that clonal strains are more prevalent in human-adapted environments, while divergent strains are more prevalent in wild environments, suggesting separate anthropized and sylvatic cycles [77,78].
5. One Parasite, Several Specialized Eukaryotic Cells
5.1. Zoites, Motile Stages
T. gondii exhibits a permanently polarized crescent-shaped cell with an anterior–posterior axis during most of its life cycle, namely, in the motile or invasive zoite stages: merozoites, tachyzoites, bradyzoites and sporozoites [79,80]. These stages present a size of 2 × 5–7 µm, with a narrower anterior or apical pole and a more rounded posterior or basal pole [16,79]. T. gondii cells possess the universal eukaryotic organelles: endoplasmic reticulum (ER), ribosomes, Golgi complex (GC), mitochondrion, centrosome and nucleus [16]. The nucleus is located centrally, and presents a spherical shape with a shallow concavity directed towards the apical pole, where the GC is located [81]. The rough ER is continuous with the nuclear envelope [79]. The single mitochondrion is long, up to 10 µm in length, folded inside the cell and ramified [82]. The centrosome is closely related to the nuclear membrane and is essential for cell division and organelle duplication [83,84]. T. gondii presents highly specialized structures as well, namely, the apicoplast, the secretory organelles, the inner membrane complex (IMC), and the apical and basal complexes (Figure 1).
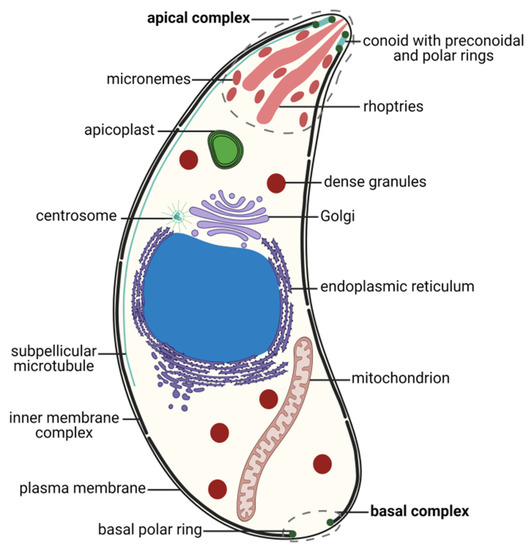
Figure 1.
Morphology of the Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoite. Schematic drawing of a transverse cut of a T. gondii tachyzoite with the main organelles and structures represented. The apical and basal complexes are highlighted with grey interrupted lines. Created with BioRender.com (accessed on 5th December 2021).
The apicoplast is a plastid organelle resulting from secondary endosymbiosis of eukaryotic photosynthetic red algae that has lost its photosynthesis function but remains an essential organelle [63,85,86]. The secretory system includes three secretory organelles: dense granules, rhoptries, and micronemes. Dense granules are distributed throughout the cell, while rhoptries and micronemes are located at the apical pole [87]. A part of the highly specialized apical complex, rhoptries and micronemes present a polarized subcellular localization connected to their roles in host cell attachment and invasion, namely, through the assembly of the moving junction [88,89]. In addition to the two secretory organelles, the apical complex is constituted by the conoid (a mesh of coiled microtubules limited at the top by the preconoidal rings and at the bottom by the inner polar ring) and two intraconoidal microtubules [79,90] (Figure 2A). The inner polar ring is a microtubule organizing center (MTOC) [91,92,93]. The conoid seems to be necessary for host cell invasion, although its function is not yet fully understood [88]. The ability of the conoid to extend and retract in extracellular zoites during the invasion process suggests a mechanical role for this structure in addition to its involvement in secretion [94,95]. The subpellicular microtubules are a set of 22 spirally arranged microtubules that originate from the inner polar ring and extend for two thirds of the cell’s length, supporting the pellicle through the cytosolic face of the IMC and conferring the cell’s shape [79,80,93]. The pellicle is a three-layer structure highly specialized in the Apicomplexa. It is formed by the outer PM layer that encloses the parasite cell and the two alveoli inner layers that consist of flattened vesicles from the GC and ER, arranged in longitudinal fused plates [79,80,93]. The alveoli are supported by the subpellicular network, a stable mesh of intermediate filaments that runs from the outer polar ring through the full length of the cell and is responsible for the cell’s mechanical stability [96]. The set of intimately associated alveoli along with the subpellicular network form the IMC, which is essential for parasite motility, host cell invasion, and replication [80,93]. Thus, the IMC forms a continuous double-layered sheet that extends from the polar ring at the apical pole of the cell to the basal complex at the basal pole of the cell, forming two circular apertures at each end. A basal complex is present at the posterior pole, including the basal polar ring where the IMC terminates [97]. Several proteins have been shown to be present in the basal complex [80,93]. These include proteins associated with the cytoskeleton and parasite replication, namely Myosin C, Centrin, Dynein and membrane occupation and recognition nexus 1 (MORN1) proteins [94,98,99,100] (Figure 2B). A 14-3-3 protein that belongs to a conserved family of signaling proteins has been localized to the basal complex as well [101]. MORN1 is present at the apical and basal rings as well as in close proximity to the centrosome [99].
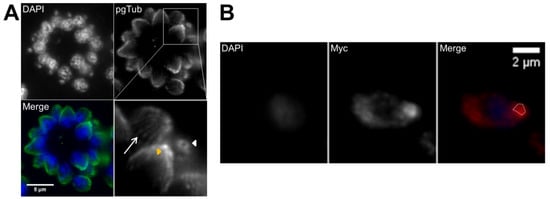
Figure 2.
Tachyzoite apical cytoskeleton and basal complex. (A) Apical cytoskeleton. Immunofluorescence of intracellular tachyzoites where retracted conoids and subpellicular microtubules are visible. The tachyzoite apical structures are identified by polyglutamylated tubulin (pgTub), namely, the conoid and attached rings (white arrowhead in top view, yellow arrowhead in side view) and the subpellicular microtubules (arrow), visible in the detail at the bottom right of the panel. The scale bar represents 5 µm. (B) Basal complex. Immunofluorescence of intracellular tachyzoites stably expressing a MORN1-Myc recombinant protein coupled to the MORN1 promoter region. MORN1-Myc accumulates at the basal pole, forming the basal polar ring (highlighted by the white dotted line). The recombinant protein is stained with anti-Myc. The scale bar represents 2 µm. DNA is stained with DAPI. IMC—inner membrane complex; PM—plasma membrane; MTs—microtubules.
The T. gondii zoite stages present slight differences in morphology regarding the position of the nucleus and the number of micronemes. Tachyzoites and merozoites present a more central nucleus and fewer micronemes compared to bradyzoites and sporozoites, which have a more basal nucleus and more numerous micronemes [38,79]. Lipid bodies are abundant in sporozoites, irregularly present in tachyzoites, and absent in bradyzoites [102]. Bradyzoites are slimmer than tachyzoites and present solid rhoptries, which are labyrinthine in tachyzoites, along with many amylopectin granules that are few or absent in tachyzoites [38,79]. Bradyzoites are more resistant to proteolytic digestion than tachyzoites [38,103,104].
5.2. Non-Motile and Gamete Stages
During its sexual development, T. gondii develops non-motile cells. First, merozoites divide frequently to form polyploid cells, schizonts, which later undergo individualization to form multiple merozoites [81]. In order to produce gametes, T. gondii form non-motile gamonts: microgamonts and macrogamonts [79,81]. Each microgamont can produce 15 to 30 mature microgametes, motile cells that present two flagella coupled to two basal bodies and a mitochondrion at the flagellar base. The macrogamont is an oval cell that forms one mature macrogamete. Synthesis of the oocyst wall begins in the macrogamont, which possesses wall-forming bodies [38,79,81]. After fertilization, the unsporulated oocyst is formed with a single sporont. During sporulation, the sporont forms two sporocysts, each containing four sporozoites, originating the sporulated oocyst [38,79,81].
6. The Complex Toxoplasma gondii Life Cycle: A Path to Success
T. gondii presents a facultative heteroxenous life cycle (Figure 3). Felids are the only animals capable of sustaining the sexual phase of the T. gondii life cycle; however, all warm-blooded animals, including felids, can act as intermediate hosts. Transmission may occur through three infective stages: bradyzoites, tachyzoites, and sporozoites. The parasite takes resistant forms in the tissues of intermediate hosts, namely, tissue cysts, and in the environment, namely, sporulated oocysts, increasing its chances of transmission. Furthermore, the three infective stages are able to produce infection in both definitive and intermediate hosts, being able to bypass the definitive host and the intermediate host. These features are fundamental for the global distribution and overall high prevalence that T. gondii presents.
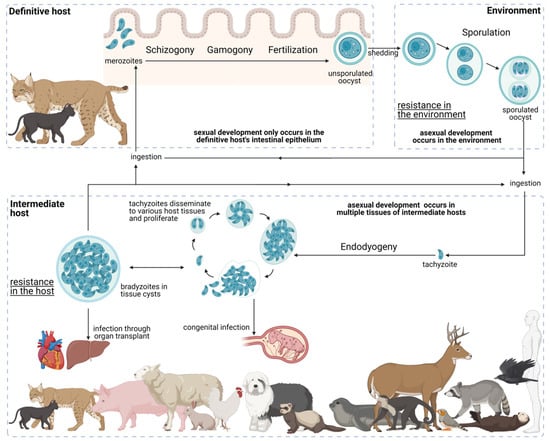
Figure 3.
Life cycle of Toxoplasma gondii. The T. gondii life cycle includes three main phases of development: in the definitive host, in the environment, and in the intermediate host (highlighted in grey interrupted lines). The various parasite stages and biological events are indicated relative to the development phase as well as to how the different entities interact. Created with BioRender.com (accessed on 5 December 2021).
6.1. Development in the Definitive Host
Only members of the Felidae family can sustain the T. gondii sexual phase. A recent study showed that this specificity is related to the absence of delta-6-desaturase intestinal activity in felids, which results in high concentrations of linoleic acid in enterocytes [105]. T. gondii sexual development was achieved in mice after reproduction of these conditions [105]. Felids are primarily infected through carnivorism by the ingestion of T. gondii-infected prey harboring tissue cysts. Although the definitive hosts are more readily infected through ingestion of tissues cysts harboring bradyzoites, infection in felids can occur through all three T. gondii infective stages (sporozoites, bradyzoites, or tachyzoites) [106,107,108]. Upon digestion of the tissue cyst wall by proteolytic enzymes, bradyzoites are released and become able to infect the felid host. In the felid gastrointestinal tract, the infective stages invade enterocytes and may differentiate to tachyzoites, which disseminate through the host body, or more frequently to merozoites, which remain in the felid gastrointestinal tract [109]. Here, merozoites initiate the sexual cycle with multiple rounds of asexual expansion in enterocytes [38,110]. This expansion occurs through endodyogeny, endopolygeny or schizogony, depending on the merozoite/schizont stage [38,109,110,111]. In endodyogeny, organelle replication is immediately followed by division and daughter cell budding [112]. Schizogony is characterized by multiple rounds of nuclear replication and division followed by a final step of merozoite individualization [112]. In endopolygeny, a form of schizogony, one merozoite first undergoes a series of nucleus, mitochondrion, and apicoplast replication without division, followed by merozoite individualization that starts with formation of the IMC and apical complex [79]. Merozoite egress from one enterocyte to invade a new enterocyte characterizes the development of a new generation of merozoites. Five types of T. gondii schizonts, designated A to E, occur successively and are considered morphologically different, with various generations per type [38,110]. No clear trigger has been identified, although it is believed that schizonts type D and E originate gametocytes which are preferentially located in the ileum, whereas schizonts are distributed through the jejunum, the ileum and occasionally the colon [38,109,110,111]. Flagellated microgametes are thought to reach the non-motile macrogametes to undergo fertilization, producing a diploid sporont [79,110]. Felids can shed 107–109 oocysts for 4–13 days following a first infection with T. gondii through tissue cyst ingestion [110,113,114]. However, microgamonts represent only 2%–5% of gamonts produced in felid enterocytes, yielding a low microgamete to macrogamete ratio [79,109,115]. Furthermore, as the oocyst wall is formed by the macrogamont, it is thought that for fertilization the biflagellate microgamete must reach the macrogamete inside the enterocyte. The complex route that has to be taken by the microgamete makes fertilization unlikely to be a very frequent event, which seems to be inconsistent with the high number of oocysts shed by felids. This has prompted the hypothesis that parthenogenesis occurs in the development of oocysts as well [79,109,115].
6.2. Environmental Development
Ovoid unsporulated oocysts containing the diploid sporont are shed in the feces of infected felids. This occurs three to ten days after ingestion of bradyzoites, although only 18 days after ingestion of oocysts [107,116]. There is a longer prepatent period upon ingestion of sporozoites when compared to bradyzoite ingestion by the felid host, consistent with the need for sporozoites to first differentiate into tachyzoites that, convert to merozoites in the enteric tract after dissemination through the felid host body, as opposed to the direct sporozoite to merozoite differentiation route [106]. The sporont undergoes sporulation with three nuclear divisions, a meiosis followed by two mitoses, and formation of the sporocyst walls [117,118]. Notably, staining of the nuclear material suggests the absence of the nuclear envelope during meiosis [117]. This, however, contrasts with reports of a closed mitosis with maintenance of nuclear envelope integrity during the whole cell cycle, a characteristic common to apicomplexans [112]. Sporulation is usually completed within one to seven days, depending on conditions such as temperature and aeration [38,109,118]. The sporulated oocyst, with two sporocysts containing four sporozoites each, is infective and remains viable in the environment. Sporulated oocysts are extremely resistant to both extreme environmental conditions and to disinfection techniques, remaining infective for up to years [118]. Once in the environment, oocysts go through sporulation, becoming a source of infection in new hosts.
6.3. Development in the Intermediate Host
T. gondii infects a wide variety of species as intermediate hosts, which are believed to include all warm-blooded animals. Notably, the asexual phase of the T. gondii life cycle occurs in felids, which can therefore act as both definitive and intermediate hosts. Intermediate hosts are readily infected through ingestion of sporulated oocysts, tissue cysts, and tachyzoites, although the latter stage presents limited epidemiologic importance [107,108]. Upon infection of an intermediate host, T. gondii infective sporozoites and bradyzoites differentiate to the tachyzoite stage [79,102]. Tachyzoites replicate inside a parasitophorous vacuole (PV) by endodyogeny and proceed to a rapid asexual expansion, disseminating to host tissues through the circulatory system. T. gondii proliferates in virtually any nucleated cell type; therefore, the parasite is able to invade and replicate in various animal tissues. Tachyzoites are able to differentiate to bradyzoites, a stage that replicates at a much slower rate, forming tissue cysts that may remain viable in the host for the course of its entire life [79,102]. Tachyzoites are responsible for parasite dissemination and acute infection, although this rapid proliferation is ultimately controlled in most immunocompetent hosts. On the other hand, bradyzoites inside tissue cysts are responsible for chronic infection without obvious clinical signs. Tachyzoite–bradyzoite interconversion is a key aspect of the T. gondii life cycle, as it allows resistance in the intermediate host and recrudescence of active infection when the host immune system is no longer able to control tachyzoite proliferation.
7. The Toxoplasma gondii Lytic Cycle: An Efficient Proliferation Strategy
Tachyzoites divide rapidly inside the host cell, and after several rounds of replication egress from the host cell and seek a new cell to invade. This is designated the lytic cycle, as tachyzoites cause lysis of the cells upon egress.
7.1. Gliding Motility
Along with other Coccidia, T. gondii zoites do not possess locomotion-specific organelles such as flagella or cilia; however, they are still able to seek out host cells to invade. This is done through a type of cellular movement without shape deformation known as gliding motility, which includes three movement types: circular gliding, upright twirling, and helical rotation [119,120]. Gliding is achieved from the interaction of the apical complex, the actin cytoskeleton, myosin motor proteins, and associated proteins which together form the glideosome [121,122,123,124,125]. Endocytosis is involved in retrograde motility [126]. Gliding motility is essential for the parasite to reach a potential host cell and for it to successfully invade and later egress from it [127].
7.2. Attachment and Invasion
Tachyzoite attachment to a host cell depends on the actomyosin system and on expression of surface antigens (SAGs) and microneme proteins (MICs) [128,129,130,131,132]. Following committed attachment, the parasite invades the host cell through a moving junction, a hoop-like structure involving close host–parasite interaction formed by the secretion of rhoptry neck proteins (RONs) and MIC apical membrane antigen 1 (AMA1) [133,134]. As parasite invasion progresses, the moving junction migrates from the apical to the posterior pole, actively eliminating selected surface proteins from both host and parasite PMs, that is, transmembrane proteins [135,136]. This process and the simultaneous active invasion generated by the glideosome give rise to an invagination of the host PM, resulting in the new PV and its surrounding PV membrane [134,135,136]. This invasion process involves rearrangement of the host microtubule cytoskeleton associated with the moving junction [137,138,139].
7.3. Establishment of the Parasitophorous Vacuole
Inside the host cell, the parasite establishes the PV by modification of the invaginated vacuole. Upon closure of the vacuole, secretion of dense granule proteins (GRAs) occurs, along with the formation of a tubulo-vesicular intravacuolar network [140,141]. The parasite manipulates the host cell through interaction with microtubules and recruitment of several host organelles to its proximity, namely, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, centrosome, and GC apparatus [79,139,142,143,144,145,146,147]. T. gondii scavenges key nutrients from the host cell to the PV as well, including sphingolipids and cholesterol from internalized organelles such as endocytic organelles, lipid droplets and Rab vesicles [147,148,149,150,151]. The PV created by the parasite allows for its intracellular replication while protected from the host cell, as the vacuole does not fuse with host acidic lysosomes [152,153].
7.4. Proliferation through Endodyogeny
T. gondii tachyzoites replicate inside the PV via endodyogeny, a mechanism of internal daughter budding that involves the formation in each round of replication of two complete daughter cells inside an intact and polarized mother cell. Tachyzoites replicate synchronously at a 2n rate where “n” equals the number replication rounds, with a predictable number of tachyzoites after each replication round until parasite egress [79,112]. This contrasts with endopolygeny and schizogony replications, which tend to be asynchronous and do not follow a geometric expansion [112]. The T. gondii tachyzoite cell cycle consists of three phases, a protein synthesis and growth gap phase (G1), a DNA synthesis phase (S), and a mitosis phase (M) [154]. The second gap phase, G2, usually presents in the eukaryotic cell cycle and is very short or absent in T. gondii [154]. The first events of replication are GC and centrosome duplication, which occur in the late G1 and early S phases, respectively [155,156,157,158,159]. The beginning of budding occurs in the late S phase with de novo formation of the daughter apical complexes, which act as scaffolds during daughter cell assembly [94,154]. The cytoskeleton grows from the apical pole to the basal pole engulfing the daughter organelles, beginning with GC and centrosome and followed by apicoplast, nucleus, and ER [83,156] (Figure 4). The mitochondrion is the last organelle to divide and be engulfed by the forming daughter cytoskeleton, while the secretory organelles are formed de novo [155,158]. At the basal pole, the basal complex ensures proper daughter segregation, with MORN1 forming a contractile ring at this subcellular localization [101] (Figure 5). Daughter cell cytoskeleton formation is therefore intimately connected to cytokinesis. At the end of daughter cell assembly, the mother cell’s cytoskeleton is degraded and its PM is recycled to the daughter cells along with newly formed PM [155,159]. Proliferating tachyzoites inside the same PV are frequently observed still attached at the basal pole by the residual body, a remnant of the mother cell cytoplasm. Mitosis occurs simultaneously with the final steps of daughter cell assembly, while the mother cell apical complex persists until the end of endodyogeny [79]. Nuclear division occurs by closed mitosis in which the nuclear envelope maintains its integrity throughout the process, an aspect common to Apicomplexa [79,112]. T. gondii is haploid (1N), with its DNA organized in 14 chromosomes. During mitosis, chromatin shows reduced condensation and the nucleolus structure is stable [160]. After DNA replication, the nucleus develops two apical protrusions in the late S phase that correspond to the location of the spindles [154]. The spindles are intranuclear, localized within a funnel-like structure formed by the nuclear envelope and known as the centrocone, and link the centrosome to the centromeres [161]. Centromeres are bundled and bound to the nuclear envelope in close proximity to the centrosome during most of the cell cycle, with the exception of spindle–microtubule interaction during DNA segregation [112] (Figure 5). Mitosis occurs shortly after centrocone formation, with the spindle microtubules migrating posteriorly into the nucleus and causing a U-shaped nucleus [112,154]. Finally, the two nuclear lobes are segregated by fission [112]. The time necessary for one replication round varies according to the strain type, mainly due to the duration of the G1 phase, with a reported five hours for type I versus nine hours for types II and III [154]. Mitosis and cytokinesis are fast processes that take around 20 min each [154].
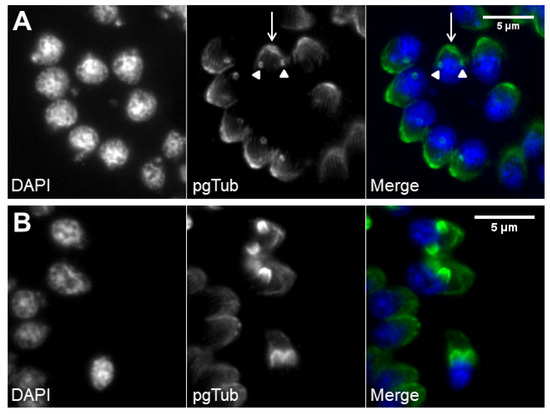
Figure 4.
De novo formation of the cytoskeleton drives daughter cell assembly. Immunofluorescence of intracellular tachyzoites in which the apical cytoskeleton is identified by polyglutamylated tubulin (pgTub) and DNA is stained with DAPI. (A) Rosette with eight tachyzoites with the apical cytoskeleton identified, namely, the conoid and attached rings (white arrow) and the subpellicular microtubules of the mother cells, as well as the conoids of the forming daughter cells (white arrowheads). (B) Three tachyzoites in the center show the forming daughter cell’s apical cytoskeleton advancing towards the basal pole. The scale bars represent 5 µm.
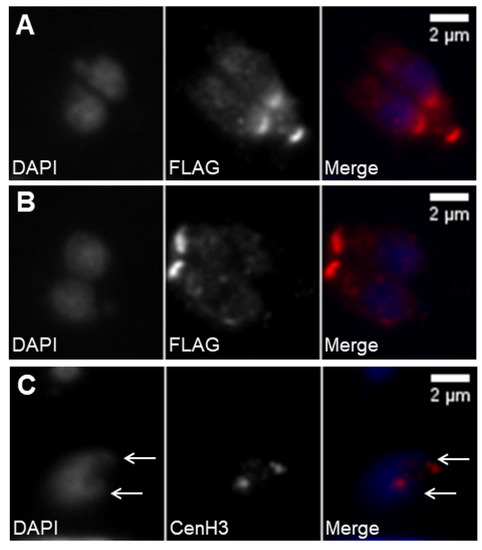
Figure 5.
Daughter cell assembly involves DNA duplication and segregation. (A,B) Immunofluorescence of intracellular tachyzoites stably expressing a FLAG-MORN1 recombinant protein coupled to the MORN1 promoter region. The recombinant protein is stained with anti-FLAG. DNA is stained with DAPI. The top panel (A) shows fully segregated DNA and the newly formed daughter cells’ basal polar rings while the mother cell’s basal polar ring is still present. The bottom panel (B) shows two fully mature, recently formed tachyzoites, each presenting one basal polar ring. (C) Immunofluorescence of an intracellular tachyzoite that has suffered DNA duplication, as marked by the presence of duplicated centromeres. The nucleus shows two apical protrusions (white arrows) indicating the centrocones. The centromeres are identified by staining with anti-CenH3. DNA is stained with DAPI. The scale bars represent 2 µm.
7.5. Egress and Repeat
Replication rounds ensue until depletion of the host cell, concluding with parasite egress. Egress is an active process that causes lysis of the host cell and enables tachyzoites to access new host cells to continue proliferation. Tachyzoite movement inside the PV signals imminent egress [162]. Successful egress is dependent on the secretion of MICs and GRAs that promote destabilization of the PV and host cell PMs [163,164,165,166,167]. Parasite motility is essential in order to reach a new host cell, destabilize the membranes, and successfully egress [123,168,169,170]. Phosphatidic acid is a signal for egress, acting through a guanylate cyclase (GC)-cGMP-protein kinase G (PKG)-inositol triphosphate (IP3) signaling pathway and promoting Ca2+ release, with consequent activation of Ca2+-dependent protein kinases (CDPKs) and microneme activity [171]. Overall, Ca2+ is a major hub to trigger egress, having been extensively used to promote tachyzoite egress in cell culture [162,172,173]. The succession of these processes (gliding motility, attachment, invasion, replication, and egress) enables tachyzoite expansion and proliferation throughout the host tissues, causing cell lysis and tissue damage (Figure 6).

Figure 6.
The lytic cycle. ER—endoplasmic reticulum; PV—parasitophorous vacuole; MJ—moving junction. Created with BioRender.com (accessed on 5 December 2021).
8. The Tissue Cyst
Tachyzoites proceed to rapid asexual expansion and dissemination in the host tissues through the circulatory system thanks to their ability to proliferate in virtually any nucleated cell type. Therefore, tachyzoite–bradyzoite conversion may occur in any host tissue and can develop in any visceral organ. However, tissue cysts are most common in striated muscles (skeletal and cardiac muscle) and nervous tissues (brain and eyes) [38]. T. gondii can interchange between the rapidly proliferating tachyzoite stage and the slowly replicating bradyzoite stage, which remains viable inside mature tissue cysts in a G0 cell cycle stage [174]. Like tachyzoites, bradyzoites replicate by endodyogeny inside a PV, the tissue cyst [79] (Figure 7). The percentage of parasites actively replicating inside a tissue cyst lowers as the cyst matures, increasing in size and bradyzoite number [79]. However, mature cyst size appears not to be solely dependent on bradyzoite number, as tissue cysts present unexpected variability regarding parasite density [175]. Furthermore, bradyzoites have been shown to present active replication in levels not previously thought possible, as it was previously believed that at this stage they remained fully quiescent (G0) inside the tissue cyst. Therefore, although the tissue cyst is a stable structure that allows the parasite to resist inside the intermediate host indefinitely, it remains an active structure with replicating parasites [175]. Bradyzoites containing PVs (tissue cysts) present structural differences to tachyzoites containing PVs; however, both are intracellular structures fully enclosed by the host cell membrane [79,102]. Early tissue cysts present a very close-fit membrane and numerous invaginations, with a shallow, irregular pattern and ruffled appearance [79,176]. The tubule–vesicle network present in tachyzoite PVs is absent in early tissue cysts, which instead present a thin layer of an amorphous material [79]. Mature tissue cysts present a thick wall ranging from 270–850 µm, with deep invaginations of the PM into the underlying granular material [79,177]. The tissue cyst wall is formed from the PV membrane and is rich in glycoproteins, binding the Dolichos biflorus agglutinin (DBA) and succinylated wheat germ agglutinin lectins [178]. Although bradyzoite markers are detected early in immature tissue cysts, the bradyzoite specific structure is only observed three to four weeks after tissue cyst formation [79].
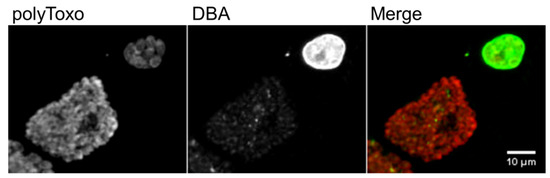
Figure 7.
Tachyzoite parasitophorous vacuoles and tissue cysts. Each panel shows tachyzoite parasitophorous vacuoles, stained only with polyclonal antisera against T. gondii surface proteins (polyToxo), and tissue cysts, stained with polyToxo and with Dolichos biflorus agglutinin (DBA) lectin which binds to the tissue cyst wall. The tissue cysts were formed spontaneously in an in vitro culture of T. gondii EGS strain [179,180] invading confluent HFF cells. The scale bar represents 10 µm.
The transition from tachyzoite to bradyzoite is an early event, and it is possible to identify immature tissue cysts containing only one or two zoites [38,79,176]. Evidence indicates that the tachyzoite–bradyzoite transition occurs upon host cell invasion or immediately afterwards [79,176]. Bradyzoite-specific markers are detected within 24 h of bradyzoite differentiation [181]. The triggers for tachyzoite–bradyzoite interconversion are not fully understood. In vitro studies show that tachyzoites and bradyzoites both spontaneously interconvert stages [103,176,182,183,184]. Tachyzoite replication rate and exposure to stress influence the rate of tachyzoite to bradyzoite conversion. The exposure of tachyzoites to exogenous stress factors may induce or enhance tachyzoite–bradyzoite conversion in vitro; treatment with acidic or alkaline pH, heat shock, and sodium arsenic or immunity modulators (IFNγ, IL-6, nitric oxide, lipopolysaccharide) have been shown to influence tachyzoite to bradyzoite conversion [183,184,185,186]. Depletion of nutrients such as arginine and cholesterol can induce tissue cyst formation [187,188]. Treatment with several different drugs can enhance tissue cyst formation, e.g., pyrimethamine, aphidicolin, atovaquone, myxothiazol, and rotenone [186,189]. Stress response signaling pathways participate in the regulation of the cell cycle and bradyzoite differentiation. Inhibition of cAMP and cGMP dependent protein kinases, modules of conserved cyclic nucleotide signaling pathways shown to participate in stress response and differentiation in other organisms, results in reduced replication and induction of bradyzoite differentiation in T. gondii [190,191]. Phosphorylation of the stress response protein eukaryotic initiation factor-2 (eIF2) is increased in tachyzoites following treatment with alkaline medium or heat shock [192]. Gene regulation through histone-mediated chromatin remodeling and epigenetic signaling are involved in tachyzoite–bradyzoite conversion as well [193,194]. Accordingly, the T. gondii transcriptome shows clear stage-specific mRNAs which are altered between virulent and avirulent strains coherently with its tissue cyst-forming abilities [195]. Metacaspases are a group of cysteine proteases conserved in plants, fungi, and protozoans which are involved in stress response, programmed cell death, and cell proliferation. The T. gondii metacaspase 2 is necessary for tissue cyst formation in vitro [196]. Transcription factors have been implicated as key components in tachyzoite–bradyzoite conversion, namely Bradyzoite-formation deficient 1 (BFD1) and various Apicomplexa Apetala-2 (ApiAP2) transcription factors [197,198,199,200]. Although bradyzoite to tachyzoite conversion is less understood, the balance of stage-specific ApiAP2 transcription factor seems to control this process [201]. Stage conversion appears to be intimately connected to cell cycle regulation, with bradyzoites presenting higher enrichment in S/M phase-associated genes compared to tachyzoites, which present higher enrichment in G1 phase-associated genes and are more likely to be in S/M phase when bradyzoite differentiation is triggered [174,202]. Furthermore, the T. gondii transcriptome presents a significantly cyclical profile, with several bradyzoite-specific transcripts peaking at late M phase and blocking the cell cycle, thereby preventing tachyzoite–bradyzoite conversion [154,203].
9. Conclusions and Prospects
T. gondii shifts between several cellular stages during its life cycle, going through its sexual cycle in the felid intestinal epithelium. When invading a host, T. gondii tachyzoites divide inside a parasitophorous vacuole produced by the parasite. Bradyzoites divide at a slower rate inside of tissue cysts, a more permanent structure requiring more control of parasite numbers. The ability to develop resistant structures in the form of cysts in the tissues of intermediate hosts is one of the key features of the T. gondii life cycle. The regulation of replication and tachyzoite–bradyzoite differentiation appear to be connected, as slower replication is associated with increased development of tissue cysts. This interconversion ability is dependent on cell cycle regulation and involves, among other events, regulation of cell proliferation and differentiation. Future research efforts continuing to focus on the mechanisms that regulate these events coupled to the emerging use of high throughput transcriptomic and proteomic technologies are likely to produce valuable knowledge on the development of novel therapeutic and prophylactic options for the control of T. gondii infections.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.L.S.D., A.L., S.N.; investigation, I.L.S.D., S.Z., D.S., A.P.B., S.N.; visualization, I.L.S.D.; supervision, A.L., S.N.; writing—original draft preparation, I.L.S.D.; writing—review and editing, I.L.S.D., S.Z., D.S., A.P.B., S.N.; funding acquisition, I.L.S.D., D.S., A.L., S.N. All images are originals. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by national funds through FCT-Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia, I.P. (Portugal) through the project UIDB/00276/2020, the grant EXPL/CVT-EPI/1945/2013 awarded to S.N., and the doctoral scholarship SFRH/BD/95330/2013 awarded to I.L.S.D., S.Z. and A.P.B. were supported by the project FCT-Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia, I.P. (Portugal)—PTDC/CVT-CVT/31840/2017.
Acknowledgments
We thank Markus Meissner (Institute for Experimental Parasitology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität Munich) for the RHΔHx T. gondii strain. We thank Marc-Jan Gubbels (Department of Biology, Boston College, USA) for the pmorn1-Morn1-Myc-Cat vector. We thank Boris Striepen (University of Pennsylvania School of Veterinary Medicine, USA) for the anti-CenH3 antibody. We thank Érica Martins-Duarte (Departamento de Parasitologia, Instituto de Ciências Biológicas, Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais, Brazil) for the EGS strain.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Entry Link on the Encyclopedia Platform
References
- Jiménez-Ruiz, E.; Wong, E.H.; Pall, G.S.; Meissner, M. Advantages and disadvantages of conditional systems for characterization of essential genes in Toxoplasma gondii. Parasitology 2014, 141, 1390–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolle, C.; Manceaux, L. Sur Une Infection à Corps de Leishman (Ou Organismes Voisins) Du Gondi. Comptes Rendus Séances L’académie Sci. 1908, 147, 763–766. [Google Scholar]
- Splendore, A. Un Nuovo Protozoa Parassita de’ Conigli. Rev. Soc. Sci. 1908, 3, 109–112. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolle, C.; Manceaux, L. Sur Un Protozoaire Nouveau Du Gondi. Comptes Rendus Séances L’académie Sci. 1909, 148, 369–372. [Google Scholar]
- McLeod, R.; Van Tubbergen, C.; Montoya, J.G.; Petersen, E. Human Toxoplasma Infection, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; ISBN 9780123964816. [Google Scholar]
- Stelzer, S.; Basso, W.; Silván, J.B.; Ortega-Mora, L.-M.; Maksimov, P.; Gethmann, J.; Conraths, F.; Schares, G. Toxoplasma gondii infection and toxoplasmosis in farm animals: Risk factors and economic impact. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2019, 15, e00037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, M.W.; Boothroyd, J.C. Lytic Cycle of Toxoplasma Gondii. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2000, 64, 607–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguirre, A.A.; Longcore, T.; Barbieri, M.; Dabritz, H.; Hill, D.; Klein, P.N.; Lepczyk, C.; Lilly, E.L. The one health approach to toxoplasmosis: Epidemiology, Control, and Prevention Strategies. Ecohealth 2019, 16, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-L.; Zhang, N.-Z.; Li, T.-T.; He, J.-J.; Elsheikha, H.M.; Zhu, X.-Q. Advances in the development of Anti-Toxoplasma Gondii Vaccines: Challenges, opportunities, and perspectives. Trends Parasitol. 2019, 35, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Malaria Report 2020: 20 Years of Global Progress and Challenges; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020; Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
- Gray, J.; Zintl, A.; Hildebrandt, A.; Hunfeld, K.P.; Weiss, L. Zoonotic babesiosis: Overview of the disease and novel aspects of pathogen identity. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2010, 1, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beugnet, F.; Moreau, Y. Babesiosis. OIE Rev. Sci. Tech. 2015, 34, 627–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzipori, S.; Ward, H. Cryptosporidiosis: Biology, pathogenesis and disease. Microbes Infect. 2002, 4, 1047–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichel, M.P.; Alejandra Ayanegui-Alcérreca, M.; Gondim, L.F.P.; Ellis, J.T. What is the global economic impact of neospora caninum in cattle-The Billion Dollar Question. Int. J. Parasitol. 2013, 43, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez-García, G.; García-Lunar, P.; Gutiérrez-Expósito, D.; Shkap, V.; Ortega-Mora, L.M. Dynamics of Besnoitia Besnoiti infection in cattle. Parasitology 2014, 141, 1419–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert-Gangneux, F.; Dardé, M.L. Epidemiology of and diagnostic strategies for toxoplasmosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 25, 264–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parise, M.E.; Hotez, P.J.; Slutsker, L. Neglected parasitic infections in the United States: Needs and opportunities. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2014, 90, 783–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Congenital toxoplasmosis. In ECDC. Annual Epidemiological Report for 2018; ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Flegr, J.; Prandota, J.; Sovičková, M.; Israili, Z.H. Toxoplasmosis-A global threat. Correlation of latent toxoplasmosis with specific disease burden in a set of 88 countries. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.D.; Frenkel, J.K. Prevalence of antibodies to toxoplasma gondii in wild mammals of missouri and east central kansas: Biologic and ecologic considerations of transmission. J. Wildl. Dis. 1995, 31, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Thoisy, B.; Demar, M.; Aznar, C.; Carme, B. Ecological Correlates of Toxoplasma Gondii Exposure in Free-Ranging Neotropical Mammals. J. Wildl. Dis. 2003, 39, 456–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabritz, H.A.; Miller, M.A.; Gardner, I.A.; Packham, A.E.; Atwill, E.R.; Conrad, P.A. Risk factors for Toxoplasma Gondii Infection in Wild Rodents from Central Coastal California and a review of T. Gondii Prevalence in Rodents. J. Parasitol. 2008, 94, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, M.; Cabezón, O.; Dubey, J.P.; Almería, S.; Ribas, M.P.; Escobar, L.E.; Ramos, B.; Medina-Vogel, G. Toxoplasma Gondii Infection in Wild Mustelids and Cats across an Urban-Rural Gradient. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Murata, F.H.A.; Cerqueira-Cézar, C.K.; Kwok, O.C.H. Public health and economic importance of Toxoplasma Gondii Infections in Goats: The Last Decade. Res. Vet. Sci. 2020, 132, 292–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Murata, F.H.A.; Cerqueira-Cézar, C.K.; Kwok, O.C.H. Toxoplasma Gondii Infections in Horses, Donkeys, and Other Equids: The Last Decade. Res. Vet. Sci. 2020, 132, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P.; Murata, F.H.A.; Cerqueira-Cézar, C.K.; Kwok, O.C.H.; Yang, Y.R. Public Health Significance of Toxoplasma Gondii Infections in Cattle: 2009–2020. J. Parasitol. 2020, 106, 772–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montazeri, M.; Mikaeili Galeh, T.; Moosazadeh, M.; Sarvi, S.; Dodangeh, S.; Javidnia, J.; Sharif, M.; Daryani, A. The Global Serological Prevalence of Toxoplasma Gondii in Felids during the Last Five Decades (1967–2017): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, K.; Bahia-Oliveira, L.; Dixon, B.; Dumètre, A.; de Wit, L.A.; VanWormer, E.; Villena, I. Environmental Transmission of Toxoplasma Gondii: Oocysts in Water, Soil and Food. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2019, 15, e00049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maleki, B.; Ahmadi, N.; Olfatifar, M.; Gorgipour, M.; Taghipour, A.; Abdoli, A.; Khorshidi, A.; Foroutan, M.; Mirzapour, A. Toxoplasma Oocysts in the Soil of Public Places Worldwide: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2021, 115, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moré, G.; Maksimov, P.; Pardini, L.; Herrmann, D.C.; Bacigalupe, D.; Maksimov, A.; Basso, W.; Conraths, F.J.; Schares, G.; Venturini, M.C. Toxoplasma Gondii Infection in Sentinel and Free-Range Chickens from Argentina. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 184, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Dubey, J.P.; Hill, D.; Buchanan, R.L.; Ray Gamble, H.; Jones, J.L.; Pradhan, A.K. Prevalence and Risk Factors for Toxoplasma Gondii Infection in Meat Animals and Meat Products Destined for Human Consumption. J. Food Prot. 2015, 78, 457–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Frenkel, J.K. Immunity to Feline Toxoplasmosis: Modification by Administration of Corticosteroids. Vet. Pathol. 1974, 11, 350–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapperud, G.; Jenum, P.A.; Stray-Pedersen, B.; Melby, K.K.; Eskild, A.; Eng, J. Risk Factors for Toxoplasma Gondii Infection in Pregnancy: Results of a Prospective Case-Control Study in Norway. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1996, 144, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, A.J.; Gilbert, R.E.; Buffolano, W.; Zufferey, J.; Petersen, E.; Jenum, P.A.; Foulon, W.; Semprini, A.E.; Dunn, D.T. Sources of Toxoplasma Infection in Pregnant Women: European Multicentre Case-Control Study. European Research Network on Congenital Toxoplasmosis. BMJ 2000, 321, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, F.; Goulet, V.; Le Strat, Y.; Desenclos, J.C. Toxoplasmosis among Pregnant Women in France: Risk Factors and Change of Prevalence between 1995 and 2003. Rev. Epidemiol. Sante Publique 2009, 57, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.L.; Dargelas, V.; Roberts, J.; Press, C.; Remington, J.S.; Montoya, J.G. Risk Factors for Toxoplasma Gondii Infection in the United States. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 49, 878–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, C.; Maier, S.; Walker, R.A.; Rehrauer, H.; Joekel, D.E.; Winiger, R.R.; Basso, W.U.; Grigg, M.E.; Hehl, A.B.; Deplazes, P.; et al. An Experimental Genetically Attenuated Live Vaccine to Prevent Transmission of Toxoplasma Gondii by Cats. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P. Advances in the Life Cycle of Toxoplasma Gondii. Int. J. Parasitol. 1998, 28, 1019–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kean, B.H.; Kimball, A.C.; Christenson, W.N. An Epidemic of Acute Toxoplasmosis. JAMA 1969, 208, 1002–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desmonts, G.; Couvreur, J.; Alison, F.; Baudelot, J.; Gerbeaux, J.; Lelong, M. Étude Épidémiologique Sur La Toxoplasmose: De l’influence de La Cuisson Des Viandes de Boucherie Sur La Fréquence de l’infection Humaine. Rev. Fr. Études Clin. Biol. 1965, 10, 952–958. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, D.; Coss, C.; Dubey, J.P.; Wroblewski, K.; Sautter, M.; Hosten, T.; Muñoz-Zanzi, C.; Mui, E.; Withers, S.; Boyer, K.; et al. Identification of a Sporozoite-Specific Antigen from Toxoplasma Gondii. J. Parasitol. 2011, 97, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasmosis in Sheep-The Last 20 Years. Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 163, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryning, F.W.; McLeod, R.; Maddox, J.C.; Hunt, S.; Remington, J.S. Probable Transmission of Toxoplasma Gondii by Organ Transplantation. Ann. Intern. Med. 1979, 90, 47–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacks, J.J.; Roberto, R.R.; Brooks, N.F. Toxoplasmosis Infection Associated With Raw Goat’s Milk. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1982, 248, 1728–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernàndez-Sabé, N.; Cervera, C.; Fariñas, M.C.; Bodro, M.; Muñoz, P.; Gurguí, M.; Torre-Cisneros, J.; Martín-Dávila, P.; Noblejas, A.; Len, Ó.; et al. Risk Factors, Clinical Features, and Outcomes of Toxoplasmosis in Solid-Organ Transplant Recipients: A Matched Case-Control Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 54, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Verma, S.K.; Ferreira, L.R.; Oliveira, S.; Cassinelli, A.B.; Ying, Y.; Kwok, O.C.H.; Tuo, W.; Chiesa, O.A.; Jones, J.L. Detection and Survival of Toxoplasma Gondii in Milk and Cheese from Experimentally Infected Goats. J. Food Prot. 2014, 77, 1747–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milne, G.; Webster, J.P.; Walker, M. Toxoplasma Gondii: An Underestimated Threat? Trends Parasitol. 2020, 36, 959–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, J.G.; Liesenfeld, O. Toxoplasmosis. Lancet 2004, 363, 1965–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calero-Berna, R.; Gennari, S.M. Clinical Toxoplasmosis in Dogs and Cats: An Update. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunay, I.R.; Gajurel, K.; Dhakal, R.; Liesenfeld, O.; Montoya, J.G. Treatment of Toxoplasmosis: Historical Perspective, Animal. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 31, 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- McPhillie, M.J.; Zhou, Y.; Hickman, M.R.; Gordon, J.A.; Weber, C.R.; Li, Q.; Lee, P.J.; Amporndanai, K.; Johnson, R.M.; Darby, H.; et al. Potent Tetrahydroquinolone Eliminates Apicomplexan Parasites. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandão, G.P.; Melo, M.N.; Caetano, B.C.; Carneiro, C.M.; Silva, L.A.; Vitor, R.W.A. Susceptibility to Re-Infection in C57BL/6 Mice with Recombinant Strains of Toxoplasma Gondii. Exp. Parasitol. 2011, 128, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, D.S.; Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasma Gondii: The Changing Paradigm of Congenital Toxoplasmosis. Parasitology 2011, 138, 1829–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulpo, D.L.; Sammi, A.S.; dos Santos, J.R.; Sasse, J.P.; Martins, T.A.; Minutti, A.F.; Cardim, S.T.; de Barros, L.D.; Navarro, I.T.; Garcia, J.L. Toxoplasma Gondii: A Study of Oocyst Re-Shedding in Domestic Cats. Vet. Parasitol. 2018, 249, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaga, R.; Aubert, D.; Thébault, A.; Perret, C.; Geers, R.; Thomas, M.; Alliot, A.; Djokic, V.; Ortis, N.; Halos, L.; et al. Toxoplasma Gondii in Beef Consumed in France: Regional Variation in Seroprevalence and Parasite Isolation. Parasite 2019, 26, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, B.F.; Oliveira, S.; Soares, H.S.; Pena, H.F.J.; Conte-Junior, C.A.; Gennari, S.M. Isolation of Viable Toxoplasma Gondii from Organs and Brazilian Commercial Meat Cuts of Experimentally Infected Pigs. Parasitol. Res. 2019, 118, 1331–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P.; Cerqueira-Cézar, C.K.; Murata, F.H.A.; Kwok, O.C.H.; Hill, D.; Yang, Y.; Su, C. All about Toxoplasma Gondii Infections in Pigs: 2009–2020. Vet. Parasitol. 2020, 288, 109185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasma Gondii Infections in Chickens (Gallus Domesticus): Prevalence, Clinical Disease, Diagnosis and Public Health Significance. Zoonoses Public Health 2010, 57, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conrad, P.A.; Miller, M.A.; Kreuder, C.; James, E.R.; Mazet, J.; Dabritz, H.; Jessup, D.A.; Gulland, F.; Grigg, M.E. Transmission of Toxoplasma: Clues from the Study of Sea Otters as Sentinels of Toxoplasma Gondii Flow into the Marine Environment. Int. J. Parasitol. 2005, 35, 1155–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, T.L.; Tinker, M.T.; Miller, M.A.; Bodkin, J.L.; Murray, M.J.; Saarinen, J.A.; Nichol, L.M.; Larson, S.; Conrad, P.A.; Johnson, C.K. Defining the Risk Landscape in the Context of Pathogen Pollution: Toxoplasma Gondii in Sea Otters along the Pacific Rim. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2018, 5, 171178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, K.; VanWormer, E.; Packham, A.; Dodd, E.; Conrad, P.A.; Miller, M. Type X Strains of Toxoplasma Gondii Are Virulent for Southern Sea Otters (Enhydra Lutris Nereis) and Present in Felids from Nearby Watersheds. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2019, 286, 20191334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frénal, K.; Dubremetz, J.F.; Lebrun, M.; Soldati-Favre, D. Gliding Motility Powers Invasion and Egress in Apicomplexa. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 645–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFadden, G.I.; Yeh, E. The Apicoplast: Now You See It, Now You Don’t. Int. J. Parasitol. 2017, 47, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, G.; Dorrell, R.G.; Schlacht, A.; Dacks, J.B. Eukaryotic Systematics: A User’s Guide for Cell Biologists and Parasitologists. Parasitology 2011, 138, 1638–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šlapeta, J.; Morin-Adeline, V. Apicomplexa Levine 1970, Sporozoa Leucart. 1879. Available online: http://tolweb.org/Apicomplexa/2446/2011.05.18 (accessed on 1 December 2021).
- Koreny, L.; Zeeshan, M.; Barylyuk, K.; Tromer, E.C.; van Hooff, J.J.E.; Brady, D.; Ke, H.; Chelaghma, S.; Ferguson, D.J.P.; Eme, L.; et al. Molecular Characterization of the Conoid Complex in Toxoplasma Reveals Its Conservation in All Apicomplexans, Including Plasmodium Species. PLoS Biol. 2021, 19, e3001081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalier-Smith, T. Kingdom Protozoa and Its 18 Phyla. Microbiol. Rev. 1993, 57, 953–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalier-Smith, T. A Revised Six-Kingdom System of Life. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 1998, 73, 203–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, M.A.; Coop, R.L.; Wall, R.L. Veterinary Parasitology; Wiley-Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2016; ISBN 978-0-470-67162-7. [Google Scholar]
- Ruggiero, M.A.; Gordon, D.P.; Orrell, T.M.; Bailly, N.; Bourgoin, T.; Brusca, R.C.; Cavalier-Smith, T.; Guiry, M.D.; Kirk, P.M. A Higher Level Classification of All Living Organisms. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, T.; Vandepitte, L.; Vanhoorne, B.; Decock, W. All Genera of the World: An Overview and Estimates Based on the March 2020 Release of the Interim Register of Marine and Nonmarine Genera (IRMNG). Megataxa 2020, 1, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, D.K.; Sibley, L.D. Toxoplasma Gondii Comprises Three Clonal Lineages: Correlation of Parasite Genotype with Human Disease. J. Infect. Dis. 1995, 172, 1561–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Evans, D.; Cole, R.H.; Kissinger, J.C.; Ajioka, J.W.; Sibley, L.D. Recent Expansion of Toxoplasma through Enhanced Oral Transmission. Science 2003, 299, 414–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; Fux, B.; Su, C.; Dubey, J.P.; Darde, M.L.; Ajioka, J.W.; Rosenthal, B.M.; Sibley, L.D. Recent Transcontinental Sweep of Toxoplasma Gondii Driven by a Single Monomorphic Chromosome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 14872–14877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena, H.F.J.; Marvulo, M.F.V.; Horta, M.C.; Silva, M.A.; Silva, J.C.R.; Siqueira, D.B.; Lima, P.A.C.P.; Vitaliano, S.N.; Gennari, S.M. Isolation and Genetic Characterisation of Toxoplasma Gondii from a Red-Handed Howler Monkey (Alouatta Belzebul), a Jaguarundi (Puma Yagouaroundi), and a Black-Eared Opossum (Didelphis Aurita) from Brazil. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 175, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fux, B.; Nawas, J.; Khan, A.; Gill, D.B.; Su, C.; Sibley, L.D. Toxoplasma Gondii Strains Defective in Oral Transmission Are Also Defective in Developmental Stage Differentiation. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 2580–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercier, A.; Ajzenberg, D.; Devillard, S.; Demar, M.P.; de Thoisy, B.; Bonnabau, H.; Collinet, F.; Boukhari, R.; Blanchet, D.; Simon, S.; et al. Human Impact on Genetic Diversity of Toxoplasma Gondii: Example of the Anthropized Environment from French Guiana. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2011, 11, 1378–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Ajzenberg, D.; Mercier, A.; Demar, M.; Simon, S.; Dardé, M.L.; Wang, Q.; Verma, S.K.; Rosenthal, B.M.; Dubey, J.P.; et al. Geographic Separation of Domestic and Wild Strains of Toxoplasma Gondii in French Guiana Correlates with a Monomorphic Version of Chromosome1a. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, D.J.P.; Dubremetz, J.-F. The Ultrastructure of Toxoplasma gondii. In Toxoplasma Gondii; Weiss, L.M., Kim, K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 19–59. ISBN 9780123964816. [Google Scholar]
- Harding, C.R.; Frischknecht, F. The Riveting Cellular Structures of Apicomplexan Parasites. Trends Parasitol. 2020, 36, 979–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attias, M.; Teixeira, D.E.; Benchimol, M.; Vommaro, R.C.; Crepaldi, P.H.; De Souza, W. The Life-Cycle of Toxoplasma Gondii Reviewed Using Animations. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, E.J.L.; Attias, M.; De Souza, W. The Single Mitochondrion of Tachyzoites of Toxoplasma Gondii. J. Struct. Biol. 2000, 130, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Striepen, B.; Crawford, M.J.; Shaw, M.K.; Tilney, L.G.; Seeber, F.; Roos, D.S. The Plastid of Toxoplasma Gondii Is Divided by Association with the Centrosomes. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 151, 1423–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.T.; Gubbels, M.J. The Toxoplasma Gondii Centrosome Is the Platform for Internal Daughter Budding as Revealed by a Nek1 Kinase Mutant. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126, 3344–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, C.F.; Johnsen, H.; van Dooren, G.G.; Muthalagi, M.; Lin, S.S.; Bohne, W.; Fischer, K.; Striepen, B. The Toxoplasma Apicoplast Phosphate Translocator Links Cytosolic and Apicoplast Metabolism and Is Essential for Parasite Survival. Cell Host Microbe 2010, 7, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janouškovec, J.; Horák, A.; Oborník, M.; Lukeš, J.; Keeling, P.J. A Common Red Algal Origin of the Apicomplexan, Dinoflagellate, and Heterokont Plastids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 10949–10954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joiner, K.A.; Roos, D.S. Secretory Traffic in the Eukaryotic Parasite Toxoplasma Gondii: Less Is More. J. Cell Biol. 2002, 157, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebrun, M.; Carruthers, V.B.; Cesbron-Delauw, M.-F. Toxoplasma Secretory Proteins and Their Roles in Cell Invasion and Intracellular Survival. In Toxoplasma Gondii; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 389–453. ISBN 9780123964816. [Google Scholar]
- Kentaro, K. How Does Toxoplama Gondii Invade Host Cells? J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2018, 80, 1702–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Lindsay, D.S.; Speer, C.A. Structures of Toxoplasma Gondii Tachyzoites, Bradyzoites, and Sporozoites and Biology and Development of Tissue Cysts. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1998, 11, 267–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, D.G.; Burns, R.G. The Polar Ring of Coccidian Sporozoites: A Unique Microtubule-Organizing Centre. J. Cell Sci. 1984, 65, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nichols, B.A.; Chiappino, M.L. Cytoskeleton of Toxoplasma Gondii 1. J. Protozool. 1987, 34, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrissette, N.S.; Sibley, L.D. Cytoskeleton of Apicomplexan Parasites. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2002, 66, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Johnson, J.; Florens, L.; Fraunholz, M.; Suravajjala, S.; DiLullo, C.; Yates, J.; Roos, D.S.; Murray, J.M. Cytoskeletal Components of an Invasion Machine-The Apical Complex of Toxoplasma Gondii. PLoS Pathog. 2006, 2, e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katris, N.J.; van Dooren, G.G.; McMillan, P.J.; Hanssen, E.; Tilley, L.; Waller, R.F. The Apical Complex Provides a Regulated Gateway for Secretion of Invasion Factors in Toxoplasma. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, T.; Beckers, C. Characterization of the Subpellicular Network, a Filamentous Membrane Skeletal Component in the Parasite Toxoplasma Gondii. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2001, 115, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K. Organizational Changes of the Daughter Basal Complex during the Parasite Replication of Toxoplasma Gondii. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delbac, F.; Sänger, A.; Neuhaus, E.M.; Stratmann, R.; Ajioka, J.W.; Toursel, C.; Herm-Götz, A.; Tomavo, S.; Soldati, T.; Soldati, D. Toxoplasma Gondii Myosins B/C: One Gene, Two Tails, Two Localizations, and a Role in Parasite Division. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 155, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gubbels, M.-J.; Vaishnava, S.; Boot, N.; Dubremetz, J.-F.; Striepen, B. A MORN-Repeat Protein Is a Dynamic Component of the Toxoplasma Gondii Cell Division Apparatus. J. Cell Sci. 2006, 119, 2236–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heaslip, A.T.; Dzierszinski, F.; Stein, B.; Hu, K. TgMORN1 Is a Key Organizer for the Basal Complex of Toxoplasma Gondii. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorestani, A.; Ivey, F.D.; Thirugnanam, S.; Busby, M.A.; Marth, G.T.; Cheeseman, I.M.; Gubbels, M.-J. Targeted Proteomic Dissection of Toxoplasma Cytoskeleton Sub-Compartments Using MORN1. Cytoskeleton 2012, 69, 1069–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoll, L.J.; Tomita, T.; Weiss, L.M. Bradyzoite Development. In Toxoplasma Gondii; Weiss, L.M., Kim, K., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 521–549. ISBN 9780123964816. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs, L.; Remington, J.S.; Melton, M.L. The Resistance of the Encysted Form of Toxoplasma Gondii. J. Parasitol. 1960, 46, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popiel, I.; Gold, M.C.; Booth, K.S. Quantification of Toxoplasma Gondii Bradyzoites. J. Parasitol. 1996, 82, 330–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Genova, B.M.; Wilson, S.K.; Dubey, J.P.; Knoll, L.J. Intestinal Delta-6-Desaturase Activity Determines Host Range for Toxoplasma Sexual Reproduction. PLoS Biol. 2019, 17, e3000364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freyre, A.; Dubey, J.P.; Smith, D.D.; Frenkel, J.K. Gondii Oocyst-Induced Infections. J. Parasitol. 1989, 75, 750–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P. Oocyst Shedding by Cats Fed Isolated Bradyzoites and Comparison of Infectivity of Bradyzoites of the VEG Strain Toxoplasma Gondii to Cats and Mice. J. Parasitol. 2001, 87, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P. Comparative Infectivity of Oocysts and Bradyzoites of Toxoplasma Gondii for Intermediate (Mice) and Definitive (Cats) Hosts. Vet. Parasitol. 2006, 140, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasina, R.; Francia, M.E. The Structural and Molecular Underpinnings of Gametogenesis in Toxoplasma Gondii. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Frenkel, J.K. Cyst-Induced Toxoplasmosis in Cats. J. Protozool. 1972, 19, 155–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speer, C.A.; Dubey, J.P. Ultrastructural Differentiation of Toxoplasma Gondii Schizonts (Types B to E) and Gamonts in the Intestines of Cats Fed Bradyzoites. Int. J. Parasitol. 2005, 35, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francia, M.E.; Striepen, B. Cell Division in Apicomplexan Parasites. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P. Duration of Immunity to Shedding of Toxoplasma Gondii Oocysts by Cats. J. Parasitol. 1995, 81, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritz, H.M.; Bowyer, P.W.; Bogyo, M.; Conrad, P.A.; Boothroyd, J.C. Proteomic Analysis of Fractionated Toxoplasma Oocysts Reveals Clues to Their Environmental Resistance. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, D.J.P. Toxoplasma Gondii and Sex: Essential or Optional Extra? Trends Parasitol. 2002, 18, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P. Pathogenicity and Infectivity of Toxoplasma Gondii Oocysts for Rats. J. Parasitol. 1996, 82, 951–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, R.; Harrison, B.; Dangoudoubiyam, S.; Bandini, G.; Cheng, K.; Kosber, A.; Agop-nersesian, C.; Howe, D.K.; Samuelson, J.; Ferguson, D.J.P.; et al. Differential Roles for Inner Membrane Complex Proteins across Toxoplasma Gondii and Sarcocystis Neurona Development. mSphere 2017, 2, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freppel, W.; Ferguson, D.J.P.; Shapiro, K.; Dubey, J.P.; Puech, P.H.; Dumètre, A. Structure, Composition, and Roles of the Toxoplasma Gondii Oocyst and Sporocyst Walls. Cell Surf. 2019, 5, 100016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, C.A. Cell Motility of Sporozoan Protozoa. Parasitol. Today 1988, 4, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Håkansson, S.; Morisaki, H.; Heuser, J.; Sibley, L.D. Time-Lapse Video Microscopy of Gliding Motility in Toxoplasma Gondii Reveals a Novel, Biphasic Mechanism of Cell Locomotion. Mol. Biol. Cell 1999, 10, 3539–3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrowolski, J.M.; Sibley, L.D. Toxoplasma Invasion of Mammalian Cells Is Powered by the Actin Cytoskeleton of the Parasite. Cell 1996, 84, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrowolski, J.M.; Carruthers, V.B.; Sibley, L.D. Participation of Myosin in Gliding Motility and Host Cell Invasion by Toxoplasma Gondii. Mol. Microbiol. 1997, 26, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meissner, M.; Schlüter, D.; Soldati, D. Role of Toxoplasma Gondii Myosin a in Powering Parasite Gliding and Host Cell Invasion. Science 2002, 298, 837–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opitz, C.; Soldati, D. “The Glideosome”: A Dynamic Complex Powering Gliding Motion and Host Cell Invasion by Toxoplasma Gondii. Mol. Microbiol. 2002, 45, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brossier, F.; Jewett, T.J.; Lovett, J.L.; Sibley, L.D. C-Terminal Processing of the Toxoplasma Protein MIC2 Is Essential for Invasion into Host Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 6229–6234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gras, S.; Jimenez-Ruiz, E.; Klinger, C.M.; Schneider, K.; Klingl, A.; Lemgruber, L.; Meissner, M. An Endocytic-Secretory Cycle Participates in Toxoplasma Gondii in Motility. PLoS Biol. 2019, 17, e3000060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldati, D.; Meissner, M. Toxoplasma as a Novel System for Motility. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2004, 16, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mineo, J.R.; Kasper, L.H. Attachment of Toxoplasma Gondii to Host Cells Involves Major Surface Protein, SAG-1 (P-30). Exp. Parasitol. 1994, 79, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquet, A.; Coulon, L.; De Nève, J.; Daminet, V.; Haumont, M.; Garcia, L.; Bollen, A.; Jurado, M.; Biemans, R. The Surface Antigen SAG3 Mediates the Attachment of Toxoplasma Gondii to Cell-Surface Proteoglycans. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2001, 116, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabenau, K.E.; Sohrabi, A.; Tripathy, A.; Reitter, C.; Ajioka, J.W.; Tomley, F.M.; Carruthers, V.B. TgM2AP Participates in Toxoplasma Gondii Invasion of Host Cells and Is Tightly Associated with the Adhesive Protein TgMIC2. Mol. Microbiol. 2001, 41, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cérède, O.; Dubremetz, J.F.; Soête, M.; Deslée, D.; Vial, H.; Bout, D.; Lebrun, M. Synergistic Role of Micronemal Proteins in Toxoplasma Gondii Virulence. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 201, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitelaw, J.A.; Latorre-Barragan, F.; Gras, S.; Pall, G.S.; Leung, J.M.; Heaslip, A.; Egarter, S.; Andenmatten, N.; Nelson, S.R.; Warshaw, D.M.; et al. Surface Attachment, Promoted by the Actomyosin System of Toxoplasma Gondii Is Important for Efficient Gliding Motility and Invasion. BMC Biol. 2017, 15, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, D.L.; Mital, J.; Ward, G.E.; Bradley, P.; Boothroyd, J.C. Identification of the Moving Junction Complex of Toxoplasma Gondii: A Collaboration between Distinct Secretory Organelles. PLoS Pathog. 2005, 1, e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carruthers, V.; Boothroyd, J.C. Pulling Together: An Integrated Model of Toxoplasma Cell Invasion. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2007, 10, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mordue, D.G.; Desai, N.; Dustin, M.; Sibley, L.D. Proteins on the Basis of Their Membrane Anchoring. J. Exp. Med 1999, 190, 1783–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charron, A.J.; Sibley, L.D. Molecular Partitioning during Host Cell Penetration by Toxoplasma Gondii. Traffic 2004, 5, 855–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, M.E.; Hjort, E.E.; Smith, S.S.; Tripathi, A.; Hornick, J.E.; Hinchcliffe, E.H.; Archer, W.; Hager, K.M. Toxoplasma Gondii Actively Remodels the Microtubule Network in Host Cells. Microbes Infect. 2008, 10, 1440–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweeney, K.R.; Morrissette, N.S.; Lachapelle, S.; Blader, I.J. Host Cell Invasion by Toxoplasma Gondii Is Temporally Regulated by the Host Microtubule Cytoskeleton. Eukaryot. Cell 2010, 9, 1680–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, R.; Nolasco, S.; Goncalves, J.; Cortes, H.C.; Leitao, A.; Soares, H. Besnoitia Besnoiti and Toxoplasma Gondii: Two Apicomplexan Strategies to Manipulate the Host Cell Centrosome and Golgi Apparatus. Parasitology 2014, 141, 1436–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sibley, L.D.; Niesman, I.R.; Parmley, S.F.; Cesbron-Delauw, M.F. Regulated Secretion of Multi-Lamellar Vesicles Leads to Formation of a Tubulovesicular Network in Host-Cell Vacuoles Occupied by Toxoplasma Gondii. J. Cell Sci. 1995, 108, 1669–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercier, C.; Dubremetz, J.-F.; Rauscher, B.; Lecordier, L.; Sibley, L.D.; Cesbron-Delauw, M.-F. Biogenesis of Nanotubular Network in Toxoplasma Parasitophorous Vacuole Induced by Parasite Proteins. Mol. Biol. Cell 2002, 13, 2397–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Melo, E.J.T.; de Carvalho, T.U.; de Souza, W. Penetration of Toxoplasma Gondii into Host Cells Induces Changes in the Distribution of the Mitochondria and the Endoplasmic Reticulum. Cell Struct. Funct. 1992, 17, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Melo, E.J.T.; De Souza, W. Relationship between the Host Cell Endoplasmic Reticulum and the Parasitophorous Vacuole Containing Toxoplasma Gondii. Cell Struct. Funct. 1997, 22, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sinai, A.P.; Webster, P.; Joiner, K.A. Association of Host Cell Endoplasmic Reticulum and Mitochondria with the Toxoplasma Gondii Parasitophorous Vacuole Membrane: A High Affinity Interaction. J. Cell Sci. 1997, 110, 2117–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, E.J.T.; Carvalho, T.M.U.; de Souza, W. Behaviour of Microtubules in Cells Infected with Toxoplasma Gondii. Biocell 2001, 25, 53–59. [Google Scholar]
- Sehgal, A.; Bettiol, S.; Pypaert, M.; Wenk, M.R.; Kaasch, A.; Blader, I.J.; Joiner, K.A.; Coppens, I. Peculiarities of Host Cholesterol Transport to the Unique Intracellular Vacuole Containing Toxoplasma. Traffic 2005, 6, 1125–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppens, I.; Dunn, J.D.; Romano, J.D.; Pypaert, M.; Zhang, H.; Boothroyd, J.C.; Joiner, K.A. Toxoplasma Gondii Sequesters Lysosomes from Mammalian Hosts in the Vacuolar Space. Cell 2006, 125, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppens, I.; Sinai, A.P.; Joiner, K.A. Toxoplasma Gondii Exploits Host Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor- Mediated Endocytosis for Cholesterol Acquisition. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 149, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, J.D.; Sonda, S.; Bergbower, E.; Smith, M.E.; Coppens, I. Toxoplasma Gondii Salvages Sphingolipids from the Host Golgi through the Rerouting of Selected Rab Vesicles to the Parasitophorous Vacuole. Mol. Biol. Cell 2013, 24, 1974–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolan, S.J.; Romano, J.D.; Coppens, I. Host Lipid Droplets: An Important Source of Lipids Salvaged by the Intracellular Parasite Toxoplasma Gondii. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romano, J.D.; Nolan, S.J.; Porter, C.; Ehrenman, K.; Hartman, E.J.; Hsia, R.-C.; Coppens, I. The Parasite Toxoplasma Sequesters Diverse Rab Host Vesicles within an Intravacuolar Network. J. Cell Biol. 2017, 216, 4235–4254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, T.C.; Hirsch, J.G. The Interaction between Toxoplasma Gondii and Mammalian Cells: II. The Absence of Lysosomal Fusion with Phagocytic Vacuoles Containing Living Parasites. J. Exp. Med. 1972, 136, 1173–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, C.S.; Melo, E.J.T. Acidification of the Parasitophorous Vacuole Containing Toxoplasma Gondii in the Presence of Hydroxyurea. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2006, 78, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Radke, J.R.; Striepen, B.; Guerini, M.N.; Jerome, M.E.; Roos, D.S.; White, M.W. Defining the Cell Cycle for the Tachyzoite Stage of Toxoplasma Gondii. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2001, 115, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheffield, H.G.; Melton, M.L. The Fine Structure and Reproduction of Toxoplasma Gondii. J. Parasitol. 1968, 54, 209–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, K.; Mann, T.; Striepen, B.; Beckers, C.J.M.; Roos, D.S.; Murray, J.M. Daughter Cell Assembly in the Protozoan Parasite Toxoplasma Gondii. Mol. Biol. Cell 2002, 13, 593–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, J.; Hu, K.; He, C.Y.; Pelletier, L.; Roos, D.S.; Warren, G. Golgi and Centrosome Cycles in Toxoplasma Gondii. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2006, 145, 125–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishi, M.; Hu, K.; Murray, J.M.; Roos, D.S. Organellar Dynamics during the Cell Cycle of Toxoplasma Gondii. J. Cell Sci. 2008, 121, 1559–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson-White, B.; Beck, J.R.; Chen, C.-T.; Meissner, M.; Bradley, P.J.; Gubbels, M.-J. Cytoskeleton Assembly in Toxoplasma Gondii Cell Division. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2012, 298, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gubbels, M.-J.; White, M.; Szatanek, T. The Cell Cycle and Toxoplasma Gondii Cell Division: Tightly Knit or Loosely Stitched? Int. J. Parasitol. 2008, 38, 1343–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francia, M.E.; Jordan, C.N.; Patel, J.D.; Sheiner, L.; Demerly, J.L.; Fellows, J.D.; de Leon, J.C.; Morrissette, N.S.; Dubremetz, J.F.; Striepen, B. Cell Division in Apicomplexan Parasites Is Organized by a Homolog of the Striated Rootlet Fiber of Algal Flagella. PLoS Biol. 2012, 10, e1001444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldas, L.; de Souza, W. A Window to Toxoplasma Gondii Egress. Pathogens 2018, 7, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafsack, B.F.C.; Pena, J.D.O.; Coppens, I.; Ravindran, S.; Boothroyd, J.C.; Carruthers, V.B. Rapid Membrane Disruption by a Perforin-like Protein Facilitates Parasite Exit from Host Cells. Science 2009, 323, 530–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, T.; Marmansari, D.; Li, Z.M.; Adilbish, A.; Canko, S.; Ueno, A.; Shono, H.; Furuoka, H.; Igarashi, M. A Novel Dense Granule Protein, GRA22, Is Involved in Regulating Parasite Egress in Toxoplasma Gondii. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2013, 189, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gras, S.; Jackson, A.; Woods, S.; Pall, G.; Whitelaw, J.; Leung, J.M.; Ward, G.E.; Roberts, C.W.; Meissner, M. Parasites Lacking the Micronemal Protein MIC2 Are Deficient in Surface Attachment and Host Cell Egress, but Remain Virulent In Vivo. Wellcome Open Res. 2017, 2, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaFavers, K.A.; Márquez-Nogueras, K.M.; Coppens, I.; Moreno, S.N.J.; Arrizabalaga, G. A Novel Dense Granule Protein, GRA41, Regulates Timing of Egress and Calcium Sensitivity in Toxoplasma Gondii. Cell. Microbiol. 2017, 19, e12749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, A.J.; Carruthers, V.B. Toxoplasma Gondii LCAT Primarily Contributes to Tachyzoite Egress. mSphere 2018, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frénal, K.; Marq, J.B.; Jacot, D.; Polonais, V.; Soldati-Favre, D. Plasticity between MyoC- and MyoA-Glideosomes: An Example of Functional Compensation in Toxoplasma Gondii Invasion. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graindorge, A.; Frénal, K.; Jacot, D.; Salamun, J.; Marq, J.B.; Soldati-Favre, D. The Conoid Associated Motor MyoH Is Indispensable for Toxoplasma Gondii Entry and Exit from Host Cells. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacot, D.; Tosetti, N.; Pires, I.; Stock, J.; Graindorge, A.; Hung, Y.F.; Han, H.; Tewari, R.; Kursula, I.; Soldati-Favre, D. An Apicomplexan Actin-Binding Protein Serves as a Connector and Lipid Sensor to Coordinate Motility and Invasion. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 20, 731–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisio, H.; Soldati-Favre, D. Signaling Cascades Governing Entry into and Exit from Host Cells by Toxoplasma Gondii. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 73, 579–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, T.; Sethi, K.K.; Piekarski, G. Toxoplasma Gondii: Calcium Lonophore A23187-Mediated Exit of Trophozoites from Infected Murine Macrophages. Exp. Parasitol. 1982, 53, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourido, S.; Tang, K.; David Sibley, L. Distinct Signalling Pathways Control Toxoplasma Egress and Host-Cell Invasion. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 4524–4534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radke, J.R.; Guerini, M.N.; Jerome, M.; White, M.W. A Change in the Premitotic Period of the Cell Cycle Is Associated with Bradyzoite Differentiation in Toxoplasma Gondii. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2003, 131, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, E.; Zhao, Y.; Dhara, A.; Eller, B.; Patwardhan, A.; Sinai, P. Novel Approaches Reveal That Toxoplasma Gondii Bradyzoites within Tissue Cysts Are Dynamic and Replicating Entities In Vivo. MBio 2015, 6, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, L.M.; Kim, K. The Development and Biology of Bradyzoites of Toxoplasma Gondii. Front. Biosci. 2000, 5, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, D.J.P.; Hutchison, W.M. An Ultrastructural Study of the Early Development and Tissue Cyst Formation of Toxoplasma Gondii in the Brains of Mice. Parasitol. Res. 1987, 73, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boothroyd, J.C.; Black, M.; Bonnefoy, S.; Hehl, A.; Knoll, L.J.; Manger, I.D.; Ortega-Barria, E.; Tomavo, S. Genetic and Biochemical Analysis of Development in Toxoplasma Gondii. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 1997, 352, 1347–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paredes-Santos, T.C.; Tomita, T.; Yan Fen, M.; de Souza, W.; Attias, M.; Vommaro, R.C.; Weiss, L.M. Development of Dual Fluorescent Stage Specific Reporter Strain of Toxoplasma Gondii to Follow Tachyzoite and Bradyzoite Development In Vitro and In Vivo. Microbes Infect. 2016, 18, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paredes-Santos, T.C.; Martins-Duarte, E.S.; Vitor, R.W.A.; de Souza, W.; Attias, M.; Vommaro, R.C. Spontaneous Cystogenesis In Vitro of a Brazilian Strain of Toxoplasma Gondii. Parasitol. Int. 2013, 62, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, A.; Soete, M.; Dubremetz, J.F.; Smith, J.E. Toxoplasma Gondii: Appearance of Specific Markers during the Development of Tissue Cysts In Vitro. Parasitol. Res. 1996, 82, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soete, M.; Fortier, B.; Camus, D.; Dubremetz, J.F. Toxoplasma Gondii: Kinetics of Bradyzoite-Tachyzoite Interconversion In Vitro. Exp. Parasitol. 1993, 76, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soete, M.; Camus, D.; Dubrametz, J.F. Experimental Induction of Bradyzoite-Specific Antigen Expression and Cyst Formation by the RH Strain of Toxoplasma Gondii In Vitro. Exp. Parasitol. 1994, 78, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, L.M.; Laplace, D.; Takvorian, P.M.; Tanowitz, H.B.; Cali, A.; Wittner, M. A Cell Culture System for Study of the Development of Toxoplasma Gondii Bradyzoites. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 1995, 42, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohne, W.; Heesemann, J.; Gross, U. Induction of Bradyzoite-Specific Toxoplasma Gondii Antigens in Gamma Interferon-Treated Mouse Macrophages. Infect. Immun. 1993, 61, 1141–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohne, W.; Heesemann, J.; Gross, U. Reduced Replication of Toxoplasma Gondii Is Necessary for Induction of Bradyzoite-Specific Antigens: A Possible Role for Nitric Oxide in Triggering Stage Conversion. Infect. Immun. 1994, 62, 1761–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, B.A.; Gigley, J.P.; Bzik, D.J. Toxoplasma Gondii Lacks the Enzymes Required for de Novo Arginine Biosynthesis and Arginine Starvation Triggers Cyst Formation. Int. J. Parasitol. 2004, 34, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihara, F.; Nishikawa, Y. Starvation of Low-Density Lipoprotein-Derived Cholesterol Induces Bradyzoite Conversion in Toxoplasma Gondii. Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomavo, S.; Boothroyd, J.C. Interconnection between Organellar Functions, Development and Drug Resistance in the Protozoan Parasite, Toxoplasma Gondii. Int. J. Parasitol. 1995, 25, 1293–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkman, L.A.; Weiss, L.M.; Kim, K. Cyclic Nucleotide Signaling in Toxoplasma Gondii Bradyzoite Differentiation. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eaton, M.S.; Weiss, L.M.; Kim, K. Cyclic Nucleotide Kinases and Tachyzoite—Bradyzoite Transition in Toxoplasma Gondii. Int. J. Parasitol. 2006, 36, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, W.J.; Narasimhan, J.; Bhatti, M.M.; Wek, R.C. Parasite-Specific EIF2 (Eukaryotic Initiation Factor-2) Kinase Required for Stress-Induced Translation Control. Biochem. J. 2004, 380, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, W.J.; Hakimi, M.A. Histone Mediated Gene Activation in Toxoplasma Gondii. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2006, 148, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougdour, A.; Maubon, D.; Baldacci, P.; Ortet, P.; Bastien, O.; Bouillon, A.; Barale, J.C.; Pelloux, H.; Ménard, R.; Hakimi, M.A. Drug Inhibition of HDAC3 and Epigenetic Control of Differentiation in Apicomplexa Parasites. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 953–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radke, J.R.; Behnke, M.S.; Mackey, A.J.; Radke, J.B.; Roos, D.S.; White, M.W. The Transcriptome of Toxoplasma Gondii. BMC Biol. 2005, 3, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Lin, M.; Li, M.; Yang, X.; Liu, J.; Liu, Q. Toxoplasma Gondii Metacaspase 2 Is an Important Factor That Influences Bradyzoite Formation in the Pru Strain. Parasitol. Res. 2020, 119, 2287–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Holmes, M.J.; Radke, J.B.; Hong, D.-P.; Liu, T.; White, M.W.; Sullivan, W.J. Toxoplasma Gondii AP2IX-4 Regulates Gene Expression during Bradyzoite Development. Host Microbe Biol. 2017, 2, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radke, J.B.; Worth, D.; Hong, D.; Huang, S.; Sullivan, W.J.; Wilson, E.H.; White, M.W. Transcriptional Repression by ApiAP2 Factors Is Central to Chronic Toxoplasmosis. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhat, D.C.; Swale, C.; Dard, C.; Cannella, D.; Ortet, P.; Barakat, M.; Sindikubwabo, F.; Belmudes, L.; De Bock, P.J.; Couté, Y.; et al. A MORC-Driven Transcriptional Switch Controls Toxoplasma Developmental Trajectories and Sexual Commitment. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 570–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldman, B.S.; Schwarz, D.; Wadsworth, M.H.; Saeij, J.P.; Shalek, A.K.; Lourido, S. Identification of a Master Regulator of Differentiation in Toxoplasma. Cell 2020, 180, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, D.; Radke, J.B.; White, M.W. Opposing Transcriptional Mechanisms Regulate Toxoplasma Development. Mol. Biol. Physiol. 2017, 2, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croken, M.M.; Qiu, W.; White, M.W.; Kim, K. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) of Toxoplasma Gondii Expression Datasets Links Cell Cycle Progression and the Bradyzoite Developmental Program. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnke, M.S.; Wootton, J.C.; Lehmann, M.M.; Radke, J.B.; Lucas, O.; Nawas, J.; Sibley, L.D.; White, M.W. Coordinated Progression through Two Subtranscriptomes Underlies the Tachyzoite Cycle of Toxoplasma Gondii. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).