Porcelain Enamel Coatings
Definition
1. History
1.1. Proto-Enamel
1.2. Origins of Enamel
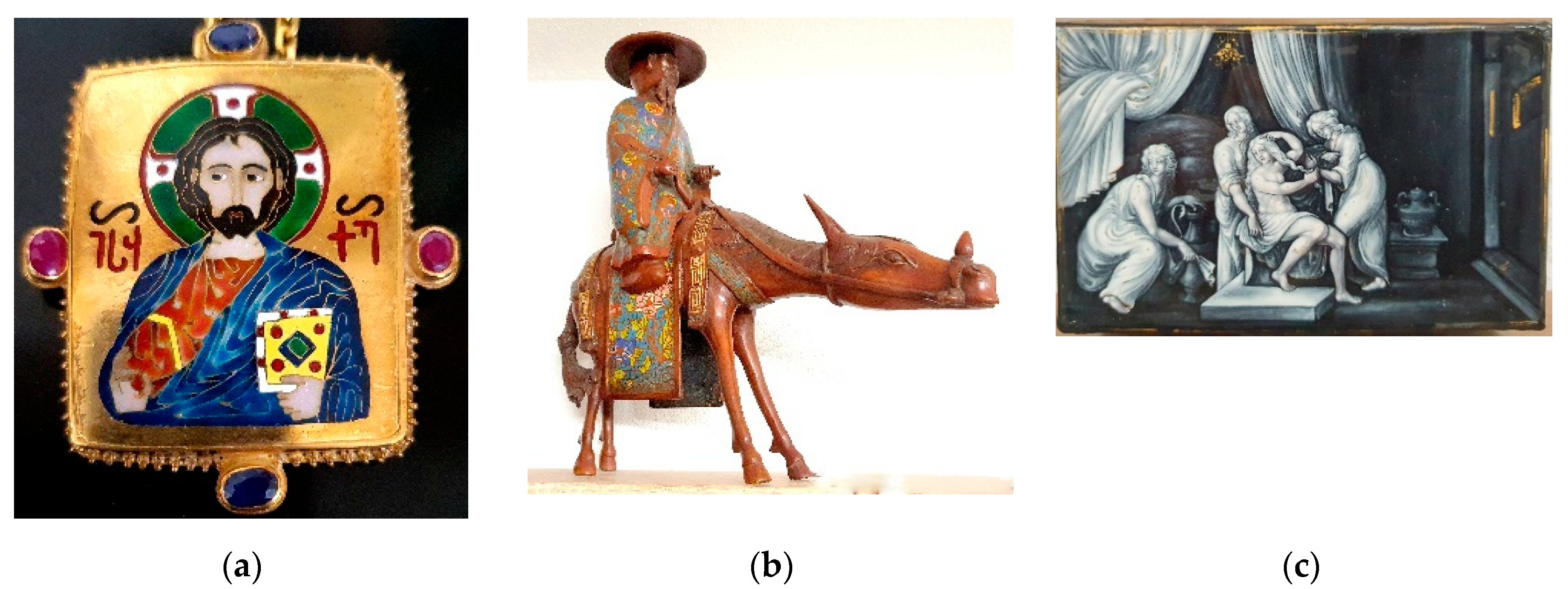
1.3. The Cloisonné and Champlevé Enameling Techniques
1.4. From the Renaissance Onwards
1.5. The Era of Technical Enameling
2. Substrates for Enameling and Surface Pretreatments
2.1. Common Substrates for Enameling
2.1.1. Cast Iron for Enameling
2.1.2. Steel for Enameling
2.1.3. Aluminum Alloys for Enameling
2.2. Surface Pretreatments
2.2.1. Pretreatment of Cast Iron Substrate
2.2.2. Pretreatment of Steel Substrate
2.2.3. Pretreatment of Aluminum Substrate
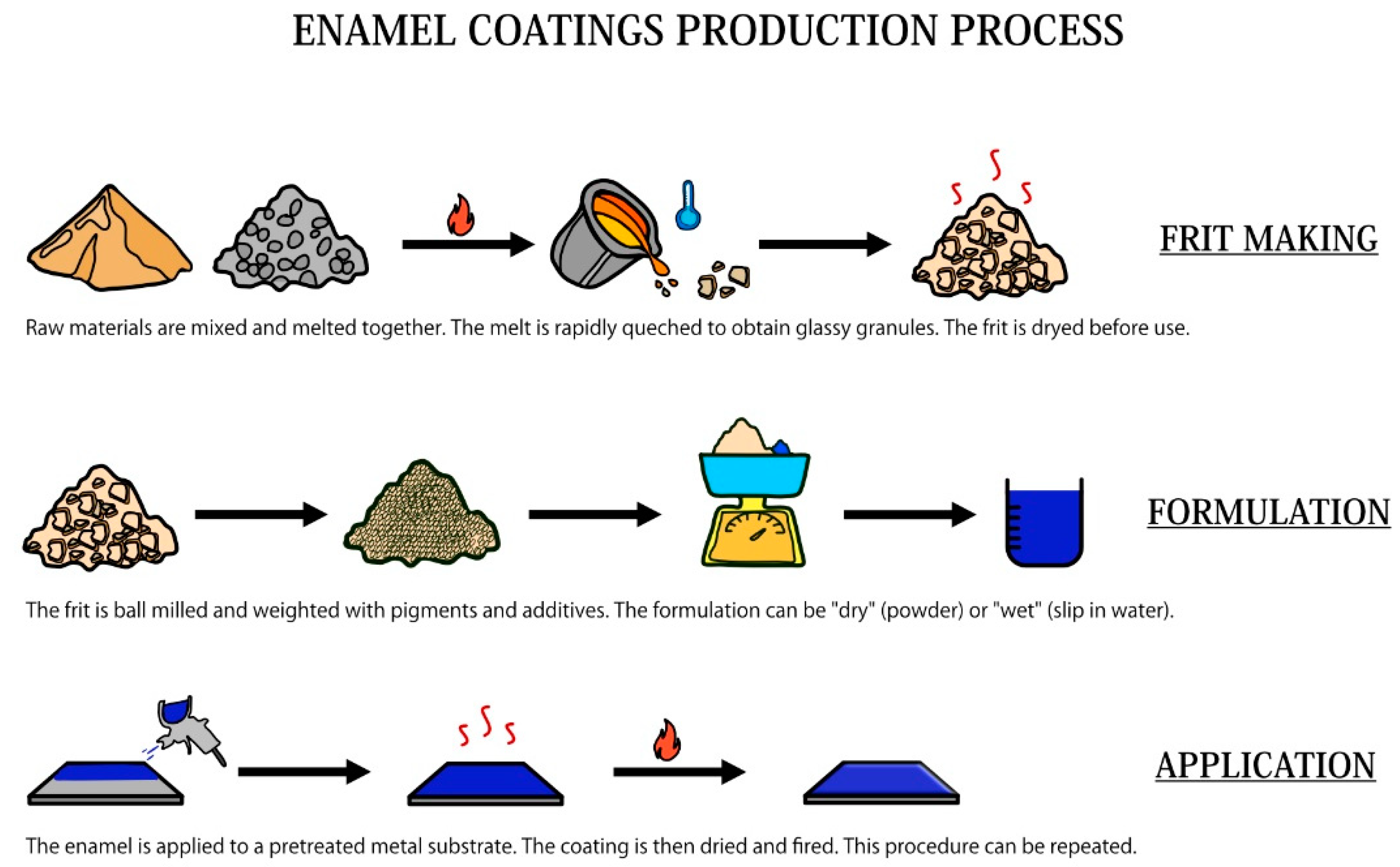
3. Production of Enamels
3.1. The Frit Making
3.2. Milling and Mill Additions
3.3. Application of Enamel on the Substrate
3.3.1. Enameling of Steel
3.3.2. Enamelling of Cast Iron and Aluminum
3.4. Drying and Firing
4. Properties of Enamel Coatings and Common Applications
4.1. Thermal Properties
4.2. Physical Properties
4.3. Chemical Properties
4.4. Mechanical Properties
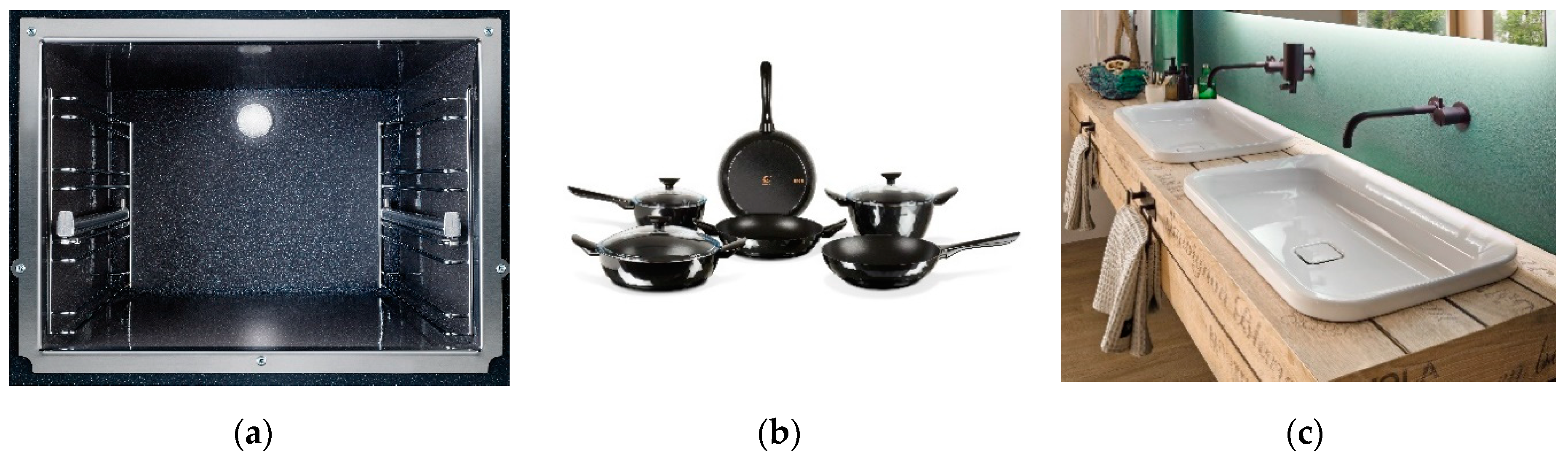
4.5. Common Application of Enamel Coatings
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Entry Link on the Encyclopedia Platform
References
- Kiefer, K.C.; Allibert, A. Pharonic blue ceramics: The process of self-glazing. Archaeology 1971, 24, 107–117. [Google Scholar]
- Carolyn, R.; Jennifer, M.; Jonathan, T. Egyptian faience inlay techniques: A process for obtaining detail and clarity by refiring. MRS Online Proc. Libr. 2001, 712, 107. [Google Scholar]
- Tite, M.S.; Bimson, M. Faience: An investigation of the microstructures associated with the different methods of glazing. Archaeometry 1986, 28, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tait, H. Enamelwork–History. Encyclopedia Britannica, 07/03/2016. Available online: https://www.britannica.com/art/enamelwork (accessed on 12 March 2021).
- The history of enamelling technique. Design 1957, 58, 158–162.
- Rogers, W.H. On the history of enamelling. J. Br. Archaeol. Assoc. 1848, 3, 280–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, J.E.; Kruszynski, M. Ancient caucasian and related material in the British Museum. In British Museum Occasional Paper 121; The British Museum: London, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Von Bothmer, D.; Picón, C.A.; Mertens, J.R.; Milleker, E.J.; Herrmann, A. Recent acquisitions: A selection 1994–1995. Bull. Metrop. Mus. Art 1995, 53, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Buckton, D.; Osborne, J. The enamel of Doge Ordelaffo Falier on the Pala d’Oro in Venice. Gesta 2000, 39, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, M. A technical study of opaque red glass of the Iron Age in Britain. Proc. Prehist. Soc. 1972, 38, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, F. A study into Romano-Bristish enamelling–with a particular focus on brooches. Sch. Hist. Stud. Postgrad. Forum E-J. Ed. 2009, 7, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, S.; Scrinzi, E.; Compagnoni, A.M.; Gallucci, A.; Gjata, Y. Enamel and design. In The Potential of Enamelled Materials; Fausto Lupetti Editore: Bologna, Italy, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- De Chancel, B.; Drake Boehm, B.; Barrière, B.; Taburet, E.; Biron, I.; Becquet, J.; Gauthier, M.M.; Wypyski, M.T.; Pastoreau, M.; Dandrige, P. Enamels of Limoges 1100–1350; The Metropolitan Museum of Art: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Britannica, The Editors of Encyclopaedia. Limoges Painted Enamel. Encyclopedia Britannica, 17/03/2016. Available online: https://www.britannica.com/art/Limoges-painted-enamel (accessed on 12 March 2021).
- Dawes, E. Some early experiences in enamelling cast iron. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1923, 6, 234–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollrath, C.A.W. Early history of enamelling in the Vollrath company. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1923, 6, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staley, H.F. Developments in enamelling technology during the past twenty-five years. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1923, 6, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenn, A.H. Porcelain enamels: Past, present and future. Analyst 1955, 11, 85–87. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, M.; Chen, M.; Zhu, S.; Wang, F. Protection mechanism of enamel–alumina composite coatings on a Cr-rich nickel-based superalloy against high-temperature oxidation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 285, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Shen, M.; Wang, X.; Zhu, S.; Wang, F. Interfacial reaction between SiO2–Al2O3–ZnO–CaO based glass coatings and K38G superalloy substrates. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 216, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poste, E.P. The blistering of cast iron enamel. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1933, 16, 277–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaitsev, A.A.; Mogil’chenko, V.S. Improving the enamelling properties and quality of cast iron equipment. Glass Ceram. 1968, 2, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Tang, R.; Yang, F.; Qiao, Y.; Sun, J.; Jiang, J.; Ma, A. Development of high-performance enamel coating on grey iron by low-temperature sintering. Materials 2018, 11, 2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Li, X. Variations of microstructure and resistance to fish-scaling of a hot rolled enamel steel before and after enamel firing. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 11, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrilovski, D.; Gavrilovski, M. Properties of hot rolled steels for enamelling. In Proceedings of the 3rd BMC, Ohrid, Macedonia, 24–27 September 2003. [Google Scholar]
- UNI EN 10209 Standard. UNI Ente Nazionale Italiano di Unificazione; UNI: Milano, Italy, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ashis Janah, A. Vitreous enamelling of aluminium—A review. Trans. Ind. Ceram. Soc. 1968, 27, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compagnoni, A.; Ferraro, A. Smaltatura dell’alluminio ad alto tenore di magnesio. In Proceedings of the 20th IEI Congress, Istanbul, Turkey, 15–19 May 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Pagliuca, S.; Faust, W.D. Porcelain Vitreous Enamels and Industrial Enamelling Processes, 3rd ed.; IEI: Milan, Italy, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Detail Explanation of Cast Iron Pretreatment. Available online: https://www.nolifrit.com/news/detail-explanation-on-cast-iron-pretreatment-104 (accessed on 14 March 2021).
- Danielson, R.R. The cleaning of sheet steel and iron for enamelling. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1919, 2, 883–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, J.E. Practical Aspects of Electrolytic Pretreatment. In Proceedings of the 43rd Porcelain Enamel Institute Technical Forum 1982, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, USA, 7–8 October 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, S.; Fedel, M.; Deflorian, F.; Parziani, N. Abrasion and chemical resistance of composite enamel coatings with hard particles. Surf. Interface Anal. 2015, 48, 827–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, S.; Russo, F.; Calovi, M. Durability of vitreous enamel coatings and their resistance to abrasion, chemicals, and corrosion: A review. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2021, 18, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, S.; Calovi, M.; Velez, D.; Rodriguez, I.; Del Rincón, M.; Munoz, J.M.; Grande, H.J. Microstructural analysis and surface modification of a vitreous enamel modified with corundum particles. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2019, 21, 1900231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiele, H.J. 2C/1F Enamelling Process—A Growing Demand. In 69th Porcelain Enamel Institute Technical Forum: Ceramic Engineering and Science Proceedings 2007; Evele, H., Vodak, P., Faust, W.D., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; p. 10. [Google Scholar]
- Willis, J.B. Electrostatic spraying of porcelain enamels. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1945, 28, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evele, H.F. Proper Care of Porcelain Enamel Powder for Electrostatic Application. Ceram. Eng. Sci. Proc. 2000, 21, 125–126. [Google Scholar]
- Fleischmann, R.; Schaper, W.; Schünemann, R. Some aspects of the electrophoretic enamel deposition. Electrochim. Acta 1984, 29, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez Garcıa, M.R.; Munoz, J.; Diez, J.A. Corrosion resistance of enamel vitreous coating obtained by electrophoretic deposition. Key Eng. Mater. 2015, 654, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Tang, F.; Chen, G.; Reis, S.T.; Koenigstein, M.L. Corrosion resistances of steel pipe coated with two types of enamel by two coating processes. J. Mater. Eng. 2018, 27, 5341–5349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Chen, G.; Volz, J.S.; Brow, R.K.; Koenigstein, M. Microstructure and corrosion resistance of enamel coatings applied to smooth reinforcing steel. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 35, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, S.; Bergamo, L.; Fontanari, V. Fire resistance and mechanical properties of enamelled aluminium foam. Mater. Des. 2017, 132, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scrinzi, E.; Rossi, S. The aesthetic and functional properties of enamel coatings on steel. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 4138–4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, J.W.; Whitelock, K.E. The importance of colour and its stability in vitreous enamels. Mater. Des. 1985, 6, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samiee, L.; Sarpoolaky, H.; Mirhabibi, A. Microstructure and adherence of cobalt containing and cobalt free enamels to low carbon steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 458, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shieu, F.S.; Lin, K.C.; Wong, J.C. Microstructure and adherence of porcelain enamel to low carbon steel. Ceram. Int. 1999, 25, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, S.; Zanella, C.; Sommerhuber, R. Influence of mill additives on vitreous enamel properties. Mater. Des. 2014, 55, 880–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, S.; Russo, F.; Calovi, M.; Del Rincòn, M.; Velez, D. The influence of the size of corundum particles on the properties of chemically resistant porcelain enamels. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 11618–11627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Function | Component | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Refractories | SiO2 | Glass-forming oxide, increases chemical resistance and viscosity |
| Al2O3 | Increases viscosity and reduces the expansion coefficient | |
| Fluxes | B2O3 | Produces the vitreous matrix and increases surface hardness |
| Na2O, K2O, Li2O | Alkaline components, lower the softening temperature of glass | |
| ZnO | Excellent flux, lowers the expansion coefficient | |
| Opacifiers | ZrO2 | Acts as an opacifier and improves resistance to acids |
| Sb2O3 | Produces a high degree of opacity and gives resistance to acids | |
| TiO2 | It increases whiteness and gives resistance to acids | |
| P2O5 | Improves color stability but reduces chemical resistance | |
| Adherence oxides | CoO, NiO, CuO | Important adherence agents |
| Application | Application Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Wet | Dip coating | Immersion of the piece in the slip |
| Flow coating | Pouring of the slip on the piece | |
| Spray coating | The slip is atomized thanks to air | |
| Electrostatic wet spray coating Electrophoretic coating | The atomized slip is charged Migration of the slip to the substrate | |
| Dry | Electrostatic dry powder coating | The enamel powder is charged |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Russo, F.; Rossi, S.; Compagnoni, A.M. Porcelain Enamel Coatings. Encyclopedia 2021, 1, 388-400. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia1020032
Russo F, Rossi S, Compagnoni AM. Porcelain Enamel Coatings. Encyclopedia. 2021; 1(2):388-400. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia1020032
Chicago/Turabian StyleRusso, Francesca, Stefano Rossi, and Attilio Monzio Compagnoni. 2021. "Porcelain Enamel Coatings" Encyclopedia 1, no. 2: 388-400. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia1020032
APA StyleRusso, F., Rossi, S., & Compagnoni, A. M. (2021). Porcelain Enamel Coatings. Encyclopedia, 1(2), 388-400. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia1020032







