Machine Learning in Healthcare Communication
Definition
:1. Introduction
2. Machine Learning Technology
2.1. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
2.2. Deep Neural Network (DNN)
3. Application of Machine Learning in Healthcare Communication
3.1. Overview of Chatbot
3.2. Patient Care
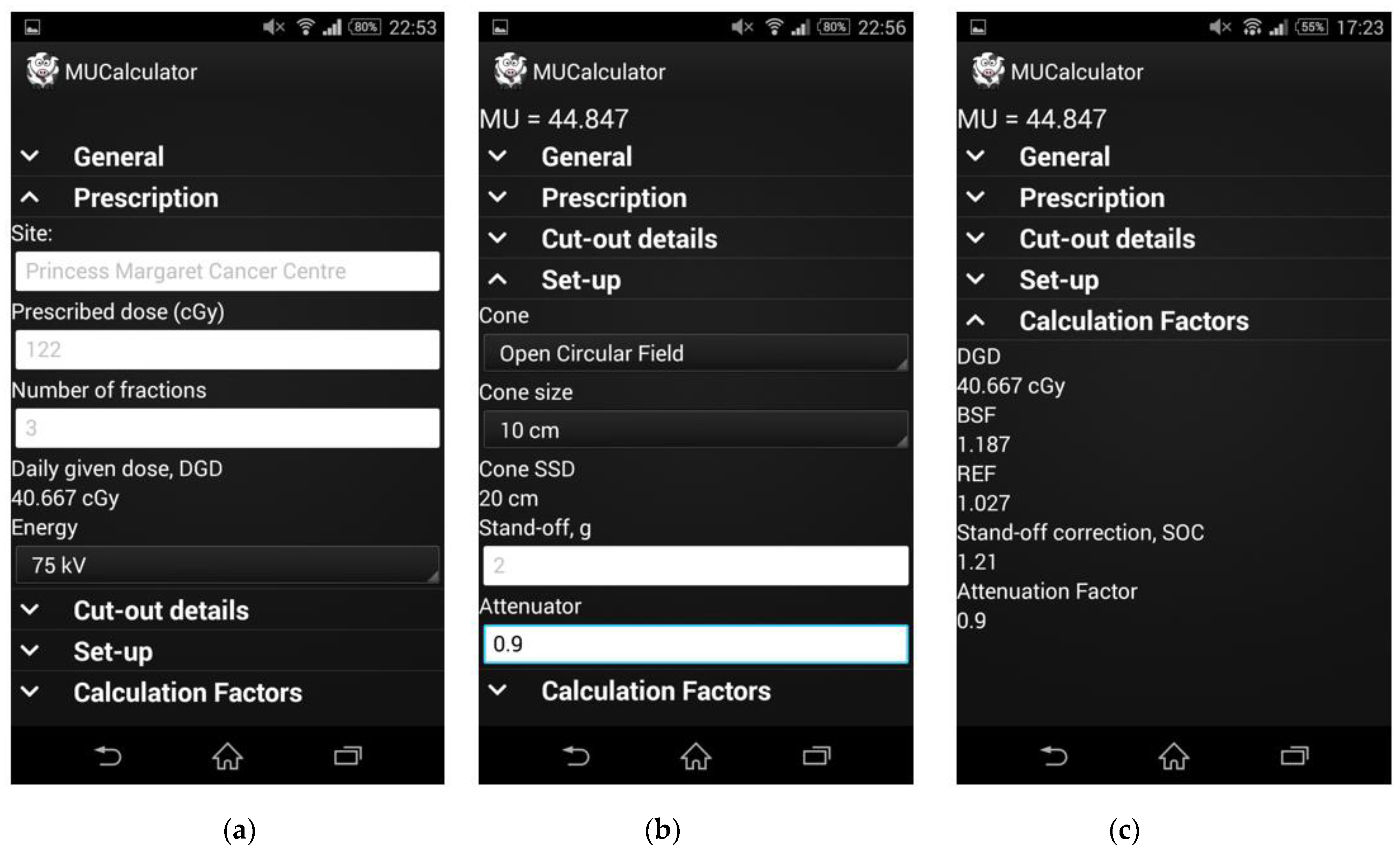
3.3. Radiology and Radiotherapy
3.4. Education and Knowledge Transfer System
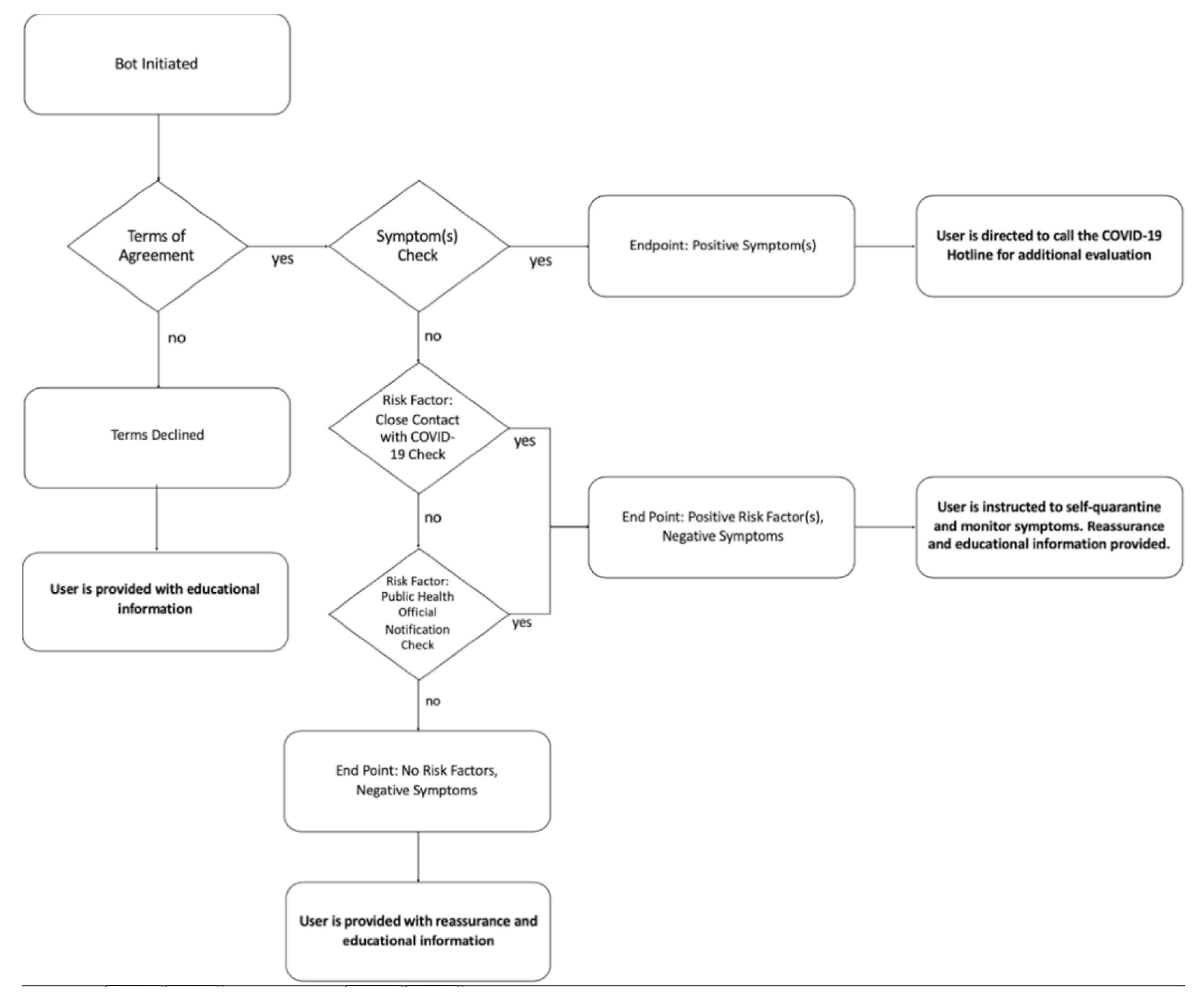
3.5. Emergency Response and COVID-19
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Entry Link on the Encyclopedia Platform
References
- Peyrou, B.; Vignaux, J.-J.; André, A. Artificial Intelligence and Health Care. In Digital Medicine; André, A., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathya, D.; Sudha, V.; Jagadeesan, D. Application of Machine Learning Techniques in Healthcare. In Handbook of Research on Applications and Implementations of Machine Learning Techniques; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2019; pp. 289–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosny, A.; Parmar, C.; Quackenbush, J.; Schwartz, L.H.; Aerts, H.J.W.L. Artificial intelligence in radiology. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzobo, K.; Adotey, S.; Thomford, N.E.; Dzobo, W. Integrating Artificial and Human Intelligence: A Partnership for Responsible Innovation in Biomedical Engineering and Medicine. Omics J. Integr. Biol. 2020, 24, 247–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson, B.J.; Korfiatis, P.; Akkus, Z.; Kline, T.L. Machine learning for medical imaging. Radiographics 2017, 37, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magrabi, F.; Ammenwerth, E.; Mcnair, J.B.; De Keizer, N.F.; Georgiou, A. Artificial Intelligence in Clinical Decision Support: Challenges for Evaluating AI and Practical Implications A Position Paper from the IMIA Technology Assessment & Quality Development in Health Informatics Working Group and the EFMI Working Group for Assessment of Health Information Systems. Yearb. Med. Inform. 2019, 28, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Buch, V.H.; Ahmed, I.; MaruthappuIs, M. Artificial intelligence in medicine: Current trends and future possibilities. Br. J. Gen. Pract. 2018, 68, 143–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayan, R. Artificial Intelligence Perspective on Healthcare. InICEAT 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topol, E.J. High-performance medicine: The convergence of human and artificial intelligence. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bibault, J.E.; Chaix, B.; Guillemassé, A.; Cousin, S.; Escande, A.; Perrin, M.; Pienkowski, A.; Delamon, G.; Nectoux, P.; Brouard, B. A chatbot versus physicians to provide information for patients with breast cancer: Blind, randomized controlled noninferiority trial. J. Med. Internet Res. 2019, 21, e15787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintz, Y.; Brodie, R. Introduction to artificial intelligence in medicine. Minim. Invasive Ther. Allied Technol. 2019, 28, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bzdok, D.; Krzywinski, M.; Altman, N. Points of significance: Machine learning: Supervised methods. Nat. Methods 2018, 15, 5–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, T.; Giannopoulos, A.A.; Yu, S.; Kelil, T.; Ripley, B.; Kumamaru, K.K.; Rybicki, F.J.; Mitsouras, D. Natural language processing technologies in radiology research and clinical applications. Radiographics 2016, 36, 176–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Z.; Deng, Y.; Li, X.; Naumann, T.; Luo, Y. Natural Language Processing for EHR-Based Computational Phenotyping. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinf. 2019, 16, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreimeyer, K.; Foster, M.; Pandey, A.; Arya, N.; Halford, G.; Jones, S.F.; Forshee, R.; Walderhaug, M.; Botsis, T. Natural language processing systems for capturing and standardizing unstructured clinical information: A systematic review. J. Biomed. Inform. 2017, 73, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chary, M.; Parikh, S.; Manini, A.F.; Boyer, E.W.; Radeos, M. A review of natural language processing in medical education. West. J. Emerg. Med. 2019, 20, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Hernandez, G.; Sarker, A.; O’Connor, K.; Savova, G. Capturing the Patient’s Perspective: A Review of Advances in Natural Language Processing of Health-Related Text. Yearb. Med. Inform. 2017, 26, 214–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filannino, M.; Uzuner, Ö. Advancing the State of the Art in Clinical Natural Language Processing through Shared Tasks. Yearb. Med. Inform. 2018, 27, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, W.H.; Wagholikar, K.B.; McCray, A.T.; Szolovits, P.; Chueh, H.C. Medical subdomain classification of clinical notes using a machine learning-based natural language processing approach. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2017, 17, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, G.; Pham, P.; Chapman, W.W.; Hwa, R.; Wiebe, J.; Hochheiser, H. NLPReViz: An interactive tool for natural language processing on clinical text. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2018, 25, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, Y.; Deng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Kim, H.; Armengol, V.D.; Acevedo, F.; Ouardaoui, N.; Wang, C.; Parmigiani, G.; Barzilay, R.; et al. Using machine learning and natural language processing to review and classify the medical literature on cancer susceptibility genes. JCO Clin. Cancer Inform. 2019, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vydiswaran, V.G.V.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, H. Special issue of BMC medical informatics and decision making on health natural language processing. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2019, 19, 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Q.-Y.; Mittal, L.P.; Nathan, M.D.; Brown, K.M.; Knudson González, D.; Cai, T.; Finan, S.; Gelaye, B.; Avillach, P.; Smoller, J.W.; et al. Use of natural language processing in electronic medical records to identify pregnant women with suicidal behavior: Towards a solution to the complex classification problem. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2019, 34, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Névéol, A.; Dalianis, H.; Velupillai, S.; Savova, G.; Zweigenbaum, P. Clinical Natural Language Processing in languages other than English: Opportunities and challenges. J. Biomed. Semant. 2018, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savova, G.K.; Danciu, I.; Alamudun, F.; Miller, T.; Lin, C.; Bitterman, D.S.; Tourassi, G.; Warner, J.L. Use of Natural Language Processing to Extract Clinical Cancer Phenotypes from Electronic Medical Records. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 5463–5470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodfellow, I. Deep learning(working version). Nat. Publ. Gr. 2011, 13, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriegeskorte, N.; Golan, T. Neural network models and deep learning. Curr. Biol. 2019, 29, R231–R236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddique, S.; Chow, J.C.L. Artificial intelligence in radiotherapy. Rep. Pract. Oncol. Radiother. 2020, 25, 656–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Jun, S.; Cho, Y.; Lee, H.; Kim, G.B.; Seo, J.B.; Kim, N. Deep Learning in Medical Imaging: General Overview. Korean J. Radiol. 2017, 18, 570–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Yu, T. A Deep Neural Network Model using Random Forest to Extract Feature Representation for Gene Expression Data Classification. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Gong, X.J.; Yu, H.; Zhou, C. Deep neural network based predictions of protein interactions using primary sequences. Molecules 2018, 23, 1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajpurkar, P.; Irvin, J.; Ball, R.L.; Zhu, K.; Yang, B.; Mehta, H.; Duan, T.; Ding, D.; Bagul, A.; Langlotz, C.P.; et al. Deep learning for chest radiograph diagnosis: A retrospective comparison of the CheXNeXt algorithm to practicing radiologists. PLoS Med. 2018, 15, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wachinger, C.; Reuter, M.; Klein, T. DeepNAT: Deep convolutional neural network for segmenting neuroanatomy. Neuroimage 2018, 170, 434–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spandorfer, A.; Branch, C.; Sharma, P.; Sahbaee, P.; Schoepf, U.J.; Ravenel, J.G.; Nance, J.W. Deep learning to convert unstructured CT pulmonary angiography reports into structured reports. Eur. Radiol. Exp. 2019, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.; Nguyen, T.; Nguyen, D.T. An empirical study on prediction of population health through social media. J. Biomed. Inform. 2019, 99, 103277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustaqeem; Kwon, S. A CNN-assisted enhanced audio signal processing for speech emotion recognition. Sensors 2020, 20, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhyani, M.; Kumar, R. Since January 2020 Elsevier Has Created a COVID-19 Resource Centre with Free Information in English and Mandarin on the Novel Coronavirus COVID-19. The COVID-19 Resource Centre Is Hosted on Elsevier Connect, the Company’s Public News and Information Website. Elsevier Hereby Grants Permission to Make All Its COVID-19-Related Research That Is Available on the COVID-19 Resource Centre—Including This Research Content—Immediately Available in PubMed Central and Other Publicly Funded Repositories, Such as the WHO COVID Database with Rights for Unrestricted Research Re-Use and Analyses in Any form or by Any Means with Acknowledgement of the Original Source. These Permissions Are Granted for Free by Elsevier for as Long as the COVID-19 Resource Centre Remains Active. An Intelligent Chatbot Using Deep Learning with Bidirectional RNN and Attention Model. 2020. Available online: https://www.binasss.sa.cr/agocovid/4.pdf (accessed on 5 January 2021).
- Lokman, A.S.; Ameedeen, M.A. Modern Chatbot Systems: A Technical Review. In Proceedings of the Future Technologies Conference (FTC) 2018; Arai, K., Bhatia, R., Kapoor, S., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 1012–1023. [Google Scholar]
- Lokman, A.S.; Zain, J.M.; Komputer, F.S.; Perisian, K. Designing a Chatbot for diabetic patients. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Software Engineering & Computer Systems (ICSECS’09), Pahang, Malaysia, 19–21 October 2009; pp. 19–21. [Google Scholar]
- Dahiya, M. A Tool of Conversation: Chatbot. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2017, 158–161. Available online: http://www.ijcseonline.org/pub_paper/27-IJCSE-02149.pdf (accessed on 5 January 2021).
- Nadarzynski, T.; Miles, O.; Cowie, A.; Ridge, D. Acceptability of artificial intelligence (AI)-led chatbot services in healthcare: A mixed-methods study. Digit. Health 2019, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibault, J.E.; Chaix, B.; Nectoux, P.; Pienkowsky, A.; Guillemasse, A.; Brouard, B. Healthcare ex Machina: Are conversational agents ready for prime time in oncology? Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 16, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Divya, S.; Indumathi, V.; Ishwarya, S.; Priyasankari, M.; Kalpana Devi, S. A Self-Diagnosis Medical Chatbot Using Artificial Intelligence. J. Web Dev. Web Des. 2018, 3, 1–7. Available online: http://matjournals.in/index.php/JoWDWD/article/view/2334 (accessed on 5 January 2021).
- Rosruen, N.; Samanchuen, T. Chatbot Utilization for Medical Consultant System. In Proceedings of the 2018 3rd Technology Innovation Management and Engineering Science International Conference (TIMES-iCON), Bangkok, Thailand, 12–14 December 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranoliya, B.R.; Raghuwanshi, N.; Singh, S. Chatbot for university related FAQs. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communications and Informatics, ICACCI 2017, Udupi, India, 13–16 September 2017; pp. 1525–1530. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, L.; Lu, C.; Liu, N.; Liu, J. MANDY: Towards a smart primary care chatbot application. Commun. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2017, 780, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saliimi Lokman, A.; Mohamad Zain, J. Extension and Prerequisite: An Algorithm to Enable Relations Between Responses in Chatbot Technology. J. Comput. Sci. 2010, 6, 1212–1218. Available online: http://thescipub.com/PDF/jcssp.2010.1212.1218.pdf (accessed on 5 January 2021). [CrossRef]
- Augello, A.; Gentile, M.; Weideveld, L.; Dignum, F. A Model of a Social Chatbot. In Proceedings of the Intelligent Interactive Multimedia Systems and Services 2016, Tenerife, Spain, 15–17 June 2016; Pietro, G., De Gallo, L., Howlett, R.J., Jain, L.C., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 637–647. [Google Scholar]
- Augello, A.; Gambino, O.; Cannella, V.; Pirrone, R.; Gaglio, S.; Pilato, G. An Emotional Talking Head for a Humoristic Chatbot. Appl. Digit. Signal Process. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, A.; Phalke, G.; Il, P.P.; Bhosale, S.; Raghatwan, J. A Survey On Chatbot Conversational Systems. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2016, 6, 3117. [Google Scholar]
- McTear, M.; Callejas, Z.; Griol, D. Creating a Conversational Interface Using Chatbot Technology. In The Conversational Interface: Talking to Smart Devices; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 125–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, A.; Liszewski, B. Artificial Intelligence and the Medical Radiation Profession: How Our Advocacy Must 763 Inform Future Practice. J. Med. Imaging Radiat Sci. 2019, 50, S15–S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadariya, D.; Venkataramanan, R.; Yip, H.Y.; Kalra, M.; Thirunarayanan, K.; Sheth, A. kBot: Knowledge-enabled Personalized Chatbot for Asthma Self-Management. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Smart Computing (SMARTCOMP), Washington, DC, USA, 12–15 June 2019; pp. 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, J.P.T. Network Diffusion and Technology Acceptance of A Nurse Chatbot for Chronic Disease Self-Management Support: A Theoretical Perspective. J. Med. Investig. 2019, 66, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawar, B.A.; Atwell, E. A chatbot system as a tool to animate a corpus. ICAME J. 2005, 29, 5–24. [Google Scholar]
- Vaidyam, A.N.; Wisniewski, H.; Halamka, J.D.; Kashavan, M.S.; Torous, J.B. Chatbots and Conversational Agents in Mental Health: A Review of the Psychiatric Landscape. Can. J. Psychiatry 2019, 64, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bott, N.; Wexler, S.; Drury, L.; Pollak, C.; Wang, V.; Scher, K.; Narducci, S. A protocol-driven, bedside digital conversational agent to support nurse teams and mitigate risks of hospitalization in older adults: Case control pre-post study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2019, 21, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, D.; Ranasinghe, W.; Bandaragoda, T.; Adikari, A.; Mills, N.; Iddamalgoda, L.; Alahakoon, D.; Lawrentschuk, N.; Persad, R.; Osipov, E.; et al. Machine learning to support social media empowered patients in cancer care and cancer treatment decisions. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarema, A.; Dixon, A. Radiology educational posts on social media. Are they effective? In Proceedings of the Annual Scientific Meeting, Washington, DC, USA, 6–8 April 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Zubaide, H.; Issa, A.A. OntBot: Ontology based ChatBot. In Proceedings of the 2011 4th International Symposium on Innovations in Information and Communications Technology, ISIICT’2011, Amman, Jordan, 29 November–1 December 2011; pp. 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.C.L. Application of Cloud Computing in Pre-clinical Radiation Treatment Planning. Int. J. Comput. Res. 2015, 22, 209–222. [Google Scholar]
- Chow, J.C.L. Monte Carlo simulation on pre-clinical irradiation: A heterogeneous phantom study on monoenergetic kilovoltage photon beams. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2012, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.C.L. Internet-based computer technology on radiotherapy. Rep. Pract. Oncol. Radiother. 2017, 22, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearse, J.; Chow, J.C.L. An Internet of Things app for monitor unit calculation in superficial and orthovoltage skin therapy. IOP SciNotes 2020, 1, 014002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, F.; Jiang, R.; Chow, J.C.L. Predicting radiation treatment planning evaluation parameter using artificial intelligence and machine learning. IOP SciNotes 2020, 1, 014003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, S.; Williams, N.L.; Ip, A.; Dicker, A.P. Clinical Integration of Digital Solutions in Health Care: An Overview of the Current Landscape of Digital Technologies in Cancer Care. JCO Clin. Cancer Inform. 2018, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, S.; Ramo, D.; Chang, Y.J.; Fu, M.; Moskowitz, J.; Haritatos, J. Use of the chatbot “vivibot” to deliver positive psychology skills and promote well-being among young people after cancer treatment: Randomized controlled feasibility trial. JMIR mHealth uHealth 2019, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Oh, Y.J.; Lange, P.; Yu, Z.; Fukuoka, Y. Artificial intelligence chatbot behavior change model for designing artificial intelligence chatbots to promote physical activity and a healthy diet: Viewpoint. J. Med. Internet Res. 2020, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piterman, L.; Newton, J.M.; Canny, B.J. Interprofessional education for interprofessional practice: Does it make a difference? Med. J. Aust. 2010, 193, 92–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Gasperis, G.; Chiari, I.; Florio, N. AIML Knowledge Base Construction from Text Corpora. In Artificial Intelligence, Evolutionary Computing and Metaheuristics: In the Footsteps of Alan Turing; Yang, X.-S., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 287–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhou, M.; Yang, D. Extracting chatbot knowledge from online discussion forums. IJCAI Int. Jt. Conf. Artif. Intell. 2007, 7, 423–428. [Google Scholar]
- Clarizia, F.; Colace, F.; Lombardi, M.; Pascale, F.; Santaniello, D. Chatbot: An Education Support System for Student. In Cyberspace Safety and Security; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bii, P. Chatbot technology: A possible means of unlocking student potential to learn how to learn. Educ. Res. 2013, 4, 218–221. Available online: http://psych.athabascau.ca/html/chatterbot/ChatAgent- (accessed on 5 January 2021).
- Heller, B.; Procter, M.; Mah, D. Freudbot: An investigation of chatbot technology in distance education. In Proceedings of the World Conference on Educational Multimedia, Hypermedia & Telecommunications, Montreal, QC, Canada, 27 June–2 July 2005; pp. 3913–3918. Available online: http://www.editlib.org/index.cfm?fuseaction=Reader.ViewFullText&paper_id=20691 (accessed on 5 January 2021).
- Ghose, S.; Barua, J.J. Toward the implementation of a topic specific dialogue based natural language chatbot as an undergraduate advisor. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Informatics, Electronics and Vision (ICIEV), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 17–18 May 2013; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J. CSIEC: A computer assisted English learning chatbot based on textual knowledge and reasoning. Knowl. Based Syst. 2009, 22, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Choi, J.; Lee, S.; Oh, C.; Kim, C.; La, S.; Lee, J.; Suh, B. Designing a chatbot for a brief motivational interview on stress management: Qualitative case study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2019, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gianfrancesco, M.A.; Tamang, S.; Yazdany, J.; Schmajuk, G. Potential Biases in Machine Learning Algorithms Using Electronic Health Record Data. JAMA Intern. Med. 2018, 178, 1544–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miner, A.S.; Shah, N.; Bullock, K.D.; Arnow, B.A.; Bailenson, J.; Hancock, J. Key Considerations for Incorporating Conversational AI in Psychotherapy. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaix, B.; Bibault, J.E.; Pienkowski, A.; Delamon, G.; Guillemassé, A.; Nectoux, P.; Brouard, B. When chatbots meet patients: One-year prospective study of conversations between patients with breast cancer and a chatbot. J. Med. Internet Res. 2019, 5, e12856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perski, O.; Crane, D.; Beard, E.; Brown, J. Does the addition of a supportive chatbot promote user engagement with a smoking cessation app? An experimental study. Digit. Health 2019, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, M.; Suvarna, S.; Srivastava, A.; Bharathiraja, S. Automated emergency paramedical response system. Health Inf. Sci. Syst. 2018, 6, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friebe, M. Developments in Health Industry in the Future; Otto Von Guericke University Magdeburg: Magdeburg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocielnik, R.; Agapie, E.; Argyle, A.; Hsieh, D.T.; Yadav, K.; Taira, B.; Hsieh, G. HarborBot: A Chatbot for Social Needs Screening. AMIA Annu. Symp. Proc. 2019, 2019, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zimmerman, A.; Kalra, D. Usefulness of machine learning in COVID-19 for the detection and prognosis of cardiovascular complications. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 21, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syeda, H.B.; Syed, M.; Sexton, K.W.; Syed, S.; Begum, S.; Syed, F.; Yu, F., Jr. The Role of Machine Learning Techniques to Tackle COVID-19 Crisis: A Systematic Review. JMIR Med. Inform. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimadadi, A.; Aryal, S.; Manandhar, I.; Munroe, P.B.; Joe, B.; Cheng, X. Artificial intelligence and machine learning to fight COVID-19. Physiol. Genom. 2020, 52, 200–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assaf, D.; Gutman, Y.; Neuman, Y.; Segal, G.; Amit, S.; Gefen-Halevi, S.; Shilo, N.; Epstein, A.; Mor-Cohen, R.; Biber, A.; et al. Utilization of machine-learning models to accurately predict the risk for critical COVID-19. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2020, 15, 1435–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, M.; Julaiti, J.; Griffin, P.; Kumara, S. Early Stage Machine Learning–Based Prediction of US County Vulnerability to the COVID-19 Pandemic: Machine Learning Approach. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2020, 6, e19446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoneoka, D.; Kawashima, T.; Tanoue, Y.; Nomura, S.; Ejima, K.; Shi, S.; Eguchi, A.; Taniguchi, T.; Sakamoto, H.; Kunishima, H.; et al. Early SNS-based monitoring system for the covid-19 outbreak in Japan: A population-level observational study. J. Epidemiol. 2020, 30, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, A.; Nateqi, J.; Gruarin, S.; Munsch, N.; Abdarahmane, I.; Zobel, M.; Knapp, B. An artificial intelligence-based first-line defence against COVID-19: Digitally screening citizens for risks via a chatbot. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battineni, G.; Chintalapudi, N.; Amenta, F. AI Chatbot Design during an Epidemic like the Novel Coronavirus. Healthcare 2020, 8, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munsch, N.; Martin, A.; Gruarin, S.; Nateqi, J.; Abdarahmane, I.; Weingartner-Ortner, R.; Knapp, B. Diagnostic accuracy of web-based COVID-19 symptom checkers: Comparison study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2020, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oniani, D.; Wang, Y. A Qualitative Evaluation of Language Models on Automatic Question-Answering for COVID-19. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.10964. [Google Scholar]
- Sedik, A.; Iliyasu, A.M.; El-Rahiem, B.A.; Abdel Samea, M.E.; Abdel-Raheem, A.; Hammad, M.; Peng, J.; Abd El-Samie, F.E.; Abd El-Latif, A.A. Deploying machine and deep learning models for efficient data-augmented detection of COVID-19 infections. Viruses 2020, 12, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.; Chen, J.; Hu, R.; Chen, C.; Zheng, C.; Su, Y.; Zhu, T. Twitter Discussions and Emotions About the COVID-19 Pandemic: Machine Learning Approach. J. Med. Internet Res. 2020, 22, e20550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, A.R.; Kim, A.; Rahimi, M.; Ayabakan, S. User reactions to COVID-19 screening chatbots from reputable providers. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2020, 27, 1727–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanoue, Y.; Nomura, S.; Yoneoka, D.; Kawashima, T.; Eguchi, A.; Shi, S.; Harada, N.; Miyata, H. Mental health of family, friends, and co-workers of COVID-19 patients in Japan. Psychiatry Res. 2020, 291, 113067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, L.; Wittbold, K.A.; Dadabhoy, F.Z.; Sato, R.; Landman, A.B.; Schwamm, L.H.; He, S.; Patel, R.; Wei, N.; Zuccotti, G.; et al. Digital triage: Novel strategies for population health management in response to the COVID-19 pandemic. Healthcare 2020, 8, 100493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Judson, T.J.; Odisho, A.Y.; Young, J.J.; Bigazzi, O.; Steuer, D.; Gonzales, R.; Neinstein, A.B. Implementation of a digital chatbot to screen health system employees during the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2020, 27, 1450–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| System Name | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| ASLForm | It is an adaptive learning system that has some fundamental rules for finding a target text. As a user selects output, it continuously and simultaneously updates. |
| COAT | It is a clinical note processing system that is rule-based and uses machine learning (through WEKA) components with the integration of MetaMap Transfer. |
| LEXIMER | It was implemented to render medical imaging and has the ability to find significant recommendations and clinical findings from CT and MRI reports. |
| Barrett et al. (unnamed) | It can identify 17 serious sentinel events such as sepsis, dyspnea, and delirium in palliative carte consult letters. |
| Martinez et al. (unnamed) | It takes NegEx, Genia Tagger, and MetaMap as input and can classify cancer staging pathology reports. |
| Otal et al. 2013 (unnamed) | It can detect T cancer staging classification. It uses WEKA. |
| Wieneke et al. 2015 (unnamed) | It can extract results, laterality and procedure from breast pathology reports, and if high NPV and high PPV classifiers do not agree, then it is sent for manual review. |
| Machine Learning Algorithm | RMSE | R-Squared | Prediction Speed (Observation/s) | Training Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Square Exponential GPR | 0.0038 | 0.99 | 4100 | 0.18 |
| Matern 5/2 GPR | 0.0038 | 0.99 | 3800 | 0.21 |
| Rational Quadratic GPR | 0.0038 | 0.99 | 2700 | 0.23 |
| Linear Regression | 0.0045 | 0.98 | 1700 | 0.37 |
| Exponential GPR | 0.0125 | 0.87 | 3900 | 0.18 |
| Linear SVM | 0.0123 | 0.87 | 4500 | 0.21 |
| Quadratic SVM | 0.0151 | 0.81 | 3400 | 0.13 |
| Cubic SVM | 0.0193 | 0.68 | 4700 | 0.11 |
| Fine Tree | 0.0218 | 0.60 | 4600 | 0.10 |
| Medium Tree | 0.0305 | 0.21 | 4600 | 0.42 |
| Coarse Tree | 0.0344 | 0.00 | 5600 | 0.09 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Siddique, S.; Chow, J.C.L. Machine Learning in Healthcare Communication. Encyclopedia 2021, 1, 220-239. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia1010021
Siddique S, Chow JCL. Machine Learning in Healthcare Communication. Encyclopedia. 2021; 1(1):220-239. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia1010021
Chicago/Turabian StyleSiddique, Sarkar, and James C. L. Chow. 2021. "Machine Learning in Healthcare Communication" Encyclopedia 1, no. 1: 220-239. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia1010021
APA StyleSiddique, S., & Chow, J. C. L. (2021). Machine Learning in Healthcare Communication. Encyclopedia, 1(1), 220-239. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia1010021







