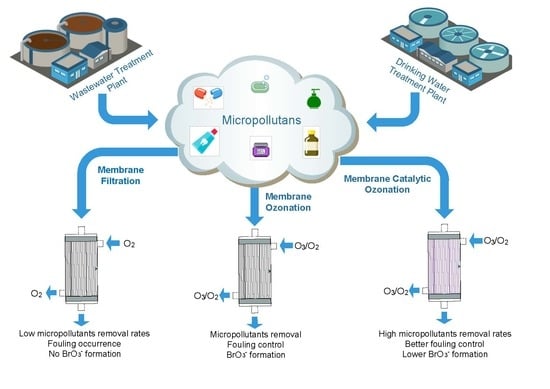
Catalytic Membrane Ozonation
Definition
:1. Introduction
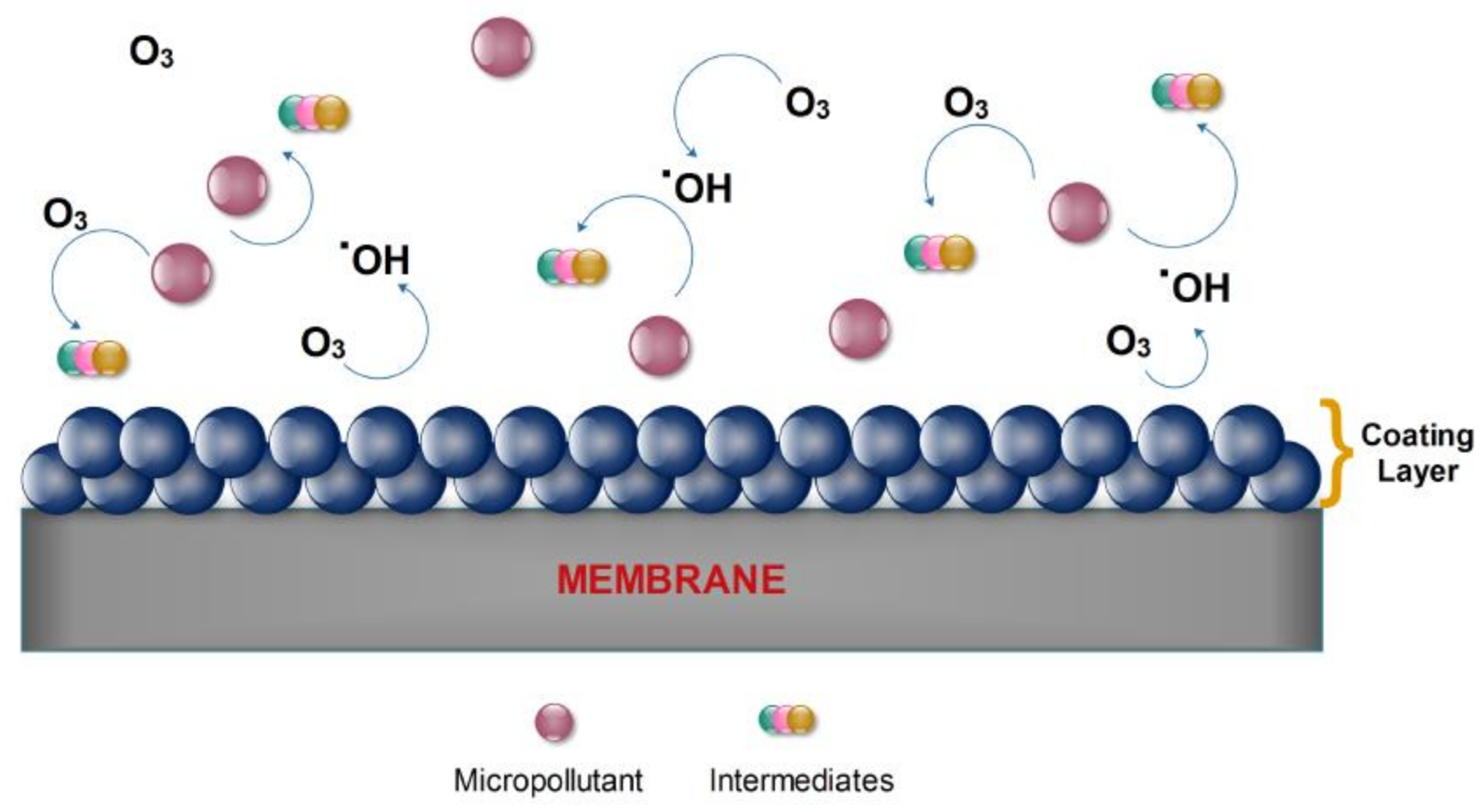
2. Catalytic Ozonation
3. Catalytic Membrane Contactors
4. Important Issues of Consideration, When Applying the Ozonation Process
4.1. Bromate Formation
- pH value: In alkaline pH region the BrO3− formation is higher. The reaction rate constants of Br−/OBr− with molecular ozone and with hydroxyl radicals are 160 M−1s−1/330 M−1s−1 and 1.1 × 109 M−1s−1/4.5 × 109 M−1s−1, respectively. When the solution pH increased, more hydroxyl radicals are formed, leading to more Br− and hypobromide ions (OBr−), which are subsequently oxidized to form BrO3− [34].
- Initial bromide concentration: The production of BrO3− increase with the increase of Br− concentration.
- Ozone dose: The BrO3− concentration increases with an increased ozone dose. In membrane ozonation there is a strong linear relationship between the BrO3− concentration in the permeate and the dissolved ozone concentration [36].
- Temperature: The BrO3− concentration increases with increasing temperature up to 25 °C, because at relatively higher temperature (>25 °C) the ozone stability also becomes a major factor. Additionally, according, to Henry’s law, the efficiency of ozone solubility in an ozonation system decreases with the increase of temperature. Under these conditions the ozone concentration could be even below the respective threshold limit required for BrO3− formation [38]. Table 2 shows the ozone escape to the gas phase at the third min of ozonation process, as well as the respective half-lives at various temperatures.
4.2. Operational Cost Evaluation
5. Limitations and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Entry Link on the Encyclopedia Platform
References
- Shannon, M.A.; Bohn, P.W.; Elimelech, M.; Georgiadis, J.G.; Mariñas, B.J.; Mayes, A.M. Science and Technology for Water Purification in the Coming Decades. Nature 2008, 452, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, M.; Zhang, L.; Lei, J.; Zong, L.; Li, J.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Z. Overview of Emerging Contaminants and Associated Human Health Effects. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 404796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.-K.; Zoh, K.-D. Occurrence and Removals of Micropollutants in Water Environment. Environ. Eng. Res. 2016, 21, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psaltou, S.; Zouboulis, A. Catalytic Ozonation and Membrane Contactors—A Review Concerning Fouling Occurrence and Pollutant Removal. Water 2020, 12, 2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottschalk, C.; Libra, J.A.; Saupe, A. Ozonation of Water and Waste Water. A Practical Guide to Understanding Ozone and Its Application; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, P.; Li, J.; Hou, D.; Wang, J.; Liu, H. A Hybrid Process Combining Homogeneous Catalytic Ozonation and Membrane Distillation for Wastewater Treatment. Chemosphere 2016, 160, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Tang, X.; Sun, Y.; Kou, H. Bioavailability of Dissolved Organic Matter in Biogas Slurry Enhanced by Catalytic Ozonation Combined with Membrane Separation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safety 2020, 196, 110547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Tian, S.; Kong, L.; Tu, Y.; Lu, J.; Xiong, Y. Efficient Degradation of Nitrobenzene by an Integrated Heterogeneous Catalytic Ozonation and Membrane Separation System with Active MgO(111) Catalyst. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 56, 2168–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, S.; Buonomenna, M.; Drioli, E. Catalytic Polymeric Membranes: Preparation and Application. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2006, 307, 167–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stylianou, S.K.; Szymanska, K.; Katsoyiannis, I.A.; Zouboulis, A.I. Novel Water Treatment Processes Based on Hybrid Membrane-Ozonation Systems: A Novel Ceramic Membrane Contactor for Bubbleless Ozonation of Emerging Micropollutants. J. Chem. 2015, 2015, 214927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, M.; Taylor, C.; King, W.; Chew, Y.; Wenk, J. Modelling of Ozone Mass-Transfer through Non-Porous Membranes for Water Treatment. Water 2017, 9, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Xu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, A.; Wang, Y.; Huang, H.; Wang, J. A Novel Electro-Catalytic Membrane Contactor for Improving the Efficiency of Ozone on Wastewater Treatment. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 249, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janknecht, P.; Picard, C.; Larbot, A.; Wilderer, P.A. Membrane Ozonation in Wastewater Treatment. Acta Hydrochim. Hydrobiol. 2004, 32, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoumpouli, G.; Baker, R.; Taylor, C.; Chippendale, M.; Smithers, C.; Xian, S.; Mattia, D.; Chew, Y.; Wenk, J. A Single Tube Contactor for Testing Membrane Ozonation. Water 2018, 10, 1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, H.T. Membrane Filtration in Water Treatment—Removal of Micropollutants. In Chemistry of Advanced Environmental Purification Processes of Water; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 199–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Hu, Y.; Kennedy, S.; Milne, N.; Morris, G.; Jin, W.; Gray, S.; Duke, M. Dual Function Filtration and Catalytic Breakdown of Organic Pollutants in Wastewater Using Ozonation with Titania and Alumina Membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 378, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Chang, J.; Shen, J.; Kang, J.; Chen, Q. Fabrication of a Low-Cost Cementitious Catalytic Membrane for p-Chloronitrobenzene Degradation Using a Hybrid Ozonation-Membrane Filtration System. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 262, 904–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Kim, Y.; An, B.; Choi, H. Characterization of Natural Organic Matter Treated by Iron Oxide Nanoparticle Incorporated Ceramic Membrane-Ozonation Process. Water Res. 2012, 46, 5861–5870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Yu, J.; Wang, H.; Yu, H.; Quan, X. A pilot-scale coupling catalytic ozonation- membrane filtration system for recirculating aquaculture wastewater treatment. Desalination 2015, 363, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corneal, L.M.; Baumann, M.J.; Masten, S.J.; Davies, S.H.R.; Tarabara, V.V.; Byun, S. Mn oxide coated catalytic membranes for hybrid ozonation-membrane filtration: Membrane microstructural characterization. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 369, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Quan, X.; Chen, F.; Fan, X.; Feng, Y. CeO2-TiO2 Coated Ceramic Membrane with Catalytic Ozonation Capability for Treatment of Tetracycline in Drinking Water. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2012, 4, 1191–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Song, Z.; Xu, B.; Li, Y.; Qi, F.; Croue, J.-P.; Yuan, D. A Novel Catalytic Ceramic Membrane Fabricated with CuMn2O4 Particles for Emerging UV Absorbers Degradation from Aqueous and Membrane Fouling Elimination. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 1229–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Brown, M.; Graham, N.J.D. Prevention of PVDF Ultrafiltration Membrane Fouling by Coating MnO2 Nanoparticles with Ozonation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.J.; Zhang, C.; Yang, C.; Zhang, T. Degradation of Nitrobenzene by Nano-TiO2/PVDF Membrane Catalytic Ozonation. In Advances in Intelligent and Soft Computing, Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Informatics, Cybernetics, and Computer Engineering (ICCE2011), Melbourne, Australia, 19–20 November 2011; Jiang, L., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X. Study on Catalytic Ozone Oxidation with Nano-TiO2 Modified Membrane for Treatment of Municipal Wastewater. Asian J. Chem. 2014, 26, 3871–3874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Milne, N.; Gray, S.; Morris, G.; Jin, W.; Duke, M.; Zhu, B. Combined TiO2 membrane filtration and ozonation for efficient water treatment to enhance the reuse of wastewater. Desalination Water Treat. 2011, 34, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.J.; Bao, Y.; Hu, X.; Lim, T.-T. Hybrid Catalytic Ozonation-Membrane Filtration Process with CeOx and MnOx Impregnated Catalytic Ceramic Membranes for Micropollutants Degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 378, 121670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaratti, G.; De Noni Júnior, A.; José, H.J.; de Fatima Peralta Muniz Moreira, R. 1,4-Dioxane Removal from Water and Membrane Fouling Elimination Using CuO-Coated Ceramic Membrane Coupled with Ozone. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 22144–22154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Sonntag, C.; von Gunten, U. Chemistry of Ozone in Water and Wastewater Treatment. From Basic Principals to Applications; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Popiel, S.; Nalepa, T.; Dzierżak, D.; Stankiewicz, R.; Witkiewicz, Z. Rate of Dibutylsulfide Decomposition by Ozonation and the O3/H2O2 Advanced Oxidation Process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 164, 1364–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnik, B.S.; Davies, S.H.; Baumann, M.J.; Masten, S.J. Removal of Escherichia Coli after Treatment Using Ozonation-Ultrafiltration with Iron Oxide-Coated Membranes. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2007, 29, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, S.H.; Baumann, M.J.; Byun, S.; Corneal, L.M.; Tarabara, V.V.; Masten, S.J. Fabrication of Catalytic Ceramic Membranes for Water Filtration. Water Supply 2010, 10, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gounden, A.N.; Jonnalagadda, S.B. Advances in Treatment of Brominated Hydrocarbons by Heterogeneous Catalytic Ozonation and Bromate Minimization. Molecules 2019, 24, 3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ji, H.; Liu, W.; Wang, Z.; Song, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Xu, B.; Qi, F. Synchronous Degradation of Aqueous Benzotriazole and Bromate Reduction in Catalytic Ozonation: Effect of Matrix Factor, Degradation Mechanism and Application Strategy in Water Treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 727, 138696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Gunten, U.; Bruchet, A.; Costentin, E. Bromate Formation in Advanced Oxidation Processes. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 1996, 88, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moslemi, M.; Davies, S.H.; Masten, S.J. Bromate Formation in a Hybrid Ozonation-Ceramic Membrane Filtration System. Water Res. 2011, 45, 5529–5534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischbacher, A.; Löppenberg, K.; von Sonntag, C.; Schmidt, T.C. A New Reaction Pathway for Bromite to Bromate in the Ozonation of Bromide. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 11714–11720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Cui, Y.; Chen, J.; Yan, Z. The Control of Bromate Formation in Ozonation of Bromide-Containing Water. Desalination Water Treat. 2014, 52, 4942–4946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psaltou, S.; Kaprara, E.; Kalaitzidou, K.; Mitrakas, M.; Zouboulis, A. The Effect of Thermal Treatment on the Physicochemical Properties of Minerals Applied to Heterogeneous Catalytic Ozonation. Sustainability 2020, 12, 10503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, F.A.; Silva, C.L.M.; Brandão, T.R.S. A Review on Ozone-Based Treatments for Fruit and Vegetables Preservation. Food Eng. Rev. 2013, 5, 77–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, B.; Chen, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Wu, Q.; Yang, C.; Hu, H.; Wang, R. Inhibition of Bromate Formation by Reduced Graphene Oxide Supported Cerium Dioxide during Ozonation of Bromide-Containing Water. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2019, 13, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q. Study on the Mechanism of Cerium Oxide Catalytic Ozonation for Controlling the Formation of Bromate in Drinking Water. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 15533–15546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Chen, W.; Ma, J.; Qiang, Z. Minimizing Bromate Formation with Cerium Dioxide during Ozonation of Bromide-Containing Water. Water Res. 2008, 42, 3651–3658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Chen, Z.; Xu, Z.; Li, X.; Xu, B.; Qi, F. Kinetics and Mechanism of Degradation of P-Chloronitrobenzene in Water by Ozonation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 1325–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibn Abdul Hamid, K.; Scales, P.J.; Allard, S.; Croue, J.-P.; Muthukumaran, S.; Duke, M. Ozone Combined with Ceramic Membranes for Water Treatment: Impact on HO Radical Formation and Mitigation of Bromate. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 253, 109655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merle, T.; Pronk, W.; von Gunten, U. MEMBRO3X, a Novel Combination of a Membrane Contactor with Advanced Oxidation (O3/H2O2) for Simultaneous Micropollutant Abatement and Bromate Minimization. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2017, 4, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahamuni, N.N.; Adewuyi, Y.G. Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) Involving Ultrasound for Waste Water Treatment: A Review with Emphasis on Cost Estimation. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2010, 17, 990–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fast, S.A.; Gude, V.G.; Truax, D.D.; Martin, J.; Magbanua, B.S. A Critical Evaluation of Advanced Oxidation Processes for Emerging Contaminants Removal. Environ. Process. 2017, 4, 283–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stylianou, S.K.; Kostoglou, M.; Zouboulis, A.I. Ozone Mass Transfer Studies in a Hydrophobized Ceramic Membrane Contactor: Experiments and Analysis. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 7587–7597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.; Tanaka, H. Energy Consumption for PPCPs Removal by O3 and O3/UV. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2011, 33, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaze, W.H.; Kang, J.-W. Advanced Oxidation Processes for Treating Groundwater Contaminated With TCE and PCE: Laboratory Studies. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 1988, 80, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramseier, M.K.; Gunten, U. von. Mechanisms of Phenol Ozonation—Kinetics of Formation of Primary and Secondary Reaction Products. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2009, 31, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrjouei, M.; Müller, S.; Möller, D. Energy Consumption of Three Different Advanced Oxidation Methods for Water Treatment: A Cost-Effectiveness Study. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 65, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, R.C.; Ramos, C.M.; Quinta-Ferreira, R.M. Low-Cost Catalysts To Enhance Ozone Action on the Depuration of Olive Mill Wastewaters. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 15357–15368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biard, P.-F.; Werghi, B.; Soutrel, I.; Orhand, R.; Couvert, A.; Denicourt-Nowicki, A.; Roucoux, A. Efficient Catalytic Ozonation by Ruthenium Nanoparticles Supported on SiO2 or TiO2: Towards the Use of a Non-Woven Fiber Paper as Original Support. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 289, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krewski, D.; Yokel, R.A.; Nieboer, E.; Borchelt, D.; Cohen, J.; Harry, J.; Kacew, S.; Lindsay, J.; Mahfouz, A.M.; Rondeau, V. Human Health Risk Assessment for Aluminium, Aluminium Oxide, and Aluminium Hydroxide. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part B 2007, 10, 1–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pines, D.S.; Reckhow, D.A. Effect of Dissolved Cobalt(II) on the Ozonation of Oxalic Acid. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 4046–4051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, J.F.; Frasson, D.; Pereira, J.L.; Gonçalves, F.J.M.; Castro, L.M.; Quinta-Ferreira, R.M.; Martins, R.C. Ecotoxicity Variation through Parabens Degradation by Single and Catalytic Ozonation Using Volcanic Rock. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 360, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertaud, F.; Croue, J.P.; Lebube, B. Ozonation of a β-0-4 Dimer Lignin Model: By-Product identification and Reaction Pathways. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2001, 23, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Catalytic Membrane | Target Parameter/Pollutant | Efficiency | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| α-Al2O3 | Color TOC (WWTP effluent) | 68% 21% | [16] |
| TiO2 | 88% 43% | ||
| Cement | p-chloro-nitro-benzene | 90% | [17] |
| IONs */α-Al2O3 | p-chlorobenzoic acid (River water) | 56% | [18] |
| Ti-Mn/TiO2/Al2O3 | NOM (aquaculture wastewater) | 52.1% | [19] |
| α-Mn2O3/CéRAM | Flux (Lake water) | 95% (flux recovery) | [20] |
| CeO2-TiO2/α-Al2O3 | Tetracycline | >80% | [21] |
| CuMn2O4/ZrO2/α-Al2O3 | Benzophenone | 76.6% | [22] |
| MnO2/PVDF | Model raw water | Prevention of membrane fouling | [23] |
| Nano-TiO2/PVDF | Nitrobenzene | 59.5% | [24] |
| Nano-TiO2/PVDF | COD (Municipal wastewater after primary treatment) | 27.6% | [25] |
| TiO2/α-Al2O3 | Color | 88.5% | [26] |
| TOC (Municipal wastewater treatment) | 48.7% | ||
| CuO/α-Al2O3-ZrO2 | 1,4-dioxane | 65% | [28] |
| Iron Oxide/CéRAM | E. Coli (Lake water) | >99%(mortality) | [31] |
| Temperature (°C) | Ozone Escape (%) | Half-Life (min) |
|---|---|---|
| 15 | 7.7 | 30 |
| 25 | 9.4 | 15 |
| 35 | 11.1 | 8 |
| Used Catalyst | Experimental Conditions | Bromate Formation (μg/L) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| LaCoO3 | [Br−] = 100 μg/L [O3] = 2 mg/L [catalyst] = 0.25 g/L pH = 6.41 | 84.4 | [34] |
| MgO | [Br−] = 50 mg/L | ≈80 | [38] |
| TiO2 | [O3] = 0.4 mg/L | ≈135 | |
| KMnO4 | [catalyst] ≈ 4 mg/L | ≈35 | |
| CeO2 | [Br−] = 1 mg/L [O3] = 10 mg/L*min [catalyst] = 0.5 g/L pH = 7 time = 10 min | 75.5 | [41] |
| FeOOH | 171.4 | ||
| Fe2O3 | 117.7 | ||
| ZnO | 222.5 | ||
| CeO2 | [Br−] = 1.8 mg/L [O3] = 5.21 mg/L [catalyst] = 0.1 g/L pH = 6.30 T = 18 °C Time = 30 min | 205.58 | [42] |
| MgO | 471.01 | ||
| FeOOH | 351.53 | ||
| CeO2 | [Br−] = 2 mg/L [O3] = 4.51 mg/L [catalyst] = 0.1 g/L pH = 6.20 T = 15 °C Time = 30 min | <300 | [43] |
| α-FeOOH | ≈350 | ||
| γ-FeOOH | <350 | ||
| α-Fe2O3 | ≈450 | ||
| MEMBRO3X | [Br−] = 180 ± 4 μg/L [O3] = 5 g/m3 [catalyst] = 5.67 mg/L pH = 8.1 T = 20 °C time = 25 min | ≈35 | [46] |
| Ozone Concentration (mg/L) | Electrical Energy (kWhm−3) | No. of PPCPs Removed by ≥90% Efficiency from a Total Number 37 | Operational Cost (Yen m−3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 0.03 | 24 | 0.5 |
| 4 | 0.06 | 32 | 0.9 |
| 6 | 0.09 | 35 | 1.4 |
| Pollutant | Ozone Concentration (mg/L) | Pollutant Concentration (mg/L) | Efficiency (%) | Operational Cost ($/1000 gal) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phenol | 2 | 235.28 | 90 | 1.2023 |
| Reactive azo dye | 12.4 | 20 | 90 | 4.0839 |
| TCE | 6 | 2.2 | 40.9 | 2.3549 |
| AOPs | Specific Energy Consumption (kWh/mM) | Treatment Costs (euro/m3) |
|---|---|---|
| Catalytic ozonation | 0.017 | 3.65 |
| Photocatalytic oxidation | 0.063 | 13.55 |
| Photocatalytic ozonation | 0.007 | 1.51 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Psaltou, S.; Mitrakas, M.; Zouboulis, A. Catalytic Membrane Ozonation. Encyclopedia 2021, 1, 131-143. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia1010014
Psaltou S, Mitrakas M, Zouboulis A. Catalytic Membrane Ozonation. Encyclopedia. 2021; 1(1):131-143. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia1010014
Chicago/Turabian StylePsaltou, Savvina, Manassis Mitrakas, and Anastasios Zouboulis. 2021. "Catalytic Membrane Ozonation" Encyclopedia 1, no. 1: 131-143. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia1010014
APA StylePsaltou, S., Mitrakas, M., & Zouboulis, A. (2021). Catalytic Membrane Ozonation. Encyclopedia, 1(1), 131-143. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia1010014