Plantar Load System Analysis Using FSR Sensors and Interpolation Methods
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
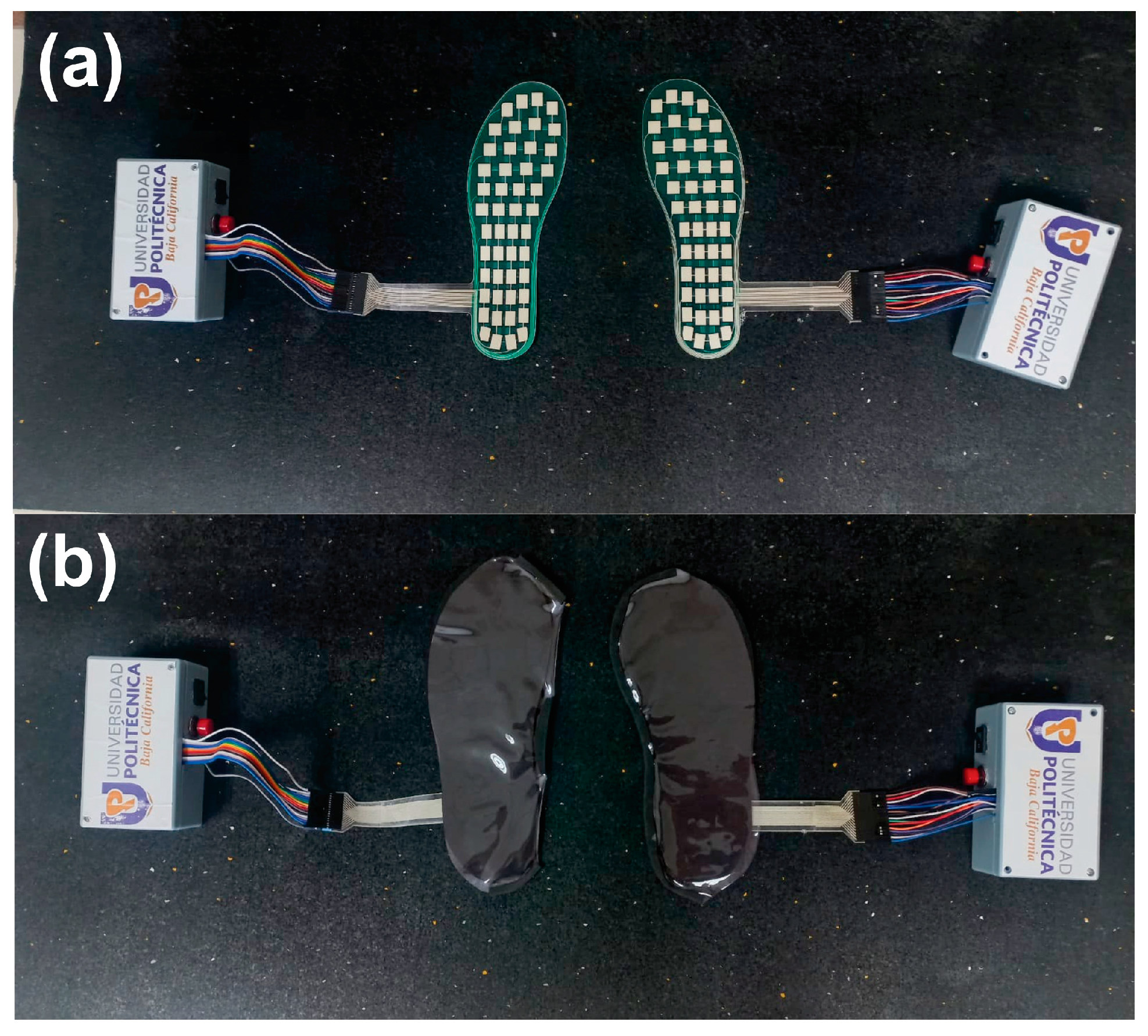
2.1. Plantar Load Insole
2.2. Conditioning Circuit
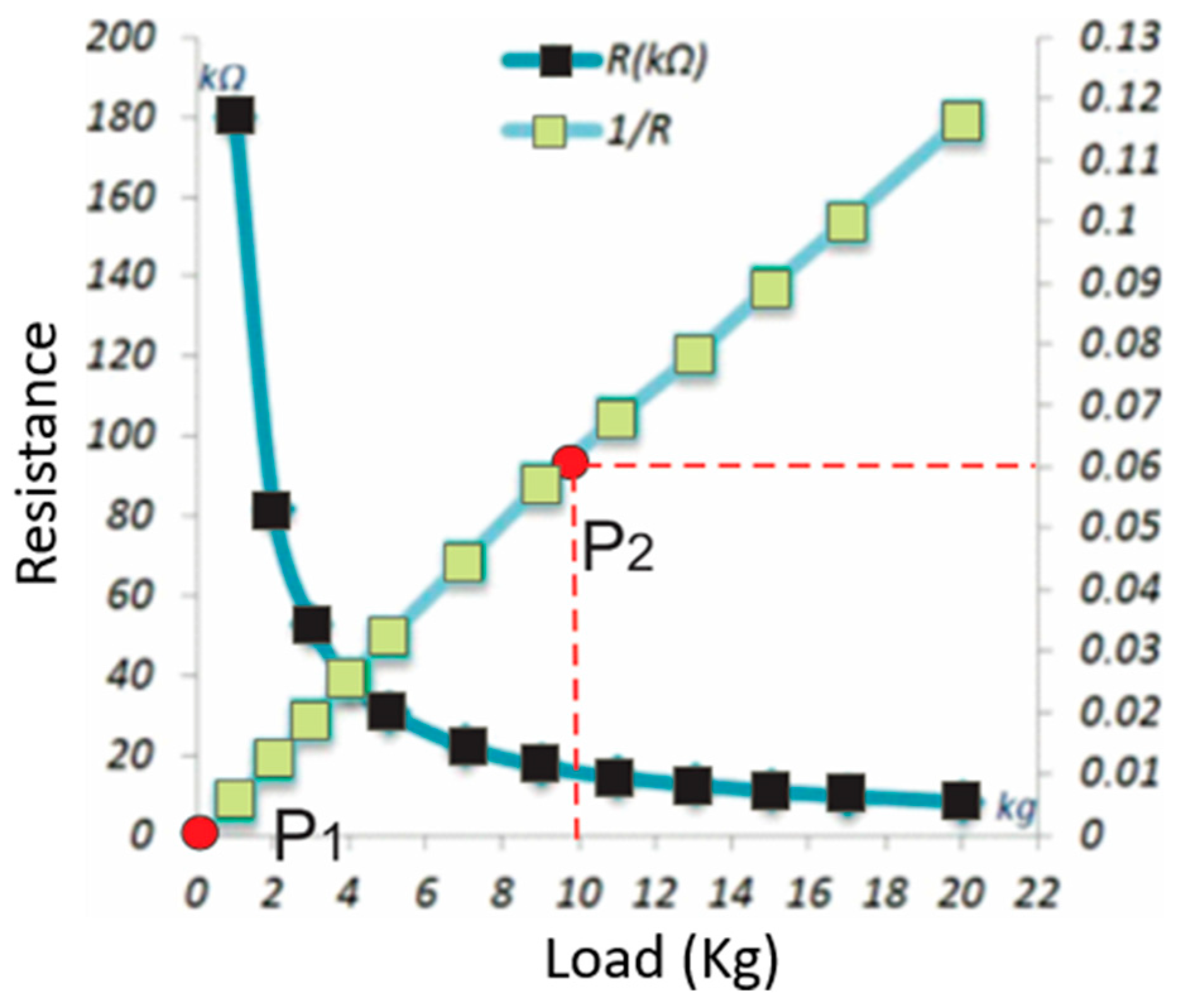
2.3. Conversion of Resistance to Load Units
2.4. Interpolation Methods
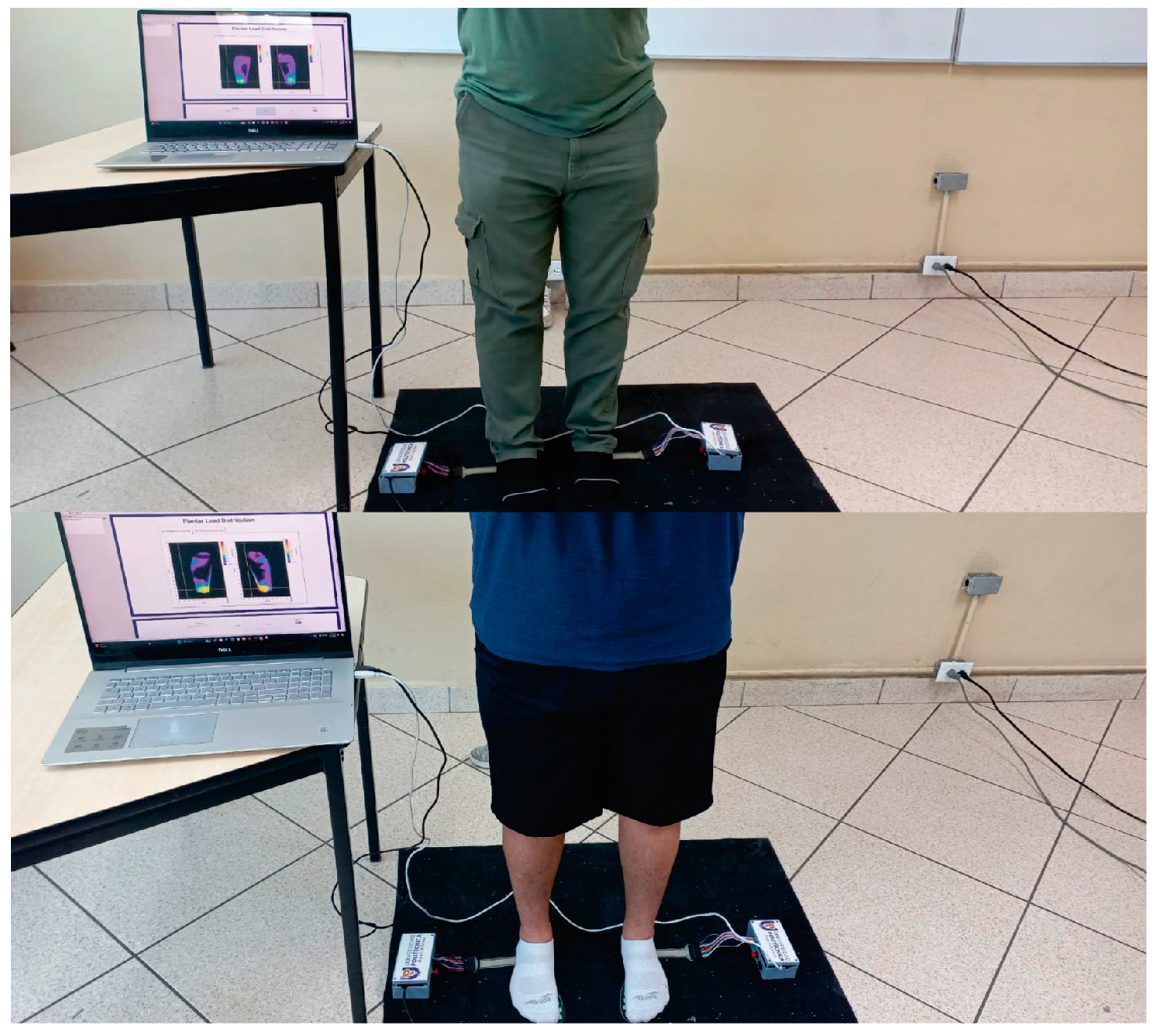
2.5. Software
2.6. Ground Truth vs. Interpolation Methods
3. Experimentation and Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reddie, M.; Frey, D. A resource-efficient plantar pressure evaluation system for diabetic foot risk assessment. Diabetology 2024, 5, 206–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockhart, M.; Dinneen, S.F.; O’Keeffe, D.T. Plantar pressure measurement in diabetic foot disease: A scoping review. J. Diabetes Investig. 2024, 8, 990–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Bader, D.L.; Moser, D.; Parker, D.J.; Forghany, S.; Nester, C.J.; Jiang, L. A wearable insole system to measure plantar pressure and shear for people with diabetes. Sensors 2023, 23, 3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musaid, R.; Ghazwan, A.; Al-Saadan, W.A. A low-cost podoscope for extracting morphological features of the foot. Period. Eng. Nat. Sci. 2023, 11, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musaid, R.; Ghazwan, A.; Al-Saadan, W.A. Assessment of foot deformities in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Al-Khwarizmi Eng. J. 2024, 20, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smondrk, M.; Babusiak, B.; Kreanova, A.; Janousek, L. Design of instrumented insole for gait dynamics monitoring. Lékař Technika 2024, 54, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Y.; Yu, J.; Ma, X.; Chen, W.M. A novel flexible multidimensional force platform for assessing regional plantar pressure and shear stress under the foot during gait. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 11723–11733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; He, Q.; Wang, X.; Lin, Y.; Qiu, J.; Wu, Y.; Yang, J. Capacitive sensors with hybrid dielectric structures and high sensitivity over a wide pressure range for monitoring biosignals. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 6217–6227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo-Hernández, G.; Rodríguez-Quiñonez, J.C.; Flores-Fuentes, W.; Sergiyenko, O.; Ontiveros-Reyes, E.; Real-Moreno, O.; Rascón, R. Development of an integrated podometry system for mechanical load measurement and visual inspection. Measurement 2022, 203, 111866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Villaseñor, D.; Rodríguez-Quiñonez, J.C.; Trujillo-Hernández, G.; Hernandez-Balbuena, D.; Flores-Fuentes, W.; Sanchez-Castro, J.J. Measurement of plantar pressures through FSR sensors and spatial resolution through interpolation. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 33rd International Symposium on Industrial Electronics (ISIE), Ulsan, Republic of Korea, 18 June 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Earshia, V.D.; Sumathi, M. A comprehensive study of 1D and 2D image interpolation techniques. In ICCCE 2018: Proceedings of the International Conference on Communications and Cyber Physical Engineering 2018; Springer: Singapore, 2018; Volume 500, pp. 383–391. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, M.S.M.M. Interpolation techniques in image resampling. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 2018, 7, 567–570. [Google Scholar]
- Hajizadeh, M.; Helfroush, M.S.; Tashk, A. Improvement of image zooming using least directional differences based on linear and cubic interpolation. In Proceedings of the 2009 2nd International Conference on Computer, Control and Communication, Karachi, Pakistan, 17 February 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Azam, N.Z.F.N.; Yazid, H.; Rahim, S.A. Super resolution with interpolation-based method: A review. IJRAR 2022, 9, 168–174. [Google Scholar]
- Fatema, A.; Kuriakose, I.; Gupta, R.; Hussain, A.M. Analysis of interpolation techniques for a flexible sensor mat for plantar pressure measurement. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE Applied Sensing Conference (APSCON), Bengaluru, India, 13 January 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Triwijoyo, B.K.; Adil, A. Analysis of medical image resizing using bicubic interpolation algorithm. J. Ilmu Komput. 2021, 14, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Li, S.; Hu, J. Fusing soft-decision-adaptive and bicubic methods for image interpolation. In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR2012), Tsukuba, Japan, 11 November 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hisham, M.B.; Yaakob, S.N.; Raof, R.A.; Nazren, A.B.; Wafi, N.M. An analysis of performance for commonly used interpolation method. Adv. Sci. Lett. 2017, 23, 5147–5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hadaad, M.H.; Thabit, R.; Zidan, K.A. A new face region recovery algorithm based on bicubic interpolation. JOIV 2023, 7, 1000–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, S.E.; Ye, Y.G.; Lin, Y.C.; Miaou, S.G. Reducing computational requirements of image dehazing using super-resolution networks. In Proceedings of the 2023 Sixth International Symposium on Computer, Consumer and Control, Taichung, Taiwan, 30 June 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Dai, Y.; Han, K.; Wang, J.; Hu, J. An efficient bicubic interpolation implementation for real-time image processing using hybrid computing. J. Real-Time Image Process. 2022, 19, 1211–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, A.; Lin, E.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J. An energy-efficient image filtering interpolation algorithm using domain-specific dynamic reconfigurable array processor. Integration 2024, 96, 102167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Cao, L. Bicubic interpolation and extrapolation iteration method for high resolution digital holographic reconstruction. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2020, 130, 106090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, S.; Khandakar, A.; Chowdhury, M.E.; AbdulMoniem, M.; Reaz, M.B.I.; Mahbub, Z.B.; Alhatou, M. Fiber Bragg Gratings based smart insole to measure plantar pressure and temperature. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2023, 350, 114092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Duan, Q.; Tang, J.; Chen, G.; Zhao, Z.; Sun, Z.; Qu, X. A low-cost instrumented shoe system for gait phase detection based on foot plantar pressure data. IEEE J. Transl. Eng. Health Med. 2023, 12, 2168–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, C.W.; Park, K.; Paek, M.C.; Jee, S.; Park, J.H. Validation of the Short Physical Performance Battery via Plantar Pressure Analysis Using Commercial Smart Insoles. Sensors 2023, 23, 9757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H. Walking speed estimation and gait classification using plantar pressure and on-device deep learning. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 23336–23347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwich, A.; Ismaiel, E.; Al-kayal, A.; Ali, M.; Masri, M.; Nazha, H.M. Recognizing different foot deformities using FSR sensors by static classification of neural networks. Baghdad Sci. J. 2023, 20, 2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, P.A.Q. Métodos Numéricos con Aplicaciones en Excel; Reverte: Barcelona, Spain, 2005; pp. 1–263. [Google Scholar]
- Steiner, E. Matemáticas para las Ciencias Aplicadas; Reverte: Barcelona, Spain, 2018; pp. 1–624. [Google Scholar]
- Bhabatosh, C. Digital Image Processing and Analysis; PHI Learning Pvt. Ltd.: Delhi, India, 2011; Volume 1, pp. 1–469. [Google Scholar]
- Esfandiari, R.S. Numerical Methods for Engineers and Scientists Using MATLAB®; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 1–493. [Google Scholar]
- Aizawa, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Satoh, S.I. (Eds.) Advances in Multimedia Information Processing-PCM 2004: 5th Pacific Rim Conference on Multimedia, Tokyo, Japan, 30 November–3December 2004, Proceedings; Springer Science & Business Media: Tokyo, Japan, 2004; pp. 1–1323.
- Shapiro, L. (Ed.) Computer Vision and Image Processing; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1992; pp. 1–431. [Google Scholar]
- Ota, K.; Ukai, T.; Wakai, T. Spatial resolution improvement by a super-resolution technique depending on training process in the background-orientated schlieren analyses. Phys. Fluids 2023, 35, 126103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Performance Parameter | Parameter Value |
|---|---|
| Static Resistance | 1 MΩ |
| Hysteresis | Less than 6% |
| Drift | Less than 8% |
| Sensor Repeatability | ±8% |
| Working Voltage | 3.3 V–5 V |
| Working Temperature | −50 °C–60 °C |
| Working Humidity | 0–95% |
| Response Time | Less than 20 ms |
| Lifespan | More than 500,000 cycles |
| Subject | Weight (kg) | Height (m) | Shoe Size (Inches) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 60 | 1.62 | 7 |
| 2 | 96 | 1.74 | 9.5 |
| 3 | 88 | 1.65 | 6.5 |
| 4 | 64 | 1.49 | 6.5 |
| 5 | 50 | 1.58 | 6 |
| 6 | 55 | 1.52 | 4 |
| 7 | 90 | 1.76 | 9 |
| 8 | 73 | 1.72 | 9.5 |
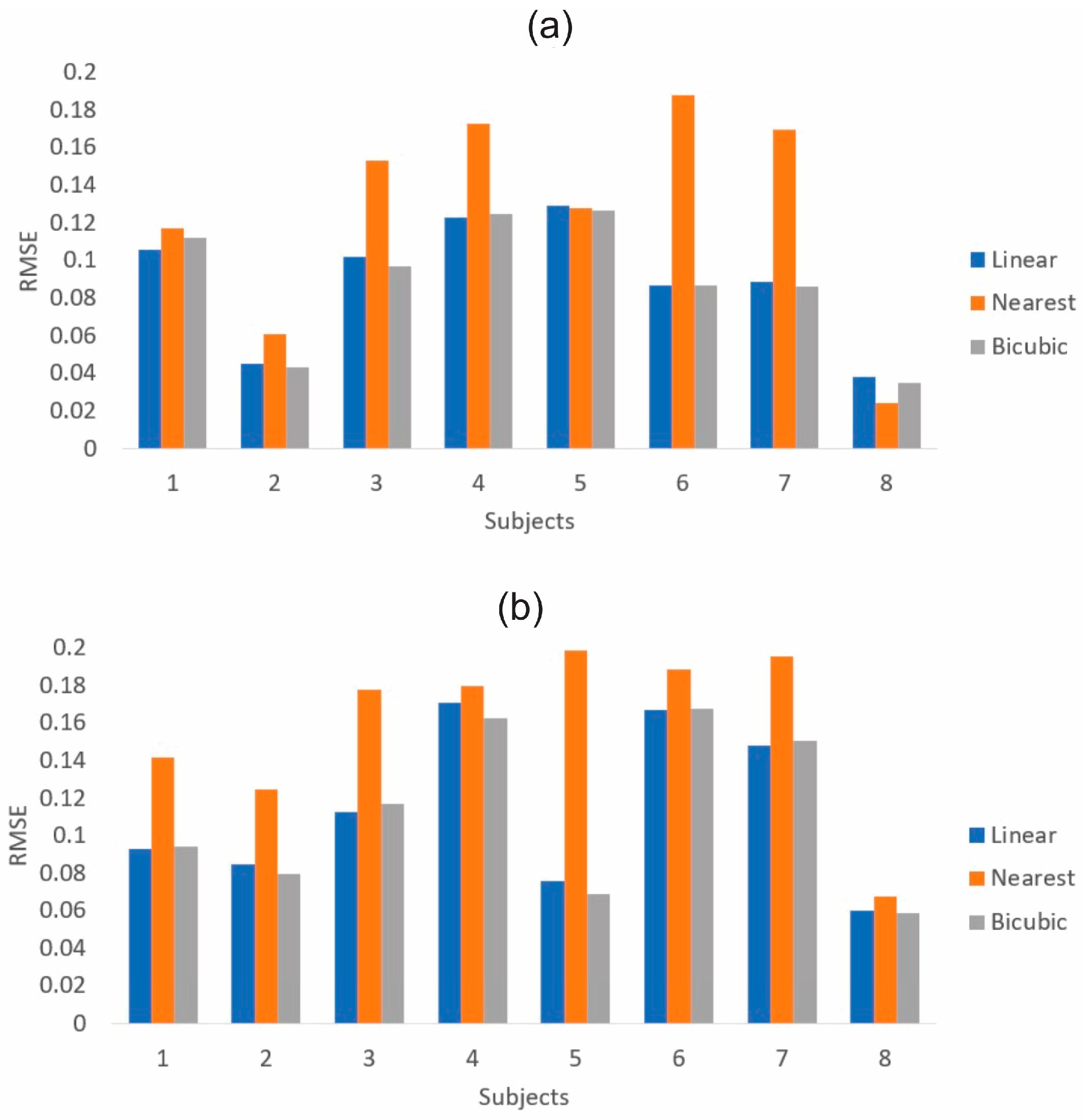
| Subject | Linear (kg) | Nearest Neighbor (kg) | Bicubic (kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.086 | 0.122 | 0.086 |
| 2 | 0.045 | 0.061 | 0.043 |
| 3 | 0.102 | 0.153 | 0.097 |
| 4 | 0.123 | 0.173 | 0.125 |
| 5 | 0.129 | 0.128 | 0.127 |
| 6 | 0.087 | 0.188 | 0.087 |
| 7 | 0.089 | 0.170 | 0.086 |
| 8 | 0.038 | 0.024 | 0.035 |
| Subject | Linear (kg) | Nearest Neighbor (kg) | Bicubic (kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.093 | 0.142 | 0.094 |
| 2 | 0.085 | 0.125 | 0.080 |
| 3 | 0.113 | 0.178 | 0.117 |
| 4 | 0.171 | 0.180 | 0.163 |
| 5 | 0.076 | 0.199 | 0.069 |
| 6 | 0.167 | 0.189 | 0.168 |
| 7 | 0.148 | 0.196 | 0.151 |
| 8 | 0.060 | 0.068 | 0.059 |
| Ground Truth (kg) | x Position | y Position | Linear Interpolation (kg) | Nearest Interpolation (kg) | Bicubic Interpolation (kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.196 | −2.5 | −1.3 | 0.096 | 0.185 | 0.100 |
| 0.280 | −0.4 | −3.5 | 0.212 | 0.245 | 0.171 |
| 0.191 | −1.9 | −5.2 | 0.112 | 0.190 | 0.113 |
| 0.204 | 0.2 | −0.7 | 0.111 | 0.000 | 0.156 |
| 0 | −0.9 | −8.7 | 0.099 | 0.185 | 0.076 |
| 0.185 | 0.2 | −10.6 | 0.134 | 0.000 | 0.144 |
| 0 | −1.1 | −12.5 | 0.095 | 0.000 | 0.102 |
| 0.268 | 0.3 | −14.5 | 0.245 | 0.302 | 0.262 |
| 0.545 | −0.8 | −16.3 | 0.436 | 0.435 | 0.452 |
| 0.567 | 0.3 | −18.2 | 0.457 | 0.729 | 0.428 |
| Ground Truth (kg) | x Position | y Position | Linear Interpolation (kg) | Nearest Interpolation (kg) | Bicubic Interpolation (kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.233 | 1.4 | −3.5 | 0.152 | 0.285 | 0.152 |
| 0 | −3.8 | −5.2 | 0.029 | 0.000 | 0.043 |
| 0 | −2.4 | −8.7 | 0.065 | 0.000 | 0.056 |
| 0.278 | 1.5 | −10.6 | 0.216 | 0.185 | 0.211 |
| 0 | −2.2 | −10.6 | 0.107 | 0.000 | 0.093 |
| 0.235 | 1.3 | −12.5 | 0.204 | 0.223 | 0.202 |
| 0 | −2.2 | −12.5 | 0.157 | 0.000 | 0.160 |
| 0.215 | 1.5 | −16.3 | 0.118 | 0.435 | 0.116 |
| 0.438 | −2 | −16.3 | 0.509 | 0.545 | 0.523 |
| 0.205 | 1.5 | −17.8 | 0.064 | 0.567 | 0.063 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trujillo-Hernández, G.; Ortiz-Villaseñor, D.; Rodríguez-Quiñonez, J.C.; Ramírez-Hernández, L.R.; Murrieta-Rico, F.N.; Mercado-Herrera, A.; Raygoza-Limón, M.E.; Orduño-Osuna, J.H. Plantar Load System Analysis Using FSR Sensors and Interpolation Methods. Metrology 2024, 4, 566-577. https://doi.org/10.3390/metrology4040035
Trujillo-Hernández G, Ortiz-Villaseñor D, Rodríguez-Quiñonez JC, Ramírez-Hernández LR, Murrieta-Rico FN, Mercado-Herrera A, Raygoza-Limón ME, Orduño-Osuna JH. Plantar Load System Analysis Using FSR Sensors and Interpolation Methods. Metrology. 2024; 4(4):566-577. https://doi.org/10.3390/metrology4040035
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrujillo-Hernández, Gabriel, Dayanna Ortiz-Villaseñor, Julio C. Rodríguez-Quiñonez, Luis Roberto Ramírez-Hernández, Fabian N. Murrieta-Rico, Abelardo Mercado-Herrera, María E. Raygoza-Limón, and Jesús Heriberto Orduño-Osuna. 2024. "Plantar Load System Analysis Using FSR Sensors and Interpolation Methods" Metrology 4, no. 4: 566-577. https://doi.org/10.3390/metrology4040035
APA StyleTrujillo-Hernández, G., Ortiz-Villaseñor, D., Rodríguez-Quiñonez, J. C., Ramírez-Hernández, L. R., Murrieta-Rico, F. N., Mercado-Herrera, A., Raygoza-Limón, M. E., & Orduño-Osuna, J. H. (2024). Plantar Load System Analysis Using FSR Sensors and Interpolation Methods. Metrology, 4(4), 566-577. https://doi.org/10.3390/metrology4040035








