Utilization of AI to Diagnose Aortic Stenosis in Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis
Abstract
1. Background
2. Methods
2.1. Study Population
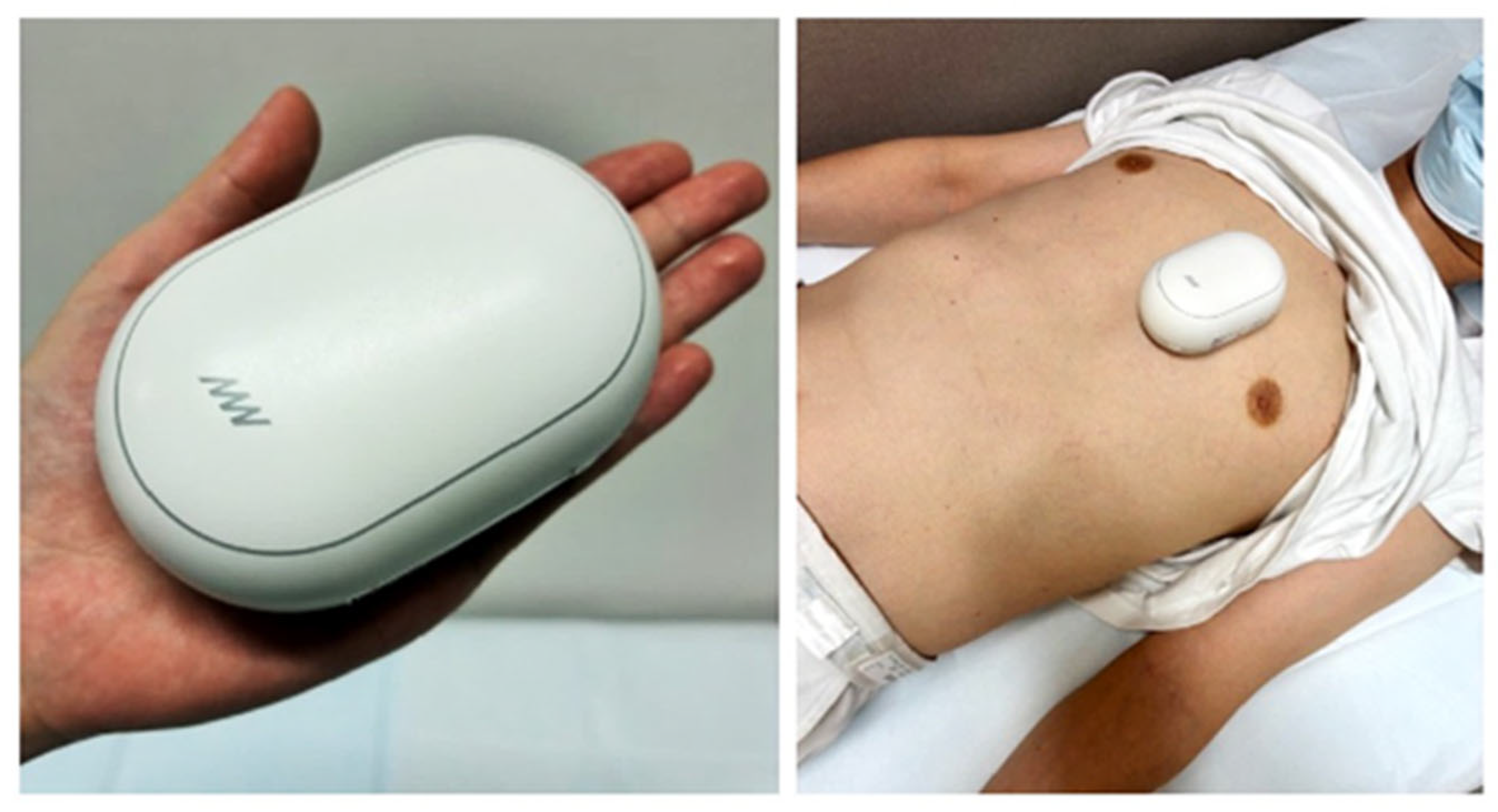
2.2. Methodology of the AI Algorithm
2.3. Comparison Between AI-Based Estimation and Echocardiography
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
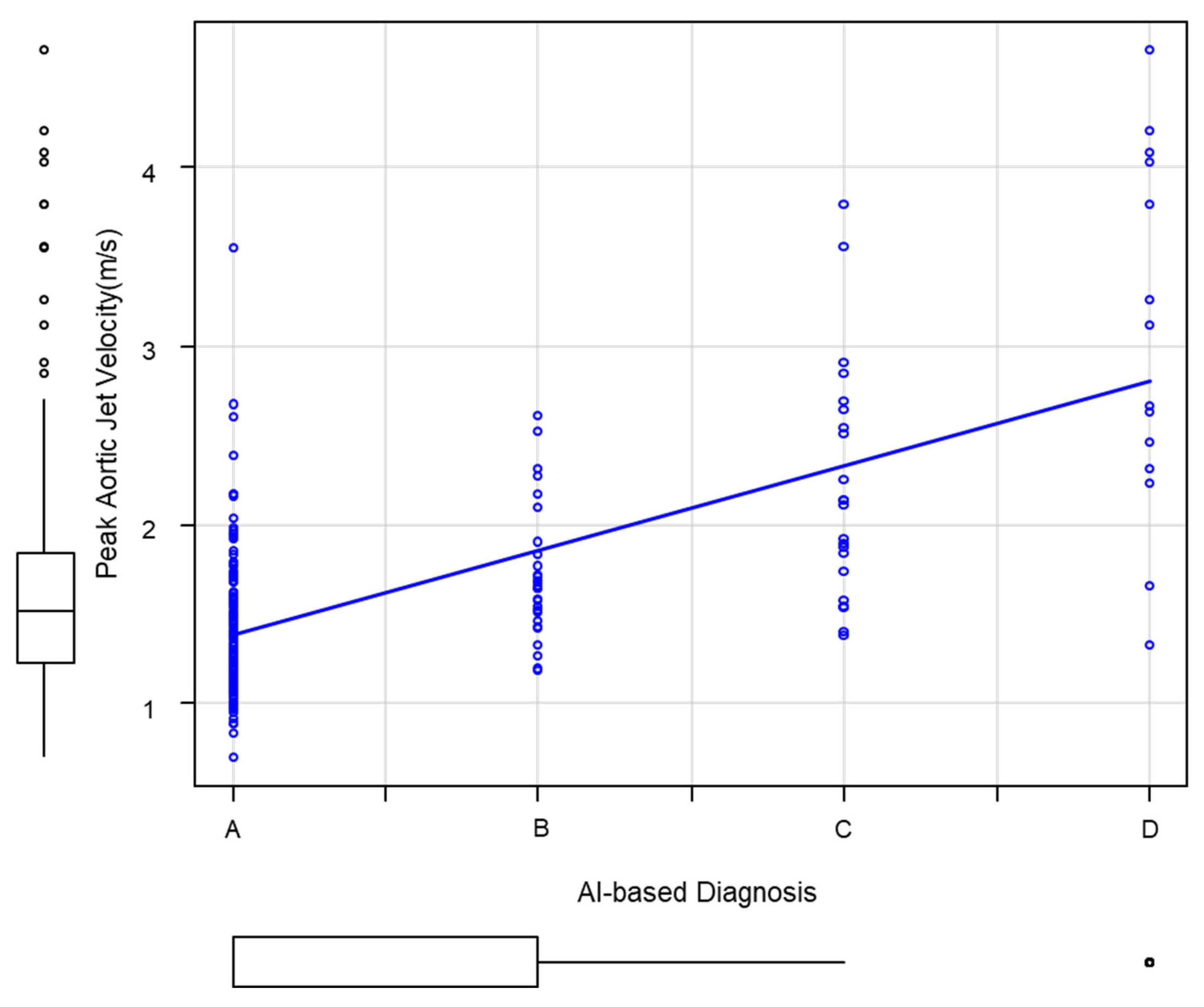
3.2. Correlation Between the Grade of AI Diagnosis and Echocardiography
3.3. A Case Showing Discrepancy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Hoshina, M.; Wada, H.; Sakakura, K.; Kubo, N.; Ikeda, K.; Sugawara, Y.; Yasu, T.; Ako, J.; Momomura, S.-I. Determinants of progression of aortic valve stenosis and outcome of adverse events in hemodialysis patients. J. Cardiol. 2012, 59, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasakawa, Y.; Okamoto, N.; Fujii, M.; Kato, J.; Yuzawa, Y.; Inaguma, D. Factors associated with aortic valve stenosis in Japanese patients with end-stage kidney disease. BMC Nephrol. 2022, 23, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masaki, T.; Hanabusa, N.; Abe, M.; Joki, N.; Hoshino, J.; Taniguchi, M.; Kikuchi, K. 2023 Annual dialysis data report, JSDT renal data registry. J. Jpn. Soc. Dial. Ther. 2024, 57, 543–620. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Ohara, T.; Hashimoto, Y.; Matsumura, A.; Suzuki, M.; Isobe, M. Accelerated progression and morbidity in patients with aortic stenosis on chronic dialysis. Circ. J. 2005, 69, 1535–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straumann, E.; Meyer, B.; Misteli, M.; Blumberg, A.; Jenzer, H.R. Aortic and mitral valve disease in patients with end stage renal failure on long-term haemodialysis. Br. Heart J. 1992, 67, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaguma, D.; Sasakawa, Y.; Suzuki, N.; Ito, E.; Takahashi, K.; Hayashi, H.; Koide, S.; Hasegawa, M.; Yuzawa, Y. Aortic stenosis is a risk factor for all-cause mortality in patients on dialysis: A multicenter prospective cohort analysis. BMC Nephrol. 2018, 19, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawase, Y.; Taniguchi, T.; Morimoto, T.; Kadota, K.; Iwasaki, K.; Kuwayama, A.; Ohya, M.; Shimada, T.; Amano, H.; Maruo, T.; et al. Severe aortic stenosis in dialysis patients. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e004961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanger, D.; Wan, D.; Moghaddam, N.; Elahi, N.; Argulian, E.; Narula, J.; Ahmadi, A. Insonation versus auscultation in valvular disorders: Is aortic stenosis the exception? A systematic review. Ann. Glob. Health 2019, 85, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anne, H.D.; Stian, A.; Peder, A.H.; Henrik, S.; Eirik, R.; Hasse, M. Diagnostic accuracy of heart auscultation for detecting valve disease: A systematic review. BMJ Open 2023, 13, e068121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, A.; Uddin, S.; Rahman, P.; Anee, M.J.; Rifat, M.M.H.; Uddin, M.M. Wavelet and spectral analysis of normal and abnormal heart sound for diagnosing cardiac disorders. Biomed. Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 9092346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrez, B.; Reem, A.; Amal, A.; Ahmed, B. Cardiovascular disease recognition based on heartbeat segmentation and selection process. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 10952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreas, V.; Andrea, M.; Thomas, H. Diagnosing aortic valve stenosis by parameter extraction of heart sound signals. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2005, 33, 1167–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraf, K.; Baek, C.I.; Wasko, M.H.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Borgstrom, P.H.; Mahajan, A.; Kaiser, W.J. Fully-Automated Diagnosis of Aortic Stenosis Using Phonocardiogram-Based Features. In Proceedings of the 2019 41st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC 2019), Berlin, Germany, 23–27 July 2019; pp. 6673–6676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, S.; Namino, F.; Mori, T.; Sato, G.; Yamakawa, T.; Saito, S. AI diagnosis of heart sounds differentiated with super StethoScope. J. Cardiol. 2024, 83, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagi, K.; Ogawa, S.; Saito, S.; Iwakawa, M.; Tsuchiya, T.; Mizuta, S.; Yamasaki, N.; Muro, T. A case of intensified fourth and second heart sounds analyzed using a visualized phonocardiogram during the 2024 Noto Peninsula earthquake recovery efforts. Intern. Med. 2024, 64, 1998–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, A.; Takeji, Y.; Shimojima, M.; Takamura, M. Digitalomics: Towards artificial intelligence/machine learning-based precision cardiovascular medicine. Circ. J. 2024, CJ-24-0865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, S.; Ishii, M.; Saito, S.; Seki, H.; Ikeda, K.; Yasui, Y.; Komatsu, T.; Sato, G.; Tabata, N.; Ohishi, M.; et al. Deep learning for cardiac overload estimation―Predicting B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) levels from heart sounds and electrocardiogram. Circ. J. 2025, 89, 1684–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.; Weerts, J.; Bekkers, A.; Achten, A.; Lievens, S.; Smeets, K.; van Empel, V.; Delhaas, T.; Prinzen, F.W. Association between phonocardiography and echocardiography in heart failure patients with preserved ejection fravtion. Eur. Heart J. Digit. Health 2023, 4, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumi, C.; Eishi, K.; Ashihara, K.; Arita, T.; Otsuji, Y.; Kunihara, T.; Komiya, T.; Shibata, T.; Seo, Y.; Daimon, M.; et al. JCS/JSCS/JATS/JSVS 2020 guidelines on the management of valvular heart disease. Circ. J. 2020, 84, 2037–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, Y. Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2013, 48, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichihara, H.; Koga, H.; Muratsu, I.; Takeguchi, Y.; Nakanishi, N.; Uemura, T.; Kusunoki, S.; Hirose, T. Severity analysis of aortic valve stenosis using the cardiac sound graph examination device AMI-SSS01. Jpn. J. Med. Tech. 2025, 74, 37–44. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provenzano, M.; Rivoli, L.; Garofalo, C.; Faga, T.; Pelagi, E.; Perticone, M.; Serra, R.; Michael, A.; Comi, N.; Andreucci, M. Renal resistive index in chronic kidney disease patients: Possible determinants and risk profile. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reetu, S.; Joel, A.S.; Leo, O.; Babu, J.; Michael, D.V. Age-related changes in the aortic valve affect leaflet stress distributions: Implications for aortic valve degeneration. J. Heart Valve Dis. 2008, 17, 290–298. [Google Scholar]
- Grimard, B.H.; Safford, R.E.; Burns, E.L. Aortic stenosis: Diagnosis and treatment. Am. Fam. Physician 2008, 78, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kjeldsen, E.W.; Thomassen, J.Q.; Rasmussen, K.L.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Tybjag-Hansen, A.; Frikke-Schmidt, R. Cardiovascular risk factors and aortic valve stenosis: Towards 10-year absolute risk charts for primary prevention. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2024, 32, zwae177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Total | Male | Female | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | 194 | 130 | 64 |
| Age (year); median (range) | 72.6 (33–98) | 72.6 (43–98) | 72.6 (33–91) |
| History of hemodialysis (months); median (range) | 132 (3–1502) | 142 (5–1501) | 125 (3–1502) |
| Underlying kidney disease | |||
| Diabetic Kidney Disease | 63 | 46 | 17 |
| Hypertensive nephrosclerosis | 50 | 40 | 10 |
| Glomerulonephlitis | 40 | 20 | 20 |
| Others | 41 | 24 | 17 |
| Echocardiography | AI-Based Analysis of Systolic Murmurs | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grade A | B | C | D | |||
| Total | Peak aortic jet velocity (m/s) | 194 | 129 | 29 | 22 | 14 |
| Normal | ≦2.0 | 156 | 121 | 23 | 10 | 2 |
| Aortic valve calcification | 2.0–2.5 | 19 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 3 |
| Aortic stenosis (AS) | 19 | 3 | 1 | 6 | 9 | |
| Mild | 2.6–2.9 | 9 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 2 |
| Moderate | 3.0–3.9 | 6 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 3 |
| Severe | 4.0–4.9 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| AI-Based Diagnosis | AS Diagnosed by Echocardiography | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|
| B and higher | Mild and higher | 0.84 | 0.72 |
| Moderate and Severe | 0.90 | 0.70 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Ito, A.; Morishita, Y.; Morizane, A.; Okazaki, M.; Kindaichi, A.; Gatto, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Shiino, K.; Ina, K. Utilization of AI to Diagnose Aortic Stenosis in Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis. Kidney Dial. 2026, 6, 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/kidneydial6010004
Ito A, Morishita Y, Morizane A, Okazaki M, Kindaichi A, Gatto K, Tanaka Y, Shiino K, Ina K. Utilization of AI to Diagnose Aortic Stenosis in Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis. Kidney and Dialysis. 2026; 6(1):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/kidneydial6010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleIto, Asuka, Yoshihiro Morishita, Atushi Morizane, Masaki Okazaki, Akihiro Kindaichi, Kouki Gatto, Yoshiteru Tanaka, Kenji Shiino, and Kenji Ina. 2026. "Utilization of AI to Diagnose Aortic Stenosis in Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis" Kidney and Dialysis 6, no. 1: 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/kidneydial6010004
APA StyleIto, A., Morishita, Y., Morizane, A., Okazaki, M., Kindaichi, A., Gatto, K., Tanaka, Y., Shiino, K., & Ina, K. (2026). Utilization of AI to Diagnose Aortic Stenosis in Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis. Kidney and Dialysis, 6(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/kidneydial6010004






