Chronic Tubulointerstitial Nephropathy of Agricultural Communities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Agricultural Communities—Problems and Challenges
3. Epidemiology of CTINAC
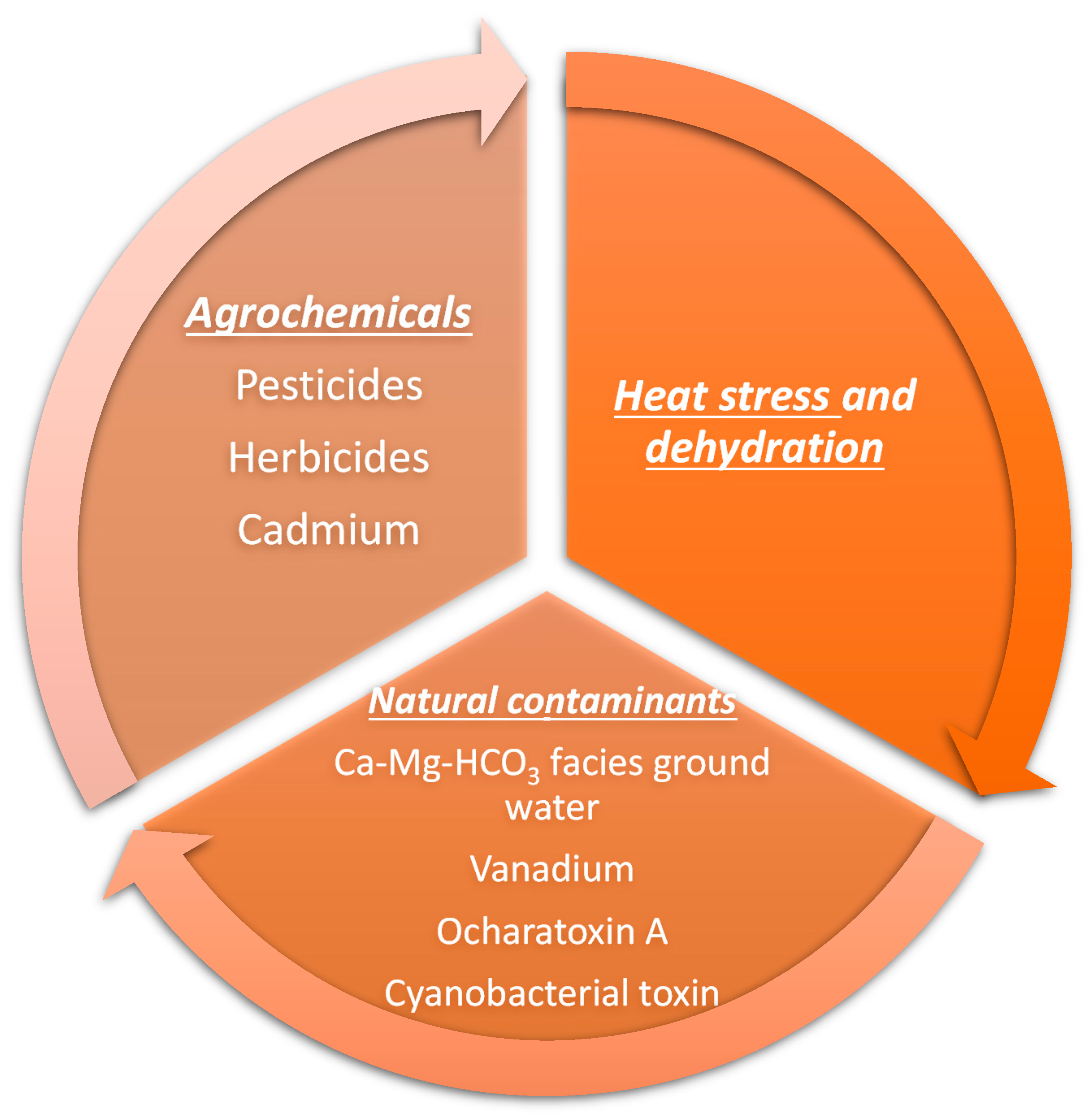
4. Risk Factors for Developing Chronic Interstitial Nephritis in Agricultural Workers
5. Pathophysiology and Pathology of CTINAC
6. Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis
- (A)
- No history of diabetes, hypertension, glomerulonephritis, snakebite, or urologic disease of known etiology;
- (B)
- Normal HbA1c level;
- (C)
- BP < 160/100 mm Hg untreated or BP < 140/90 mm Hg on two or fewer antihypertensive medications.
- 1
- Suspected CTINAC-
- a
- Essential criteria: CKD stage 3–5 (eGFR calculation by CKD-EPI equation)/albuminuria ≥ 30 mg per gram creatinine/proteinuria ≥ 150 mg per gram creatinine.
- b
- Exclusion criteria: Proteinuria > 3000 mg per gram creatinine/albuminuria > 300 mg per gram creatinine/diabetes/hypertension (on two or more antihypertensive medications or untreated BP > 160/100 mm Hg)/history of dialysis requiring acute kidney injury/age > 70 years.
- 2
- Probable CTINAC-
- a
- Essential criteria: Criteria of suspected CTINAC persistent on repeat evaluation after 3 months.
- b
- Exclusion criteria: Diabetes mellitus/clinicopathological evidence of the presence of other known CKD etiologies/radiological evidence of unequal kidney sizes with a discrepancy of >15 mm, obstructive nephropathy, kidney stones with either obstruction or non-obstructive single stone > 1 cm/non-obstructive unilateral or bilateral multiple stones > 5 mm in size.
- 3
- Confirmed CTINAC-
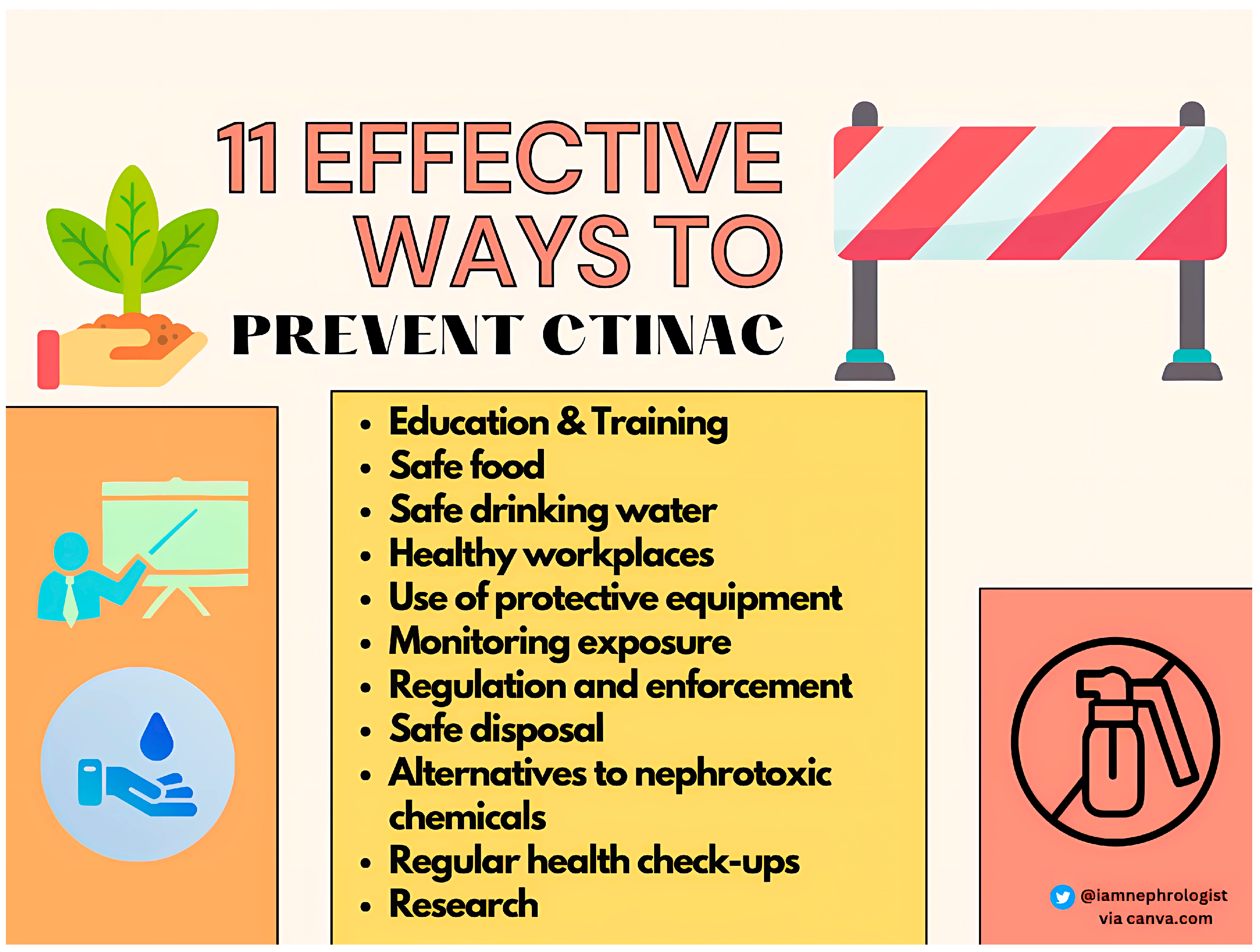
7. Prevention and Management
- Education and training: educating agricultural workers about the risks associated with exposure to nephrotoxic chemicals and training them on the safe handling, storage, and use of these chemicals is essential.
- Safe food: we need to ensure the delivery of safe food to agricultural workers to avoid recurrent toxin exposure.
- Safe drinking water: We need to monitor and ensure the delivery of toxin-free safe drinking water in CTINAC-endemic areas. This will require political will and the involvement of community workers. We need to teach agricultural workers about adequate fluid intake and avoid fructose-rich fluids.
- Healthy workplaces: farm workers should be employed in a healthy work environment with frequent breaks, drinking water facilities, healthy food, and fixed working hours.
- Use of protective equipment: Providing agricultural workers with personal protective equipment such as gloves, boots, and masks can help prevent exposure to nephrotoxic chemicals.
- Monitoring exposure: Regular monitoring of agricultural workers for exposure to nephrotoxic chemicals can help identify individuals who are at risk of developing CTINAC and allow for early intervention.
- Regulation and enforcement: Governments and regulatory bodies should implement and enforce strict regulations on the use of nephrotoxic chemicals in agriculture to protect workers from exposure.
- Safe disposal: Proper disposal of nephrotoxic chemicals and their containers is essential to prevent environmental contamination and reduce the risk of exposure to agricultural workers.
- Alternatives to nephrotoxic chemicals: Encouraging the use of safer, non-nephrotoxic chemicals in agriculture or adopting alternative methods of pest control can reduce the risk of exposure to nephrotoxic chemicals.
- Regular health check-ups: Regular health check-ups of agricultural workers can help detect the early signs of CTINAC and allow for timely intervention.
- Research: we need to promote collaborative basic and clinical research for a better understanding of CTINAC pathophysiology and identify protective and preventive strategies against CTINAC.
8. Recent Advances and Future Research in the Understanding of CTINAC
- Further epidemiological studies investigate the prevalence and incidence of chronic interstitial nephritis in agricultural communities in various regions and countries and identify risk factors associated with the disease.
- Development and validation of non-invasive diagnostic biomarkers for early detection of CTINAC, including urinary and blood-based markers.
- Investigation of the mechanisms by which environmental toxins, such as pesticides and heavy metals, cause CTINAC, and development of effective prevention and intervention strategies.
- Evaluation of the impact of CTINAC on the overall health and well-being of affected individuals, including physical, social, and economic consequences.
- Examination of potential interactions between CTINAC and other health conditions prevalent in agricultural communities, such as infectious diseases and malnutrition.
- To Investigate potential genetic and epigenetic factors contributing to the development of CTINAC.
- Exploration of novel therapeutic approaches for the treatment of CTINAC, including targeted drug therapies and regenerative medicine approaches.
- Development and implementation of educational programs aimed at raising awareness of chronic interstitial nephritis among agricultural workers and their families, as well as healthcare professionals and policymakers.
- Examination of potential links between CTINAC and environmental sustainability, including impacts on agricultural productivity and food security.
- Collaboration across disciplines and sectors to address the complex and multifaceted nature of CTINAC, including partnerships with government agencies, non-governmental organizations, and community-based organizations.
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Perazella, M.A.; Markowitz, G.S. Drug-induced acute interstitial nephritis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2010, 6, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praga, M.; González, E. Acute interstitial nephritis. Kidney Int. 2010, 77, 956–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heptinstall, R.H. Interstitial nephritis. A brief review. Am. J. Pathol. 1976, 83, 213–236. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Naik, R.H.; Annamaraju, P. Interstitial Nephritis. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Perazella, M.A. Clinical Approach to Diagnosing Acute and Chronic Tubulointerstitial Disease. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2017, 24, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasumana, C.; Orantes, C.; Herrera, R.; Almaguer, M.; Lopez, L.; Silva, L.C.; Ordunez, P.; Siribaddana, S.; Gunatilake, S.; De Broe, M.E. Chronic interstitial nephritis in agricultural communities: A worldwide epidemic with social, occupational and environmental determinants. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2017, 32, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orantes, C.; Olano, C.G.; Akram, S.M. Chronic Interstitial Nephritis in Agricultural Communities (CINAC). In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Liyanage, T.; Toyama, T.; Hockham, C.; Ninomiya, T.; Perkovic, V.; Woodward, M.; Fukagawa, M.; Matsushita, K.; Praditpornsilpa, K.; Hooi, L.S.; et al. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in Asia: A systematic review and analysis. BMJ Glob. Health 2022, 7, e007525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, V.; Garcia-Garcia, G.; Iseki, K.; Li, Z.; Naicker, S.; Plattner, B.; Saran, R.; Wang, A.Y.-M.; Yang, C.-W. Chronic kidney disease: Global dimension and perspectives. Lancet 2013, 382, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cockwell, P.; Fisher, L.-A. The global burden of chronic kidney disease. Lancet 2020, 395, 662–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liyanage, T.; Ninomiya, T.; Jha, V.; Neal, B.; Patrice, H.M.; Okpechi, I.; Zhao, M.-h.; Lv, J.; Garg, A.X.; Knight, J.; et al. World-wide access to treatment for end-stage kidney disease: A systematic review. Lancet 2015, 385, 1975–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guariguata, L.; Whiting, D.R.; Hambleton, I.; Beagley, J.; Linnenkamp, U.; Shaw, J.E. Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2013 and projections for 2035. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2014, 103, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanditha, A.; Ma, R.C.; Ramachandran, A.; Snehalatha, C.; Chan, J.C.; Chia, K.S.; Shaw, J.E.; Zimmet, P.Z. Diabetes in Asia and the Pacific: Implications for the Global Epidemic. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 472–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranasinghe, A.V.; Kumara, G.W.G.P.; Karunarathna, R.H.; De Silva, A.P.; Sachintani, K.G.D.; Gunawardena, J.M.C.N.; Kumari, S.K.C.R.; Sarjana, M.S.F.; Chandraguptha, J.S.; De Silva, M.V.C. The incidence, prevalence and trends of Chronic Kidney Disease and Chronic Kidney Disease of uncertain aetiology (CKDu) in the North Central Province of Sri Lanka: An analysis of 30,566 patients. BMC Nephrol. 2019, 20, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatapudi, R.R.; Rentala, S.; Gullipalli, P.; Komarraju, A.L.; Singh, A.K.; Tatapudi, V.; Goru, K.B.; Bhimarasetty, D.M.; Narni, H. High Prevalence of CKD of Unknown Etiology in Uddanam, India. Kidney Int. Rep. 2018, 4, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan American Health Organization; Document CE152/25 PAHO; 152nd Session of the Executive Committee; Resolution 52nd Directing Council. Chronic Kidney Disease in Agricultural Communities in Central America; Pan American Health Organization: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; p. 3. Available online: http://www.paho.org/hq/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=8486%3A152nd-session-ofthe-executive-committee-&catid=4877%3Agbo-152nd-session-of-theexecutive-committee&Itemid=39950&lang=en (accessed on 9 April 2023).
- Ramírez-Rubio, O.; Amador, J.J.; Kaufman, J.S.; Weiner, D.E.; Parikh, C.R.; Khan, U.; McClean, M.D.; Laws, R.L.; López-Pilarte, D.; Friedman, D.J.; et al. Urine biomarkers of kidney injury among adolescents in Nicaragua, a region affected by an epidemic of chronic kidney disease of unknown aetiology. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2015, 31, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Government Medical Officer’s Association of Sri Lanka. Press Release 13 November 2013. Available online: https://www.gmoa.lk/documents/press-realeases/press-releases-2013/ (accessed on 5 April 2023).
- Ministry of Health. Data Presented at the Presidential Task Force for Prevention of Kidney Diseases; Presidents House: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2014.
- Data available at Renal Unit, Provincial Director’s Office, North Central Province, Anuradhapura, Sri Lanka. Available online: https://healthdept.nc.gov.lk/renal-care-unit/ (accessed on 5 April 2023).
- Athuraliya, T.N.C.; Abeysekera, D.T.D.J.; Amerasinghe, P.H.; Kumarasiri, P.V.R.; Dissanayake, V. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in two tertiary care hospitals: High proportion of cases with uncertain aetiology. Ceylon Med. J. 2009, 54, 23–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayasekara, K.B.; Dissanayake, D.M.; Sivakanesan, R.; Ranasinghe, A.; Karunarathna, R.H.; Kumara, G.W.G.P. Epidemiology of Chronic Kidney Disease, With Special Emphasis on Chronic Kidney Disease of Uncertain Etiology, in the North Central Region of Sri Lanka. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 25, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.P.; Gupta, A.K.; Kaur, G.; Khanna, T. Chronic Kidney Disease of Unknown Origin—What do we know? J. Assoc. Physicians India 2020, 68, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rajapurkar, M.M.; John, G.T.; Kirpalani, A.L.; Abraham, G.; Agarwal, S.K.; Almeida, A.F. What do we know about chronic kidney disease in India: First report of the Indian CKD registry? BMC Nephrol. 2012, 13, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadde, P.; Sanikommu, S.; Manumanthu, V.R.; Akkaloori, A. Uddanam nephropathy in India: A challenge for epidemiologists. Bull. World Health Organ. 2017, 95, 848–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguli, A. Uddanam Nephropathy/Regional Nephropathy in India: Preliminary Findings and a Plea for Further Research. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2016, 68, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Congress of Nephrology (WCN). Sociedad Chilena de Nefrologia: Santiago, Chile,2012. Available online: http://www.nefro.cl/site/content.php?id=130 (accessed on 8 April 2023).
- Abraham, G.; Varughese, S.; Thandavan, T.; Iyengar, A.; Fernando, E.; Naqvi, S.A.J.; Sheriff, R.; Ur-Rashid, H.; Gopalakrishnan, N.; Kafle, R.K. Chronic kidney disease hotspots in developing countries in South Asia. Clin. Kidney J. 2015, 9, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athuraliya, N.T.C.; Abeysekera, T.D.J.; Amerasinghe, P.H.; Kumarasiri, R.; Bandara, P.; Karunaratne, U.; Milton, A.H.; Jones, A.L. Uncertain etiologies of proteinuric-chronic kidney disease in rural Sri Lanka. Kidney Int. 2011, 80, 1212–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, C.; Aragón, A.; Gonzalez-Quiroz, M.; López, I.; Jakobsson, K.; Elinder, C.-G.; Lundberg, I.; Wesseling, C. Decreased Kidney Function of Unknown Cause in Nicaragua: A Community-Based Survey. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2010, 55, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanayakkara, S.; Senevirathna, S.T.M.L.D.; Abeysekera, T.; Chandrajith, R.; Ratnatunga, N.; Gunarathne, E.D.L.; Yan, J.; Hitomi, T.; Muso, E.; Komiya, T.; et al. An Integrative Study of the Genetic, Social and Environmental Determinants of Chronic Kidney Disease Characterized by Tubulointerstitial Damages in the North Central Region of Sri Lanka. J. Occup. Health 2014, 56, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siriwardhana, E.A.R.I.E.; Perera, P.A.J.; Sivakanesan, R.; Abeysekara, T.; Nugegoda, D.; Jayaweera, J.A.A.S. Dehydration and malaria augment the risk of developing chronic kidney disease in Sri Lanka. Indian J. Nephrol. 2015, 25, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanigasuriya, K.P.; Peiris, H.; Ileperuma, N.; Peiris-John, R.J.; Wickremasinghe, R. Could ochratoxin A in food commodities be the cause of chronic kidney disease in Sri Lanka? Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2008, 102, 726–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dlssananyake, D.M.; Jayasekera JM, K.; Ratnayake, P.; Wickramasinghe, W.; Radella, Y.A. The short term effect of cyanobacterial toxin extracts on mice kidney. In Proceedings Peradeniya University Research Sessions; University of Peradeniya: Peradeniya, Sri Lanka, 2011; Volume 16, p. 95. [Google Scholar]
- Gamage, C.D.; Yoshimatsu, K.; Sarathkumara, Y.D.; Kulendiran, T.; Nanayakkara, N.; Arikawa, J. Serological evidence of hantavirus infection in Girandurukotte, an area endemic for chronic kidney disease of unknown aetiology (CKDu) in Sri Lanka. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 57, 77–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, U.; Zanetta, D.M.T.; Terra-Filho, M.; Burdmann, E. Burnt sugarcane harvesting is associated with acute renal dysfunction. Kidney Int. 2015, 87, 792–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roncal-Jimenez, C.; García-Trabanino, R.; Barregard, L.; Lanaspa, M.A.; Wesseling, C.; Harra, T.; Aragón, A.; Grases, F.; Jarquin, E.R.; González, M.A.; et al. Heat Stress Nephropathy From Exercise-Induced Uric Acid Crystalluria: A Perspective on Mesoamerican Nephropathy. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2016, 67, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roncal-Jimenez, C.; Lanaspa, M.A.; Jensen, T.; Sanchezlozada, L.G.; Johnson, R.J. Mechanisms by Which Dehydration May Lead to Chronic Kidney Disease. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2015, 66 (Suppl. 3), 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, C.A.R.; Ishimoto, T.; Lanaspa, M.A.; Rivard, C.J.; Nakagawa, T.; Ejaz, A.A.; Cicerchi, C.; Inaba, S.; Le, M.; Miyazaki, M.; et al. Fructokinase activity mediates dehydration-induced renal injury. Kidney Int. 2014, 86, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaguer, M.; Herrera, R.; Alfonzo, J.; Magrans, C.; Mañalich, R.; Martinez, A.; Davalos, J.; Perez-Oliva, J.; Landrove, O. Chronic Kidney Disease in Cuba: Epidemiological Studies, Integral Medical Care, and Strategies for Prevention. Ren. Fail. 2006, 28, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés, R.H.; Orantes, C.M.; López, M.A.; Marín, L.L.; Arévalo, P.A.; González, M.S. Clinical characteristics of chronic kidney disease of non-traditional causes in women of agricultural communities in El Salvador. Clin. Nephrol. 2015, 83 (Suppl. 1), 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orantes-Navarro, C.M.; Herrera-Valdés, R.; Almaguer-López, M.; Brizuela-Díaz, E.G.; Alvarado-Ascencio, N.P.; Fuentes-de Morales, E.J. Chronic kidney disease in children and adolescents in Salvadoran farming communities: NefroSalva Pediatric Study (2009–2011). MEDICC Rev. 2016, 18, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wanigasuriya, K.P.; Peiris-John, R.; Wickremasinghe, R.; Hittarage, A. Chronic renal failure in North Central Province of Sri Lanka: An environmentally induced disease. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2007, 101, 1013–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandara, J.M.R.S.; Senevirathna, D.M.A.N.; Dasanayake, D.M.R.S.B.; Herath, V.; Abeysekara, T.; Rajapaksha, K.H. Chronic renal failure among farm families in cascade irrigation systems in Sri Lanka associated with elevated dietary cadmium levels in rice and freshwater fish (Tilapia). Environ. Geochem. Health 2008, 30, 465–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meharg, A.A.; Norton, G.; Deacon, C.; Williams, P.; Adomako, E.E.; Price, A.; Zhu, Y.; Li, G.; Zhao, F.-J.; McGrath, S.; et al. Variation in Rice Cadmium Related to Human Exposure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 5613–5618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrajith, R.; Dissanayake, C.; Ariyarathna, T.; Herath, H.; Padmasiri, J. Dose-dependent Na and Ca in fluoride-rich drinking water —Another major cause of chronic renal failure in tropical arid regions. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayawardana, D.T.; Pitawala, H.M.T.G.A.; Ishiga, H. Geochemical evidence for the accumulation of vanadium in soils of chronic kidney disease areas in Sri Lanka. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 5415–5424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orantes-Navarro, C.M.; Herrera-Valdés, R.; Almaguer-López, M.; López-Marín, L.; Vela, X.; Hernandez-Cuchillas, M.; Barba, L.M. Toward a Comprehensive Hypothesis of Chronic Interstitial Nephritis in Agricultural Communities. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2017, 24, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, R.; Orantes, C.; Almaguer, M.; Alfonso, P.; Bayarre, H.D.; Leiva, I.M.; Smith, M.J.; Cubias, R.A.; Torres, C.G.; Almendárez, W.O.; et al. Clinical characteristics of chronic kidney disease of nontraditional causes in Salvadoran farming communities. MEDICC Rev. 2014, 16, 39–48. [Google Scholar]
- Jayasumana, C.; Gunatilake, S.; Siribaddana, S. Simultaneous exposure to multiple heavy metals and glyphosate may contribute to Sri Lankan agricultural nephropathy. BMC Nephrol. 2015, 16, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramarathna, S.; Balasooriya, S.; Diyabalanage, S.; Chandrajith, R. Tracing environmental aetiological factors of chronic kidney diseases in the dry zone of Sri Lanka—A hydrogeochemical and isotope approach. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2017, 44, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijkström, J.; Jayasumana, C.; Dassanayake, R.; Priyawardane, N.; Godakanda, N.; Siribaddana, S.; Ring, A.; Hultenby, K.; Söderberg, M.; Elinder, C.-G.; et al. Morphological and clinical findings in Sri Lankan patients with chronic kidney disease of unknown cause (CKDu): Similarities and differences with Mesoamerican Nephropathy. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Marín, L.; Chavez, Y.; García, X.A. Histopathology of chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology in Salvadoran agricultural communities. MEDICC Rev. 2014, 16, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jayasinghe, S. Chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology should be renamed chronic agrochemical nephropathy. MEDICC Rev. 2014, 16, 72–74. [Google Scholar]
- Weaver, V.M.; Fadrowski, J.J.; Jaar, B.G. Global dimensions of chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology (CKDu): A modern era environmental and occupational nephropathy? BMC Nephrol. 2015, 16, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigo, C.; Nawarathne, P.; Jayasinghe, S. Chronic interstitial nephritis in agricultural communities (CINAC) and lysosomal tubulopathy: Is there a place for anti-oxidants? Med. Hypotheses 2021, 146, 110414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liakopoulos, V.; Roumeliotis, S.; Gorny, X.; Dounousi, E.; Mertens, P.R. Oxidative Stress in Hemodialysis Patients: A Review of the Literature. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 3081856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Seok, Y.M.; Jung, K.-J.; Park, K.M. Reactive oxygen species/oxidative stress contributes to progression of kidney fibrosis following transient ischemic injury in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2009, 297, F461–F470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visarius, T.M.; Putt, D.A.; Schare, J.M.; Pegouske, D.M.; Lash, L. Pathways of glutathione metabolism and transport in isolated proximal tubular cells from rat kidney. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1996, 52, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vervaet, B.A.; Nast, C.C.; Jayasumana, C.; Schreurs, G.; Roels, F.; Herath, C.; Kojc, N.; Samaee, V.; Rodrigo, S.; Gowrishankar, S.; et al. Chronic interstitial nephritis in agricultural communities is a toxin-induced proximal tubular nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2020, 97, 350–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, G.; Agarwal, S.K.; Gowrishankar, S.; Vijayan, M. Chronic Kidney Disease of Unknown Etiology: Hotspots in India and Other Asian Countries. Semin. Nephrol. 2019, 39, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vervaet, B.A.; Nast, C.C.; Schreurs, G.; Jayasumana, C.; Herath, C.; Kojc, N.; De Broe, M.E. Chronic interstitial nephritis in agricultural communities: A new perspective on etiology, diagnosis and mechanism. Nephrol. Ther. 2021, 17, S45–S50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayasumana, C. Chronic Interstitial Nephritis in Agricultural Communities (CINAC) in Sri Lanka. Semin. Nephrol. 2019, 39, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayasumana, C. Sri Lankan agricultural nephropathy. In International Workshop on Chronic Kidney Disease of Nontraditional Causes; National Institute of Health El Salvador: San Salvador, El Salvador, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Nanayakkara, S.; Senevirathna, L.; Karunaratne, U.; Chandrajith, R.; Harada, K.H.; Hitomi, T.; Watanabe, T.; Abeysekara, T.; Aturaliya, T.N.C.; Koizumi, A. Evidence of tubular damage in the very early stage of chronic kidney disease of uncertain etiology in the North Central Province of Sri Lanka: A cross-sectional study. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2012, 17, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epidemiology—Unit. Weekly Epidimiological Report Vol:36 No:49. In Research Programme for Chronic Kidney Disease of Unknown Aetiology in Sri Lanka; Palihawadana, P., Ed.; Ministry of Healthcare and Nutrition: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wanigasuriya, K.; Jayawardene, I.; Amarasiriwardena, C.; Wickremasinghe, R. Novel urinary biomarkers and their association with urinary heavy metals in chronic kidney disease of unknown aetiology in Sri Lanka: A pilot study. Ceylon Med. J. 2017, 62, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnayake, S.; Badurdeen, Z.; Nanayakkara, N.; Abeysekara, T.; Ratnatunga, N.; Kumarasiri, R. Screening for chronic kidney disease of uncertain aetiology in Sri Lanka: Usability of surrogate biomarkers over dipstick proteinuria. BMC Nephrol. 2017, 18, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, P.M.C.S.; Abdul, K.S.M.; Eakanayake, E.M.D.V.; Jayasinghe, S.S.; Jayasumana, C.; Asanthi, H.B.; Perera, H.S.D.; Chaminda, G.G.T.; Chandana, E.P.S.; Siribaddana, S.H. Urinary Biomarkers KIM-1 and NGAL for Detection of Chronic Kidney Disease of Uncertain Etiology (CKDu) among Agricultural Communities in Sri Lanka. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijewickrama, S.; Gunawardena, N.; Jayasingha, S.; Herath, C. Chronic Kidney Disease of Unknown Aetiology (CKDu) in Sri Lanka: A multilevel clinical case definition for surveillance and epidemiological studies. Kidney Int. Rep. 2019, 4, 781–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asleh, R.; Nakhoul, F.M.; Miller-Lotan, R.; Awad, H.; Farbstein, D.; Levy, N.S.; Nakhoul, N.; Iancu, T.C.; Manov, I.; Laue, M.; et al. Poor lysosomal membrane integrity in proximal tubule cells of haptoglobin 2-2 genotype mice with diabetes mellitus. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 53, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, M.; Venkataraman, V.; Razavian, M.; Cooper, B.; Zoungas, S.; Ninomiya, T.; Webster, A.C.; Perkovic, V. Antioxidants for chronic kidney disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 2014, CD008176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Risk Factors | Comments |
|---|---|
| Occupation |
|
| Age | |
| Sex |
|
| Genetic |
|
| Heat stress |
|
| Recurrent dehydration |
|
| Water source |
|
| Food source |
|
| Extreme physical exertion |
|
| Nephrotoxic drugs |
|
| Infections |
|
| High fructose drinks |
|
| Snake bite | |
| Family history of CKD |
|
| Neighbor with CKD |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sharma, S.; Sharma, N.; Anandh, U.; Gowrishankar, S. Chronic Tubulointerstitial Nephropathy of Agricultural Communities. Kidney Dial. 2023, 3, 229-243. https://doi.org/10.3390/kidneydial3020021
Sharma S, Sharma N, Anandh U, Gowrishankar S. Chronic Tubulointerstitial Nephropathy of Agricultural Communities. Kidney and Dialysis. 2023; 3(2):229-243. https://doi.org/10.3390/kidneydial3020021
Chicago/Turabian StyleSharma, Sourabh, Neha Sharma, Urmila Anandh, and Swarnalata Gowrishankar. 2023. "Chronic Tubulointerstitial Nephropathy of Agricultural Communities" Kidney and Dialysis 3, no. 2: 229-243. https://doi.org/10.3390/kidneydial3020021
APA StyleSharma, S., Sharma, N., Anandh, U., & Gowrishankar, S. (2023). Chronic Tubulointerstitial Nephropathy of Agricultural Communities. Kidney and Dialysis, 3(2), 229-243. https://doi.org/10.3390/kidneydial3020021