Abstract
Human coronavirus 229E (HCoV-229E) is an alpha coronavirus that infects humans and bats. In common with all positive-strand RNA viruses, 229E infection causes rearrangements of the host’s intracellular membranes to form replication organelles, a highly conserved and vital step in the viral replication cycle. Here, we investigated the role of the ESCRT protein VPS4A in 229E infection. We found that functional VPS4A was required for the formation of replication organelles and localizing viral RNA to these structures in host cells to facilitate viral genome replication. We validated this effect using small molecule inhibitors to VPS4A, significantly reducing virus replication. We also showed that other ESCRTS, like CHMP4B, were required for the virus replication step, whereas VPS37A was involved in the post-replication stages. The absence of a functional VPS4A prevented the remodeling of membranes to form viral replication centers and, therefore, exposed the viral RNA, triggering an inflammatory immune response as indicated by elevated levels of IL-6. Interestingly, we observed the role of VPS4A to be similar for the OC43 coronavirus, indicating it could be conserved across all four coronavirus genera, including SARS-CoV-2. Understanding more about the replication of coronaviruses is imperative to finding more effective ways to control them.
1. Introduction
The endosomal sorting complex required for transport (ESCRT) machinery plays a significant role in replicating many human viruses. Emerging evidence suggests that viruses from several different families, such as herpes simplex virus-1 (HSV-1) [1] human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) [2,3], hepatitis B virus (HBV) [4,5], vaccinia [6], human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) [7,8], Marburg and Ebola viruses VP40 [9,10], and Rabies virus [11,12] hijack the ESCRT machinery to facilitate replication, maturation, or egress steps. Depending on the virus, these viruses may antagonize or embrace ESCRT-mediated physiological processes to promote productive and efficient viral replication.
The ESCRT membrane scission machinery was originally discovered for its role in ubiquitinated cargo sorting in the multi-vesicular body (MVB) pathway [13]. Recent studies have revealed its involvement in several other viral and cellular processes, including virus budding, cytokinesis, micro-vesicle generation, plasma membrane wound repair, nuclear envelope reformation, nuclear pore complex quality control, and endolysosomal repair [14,15,16,17,18]. The ESCRT pathway is conserved in eukaryotes and the ESCRT machinery consists of an assembly of protein subcomplexes that cooperate to mediate reverse-topology membrane scission [19,20]. Several distinct heteromeric complexes are sequentially recruited to sites of membrane deformation, followed by the recruitment of VPS4A ATPase complexes, which function in the disassembly and recycling of all ESCRT factors [20,21]. In mammalian cells, nearly 40 ESCRT proteins have been identified. However, only specific subsets of these factors are necessary to complete each ESCRT-mediated process.
During infection, coronaviruses (CoV) make extensive use of the membrane-trafficking pathways of the host cell and subvert some of these to build a specialized organelle, the replication organelle (RO) [22]. The RO provides CoVs with a controlled and safe microenvironment to replicate, although the details of how they are formed during the replication cycle have yet to be fully understood. This viral niche, obtained by extensive rearrangements of host cell membranes, is crucial to concentrate the viral replicase, to confine and regulate the replication process in space and time, and to protect viral RNAs from recognition and degradation by the host innate immune defense [22]. The interest in CoVs has peaked since the 2020 pandemic caused by SARS-CoV-2, and recent studies have tried to elucidate the role of host and viral proteins in this process. For example, components of the ESCRT complex were identified in six high-throughput screens of SARS-CoV-2 infection [23,24,25]. In all cases, the ESCRT components behaved as restriction factors (i.e., antiviral) in different cell lines and under different conditions of infection, but the underlying mechanism of the antiviral activity of ESCRT is unknown but likely is complex, given the multiple roles of ESCRT (in not only endolysosomal trafficking but also cytokinesis) [22,26]. For example, ESCRT complexes could exert antiviral effects by altering the membrane-trafficking pathways of the virion and/or viral proteins. This could be tested by assessing the impact of ‘acute’ inactivation of the ESCRT machinery (via degron or dominant-negative mutants) on viral infection. Here, we explored the role of VPS4A ATPase and other ESCRT factors and found they played crucial roles in virus replication.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
MRC-5 cells (ATCC CCL-171) and HEK 293TN cells were maintained in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) (Corning, Corning, NY, USA) containing 10% fetal bovine serum, 2 mM GlutaMAX (Gibco, Billings, MT, USA), 100 U/mL penicillin, and 100 µg/mL streptomycin (Corning). Cells were maintained at 37 °C under 5% CO2.
2.2. 229E Virus Infections, Growth Curves, and Virus Titrations
MRC-5 cells were plated in multiple 15 cm plates to generate virus stocks, and cells were infected with the virus at 0.01 MOI and incubated at 35 °C as described previously [27]. Briefly, the virus was harvested at 3–4 days post-infection based on CPE. The supernatant from multiple plates was pooled and centrifuged. The supernatant was then aliquoted into smaller volumes and frozen at −80 °C. It was titered by the TCID50 method before use. 229E infections were carried out at a MOI of 0.05. Cells were incubated for 2 h at 35 °C before the addition of doxycycline (100 ng/mL) and subsequently incubated at 35 °C for the duration of the experiment.
2.3. TCID50 Titer Assays
For viral titer assays, samples were harvested at 24, 48, and 72 hpi for each experiment and flash-frozen in liquid nitrogen before storage at −80 °C. A total of 20,000 MRC-5 cells were plated in 96 well plates overnight. Supernatants to be titered were thawed on ice. Ten-fold serial dilutions were made in 10% DMEM complete media. Dilutions were added to the 96-well plate containing the MRC-5 cells (100 µL per well). Cells were incubated at 35 °C for 5–7 days. CPE in each well was counted to determine the titers based on the TCID50 conversion table.
2.4. Lentivirus Production and Cell Selection
Lentivirus was generated using the 3rd generation packaging system: pCMV-VSV-G (gift from Bob Weinberg, Addgene #8454), pMDLg-RRE (gift from Dr. Didier Trono, Addgene #12251), and pRSV-Rev (gift from Dr. Didier Trono, Addgene #12253) in 293TN cells as described previously [28]. Tet-Act, pCDH(i)GFP-VPS4AE228Q, pCDH(i)GFP-CHMP4B, and pCDH(i)GFP plasmids were cloned, generated, and characterized as described previously [7]. For the purpose of this study, these are henceforth referred to as VPS4AE228Q, CHMP4B, and GFP vectors. VPS37A and scrambled shRNA lentivirus were a kind gift from Yoshi Takahashi (PSU) [17].
For lentivirus transduction, sub-confluent fibroblasts were seeded overnight and transduced with lentivirus and 8 µg/mL Polybrene (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) as described previously [28]. Transduced cells were selected using 2 µg/mL puromycin (Thermo Fisher, Waltham, MA, USA). Following selection, cells were seeded at sub-confluence for a second lentiviral transduction with the EF1a-Tet3G lentivirus selected with both puromycin and G418. Following the second lentivirus transduction, cells were expanded and used for 229E infections. For subsequent transduction, selected cells were seeded overnight and transduced as before.
2.5. RNA Isolation and RT-qPCR
Total RNA was isolated using RNeasy Mini Kit (cat# 74034) under RNase-free conditions and precipitated with isopropanol according to the manufacturer’s instructions. DNase treatment removed DNA contaminants using a DNA-free DNA removal kit (Qiagen cat# 79254). RNA concentrations were determined, and equal amounts were used to generate cDNA using the Invitrogen™ (Waltham, MA, USA) SuperScript™ III First-Strand Synthesis System (cat# 18080051) with oligo dT primers according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Equal amounts of cDNA were analyzed by quantitative PCR (qPCR) in triplicate using Power SYBR green master mix (Applied Biosystems, Waltham, MA, USA) on the Applied Biosystems (ABI) real-time qPCR machine. Primers are listed in Table 1. β-Actin (ACTB) or GAPDH were used as housekeeping controls. Genes with quantification cycle (Ct) values > 35 were considered undetected and assigned a Ct of 35 to calculate fold induction.

Table 1.
Primers used for real-time qPCR.
To determine the genome copies of 229E, one-step real-time was performed using Biorad’s iTaq Universal SYBR green one-step kit (cat# 171-5150). Real-time was set up according to the manufacturer’s protocol.
2.6. Antibodies and Reagents
N#18 antibody against the nucleocapsid protein of NL63 CoV was generated as described previously by Neil Christensen (PSU) [29]. Its cross-reactivity with 229E allowed its use in both immunoblotting and immunostaining experiments. J2 dsRNA antibody was purchased from Absolute antibodies (Oxford, UK) (cat no. #Ab01299-23.0). Secondary antibodies conjugated to Alexa fluor 564, cy5, or 488 were purchased from ThermoFisher. Inhibitors designed to target VPS4A: DBeQ and #4107 were obtained from H.G Wang (PSU) and reconstituted in DMSO, used at a final working concentration of 10 μM [30]. Puromycin, G418, and DMSO were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich.
2.7. Immunofluorescence Staining and Imaging
Immunofluorescence staining was done as described previously [31]. Briefly, coverslips with MRC-5 cells—transduced, uninfected, or 229E-infected cells—were fixed at the required time point in 4% paraformaldehyde for 15 min at room temperature. Cells were blocked in 1X PBS containing 10% human serum, 0.5% Tween-20, and 5% glycine. Triton X-100 (0.1%) was added for permeabilization. Primary and secondary antibodies were diluted in blocking buffer and incubated for one hour each at room temperature. The primary antibodies to nucleocapsid (N) protein antibody [29] were used. Alexa Fluor 568-conjugated secondary antibodies (Invitrogen) were used as secondary antibodies. Coverslips were mounted with ProLong Diamond antifade containing DAPI (Thermo Scientific). Images were taken on a confocal microscope system (Nikon Eclipse Ti) (Nikon USA, Melville, NY, USA). Images were processed using the NIS Elements AR Analysis 4.30 software.
2.8. Transmission Electron Microscopy
Cells were seeded on 60 mm Permanox tissue culture dishes (Nalge Nunc International, Rochester, NY, USA). Cells were infected at an MOI of 0.05 for 36 h. At 36 hpi, cells were washed with PBS and fixed at 4 °C in fixation buffer (0.5% (v/v) glutaraldehyde, 0.04% (w/v) paraformaldehyde, 0.1 M sodium cacodylate). Cells were processed at the TEM Core Facility (RRID:SCR_021200) at Pennsylvania State University College of Medicine). Briefly, the fixed samples were washed three times with 0.1 M sodium cacodylate, followed by post-fixation in 1% osmium–1.5% potassium ferrocyanide overnight at 4 °C. Samples were then washed 3 times in 0.1 M sodium cacodylate, dehydrated with ethanol, and embedded in Epon 812 for staining and sectioning. Images were acquired using a JEOL JEM-1400 Digital Capture transmission electron microscope.
2.9. smFISH of Viral RNA, Imaging, and Analysis
To visualize 229E viral RNA, transduced MRC-5 cells were seeded on coverslips overnight. Cells were infected and treated with or without dox as described above and fixed at 48 hpi for FISH staining. Cells were quickly rinsed with RNase-free 1× PBS and fixed for 10 min in RNase-free 3.7% formaldehyde at room temperature, followed by 2 × 5 min washes with 1× PBS. The fixed cells were dehydrated in 70% ethanol at 4 °C for at least 24 h. Cells were rehydrated in wash buffer (WB: 10% formamide, 2× SSPE, DEPC H2O) for 20 min at room temperature. Coverslips were incubated in a humid chamber for 16–20 h at 37 °C with 100 µL of hybridization buffer (10% dextran sulfate, 2× SSPE, 10% formamide) containing 1 µL of a 25 µM stock of 48 Stellaris RNA smFISH probes conjugated to Quasar 570 tiling the 229E genome (Biosearch, Hoddesdon, UK) [32,33]. The next day, coverslips were incubated for 30 min at 37 °C in WB. Coverslips were washed once more in WB for 30 min at 37 °C and then stained with DAPI and mounted in ProLong Diamond (Thermo Fisher Scientific P36961, Waltham, MA, USA). Two technical replicates were conducted for each condition.
Slides were imaged on a Leica AOBS SP8 FALCON confocal microscope with hybrid detectors. Uninfected and uninduced controls were imaged to confirm no background or crosstalk. Slides were imaged with a 40X/NA 1.3 oil objective at a pixel format of 1024 × 1024, a scan speed of 400 Hz, a 1× zoom, and a frame average of 4. DAPI was excited with the 405 nm UV laser at 8% laser power and detected using a PMT detector. The GFP and Quasar 570 signals were excited with the white light laser at 488 nm and 555 nm, respectively, and detected using hybrid detectors. The differential interference contrast images were obtained with a laser at 488 nm and detected with a PMT.
To determine the effect of factor expression on viral replication, the sum intensity of the 229E signal was measured for individual cells using FIJI [34]. Cells expressing both GFP and Quasar 570 signal, except the VPS37 knockdown cells, were chosen for analysis. Cells were outlined with fluorescent channels or DIC to delineate the cell’s borders and added to the ROI manager. The sum of the pixels in the cells was measured as the “Raw intensity density”. Images were adjusted for display using Imaris (bitplane) Version 10.2. The sum intensities values are expressed as averages ± SEM.
2.10. Statistical Analysis
Prism 7 GraphPad was used for statistical analysis and graph generation. Unpaired student t-tests were performed to determine the statistics between 229E-infected untreated and treated.
3. Results
3.1. Functional VPS4A Was Required for the Formation of HCoV-229E Replication Centers
The ESCRT-III machinery works by sequential recruitment, polymerization, and replacement of different subunits, resulting in constriction and, finally, membrane fission. ESCRT-III subunits polymerize sequentially at the membrane driven by the VPS4A ATPase [7]. To investigate the role of VPS4A ATPase during 229E virus infection, we generated a dominant-negative GFP-tagged VPS4A, with a single amino acid change at amino acid 228 from E to Q, henceforth referred to as GFP-VPS4AE228Q, under the control of a dox inducible promoter (TetAct). This mutation silenced the VPS4A ATPase activity, and its inability to incorporate into hexamers with the wild type prevents its function in the ESCRT pathway [7]. As a control, we generated a lentivirus expressing only GFP under the control of the same inducible promoter. MRC-5 cells were first transduced with lentivirus expressing the tetracycline activator (TetAct) and selected using G418. The selected cells were then transduced with the GFP-VPS4AE228Q lentivirus and subjected to puromycin selection in addition to G418. MRC-5 cells were transduced and selected similarly as a control using a lentivirus expressing just the GFP. After the double transduction and selection, cells were infected with the 229E virus at 0.05 MOI in the presence or absence of doxycycline at 100 ng/mL. The supernatants were collected every day, and fresh media with or without doxycycline (dox) was added until 72 h post-infection (hpi). The supernatants were used to quantify infectious viruses using the TCID50 technique described in the methods. After induction of GFP protein expression with dox, comparable virus titers to the no dox samples were produced over the time course of infection, with a peak on day 2 and steep reduction by day 3 due to cytopathic effect (CPE) and cell death (Figure 1A). Figure 1B shows that the expression of the dominant-negative GFP-VPS4AE228Q protein in the presence of dox resulted in a log reduction of virus titers on day 2 compared to viral titers in the no dox samples. We noted that the transduction efficiency was not 100% and believe it could have dampened the effect on titers, which otherwise could have been greater. The measured titers in each experiment were from the extracellular supernatant, suggesting that a functional VPS4A was required to release infectious virus particles.
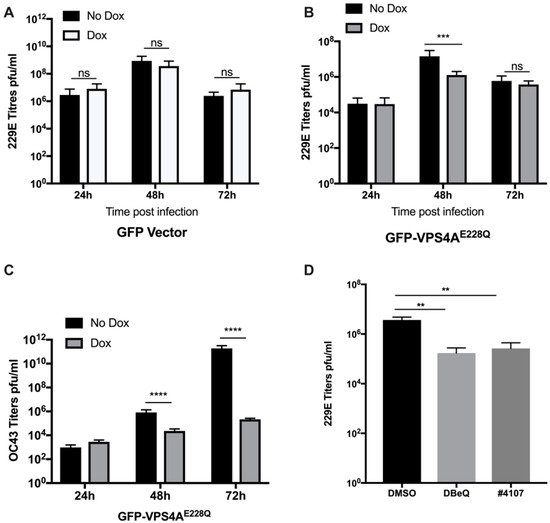
Figure 1.
Functional VPS4A is necessary for coronavirus (CoV) propagation. MRC-5 cells were transduced and selected with lentiviruses to express GFP-VPS4AE228Q or GFP-vector under a dox-inducible promoter. Cells were infected at 0.05 MOI with 229E virus and then incubated in the presence or absence of doxycycline (dox) (100 ng/mL). Supernatants were harvested daily for 3 days, and media was replenished daily with or without dox. (A,B) 229E virus titers were assessed using TCID50 assay for the GFP-vector and GFP-VPS4AE228Q. Graphs show results from three independent experiments carried out in triplicate. Results are shown as mean ± SD. *** p < 0.005, ns = not significant. (C) Transduced and selected MRC-5 cells were infected with OC43 at an MOI of 0.05 in the presence or absence of doxycycline. Supernatants were harvested at 24, 48, and 72 hpi. Virus titers were assessed using TCID50 assay. Graphs show results from two independent experiments performed in triplicate. Results are shown as mean ± SD. **** p < 0.0001. (D) Normal MRC-5 cells were infected with 229E virus at an MOI of 0.05 and treated with either DMSO, DBeQ, or #4107 (inhibitors targeting VPS4A). Supernatants were collected at 48 hpi, and virus titers were assessed using TCID50 assay. Graphs show results from two independent experiments performed in triplicate. Results are shown as mean ± SD. ** p < 0.005.
To test whether this effect was specific to the 229E virus, which belongs to the alpha family of coronaviruses, we used another CoV belonging to the beta coronavirus family, OC43 (SARS-CoV-1 and SARS-CoV-2 also belong to the beta CoV family) and performed similar infections to assess the virus titers. Figure 1C showed 2 logs (48 hp) and 6 logs (72 hp) reductions in viral titers when the dominant-negative GFP-VPS4AE228Q was expressed in the presence of dox. This result demonstrates that this effect was not restricted to alpha CoVs such as 229E. Still, it may exert a pan-CoV effect, indicating the potential importance of VPS4A in the virus replication cycle.
We then tested the effects of two drugs, DBeQ [30] and #4107 (unpublished), that target the VPS4A protein, on 229E virus replication. MRC-5 cells were infected with 229E virus at 0.05 MOI and treated with either DMSO, DBeQ, or #4107 at a concentration of 10 µM. Supernatants were collected at 48 hpi and titers were measured using the TCID50 technique described in the Methods Section. Figure 1D shows that both drugs inhibited virus production by more than one log. However, it is important to note that neither of these drugs is absolutely specific for VPS4A. Still, together with the results of the genetic experiments, it is reasonable to conclude that the biological effects are related to the modulation of VPS4 activity. Our data showed that they recapitulated the effect seen with the dominant-negative VPS4A.
Since ESCRT proteins are key players in the membrane scission machinery, which are critical for the release of some viruses (HIV-1, for example [35]) from the cell, we hypothesized that the absence of a functional VPS4A disrupts the membrane scission step due to a lack of ATPase activity. If this were the case, virus particles would be trapped within the cell, inhibiting the formation of infectious extracellular viruses. To visualize any cell and membrane morphology defects, we examined 229E-infected cells expressing GFP-VPS4AE228Q using transmission electron microscopy. Figure 2A shows electron micrographs of 229E-infected MRC-5 cells with or without dox. First, in the absence of dox, when wild-type VPS4A is present, we observed virus particles with the distinctive “corona” structure of the spike protein in the extracellular space, as shown by the arrow (Figure 2A), suggesting the expected result of virus replication and release.
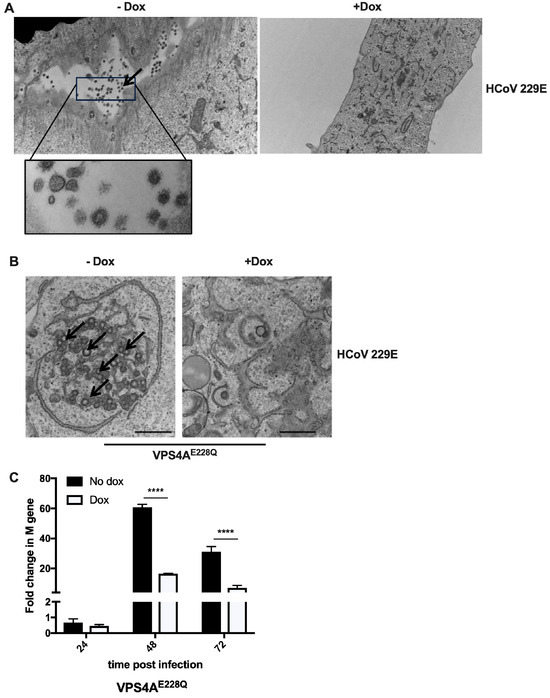
Figure 2.
VPS4A plays a significant role in the formation of replication centers. Transduced and selected MRC–5 cells were plated in 6 cm Petri dishes (compatible with sample processing for electron microscopy). Cells were infected with 229E at an MOI of 0.05 in the presence or absence of doxycycline, fixed at ~36 hpi, and processed. Copper grids were imaged. (A). 229E virus particles were visualized in the intercellular space in control cells containing GFP–VPS4AE228Q in the absence of dox (–dox), while no virus particles were observed in the presence of dox (+dox). (B). Representative images of GFP–VPS4AE228Q cells in the absence and presence of dox are shown. Scale bar, 600 nm. Arrows indicate replication centers. (C). GFP–VPS4AE228Q cells were infected with 229E in the presence or absence of doxycycline (dox) and harvested at 24, 48, and 72 hpi for RNA isolation. Relative genome levels using the 229E M gene were analyzed using One-Step RT–qPCR, and fold changes are shown. Three independent experiments were performed in triplicate. Results are shown as mean ± SD. **** p < 0.0001.
However, extracellular viral particles were largely absent in the presence of dox, which resulted in the expression of the VPS4AE228Q protein (Figure 2A). This result indicated that virus propagation was impaired in the presence of VPS4AE228Q. Secondly, in the absence of dox, i.e., normal VPS4A expression conditions, replication compartments/organelles, described previously as spherular membrane invaginations [36], were seen in the cytoplasm, as indicated by the arrows (Figure 2B). These organelles are the characteristic sites of viral replication that allow the viral replication machinery to assemble and initiate genome replication. Surprisingly, in dox-treated cells expressing the dominant-negative GFP-VPS4AE228Q mutant, we did not observe any trapped virus particles inside the cell, nor the replication compartments/organelles necessary to replicate viral RNA (Figure 2B). Formation of replication compartments is a critical step for virus replication, suggesting that VPS4A may not only play the conventional role of scission of membranes and release of the virus at the egress step but is also required for membrane remodeling and the formation of replication compartments, which protect the viral genome and facilitate virus replication. These results imply that virus replication was reduced in the absence of a functional VPS4A. To verify this conclusion, we assessed the viral genome levels in the cells infected with 229E with or without dox at 24, 48, and 72 hpi. Figure 2C shows that the genome copies were drastically reduced in the cells expressing dominant-negative GFP-VPS4AE228Q on day 2 and day 3. This finding indicates that the reduced viral titers were due to reduced virus replication rather than virus particles trapped within the cell due to impaired release/egress.
To visually observe the effect of various ESCRT machinery components on 229E genomic RNA expression, we adopted an imaging approach in which ESCRT members were overexpressed or knocked down in infected cells. Cells were infected with 229E for 48 h and genomic RNA was visualized via single-molecule RNA FISH (smFISH) using probes tiling the genome [32,33]. Cells were transfected and selected with VPS4AE228Q dominant-negative mutant or GFP, which are all controlled by a doxycycline-inducible promoter. The effect on genomic RNA expression was determined by measuring the sum fluorescence intensity of the RNA signal. The free GFP control caused a small but not statistically significant decrease in 229E signal between 229E –dox (26,664 ± 3497 A.U., n = 49) and 229E +dox (22,382 ± 2020 A.U, n = 60) (Figure 3A,B), suggesting that free GFP is not the cause of the observed change in 229E genomic RNA levels. Alternatively, VPS4AE228Q, the dominant-negative mutant, had a statistically significant (**** p < 0.0001) decrease in 229E genome signal from 229E –dox (145,974 ± 16,617 A.U, n = 26) to 229E +dox (45,866 ± 6419 A.U., n = 22) (Figure 3C,D). Similarly, overexpression of GFP-CHMP4B, a core component of the ESCRT-III machinery [37], also decreased 229E genomic RNA levels, which were statistically significant (p = 0.299). Still, the decrease in signal intensity was not as drastic as that of VPS4AE228Q. The 229E signal in the presence of GFP– CHMP4B decreased from 23,627 ± 2928 A.U. (229E –dox, n = 56) to 15,058 ± 2076 A.U. (229E +dox, n = 40). Interestingly, knockdown of VPS37A, a component of ESCRT-I involved in phagophore recruitment and autophagosome closure [38], did not show any statistically significant differences in 229E genomic RNA levels (229E + NTC = 23,145 ± 1890 A.U, n = 57, vs. 229E + VPS37a KD = 25,153 ± 3464 A.U., n = 52). These data indicate that the three ESCRT components tested play different roles in 229E viral replication, perhaps acting at different stages of the replication cycle.
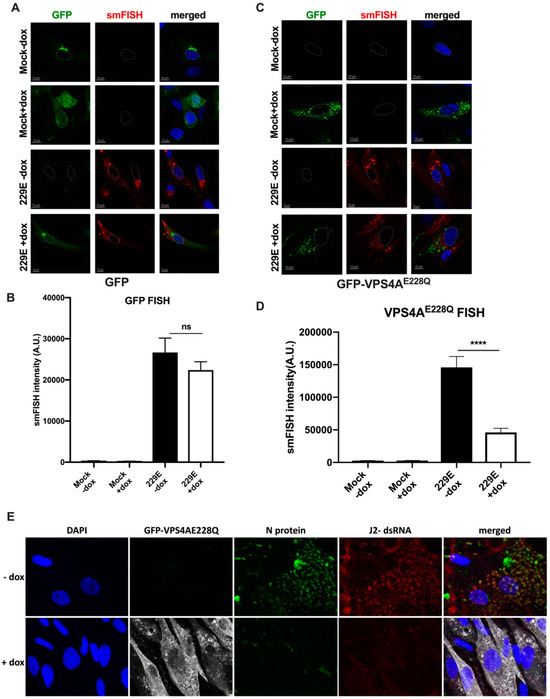
Figure 3.
GFP–VPS4AE228Q mutation causes a decrease in 229E genome replication. (A) Cells containing a dox-inducible gfp gene were subjected to infection for 48 h with 229E. In the absence of dox-induction, GFP (green) is slightly leaky but is greatly upregulated in the presence of dox. Single-molecule RNA FISH (smFISH) with probes targeting the 229E genome (red) were used to indicate 229E replication. (B) Sum fluorescence intensity was measured for the RNA channel. There was no statistically significant change in 229E expression. (C) Cells containing a dox-inducible GFP-VPS4AE228Q dominant-negative mutant gene were subjected to infection for 48 h with 229E. GFP-VPS4AE228Q (green) is only expressed in the presence of dox. SmFISH was used to label 229E genomes (red). (D) Dox-induced GFP–VPS4AE228Q expression significantly decreased 229E genomic RNA levels, as indicated by a change in the sum fluorescence intensity of the RNA channel. **** p < 0.0001, ns = not significant. Nucleus blue, DAPI, white outline. Scale bar = 10 µm. (E) MRC–5 cells transduced and selected for GFP–VPS4AE228Q expression were plated on coverslips and infected with 229E in the presence or absence of dox for 48 h. Cells were fixed and stained for viral nucleocapsid protein (green), dsRNA (red), GFP (shown as white), and DAPI (blue).
In common with all coronaviruses, four structural proteins, M, N, E, and S, together form the capsid and envelop the genomic RNA. The N protein is involved in viral RNA genome packaging into a ribonucleoprotein complex (RNP) and assembly into virus particles [22,39]. Therefore, we assessed the effect of GFP-VPS4AE228Q expression on the localization of the N protein. Transduced cells were infected as described above, and at 48 hpi, cells were fixed in PFA and stained, as described in the Methods Section. The dsRNA (red) and N protein (green) co-staining revealed the two proteins to be near each other. Although quantitation was not performed, colocalization of N and dsRNA in the control cells was evident (Figure 3E). In contrast, in the GFP-VPS4AE228Q-expressing cells, there was significantly reduced dsRNA and N protein staining (Figure 3E). This finding corroborates the FISH staining data in Figure 3A–D, in which reduced genomes were seen in GFP-VPS4AE228Q-expressing cells and indicated that viral protein expression was also affected.
3.2. HCoV-229E Infection Triggers an Inflammatory Response in the Absence of a Functional VPS4A
As we did not observe the formation of assembly compartments using TEM when GFP-VPS4AE228Q was expressed (Figure 2B), we investigated whether the viral RNA in the cytosol, although at reduced levels, was being detected by the cytosolic innate immune system. One hallmark of antiviral responses to infection is the production of interferons and, subsequently, the expression of interferon-stimulated genes. Interferon-stimulated gene 15 (ISG15) is among the earliest and most abundant proteins induced upon interferon signaling, encompassing versatile functions in host immunity [40]. To evaluate the expression of ISGs, we examined mRNA transcripts of some of the immune response genes. As seen in Figure 4A, a higher induction of ISG15 (3-fold) and MX1 (15-fold) (Figure 4B) was seen in dox-positive samples on day 2 of infection. This demonstrates that a lesser amount of viral RNA (as shown by genome levels in Figure 2C) resulted in a stronger immune response than the controls. This resulted from the absence of the protective replication organelle (RO) and exposure of the viral RNA. Interestingly, this resulted in a very strong induction of IL-6 (250-fold) (Figure 4C) but not of IFN-β (Figure 4D), suggesting the stimulation of an inflammation response in the cell, which could be a result of the disruption of the host cell machinery in addition to the virus infection.
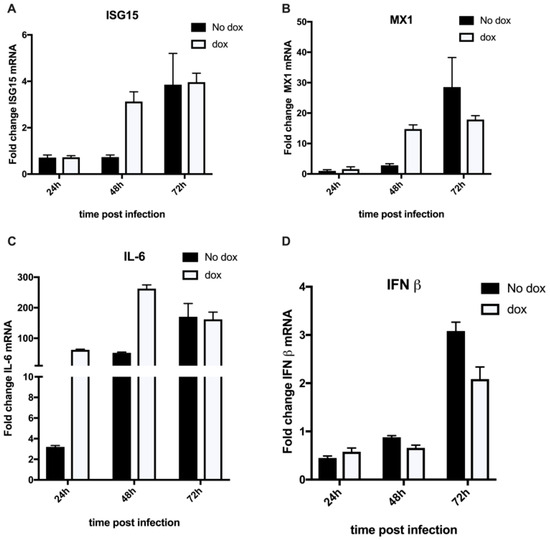
Figure 4.
229E induces an inflammatory immune response in the presence of GFP-VPS4AE228Q. MRC-5 cells transduced and selected with GFP-VPS4AE228Q were infected at 0.05 MOI with 229E virus and then incubated in the presence or absence of doxycycline (dox) (100 ng/mL). Cells were harvested for RNA isolation at 24, 48, and 72 hpi. Following cDNA synthesis, the mRNA levels of (A) ISG15, (B) MX1, (C) IL-6, and (D) IFN-β were analyzed using RT-qPCR and normalized to GAPDH. Three independent experiments were performed in triplicate. Relative fold changes are shown as mean ± SD.
3.3. Effect of Other ESCRT Proteins on 229E Virus Growth
VPS4A is an accessory protein that functions downstream of the ESCRT-III complex that recognizes membrane-associated ESCRT-III assemblies and catalyzes their disassembly, possibly in combination with membrane fission [20]. CHMP4B is part of the ESCRT-III complex upstream of accessory proteins. It has been shown that HIV-1 budding requires only a subset of the known human ESCRT-III proteins, with the CHMP2 and CHMP4 families playing key functional roles [35]. Disturbing the function of the accessory proteins drastically impaired 229E virus replication; therefore, we wondered whether one of the upstream ESCRTs could also be involved. We used a lentivirus expressing wild-type GFP-CHMP4B under the control of the doxycycline promoter to transduce MRC-5 cells previously selected for TeT-Act (using G418). We selected this time using puromycin, as described in the methods section. The cells were then infected with 229E at 0.05 MOI, and supernatants were collected on day 2. Figure 5A shows a marginal decrease in virus titers compared to the dominant-negative mutant of VPS4A. In addition, overexpression of GFP-CHMP4B, which in conjunction with VPS4A is involved in vesicular closure in the canonical pathway, also affected genome replication, as lower genome copies were seen in Figure 5D and by FISH staining, which correlated with the lower viral titers. Taken together, these results indicate that the role of CHMP4B in virus replication is not the same as that of VPS4A, suggesting that even though the same stage of viral replication was affected by these two components of the ESCRT machinery, the precise mechanisms appear to be different.
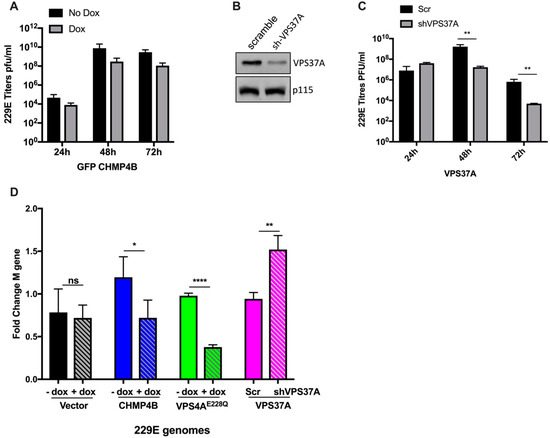
Figure 5.
Effect of other ESCRTs on 229E replication. (A) MRC–5 cells transduced with GFP-CHMP4B were infected at an MOI of 0.05 with 229E in the absence or presence of dox. Supernatants were collected at 24, 48, and 72 hpi. Virus titers were assessed using TCID50 assay. Graphs show results from two independent experiments conducted in triplicate. (B) MRC–5 cells transduced with lentivirus expressing either sh–NTC or sh–VPS37A and selected using puromycin. Knockdown was assessed on mock lysates by western blot and probed for VPS37A using antibodies against VPS37A and p115 (loading control). (C) The NTC and sh-VPS37A KD cells were infected with 229E at an MOI of 0.05. Supernatants were collected at 24, 48, and 72 hpi. Virus titers were assessed using TCID50 assay. Graphs show results from two independent experiments conducted in triplicate. ** p = 0.009 (48 h) and ** p = 0.0052 (72 h). (D) GFP-vector, GFP-VPS4AE228Q, GFP-CHMP4B, NTC, and VPS37A KD cells were infected with 229E at an MOI of 0.05 for 48 h. Dox treatment was conducted as previously described for all except the NTC and VPS37A KD cells. Cells were harvested at 48 hpi for RNA isolation. Relative genome levels using the 229E M gene were analyzed using One-Step RT-qPCR, and fold changes are shown. Three independent experiments were performed in triplicate. Results are shown as mean ± SD. ns = not significant, * p = 0.024 (CHMP4B), ** p = 0.0052 (VPS37A), and **** p < 0.0001 (GFP-VPS4AE228Q), respectively.
It has been shown previously that the VPS37A protein is responsible for the recruitment of the ESCRT machinery for VPS4-mediated membrane scission and closure of the phagophore [17]. Therefore, we next investigated the effect of VPS37A knockdown on 229E virus replication using lentivirus-mediated knockdown of VPS37A gene expression. Cells were transduced, selected, and infected as described in the Methods Section. Based on previous time course data showing that peak infection levels were seen at 48 hpi, samples were collected at this time point for comparison. A significant reduction in VPS37A protein levels was seen in sh-VPS37A compared to the control (Figure 5B). Virus titers were reduced by 2 logs in sh-VPS37A samples compared to scrambled shRNA (Figure 5C). This finding suggests that VPS37A plays an important role in virus production. Because VPS37A plays a role in recruiting VPS4A, its knockdown could affect VPS4A activity as well, hence contributing to the greater reduction in virus titers compared to VPS4A alone (see Figure 1A). Interestingly, when we measured genome copy numbers, there was no difference in the scrambled shRNA vs sh-VPS37A knockdown samples (Figure 5D). This result was surprising and interesting, implying that VPS37A does not play a role at the viral RNA replication stage but rather in the post-replication stages, potentially affecting virus particle egress, based on findings that the virus output was significantly reduced (Figure 5C).
4. Discussion
Enveloped virus infection begins with the attachment of the virus to the host cell plasma membrane and is completed when mature virus particles undergo egress from the cell. Nearly all viruses that utilize ESCRT machinery for virus budding require the recruitment of VPS4 [41]. Since VPS4A is essential for cell viability, we employed an inducible dominant-negative form (GFP-VPS4AE228Q) to study its effect on 229E virus infection. We show that overexpression of the non-functional VPS4A mutant led to a reduction in 229E titers by one log and a two-log decrease in OC43 titers compared to the control at 48 hpi (Figure 1B,C). Initial studies using HIV-1 found that its budding requires hijacking of the host ESCRT system [42]. Subsequent research has concluded that various viruses hijacking the ESCRT system occur at different steps in the virus replication cycle in different cells, with a common theme that facilitates virus proliferation, budding, and dissemination [43]. Thus, the ESCRT system can be an integral component of the proliferation of enveloped viruses [43,44]. For CoV 229E, surprisingly, we found that VPS4A ATPase does not result in virus particles becoming trapped within membranes due to lack of scission of the budding virus. Instead, we observed that the VPS4A ATPase and CHMP4B were required earlier in the virus replication cycle rather than the post-replication step. Due to their role in membrane remodeling, both proteins could be involved in the recruitment of viral RNA to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane and ingress to the ER lumen to form ROs. We observed that in the absence of a functional VPS4A ATPase, the formation of the initial replication centers was impaired, as seen in the TEM images, which explained the significantly reduced genomic RNA levels at 48 dpi and 72 hp. Based on our findings that OC43, a member of the beta family of CoVs, showed an even higher reduction in viral titers in the presence of GFP-VPS4AE228Q, it is highly likely that VPS4A plays a similar and significant role across CoVs families, including SARS-CoV-2. Studies by Hou et al. reported that ESCRT-related protein–protein interaction (PPI) subnetworks act as antiviral factors, including VPS4A and CHMP4B, supporting the possibility that the ESCRT pathway plays an important function in mediating SARS-CoV-2 infection [45].
Using smFISH, we verified that 229E viral RNA levels were significantly reduced in cells expressing VPS4AE228Q (Figure 3C,D) and CHMP4B. Furthermore, immunostaining of double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) and the viral nucleocapsid protein in control cells showed their accumulation in what could represent replication centers, which were completely abolished when the non-functional GFP-VPS4AE228Q was expressed (Figure 3E), as visualized using TEM (Figure 2B). We cannot conclude the direct involvement of VPS4A in the virus replication. Still, the ESCRT machinery is an evolutionarily conserved membrane remodeling complex with the unique ability to catalyze membrane constriction within necks. Among them, ESCRT-III proteins like CHMP4B, in collaboration with the VPS4 ATPase, play a central role in the membrane remodeling and scission functions of the ESCRT machinery [46]. However, we cannot rule out that VPS4A may play a different role or act in a non-canonical pathway during CoV infection. Furthermore, several enveloped and non-enveloped viruses induce profound membrane remodeling/proliferation in infected cells to create specialized compartments where viral genome replication and/or new virion assembly occurs [18,47,48,49]. The reduced expression of the 229E nucleocapsid protein, as seen in infected cells expressing GFP-VPS4AE228Q (Figure 3E), suggests that the replication machinery could not be assembled properly due to a lack of safe replication compartments and reduced viral protein expression. Furthermore, other non-structural viral proteins, which were not investigated in this study, may be affected or involved in this process.
Viral RNA recognition occurs primarily in the cytoplasmic or endosomal compartments within an infected cell [39]. The innate immune system recognizes the pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) comprising viral nucleic acids, protein, lipids, structural components, and other viral intermediates including single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) or dsRNA, via distinct pattern recognition receptors (PRRs). CoVs are ssRNA viruses that can be detected by TLR7 or TLR8 and potentially RIG-I and PKR. They form dsRNAs during their replicative stage, which TLR3 detects in the endosome and RIG-I, MDA5, and PKR in the cytosol. Activation of these pathways was more pronounced in cells expressing dominant-negative GFP-VPS4AE228Q, as evident from the higher induction of ISG15 (3-fold) and MX1 (15-fold) in dox-positive samples on day 2 of infection (Figure 4A,B). This result was not surprising as cells expressing VPS4AE228Q did not allow the formation of replication centers, leaving the viral RNA exposed and readily sensed by the PRRs, resulting in a heightened host immune response.
These PRRs initiate a signaling cascade culminating in primary type I interferon (IFN-α/β) response and inflammatory cytokine production [39]. Interestingly, a very strong induction of IL-6 (250-fold) (Figure 4C), but not IFN-β (Figure 4D), was observed, suggesting stimulation of an inflammation response, which could be due to the disruption of the host cell machinery in addition to the virus infection and/or the exposed viral RNA in the cytosol. Studies have shown that during SARS-CoV-2 infection, evasion mechanisms trigger the activation of NOD-signaling and NLRP3 pathways, leading to the production of inflammatory cytokines IL-1β and IL-6 while muting or blocking cGAS-STING and interferon-type I and III pathways. Thus, infection results in decreased production of antiviral interferons and delayed innate response [39], which corroborates our findings in 229E infection. Thus, because of these cellular immune responses, CoVs can only replicate in a specific microenvironment. This viral niche, created by extensive rearrangements of host cell membranes, protects viral RNAs from being recognized and degraded by the host’s innate immune defenses. VPS4A appears to play a critical role in this aspect, as in its absence, the exposed 229E viral RNA induced a strong inflammatory response.
To date, all viruses that bud in an ESCRT-dependent manner require the membrane-remodeling functions provided by ESCRT-III and VPS4, although their requirements for particular upstream factors may vary. For instance, HIV-1 recruits the ESCRT pathway through specific motifs in the viral Gag protein [35], and VP40 from Marburg and Ebola viruses interact with ESCRT-associated proteins such as Alix and TSG101 through their late domains to facilitate budding [9,10]. Our data showed that overexpression of CHMP4B, part of the ESCRT-III complex upstream of the accessory proteins, is important for the virus but harmful when supplied in excess because it impacts viral titers and genome levels. Therefore, the protein’s activity and the optimum protein levels of ESCRTs are critical for the proper functioning of this host machinery.
Interestingly, we found that VPS37A, which is part of the ESCRT-I group consisting of VPS23/TSG101, VPS28, VPS37, and MVB12/UBAP1 [50], played a role at the post-replication stage since its knockdown did not affect virus genome levels (Figure 5D) but significantly reduced virus titers released from infected cells (Figure 5C). This result is consistent with its role in recruiting the ESCRT machinery for VPS4-mediated membrane scission. Thus, reduced levels of VPS37A protein affected a post-replication step, potentially resulting in virus release from the cell, which resulted in lower viral titers. Although we did not pursue this finding further in this study, it would be worth investigating whether the lack of VPS37A protein would result in trapped virus particles within the cell.
Based on our observations and previous findings from other groups, the ESCRTS may play antiviral or proviral roles under different circumstances and stages of viral infection. This complex interplay needs to be further studied but fits well with the hypothesis that different ESCRTs are involved in specific stages of virus replication.
5. Conclusions
Although different ESCRT groups that are comprised of several factors may have redundant roles and complement each other in the normal cascade of the pathway’s activities, each group could play an important role at different stages of CoV infection. Although studies are ongoing to better understand the host interface with the budding pathway of SARS-CoV-2, research using related CoVs is equally important to elucidate the basic and key aspects of virus replication, which can be used as a strategy to target multiple viruses using a common pathway or factor. The work presented here revealed previously unknown functions of VPS4A, CHMP4B, and VPS37A in CoV infection. This can be a launching pad for a deeper understanding of the specific mechanisms ESCRTs play in CoV infections.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: N.J.B., J.M.F. and L.J.P.; methodology, N.J.B., R.K., R.K.M. and L.J.P.; software: R.K., N.J.B. and R.K.M.; validation: R.K. and R.K.M.; formal analysis: R.K., N.J.B., R.K.M., L.J.P., J.M.F. and M.C.B.; investigation: R.K. and R.K.M.; resources: N.J.B., L.J.P., R.K., J.M.F., N.D.C. and M.C.B.; data curation: R.K. and R.K.M.; writing—original draft preparation, R.K. and R.K.M.; writing—review and editing, R.K., R.K.M., N.J.B., J.M.F., M.C.B., N.D.C. and L.J.P.; visualization, R.K. and R.K.M.; supervision, N.J.B. and L.J.P.; project administration, N.J.B. and L.J.P.; funding acquisition, N.J.B., L.J.P., J.M.F., M.C.B. and N.D.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported in part by the Penn State College of Medicine Bridge Grant (N.J.B., L.J.P., J.M.F., N.D.C.); the Pennsylvania Department of Community & Economic Development (N.J.B., L.J.P., J.M.F., M.C.B., N.D.C.); the Department of Medicine Spring 2020 (COVID) Innovation Pilot Award (L.J.P., N.J.B., J.M.F.); the 4-Diamonds (J.M.F), and the Departments of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine, Microbiology and Immunology, and Pathology at the Penn State College of Medicine.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data are made available within this manuscript.
Acknowledgments
The Advanced Light Microscopy (RRID: SCR_022526) and Transmission Electron Microscopy (RRID: SCR_021200) core services and instruments used in this project were funded in part by the Pennsylvania State University College of Medicine via the Office of the Vice Dean of Research and Graduate Students and the Pennsylvania Department of Health using Tobacco Settlement Funds (CURE). The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the views of the University or College of Medicine. The Pennsylvania Department of Health specifically disclaims responsibility for any analyses, interpretations, or conclusions. We would like to thank Han Chen for assistance with TEM sample processing and imaging. We would like to thank H.G Wang, and Yoshi Takahashi, at Penn State College of Medicine, Hershey, PA, for providing reagents.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Pawliczek, T.; Crump, C.M. Herpes simplex virus type 1 production requires a functional ESCRT-III complex but is independent of TSG101 and ALIX expression. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 11254–11264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirov, D.G.; Ono, A.; Orenstein, J.M.; Freed, E.O. Overexpression of the N-terminal domain of TSG101 inhibits HIV-1 budding by blocking late domain function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 955–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goila-Gaur, R.; Demirov, D.G.; Orenstein, J.M.; Ono, A.; Freed, E.O. Defects in human immunodeficiency virus budding and endosomal sorting induced by TSG101 overexpression. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 6507–6519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Sorensen, E.M.; Naito, A.; Schott, M.; Kim, S.; Ahlquist, P. Involvement of host cellular multivesicular body functions in hepatitis B virus budding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 10205–10210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prange, R. Host factors involved in hepatitis B virus maturation, assembly, and egress. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2012, 201, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honeychurch, K.M.; Yang, G.; Jordan, R.; Hruby, D.E. The vaccinia virus F13L YPPL motif is required for efficient release of extracellular enveloped virus. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 7310–7315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streck, N.T.; Carmichael, J.; Buchkovich, N.J. Nonenvelopment Role for the ESCRT-III Complex during Human Cytomegalovirus Infection. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e02096-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandon, R.; AuCoin, D.P.; Mocarski, E.S. Human cytomegalovirus exploits ESCRT machinery in the process of virion maturation. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 10797–10807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmins, J.; Schoehn, G.; Ricard-Blum, S.; Scianimanico, S.; Vernet, T.; Ruigrok, R.W.; Weissenhorn, W. Ebola virus matrix protein VP40 interaction with human cellular factors Tsg101 and Nedd4. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 326, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urata, S.; Noda, T.; Kawaoka, Y.; Morikawa, S.; Yokosawa, H.; Yasuda, J. Interaction of Tsg101 with Marburg virus VP40 depends on the PPPY motif, but not the PT/SAP motif as in the case of Ebola virus, and Tsg101 plays a critical role in the budding of Marburg virus-like particles induced by VP40, NP, and GP. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 4895–4899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itakura, Y.; Tabata, K.; Saito, T.; Intaruck, K.; Kawaguchi, N.; Kishimoto, M.; Torii, S.; Kobayashi, S.; Ito, N.; Harada, M.; et al. Morphogenesis of Bullet-Shaped Rabies Virus Particles Regulated by TSG101. J. Virol. 2023, 97, e0043823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finke, S.; Conzelmann, K.K. Replication strategies of rabies virus. Virus Res. 2005, 111, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katzmann, D.J.; Babst, M.; Emr, S.D. Ubiquitin-dependent sorting into the multivesicular body pathway requires the function of a conserved endosomal protein sorting complex, ESCRT-I. Cell 2001, 106, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurley, J.H. ESCRTs are everywhere. EMBO J. 2015, 34, 2398–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christ, L.; Raiborg, C.; Wenzel, E.M.; Campsteijn, C.; Stenmark, H. Cellular Functions and Molecular Mechanisms of the ESCRT Membrane-Scission Machinery. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2017, 42, 42–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skowyra, M.L.; Schlesinger, P.H.; Naismith, T.V.; Hanson, P.I. Triggered recruitment of ESCRT machinery promotes endolysosomal repair. Science 2018, 360, eaar5078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, Y.; Liang, X.; Hattori, T.; Tang, Z.; He, H.; Chen, H.; Liu, X.; Abraham, T.; Imamura-Kawasawa, Y.; Buchkovich, N.J.; et al. VPS37A directs ESCRT recruitment for phagophore closure. J. Cell Biol. 2019, 218, 3336–3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calistri, A.; Reale, A.; Palù, G.; Parolin, C. Why Cells and Viruses Cannot Survive without an ESCRT. Cells 2021, 10, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöneberg, J.; Lee, I.H.; Iwasa, J.H.; Hurley, J.H. Reverse-topology membrane scission by the ESCRT proteins. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöneberg, J.; Pavlin, M.R.; Yan, S.; Righini, M.; Lee, I.H.; Carlson, L.A.; Bahrami, A.H.; Goldman, D.H.; Ren, X.; Hummer, G.; et al. ATP-dependent force generation and membrane scission by ESCRT-III and Vps4. Science 2018, 362, 1423–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henne, W.M.; Buchkovich, N.J.; Emr, S.D. The ESCRT pathway. Dev. Cell 2011, 21, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sergio, M.C.; Ricciardi, S.; Guarino, A.M.; Giaquinto, L.; De Matteis, M.A. Membrane remodeling and trafficking piloted by SARS-CoV-2. Trends Cell Biol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, H.H.; Sánchez-Rivera, F.J.; Schneider, W.M.; Luna, J.M.; Soto-Feliciano, Y.M.; Ashbrook, A.W.; Le Pen, J.; Leal, A.A.; Ricardo-Lax, I.; Michailidis, E.; et al. Functional interrogation of a SARS-CoV-2 host protein interactome identifies unique and shared coronavirus host factors. Cell Host Microbe 2021, 29, 267–280.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebendenne, A.; Roy, P.; Bonaventure, B.; Chaves Valadão, A.L.; Desmarets, L.; Arnaud-Arnould, M.; Rouillé, Y.; Tauziet, M.; Giovannini, D.; Touhami, J.; et al. Bidirectional genome-wide CRISPR screens reveal host factors regulating SARS-CoV-2, MERS-CoV and seasonal HCoVs. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 1090–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, W.M.; Luna, J.M.; Hoffmann, H.H.; Sánchez-Rivera, F.J.; Leal, A.A.; Ashbrook, A.W.; Le Pen, J.; Ricardo-Lax, I.; Michailidis, E.; Peace, A.; et al. Genome-Scale Identification of SARS-CoV-2 and Pan-coronavirus Host Factor Networks. Cell 2021, 184, 120–132.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vietri, M.; Radulovic, M.; Stenmark, H. The many functions of ESCRTs. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, N.; Jacob-Hirsch, J.; Drori, Y.; Eran, E.; Kol, N.; Nayshool, O.; Mendelson, E.; Rechavi, G.; Mandelboim, M. Transcriptomic profiling and genomic mutational analysis of Human coronavirus (HCoV)-229E -infected human cells. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0247128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Cruz, L.; Sandhu, P.K.; Buchkovich, N.J. UL88 Mediates the Incorporation of a Subset of Proteins into the Virion Tegument. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e00474-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Christensen, N.D.; Kaddis Maldonado, R.J.; Bewley, M.C.; Ostman, A.; Sudol, M.; Chen, E.C.; Buchkovich, N.W.; Gontu, A.; Surendran Nair, M.; et al. Monoclonal Antibodies to S and N SARS-CoV-2 Proteins as Probes to Assess Structural and Antigenic Properties of Coronaviruses. Viruses 2021, 13, 1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, K.; Frankowski, K.J.; Li, S.; Wong, D.E.; Moen, D.R.; Porubsky, P.R.; Lin, H.J.; Schoenen, F.J.; et al. Evaluating p97 Inhibitor Analogues for Potency against p97-p37 and p97-Npl4-Ufd1 Complexes. ChemMedChem 2016, 11, 953–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M.; Sandhu, P.; Kumar, R.; Buchkovich, N.J. The Immune-Specific E3 Ubiquitin Ligase MARCH1 Is Upregulated during Human Cytomegalovirus Infection to Regulate Iron Levels. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0180621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahal, S.; Clayton, K.; Cabral, T.; Cheng, R.; Jahanshahi, S.; Ahmed, C.; Koirala, A.; Villasmil Ocando, A.; Malty, R.; Been, T.; et al. On a path toward a broad-spectrum anti-viral: Inhibition of HIV-1 and coronavirus replication by SR kinase inhibitor harmine. J. Virol. 2023, 97, e0039623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahanshahi, S.; Ouyang, H.; Ahmed, C.; Zahedi Amiri, A.; Dahal, S.; Mao, Y.Q.; Van Ommen, D.A.J.; Malty, R.; Duan, W.; Been, T.; et al. Broad spectrum post-entry inhibitors of coronavirus replication: Cardiotonic steroids and monensin. Virology 2024, 589, 109915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, E.; Sandrin, V.; McCullough, J.; Katsuyama, A.; Baci Hamilton, I.; Sundquist, W.I. ESCRT-III protein requirements for HIV-1 budding. Cell Host Microbe 2011, 9, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Boon, J.A.; Nishikiori, M.; Zhan, H.; Ahlquist, P. Positive-strand RNA virus genome replication organelles: Structure, assembly, control. Trends Genet. 2024, 40, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elia, N.; Sougrat, R.; Spurlin, T.A.; Hurley, J.H.; Lippincott-Schwartz, J. Dynamics of endosomal sorting complex required for transport (ESCRT) machinery during cytokinesis and its role in abscission. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4846–4851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Liang, X.; Wang, G.; Bewley, M.C.; Hamamoto, K.; Liu, X.; Flanagan, J.M.; Wang, H.G.; Takahashi, Y.; Tian, F. Identification of membrane curvature sensing motifs essential for VPS37A phagophore recruitment and autophagosome closure. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mdkhana, B.; Saheb Sharif-Askari, N.; Ramakrishnan, R.K.; Goel, S.; Hamid, Q.; Halwani, R. Nucleic Acid-Sensing Pathways During SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Expectations versus Reality. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 199–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munnur, D.; Banducci-Karp, A.; Sanyal, S. ISG15 driven cellular responses to virus infection. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2022, 50, 1837–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, J.H.; Hanson, P.I. Membrane budding and scission by the ESCRT machinery: It’s all in the neck. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 556–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, J.H.; Cada, A.K. Inside job: How the ESCRTs release HIV-1 from infected cells. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2018, 46, 1029–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Votteler, J.; Sundquist, W.I. Virus budding and the ESCRT pathway. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 14, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, B.; Lever, A.M.L. The Interplay between ESCRT and Viral Factors in the Enveloped Virus Life Cycle. Viruses 2021, 13, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.; Wei, Y.; Zou, J.; Jaffery, R.; Liang, S.; Zheng, C.; Chen, K.; Shi, P.Y.; Chen, Y.; Xie, X.; et al. Integrated multi-omics analyses identify key anti-viral host factors and pathways controlling SARS-CoV-2 infection. Res. Sq. 2022; preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoten, C.L.; Carlton, J.G. ESCRT-dependent control of membrane remodelling during cell division. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 74, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Zhou, S.; Gao, S.; Deng, H. Remodeling of host membranes during herpesvirus assembly and egress. Protein Cell 2019, 10, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lan, Y.; Sanyal, S. Membrane heist: Coronavirus host membrane remodeling during replication. Biochimie 2020, 179, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.; Krijnse-Locker, J. Modification of intracellular membrane structures for virus replication. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, Y.; Hu, S.; Liu, X. Insights into the function of ESCRT and its role in enveloped virus infection. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1261651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).