Abstract
Introduction: SARS-CoV-2 is the newest beta coronavirus family member to demonstrate neuroinvasive capability in severe cases of infection. Despite much research activity in the SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19 space, the gene-level biology of this phenomenon remains poorly understood. In the present analysis, we leveraged spatial transcriptomics methodologies to examine relevant gene heterogeneity in tissue retrieved from the human prefrontal cortex. Methods: Expression profiles of genes with established relations to the SARS-CoV-2 neuroinvasion process were spatially resolved in dorsolateral prefrontal cortex tissue (N = 4). Spotplots were generated with mapping to six (6) previously defined gray matter layers. Results: Docking gene BSG, processing gene CTSB, and viral defense gene LY6E demonstrated similar spatial enrichment. Docking gene ACE2 and transmembrane series proteases involved in spike protein processing were lowly expressed across DLPFC samples. Numerous other findings were obtained. Conclusion: Efforts to spatially represent expression levels of key SARS-CoV-2 brain infiltration genes remain paltry to date. Understanding the sobering history of beta coronavirus neuroinvasion represents a weak point in viral research. Here we provide the first efforts to characterize a motley of such genes in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex.
1. Introduction
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) produced a global pandemic with over six million reported deaths and an estimated case fatality rate of 2.2% [1]. In the United States, COVID-19 was the third leading cause of death in 2020 [2]. The causative agent, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), is a highly contagious RNA virus that principally targets the respiratory system [1]. However, SARS-CoV-2 has the potential to affect other organ systems, especially the central nervous system (CNS) [1]. The neurologic manifestations of acute COVID-19 include headaches, anosmia, ageusia, dysexecutive syndromes, strokes, seizures, encephalitis, meningitis, neuromuscular disorders, and Guillain–Barre syndrome [3]. The role of the CNS in COVID-19 has been especially emphasized due to the prevalence of neuropsychiatric symptoms in post-COVID syndrome. These patients report high rates of fatigue (37%), brain fog (32%), sleep disturbances (31%), memory issues (27%), anxiety (23%), attention disorders (22%), and depression (12%) [4]. However, despite the extensive clinical characterization of neuropsychiatric symptoms in COVID-19, the causative mechanism is unclear.
Multiple studies have found the presence of SARS CoV-2 RNA in brain tissue [5,6,7,8]. SARS-CoV-2 utilizes the angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ACE2) as its primary receptor for cell entry. Since this receptor is highly expressed in multiple distinct CNS structures, including the choroid plexus and neocortical neurons, this further reinforces the idea behind the capability of SARS-CoV-2 to infect the brain and lead to the CNS symptoms experienced by COVID-19 patients [9]. Current research suggests that there may be multiple structural pathways for CNS entry, including through the olfactory tract, blood-brain barrier, and infiltration by infected immune cells [9,10]. Additional research has shown more specific mechanisms of viral entry and replication involving non-canonical docking receptors such as basigin (BSG) [11] and neuropilin-1 (NRP1) [11,12], as well as a variety of processing proteases [PMID: 32376634]. Neurotropism of other coronaviruses, particularly SARS-CoV-1, further supports the case for CNS invasion in SARS-CoV-2 [13]. Although there may be multiple viral mechanisms/routes of entry into the CNS, further evaluation of brain architecture is required before more definitive conclusions can be made.
The human cerebral cortex is organized into laminar layers whereby the cells of each layer demonstrate different patterns of gene expression and, therefore, physiologic functions [14]. Spatial transcriptomic technologies utilize transcriptome-level measurements to produce tissue atlases that describe the spatial arrangement of genes using intact tissue, which can then be used to identify mechanisms underlying abnormal function in disease [15,16]. Sequencing-based spatial transcriptomics, for instance, may preserve cellular coordinate information via direct capture and measure (e.g., laser capture microdissection) or the use of a microarray equipped with spatially-barcoded probes [16,17,18]. With regard to COVID-19, the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex is a six-layer region [14] whose functional impairment results in disorders of executive function and memory [19]. Pathology (or aberrant activity) in this region may be implicated in the cognitive impairment reported by some COVID-19 patients. Here we generate spatial expression profiles for a subset of genes with established relevancy to SARS-CoV-2 brain entry. The aim of the present supervised study is to nominate novel and testable genes plus dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPC) regions for future, focused investigation.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Acquisition
Spatial transcriptomics data gathered from postmortem human DLPC tissue using the 10x Genomics’ Visium platform was retrieved from the spatialLIBD project (http://research.libd.org/spatialLIBD/), (accessed on 16 October 2022) [14,20]. These source data were represented by two pairs of replicates from three healthy adult donors for a total of 12 DLPC tissue samples [14]. Of these, sample IDs 151507, 151508, 151509, and 151510 were analyzed in the present study as these samples contained all cortical layer data as originally reported by Maynard and colleagues [14] (Table 1). Additional tissue sample metadata is accessible through Globus endpoint “jhpce#HumanPilot10x” or GitHub (https://github.com/LieberInstitute/HumanPilot/tree/master/10X), (accessed on 16 October 2022). The selection of docking, processing, and viral defense genes pertinent to SARS-CoV-2 entry into the brain (observed in severe COVID-19 cases) was informed by prior work [11,21].

Table 1.
Metrics summary of selected tissue samples, as retrieved from 10x Genomics.
2.2. Spatial Mapping
Preprocessed and normalized data were fetched from spatialLIBD as a spatial experiment object containing logCounts for DLPC sample IDs 151507, 151508, 151509, and 151510. The spatial distribution of ACE2, BSG, CTSB, CTSL, FURIN, IFITM1, IFITM2, IFITM3, IFNAR1, IFNAR2, LY6E, NRP1, NRP2, TMPRSS2, and TMPRSS11A was then plotted along with the pre-defined layers of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex for each tissue sample. Spotplots depicted log-transformed normalized expression counts. Spatial annotation was maintained in accordance with the originally defined six (6) neocortical layers plus white matter regions.
2.3. Software
All analysis and visualization were conducted using the programming language R (v4.2.2). Code available at https://github.com/Batchu-Sai/DLPFC_covid19.
3. Results
To investigate the spatial organization of the selected gene set, we utilized pre-defined layer margins (Figure 1). Six distinct layers were retained, with approximately equal spatial organization across tissue samples. Spotplots represented by logCounts of the following genes were generated: (docking) ACE2, BSG, NRP1, and NRP2; (processing of spike protein) TMPRSS2, TMPRSS11A, FURIN, CTSB, and CTSL; (viral defense) LY6E, IFITM1, IFITM2, IFITM3, IFNAR1, and IFNAR2 (Figure 2).
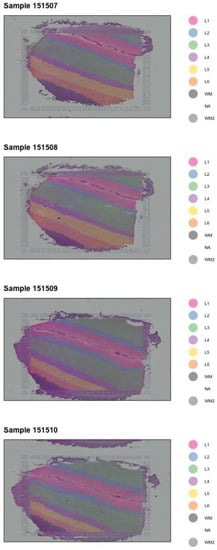
Figure 1.
Layer plot of the four analyzed DLPC tissue samples.
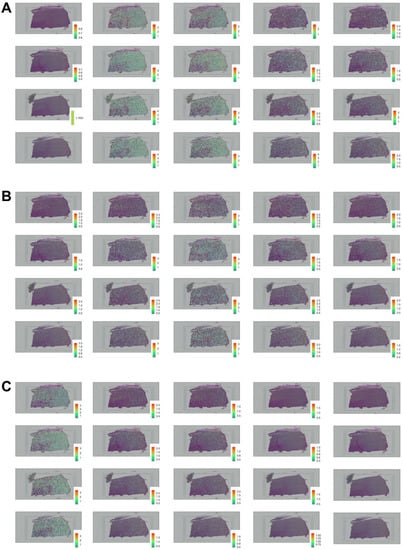
Figure 2.
Spatial distribution of docking, processing, and viral defense genes involved in SARS-CoV-2 brain entry. ((A), from left to right) Spatial distribution of ACE2, BSG, CTSB, CTSL, and FURIN across four DLPFC samples plotted column-wise and mapped as illustrated in Figure 1. ((B), from left to right) Spatial distribution of IFITM1, IFITM2, IFITM3, IFNAR1, and IFNAR2 across four DLPC samples plotted column-wise and mapped as illustrated in Figure 1. ((C), from left to right) Spatial distribution of LY6E, NRP1, NRP2, TMPRSS2, and TMPRSS11A across four DLPC samples plotted column-wise and mapped as illustrated in Figure 1.
These data reflected significant spatial heterogeneity within the DLPFC environment. TMPRSS11A, TMPRSS2, and NRP1 revealed sparse gene expression profiles across all the layers in all the samples (Figure 2A,C). IFNAR2 exhibited L3 and L4 preferential expression and decreased gene expression in L1 and L2 (Figure 2B). The layer-enriched profiles for NRP2 and IFITM1 were lowly expressed in the different layers across all samples (Figure 2B,C). IFNAR2 exhibited localized increased expression in L3 and L4 and low-gene expression in the upper layers of L1 and L2 (Figure 2B). CTSL experienced low expression in L1 and L2 of their layer-enriched gene profiles, while the deeper layers of L3, L4, L5, and L6 were highly expressed in samples 151507, 151508, and 151509 (Figure 1 and Figure 2A). INFAR1, FURIN, LY6E, IFITM2, IFITM3, and CTSB revealed preferentially higher gene expression across all samples in L3, L4, L5, and L6 (Figure 2A–C). Notably, docking gene BSG, processing gene CTSB, and viral defense gene LY6E demonstrated preferential expression in neocortical layers 1–4 (Figure 2A,C). The expression profile of BSG showed extensive enrichment across all the layers with consistently increased expression in L3, L4, L5, and L6 (Figure 2A). Viral defense gene IFITM3 reported unique enrichment in layers five and six across all analyzed DLPFC samples (Figure 2B). ACE2 and examined transmembrane series proteases were lowly expressed in all layers in all the samples except in L1 and L3 of Sample 151508 (Figure 2A,C). The findings from these four tissue samples indicate how the spatial distribution of various genes was localized to the deeper layers in the DLPC.
4. Discussion
The spatial transcriptomic profiles for the cortical expression in the DLPFC involve examining the differences in gene expression and localizations to individual cortical layers to provide critical insights into genes implicated in the mechanism of SARS-CoV-2 invasion of the brain. Due to the interrelationship between the brain tissue architecture and function, the differences in the spatial arrangement of genes in the six-layer region of the DLPFC may offer an understanding not only of the potential pathways for SARS-CoV-2 neuroinvasion but also implicate associations with the neuropsychiatric disorders and symptoms, as the DLPFC serves different cognitive functions and is involved in the cognitive processing of emotions [14,22].
By employing spatial transcriptomics technology, we generated spatial gene expression maps to profile the enrichment of genes within the human DLPFC. The Spotplots depict log-transformed normalized expression (log(counts) for a curated collection of genes related to SARS-CoV-2 neuroinvasion (Figure 1 and Figure 2). The layer-enriched gene profiles for ACE2, TMPRSS11A, and TMPRSS2 showed scant expression in all samples across all the layers except for Sample 151508 in L1 and L3 for ACE2 (Figure 2A). This analysis corresponds to how Torices et al. found that low expression of ACE2 and TMPRSS2 could provide slight protection against the entry of SARS-CoV-2 into the brain [23]. ACE2 is a polymorphic gene located on chromosome Xp22 [24], while the gene encoding TMPRSS2 resides at chromosome 21.q22.3 [25]. TMPRSS11A is positioned at 4q13.3 on chromosome 4 [26]. NRP1 has been demonstrated to facilitate the entry of SARS-CoV-2 when ACE2 is expressed, and the presence of these two cell surface receptors in neurons implicates the high probability of neurotropism [27]. Furthermore, in a pharmacological blocking experiment, TMPRSS2 and NRP1 were identified as prospective intervention targets due to their involvement in the entry of SARS-CoV-2 [28]. NRP1 exhibited low-gene expressions across all the layers in all samples, supporting NRP1′s activity as a regulator of ACE2 expression in SARS-CoV-2 infectivity (Figure 2C) [27]. NRP1 and NRP2 are homologous isoforms located on chromosomes 10p12 and 2q34, respectively [29]. The finding emphasizes the significance of ACE2 in the SARS-CoV-2 invasion [28]. The expression profile of IFNAR2 revealed higher expression in L3 and L4 and lower expression in L1 and L2 (Figure 2B). IFNAR2 was identified as one of the 12 significant genes in the brain and blood associated with hospitalized patients with COVID-19 [30]. Chromosome 21q22.11 harbors IFNAR1 and IFNAR2, which make up the interferon alpha/beta receptor [31]. NRP2 and IFITM1 showed consistently low gene expression in all samples across all layers (Figure 2B,C). IFITM1, IFITM2, and IFITM3 genes are located on chromosome 11 at position 11p15.5 [32]. BSG indicated high gene expression in all the layers but progressively increased expression through L3, L4, L5, and L6 (Figure 2A). The ubiquitously expressed BSG gene is positioned at chromosome 19p13.3 [33]. The layer-enriched gene expressions of CTSL presented low expression in L1 and L2 and increased expression for L3, L4, L5, and L6 for samples 151507, 151508, and 151509 (Figure 1 and Figure 2A). CTSL, a cysteine protease, resides on chromosome 9 at the position of 9q21-q22 [34]. INFAR1, FURIN, LY6E, IFITM2, IFITM3, and CTSB experienced higher gene expression in L3, L4, L5, and L6 in all samples (Figure 2A–C). FURIN, a proprotein convertase, is located at chromosome 15q26.1 [35]. The CTSB gene, a lysosomal protease, is positioned at chromosome 8p22 [36], while chromosome 8q24.3 contains the LY6E gene [37]. Single-nucleus transcriptomic analyses revealed that there was an elevated expression of SARS-CoV-2 host factors, BSG and FURIN, and antiviral defense genes, LY6E, IFITM2, IFITM3, and IFNAR1, in the brain endothelial cells of patients with Alzheimer’s disease, signifying a potential role for microvascular brain injury in the cognitive impairment of COVID-19 [38]. CTSB was found to be expressed in the veins and capillaries of the brain vasculature [39]. These combined findings showed that many of the genes were preferentially localized in the deeper layers offering implications for the spatial transcriptomic expressions and alterations in the DLPFC and demonstrating how transcriptomic changes within the cortical layers can elucidate the neurological manifestations of COVID-19 to impart guidance in the development of prophylactics and therapeutics. Collectively, these spatial transcriptome analyses underscore the potential of the functional utility in deriving clinical insights from the layer-enriched gene expression profiles of DLPFC into the characterization of risk genes and disease mechanisms.
Single-cell spatial transcriptomics provides advanced methods to explore spatial localizations of gene expressions for the characterization of cell types, exploration of tissues, and differential expression analysis [40]. However, these spatial technologies encounter challenges involving low output, costly labor, restricted capture capabilities of information in a large area, and difficulties resolving spatial expression patterns of tissue-specific genes [41]. Furthermore, signal detection in spatial transcriptomic technologies experiences noisiness and sparseness, affecting the feasibility of segmentation [42].
5. Conclusions
In summary, the present analysis represents a first-use case of spatial transcriptomics to characterize the expression of genes relevant to SARS-CoV-2 neuroinvasion within segmented brain tissue. Significant findings include, but are not limited to, the following: docking receptor gene BSG, spike protein processing gene CTSB, and viral defense gene LY6E revealed preferential L1-4 expression; several viral defense genes were upregulated in L3; expression levels of INFAR1, FURIN, LY6E, IFITM2, IFITM3, and CTSB were demonstrably mapped to L3-6. Limitations of this study include gene dropout inherent to single-cell sequencing and the low tissue sample size. Still, the authors maintain that the findings shared here do much to elucidate the spatial activity of genes responsible for the neurobiological change in cases of severe SARS-CoV-2 infection, potentially encouraging β-CoV gene therapy efforts. In the future, we hope to expand these basic results to other affected regions by incorporating tissue samples sourced from the choroid plexus and medulla oblongata.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.B.; Formal analysis, S.B., M.J.D., J.T.T., A.F., K.T. and K.P.; Methodology, S.B. and M.J.D.; Project administration, B.L.-W.; Software, S.B.; Supervision, B.L.-W.; Validation, S.B., M.J.D., J.T.T., A.F., K.T. and K.P.; Visualization, S.B.; Writing—original draft, M.J.D., J.T.T. and A.F.; Writing—review & editing, S.B., M.J.D., J.T.T., A.F., K.T., K.P. and B.L.-W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Code available at https://github.com/Batchu-Sai/DLPFC_covid19.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Cascella, M.; Rajnik, M.; Aleem, A.; Dulebohn, S.C.; Di Napoli, R. Features, Evaluation, and Treatment of Coronavirus (COVID-19). In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA.
- Ahmad, F.B.; Cisewski, J.A.; Miniño, A.; Anderson, R.N. Provisional Mortality Data—United States, 2020. MMWR. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2021, 70, 519–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinakaran, D.; Manjunatha, N.; Naveen Kumar, C.; Suresh, B.M. Neuropsychiatric aspects of COVID-19 pandemic: A selective review. Asian J. Psychiatry 2020, 53, 102188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premraj, L.; Kannapadi, N.V.; Briggs, J.; Seal, S.M.; Battaglini, D.; Fanning, J.; Suen, J.; Robba, C.; Fraser, J.; Cho, S.M. Mid and long-term neurological and neuropsychiatric manifestations of post-COVID-19 syndrome: A meta-analysis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2022, 434, 120162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.K.; Chaubey, G.; Chen, J.Y.; Suravajhala, P. Decoding SARS-CoV-2 hijacking of host mitochondria in COVID-19 pathogenesis. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2020, 319, C258–C267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najjar, S.; Najjar, A.; Chong, D.J.; Pramanik, B.K.; Kirsch, C.; Kuzniecky, R.I.; Pacia, S.V.; Azhar, S. Central nervous system complications associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection: Integrative concepts of pathophysiology and case reports. J. Neuroinflammation 2020, 17, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.E.; Fazal, F.M.; Parker, K.R.; Zou, J.; Chang, H.Y. RNA-GPS Predicts SARS-CoV-2 RNA Residency to Host Mitochondria and Nucleolus. Cell Syst. 2020, 11, 102–108.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Generoso, J.S.; Barichello de Quevedo, J.L.; Cattani, M.; Lodetti, B.F.; Sousa, L.; Collodel, A.; Diaz, A.P.; Dal-Pizzol, F. Neurobiology of COVID-19: How can the virus affect the brain? Braz. J. Psychiatry 2021, 43, 650–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Wang, K.; Yu, J.; Howard, D.; French, L.; Chen, Z.; Wen, C.; Xu, Z. The Spatial and Cell-Type Distribution of SARS-CoV-2 Receptor ACE2 in the Human and Mouse Brains. Front. Neurol. 2021, 11, 573095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, C.C.; Lane, T.E.; Stohlman, S.A. Coronavirus infection of the central nervous system: Host-virus stand-off. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 4, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iadecola, C.; Anrather, J.; Kamel, H. Effects of COVID-19 on the Nervous System. Cell 2020, 183, 16–27.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Z.; Deng, Y.; Lian, J.Q.; Du, P.; Wei, D.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, X.X.; Gong, L.; et al. CD147-spike protein is a novel route for SARS-CoV-2 infection to host cells. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantuti-Castelvetri, L.; Ojha, R.; Pedro, L.D.; Djannatian, M.; Franz, J.; Kuivanen, S.; van der Meer, F.; Kallio, K.; Kaya, T.; Anastasina, M.; et al. Neuropilin-1 facilitates SARS-CoV-2 cell entry and infectivity. Science 2020, 370, 856–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maynard, K.R.; Collado-Torres, L.; Weber, L.M.; Uytingco, C.; Barry, B.K.; Williams, S.R.; Catallini, J.L., II; Tran, M.N.; Besich, Z.; Tippani, M.; et al. Transcriptome-scale spatial gene expression in the human dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. Nat. Neurosci. 2021, 24, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.; Barkley, D.; França, G.S.; Yanai, I. Exploring tissue architecture using spatial transcriptomics. Nature 2021, 596, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Yoo, M.; Choi, J. Recent advances in spatially resolved transcriptomics: Challenges and opportunities. BMB Rep. 2022, 55, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teves, J.M.; Won, K.J. Mapping Cellular Coordinates through Advances in Spatial Transcriptomics Technology. Mol. Cells 2020, 43, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapur, A.; Marwah, K.; Alterovitz, G. Gene expression prediction using low-rank matrix completion. BMC Bioinform. 2016, 17, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panikratova, Y.R.; Vlasova, R.M.; Akhutina, T.V.; Korneev, A.A.; Sinitsyn, V.E.; Pechenkova, E.V. Functional connectivity of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex contributes to different components of executive functions. Int. J. Psychophysiol. Off. J. Int. Organ. Psychophysiol. 2020, 151, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, B.; Spangler, A.; Weber, L.M.; Hicks, S.C.; Jaffe, A.E.; Martinowich, K.; Maynard, K.R.; Collado-Torres, L. spatialLIBD: An R/Bioconductor package to visualize spatially-resolved transcriptomics data. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.C.; Kern 2022, F.; Losada, P.M.; Agam, M.R.; Maat, C.A.; Schmartz, G.P.; Fehlmann, T.; Stein, J.A.; Schaum, N.; Lee, D.P.; et al. Dysregulation of brain and choroid plexus cell types in severe COVID-19. Nature 2021, 595, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejati, V.; Majdi, R.; Salehinejad, M.A.; Nitsche, M.A. The role of dorsolateral and ventromedial prefrontal cortex in the processing of emotional dimensions. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torices, S.; Cabrera, R.; Stangis, M.; Naranjo, O.; Fattakhov, N.; Teglas, T.; Adesse, D.; Toborek, M. Expression of SARS-CoV-2-related receptors in cells of the neurovascular unit: Implications for HIV-1 infection. J. Neuroinflammation 2021, 18, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina-Enríquez, M.M.; Lopez-León, S.; Carlos-Escalante, J.A.; Aponte-Torres, Z.; Cuapio, A.; Wegman-Ostrosky, T. ACE2: The molecular doorway to SARS-CoV-2. Cell Biosci. 2020, 10, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wulandari, L.; Hamidah, B.; Pakpahan, C.; Damayanti, N.S.; Kurniati, N.D.; Adiatmaja, C.O.; Wigianita, M.R.; Soedarsono, H.D.; Tinduh, D.; Prakoeswa, C.R.S.; et al. Initial study on TMPRSS2 p.Val160Met genetic variant in COVID-19 patients. Hum. Genom. 2021, 15, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callies, L.K.; Tadeo, D.; Simper, J.; Bugge, T.H.; Szabo, R. Iterative, multiplexed CRISPR-mediated gene editing for functional analysis of complex protease gene clusters. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 15987–15996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.B.; Logue, J.; Yang, P.; Baracco, L.; Elahi, M.; Reece, E.A.; Wang, B.; Li, L.; Blanchard, T.G.; Han, Z.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 invades cognitive centers of the brain and induces Alzheimer’s-like neuropathology. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasemann, S.; Haferkamp, U.; Pfefferle, S.; Woo, M.S.; Heinrich, F.; Schweizer, M.; Appelt-Menzel, A.; Cubukova, A.; Barenberg, J.; Leu, J.; et al. The blood-brain barrier is dysregulated in COVID-19 and serves as a CNS entry route for SARS-CoV-2. Stem Cell Rep. 2022, 17, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Bag, A.K.; Singh, R.K.; Talmadge, J.E.; Batra, S.K.; Datta, K. Multifaceted Role of Neuropilins in the Immune System: Potential Targets for Immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fullard, J.F.; Lee, H.C.; Voloudakis, G.; Suo, S.; Javidfar, B.; Shao, Z.; Peter, C.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, S.; Corvelo, A.; et al. Single-nucleus transcriptome analysis of human brain immune response in patients with severe COVID-19. Genome Med. 2021, 13, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanmohammadi, S.; Rezaei, N.; Khazaei, M.; Shirkani, A. A Case of Autosomal Recessive Interferon Alpha/Beta Receptor Alpha Chain (IFNAR1) Deficiency with Severe COVID-19. J. Clin. Immunol. 2022, 42, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, M.S.; Farzan, M. The broad-spectrum antiviral functions of IFIT and IFITM proteins. Nature reviews. Immunology 2013, 13, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łacina, P.; Butrym, A.; Frontkiewicz, D.; Mazur, G.; Bogunia-Kubik, K. Soluble CD147 (BSG) as a Prognostic Marker in Multiple Myeloma. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022, 44, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, C.P.; Fernandes, D.E.; Casimiro, F.; da Mata, G.F.; Passos, M.T.; Varela, P.; Mastroianni-Kirsztajn, G.; Pesquero, J.B. Cathepsin L in COVID-19: From Pharmacological Evidences to Genetics. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 589505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, X.; Bai, X.; Yao, S.; Chang, Y.Z.; Gao, G. The emerging role of furin in neurodegenerative and neuropsychiatric diseases. Transl. Neurodegener. 2022, 11, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Yin, H.; Zhang, D.; Peng, L.; Li, K.; Cui, F.; Xia, C.; Li, Z.; Huang, H. Bibliometric Analysis of Cathepsin B Research From 2011 to 2021. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 898455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upadhyay, G. Emerging Role of Lymphocyte Antigen-6 Family of Genes in Cancer and Immune Cells. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Xu, J.; Hou, Y.; Leverenz, J.B.; Kallianpur, A.; Mehra, R.; Liu, Y.; Yu, H.; Pieper, A.A.; Jehi, L.; et al. Network medicine links SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19 infection to brain microvascular injury and neuroinflammation in dementia-like cognitive impairment. bioRxiv 2021. [CrossRef]
- McQuaid, C.; Brady, M.; Deane, R. SARS-CoV-2: Is there neuroinvasion? Fluids Barriers CNS 2021, 18, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Shi, X.; Liu, W.; Zhou, Q.; Chan Lau, M.; Chun Tatt Lim, J.; Sun, L.; Ng, C.; Yeong, J.; Liu, J. SC-MEB: Spatial clustering with hidden Markov random field using empirical Bayes. Brief. Bioinform. 2022, 23, bbab466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, D.; Song, D.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, X. Clinical and translational values of spatial transcriptomics. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cang, Z.; Ning, X.; Nie, A.; Xu, M.; Zhang, J. SCAN-IT: Domain segmentation of spatial transcriptomics images by graph neural network. BMVC: Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference. Br. Mach. Vis. Conf. 2021, 32, 406. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).