Microwave-Assisted Carbonization Processing for Carbon Dot-like Nanomaterials with Antimicrobial Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
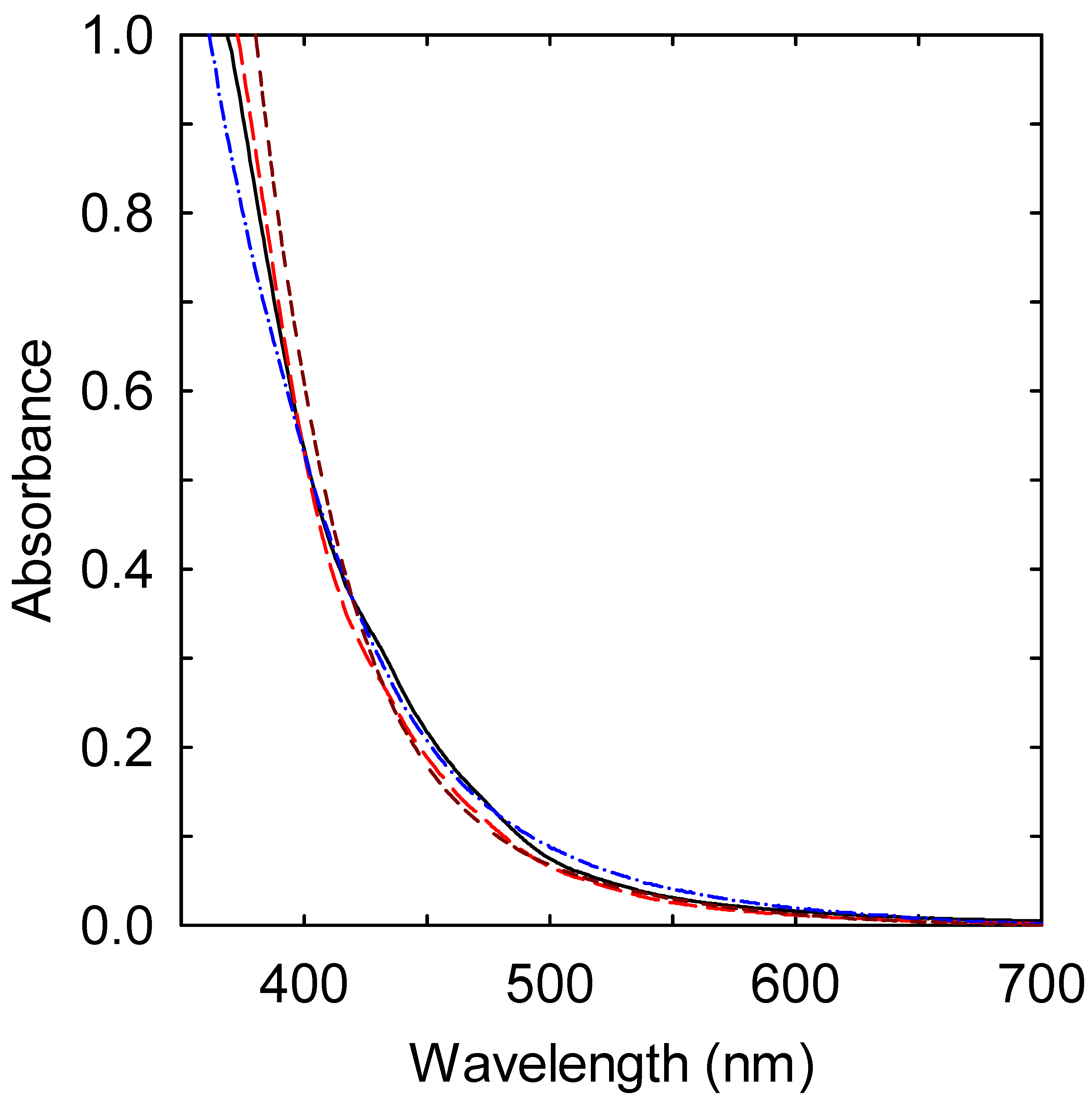
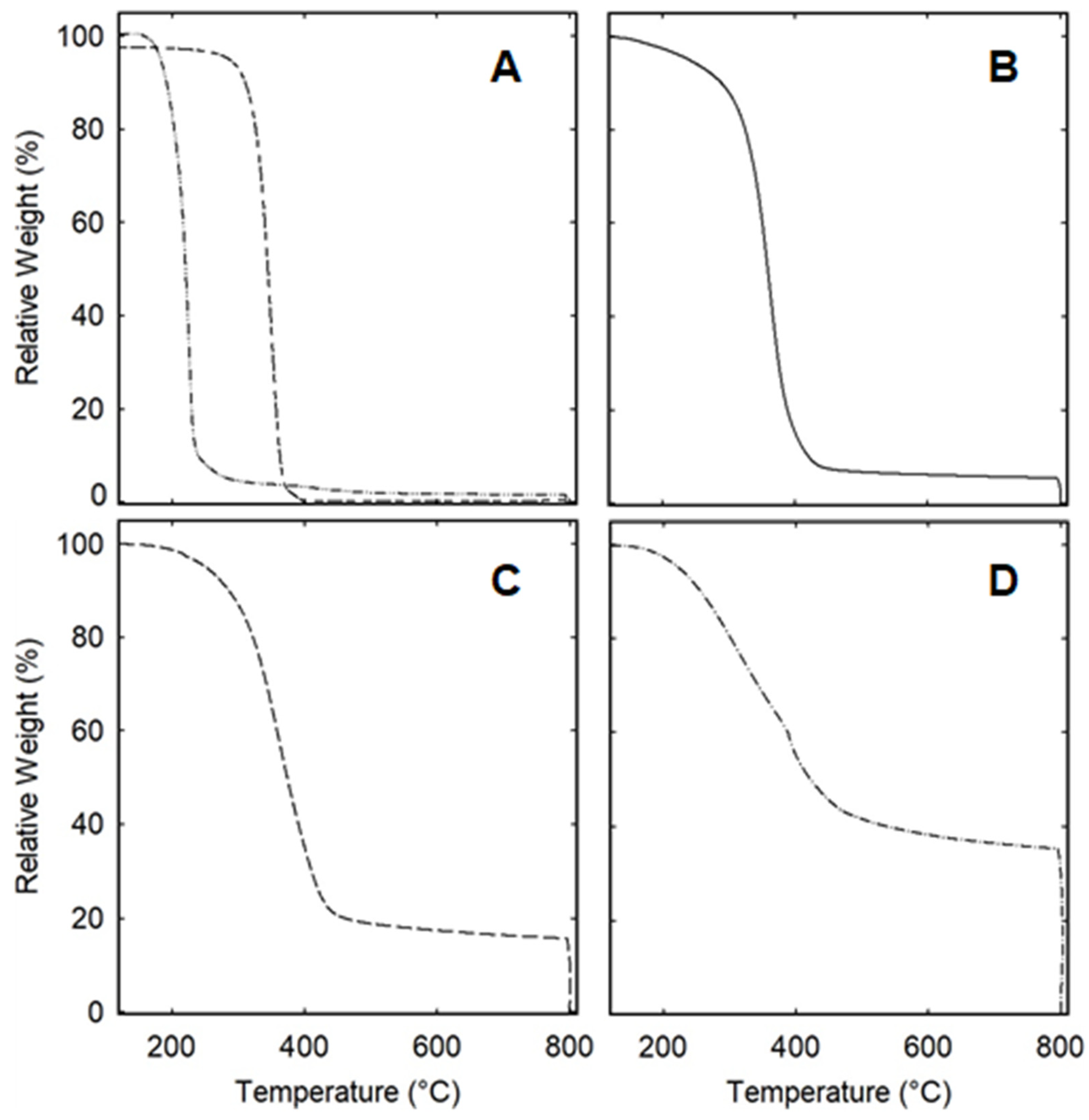
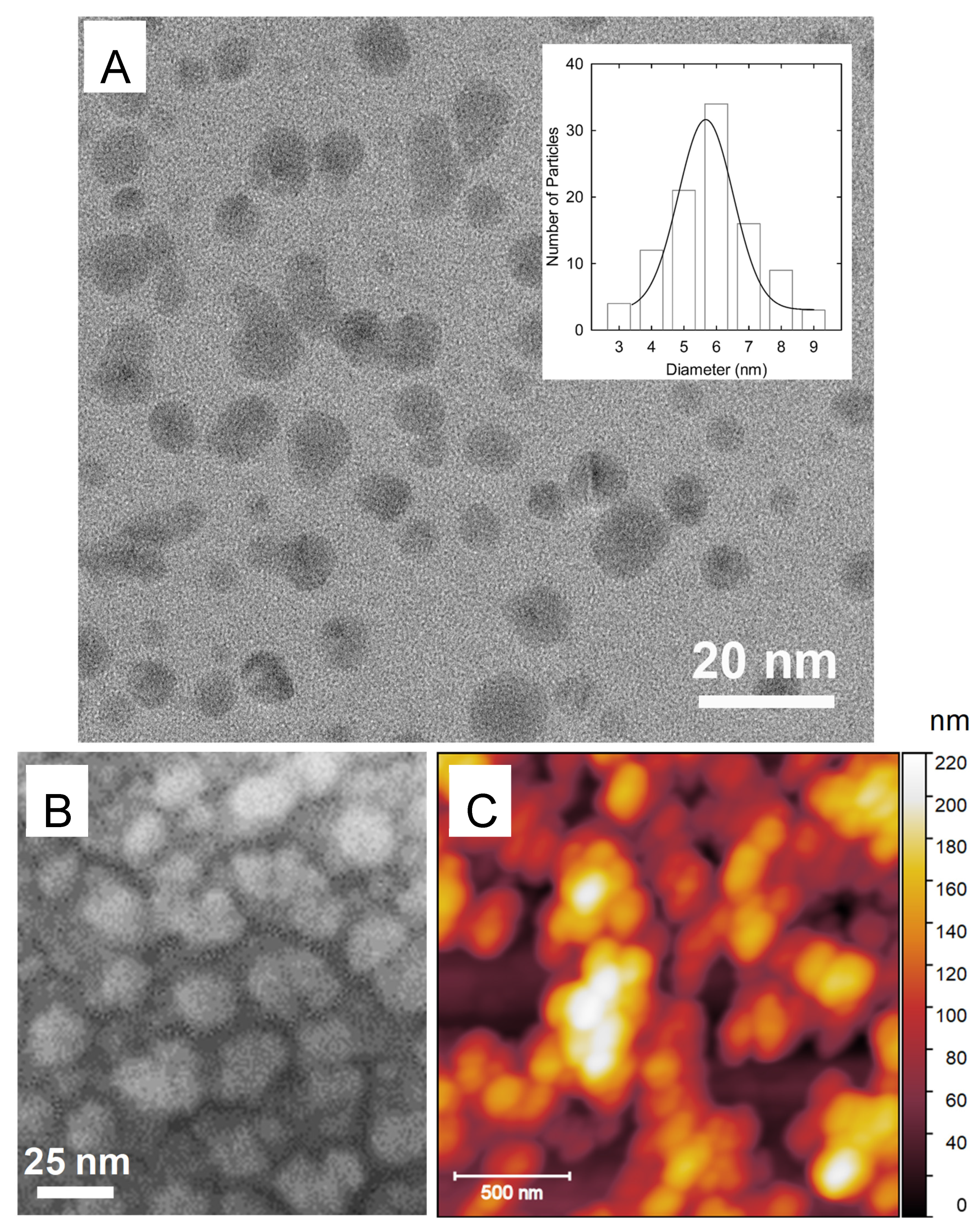
3. Results and Discussion
4. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, Y.-P.; Zhou, B.; Lin, Y.; Wang, W.; Fernando, K.A.S.; Pathak, P.; Meziani, M.J.; Harruff, B.A.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; et al. Quantum-Sized carbon dots for bright and colorful photoluminescence. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 7756–7757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.-P. Fluorescent Carbon Nanoparticles. U.S. Patent 7,829,772 B2, 9 November 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.-P. Carbon Dots—Exploring Carbon at Zero-Dimension; Springer International Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, C.; Zhu, A.; Tian, Y. Functional Surface Engineering of C-Dots for Fluorescent Biosensing and in Vivo Bioimaging. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.Y.; Shen, W.; Gao, Z. Carbon Quantum Dots and Their Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 362–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Zhu, M.; Huang, H.; Liu, Y.; Kang, Z. Advances, Challenges and Promises of Carbon Dots. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2017, 4, 1963–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Xu, N.; Fan, J.; Sun, W.; Peng, X. Carbon Dots for In Vivo Bioimaging and Theranostics. Small 2019, 15, 1805087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Z.; Lee, S.-T. Carbon Dots: Advances in Nanocarbon Applications. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 19214–19224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosso, C.; Filippini, G.; Prato, M. Carbon Dots as Nano-Organocatalysts for Synthetic Applications. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 8090–8105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, R.; Yang, B. Carbon Dots: A New Type of Carbon-Based Nanomaterial with Wide Applications. ACS. Cent. Sci. 2020, 6, 2179–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Tao, S.; Yue, D.; Zeng, Q.; Chen, W.; Yang, B. Recent Advances in Energy Conversion Applications of Carbon Dots: From Optoelectronic Devices to Electrocatalysis. Small 2020, 16, 2001295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yan, X.; Kong, D.; Jin, R.; Sun, C.; Du, D.; Lin, Y.; Lu, G. Recent Advances in Carbon Dots for Bioimaging Applications. Nanoscale Horiz. 2020, 5, 218–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhenadhayalan, N.; Lin, K.-C.; Saleh, T.A. Recent Advances in Functionalized Carbon Dots toward the Design of Efficient Materials for Sensing and Catalysis Applications. Small 2020, 16, 1905767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Xu, P.; Zhang, X.; Long, W. The Synthetic Strategies, Photoluminescence Mechanisms and Promising Applications of Carbon Dots: Current State and Future Perspective. Carbon 2022, 186, 91–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ðorđević, L.; Arcudi, F.; Cacioppo, M.; Prato, M. A Multifunctional Chemical Toolbox to Engineer Carbon Dots for Biomedical and Energy Applications. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2022, 17, 112–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, P.K.; Chandra, S.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, D.; Hasan, S.H. Carbon Quantum Dots: Synthesis, Structure, Properties, and Catalytic Applications for Organic Synthesis. Catalysts 2023, 13, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dua, S.; Kumar, P.; Pani, B.; Kaur, A.; Khanna, M.; Bhatt, G. Stability of Carbon Quantum Dots: A Critical Review. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 13845–13861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, H.H.; Bardakci, F.; Akgöl, S.; Kusat, K.; Adnan, M.; Alam, M.J.; Gupta, R.; Sahreen, S.; Chen, Y.; Gopinath, S.C.; et al. Green Carbon Dots: Synthesis, Characterization, Properties and Biomedical Applications. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, T.; Shin, G.H.; Kim, J.T. Carbon Dots: Opportunities and Challenges in Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.-B.; Liu, K.-K.; Wang, Y.; Li, F.-K.; Guo, R.; Song, S.-Y.; Shan, C.-X. Antibacterial Carbon Dots: Mechanisms, Design, and Applications. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 12, 2300324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggs, J.E.; Guo, Z.; Carroll, D.L.; Sun, Y.-P. Strong Luminescence of Solubilized Carbon Nanotubes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 5879–5880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guldi, D.M.; Holzinger, M.; Hirsch, A.; Georgakilasc, V.; Prato, M. First Comparative Emission Assay of Single-Wall Carbon Nanotubes—Solutions and Dispersions. Chem. Commun. 2003, 10, 1130–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Sheriff, K.; Singh, B.; Qian, H.; Dumra, S.; Collins, J.; Yerra, S.; Yang, L.; Sun, Y.-P. On Carbon “Replacing” the Core in Classical Core/ZnS Quantum Dots. Gen. Chem. 2024, 10, 240001. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; Chen, F.; Lagally, M.G.; Denes, F.S. New Strategy for Synthesis and Functionalization of Carbon Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2010, 26, 1991–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Pan, N.; Jin, J.; Wang, P.; LeCroy, G.E.; Liang, W.; Yang, L.; Teisl, L.R.; Tang, Y.; Sun, Y.-P. Systematic Comparison of Carbon Dots from Different Preparations—Consistent Optical Properties and Photoinduced Redox Characteristics in Visible Spectrum, and Structural and Mechanistic Implications. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 21667–21676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Kang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Lee, S.-T. Carbon Nanodots: Synthesis, Properties and Applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 24230–24253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Pang, J.; Xu, F.; Zhang, X. Simple Approach to Synthesize Amino-Functionalized Carbon Dots by Carbonization of Chitosan. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, C.; Zhu, S.; Feng, T.; Yang, M.; Yang, B. Evolution and Synthesis of Carbon Dots: From Carbon Dots to Carbonized Polymer Dots. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1901316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Medeiros, T.V.; Manioudakis, J.; Noun, F.; Macairan, J.-R.; Victoria, F.; Naccache, R. Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Carbon Dots and Their Applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 7175–7195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semeniuk, M.; Yi, Z.; Poursorkhabi, V.; Tjong, J.; Jaffer, S.; Lu, Z.-H.; Sain, M. Future Perspectives and Review on Organic Carbon Dots in Electronic Applications. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 6224–6255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, J.-C.; Tseng, I.-T.; Chien, C.-S.; Lin, S.-H.; Wang, C.-C.; Shih, C.-J. Microwave Assisted Synthesis of Negative-Charge Carbon Dots with Potential Antibacterial Activity against Multi-Drug Resistant Bacteria. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 41202–41208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Li, G.; Lei, J.; Liu, M.; Jin, Y.; Li, B. One-Step and One-Precursor Hydrothermal Synthesis of Carbon dots with Superior Antibacterial Activity. ACS Appl. Bio. Mater. 2020, 3, 7095–7102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.R.; Saha, N.; Quaid, T.; Reza, M.T. Formation of Carbon Quantum Dots via Hydrothermal Carbonization: Investigate the Effect of Precursors. Energies 2021, 14, 986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, G.; Luo, J.; Cui, T.; Zou, J.; Xu, M.; Ma, Y.; Shi, L.; Jia, J.; Ma, C.; Li, H.; et al. Microwave-Assisted One-Pot Synthesis of Carbon Dots for Highly Sensitive and Selective Detection of Selenite. Microchem. J. 2022, 179, 107440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Gu, H.; Liu, W.; Lv, C.; Du, J.; Fan, J.; Peng, X. NIR-emitting Carbon Dots for Discriminative Imaging and Photo-Inactivation of Pathogenic Bacteria. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 450, 137384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.; Tao, S.; Yang, F.; Yang, B. Aggregation and Luminescence in Carbonized Polymer Dots. Aggregate 2022, 3, e169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadh, M.J.; Al-dolaimy, F.; Alamir, H.T.A.; Kadhim, O.; Al-Abdeen, S.H.Z.; Sattar, R.; Abid, M.K.; Jetti, R.; Alawadi, A.; Alsalamy, A. Emerging Pathways in Environmentally Friendly Synthesis of Carbon-Based Quantum Dots for Exploring Antibacterial Resistance. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2024, 161, 112012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, R.; Rodrigues, J.; Neto, V.; Monteiro, T.; Gonçalves, G. Carbon Dots: A Bright Future as Anticounterfeiting Encoding Agents. Small 2024, 20, 2311526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Yang, B.; Lu, S. Advances in Shell and Core Engineering of Carbonized Polymer Dots for Enhanced Applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2024, 57, 2928–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhong, X.; Pan, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, W.; Zou, G.; Hou, H.; Ji, X. A Review of Carbon Dots in Synthesis Strategy. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2024, 498, 215468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
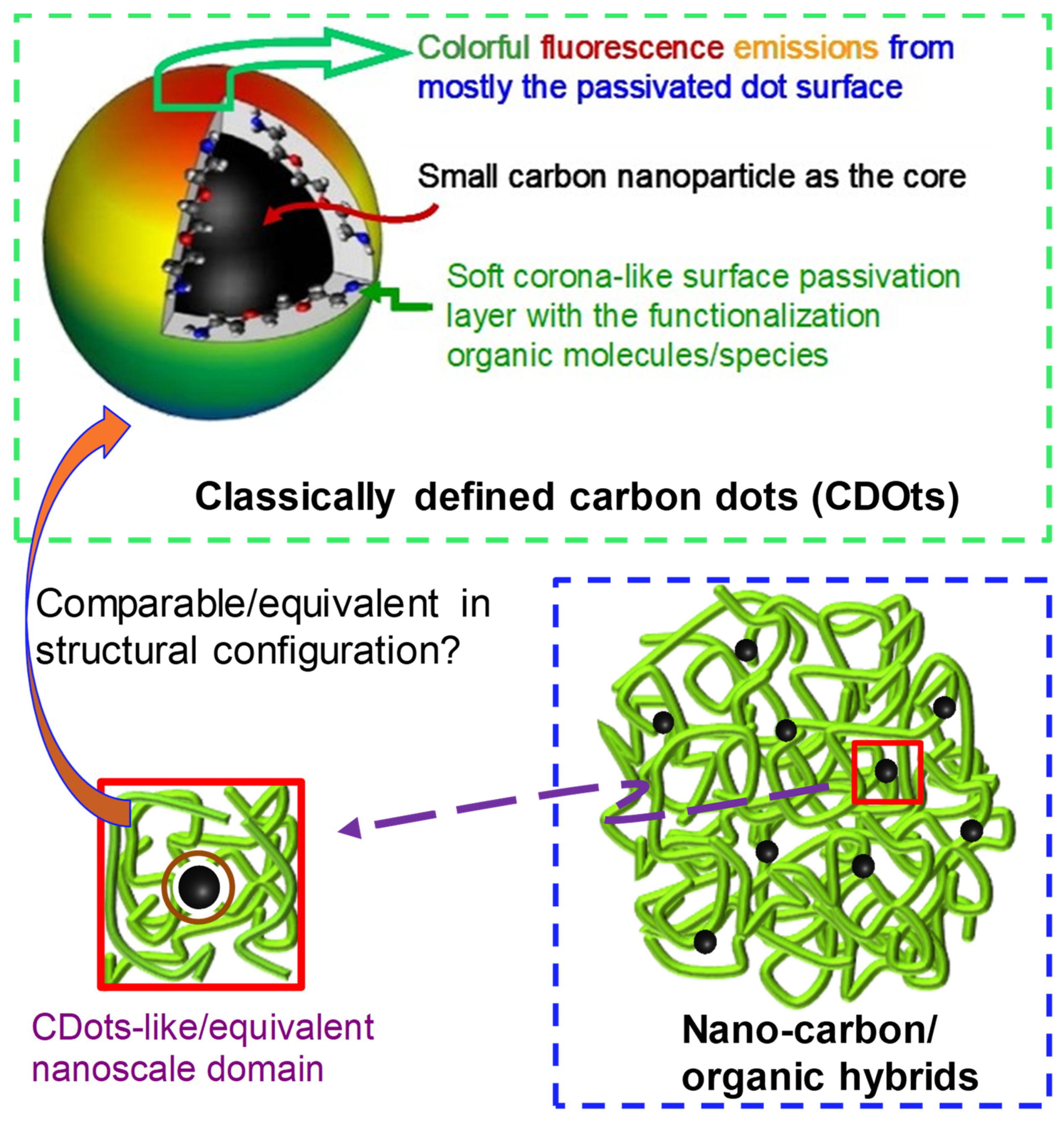
- Liang, W.; Sonkar, S.K.; Saini, D.; Sheriff, K.; Singh, B.; Yang, L.; Wang, P.; Sun, Y.-P. Carbon Dots: Classically Defined versus Organic Hybrids on Shared Properties, Divergences, and Myths. Small 2023, 19, 2206680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adcock, A.F.; Wang, P.; Cao, E.Y.; Ge, L.; Tang, Y.; Ferguson, I.S.; Abu Sweilem, F.S.; Petta, L.; Cannon, W.; Yang, L.; et al. Carbon Dots versus Nano-Carbon/Organic Hybrids—Divergence between Optical Properties and Photoinduced Antimicrobial Activities. C 2022, 8, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Sahu, S.; Cao, L.; Anilkumar, P.; Tackett, K.N., II; Qian, H.; Bunker, C.E.; Guliants, E.A.; Parenzan, A.; Sun, Y.-P. Carbon Nanoparticles as Chromophores for Photon Harvesting and Photoconversion. ChemPhysChem 2011, 12, 3604–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, J.; Zhou, J.; Yao, Z.; Jiao, Z.; Wei, B.; Tan, R.; Li, Z. Multi-Shell Hollow Porous Carbon Nanoparticles with Excellent Microwave Absorption Properties. Carbon 2021, 172, 542–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, B.L. Microwave Synthesis: Chemistry at the Speed of Light; CEM Publishing: Matthews, NC, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson, A.A.; Hutcheon, R.; Zhang, Z. Dielectric Properties of Quinoline, 4,6-Dimethyldibenzothiophene and Hexadecane as Model Compounds in the Upgrading of LCO. Fuel Process. Technol. 2011, 92, 1733–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, S.; Fu, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhao, X.; Yang, B. Investigation from Chemical Structure to Photoluminescent Mechanism: A Type of Carbon Dots from The Pyrolysis of Citric Acid and an Amine. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 5976–5984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Meziani, M.J.; Fu, Y.; Bunker, C.E.; Hou, X.; Yang, L.; Msellek, H.; Zaharias, M.; Darby, J.P.; Sun, Y.-P. Carbon Dots versus Nano-Carbon/Organic Hybrids–Dramatically Different Behaviors in Fluorescence Sensing of Metal Cations with Structural and Mechanistic Implications. Nanoscale Adv. 2021, 3, 2316–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Wang, C.F.; Liu, C.; Chen, S. Facile Access to Fabricate Carbon Dots and Perspective of Large-Scale Applications. Small 2023, 19, 2206671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Ge, L.; Abu Rabe, D.I.; Mohammed, O.O.; Wang, P.; Tang, Y.; Kathariou, S.; Yang, L.; Sun, Y.-P. Photoexcited State Properties and Antibacterial Activities of Carbon Dots Relevant to Mechanistic Features and Implications. Carbon 2020, 170, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtney, C.M.; Goodman, S.M.; McDaniel, J.A.; Madinger, N.E.; Chatterjee, A. Photoexcited Quantum Dots for Killing Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria. Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Rabe, D.I.; Mohammed, O.O.; Dong, X.; Patel, A.K.; Overton, C.M.; Tang, Y.; Kathariou, S.; Sun, Y.-P.; Yang, L. Carbon Dots for Highly Effective Photodynamic Inactivation of Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria. Mater. Adv. 2020, 1, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, C.E.; Adcock, A.F.; Singh, B.; Yerra, S.; Tang, Y.; Sun, Y.-P.; Yang, L. Divergence in Antiviral Activities of Carbon Dots versus Nano-Carbon/Organic Hybrids and Implications. C 2023, 9, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Singh, B.; Adcock, A.F.; Dumra, S.; Collins, J.; Yang, L.; Bunker, C.E.; Qian, H.; Meziani, M.J.; Sun, Y.-P. Microwave-Assisted Carbonization Processing for Carbon Dot-like Nanomaterials with Antimicrobial Properties. Micro 2025, 5, 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro5010014
Singh B, Adcock AF, Dumra S, Collins J, Yang L, Bunker CE, Qian H, Meziani MJ, Sun Y-P. Microwave-Assisted Carbonization Processing for Carbon Dot-like Nanomaterials with Antimicrobial Properties. Micro. 2025; 5(1):14. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro5010014
Chicago/Turabian StyleSingh, Buta, Audrey F. Adcock, Simran Dumra, Jordan Collins, Liju Yang, Christopher E. Bunker, Haijun Qian, Mohammed J. Meziani, and Ya-Ping Sun. 2025. "Microwave-Assisted Carbonization Processing for Carbon Dot-like Nanomaterials with Antimicrobial Properties" Micro 5, no. 1: 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro5010014
APA StyleSingh, B., Adcock, A. F., Dumra, S., Collins, J., Yang, L., Bunker, C. E., Qian, H., Meziani, M. J., & Sun, Y.-P. (2025). Microwave-Assisted Carbonization Processing for Carbon Dot-like Nanomaterials with Antimicrobial Properties. Micro, 5(1), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro5010014







