Fluorescence Sensing of Some Important Nitroaromatic Compounds by Using Polyaniline Ag Composite
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Synthesis of PANI-Ag Composites via Interfacial Polymerization
3. Results
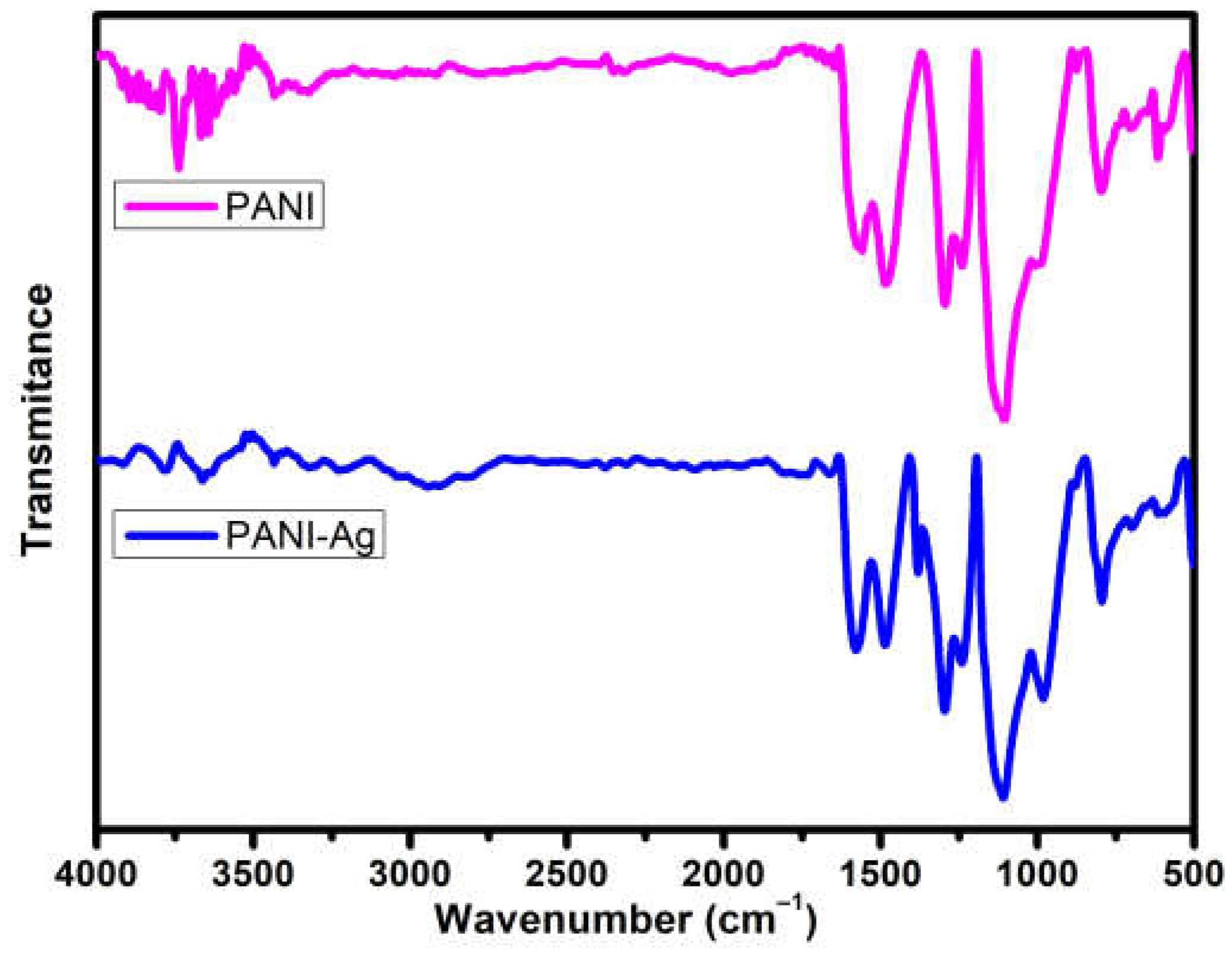
3.1. FTIR Studies
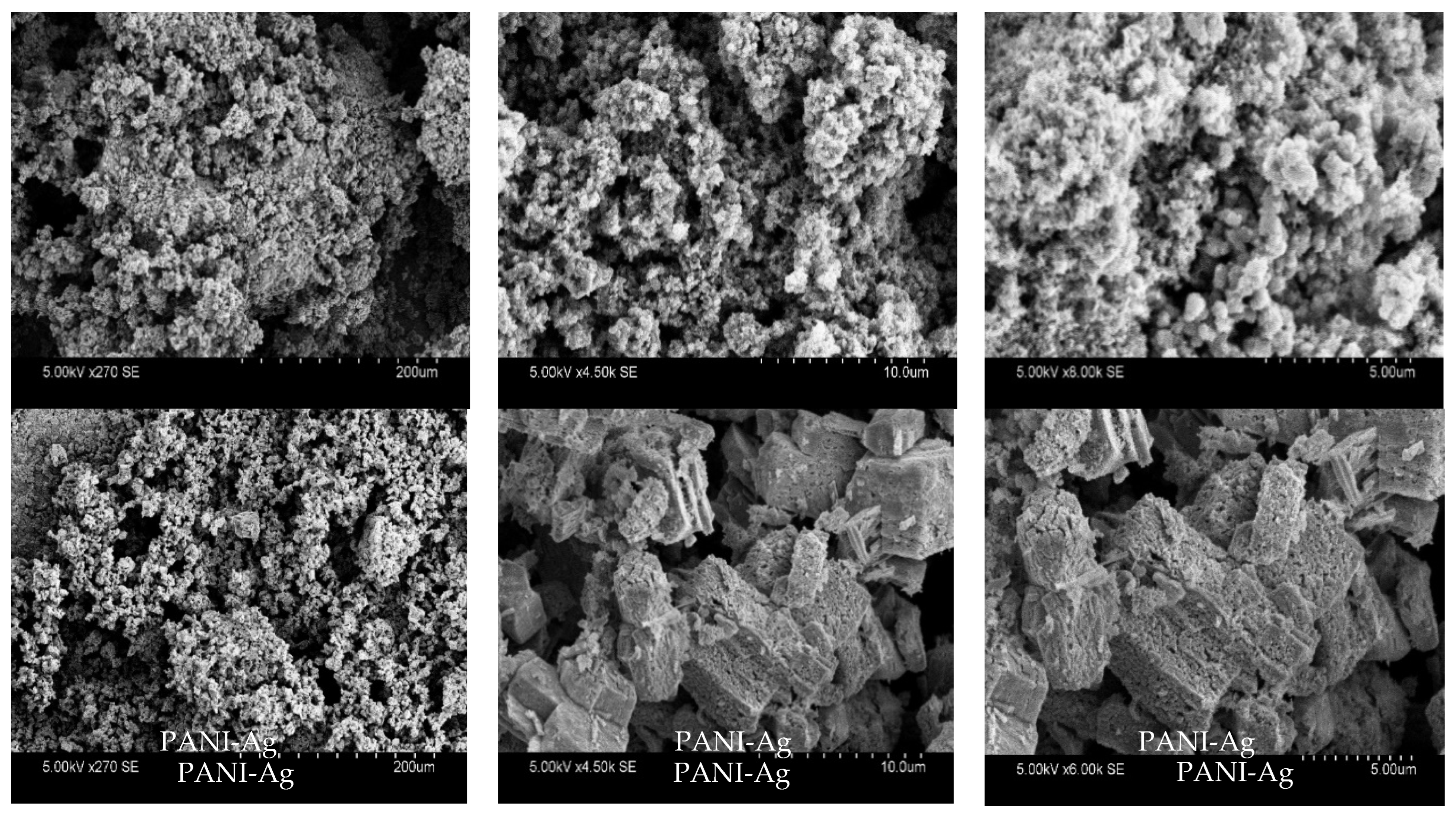
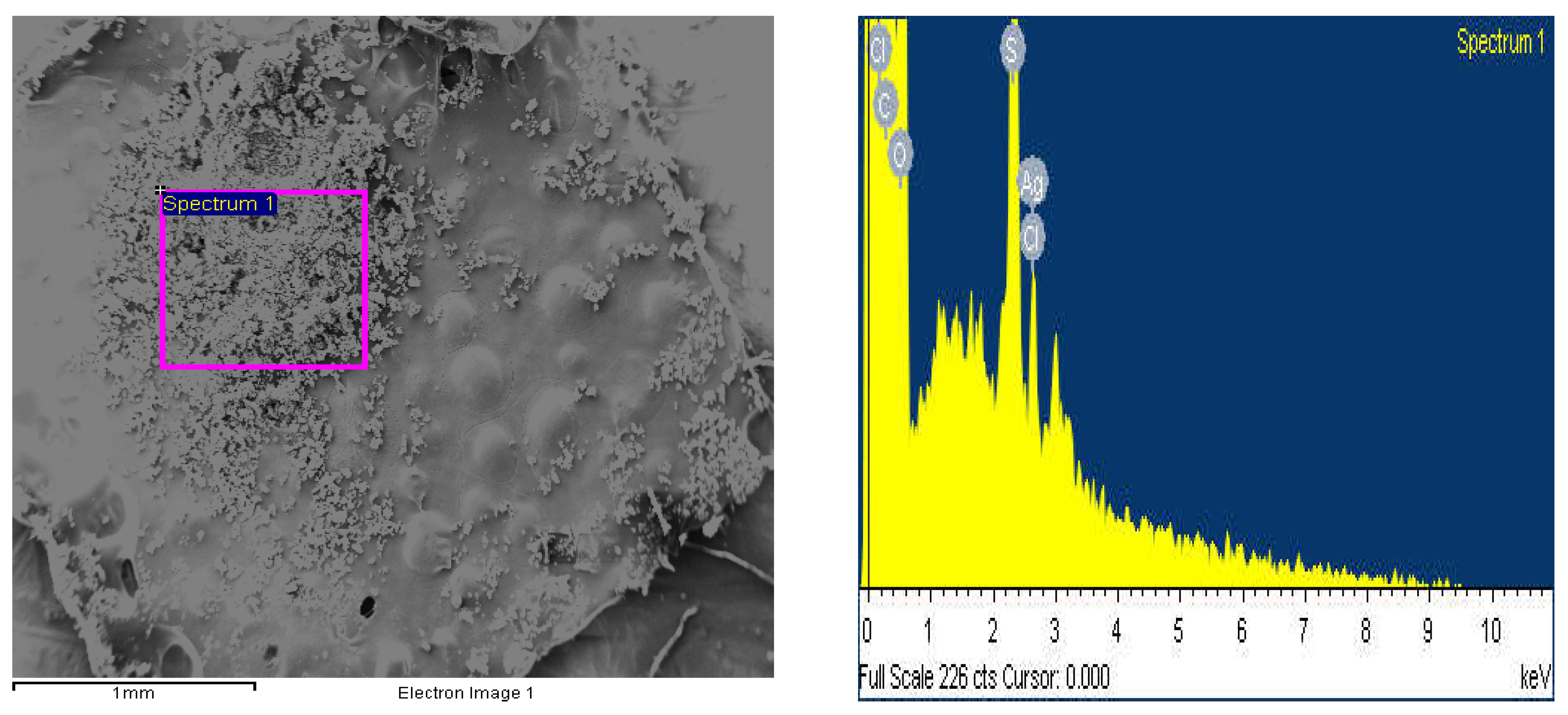
3.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM/EDAX)
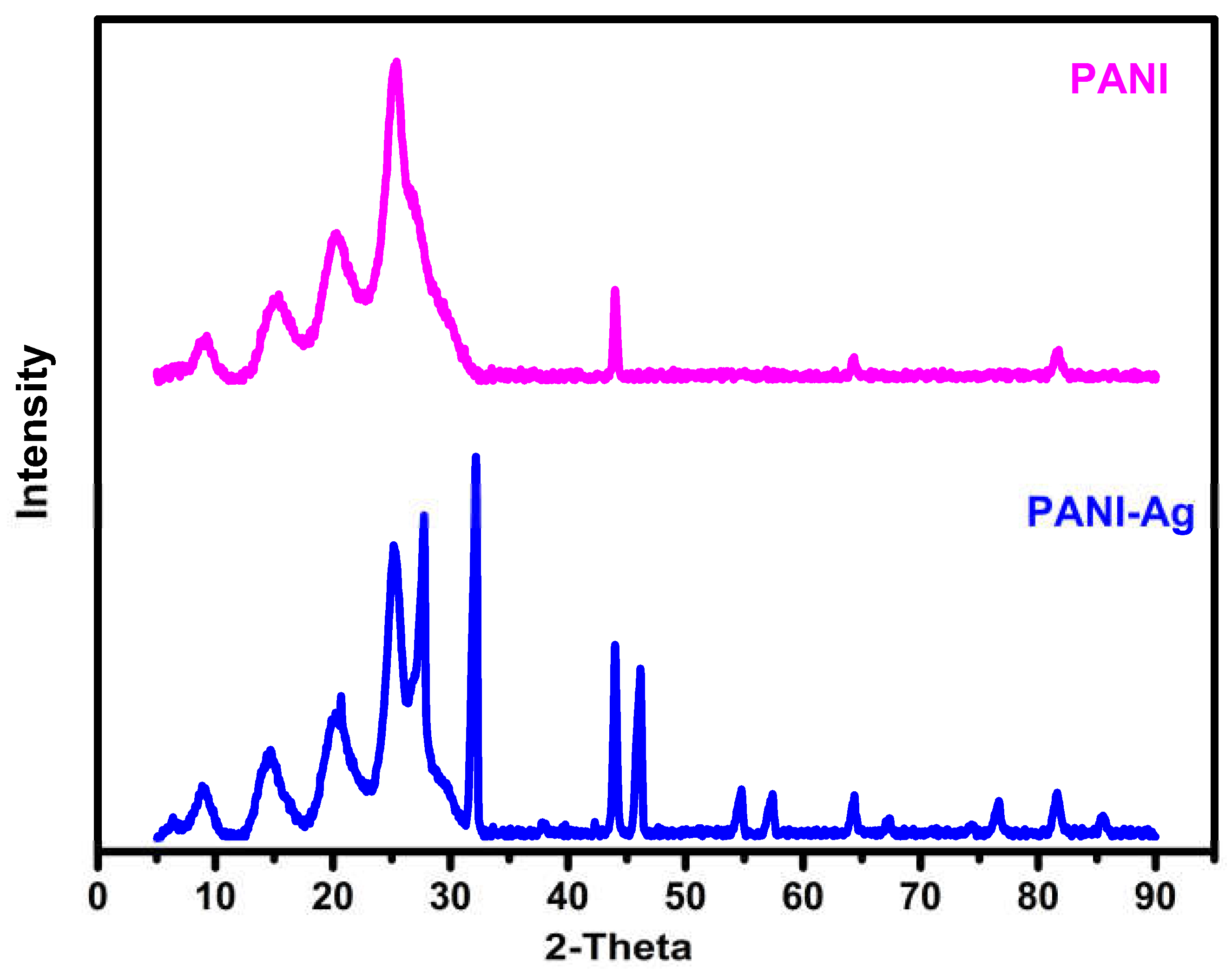
3.3. X-ray Powder Diffraction Studies
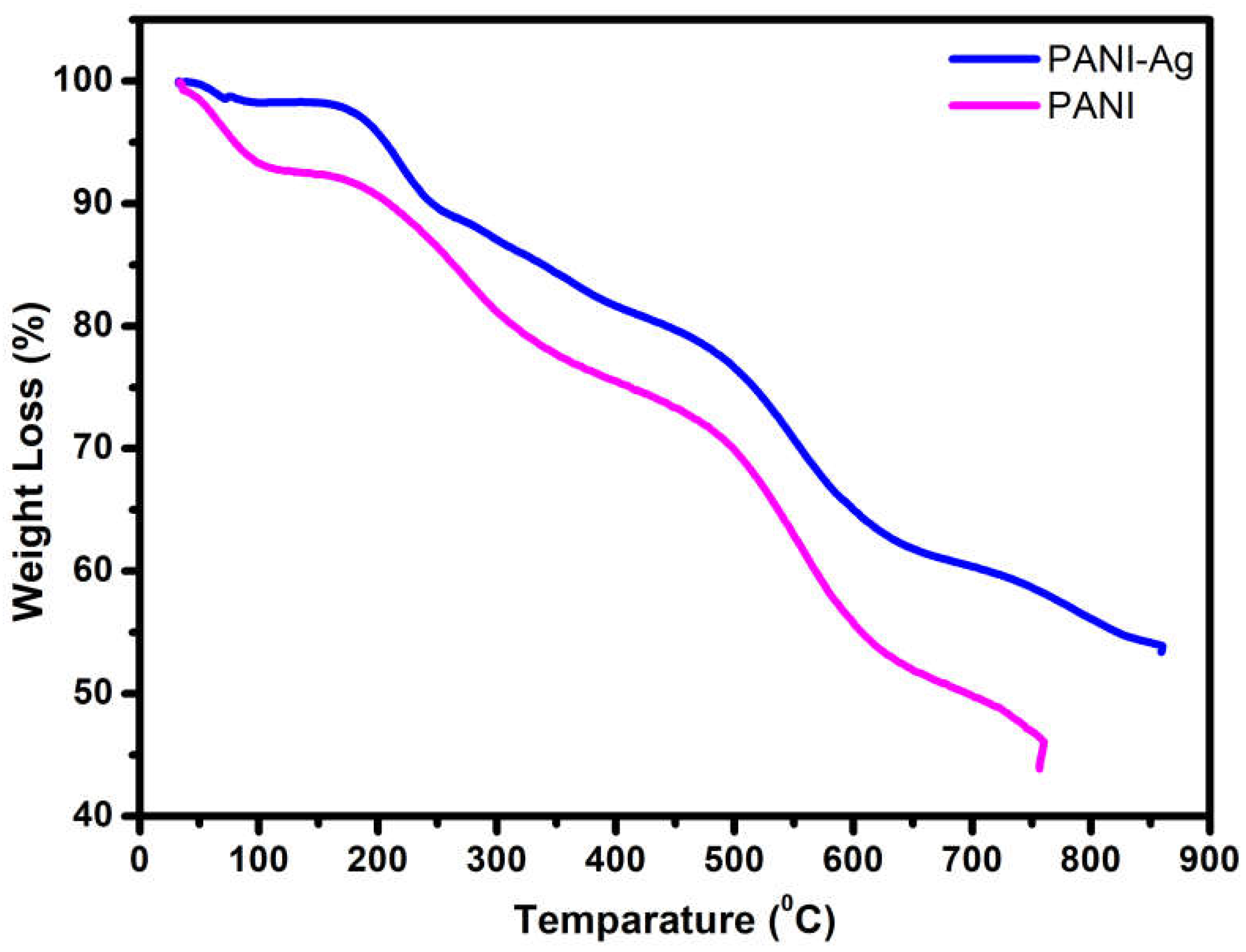
3.4. Thermal Analysis (TGA)
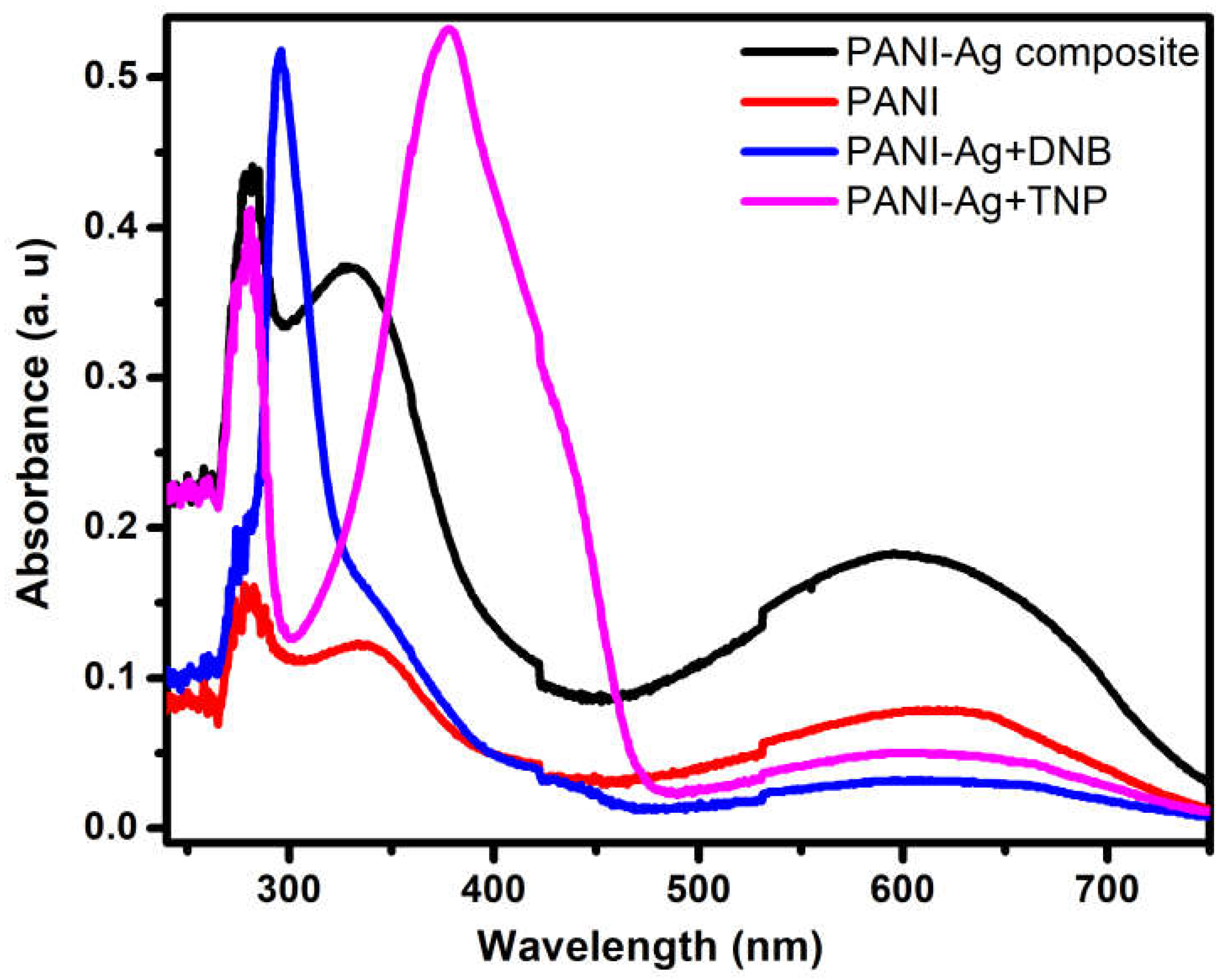
3.5. UV-vis Spectroscopy
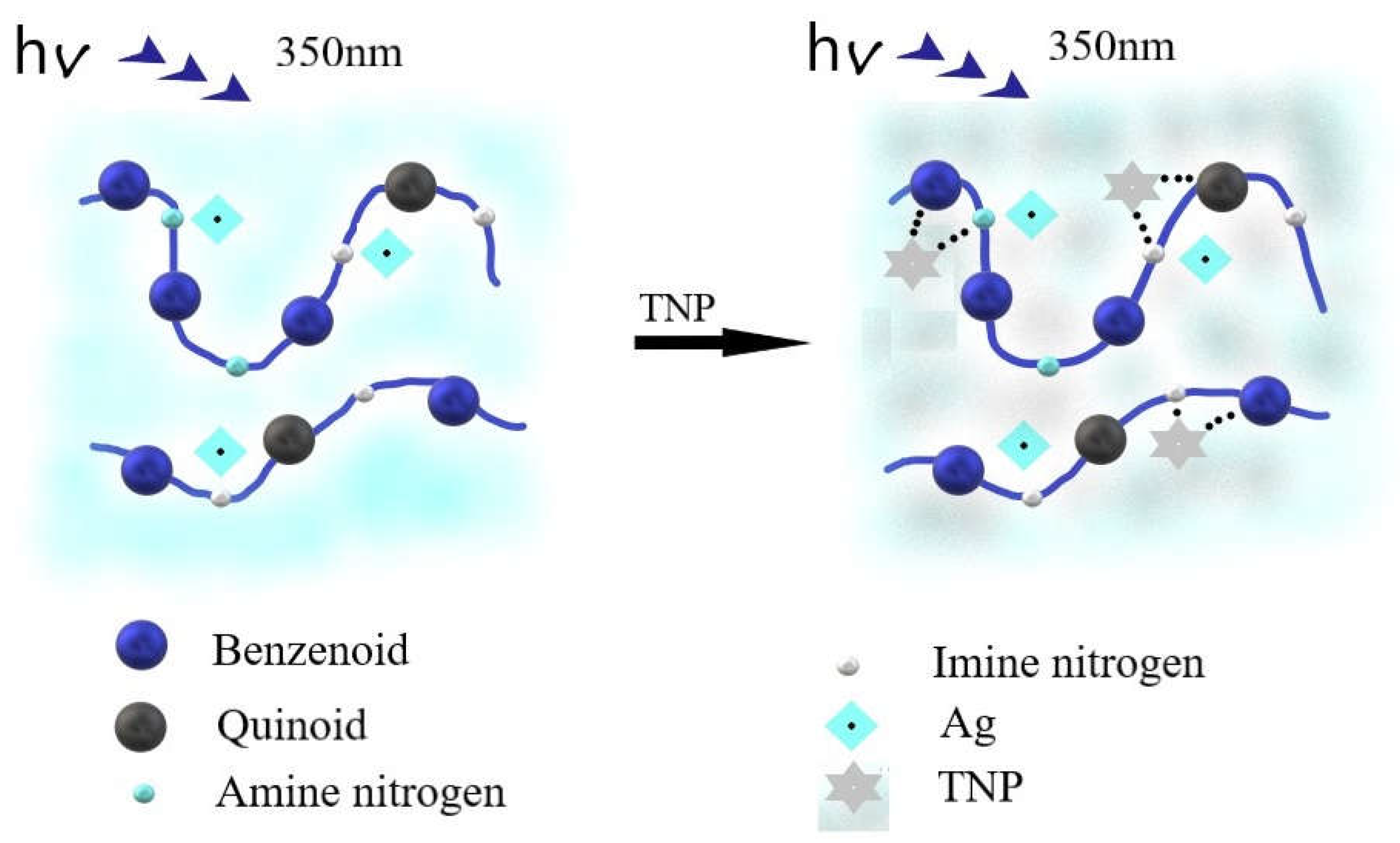
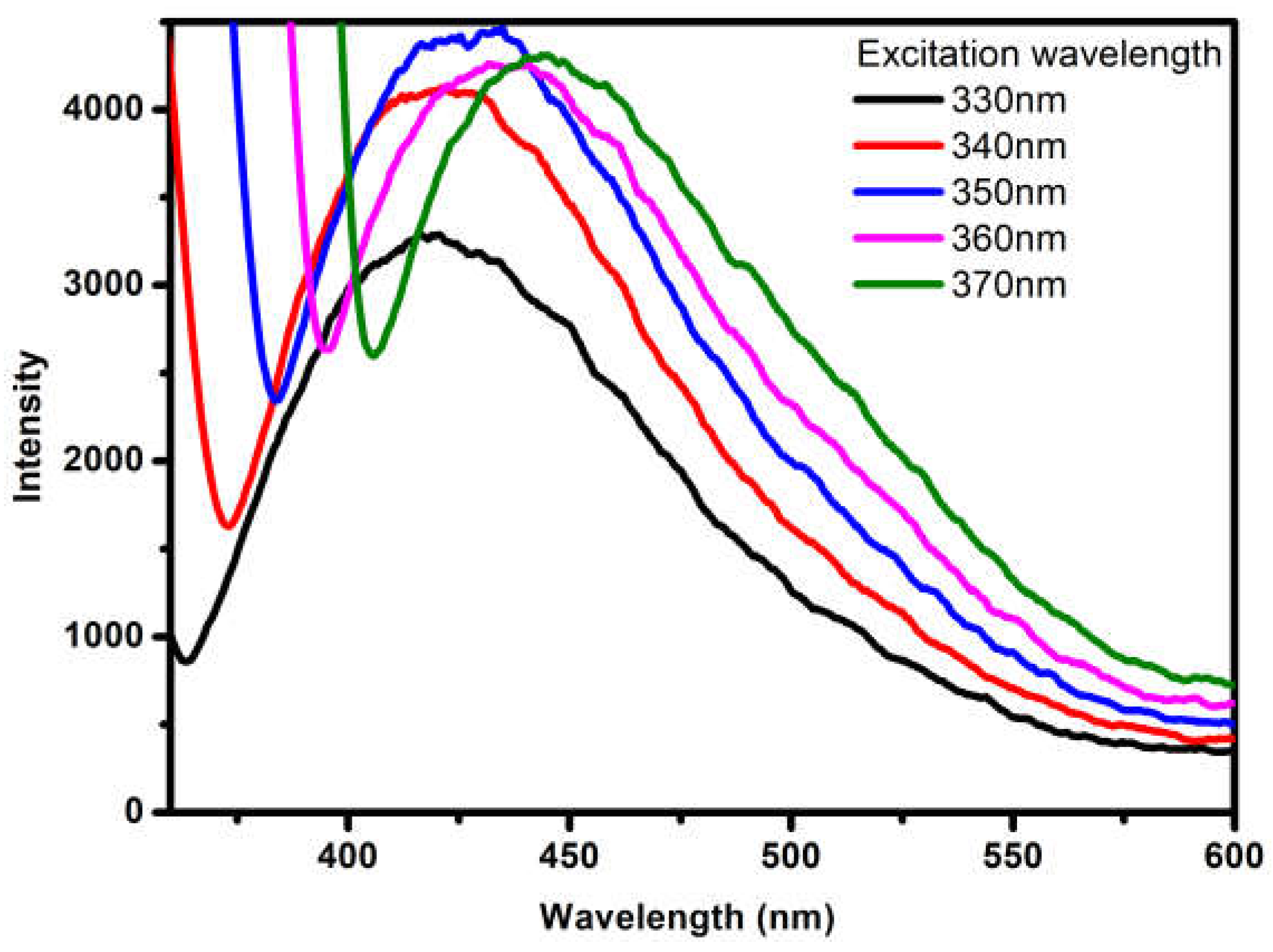
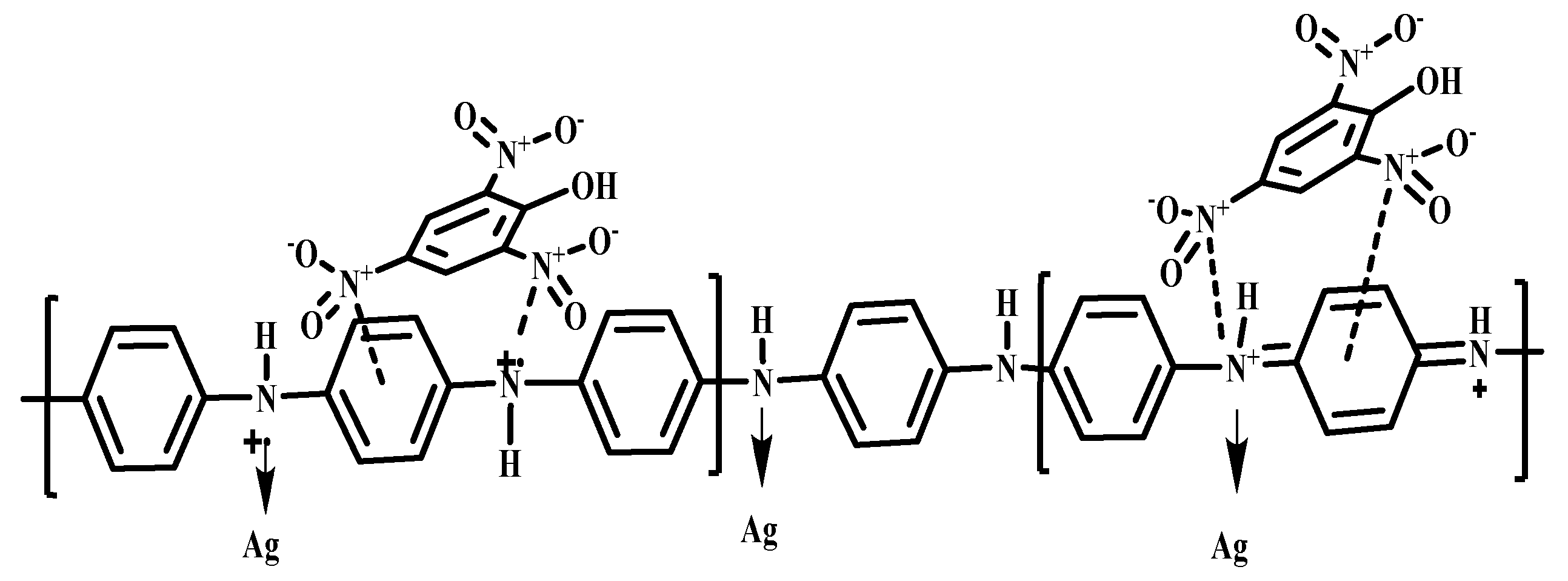
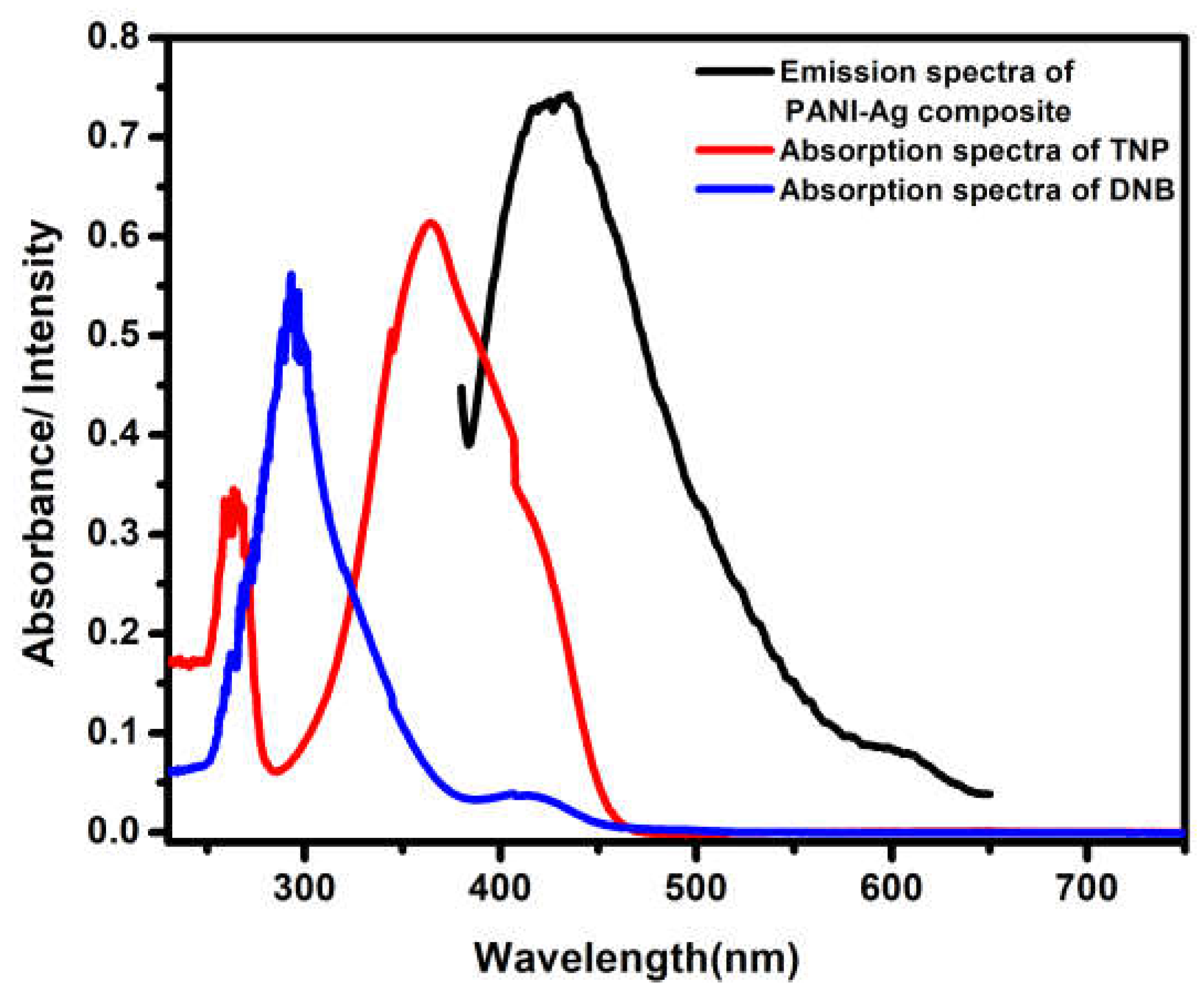
3.6. Fluorescence Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shanmugaraju, S.; Joshi, S.A.; Mukherjee, P.S. Fluorescence and visual sensing of nitroaromatic explosives using electron rich discrete fluorophores. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 9130–9138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, M.; Lin, L.; Song, X.; Zhao, T.; Zhong, Y.; Yan, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X. A Label-Free Fluorescence Sensing Approach for Selective and Sensitive Detection of 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol (TNP) in Aqueous Solution Using Graphitic Carbon Nitride Nanosheets. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 1288–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, D.S. Instrumentation for trace detection of high explosives. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2004, 75, 2499–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehnert, A.L.; Kearfott, K.J. The Detection of Explosive Materials: Review of Considerations and Methods. Nucl. Technol. 2010, 172, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.W.; Joly, G.D.; Swager, T.M. Chemical Sensors Based on Amplifying Fluorescent Conjugated Polymers. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 1339–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandya, A.; Goswami, H.; Lodha, A.; Menon, S.K. A novel nanoaggregation detection technique of TNT using selective and ultrasensitive nanocurcumin as a probe. Analyst 2012, 137, 1771–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasary, S.S.R.; Singh, A.K.; Lee, K.S.; Yu, H.; Ray, P.C. A miniaturized fiber-optic fluorescence analyzer for detection of Picric-acid explosive from commercial and environmental samples. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 255, 1646–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartha, K.K.; Sandeep, A.; Praveen, V.K.; Ajayaghosh, A. Detection of Nitroaromatic Explosives with Fluorescent Molecular Assemblies and π-Gels. Chem. Rec. 2015, 15, 252–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Praveen, V.K.; Ajayaghosh, A. The Chemistry and Applications of π-Gels. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2016, 46, 235–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, S.; Bing, Q.; Qi, H.; Liu, J.; Bai, T.; Li, G.; Shi, Z.; Feng, S.; Xu, R. Rational Design and Functionalization of a Zinc Metal–Organic Framework for Highly Selective Detection of 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 23828–23835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, S.; Shi, R.; Ji, J.; Wang, D.; Jin, S.; Han, T.; Zhou, C.; Shu, Q. A single molecular fluorescent probe for selective and sensitive detection of nitroaromatic explosives: A new strategy for the mask-free discrimination of TNT and TNP within same sample. Talanta 2017, 166, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Li, B.; Zhang, L.; Han, D.; Zhu, G. Targeted synthesis of core–shell porous aromatic frameworks for selective detection of nitro aromatic explosives via fluorescence two-dimensional response. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 19346–19352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Xia, L.; Li, D.; Wu, P.; Zou, T.; Yuan, X.; Wei, W.; Wang, J. An Ultrasensitive Picric Acid Sensor Based on a Robust 3D Hydrogen-Bonded Organic Framework. Biosensors 2022, 12, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Chen, S.; Nie, S.; Luo, J.; Lin, S.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H. Waste PET as a Reactant for Lanthanide MOF Synthesis and Application in Sensing of Picric Acid. Polymers 2019, 11, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, D.; Akkanaboina, M.; Ghosh, S.; Soma, V.R. Picosecond Bessel Beam Fabricated Pure, Gold-Coated Silver Nanostructures for Trace-Level Sensing of Multiple Explosives and Hazardous Molecules. Materials 2022, 15, 4155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabu, H.G.; Talawar, M.B.; Mukundan, T.; Asthana, S.N. Studies on the utilization of stripping voltammetry technique in the detection of high-energy materials. Combust. Explos. Shock Waves 2011, 47, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubniene, U.S.; Ratautaite, V.; Ramanavicius, A.; Bucinskas, V. Conducting Polymers for the Design of Tactile Sensors. Polymers 2022, 14, 2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koster, L.J.A.; Mihailetchi, V.D.; Blom, P.W.M. Ultimate efficiency of polymer/fullerene bulk heterojunction solar cells. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 093511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavatharani, C.; Muthusankar, E.; Wabaidur, S.M.; Alothman, Z.A.; Alsheetan, K.M.; Al-Anazy, M.M.; Ragupathy, D. Electrospinning technique for production of polyaniline nanocomposites/nanofibres for multi-functional applications: A review. Synth. Met. 2021, 271, 116609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; He, Q.; Xu, S.; Wang, L. Polyaniline-Based Photothermal Paper Sensor for Sensitive and Selective Detection of 2,4,6-Trinitrotoluene. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 5451–5456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wu, Z.; Hu, J.; Cao, Y.; Guo, J.; Long, M.; Duan, H.; Jia, D. Flexible chemiresistive sensor of polyaniline coated filter paper prepared by spraying for fast and non-contact detection of nitroaromatic explosives. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 304, 127233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.L.; Chang, C.P.; Hong, Y.S.; Sung, Y. Fabrication of MWNTs-PANI composite - a chemiresistive sensor material for the detection of explosive gases. Mater. Sci. 2009, 27, 509–520. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.; Samanta, S.; Roy, P.; Kar, P. Poly(m-aminophenol)/Silver Nanorod Composite Based Paper Strip for Chemo-Resistive Picric Acid Sensing. Sens. Lett. 2019, 17, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnikov, P.; Bobrov, A.; Marfin, Y. On the Use of Polymer-Based Composites for the Creation of Optical Sensors: A Review. Polymers 2022, 14, 4448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtar, N.A.I.M.; Zawawi, R.M.; Khairul, W.M.; Yusof, N.A. Electrochemical and optical sensors made of composites of metal–organic frameworks and carbon-based materials. A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 3099–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatappa, L.; Ture, S.A.; Yelamaggad, C.V.; Sundaram, V.N.N.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Abbaraju, V. Mechanistic Insight into the Turn-Off Sensing of Nitroaromatic Compounds Employing Functionalized Polyaniline. ChemistrySelect 2020, 5, 6321–6330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ture, S.A.; Pattathil, S.D.; Patil, V.B.; Yelamaggad, C.V.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Abbaraju, V. Synthesis and fluorescence sensing of energetic materials using benzenesulfonic acid-doped polyaniline. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2022, 33, 8551–8565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Wang, K.; Xiao, Y.; Zhai, Q.; An, D.; Huang, S.; Li, D. The amplified fluorescence quenching of heteroatomic conjugated polymers based on the “molecular wire” effects. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2003, 48, 1947–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedre, M.D.; Basavaraja, S.; Salwe, B.D.; Shivakumar, V.; Arunkumar, L.; Venkataraman, A. Preparation and characterization of Pani and Pani-Ag nanocomposites via interfacial polymerization. Polym. Compos. 2009, 30, 1668–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, M.L.; Carrillo, A.; Verdugo, A.J.; Olivas, A.; Guerrero, J.M.; De la Cruz, E.C.; Noriega Ramírez, N. Synthesis and Novel Purification Process of PANI and PANI/AgNPs Composite. Molecules 2019, 24, 1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morávková, Z.; Bober, P. Writing in a Polyaniline Film with Laser Beam and Stability of the Record: A Raman Spectroscopy Study. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2018, 2018, 1797216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.E.P.D.; Temperini, M.L.A.; Torresi, S.I.C.D. Characterization of conducting polyaniline blends by Resonance Raman Spectroscopy. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2005, 16, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trchová, M.; Stejskal, J. Polyaniline: The infrared spectroscopy of conducting polymer nanotubes (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2011, 83, 1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ture, S.A.; Patil, V.B.; Yelamaggad, C.V.; Martinez-Mañez, R.; Abbaraju, V. Understanding of Mechanistic Perspective in Sensing of Energetic Nitro Compounds through Spectroscopic and Electrochemical studies. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 50776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Duan, Y. Facile synthesis of hierarchical nanocomposites of aligned polyaniline nanorods on reduced graphene oxide nanosheets for microwave absorbing materials. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 54031–54038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y. A Sustainable Approach to Fabricating Ag Nanoparticles/PVA Hybrid Nanofiber and Its Catalytic Activity. Nanomaterials 2015, 5, 1124–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Du, Y.; Li, D.; Lv, Z.; Wang, E. One-step synthesized silver micro-dendrites used as novel separation mediums and their applications in multi-DNA analysis. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 10581–10583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowmyya, T.; Lakshmi, G.V. Soymida febrifuga aqueous root extract maneuvered silver nanoparticles as mercury nanosensor and potential microbicide. World Sci. News 2018, 114, 84–105. [Google Scholar]
- Christensen, L.; Vivekanandhan, S.; Misra, M.; Kumar Mohanty, A. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using murraya koenigii (curry leaf): An investigation on the effect of broth concentration in reduction mechanism and particle size. Adv. Mater. Lett. 2011, 2, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.M. Preparation and degradation of highly conducting polyaniline doped with picric acid. Eur. Polym. J. 2002, 38, 1151–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanik, S.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, C.; Kelly, S.; Li, J. A Systematic Study of Fluorescence-Based Detection of Nitroexplosives and Other Aromatics in the Vapor Phase by Microporous Metal–Organic Frameworks. Chem. A Eur. J. 2013, 19, 15964–15971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samworth, C.M.; Esposti, M.D.; Lenaz, G. Quenching of the intrinsic tryptophan fluorescence of mitochondrial ubiquinol—cytochrome-c reductase by the binding of ubiquinone. Eur. J. Biochem. 1988, 171, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Tan, X.; Fu, L.; Liu, Q.; Tang, W. A novel fluorescence and resonance Rayleigh scattering probe based on quantum dots for the detection of albendazole. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattathil, D.S.; Ture, A.S.; Martinez-Manez, R.; Abbaraju, V. The Role of Polyvinylpyrrolidone as a Potential Fluorophore for the Detection of Nitroaromatic Explosives. Curr. Chin. Chem. 2022, 2, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambyal, P.; Singh, A.P.; Verma, M.; Farukh, M.; Singh, B.P.; Dhawan, S.K. Tailored polyaniline/barium strontium titanate/expanded graphite multiphase composite for efficient radar absorption. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 12614–12624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hengchang, M.; Zhongwei, Z.; Yuanyuan, J.; Lajia, Z.; Chunxuan, Q.; Haiying, C.; Zengming, Y.; Zhiwang, Y.; Ziqiang, L. Triphenylamine-decorated BODIPY fluorescent probe for trace detection of picric acid. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 87157–87167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalla, V.; Gupta, A.; Kumar, M.; Rao, D.S.S.; Prasad, S.K. Self-Assembled Pentacenequinone Derivative for Trace Detection of Picric Acid. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaleeswaran, D.; Murugavel, R. Picric acid sensing and CO2 capture by a sterically encumbered azo-linked fluorescent triphenylbenzene based covalent organic polymer. J. Chem. Sci. 2018, 130, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmidevi, V.; Yelamaggad, C.V.; Venkataraman, A. Studies on Fluorescence Quenching of DBSA-PANI-Employing Nitroaromatics. ChemistrySelect 2018, 3, 2655–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Gao, B.; Guo, X.; Dong, W. Polyfluorene based fluorescent sensor for sensitive and selective detection of picric acid. Mater. Lett. 2022, 306, 130860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Mitra, K.; Singh, S.; Senapati, S.; Patel, V.K.; Vishwakarma, S.; Kumari, A.; Singh, J.; Sen Gupta, S.K.; Misra, N.; et al. Highly selective fluorescence ‘turn off’ sensing of picric acid and efficient cell labelling by water-soluble luminescent anthracene-bridged poly(N-vinyl pyrrolidone). Analyst 2019, 144, 3620–3634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, R.; Ali, A.; Ahmad, M.; Alsalme, A.; Khan, R.A.; Ali, F. Phenanthroimidazole derivatives as a chemosensor for picric acid: A first realistic approach. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 20092–20100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvathy, P.A.; Dheepika, R.; Abhijnakrishna, R.; Imran, P.K.M.; Nagarajan, S. Fluorescence quenching of triarylamine functionalized phenanthroline-based probe for detection of picric acid. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2020, 401, 112780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, D.; Basak, M.; Deka, D.; Das, G. Fabrication and photophysical assessment of quinoxaline based chemosensor: Selective determination of picric acid in hydrogel and aqueous medium. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 363, 119816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiwat, T.; Sornkaew, N.; Srikittiwanna, K.; Sukwattanasinitt, M.; Niamnont, N. Electrospun nanofiber sheets mixed with a novel triphenylamine-pyrenyl salicylic acid fluorophore for the selective detection of picric acid. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2023, 434, 114258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Nath, P.; Kumar, V.; Kumar Tailor, N.; Satapathi, S. 3D printed optical sensor for highly sensitive detection of picric acid using perovskite nanocrystals and mechanism of photo-electron transfer. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2023, 286, 121956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, D.; Das, P.; Kundu, S.; Mandal, B. Engineering of graphene quantum dots by varying the properties of graphene oxide for fluorescence detection of picric acid. Chemosphere 2022, 300, 134432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Chu, H.; Chen, J.; Gao, L.; Zong, W.; Han, S.; Li, J. Dual-emission ratiometric fluorescence probe based on copper nanoclusters for the detection of rutin and picric acid. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 270, 120829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Zhang, T.; Zeng, W.; He, S.; Liu, X.; Tian, H.; Shi, J.; Cao, T. A Fluorescence Sensing Determination of 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol Based on Cationic Water-Soluble Pillar[6]arene Graphene Nanocomposite. Sensors 2019, 19, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| PANI | PANI-Ag | Assignments |
|---|---|---|
| 1558 | 1577 | N=Q=N Quinoid (Q) ring stretching |
| 1479 | 1485 | N-B-N Benzenoid (B) ring stretching |
| 1381 | C–N stretching in QBQ units | |
| 1294 | 1296 | (C–N) stretching of secondary aromatic amine |
| 1238 | 1240 | (C–N) stretching of primary aromatic amine |
| 1105 | 1109 | Q=NH+–B or B–NH+•–B |
| 1008 | 981 | HNO3/NO3– group on aromatic ring gamma (C–H) (1,4-disubstituted ring)/Q ring Deformation |
| 875 | 879 | HNO3, NO3– |
| 794 | 794 | c(C–H) (monosubstituted or 1,2-disubstituted ring) |
| 702 | 702 | Out-of-plane ring bending (monosubstituted ring) |
| 615 | 594 | HNO3 |
| Sample | 2θ | (h k l) Values | Sample | 2θ | (h k l) Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PANI | 9.2 15.4 20.3 25.4 43.9 64.3 | // (0 1 1) (0 2 0) (2 0 0) // // | PANI-Ag composite | 8.9 14.7 20.7 25.1 27.7 32.1 44 46.1 54.7 57.4 64.3 67 76 | // (0 1 1) (0 2 0) (2 0 0) (2 1 0) (1 1 1) (2 0 0) (2 3 1) (1 4 2) (2 4 1) // (2 2 0) (3 1 1) |
| Sl. No (Paper) | Fluorescent Probe | LOD |
|---|---|---|
| 50 | Poly fluorene derivatives | 0.27 ppm |
| 51 | Anthracene-bridged poly (N-vinylpyrrolidone) | 6 × 10−6 M |
| 52 | Phenanthroimidazole derivatives | 0.64, 0.53 and 1.05 ppm |
| 53 | Triarylamine-functionalized phenanthroline | micromolar level |
| 54 | Quinoxaline-amine-based probe | 5.21 ppm |
| 55 | Triphenylamine-pyrenyl salicylic acid | 0.57 × 10−6 M |
| 56 | P-xylylene-diamine-capped CH3NH3PbBr3 perovskite | 0.3 × 10−6 M |
| 57 | Graphene oxide (GO) on the synthesis of graphene quantum dots (GQD) | 1.2 × 10−6 M |
| 58 | Polyvinylpyrrolidone-templated copper nanoclusters | 0.84 × 10−6 M and 0.27 × 10−6 M |
| 26 | CSA-PANI | 6.14 × 10−7 M |
| 49 | DBSA-PANI | 1 × 10−6 M |
| Present work | PANI-Ag composite | 5.58 × 10−7 M (0.127 ppm) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ture, S.A.; Pattathil, S.D.; Zing, B.Z.; Abbaraju, V. Fluorescence Sensing of Some Important Nitroaromatic Compounds by Using Polyaniline Ag Composite. Micro 2023, 3, 224-238. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro3010016
Ture SA, Pattathil SD, Zing BZ, Abbaraju V. Fluorescence Sensing of Some Important Nitroaromatic Compounds by Using Polyaniline Ag Composite. Micro. 2023; 3(1):224-238. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro3010016
Chicago/Turabian StyleTure, Satish Ashok, Shruthy D. Pattathil, Bertrand Zing Zing, and Venkataraman Abbaraju. 2023. "Fluorescence Sensing of Some Important Nitroaromatic Compounds by Using Polyaniline Ag Composite" Micro 3, no. 1: 224-238. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro3010016
APA StyleTure, S. A., Pattathil, S. D., Zing, B. Z., & Abbaraju, V. (2023). Fluorescence Sensing of Some Important Nitroaromatic Compounds by Using Polyaniline Ag Composite. Micro, 3(1), 224-238. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro3010016








