Nano-Sized Polyelectrolyte Complexes Formed between Poly(vinyl benzyl trimethyl ammonium chloride) and Insulin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis and Preparation of PVBTMAC Homo-Polymer
2.3. Preparation of PVBTMAC/INS Complexes
2.4. FBS Interaction with PVBTMAC Homo-Polymer and PVBTMAC/INS Complexes
2.5. Methods
3. Results and Discussion
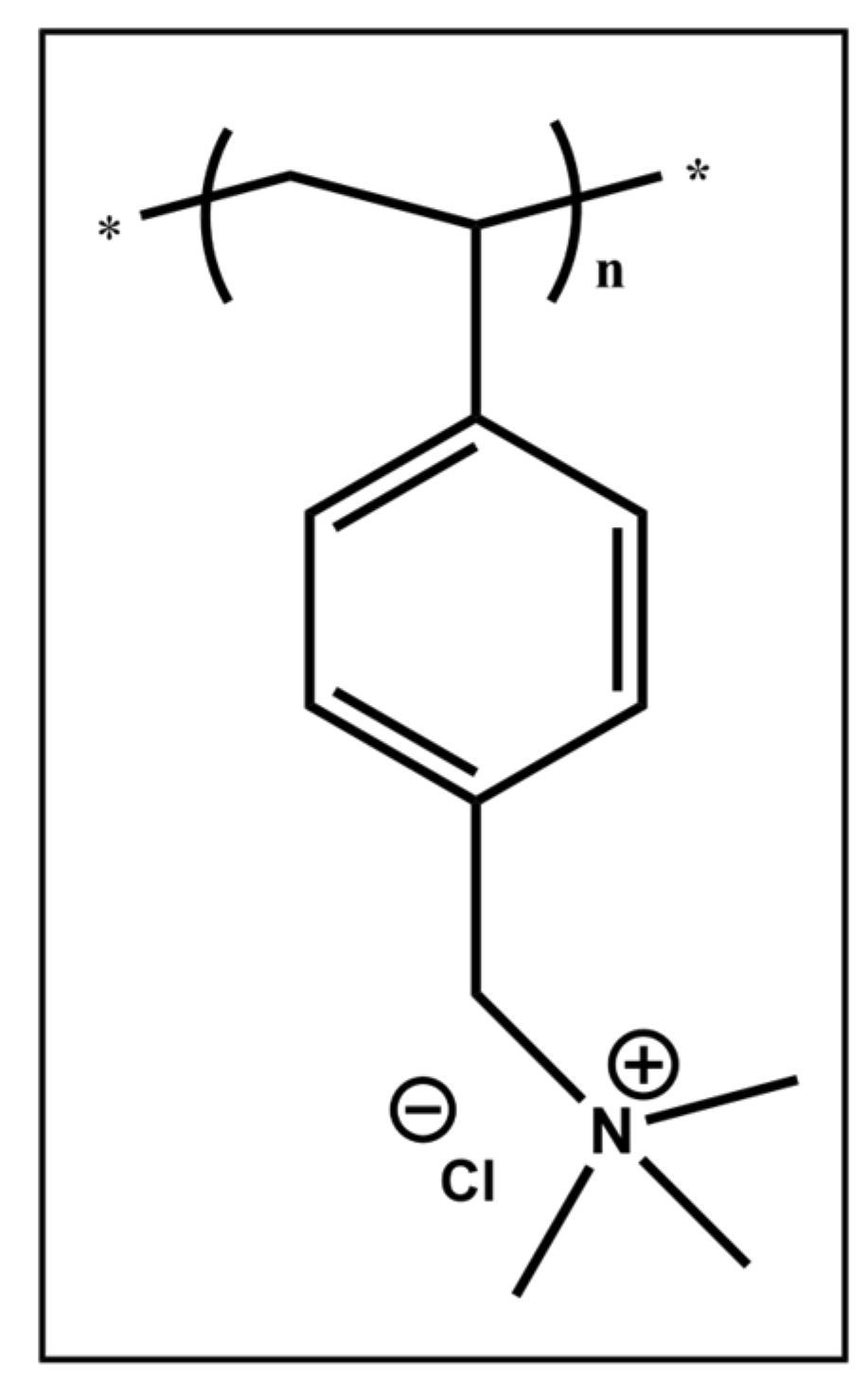
3.1. Synthesis of PVBTMAC Homo-Polymer
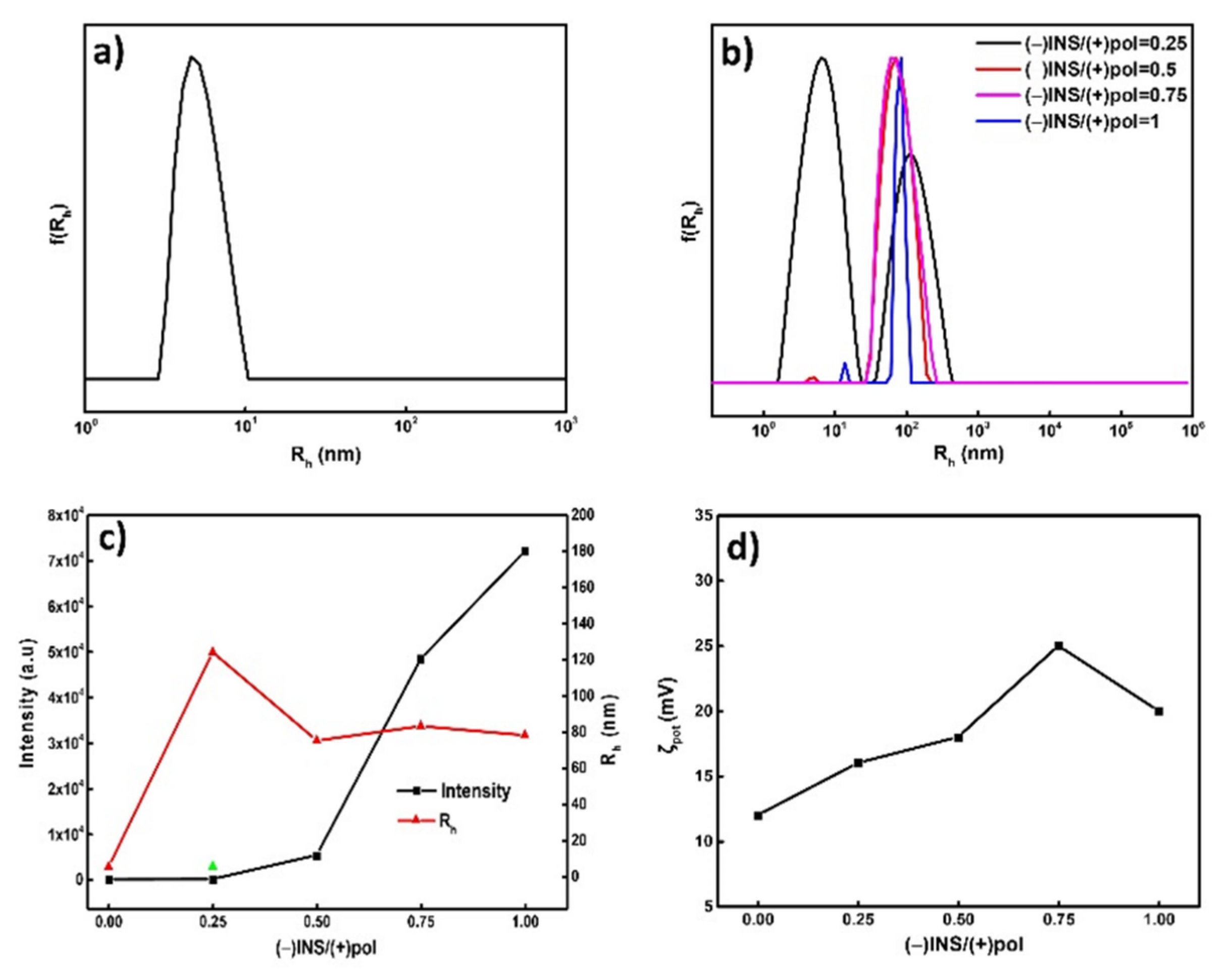
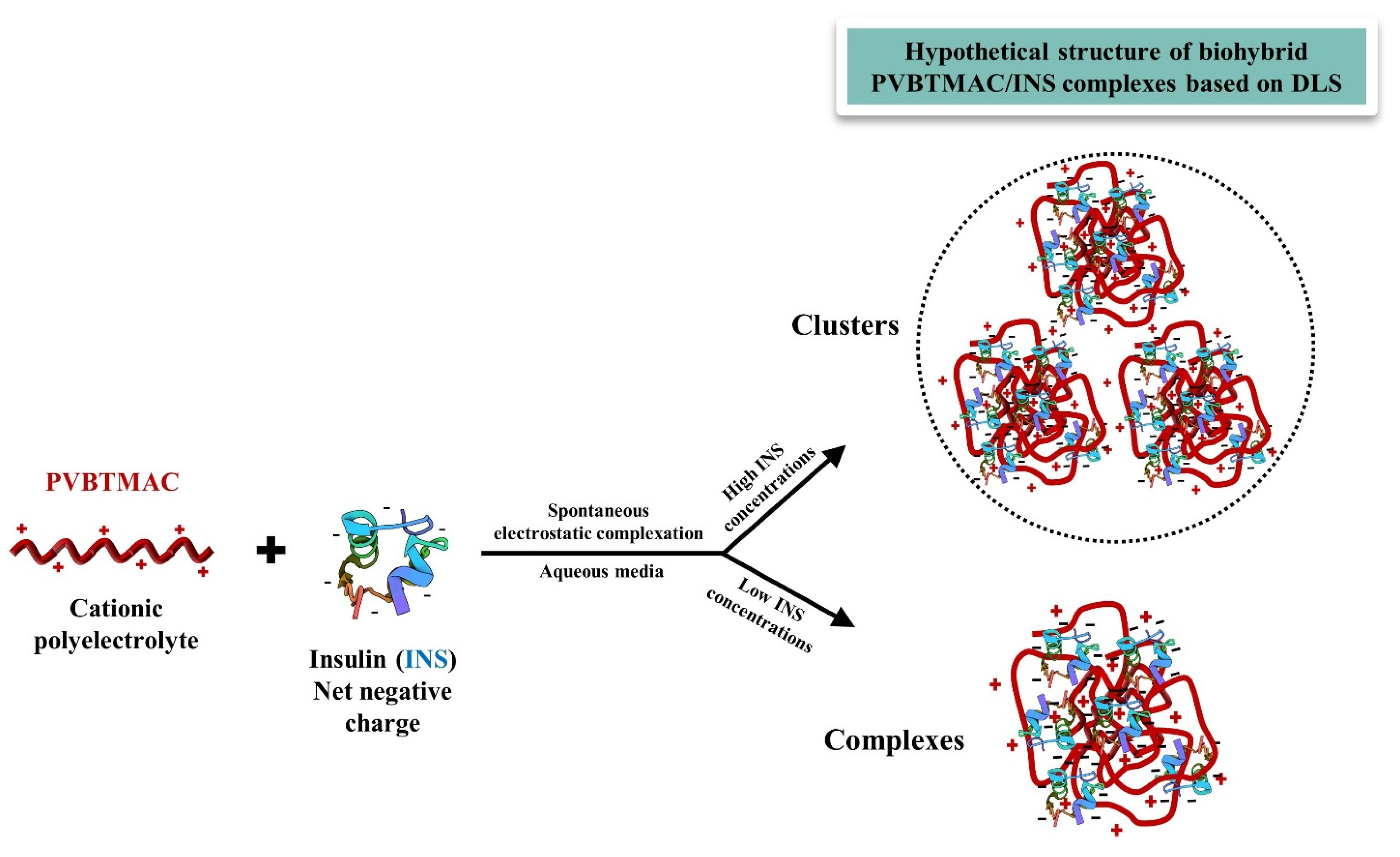
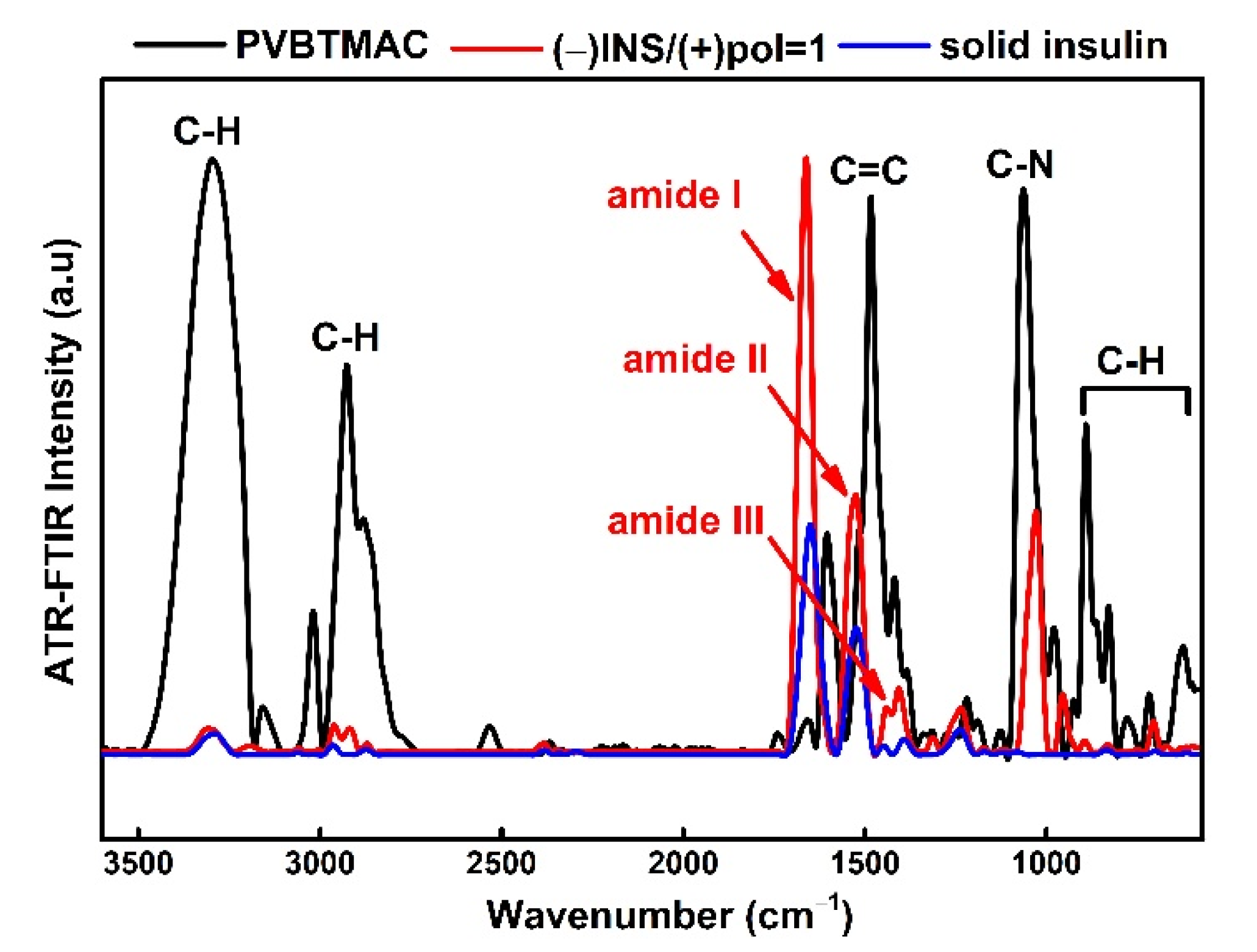
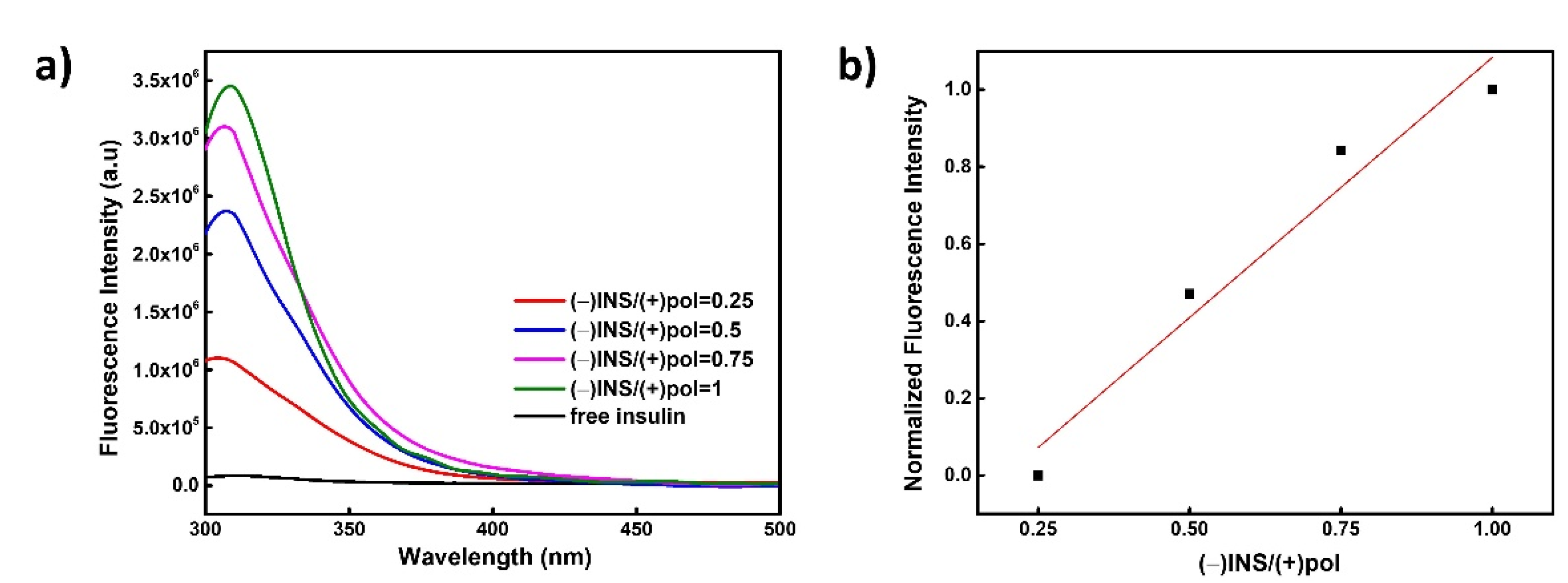
3.2. Physicochemical Characterization of PVBTMAC Homo-Polymer and PVBTMAC/INS Complexes
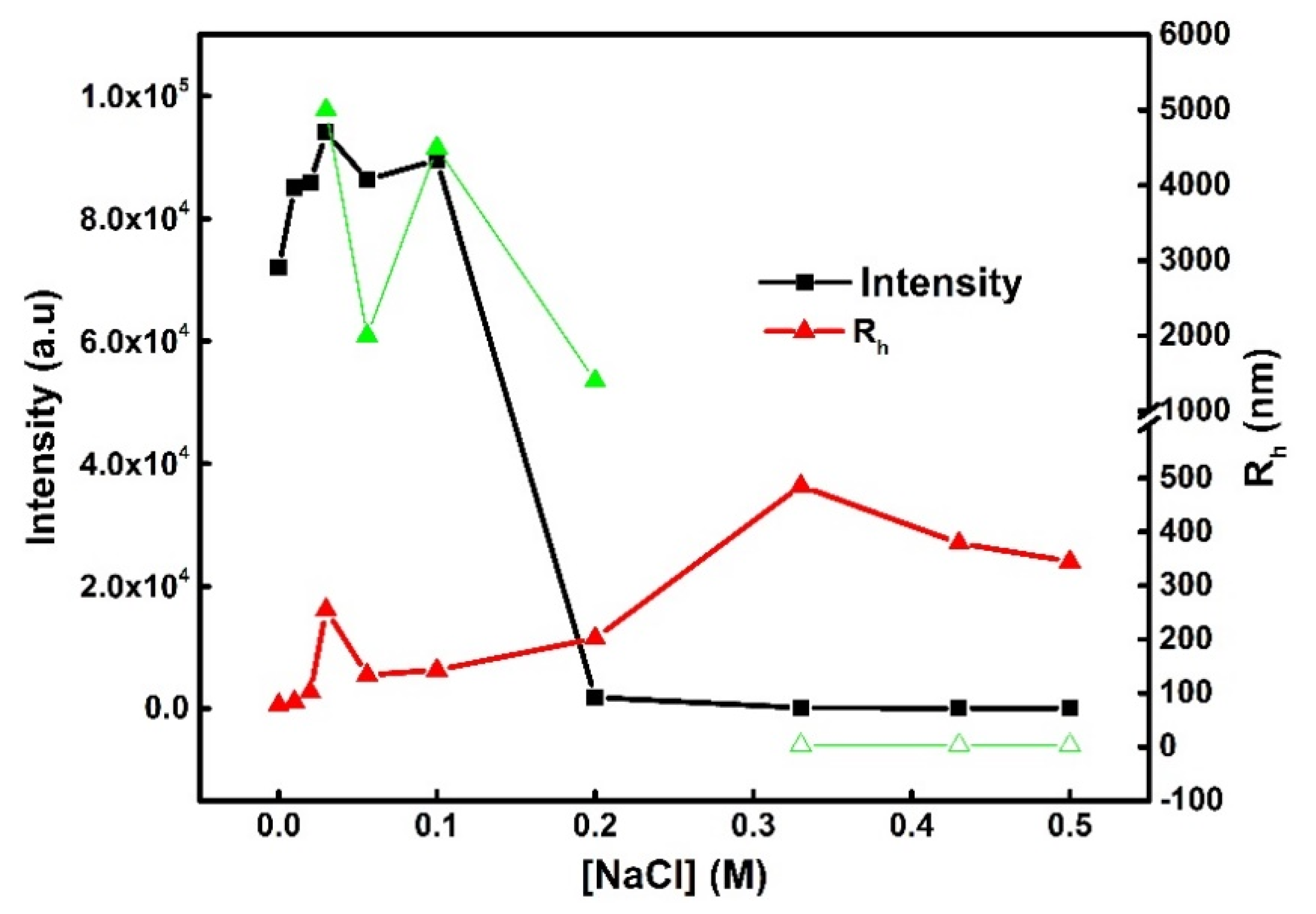
3.3. Behavior of PVBTMAC/INS Complexes in the Presence of Salt
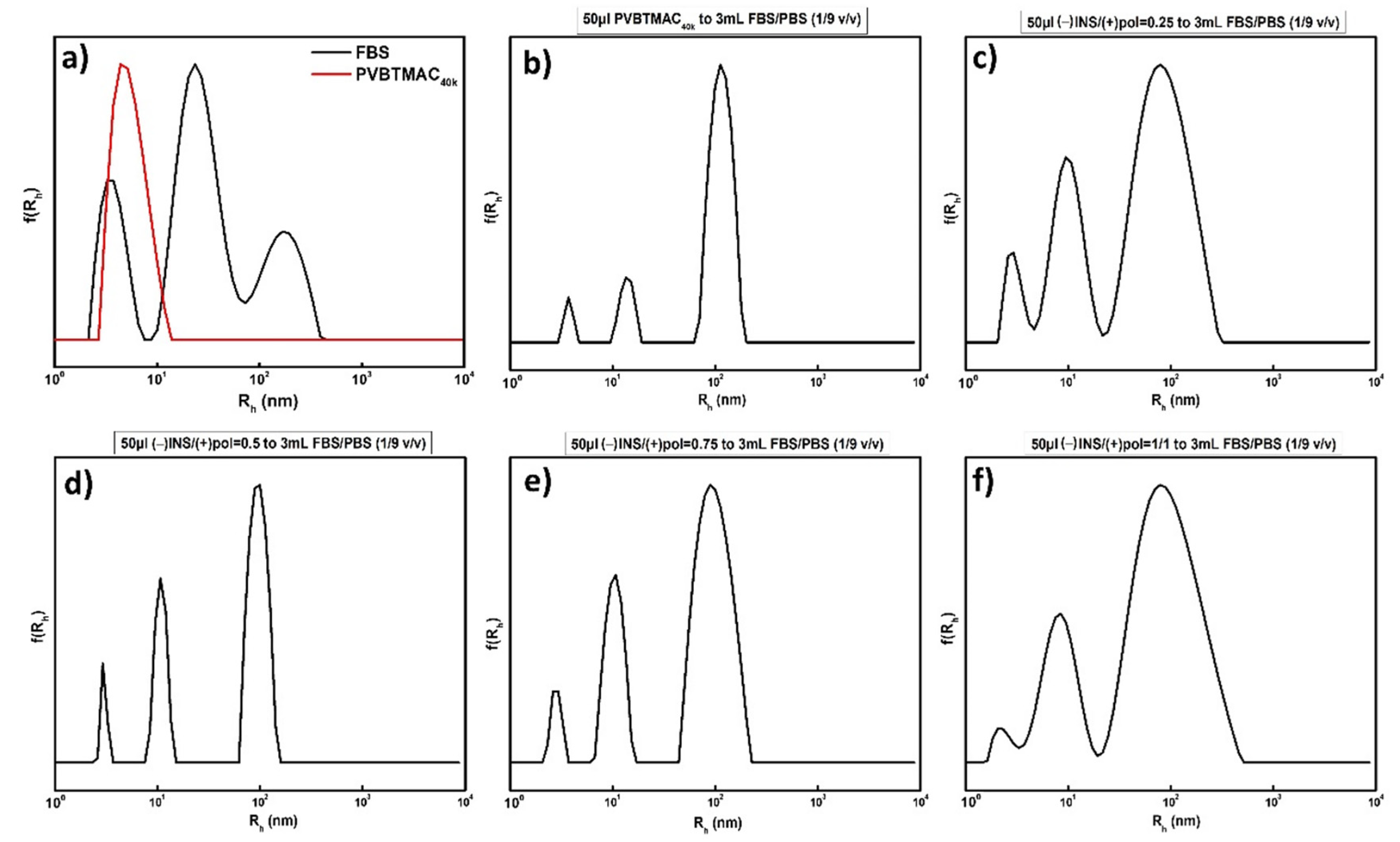
3.4. FBS Interactions with PVBTMAC Homo-Polymer and PVBTMAC/INS Complexes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Armstrong, J.P.; Olof, S.N.; Jakimowicz, M.D.; Hollander, A.P.; Mann, S.; Davis, S.A.; Miles, M.J.; Patil, A.J.; Perriman, A.W. Cell paintballing using optically targeted coacervate microdroplets. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 6106–6111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eghbal, N.; Choudhary, R. Complex coacervation: Encapsulation and controlled release of active agents in food systems. Lwt 2018, 90, 254–264. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.Q.; Du, Y.L.; Xiao, J.X.; Wang, G.Y. Effect of coacervation conditions on the viscoelastic properties of N,O-carboxymethyl chitosan–gum Arabic coacervates. Food Chem. 2017, 228, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Pei, Y.; Xiong, W.; Zhang, C.; Xu, W.; Liu, S.; Li, B. Curcumin encapsulated in the complex of lysozyme/carboxymethylcellulose and implications for the antioxidant activity of curcumin. Food Res. Int. 2015, 75, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, C.; Dubin, P.; Kayitmazer, A.; Turksen, S. Polyelectrolyte–protein complexes. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 10, 52–78. [Google Scholar]
- Kayitmazer, A.B.; Seeman, D.; Minsky, B.B.; Dubin, P.L.; Xu, Y. Protein–polyelectrolyte interactions. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 2553–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, M.; Jones, R.G.; Kahovec, J.; Kitayama, T.; Kratochvíl, P.; Kubisa, P.; Mormann, W.; Stepto, R.; Tabak, D.; Vohlídal, J. Terminology of polymers containing ionizable or ionic groups and of polymers containing ions (IUPAC Recommendations 2006). Pure Appl. Chem. 2006, 78, 2067–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, R.G.; Cherstvy, A.G. Strong and weak polyelectrolyte adsorption onto oppositely charged curved surfaces. In Polyelectrolyte Complexes in the Dispersed and Solid State I: Principles and Theory; Müller, M., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 255, pp. 1–56. [Google Scholar]
- Horn, J.M.; Kapelner, R.A.; Obermeyer, A.C. Macro-and microphase separated protein-polyelectrolyte complexes: Design parameters and current progress. Polymers 2019, 11, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Semenyuk, P.; Muronetz, V. Protein interaction with charged macromolecules: From model polymers to unfolded proteins and post-translational modifications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Qian, C.; Roman, M. Effects of pH and salt concentration on the formation and properties of chitosan–cellulose nanocrystal polyelectrolyte–macroion complexes. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 3708–3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayat, A.; Dorkoosh, F.A.; Dehpour, A.R.; Moezi, L.; Larijani, B.; Junginger, H.E.; Rafiee-Tehrani, M. Nanoparticles of quaternized chitosan derivatives as a carrier for colon delivery of insulin: Ex vivo and in vivo studies. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 356, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, A.M.M.; Dorkoosh, F.A.; Avadi, M.R.; Weinhold, M.; Bayat, A.; Delie, F.; Gurny, R.; Larijani, B.; Rafiee-Tehrani, M.; Junginger, H.E. Permeation enhancer effect of chitosan and chitosan derivatives: Comparison of formulations as soluble polymers and nanoparticulate systems on insulin absorption in Caco-2 cells. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 70, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Gao, H.; Li, C.; Yang, Y.W.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Y.; Wu, G.; Ma, J. Polyelectrolyte complex nanoparticles of amino poly (glycerol methacrylate)s and insulin. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 423, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, C.; Tetley, L.; Uchegbu, I.; Cheng, W. The complexation between novel comb shaped amphiphilic polyallylamine and insulin—towards oral insulin delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 376, 46–55. [Google Scholar]
- Jintapattanakit, A.; Junyaprasert, V.B.; Mao, S.; Sitterberg, J.; Bakowsky, U.; Kissel, T. Peroral delivery of insulin using chitosan derivatives: A comparative study of polyelectrolyte nanocomplexes and nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 342, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, B.; Beztsinna, N.; Mountrichas, G.; van den Dikkenberg, J.B.; Pispas, S.; Hennink, W.E. Small nanosized poly (vinyl benzyl trimethylammonium chloride) based polyplexes for siRNA delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 525, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haladjova, E.; Mountrichas, G.; Pispas, S.; Rangelov, S. Poly (vinyl benzyl trimethylammonium chloride) Homo and Block Copolymers Complexation with DNA. J. Phys. Chem. B 2016, 120, 2586–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pippa, N.; Kaditi, E.; Pispas, S.; Demetzos, C. PEO-b-PCL–DPPC chimeric nanocarriers: Self-assembly aspects in aqueous and biological media and drug incorporation. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 4073–4082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chroni, A.; Forys, A.; Sentoukas, T.; Trzebicka, B.; Pispas, S. Poly [(vinyl benzyl trimethylammonium chloride)]-based nanoparticulate copolymer structures encapsulating insulin. Eur. Polym. J. 2022, 169, 111158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Willcock, H.; Patterson, J.P.; Portman, I.; O’Reilly, R.K. Self-Assembly of Hydrophilic Homopolymers: A Matter of RAFT End Groups. Small 2011, 7, 2070–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delbeck, S.; Heise, H.M. Quality assurance of commercial insulin formulations: Novel assay using infrared spectroscopy. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2021, 15, 865–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, M.; Neves-Petersen, M.T.; Jeppesen, P.B.; Gregersen, S.; Petersen, S.B. UV-light exposure of insulin: Pharmaceutical implications upon covalent insulin dityrosine dimerization and disulphide bond photolysis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chroni, A.; Forys, A.; Trzebicka, B.; Alemayehu, A.; Tyrpekl, V.; Pispas, S. Poly [oligo (ethylene glycol) methacrylate]-b-poly [(vinyl benzyl trimethylammonium chloride)] Based Multifunctional Hybrid Nanostructures Encapsulating Magnetic Nanoparticles and DNA. Polymers 2020, 12, 1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karayianni, M.; Pispas, S.; Chryssikos, G.D.; Gionis, V.; Giatrellis, S.; Nounesis, G. Complexation of lysozyme with poly (sodium (sulfamate-carboxylate) isoprene). Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 1697–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, R.; Andrade, J.D. Minimizing the aggregation of neutral insulin solutions. J. Pharm. Sci. 1983, 72, 1472–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.S.; Bütün, V.; Vamvakaki, M.; Armes, S.P.; Pople, J.A.; Gast, A.P. Structure of pH-dependent block copolymer micelles: Charge and ionic strength dependence. Macromolecules 2002, 35, 8540–8551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, A.K.; Islam, M.R.; Choudhury, Z.S.; Mostafa, A.; Kadir, M.F. Nanotechnology based approaches in cancer therapeutics. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 5, 043001. [Google Scholar]

| (−)INS/(+)pol | VPVBTMAC (mL) | VINS (mL) | VNaCl (mL) | Vfinal (mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.25 | 2 | 0.380 | 7.6 | 10 |
| 0.5 | 2 | 0.285 | 7.7 | 10 |
| 0.75 | 2 | 0.19 | 7.8 | 10 |
| 1 | 2 | 0.095 | 7.9 | 10 |
| Sample | Intensity a (a.u) | Rh a (nm) | PDI a | ζpot b (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVBTMAC | 21 | 5 | 0.56 | +12 |
| (−)INS/(+)pol = 0.25 | 33 | 6/124 * | 0.51 | +16 |
| (−)INS/(+)pol = 0.50 | 5310 | 75 | 0.17 | +18 |
| (−)INS/(+)pol = 0.75 | 48,400 | 83 | 0.17 | +25 |
| (−)INS/(+)pol = 1 | 72,000 | 78 | 0.14 | +20 |
| Sample | (−)INS/(+)pol | Rh (nm) | Intensity (a.u) |
|---|---|---|---|
| FBS | - | 3/23/170 * | 5760 |
| PVBTMAC | - | 5 | 30 |
| PVBTMAC+FBS:PBS (1/9 v/v) | - | 5/14/113 * | 1948 |
| PVBTMAC/INS+FBS:PBS (1/9 v/v) | 0.25 | 3/10/79 * | 772 |
| PVBTMAC/INS+FBS:PBS (1/9 v/v) | 0.5 | 3/11/96 * | 849 |
| PVBTMAC/INS+FBS:PBS (1/9 v/v) | 0.75 | 3/10/96 * | 897 |
| PVBTMAC/INS+FBS:PBS (1/9 v/v) | 1 | 3/9/80 * | 1116 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chroni, A.; Pispas, S. Nano-Sized Polyelectrolyte Complexes Formed between Poly(vinyl benzyl trimethyl ammonium chloride) and Insulin. Micro 2022, 2, 313-324. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro2020020
Chroni A, Pispas S. Nano-Sized Polyelectrolyte Complexes Formed between Poly(vinyl benzyl trimethyl ammonium chloride) and Insulin. Micro. 2022; 2(2):313-324. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro2020020
Chicago/Turabian StyleChroni, Angeliki, and Stergios Pispas. 2022. "Nano-Sized Polyelectrolyte Complexes Formed between Poly(vinyl benzyl trimethyl ammonium chloride) and Insulin" Micro 2, no. 2: 313-324. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro2020020
APA StyleChroni, A., & Pispas, S. (2022). Nano-Sized Polyelectrolyte Complexes Formed between Poly(vinyl benzyl trimethyl ammonium chloride) and Insulin. Micro, 2(2), 313-324. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro2020020







